Sponges, the members of the
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a
basal animal clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter ...
as a sister of the
diploblast
Eumetazoa (), also known as diploblasts, Epitheliozoa, or Histozoa, are a proposed basal animal clade as a sister group of the Porifera (sponges). The basal eumetazoan clades are the Ctenophora and the ParaHoxozoa. Placozoa is now also seen ...
s.
They are
multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like
mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
.
Sponges have unspecialized cells that can
transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have
nervous,
digestive or
circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
s. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the
evolutionary tree from the
last common ancestor of all animals, making them the
sister group of all other animals.
Etymology
The term ''sponge'' derives from the
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
word ( 'sponge').
Overview

Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are
multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
,
heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
ic, lack
cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mec ...
s and produce
sperm cell
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
s. Unlike other animals, they lack true
tissues and
organs. Some of them are radially symmetrical, but most are asymmetrical. The shapes of their bodies are adapted for maximal efficiency of water flow through the central cavity, where the water deposits nutrients and then leaves through a hole called the
osculum. Many sponges have internal skeletons of spicules (skeletal-like fragments of
calcium carbonate or
silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
), and/or
spongin (a modified type of collagen protein).
All adult sponges are
sessile aquatic animals, meaning that they attach to an underwater surface and remain fixed in place (i.e., do not travel) while in
larval stage of life they are
motile . Although there are freshwater species, the great majority are marine (salt-water) species, ranging in habitat from tidal zones to depths exceeding .
Although most of the approximately 5,000–10,000 known species of sponges feed on
bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
and other microscopic food in the water, some host
photosynthesizing microorganisms as
endosymbionts, and these alliances often produce more food and oxygen than they consume. A few species of sponges that live in food-poor environments have evolved as
carnivores that prey mainly on small
crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapoda, decapods, ostracoda, seed shrimp, branchiopoda, branchiopods, argulidae, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopoda, isopods, barnacles, copepods, ...
s.
Most species use
sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
, releasing
sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
cells into the water to fertilize
ova that in some species are released and in others are retained by the "mother". The fertilized eggs develop into
larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e, which swim off in search of places to settle. Sponges are known for regenerating from fragments that are broken off, although this only works if the fragments include the right types of cells. A few species reproduce by budding. When environmental conditions become less hospitable to the sponges, for example as temperatures drop, many freshwater species and a few marine ones produce
gemmules, "survival pods" of unspecialized cells that remain dormant until conditions improve; they then either form completely new sponges or recolonize the skeletons of their parents.
In most sponges, an internal gelatinous matrix called mesohyl functions as an
endoskeleton, and it is the only skeleton in soft sponges that encrust such hard surfaces as rocks. More commonly, the mesohyl is stiffened by
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
spicules
Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms
Spicule may also refer to:
*Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea sponges
*Spicule (nematode), reproductive structures found in male nematodes ( ...
, by spongin fibers, or both.
Demosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a har ...
s use spongin; many species have
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
spicules, whereas some species have calcium carbonate
exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
s.
Demosponges constitute about 90% of all known sponge species, including all freshwater ones, and they have the widest range of habitats.
Calcareous sponge
The calcareous sponges of class Calcarea are members of the animal phylum Porifera, the cellular sponges. They are characterized by spicules made of calcium carbonate in the form of calcite or aragonite. While the spicules in most species ha ...
s, which have calcium carbonate spicules and, in some species, calcium carbonate exoskeletons, are restricted to relatively shallow marine waters where production of calcium carbonate is easiest. The fragile
glass sponges, with "
scaffolding" of silica spicules, are restricted to polar regions and the ocean depths where predators are rare. Fossils of all of these types have been found in rocks dated from . In addition
Archaeocyathids, whose fossils are common in rocks from , are now regarded as a type of sponge.
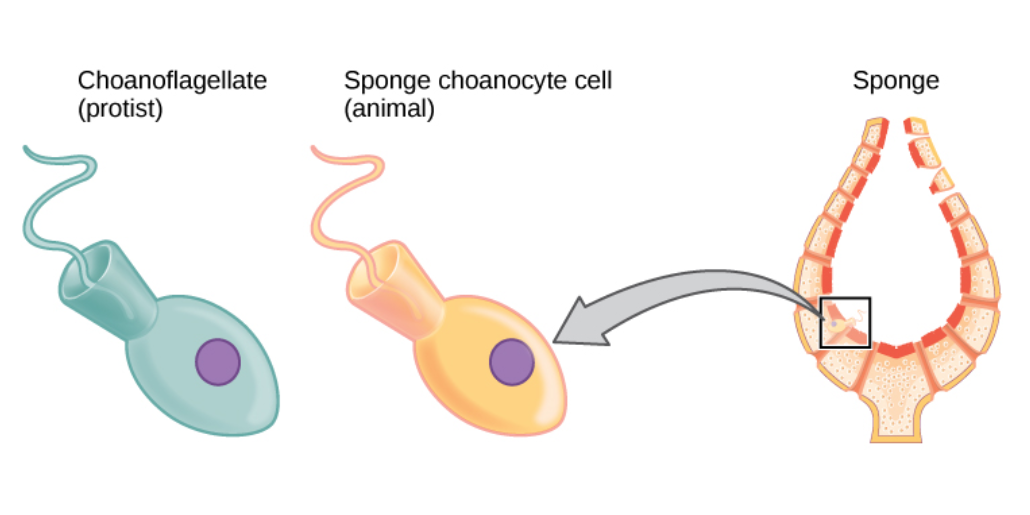
The
single-celled choanoflagellate
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconne ...
s resemble the choanocyte cells of sponges which are used to drive their water flow systems and capture most of their food. This along with phylogenetic studies of ribosomal molecules have been used as morphological evidence to suggest sponges are the sister group to the rest of animals.
Some studies have shown that sponges do not form a
monophyletic group, in other words do not include ''all and only'' the descendants of a common ancestor. Recent phylogenetic analyses suggested that
comb jellies rather than sponges are the sister group to the rest of animals.
However reanalysis of the data showed that the computer algorithms used for analysis were misled by the presence of specific ctenophore genes that were markedly different from those of other species, leaving sponges as either the sister group to all other animals, or an ancestral paraphyletic grade.
The few species of demosponge that have entirely soft fibrous skeletons with no hard elements have been used by humans over thousands of years for several purposes, including as padding and as cleaning tools. By the 1950s, though, these had been
overfished
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in ...
so heavily that the industry almost collapsed, and most sponge-like materials are now synthetic. Sponges and their microscopic endosymbionts are now being researched as possible sources of medicines for treating a wide range of diseases.
Dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the b ...
s have been observed using sponges as tools while
foraging.
Distinguishing features
Sponges constitute the
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
Porifera, and have been defined as
sessile metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
ns (multicelled immobile animals) that have water intake and outlet openings connected by chambers lined with
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
s, cells with whip-like flagella. However, a few carnivorous sponges have lost these water flow systems and the choanocytes.
All known living sponges can remold their bodies, as most types of their cells can move within their bodies and a few can change from one type to another.
Even if a few sponges are able to produce mucus – which acts as a microbial barrier in all other animals – no sponge with the ability to secrete a functional mucus layer has been recorded. Without such a mucus layer their living tissue is covered by a layer of microbial symbionts, which can contribute up to 40–50% of the sponge wet mass. This inability to prevent microbes from penetrating their porous tissue could be a major reason why they have never evolved a more complex anatomy.
Like
cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
ns (jellyfish, etc.) and
ctenophores
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), ...
(comb jellies), and unlike all other known metazoans, sponges' bodies consist of a non-living jelly-like mass (
mesohyl) sandwiched between two main layers of cells.
Cnidarians and ctenophores have simple nervous systems, and their cell layers are bound by internal connections and by being mounted on a basement membrane (thin fibrous mat, also known as "
basal lamina").
Sponges have no nervous systems, their middle jelly-like layers have large and varied populations of cells, and some types of cells in their outer layers may move into the middle layer and change their functions.
Basic structure
Cell types
A sponge's body is hollow and is held in shape by the
mesohyl, a jelly-like substance made mainly of
collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
and reinforced by a dense network of fibers also made of collagen. The inner surface is covered with
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
s, cells with cylindrical or conical collars surrounding one
flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
per choanocyte. The wave-like motion of the whip-like flagella drives water through the sponge's body. All sponges have ostia, channels leading to the interior through the mesohyl, and in most sponges these are controlled by tube-like
porocytes that form closable inlet valves.
Pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s, plate-like cells, form a single-layered external skin over all other parts of the mesohyl that are not covered by choanocytes, and the pinacocytes also digest food particles that are too large to enter the ostia,
while those at the base of the animal are responsible for anchoring it.
Other types of cell live and move within the mesohyl:
*
Lophocytes are
amoeba-like cells that move slowly through the mesohyl and secrete collagen fibres.
*
Collencytes are another type of collagen-producing cell.
*
Rhabdiferous cells secrete
polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with w ...
s that also form part of the mesohyl.
*
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ...
s and
spermatocytes are reproductive cells.
*
Sclerocyte Sclerocytes are specialised cells that secrete the mineralized structures in the body wall of some invertebrates.
In sponges they secrete calcareous or siliceous spicules which are found in the mesohyl layer of sponges. The sclerocytes produce spic ...
s secrete the mineralized
spicules
Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms
Spicule may also refer to:
*Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea sponges
*Spicule (nematode), reproductive structures found in male nematodes ( ...
("little spines") that form the
skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
s of many sponges and in some species provide some defense against predators.
* In addition to or instead of sclerocytes,
demosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a har ...
s have
spongocytes that secrete a form of collagen that
polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
izes into
spongin, a thick fibrous material that stiffens the mesohyl.
*
Myocytes ("muscle cells") conduct signals and cause parts of the animal to contract.
* "Grey cells" act as sponges' equivalent of an
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
.
*
Archaeocytes
Archaeocytes (from Greek '' archaios'' "beginning" and '' kytos'' "hollow vessel") or amoebocytes are amoeboid cells found in sponges. They are totipotent and have varied functions depending on the species.
The structure of these cells match to ...
(or
amoebocytes) are
amoeba-like cells that are
totipotent, in other words each is capable of transformation into any other type of cell. They also have important roles in feeding and in clearing debris that block the ostia.
Many larval sponges possess neuron-less
eyes that are based on
cryptochromes. They mediate phototaxic behavior.
Glass sponges' syncytia
Glass sponges present a distinctive variation on this basic plan. Their spicules, which are made of
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
, form a
scaffolding-like framework between whose rods the living tissue is suspended like a
cobweb that contains most of the cell types.
This tissue is a
syncytium that in some ways behaves like many cells that share a single external
membrane, and in others like a single cell with multiple
nuclei. The mesohyl is absent or minimal. The syncytium's
cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
, the soupy fluid that fills the interiors of cells, is organized into "rivers" that transport nuclei,
organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
s ("organs" within cells) and other substances.
Instead of choanocytes, they have further syncytia, known as choanosyncytia, which form bell-shaped chambers where water enters via perforations. The insides of these chambers are lined with "collar bodies", each consisting of a collar and flagellum but without a nucleus of its own. The motion of the flagella sucks water through passages in the "cobweb" and expels it via the open ends of the bell-shaped chambers.
Some types of cells have a single nucleus and membrane each, but are connected to other single-nucleus cells and to the main syncytium by "bridges" made of
cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
. The
sclerocyte Sclerocytes are specialised cells that secrete the mineralized structures in the body wall of some invertebrates.
In sponges they secrete calcareous or siliceous spicules which are found in the mesohyl layer of sponges. The sclerocytes produce spic ...
s that build spicules have multiple nuclei, and in glass sponge larvae they are connected to other tissues by cytoplasm bridges; such connections between sclerocytes have not so far been found in adults, but this may simply reflect the difficulty of investigating such small-scale features. The bridges are controlled by "plugged junctions" that apparently permit some substances to pass while blocking others.
Water flow and body structures
Most sponges work rather like
chimney
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typ ...
s: they take in water at the bottom and eject it from the
osculum ("little mouth") at the top. Since ambient currents are faster at the top, the suction effect that they produce by
Bernoulli's principle does some of the work for free. Sponges can control the water flow by various combinations of wholly or partially closing the osculum and ostia (the intake pores) and varying the beat of the flagella, and may shut it down if there is a lot of sand or silt in the water.
Although the layers of
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s and
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
s resemble the
epithelia of more complex animals, they are not bound tightly by cell-to-cell connections or a basal lamina (thin fibrous sheet underneath). The flexibility of these layers and re-modeling of the mesohyl by lophocytes allow the animals to adjust their shapes throughout their lives to take maximum advantage of local water currents.
The simplest body structure in sponges is a tube or vase shape known as "asconoid", but this severely limits the size of the animal. The body structure is characterized by a stalk-like spongocoel surrounded by a single layer of choanocytes. If it is simply scaled up, the ratio of its volume to surface area increases, because surface increases as the square of length or width while volume increases proportionally to the cube. The amount of tissue that needs food and
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
is determined by the volume, but the pumping capacity that supplies food and oxygen depends on the area covered by choanocytes. Asconoid sponges seldom exceed in diameter.
Some sponges overcome this limitation by adopting the "syconoid" structure, in which the body wall is
pleated. The inner pockets of the pleats are lined with choanocytes, which connect to the outer pockets of the pleats by ostia. This increase in the number of choanocytes and hence in pumping capacity enables syconoid sponges to grow up to a few centimeters in diameter.
The "leuconoid" pattern boosts pumping capacity further by filling the interior almost completely with mesohyl that contains a network of chambers lined with choanocytes and connected to each other and to the water intakes and outlet by tubes. Leuconid sponges grow to over in diameter, and the fact that growth in any direction increases the number of choanocyte chambers enables them to take a wider range of forms, for example "encrusting" sponges whose shapes follow those of the surfaces to which they attach. All freshwater and most shallow-water marine sponges have leuconid bodies. The networks of water passages in
glass sponges are similar to the leuconid structure.
In all three types of structure the cross-section area of the choanocyte-lined regions is much greater than that of the intake and outlet channels. This makes the flow slower near the choanocytes and thus makes it easier for them to trap food particles.
For example, in ''
Leuconia'', a small leuconoid sponge about tall and in diameter, water enters each of more than 80,000 intake canals at 6 cm per ''minute''. However, because ''Leuconia'' has more than 2 million flagellated chambers whose combined diameter is much greater than that of the canals, water flow through chambers slows to 3.6 cm per ''hour'', making it easy for choanocytes to capture food. All the water is expelled through a single
osculum at about 8.5 cm per ''second'', fast enough to carry waste products some distance away.
Skeleton
In zoology a
skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
is any fairly rigid structure of an animal, irrespective of whether it has joints and irrespective of whether it is
biomineralized. The mesohyl functions as an
endoskeleton in most sponges, and is the only skeleton in soft sponges that encrust hard surfaces such as rocks. More commonly the mesohyl is stiffened by mineral
spicules
Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms
Spicule may also refer to:
*Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea sponges
*Spicule (nematode), reproductive structures found in male nematodes ( ...
, by spongin fibers or both. Spicules, which are present in most but not all species, may be made of
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
or calcium carbonate, and vary in shape from simple rods to three-dimensional "stars" with up to six rays. Spicules are produced by
sclerocyte Sclerocytes are specialised cells that secrete the mineralized structures in the body wall of some invertebrates.
In sponges they secrete calcareous or siliceous spicules which are found in the mesohyl layer of sponges. The sclerocytes produce spic ...
cells,
and may be separate, connected by joints, or fused.
Some sponges also secrete
exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
s that lie completely outside their organic components. For example,
sclerosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a hard, ...
s ("hard sponges") have massive calcium carbonate exoskeletons over which the organic matter forms a thin layer with
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
chambers in pits in the mineral. These exoskeletons are secreted by the
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s that form the animals' skins.
Vital functions

Movement
Although adult sponges are fundamentally
sessile animals, some marine and freshwater species can move across the sea bed at speeds of per day, as a result of
amoeba-like movements of
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s and other cells. A few species can contract their whole bodies, and many can close their
oscula and
ostia. Juveniles drift or swim freely, while adults are stationary.
Respiration, feeding and excretion

Sponges do not have distinct
circulatory
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, t ...
,
respiratory,
digestive, and
excretory systems – instead the water flow system supports all these functions. They
filter food particles out of the water flowing through them. Particles larger than 50 micrometers cannot enter the
ostia and
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s consume them by
phagocytosis (engulfing and intracellular digestion). Particles from 0.5 μm to 50 μm are trapped in the ostia, which taper from the outer to inner ends. These particles are consumed by pinacocytes or by
archaeocytes which partially extrude themselves through the walls of the ostia. Bacteria-sized particles, below 0.5 micrometers, pass through the ostia and are caught and consumed by
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
s.
Since the smallest particles are by far the most common, choanocytes typically capture 80% of a sponge's food supply.
Archaeocytes transport food packaged in
vesicles
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
from cells that directly digest food to those that do not. At least one species of sponge has internal fibers that function as tracks for use by nutrient-carrying archaeocytes,
and these tracks also move inert objects.
It used to be claimed that
glass sponges could live on nutrients dissolved in sea water and were very averse to silt.
However, a study in 2007 found no evidence of this and concluded that they extract bacteria and other micro-organisms from water very efficiently (about 79%) and process suspended sediment grains to extract such prey. Collar bodies digest food and distribute it wrapped in vesicles that are transported by
dynein "motor" molecules along bundles of
microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 1 ...
s that run throughout the
syncytium.
Sponges' cells absorb oxygen by
diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical ...
from water into cells as water flows through body, into which
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
and other soluble waste products such as
ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
also diffuse. Archeocytes remove mineral particles that threaten to block the ostia, transport them through the mesohyl and generally dump them into the outgoing water current, although some species incorporate them into their skeletons.
Carnivorous sponges

In waters where the supply of food particles is very poor, some species prey on
crustaceans and other small animals. So far only 137 species have been discovered. Most belong to the
family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Cladorhizidae
Cladorhizidae is a family of demosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are s ...
, but a few members of the
Guitarridae
Guitarridae is a family of sponges
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels a ...
and
Esperiopsidae are also carnivores.
In most cases little is known about how they actually capture prey, although some species are thought to use either sticky threads or hooked
spicules
Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms
Spicule may also refer to:
*Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea sponges
*Spicule (nematode), reproductive structures found in male nematodes ( ...
.
Most carnivorous sponges live in deep waters, up to ,
and the development of deep-ocean exploration techniques is expected to lead to the discovery of several more.
However, one species has been found in
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
caves at depths of , alongside the more usual
filter feeding sponges. The cave-dwelling predators capture crustaceans under long by entangling them with fine threads, digest them by enveloping them with further threads over the course of a few days, and then return to their normal shape; there is no evidence that they use
venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a st ...
.
Most known carnivorous sponges have completely lost the water flow system and
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
s. However, the
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''
Chondrocladia
''Chondrocladia'' is a genus of carnivorous demosponges of the family Cladorhizidae. '' Neocladia'' was long considered a junior synonym, but has recently become accepted as a distinct genus.
33 named species are placed in this genus at present ...
'' uses a highly modified water flow system to inflate balloon-like structures that are used for capturing prey.
Endosymbionts
Freshwater sponges often host
green algae as
endosymbionts within
archaeocytes and other cells, and benefit from nutrients produced by the algae. Many marine species host other
photosynthesizing organisms, most commonly
cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
but in some cases
dinoflagellates. Symbiotic cyanobacteria may form a third of the total mass of living tissue in some sponges, and some sponges gain 48% to 80% of their energy supply from these micro-organisms.
In 2008 a
University of Stuttgart team reported that spicules made of
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
conduct light into the
mesohyl, where the photosynthesizing endosymbionts live. Sponges that host photosynthesizing organisms are most common in waters with relatively poor supplies of food particles, and often have leafy shapes that maximize the amount of sunlight they collect.
A recently discovered carnivorous sponge that lives near
hydrothermal vents hosts
methane-eating bacteria, and digests some of them.
"Immune" system
Sponges do not have the complex
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
s of most other animals. However, they reject
grafts from other species but accept them from other members of their own species. In a few marine species, gray cells play the leading role in rejection of foreign material. When invaded, they produce a chemical that stops movement of other cells in the affected area, thus preventing the intruder from using the sponge's internal transport systems. If the intrusion persists, the grey cells concentrate in the area and release toxins that kill all cells in the area. The "immune" system can stay in this activated state for up to three weeks.
Reproduction
Asexual

Sponges have three
asexual methods of reproduction: after fragmentation, by
budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is kno ...
, and by producing
gemmules. Fragments of sponges may be detached by currents or waves. They use the mobility of their
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s and
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
s and reshaping of the
mesohyl to re-attach themselves to a suitable surface and then rebuild themselves as small but functional sponges over the course of several days. The same capabilities enable sponges that have been squeezed through a fine cloth to regenerate. A sponge fragment can only regenerate if it contains both
collencytes to produce
mesohyl and
archeocytes to produce all the other cell types.
A very few species reproduce by budding.
Gemmules are "survival pods" which a few marine sponges and many freshwater species produce by the thousands when dying and which some, mainly freshwater species, regularly produce in autumn.
Spongocytes make gemmules by wrapping shells of spongin, often reinforced with spicules, round clusters of
archeocytes that are full of nutrients. Freshwater gemmules may also include photosynthesizing symbionts.
The gemmules then become dormant, and in this state can survive cold, drying out, lack of oxygen and extreme variations in
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
.
Freshwater gemmules often do not revive until the temperature drops, stays cold for a few months and then reaches a near-"normal" level.
When a gemmule germinates, the archeocytes round the outside of the cluster transform into
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s, a membrane over a pore in the shell bursts, the cluster of cells slowly emerges, and most of the remaining archeocytes transform into other cell types needed to make a functioning sponge. Gemmules from the same species but different individuals can join forces to form one sponge. Some gemmules are retained within the parent sponge, and in spring it can be difficult to tell whether an old sponge has revived or been "recolonized" by its own gemmules.
Sexual
Most sponges are
hermaphrodites (function as both sexes simultaneously), although sponges have no
gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sp ...
s (reproductive organs). Sperm are produced by
choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a ...
s or entire choanocyte chambers that sink into the
mesohyl and form spermatic
cysts while eggs are formed by transformation of
archeocytes, or of choanocytes in some species. Each egg generally acquires a
yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example ...
by consuming "nurse cells". During spawning, sperm burst out of their cysts and are expelled via the
osculum. If they contact another sponge of the same species, the water flow carries them to choanocytes that engulf them but, instead of digesting them, metamorphose to an
ameboid form and carry the sperm through the mesohyl to eggs, which in most cases engulf the carrier and its cargo.
A few species release fertilized eggs into the water, but most retain the eggs until they hatch. There are four types of larvae, but all are balls of cells with an outer layer of cells whose
flagellae or
cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proje ...
enable the larvae to move. After swimming for a few days the larvae sink and crawl until they find a place to settle. Most of the cells transform into archeocytes and then into the types appropriate for their locations in a miniature adult sponge.
Glass sponge embryos start by dividing into separate cells, but once 32 cells have formed they rapidly transform into larvae that externally are
ovoid
An oval () is a closed curve in a plane which resembles the outline of an egg. The term is not very specific, but in some areas ( projective geometry, technical drawing, etc.) it is given a more precise definition, which may include either o ...
with a band of
cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proje ...
round the middle that they use for movement, but internally have the typical glass sponge structure of spicules with a cobweb-like main
syncitium
A syncytium (; plural syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucleus) ...
draped around and between them and
choanosyncytia with multiple collar bodies in the center. The larvae then leave their parents' bodies.
Life cycle
Sponges in
temperate regions live for at most a few years, but some
tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
species and perhaps some deep-ocean ones may live for 200 years or more. Some calcified
demosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a har ...
s grow by only per year and, if that rate is constant, specimens wide must be about 5,000 years old. Some sponges start sexual reproduction when only a few weeks old, while others wait until they are several years old.
Coordination of activities
Adult sponges lack
neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa ...
s or any other kind of
nervous tissue
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the bra ...
. However, most species have the ability to perform movements that are coordinated all over their bodies, mainly contractions of the
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s, squeezing the water channels and thus expelling excess sediment and other substances that may cause blockages. Some species can contract the
osculum independently of the rest of the body. Sponges may also contract in order to reduce the area that is vulnerable to attack by predators. In cases where two sponges are fused, for example if there is a large but still unseparated bud, these contraction waves slowly become coordinated in both of the "
Siamese twins". The coordinating mechanism is unknown, but may involve chemicals similar to
neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
s. However,
glass sponges rapidly transmit electrical impulses through all parts of the
syncytium, and use this to halt the motion of their
flagella if the incoming water contains toxins or excessive sediment.
s are thought to be responsible for closing the osculum and for transmitting signals between different parts of the body.
Sponges contain
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s very similar to those that contain the "recipe" for the post-
synaptic density, an important signal-receiving structure in the neurons of all other animals. However, in sponges these genes are only activated in "flask cells" that appear only in larvae and may provide some sensory capability while the larvae are swimming. This raises questions about whether flask cells represent the predecessors of true neurons or are evidence that sponges' ancestors had true neurons but lost them as they adapted to a sessile lifestyle.
Ecology
Habitats
Sponges are worldwide in their distribution, living in a wide range of ocean habitats, from the polar regions to the tropics.
Most live in quiet, clear waters, because sediment stirred up by waves or currents would block their pores, making it difficult for them to feed and breathe.
The greatest numbers of sponges are usually found on firm surfaces such as rocks, but some sponges can attach themselves to soft sediment by means of a root-like base.

Sponges are more abundant but less diverse in temperate waters than in tropical waters, possibly because organisms that prey on sponges are more abundant in tropical waters.
Glass sponges are the most common in polar waters and in the depths of temperate and tropical seas, as their very porous construction enables them to extract food from these resource-poor waters with the minimum of effort.
Demosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a har ...
s and
calcareous sponges are abundant and diverse in shallower non-polar waters.
The different
classes of sponge live in different ranges of habitat:
:
As primary producers
Sponges with
photosynthesizing endosymbionts produce up to three times more
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
than they consume, as well as more organic matter than they consume. Such contributions to their habitats' resources are significant along Australia's
Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, A ...
but relatively minor in the Caribbean.
Defenses

Many sponges shed
spicules
Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms
Spicule may also refer to:
*Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea sponges
*Spicule (nematode), reproductive structures found in male nematodes ( ...
, forming a dense carpet several meters deep that keeps away
echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the ...
s which would otherwise prey on the sponges.
They also produce toxins that prevent other sessile organisms such as
bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a ...
ns or
sea squirts from growing on or near them, making sponges very effective competitors for living space. One of many examples includes
ageliferin
Ageliferin is a chemical compound produced by some sponges. It was first isolated from Caribbean and then Okinawan marine sponges in the genus ''Agelas''. It often co-exists with the related compound sceptrin and other similar compounds. It has ...
.
A few species, the
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
fire sponge ''
Tedania ignis'', cause a severe rash in humans who handle them.
Turtles and some fish feed mainly on sponges. It is often said that sponges produce
chemical defenses against such predators.
However, experiments have been unable to establish a relationship between the toxicity of chemicals produced by sponges and how they taste to fish, which would diminish the usefulness of chemical defenses as deterrents. Predation by fish may even help to spread sponges by detaching fragments.
However, some studies have shown fish showing a preference for non chemically defended sponges, and another study found that high levels of coral predation did predict the presence of chemically defended species.
Glass sponges produce no toxic chemicals, and live in very deep water where predators are rare.
Predation
Sponge flies, also known as spongilla-flies (
Neuroptera
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species. Neuroptera can be grouped together with the Megaloptera and Raphidioptera in th ...
,
Sisyridae), are specialist predators of freshwater sponges. The female lays her eggs on vegetation overhanging water. The larvae hatch and drop into the water where they seek out sponges to feed on. They use their elongated mouthparts to pierce the sponge and suck the fluids within. The larvae of some species cling to the surface of the sponge while others take refuge in the sponge's internal cavities. The fully grown larvae leave the water and spin a cocoon in which to pupate.
Bioerosion
The Caribbean chicken-liver sponge ''
Chondrilla nucula'' secretes toxins that kill coral
polyps, allowing the sponges to grow over the coral skeletons.
Others, especially in the family
Clionaidae
Clionaidae is a family of demosponges which are found worldwide. This family is known for parasitically boring holes in calcareous material such as mollusc shells and corals, using both chemical and mechanical processes.Brusca, R.C. & Brusca, G. ...
, use corrosive substances secreted by their archeocytes to tunnel into rocks, corals and the shells of dead
mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is e ...
s.
Sponges may remove up to per year from reefs, creating visible notches just below low-tide level.
Diseases
Caribbean sponges of the genus ''
Aplysina'' suffer from
Aplysina red band syndrome
''Aplysina'' is a genus of sea sponges in the order Verongiida. It was first authenticated and described by Giovanni Domenico Nardo
Giovanni Domenico Nardo (4 March 1802 – 7 April 1877) was an Italian naturalist from Venice, although he sp ...
. This causes ''Aplysina'' to develop one or more rust-colored bands, sometimes with adjacent bands of
necrotic tissue. These lesions may completely encircle branches of the sponge. The disease appears to be
contagious
Contagious may refer to:
* Contagious disease
Literature
* Contagious (magazine), a marketing publication
* ''Contagious'' (novel), a science fiction thriller novel by Scott Sigler
Music
Albums
*''Contagious'' (Peggy Scott-Adams album), 1997
...
and impacts approximately 10 percent of ''A. cauliformis'' on Bahamian reefs.
The rust-colored bands are caused by a
cyanobacterium, but it is unknown whether this organism actually causes the disease.
Collaboration with other organisms
In addition to hosting photosynthesizing endosymbionts,
sponges are noted for their wide range of collaborations with other organisms. The relatively large encrusting sponge ''
Lissodendoryx colombiensis'' is most common on rocky surfaces, but has extended its range into
seagrass meadow
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems an ...
s by letting itself be surrounded or overgrown by seagrass sponges, which are distasteful to the local
starfish
Starfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish a ...
and therefore protect ''Lissodendoryx'' against them; in return the seagrass sponges get higher positions away from the sea-floor sediment.
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are ref ...
s of the genus ''
Synalpheus
''Synalpheus'' is a genus of snapping shrimp of the family Alpheidae, presently containing more than 100 species; new ones are described on a regular basis, and the exact number even of described species is disputed.
''Zuzalpheus''
The genus ''Z ...
'' form colonies in sponges, and each shrimp species inhabits a different sponge species, making ''Synalpheus'' one of the most diverse
crustacean genera. Specifically,
Synalpheus regalis
''Synalpheus regalis'' is a species of snapping shrimp that commonly live in sponges in the coral reefs along the tropical West Atlantic. They form a prominent component of the diverse marine cryptofauna of the region. For the span of their e ...
utilizes the sponge not only as a food source, but also as a defense against other shrimp and predators. As many as 16,000 individuals inhabit a single
loggerhead sponge, feeding off the larger particles that collect on the sponge as it filters the ocean to feed itself. Other crustaceans such as hermit crabs commonly have a specific species of sponge, ''
Pseudospongosorites'', grow on them as both the sponge and crab occupy gastropod shells until the crab and sponge outgrow the shell, eventually resulting in the crab using the sponge's body as protection instead of the shell until the crab finds a suitable replacement shell.

Sponge loop
Most sponges are
detritivore
Detritivores (also known as detrivores, detritophages, detritus feeders, or detritus eaters) are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus (decomposing plant and animal parts as well as feces). There are many kinds of invertebrate ...
s which filter
organic debris particles and
microscopic life forms from ocean water. In particular, sponges occupy an important role as detritivores in
coral reef food webs by recycling detritus to higher
trophic levels.
The hypothesis has been made that coral reef sponges facilitate the transfer of coral-derived organic matter to their associated detritivores via the production of sponge detritus, as shown in the diagram. Several sponge species are able to convert coral-derived DOM into sponge detritus, and transfer organic matter produced by corals further up the reef food web. Corals release organic matter as both dissolved and particulate mucus,
[Wild C, Huettel M, Klueter A, Kremb S, Rasheed M, Jorgensen B (2004) Coral mucus functions as an energy carrier and particle trap in the reef ecosystem. Nature 428: 66−70] as well as cellular material such as expelled ''
Symbiodinium''.
[Hoegh-Guldberg O, McCloskey LR, Muscatine L (1987) Expulsion of zooxanthellae by symbiotic cnidarians from the Red Sea. Coral Reefs 5: 201−204]
Organic matter could be transferred from corals to sponges by all these pathways, but DOM likely makes up the largest fraction, as the majority (56 to 80%) of coral mucus dissolves in the water column,
and coral loss of fixed carbon due to expulsion of ''Symbiodinium'' is typically negligible (0.01%)
compared with mucus release (up to ~40%). Coral-derived organic matter could also be indirectly transferred to sponges via bacteria, which can also consume coral mucus.

Sponge holobiont
Besides a one to one
symbiotic relationship, it is possible for a host to become symbiotic with a
microbial consortium. Sponges are able to host a wide range of
microbial communities Microbial population biology is the application of the principles of population biology to microorganisms.
Distinguishing from other biological disciplines
Microbial population biology, in practice, is the application of population ecology and popu ...
that can also be very specific. The microbial communities that form a symbiotic relationship with the sponge can amount to as much as 35% of the
biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
of its host. The term for this specific symbiotic relationship, where a microbial consortia pairs with a host is called a
holobiotic relationship. The sponge as well as the microbial community associated with it will produce a large range of secondary
metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
s that help protect it against predators through mechanisms such as
chemical defense.
Some of these relationships include endosymbionts within bacteriocyte cells, and cyanobacteria or microalgae found below the pinacoderm cell layer where they are able to receive the highest amount of light, used for phototrophy. They can host over 50 different microbial phyla and candidate phyla, including Alphaprotoebacteria,
Actinomycetota,
Chloroflexota
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for p ...
,
Nitrospirota, "
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
", the taxa Gamma-, the candidate phylum
Poribacteria
Poribacteria are a candidate phylum of bacteria originally discovered in the microbiome of marine sponges (''Porifera''). Poribacteria are Gram-negative primarily aerobic mixotrophs with the ability for oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis, ...
, and Thaumarchaea.
Systematics and evolutionary history
Taxonomy
Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus, who classified most kinds of sessile animals as belonging to the order Vermes in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae#Zoophyta, Zoophyta in the class Vermes, mistakenly identified the genus ''Spongia'' as plants in the order Algae.
For a long time thereafter sponges were assigned to a separate subkingdom, Parazoa ("beside the animals"), separate from the Eumetazoa which formed the rest of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia.
They have been regarded as a paraphyly, paraphyletic
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
, from which the higher animals have evolved. Other research indicates Porifera is monophyletic.
The phylum Porifera is further divided into
classes mainly according to the composition of their
skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
s:
* Hexactinellida (glass sponges) have silicate spicules, the largest of which have six rays and may be individual or fused.
The main components of their bodies are syncytia in which large numbers of cell share a single external
membrane.
* Calcarea have skeletons made of calcite, a form of
calcium carbonate, which may form separate spicules or large masses. All the cells have a single nucleus and membrane.
* Most Demospongiae have silicate spicules or
spongin fibers or both within their soft tissues. However, a few also have massive external skeletons made of aragonite, another form of calcium carbonate.
All the cells have a single nucleus and membrane.
* Archeocyatha are known only as fossils from the Cambrian period.
In the 1970s, sponges with massive calcium carbonate skeletons were assigned to a separate class, Sclerospongiae, otherwise known as "coralline sponges".
However, in the 1980s it was found that these were all members of either the Calcarea or the Demospongiae.
So far scientific publications have identified about 9,000 poriferan species,
of which: about 400 are glass sponges; about 500 are calcareous species; and the rest are demosponges.
However, some types of habitat, vertical rock and cave walls and galleries in rock and coral boulders, have been investigated very little, even in shallow seas.
Classes
Sponges were traditionally distributed in three classes: calcareous sponges (Calcarea), glass sponges (Hexactinellida) and demosponges (Demospongiae). However, studies have shown that the Homoscleromorpha, a group thought to belong to the Demospongiae, is actually phylogenetically well separated. Therefore, they have recently been recognized as the fourth class of sponges.
Sponges are divided into
classes mainly according to the composition of their
skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
s:
These are arranged in evolutionary order as shown below in ascending order of their evolution from top to bottom:
:
Fossil record

Although molecular clocks and biomarkers suggest sponges existed well before the Cambrian explosion of life,
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
spicules like those of demosponges are absent from the fossil record until the Cambrian. An unsubstantiated 2002 report exists of spicules in rocks dated around . Well-preserved fossil sponges from about in the Ediacaran period have been found in the Doushantuo Formation. These fossils, which include: spicules;
pinacocyte Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes ...
s; porocytes;
archeocytes;
sclerocyte Sclerocytes are specialised cells that secrete the mineralized structures in the body wall of some invertebrates.
In sponges they secrete calcareous or siliceous spicules which are found in the mesohyl layer of sponges. The sclerocytes produce spic ...
s; and the internal cavity, have been classified as demosponges. Fossils of
glass sponges have been found from around in rocks in Australia, China, and Mongolia.
Early Cambrian sponges from Mexico belonging to the genus ''Kiwetinokia'' show evidence of fusion of several smaller spicules to form a single large spicule. Calcium carbonate spicules of
calcareous sponges have been found in Early Cambrian rocks from about in Australia. Other probable demosponges have been found in the Early Cambrian Chengjiang fauna, from .
Fossils found in the Canadian Northwest Territories dating to may be sponges; if this finding is confirmed, it suggests the first animals appeared before the Neoproterozoic oxygenation event.

Freshwater sponges appear to be much younger, as the earliest known fossils date from the Mid-Eocene period about .
Although about 90% of modern sponges are demosponges, fossilized remains of this type are less common than those of other types because their skeletons are composed of relatively soft spongin that does not fossilize well.
Earliest sponge symbionts are known from the Llandovery epoch, early Silurian.
A chemical tracer is 24-isopropylcholestane, which is a stable derivative of 24-isopropylcholesterol, which is said to be produced by
demosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a har ...
s but not by eumetazoans ("true animals", i.e.
cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
ns and bilaterians). Since
choanoflagellate
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconne ...
s are thought to be animals' closest single-celled relatives, a team of scientists examined the biochemistry and
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s of one
choanoflagellate
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconne ...
species. They concluded that this species could not produce 24-isopropylcholesterol but that investigation of a wider range of choanoflagellates would be necessary in order to prove that the fossil 24-isopropylcholestane could only have been produced by demosponges.
Although a previous publication reported traces of the chemical 24-isopropylcholestane in ancient rocks dating to , recent research using a much more accurately dated rock series has revealed that these biomarkers only appear before the end of the Marinoan glaciation approximately , and that "Biomarker analysis has yet to reveal any convincing evidence for ancient sponges pre-dating the first globally extensive Neoproterozoic glacial episode (the Sturtian, ~ in Oman)". While it has been argued that this 'sponge biomarker' could have originated from marine algae, recent research suggests that the algae's ability to produce this biomarker evolved only in the Carboniferous; as such, the biomarker remains strongly supportive of the presence of demosponges in the Cryogenian.
s, which some classify as a type of coralline sponge, are very common fossils in rocks from the Early Cambrian about , but apparently died out by the end of the Cambrian .
It has been suggested that they were produced by: sponges;
cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
ns; algae; foraminiferans; a completely separate
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
of animals, Archaeocyatha; or even a completely separate Kingdom (biology), kingdom of life, labeled Archaeata or Inferibionta. Since the 1990s archaeocyathids have been regarded as a distinctive group of sponges.
It is difficult to fit chancelloriids into classifications of sponges or more complex animals. An analysis in 1996 concluded that they were closely related to sponges on the grounds that the detailed structure of chancellorid sclerites ("armor plates") is similar to that of fibers of spongin, a
collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
protein, in modern keratose (horny)
demosponge
Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a har ...
s such as ''Darwinella (sponge), Darwinella''. However, another analysis in 2002 concluded that chancelloriids are not sponges and may be intermediate between sponges and more complex animals, among other reasons because their skins were thicker and more tightly connected than those of sponges.
[ free text at ] In 2008 a detailed analysis of chancelloriids' sclerites concluded that they were very similar to those of halkieriids, mobile bilaterian animals that looked like slugs in chain mail and whose fossils are found in rocks from the very Early Cambrian to the Mid Cambrian. If this is correct, it would create a dilemma, as it is extremely unlikely that totally unrelated organisms could have developed such similar sclerites independently, but the huge difference in the structures of their bodies makes it hard to see how they could be closely related.
Relationships to other animal groups

In the 1990s sponges were widely regarded as a
monophyletic group, all of them having descended from a last universal common ancestor, common ancestor that was itself a sponge, and as the "sister-group" to all other animals, metazoans (multi-celled animals), which themselves form a monophyletic group. On the other hand, some 1990s analyses also revived the idea that animals' nearest evolutionary relatives are
choanoflagellate
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconne ...
s, single-celled organisms very similar to sponges' choanocytes – which would imply that most Metazoa evolved from very sponge-like ancestors and therefore that sponges may not be monophyletic, as the same sponge-like ancestors may have given rise both to modern sponges and to non-sponge members of Metazoa.
Analyses since 2001 have concluded that Eumetazoa (more complex than sponges) are more closely related to particular groups of sponges than to other sponge groups. Such conclusions imply that sponges are not monophyletic, because the most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor of all sponges would also be a direct ancestor of the Eumetazoa, which are not sponges. A study in 2001 based on comparisons of ribosome DNA concluded that the most fundamental division within sponges was between
glass sponges and the rest, and that Eumetazoa are more closely related to
calcareous sponges (those with calcium carbonate spicules) than to other types of sponge.
In 2007 one analysis based on comparisons of RNA and another based mainly on comparison of spicules concluded that demosponges and glass sponges are more closely related to each other than either is to the calcareous sponges, which in turn are more closely related to Eumetazoa.
Other anatomical and biochemical evidence links the Eumetazoa with Homoscleromorpha, a sub-group of demosponges. A comparison in 2007 of cell nucleus, nuclear DNA, excluding glass sponges and
comb jellies, concluded that:
* Homoscleromorpha are most closely related to Eumetazoa;
* calcareous sponges are the next closest;
* the other demosponges are evolutionary "aunts" of these groups; and
* the chancelloriidae, chancelloriids, bag-like animals whose fossils are found in Cambrian rocks, may be sponges.
The
sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
of Homoscleromorpha share features with the sperm of Eumetazoa, that sperm of other sponges lack. In both Homoscleromorpha and Eumetazoa layers of cells are bound together by attachment to a carpet-like basal membrane composed mainly of "typ IV"
collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
, a form of collagen not found in other sponges – although the
spongin fibers that reinforce the mesohyl of all demosponges is similar to "type IV" collagen.
The analyses described above concluded that sponges are closest to the ancestors of all Metazoa, of all multi-celled animals including both sponges and more complex groups. However, another comparison in 2008 of 150 genes in each of 21 genera, ranging from fungi to humans but including only two species of sponge, suggested that ctenophora, comb jellies (ctenophora) are the most basal lineage of the Metazoa included in the sample. If this is correct, either modern comb jellies developed their complex structures independently of other Metazoa, or sponges' ancestors were more complex and all known sponges are drastically simplified forms. The study recommended further analyses using a wider range of sponges and other simple Metazoa such as Placozoa.
The results of such an analysis, published in 2009, suggest that a return to the previous view may be warranted. 'Family trees' constructed using a combination of all available data – morphological, developmental and molecular – concluded that the sponges are in fact a monophyletic group, and with the cnidarians form the sister group to the bilaterians.
A very large and internally consistent alignment of 1,719 proteins at the metazoan scale, published in 2017, showed that (i) sponges – represented by Homoscleromorpha, Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae – are monophyletic, (ii) sponges are sister-group to all other multicellular animals, (iii) ctenophores emerge as the second-earliest branching animal lineage, and (iv) placozoans emerge as the third animal lineage, followed by Planulozoa, cnidarians sister-group to bilaterians.
In March 2021, scientists from Dublin found additional evidence that sponges are the sister group to all other animals.
Notable spongiologists
* Céline Allewaert
* Patricia Bergquist
* James Scott Bowerbank
* Maurice Burton
* Henry John Carter
* Max Walker de Laubenfels
* Arthur Dendy
* Édouard Placide Duchassaing de Fontbressin
* Randolph Kirkpatrick
* Robert J. Lendlmayer von Lendenfeld
* Edward Alfred Minchin
* Giovanni Domenico Nardo
* Eduard Oscar Schmidt
* Émile Topsent
Use
By dolphins
A report in 1997 described use of sponges animal tool use, as a tool by bottlenose dolphins in Shark Bay in Western Australia. A dolphin will attach a marine sponge to its rostrum (anatomy), rostrum, which is presumably then used to protect it when searching for food in the sandy sea floor, sea bottom.
The behavior, known as ''sponging'', has only been observed in this bay, and is almost exclusively shown by females. A study in 2005 concluded that mothers teach the behavior to their daughters, and that all the sponge-users are closely related, suggesting that it is a fairly recent innovation.
By humans


Skeleton
The
calcium carbonate or
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
spicules
Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms
Spicule may also refer to:
*Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea sponges
*Spicule (nematode), reproductive structures found in male nematodes ( ...
of most sponge genus, genera make them too rough for most uses, but two genera, ''Hippospongia'' and ''Spongia'', have soft, entirely fibrous skeletons. Early Europeans used soft sponges for many purposes, including padding for helmets, portable drinking utensils and municipal water filters. Until the invention of synthetic sponges, they were used as cleaning tools, applicators for paints and ceramic glazes and discreet contraceptives. However, by the mid-20th century, over-fishing brought both the animals and the industry close to extinction.
Many objects with sponge-like textures are now made of substances not derived from poriferans. Synthetic sponges include personal and household Sponge (material), cleaning tools, breast implants, and contraceptive sponges.
Typical materials used are cellulose foam, polyurethane foam, and less frequently, silicone foam.
The luffa "sponge", also spelled ''loofah'', which is commonly sold for use in the kitchen or the shower, is not derived from an animal but mainly from the fibrous "skeleton" of the Luffa aegyptiaca, sponge gourd (''Luffa aegyptiaca'', Cucurbitaceae).
Antibiotic compounds
Sponges have medicine, medicinal potential due to the presence in sponges themselves or their microbial symbiosis, symbionts of chemicals that may be used to control viruses,
bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, tumors and fungi.
Other biologically active compounds

Lacking any protective shell or means of escape, sponges have evolved to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds. One such class is the oxidized fatty acid derivatives called oxylipins. Members of this family have been found to have anti-cancer, anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties. One example isolated from the Okinawan ''plakortis'' sponges, plakoridine A, has shown potential as a cytotoxin to murine lymphoma cells.
See also
* Lists of sponges
* Sponge Reef Project
* SpongeBob SquarePants
* 3-Alkylpyridinium, compounds found in marine Haplosclerida sponges
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Water flow and feeding in the phylum Porifera (sponges)– Adobe Flash, Flash animations of sponge body structures, water flow and feeding
Carsten's Spongepage Information on the ecology and the biotechnological potential of sponges and their associated bacteria.
Tarpon Springs, Florida
Nature's 'fibre optics' expertsQueensland Museum information about spongesQueensland Museum Sessile marine invertebrates collectionsQueensland Museum Sessile marine invertebrates researchSponge Guide for Britain and Ireland Bernard Picton, Christine Morrow & Rob van Soest
World Porifera database the world list of extant sponges, includes a searchable database.
// Food and Agriculture Organisation
{{Authority control
Sponges,
Aquatic animals
Ediacaran first appearances
Parazoa
 Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are
Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are  The single-celled
The single-celled 
 Sponges do not have distinct
Sponges do not have distinct  In waters where the supply of food particles is very poor, some species prey on crustaceans and other small animals. So far only 137 species have been discovered. Most belong to the
In waters where the supply of food particles is very poor, some species prey on crustaceans and other small animals. So far only 137 species have been discovered. Most belong to the  Sponges have three asexual methods of reproduction: after fragmentation, by
Sponges have three asexual methods of reproduction: after fragmentation, by  Sponges are more abundant but less diverse in temperate waters than in tropical waters, possibly because organisms that prey on sponges are more abundant in tropical waters. Glass sponges are the most common in polar waters and in the depths of temperate and tropical seas, as their very porous construction enables them to extract food from these resource-poor waters with the minimum of effort.
Sponges are more abundant but less diverse in temperate waters than in tropical waters, possibly because organisms that prey on sponges are more abundant in tropical waters. Glass sponges are the most common in polar waters and in the depths of temperate and tropical seas, as their very porous construction enables them to extract food from these resource-poor waters with the minimum of effort. 

 Although molecular clocks and biomarkers suggest sponges existed well before the Cambrian explosion of life,
Although molecular clocks and biomarkers suggest sponges existed well before the Cambrian explosion of life,  Freshwater sponges appear to be much younger, as the earliest known fossils date from the Mid-Eocene period about . Although about 90% of modern sponges are demosponges, fossilized remains of this type are less common than those of other types because their skeletons are composed of relatively soft spongin that does not fossilize well.
Earliest sponge symbionts are known from the Llandovery epoch, early Silurian.
A chemical tracer is 24-isopropylcholestane, which is a stable derivative of 24-isopropylcholesterol, which is said to be produced by
Freshwater sponges appear to be much younger, as the earliest known fossils date from the Mid-Eocene period about . Although about 90% of modern sponges are demosponges, fossilized remains of this type are less common than those of other types because their skeletons are composed of relatively soft spongin that does not fossilize well.
Earliest sponge symbionts are known from the Llandovery epoch, early Silurian.
A chemical tracer is 24-isopropylcholestane, which is a stable derivative of 24-isopropylcholesterol, which is said to be produced by  In the 1990s sponges were widely regarded as a monophyletic group, all of them having descended from a last universal common ancestor, common ancestor that was itself a sponge, and as the "sister-group" to all other animals, metazoans (multi-celled animals), which themselves form a monophyletic group. On the other hand, some 1990s analyses also revived the idea that animals' nearest evolutionary relatives are
In the 1990s sponges were widely regarded as a monophyletic group, all of them having descended from a last universal common ancestor, common ancestor that was itself a sponge, and as the "sister-group" to all other animals, metazoans (multi-celled animals), which themselves form a monophyletic group. On the other hand, some 1990s analyses also revived the idea that animals' nearest evolutionary relatives are  The analyses described above concluded that sponges are closest to the ancestors of all Metazoa, of all multi-celled animals including both sponges and more complex groups. However, another comparison in 2008 of 150 genes in each of 21 genera, ranging from fungi to humans but including only two species of sponge, suggested that ctenophora, comb jellies (ctenophora) are the most basal lineage of the Metazoa included in the sample. If this is correct, either modern comb jellies developed their complex structures independently of other Metazoa, or sponges' ancestors were more complex and all known sponges are drastically simplified forms. The study recommended further analyses using a wider range of sponges and other simple Metazoa such as Placozoa.
The results of such an analysis, published in 2009, suggest that a return to the previous view may be warranted. 'Family trees' constructed using a combination of all available data – morphological, developmental and molecular – concluded that the sponges are in fact a monophyletic group, and with the cnidarians form the sister group to the bilaterians.
A very large and internally consistent alignment of 1,719 proteins at the metazoan scale, published in 2017, showed that (i) sponges – represented by Homoscleromorpha, Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae – are monophyletic, (ii) sponges are sister-group to all other multicellular animals, (iii) ctenophores emerge as the second-earliest branching animal lineage, and (iv) placozoans emerge as the third animal lineage, followed by Planulozoa, cnidarians sister-group to bilaterians.
In March 2021, scientists from Dublin found additional evidence that sponges are the sister group to all other animals.
The analyses described above concluded that sponges are closest to the ancestors of all Metazoa, of all multi-celled animals including both sponges and more complex groups. However, another comparison in 2008 of 150 genes in each of 21 genera, ranging from fungi to humans but including only two species of sponge, suggested that ctenophora, comb jellies (ctenophora) are the most basal lineage of the Metazoa included in the sample. If this is correct, either modern comb jellies developed their complex structures independently of other Metazoa, or sponges' ancestors were more complex and all known sponges are drastically simplified forms. The study recommended further analyses using a wider range of sponges and other simple Metazoa such as Placozoa.
The results of such an analysis, published in 2009, suggest that a return to the previous view may be warranted. 'Family trees' constructed using a combination of all available data – morphological, developmental and molecular – concluded that the sponges are in fact a monophyletic group, and with the cnidarians form the sister group to the bilaterians.
A very large and internally consistent alignment of 1,719 proteins at the metazoan scale, published in 2017, showed that (i) sponges – represented by Homoscleromorpha, Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae – are monophyletic, (ii) sponges are sister-group to all other multicellular animals, (iii) ctenophores emerge as the second-earliest branching animal lineage, and (iv) placozoans emerge as the third animal lineage, followed by Planulozoa, cnidarians sister-group to bilaterians.
In March 2021, scientists from Dublin found additional evidence that sponges are the sister group to all other animals.

 Lacking any protective shell or means of escape, sponges have evolved to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds. One such class is the oxidized fatty acid derivatives called oxylipins. Members of this family have been found to have anti-cancer, anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties. One example isolated from the Okinawan ''plakortis'' sponges, plakoridine A, has shown potential as a cytotoxin to murine lymphoma cells.
Lacking any protective shell or means of escape, sponges have evolved to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds. One such class is the oxidized fatty acid derivatives called oxylipins. Members of this family have been found to have anti-cancer, anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties. One example isolated from the Okinawan ''plakortis'' sponges, plakoridine A, has shown potential as a cytotoxin to murine lymphoma cells.