Sulu on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu ( Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the
 A landmark born of the social process was the founding of the Sultanate of Sulu. Year 1380 CE, Karim-ul Makhdum came to Sulu and introduced
A landmark born of the social process was the founding of the Sultanate of Sulu. Year 1380 CE, Karim-ul Makhdum came to Sulu and introduced
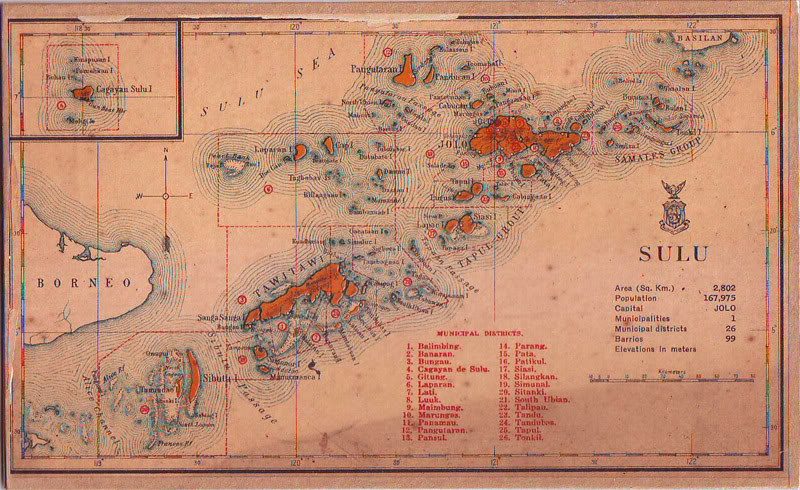 The Department of Mindanao and Sulu under Gov. Carpenter was created by ''Philippine Commission Act 2309'' (1914) and ended on February 5, 1920, by Act of Philippine Legislature No. 2878. The Bureau of Non-Christian Tribes was organized and briefly headed by
The Department of Mindanao and Sulu under Gov. Carpenter was created by ''Philippine Commission Act 2309'' (1914) and ended on February 5, 1920, by Act of Philippine Legislature No. 2878. The Bureau of Non-Christian Tribes was organized and briefly headed by 
 The province covers an area of . Sulu's main island, Jolo, has an area of , making it the 16th largest island of the Philippine Archipelago by area.
Sulu is a part of the Sulu Archipelago, which stretches from the tip of the Zamboanga Peninsula on the north to the island of
The province covers an area of . Sulu's main island, Jolo, has an area of , making it the 16th largest island of the Philippine Archipelago by area.
Sulu is a part of the Sulu Archipelago, which stretches from the tip of the Zamboanga Peninsula on the north to the island of
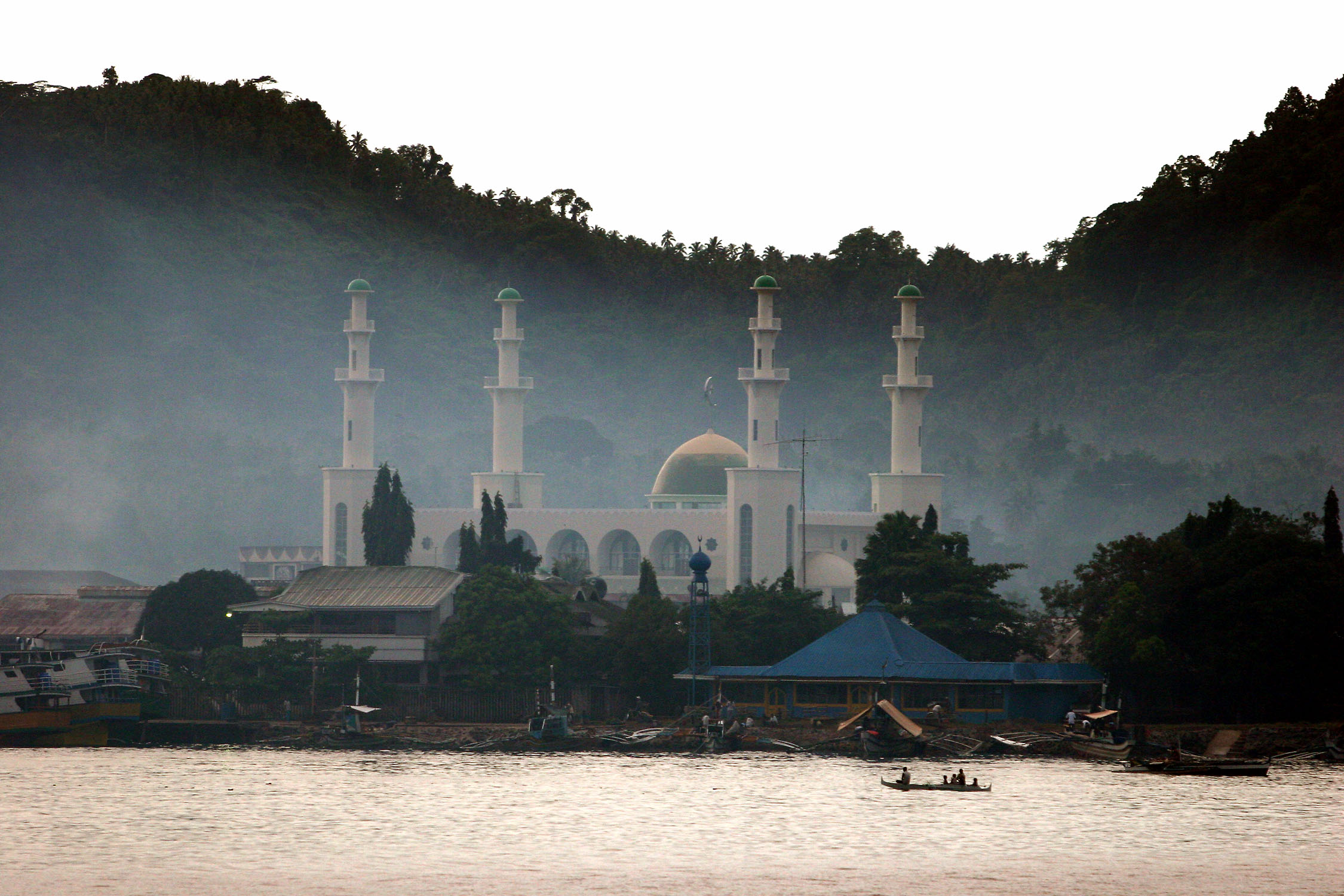 Sulu inhabitants are predominantly Muslim, constituting about 99% of the provincial population in 2015.
A majority of Sulu's Muslim population practice
Sulu inhabitants are predominantly Muslim, constituting about 99% of the provincial population in 2015.
A majority of Sulu's Muslim population practice
Philippine Standard Geographic Code
Local Governance Performance Management System
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sulu (Province) Provinces of the Philippines Provinces of Bangsamoro Sulu Archipelago Sulu Sea States and territories established in 1914 1914 establishments in the Philippines Island provinces of the Philippines
Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو
, native_name =
, settlement_type = Autonomous region
, anthem = Bangsamoro Hymn
, image_skyline ...
(BARMM).
Its capital is Jolo on the island of the same name. Maimbung
Maimbung, officially the Municipality of Maimbung ( Tausūg: كاومن سين ماءيمبوڠ; tl, Bayan ng Maimbung), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59,597 ...
, the royal capital of the Sultanate of Sulu, is also located in the province. Sulu is along the southern border of the Sulu Sea
The Sulu Sea ( fil, Dagat Sulu; Tausug: ''Dagat sin Sūg''; Chavacano: ''Mar de Sulu''; Cebuano: ''Dagat sa Sulu''; Hiligaynon: ''Dagat sang Sulu''; Karay-a: ''Dagat kang Sulu''; Cuyonon: ''Dagat i'ang Sulu''; ms, Laut Sulu) is a body o ...
and the northern boundary of the Celebes Sea.
History
Pre-Spanish and Spanish eras
Prior to the arrival of Islam in Sulu, the province used to adhere to local animist religions; this later changed to Hindu and Buddhist belief systems. Throughout this time, the Kingdom ofLupah Sug
In the Philippine history, the ''Lupah Sug'' ( Jawi: سوگ; ''Sūg'') was a predecessor state before the establishment of Sultanate of Sulu.
History
Hindu principality of Maimbung
Sulu that time was called ''Lupah Sug'' and ruled by the In ...
had been established centuries before Islam arrived.
The advent of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
around 1138 through merchants and traders had a distinct influence on Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
. The coming of Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
and other Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
paved the way for the arrival of religious missionaries, traders, scholars and travelers to Sulu and Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
in the 12th century.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
to the Philippines. In 1450 CE, Johore-born Arab adventurer Sayyid Abubakar Abirin came to Sulu and lived with Rajah Baguinda Ali. Sayyid Abubakar eventually married Ali's daughter, Dayang-dayang Paramisuli, and inherited Rajah Baguinda's polity (which was a principality before), which he turned into the Sultanate of Sulu and become its first Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it c ...
. To consolidate his rule, Sayyid Abubakar united the local political units under the umbrella of the Sultanate. He brought Sulu, Zamboanga Peninsula, Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in t ...
, and Basilan under its aegis.
The navigational error that landed Ferdinand Magellan in Limasawa brought awareness of Europe to the Philippines and opened the door to Spanish colonial incursion. The Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex history, including a number of different languages, both ...
introduced Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
and a political system of church-state dichotomy, which encountered fierce resistance in the devastating Moro wars from 1578 to 1899. The Sultanate of Sulu formally recognised Spanish sovereignty in Tawi-Tawi and Sulu in middle of 19th century, but these areas remained partially ruled by the Spanish as their sovereignty was limited to military stations, garrisons, and pockets of civilian settlements, until they had to abandon the region as a consequence of their defeat in the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
.
American and Japanese eras
After Spain ceded the Philippines to theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, American forces came to Jolo and ended the 23 years of Spanish military occupation (1876 to 1899). On August 20, Sultan Jamalul Kiram II and Brig. Gen. John C. Bates signed the Bates Agreement that continued the gradual emasculation of the Sultanate started by Spain (Treaty of 1878) until March 1915 when the Sultan abdicated his temporal powers in the Carpenter Agreement. The Agreement eliminated opposition to the civilian government of Gov. Clinton Solidum.
Teofisto Guingona Sr.
Teofisto Jamora Guingona Sr. (born Teofisto Guingona y Jamora; September 20, 1883 – April 11, 1963) was a Filipino revolutionary soldier, lawyer, judge, and politician. He was father of former Vice President Teofisto Guingona Jr. and the ...
With the enactment by the US Congress of the Jones Law (Philippine Autonomy Law) in 1916, ultimate Philippine independence was guaranteed and the Filipinization of public administration began. Sulu, however, had an appointed American governor until 1935, and the Governor General in Manila had a say in Sulu affairs.
At any rate, the essence of local governance forged by Rajah Baguinda
Rajah Baguinda Ali, also known as Rajah Baginda Ali, Rajah Baginda, Raha Baguinda, or ''Rajah Baguinda'', was a prince from a Minangkabau kingdom in Sumatra, Indonesia called "Pagaruyung". (Baginda/Baguinda is a Minangkabau honorific for ''prin ...
continued to permeate the ethos of Sulu politics despite centuries of colonial presence. History points to a local government in Sulu that antedates other similar systems in the country.
The province hosted the Daru Jambangan
The Darul Jambangan (Palace of Flowers) was the palace of the Sultanate of Sulu based in Maimbung, Sulu, Philippines. It was destroyed by a typhoon in 1932. It was "believed to be the largest royal palace in the Philippines."
A contemporary life ...
(Palace of Flowers) which was the royal palace of the Sultan of Sulu since historical times. The palace, located in Maimbung
Maimbung, officially the Municipality of Maimbung ( Tausūg: كاومن سين ماءيمبوڠ; tl, Bayan ng Maimbung), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59,597 ...
was made of wood, and was destroyed in 1932 by a huge storm.
During the brief Japanese occupation years, Sulu was bombed by the Japanese and was conquered afterwards. The Japanese were eventually expelled by the Americans and the natives of Sulu, and the Americans started to push for the independence of the Philippines as 'one country'. This prompted various leaders from Mindanao and the Sulu archipelago to campaign against being lumped with the Catholic natives of Luzon and the Visayas. Despite the campaign against the 'one Philippines model', the United States granted independence to the Philippines, effectively giving control of Mindanao and the Sulu archipelago to the Filipino government in Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
.

Postwar era
At the beginning of Philippine independence era, the reconstruction of the Daru Jambangan continued to be of huge importance to the people of Sulu as only a few arches and posts remain from the once grand palace complex. Many members of the royal family advocated for the reconstruction of the palace, however, the government of the Philippines made no official position or fund for the matter. During that time, the Mindanao sentiment to become a free country on its own was also felt in Sulu. In 1948,Hadji Kamlon
Datu Hadji Kamlon, also known as Maas Kamlon, was a Tausūg who fought during World War II, and afterwards, staged his own uprising against the Philippine government under Presidents Elpidio Quirino and Ramon Magsaysay. He is regarded as a folk ...
, a World War II veteran, started an uprising on Luuk, Sulu. He surrendered in 1949 but started another uprising in 1952. He then surrendered on 31 July 1952 to Secretary of Defense Ramon Magsaysay. However, he started a third uprising a week later. He surrendered again on 9 November 1952 but would start another uprising in early 1953. He would then surrender on 11 August 1953 after an encounter with Philippines Government troops. He violated the terms of his surrender a week later. Two years later, on 24 September 1955, he would then surrender after an encounter with government troops in Tandu Panuan, Luuk.
In 1973, the municipalities of South Ubian, Tandubas, Simunul, Sitangkai, Balimbing (Panglima Sugala), Bungao, Cagayan de Sulu (Mapun), and Turtle Island were transferred from the jurisdiction of Sulu to the newly formed province of Tawi-Tawi pursuant to Presidential Decree No. 302 of September 11, 1973.
The Marcos Administration
During Marcos era, Sulu was one of the provinces that fought back against Ferdinand Marcos as his regime tortured, killed, and exterminated hundreds of Moros. When news broke out regarding the planned invasion of easternSabah
Sabah () is a state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indonesia to the south. The Federal Territory ...
, Marcos ordered the military to massacre Tausug warriors, which led to the brutal 1968 Jabidah massacre, the worst human rights violation against the natives of Sulu.
News about the Jabidah Massacre led to the rise of numerous separatist movements in Mindanao, including Sulu, eventually leading to groups engaging in armed conflict with the Philippine government. One of the most destructive clashes, the 1974 Battle of Jolo, was so destructive that it was estimated to have rendered 40,000 people homeless in Jolo, the capital of Sulu.
The Sultan of Sulu, members of the royal family, and the leaders of Sulu were in favor of the People Power Revolution
The People Power Revolution, also known as the EDSA Revolution or the February Revolution, was a series of popular demonstrations in the Philippines, mostly in Metro Manila, from February 22 to 25, 1986. There was a sustained campaign of c ...
in Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
that successfully toppled the dictatorship and restored democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
in the country.
Autonomy and recent history
In 1989, the province of Sulu became part of the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao or ARMM. A peace pact between the Moro National Liberation Front or MNLF and the Philippine government was also made. The founder and leader of the MNLF, Nur Misuari, who was a native of Sulu and adhered to the Sultanate of Sulu, became the governor of the entire ARMM from 1996 to 2001. In 2016, a small replica of Daru Jambangan was built in the neighboring town ofTalipao
Talipao, officially the Municipality of Talipao ( Tausūg: ''Kawman sin Talipao''; tl, Bayan ng Talipao), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 80,255 people.
Etymo ...
and became a centerpiece for a 'vacation park'. The replica was about 25% of the actual size of the real Daru Jambangan during its heyday. A campaign to restore the Daru Jambangan in its original location in Maimbung is still ongoing. The National Commission for Culture and the Arts
The National Commission for Culture and the Arts of the Philippines ( fil, Pambansang Komisyon para sa Kultura at mga Sining, ceb, Nasodnong Komisyon alang sa Budaya ug mga Arte) is the official government agency for culture in the Philippines. ...
and the National Museum of the Philippines were tasked to faithfully restore or reconstruct the Daru Jambangan in Maimbung.
In 2019, the Bangsamoro autonomy plebiscite led to the ratification of the Bangsamoro Organic Law (BOL) creating the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) to replace the ARMM. The initiative lost by a 54.3% margin in Sulu, but was carried nonetheless because the votes of the entire ARMM were counted as one. (Several other localities in Mindanao which had not originally been part of the ARMM also ratified the BOL and were thus added to the BARMM.)
Geography
 The province covers an area of . Sulu's main island, Jolo, has an area of , making it the 16th largest island of the Philippine Archipelago by area.
Sulu is a part of the Sulu Archipelago, which stretches from the tip of the Zamboanga Peninsula on the north to the island of
The province covers an area of . Sulu's main island, Jolo, has an area of , making it the 16th largest island of the Philippine Archipelago by area.
Sulu is a part of the Sulu Archipelago, which stretches from the tip of the Zamboanga Peninsula on the north to the island of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
in the south. The main island and its islets are situated between the island-provinces of Basilan to the northeast, and Tawi-Tawi to the southwest. Sulu is bordered by two seas; the Sulu Sea
The Sulu Sea ( fil, Dagat Sulu; Tausug: ''Dagat sin Sūg''; Chavacano: ''Mar de Sulu''; Cebuano: ''Dagat sa Sulu''; Hiligaynon: ''Dagat sang Sulu''; Karay-a: ''Dagat kang Sulu''; Cuyonon: ''Dagat i'ang Sulu''; ms, Laut Sulu) is a body o ...
to the north, and the Celebes Sea to its south. Sulu has over 157 islets, some of which remain unnamed.
The islands are organized into four groups:
* Jolo group
* Pangutaran group
* Tongkil-Banguingui (Samales) group
* Siasi-Tapul group
Administrative divisions
Sulu comprises 19municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
that are organized into two legislative districts and further subdivided into 410 barangay
A barangay (; abbreviated as Brgy. or Bgy.), historically referred to as barrio (abbreviated as Bo.), is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines and is the native Filipino term for a village, district, or ward. In metropolita ...
s.
Demographics
The population of Sulu in the 2020 census was 1,000,108 people, with a density of . Although consisting of a mixed community ofMuslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s, the Tausugs dominate the Sulu Archipelago. The Tausug were among the first inhabitants of the Philippines to embrace Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
as a religion and a way of life. They are referred to as ‘people of the current’, reflective of their close ties to the sea.
Religion
 Sulu inhabitants are predominantly Muslim, constituting about 99% of the provincial population in 2015.
A majority of Sulu's Muslim population practice
Sulu inhabitants are predominantly Muslim, constituting about 99% of the provincial population in 2015.
A majority of Sulu's Muslim population practice Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disag ...
of the Shafi'i
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
tradition, as taught by Arab, Persian, Indian Muslim, Chinese Muslim and Malaccan missionaries from the 14th Century onwards.
Relatively newer Islamic sects, mostly brought by returning veterans of the Afghan wars and missionaries from Pakistan's stricter Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
traditions, referred to as the Tableegh, have been active in propagating what they believe to be a "purer" Islamic way of life and worship. A very small number who have since married into Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
or Iraqi families have converted to Shiite Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most n ...
.
The majority of Sulu Christians are Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. They are under the jurisdiction of Archdiocese of Zamboanga through its suffragan Apostolic Vicariate of Jolo
The Apostolic Vicariate of Jolo is a Latin Catholic missionary pre-diocesan jurisdiction covering the Sulu and Tawi-Tawi provinces in southern Philippines.
It is directly exempt to the Holy See, specifically Roman Congregation for the Evangeli ...
. Non-Catholic Christians include Evangelicals, Jesus Miracle Crusade The Jesus Miracle Crusade International Ministry (JMCIM) is a Christian church in the Philippines which believes particularly in the promotion of miracles, and faith in God for healing. They currently claim 1,500,000 members in the Philippines and o ...
, Episcopalian, Iglesia ni Cristo (INC), Mormons, Seventh-day Adventists, Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
, and a number of other Protestant denominations. Only the most recent Chinese immigrants adhere to Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
or Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, while most of the older Chinese families have acculturated and have either converted to Christianity or Islam while retaining many of their Chinese beliefs.
Languages
The Tausug language is the '' lingua franca'' of Sulu. The other local language is the indigenous Sama, which is widely used in varied tones and accents. This variety led to the development of Sinama dialects. The major ones are Sinama Sibutu (spoken mainly in the Sibutu-Sitangkai Region), Sinama Simunul (concentrated in Simunul-Manuk-Mangkaw Islands), Sinama Kapoan (spoken in the South Ubian-Tandubas and Sapa-Sapa Regions) and Sinama Banguingui (concentrated in Buan Island and spoken by Banguingui people). The Bajau-Sama language is also spoken, as are the official languages ofTagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Taga ...
(Filipino) and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
. Many locals and barter traders can speak Sabah Malay, while Chavacano
Chavacano or Chabacano is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of speaker ...
is also spoken by Christian and Muslim locals who maintain contacts and trade with the mainland Zamboanga Peninsula and Basilan. Many Muslims can also speak Cebuano because of the mass influx of Cebuano settlers to Mindanao, especially among the Tau Sūg since Tausug is a related Visayan language.
Government
Governors after People Power Revolution 1986: Vice Governors after People Power Revolution 1986:Economy
Sulu is predominantly agricultural with farming and fishing as its main livelihood activities. Its fertile soil and ideal climate can grow a variety of crops such as abaca,coconuts
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or t ...
, Sulu coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
, oranges, and lanzones as well as exotic fruits seldom found elsewhere in the country such as durian and mangosteen
Mangosteen (''Garcinia mangostana''), also known as the purple mangosteen, is a tropical evergreen tree with edible fruit native to tropical lands surrounding the Indian Ocean. Its origin is uncertain due to widespread prehistoric cultivation. ...
.
Fishing is the most important industry since the Sulu Sea
The Sulu Sea ( fil, Dagat Sulu; Tausug: ''Dagat sin Sūg''; Chavacano: ''Mar de Sulu''; Cebuano: ''Dagat sa Sulu''; Hiligaynon: ''Dagat sang Sulu''; Karay-a: ''Dagat kang Sulu''; Cuyonon: ''Dagat i'ang Sulu''; ms, Laut Sulu) is a body o ...
is one of the richest fishing grounds in the country. The province also has an extensive pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
industry, with a pearl farm on Marungas Island. The backs of sea turtles
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhe ...
are made into beautiful trays and combs. During breaks from fishing, the people build boats and weave mats. Other industries include coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
processing and fruit preservation.
The handicrafts of Sulu have both Islamic and Malay influences. Skilled artisans make boats, bladed weapons, bronze and brassware, pis cloth, embroidered textiles, shellcraft, traditional house carvings, and carved wooden grave markers.
The province used to be one of the most prosperous in the southern Philippines. However, due to conflicts, terrorism, and the establishment of jihadists groups such as the Abu Sayyaf, the province's economy has suffered badly and has been reduced to its current state.
Transportation
After the success of new flight of Philippine Airlines inside Bangsamoro region, the government is already looking forward to open the route to Cotabato City. As of to date Gove Leading Edge, Cebu Pacific Cebgo andPlatinum Skies
Air transportation in the Philippines goes back to the early days of aviation prior to World War II, during the American colonial period of the Philippines. Currently, the Philippines has several registered airline companies, but they are m ...
from Zamboanga are existing operational flight utilizing the newly renovated Jolo Airport.
Notable people
* Hadji Butu – Filipino statesman, first Muslim member of theSenate of the Philippines
The Senate of the Philippines ( Filipino: ''Senado ng Pilipinas'', also ''Mataas na Kapulungan ng Pilipinas'' or "upper chamber") is the upper house of Congress of the bicameral legislature of the Philippines with the House of Representatives ...
.
* Santanina Tillah Rasul – Filipina politician and the first Muslim woman member of the Senate of the Philippines
The Senate of the Philippines ( Filipino: ''Senado ng Pilipinas'', also ''Mataas na Kapulungan ng Pilipinas'' or "upper chamber") is the upper house of Congress of the bicameral legislature of the Philippines with the House of Representatives ...
.
* Antonio Kho Jr. – 193rd Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines
The Supreme Court ( fil, Kataas-taasang Hukuman; colloquially referred to as the ''Korte Suprema'' lso used in formal writing is the highest court in the Philippines. The Supreme Court was established by the Second Philippine Commission on J ...
*Abdulmari Imao
Abdulmari Asia Imao (January 14, 1936 – December 16, 2014) was a Filipino painter and sculptor. Imao was named National Artist of the Philippines for Visual Arts in 2006. A Tausūg, Imao is the first Moro to receive the recognition. Aside fr ...
– National Artist of the Philippines
The Order of National Artists of the Philippines ( Filipino: ''Orden ng mga Pambansang Alagad ng Sining ng Pilipinas'') is an order bestowed by the Philippines on Filipinos who have made significant contributions to the development of Philipp ...
for Visual Arts – Sculpture
*Leonor Orosa-Goquingco
Leonor Orosa Goquingco (24 July 1917 – 15 July 2005) was a Filipino national artist in creative dance, who was also known for breaking tradition within dance. She played the piano, drew art, designed scenery and costumes, sculpted, acted, direct ...
– National Artist of the Philippines
The Order of National Artists of the Philippines ( Filipino: ''Orden ng mga Pambansang Alagad ng Sining ng Pilipinas'') is an order bestowed by the Philippines on Filipinos who have made significant contributions to the development of Philipp ...
for Dance
*Samuel K. Tan
Samuel Kong Tan (December 30, 1933 – January 6, 2022) was a Filipino historian, academic and author. He has headed various cultural institutions including the National Historical Institute and the National Commission for Culture and the Arts.
...
– historian and former chairperson of National Historical Commission of the Philippines
The National Historical Commission of the Philippines ( fil, Pambansang Komisyong Pangkasaysayan ng Pilipinas, abbreviated NHCP) is a government agency of the Philippines. Its mission is "the promotion of Philippine history and cultural herit ...
*Kerima Polotan Tuvera Kerima Polotan-Tuvera (December 16, 1925 – August 19, 2011) was a Filipino fiction writer, essayist, and journalist. Some of her stories were published under the pseudonym "Patricia S. Torres".
Personal life
Born in Jolo, Sulu, she was christen ...
– fiction writer, essayist, and journalist
*Mohammed Esmail Kiram I
Sultan Mohammed Esmail Kiram was a Sultan of Sulu. He ruled from 1950 to 1974.
Personal life
He was the eldest son of Raja Muda Muwallil Wasit II and Mora Napsa. He became the legally recognized successor of the Sultan of Sulu upon his father' ...
– Sultan of Sulu from 1950 to 1974
* Princess Tarhata Kiram
Princess Tarhata Kiram was a Moro leader. She was the niece and adopted daughter of Jaramul Kiram II, Sultan of Sulu. After being educated in Manila and the United States, she returned to Jolo and married a Moro chieftain, Datu Tahil. In 1927, th ...
– Moro leader
*Mohammed Mahakuttah Abdullah Kiram
Sultan Mohammad Mahakuttah Abdulla Kiram was the 34th Sultan of Sulu (1974–1986). He was the eldest son of Sultan Mohammed Esmail Kiram I and the heir apparent to the throne. He was the last Sultan of Sulu officially recognised by the Philip ...
– last Sultan of Sulu officially recognized by Philippine government
*Jamalul Kiram III
Jamalul ibni Punjungan Kiram III (16 July 1938 – 20 October 2013) was a former self-proclaimed Sultan of the Sulu Sultanate who claimed to be "the poorest sultan in the world". He was known as an unsuccessful candidate for senator in the Ph ...
– self-proclaimed Sultan of Sulu
* Nur Misuari - leader of the Moro National Liberation Front
*Muedzul Lail Tan Kiram
Muedzul Lail Tan Kiram (born 28 August 1966) is the head of the Royal House of Sulu, a position which he has held since 16 February 1986. As the eldest son of the former Sultan Mohammad Mahakuttah Abdulla Kiram (who reigned 1974–1986), he i ...
– crown prince of Sultan Mahakuttah Kiram and current head of the Royal house of Sulu
*Tuburan Tamse
Tuburan Kontong Tamse (born 1911) was a Filipino athlete, and the first Muslim Filipino Olympian.
Biography
Tamse came from a small town in the municipality of Siasi, Sulu Province, in the southern part of the Philippines. At age 17, he was sen ...
– swimmer and the first Muslim Filipino Olympian
See also
* Bangsamoro * Moro people * Islam in the Philippines * Moro Islamic Liberation Front * Sultanate of Sulu * Moro National Liberation Front *Battle of Jolo (1974)
The Battle of Jolo, also referred to as the Burning of Jolo or the Siege of Jolo, was a military confrontation between the Moro National Liberation Front (MNLF) and the government of the Philippines in February 1974 in the municipality of Jolo ...
References
External links
* *Philippine Standard Geographic Code
Local Governance Performance Management System
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sulu (Province) Provinces of the Philippines Provinces of Bangsamoro Sulu Archipelago Sulu Sea States and territories established in 1914 1914 establishments in the Philippines Island provinces of the Philippines