Ontario Sports on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen
 The thinly populated Canadian Shield, which dominates the northwestern and central portions of the province and comprises over half the land area of Ontario. Although this area mostly does not support agriculture, it is rich in
The thinly populated Canadian Shield, which dominates the northwestern and central portions of the province and comprises over half the land area of Ontario. Although this area mostly does not support agriculture, it is rich in
 Ontario's climate varies by season and location. Three air sources affect it: cold, dry, arctic air from the north (dominant factor during the winter months, and for a longer part of the year in far northern Ontario); Pacific polar air crossing in from the western Canadian Prairies/US Northern Plains; and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. The effects of these major air masses on temperature and precipitation depend mainly on latitude, proximity to major bodies of water and to a small extent, terrain relief. In general, most of Ontario's climate is classified as humid continental.
Ontario has four main climatic regions:
* The surrounding Great Lakes greatly influence the climatic region of southern Ontario. During the fall and winter, the release of heat stored by the lakes moderates the climate near the shores. This gives parts of southern Ontario milder winters than mid-continental areas at lower latitudes. Parts of Southwestern Ontario (generally south of a line from Sarnia–Toronto) have a moderate humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification ''Dfa''), similar to the inland Mid-Atlantic states and the
Ontario's climate varies by season and location. Three air sources affect it: cold, dry, arctic air from the north (dominant factor during the winter months, and for a longer part of the year in far northern Ontario); Pacific polar air crossing in from the western Canadian Prairies/US Northern Plains; and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. The effects of these major air masses on temperature and precipitation depend mainly on latitude, proximity to major bodies of water and to a small extent, terrain relief. In general, most of Ontario's climate is classified as humid continental.
Ontario has four main climatic regions:
* The surrounding Great Lakes greatly influence the climatic region of southern Ontario. During the fall and winter, the release of heat stored by the lakes moderates the climate near the shores. This gives parts of southern Ontario milder winters than mid-continental areas at lower latitudes. Parts of Southwestern Ontario (generally south of a line from Sarnia–Toronto) have a moderate humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification ''Dfa''), similar to the inland Mid-Atlantic states and the  * The northernmost parts of Ontario – primarily north of 50°N – have a subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfc'') with long, severely cold winters and short, cool to warm summers with dramatic temperature changes possible in all seasons. With no major mountain ranges blocking sinking Arctic air masses, temperatures of are not uncommon; snow remains on the ground for sometimes over half the year. Snow accumulation can be high in some areas. Precipitation is generally less than and peaks in the summer months in the form of rain or thunderstorms.
Severe thunderstorms peak in summer. Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, in Southern Ontario, Southern Southwestern Ontario, (Southwestern) Ontario, has the most lightning strikes per year in Canada, averaging 33 days of thunderstorm activity per year. In a typical year, Ontario averages 11 confirmed tornado touchdowns. However, over the last 4 years, it has had upwards of 20 tornado touchdowns per year, with the highest frequency in the Windsor-Essex – Chatham Kent area, though few are very destructive (the majority between F0 to F2 on the Fujita scale). Ontario had a record 29 tornadoes in both 2006 and 2009. Tropical cyclone, Tropical depression remnants occasionally bring heavy rains and winds in the south, but are rarely deadly. A notable exception was Hurricane Hazel which struck Southern Ontario centred on Toronto, in October 1954.
* The northernmost parts of Ontario – primarily north of 50°N – have a subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfc'') with long, severely cold winters and short, cool to warm summers with dramatic temperature changes possible in all seasons. With no major mountain ranges blocking sinking Arctic air masses, temperatures of are not uncommon; snow remains on the ground for sometimes over half the year. Snow accumulation can be high in some areas. Precipitation is generally less than and peaks in the summer months in the form of rain or thunderstorms.
Severe thunderstorms peak in summer. Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, in Southern Ontario, Southern Southwestern Ontario, (Southwestern) Ontario, has the most lightning strikes per year in Canada, averaging 33 days of thunderstorm activity per year. In a typical year, Ontario averages 11 confirmed tornado touchdowns. However, over the last 4 years, it has had upwards of 20 tornado touchdowns per year, with the highest frequency in the Windsor-Essex – Chatham Kent area, though few are very destructive (the majority between F0 to F2 on the Fujita scale). Ontario had a record 29 tornadoes in both 2006 and 2009. Tropical cyclone, Tropical depression remnants occasionally bring heavy rains and winds in the south, but are rarely deadly. A notable exception was Hurricane Hazel which struck Southern Ontario centred on Toronto, in October 1954.
 As for Northern Ontario, the English explorer Henry Hudson sailed into Hudson Bay in 1611 and claimed its drainage basin for England. The area would become known as Rupert's Land.
Samuel de Champlain reached Lake Huron in 1615, and French missionaries, such as the Jésuites and Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice, Supliciens, began to establish posts along the Great Lakes. The French allied with most Indigenous groups of Ontario, all for the fur trade and for defence against Iroquois attacks (which would later be called the Iroquois Wars). The French would declare their Indigenous allies to be subjects of the King of France and would often act as mediators between different groups. The Iroquois later allied themselves with the British.
From 1634 to 1640, the Huron were devastated by European infectious diseases, such as measles and smallpox, to which they had no immunity. By 1700, the Iroquois had been driven out or left the area that would become Ontario and the Mississaugas of the Ojibwa had settled the north shore of Lake Ontario. The remaining Huron settled north of Quebec.
During the French and Indian War, the North American theater of the Seven Years' War of 1754 to 1763, the British defeated the armies of New France and its Indigenous allies. In the Treaty of Paris 1763 France ceded most of its possessions in North America to Britain. Using the Quebec Act, Britain re-organised the territory into the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Province of Quebec.
As for Northern Ontario, the English explorer Henry Hudson sailed into Hudson Bay in 1611 and claimed its drainage basin for England. The area would become known as Rupert's Land.
Samuel de Champlain reached Lake Huron in 1615, and French missionaries, such as the Jésuites and Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice, Supliciens, began to establish posts along the Great Lakes. The French allied with most Indigenous groups of Ontario, all for the fur trade and for defence against Iroquois attacks (which would later be called the Iroquois Wars). The French would declare their Indigenous allies to be subjects of the King of France and would often act as mediators between different groups. The Iroquois later allied themselves with the British.
From 1634 to 1640, the Huron were devastated by European infectious diseases, such as measles and smallpox, to which they had no immunity. By 1700, the Iroquois had been driven out or left the area that would become Ontario and the Mississaugas of the Ojibwa had settled the north shore of Lake Ontario. The remaining Huron settled north of Quebec.
During the French and Indian War, the North American theater of the Seven Years' War of 1754 to 1763, the British defeated the armies of New France and its Indigenous allies. In the Treaty of Paris 1763 France ceded most of its possessions in North America to Britain. Using the Quebec Act, Britain re-organised the territory into the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Province of Quebec.
 In 1782–1784, 5,000 United Empire Loyalists entered what is now Ontario following the American Revolution. The Kingdom of Great Britain granted them land and other items with which to rebuild their lives. The British also set up reserves in Ontario for the Mohawk people, Mohawks who had fought for the British and had lost their land in New York state. Other Iroquois, also displaced from New York were resettled in 1784 at the Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations reserve at the west end of Lake Ontario. The Mississaugas, displaced by European settlements, would later move to Six Nations also.
After the American War of Independence, the first reserves for First Nations were established. These are situated at Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations (1784), Tyendinaga Mohawk Territory, Tyendinaga (1793) and Akwesasne (1795). Six Nations and Tyendinaga were established by the British for those Indigenous groups who had fought on the side of the British, and were expelled from the new United States. Akwesasne was a pre-existing Mohawk community and its borders were formalized under the 1795 Jay Treaty.
In 1788, while part of the Province of Quebec, southern Ontario was divided into four District#Ontario, districts: Western District, Upper Canada, Hesse, Eastern District, Upper Canada, Lunenburg, Midland District, Upper Canada, Mecklenburg, and Home District, Nassau. In 1792, the four districts were renamed: Hesse became the Western District, Lunenburg became the Eastern District, Mecklenburg became the Midland District, and Nassau became the Home District. Counties were created within the districts.
The population of Canada west of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence substantially increased during this period, a fact recognized by the Constitutional Act 1791, ''Constitutional Act'' of 1791, which split Quebec into the Canadas: Upper Canada southwest of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence, and Lower Canada east of it.
In 1782–1784, 5,000 United Empire Loyalists entered what is now Ontario following the American Revolution. The Kingdom of Great Britain granted them land and other items with which to rebuild their lives. The British also set up reserves in Ontario for the Mohawk people, Mohawks who had fought for the British and had lost their land in New York state. Other Iroquois, also displaced from New York were resettled in 1784 at the Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations reserve at the west end of Lake Ontario. The Mississaugas, displaced by European settlements, would later move to Six Nations also.
After the American War of Independence, the first reserves for First Nations were established. These are situated at Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations (1784), Tyendinaga Mohawk Territory, Tyendinaga (1793) and Akwesasne (1795). Six Nations and Tyendinaga were established by the British for those Indigenous groups who had fought on the side of the British, and were expelled from the new United States. Akwesasne was a pre-existing Mohawk community and its borders were formalized under the 1795 Jay Treaty.
In 1788, while part of the Province of Quebec, southern Ontario was divided into four District#Ontario, districts: Western District, Upper Canada, Hesse, Eastern District, Upper Canada, Lunenburg, Midland District, Upper Canada, Mecklenburg, and Home District, Nassau. In 1792, the four districts were renamed: Hesse became the Western District, Lunenburg became the Eastern District, Mecklenburg became the Midland District, and Nassau became the Home District. Counties were created within the districts.
The population of Canada west of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence substantially increased during this period, a fact recognized by the Constitutional Act 1791, ''Constitutional Act'' of 1791, which split Quebec into the Canadas: Upper Canada southwest of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence, and Lower Canada east of it.
 John Graves Simcoe was appointed Upper Canada's first Lieutenant governor (Canada), Lieutenant governor in 1793. A second wave of Americans, not all of them necessarily loyalists moved to Upper Canada after 1790 until the pre-war of 1812, many seeking available cheap land, and at the time, lower taxation.
By 1798, there were eight districts: Eastern, Home, Johnstown District, Upper Canada, Johnstown, London District, Upper Canada, London, Midland, Newcastle District, Newcastle, Niagara District, Niagara, and Western. By 1826, there were eleven districts: Bathurst District, Bathurst, Eastern, Gore District, Upper Canada, Gore, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa District, Ottawa, and Western. By 1838, there were twenty districts: Bathurst, Brock, Colbourne, Dalhousie District, Dalhousie, Eastern, Gore, Home, Huron, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, Prince Edward, Simcoe County, Simcoe, Talbot, Victoria, Wellington District, Upper Canada, Wellington, and Western.
American troops in the War of 1812 invaded Upper Canada across the Niagara River and the Detroit River, but were defeated and pushed back by the British, Canadian fencibles and militias, and First Nations in Canada, First Nations warriors. However, the Americans eventually gained control of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario. The 1813 Battle of York saw American troops defeat the garrison at the Upper Canada capital of York, Upper Canada, York. The Americans looted the town and burned the Upper Canada Parliament Buildings during their brief occupation. The British would Burning of Washington, burn the American capital of Washington, D.C. in 1814.
John Graves Simcoe was appointed Upper Canada's first Lieutenant governor (Canada), Lieutenant governor in 1793. A second wave of Americans, not all of them necessarily loyalists moved to Upper Canada after 1790 until the pre-war of 1812, many seeking available cheap land, and at the time, lower taxation.
By 1798, there were eight districts: Eastern, Home, Johnstown District, Upper Canada, Johnstown, London District, Upper Canada, London, Midland, Newcastle District, Newcastle, Niagara District, Niagara, and Western. By 1826, there were eleven districts: Bathurst District, Bathurst, Eastern, Gore District, Upper Canada, Gore, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa District, Ottawa, and Western. By 1838, there were twenty districts: Bathurst, Brock, Colbourne, Dalhousie District, Dalhousie, Eastern, Gore, Home, Huron, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, Prince Edward, Simcoe County, Simcoe, Talbot, Victoria, Wellington District, Upper Canada, Wellington, and Western.
American troops in the War of 1812 invaded Upper Canada across the Niagara River and the Detroit River, but were defeated and pushed back by the British, Canadian fencibles and militias, and First Nations in Canada, First Nations warriors. However, the Americans eventually gained control of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario. The 1813 Battle of York saw American troops defeat the garrison at the Upper Canada capital of York, Upper Canada, York. The Americans looted the town and burned the Upper Canada Parliament Buildings during their brief occupation. The British would Burning of Washington, burn the American capital of Washington, D.C. in 1814.
 After the War of 1812, relative stability allowed for increasing numbers of immigrants to arrive from Europe rather than from the United States. As was the case in the previous decades, this immigration shift was encouraged by the colonial leaders. Despite affordable and often free land, many arriving newcomers, mostly from Britain and Ireland, found frontier life with the harsh climate difficult, and some of those with the means eventually returned home or went south. However, population growth far exceeded emigration in the following decades. It was a mostly agrarian-based society, but canal projects and a new network of plank roads spurred greater trade within the colony and with the United States, thereby improving previously damaged relations over time.
Meanwhile, Ontario's numerous waterways aided travel and transportation into the interior and supplied Hydropower, water power for development. As the population increased, so did the industries and transportation networks, which in turn led to further development. By the end of the century, Ontario vied with Quebec as the nation's leader in terms of growth in population, industry, arts and communications.
Unrest in the colony began to chafe against the aristocratic Family Compact who governed while benefiting economically from the region's resources, and who did not allow elected bodies power. This resentment spurred republican ideals and sowed the seeds for early Canadian nationalism. Accordingly, rebellion in favour of responsible government rose in both regions; Louis-Joseph Papineau led the Lower Canada Rebellion and William Lyon Mackenzie, first
After the War of 1812, relative stability allowed for increasing numbers of immigrants to arrive from Europe rather than from the United States. As was the case in the previous decades, this immigration shift was encouraged by the colonial leaders. Despite affordable and often free land, many arriving newcomers, mostly from Britain and Ireland, found frontier life with the harsh climate difficult, and some of those with the means eventually returned home or went south. However, population growth far exceeded emigration in the following decades. It was a mostly agrarian-based society, but canal projects and a new network of plank roads spurred greater trade within the colony and with the United States, thereby improving previously damaged relations over time.
Meanwhile, Ontario's numerous waterways aided travel and transportation into the interior and supplied Hydropower, water power for development. As the population increased, so did the industries and transportation networks, which in turn led to further development. By the end of the century, Ontario vied with Quebec as the nation's leader in terms of growth in population, industry, arts and communications.
Unrest in the colony began to chafe against the aristocratic Family Compact who governed while benefiting economically from the region's resources, and who did not allow elected bodies power. This resentment spurred republican ideals and sowed the seeds for early Canadian nationalism. Accordingly, rebellion in favour of responsible government rose in both regions; Louis-Joseph Papineau led the Lower Canada Rebellion and William Lyon Mackenzie, first
 In 1849, the districts of southern Ontario were abolished by the Province of Canada, and county governments took over certain municipal responsibilities. The Province of Canada also began creating ''districts'' in sparsely populated Northern Ontario with the establishment of Algoma District and Nipissing District in 1858.
An economic boom in the 1850s coincided with railway expansion across the province, further increasing the economic strength of Central Canada. With the repeal of the Corn Laws and a reciprocity agreement in place with the United States, various industries such as timber, mining, farming and alcohol distilling benefited tremendously.
A political stalemate between the Canadian French, French- and Canadian English, English-speaking legislators, as well as fear of aggression from the United States during and immediately after the American Civil War, led the political elite to hold a series of conferences in the 1860s to effect a broader federal union of all British North American colonies. The ''Constitution Act, 1867, British North America Act'' took effect on July 1, 1867, establishing the Dominion of Canada, initially with four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. The Province of Canada was divided into Ontario and Quebec so that each linguistic group would have its own province. Both Quebec and Ontario were required by section 93 of the ''British North America Act'' to safeguard existing educational rights and privileges of the Protestant and Catholic minorities. Thus, separate Catholic schools and board of education, school boards were permitted in Ontario. However, neither province had a constitutional requirement to protect its French- or English-speaking minority. Toronto was formally established as Ontario's provincial capital.
In 1849, the districts of southern Ontario were abolished by the Province of Canada, and county governments took over certain municipal responsibilities. The Province of Canada also began creating ''districts'' in sparsely populated Northern Ontario with the establishment of Algoma District and Nipissing District in 1858.
An economic boom in the 1850s coincided with railway expansion across the province, further increasing the economic strength of Central Canada. With the repeal of the Corn Laws and a reciprocity agreement in place with the United States, various industries such as timber, mining, farming and alcohol distilling benefited tremendously.
A political stalemate between the Canadian French, French- and Canadian English, English-speaking legislators, as well as fear of aggression from the United States during and immediately after the American Civil War, led the political elite to hold a series of conferences in the 1860s to effect a broader federal union of all British North American colonies. The ''Constitution Act, 1867, British North America Act'' took effect on July 1, 1867, establishing the Dominion of Canada, initially with four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. The Province of Canada was divided into Ontario and Quebec so that each linguistic group would have its own province. Both Quebec and Ontario were required by section 93 of the ''British North America Act'' to safeguard existing educational rights and privileges of the Protestant and Catholic minorities. Thus, separate Catholic schools and board of education, school boards were permitted in Ontario. However, neither province had a constitutional requirement to protect its French- or English-speaking minority. Toronto was formally established as Ontario's provincial capital.
 The borders of Ontario, its new name in 1867, were provisionally expanded north and west. When the Province of Canada was formed, its borders were not entirely clear, and Ontario claimed eventually to reach all the way to the Rocky Mountains and Arctic Ocean. With Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land, Ontario was interested in clearly defining its borders, especially since some of the new areas in which it was interested were rapidly growing. After the federal government asked Ontario to pay for construction in the new disputed area, the province asked for an elaboration on its limits, and its boundary was moved north to the 51st parallel north.
The borders of Ontario, its new name in 1867, were provisionally expanded north and west. When the Province of Canada was formed, its borders were not entirely clear, and Ontario claimed eventually to reach all the way to the Rocky Mountains and Arctic Ocean. With Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land, Ontario was interested in clearly defining its borders, especially since some of the new areas in which it was interested were rapidly growing. After the federal government asked Ontario to pay for construction in the new disputed area, the province asked for an elaboration on its limits, and its boundary was moved north to the 51st parallel north.
 Once constituted as a province, Ontario proceeded to assert its economic and legislative power. In 1872, the lawyer Oliver Mowat became Premier of Ontario and remained as premier until 1896. He fought for provincial rights, weakening the power of the Government of Canada, federal government in provincial matters, usually through well-argued appeals to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. His battles with the federal government greatly Decentralization, decentralized Canada, giving the provinces far more power than John A. Macdonald had intended. He consolidated and expanded Ontario's educational and provincial institutions, created districts in Northern Ontario, and fought to ensure that those parts of Northwestern Ontario not historically part of Upper Canada (the vast areas north and west of the Lake Superior-Hudson Bay watershed, known as the District of Keewatin) would become part of Ontario, a victory embodied in the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889''. He also presided over the emergence of the province into the economic powerhouse of Canada. Mowat was the creator of what is often called ''Empire Ontario''.
Beginning with Macdonald's National Policy (1879) and the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway (1875–1885) through Northern Ontario and the Canadian Prairies to British Columbia, Ontario manufacturing and industry flourished. However, population increases slowed after a large recession hit the province in 1893, thus slowing growth drastically but for only a few years. Many newly arrived immigrants and others moved west along the railway to the Prairie Provinces and British Columbia, sparsely settling Northern Ontario.
The northern and western boundaries of Ontario were in dispute after Canadian Confederation. Ontario's right to Northwestern Ontario was determined by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in 1884 and confirmed by the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889'' of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. By 1899, there were seven northern districts: Algoma, Manitoulin, Muskoka, Nipissing, Parry Sound, Rainy River, and Thunder Bay. Four more northern districts were created between 1907 and 1912: Cochrane, Kenora, Sudbury and Timiskaming.
Mineral exploitation accelerated in the late 19th century, leading to the rise of important mining centres in the northeast, such as Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, Cobalt, Ontario, Cobalt and Timmins. The province harnessed its water power to generate hydro-electric power and created the state-controlled Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, later Ontario Hydro. The availability of cheap electric power further facilitated the development of industry. The Ford Motor Company of Canada was established in 1904 and the McLaughlin Motor Car Company (later General Motors Canada) was founded in 1907. The motor vehicle industry became the most lucrative industry for the Ontario economy during the 20th century.
In July 1912, the Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, Conservative government of James Whitney (politician), James Whitney issued Regulation 17 which severely limited the availability of French-language schooling to the province's French-speaking minority. French Canadians reacted with outrage, journalist Henri Bourassa denouncing the "Prussians of Ontario". The regulation was eventually repealed in 1927.
Once constituted as a province, Ontario proceeded to assert its economic and legislative power. In 1872, the lawyer Oliver Mowat became Premier of Ontario and remained as premier until 1896. He fought for provincial rights, weakening the power of the Government of Canada, federal government in provincial matters, usually through well-argued appeals to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. His battles with the federal government greatly Decentralization, decentralized Canada, giving the provinces far more power than John A. Macdonald had intended. He consolidated and expanded Ontario's educational and provincial institutions, created districts in Northern Ontario, and fought to ensure that those parts of Northwestern Ontario not historically part of Upper Canada (the vast areas north and west of the Lake Superior-Hudson Bay watershed, known as the District of Keewatin) would become part of Ontario, a victory embodied in the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889''. He also presided over the emergence of the province into the economic powerhouse of Canada. Mowat was the creator of what is often called ''Empire Ontario''.
Beginning with Macdonald's National Policy (1879) and the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway (1875–1885) through Northern Ontario and the Canadian Prairies to British Columbia, Ontario manufacturing and industry flourished. However, population increases slowed after a large recession hit the province in 1893, thus slowing growth drastically but for only a few years. Many newly arrived immigrants and others moved west along the railway to the Prairie Provinces and British Columbia, sparsely settling Northern Ontario.
The northern and western boundaries of Ontario were in dispute after Canadian Confederation. Ontario's right to Northwestern Ontario was determined by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in 1884 and confirmed by the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889'' of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. By 1899, there were seven northern districts: Algoma, Manitoulin, Muskoka, Nipissing, Parry Sound, Rainy River, and Thunder Bay. Four more northern districts were created between 1907 and 1912: Cochrane, Kenora, Sudbury and Timiskaming.
Mineral exploitation accelerated in the late 19th century, leading to the rise of important mining centres in the northeast, such as Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, Cobalt, Ontario, Cobalt and Timmins. The province harnessed its water power to generate hydro-electric power and created the state-controlled Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, later Ontario Hydro. The availability of cheap electric power further facilitated the development of industry. The Ford Motor Company of Canada was established in 1904 and the McLaughlin Motor Car Company (later General Motors Canada) was founded in 1907. The motor vehicle industry became the most lucrative industry for the Ontario economy during the 20th century.
In July 1912, the Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, Conservative government of James Whitney (politician), James Whitney issued Regulation 17 which severely limited the availability of French-language schooling to the province's French-speaking minority. French Canadians reacted with outrage, journalist Henri Bourassa denouncing the "Prussians of Ontario". The regulation was eventually repealed in 1927.
 Influenced by events in the United States, the government of William Howard Hearst, William Hearst introduced Prohibition in Canada, prohibition of alcoholic drinks in 1916 with the passing of the ''Ontario Temperance Act''. However, residents could distil and retain their own personal supply, and liquor producers could continue distillation and export for sale, allowing this already sizeable industry to strengthen further. Ontario became a hotbed for the illegal smuggling of liquor and the biggest supplier into the United States, which was under complete Prohibition in the United States, prohibition. Prohibition in Ontario came to an end in 1927 with the establishment of the Liquor Control Board of Ontario under the government of Howard Ferguson. The sale and consumption of liquor, wine, and beer are still controlled by some of the most extreme laws in North America to ensure strict community standards and revenue generation from the alcohol retail monopoly are upheld.
The post-World War II period was one of exceptional prosperity and growth. Ontario has been the recipients of most immigration to Canada, largely immigrants from war-torn Europe in the 1950s and 1960s and following changes in federal immigration law, a massive influx of non-Europeans since the 1970s. From a largely ethnic group, ethnically British province, Ontario has rapidly become culturally very diverse.
The nationalist movement in Quebec, particularly after the election of the ''Parti Québécois'' in 1976, contributed to driving many businesses and English-speaking people out of Quebec to Ontario, and as a result, Toronto surpassed Montreal as the largest city and economic centre of Canada. Depressed economic conditions in the Atlantic Canada, Maritime Provinces have also resulted in de-population of those provinces in the 20th century, with heavy migration into Ontario.
Ontario's official language is English, although there exists a number of List of francophone communities in Ontario, French-speaking communities across Ontario. French-language services are made available for communities with a sizeable French-speaking population; a service that is ensured under the ''French Language Services Act'' of 1989.
Influenced by events in the United States, the government of William Howard Hearst, William Hearst introduced Prohibition in Canada, prohibition of alcoholic drinks in 1916 with the passing of the ''Ontario Temperance Act''. However, residents could distil and retain their own personal supply, and liquor producers could continue distillation and export for sale, allowing this already sizeable industry to strengthen further. Ontario became a hotbed for the illegal smuggling of liquor and the biggest supplier into the United States, which was under complete Prohibition in the United States, prohibition. Prohibition in Ontario came to an end in 1927 with the establishment of the Liquor Control Board of Ontario under the government of Howard Ferguson. The sale and consumption of liquor, wine, and beer are still controlled by some of the most extreme laws in North America to ensure strict community standards and revenue generation from the alcohol retail monopoly are upheld.
The post-World War II period was one of exceptional prosperity and growth. Ontario has been the recipients of most immigration to Canada, largely immigrants from war-torn Europe in the 1950s and 1960s and following changes in federal immigration law, a massive influx of non-Europeans since the 1970s. From a largely ethnic group, ethnically British province, Ontario has rapidly become culturally very diverse.
The nationalist movement in Quebec, particularly after the election of the ''Parti Québécois'' in 1976, contributed to driving many businesses and English-speaking people out of Quebec to Ontario, and as a result, Toronto surpassed Montreal as the largest city and economic centre of Canada. Depressed economic conditions in the Atlantic Canada, Maritime Provinces have also resulted in de-population of those provinces in the 20th century, with heavy migration into Ontario.
Ontario's official language is English, although there exists a number of List of francophone communities in Ontario, French-speaking communities across Ontario. French-language services are made available for communities with a sizeable French-speaking population; a service that is ensured under the ''French Language Services Act'' of 1989.

 As of the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 Canadian Census, the ten most spoken languages in the province included English (13,650,230 or 97.28%), French (1,550,545 or 11.05%), Mandarin (467,420 or 3.33%), Hindi (436,125 or 3.11%), Spanish (401,205 or 2.86%), Punjabi (397,865 or 2.84%), Cantonese (352,135 or 2.51%), Arabic (342,860 or 2.44%), Italian (312,800 or 2.23%), and Urdu (295,175 or 2.1%). The question on knowledge of languages allows for multiple responses.
The principal language of Ontario is English, the province's ''de facto'' official language, with approximately 97.2 per cent of Ontarians having proficiency in the language, although only 69.5 per cent of Ontarians reported English as their mother tongue in the 2016 Census. English is one of two official languages of Canada, with the other being French. English and French are the official languages of the courts in Ontario. Approximately 4.6 per cent of the population identified as francophone, and a total of 11.5 per cent of Ontarians reported having proficiency in French. Approximately 11.2 per cent of Ontarians reported being bilingual in both English and French. Approximately 2.5 per cent of Ontarians have no proficiency in either English or French.
Franco-Ontarians are concentrated in the northeastern, eastern, and extreme southern parts of the province, where under the ''French Language Services Act'', provincial government services are required to be available in French if at least 10 per cent of a designated area's population report French as their native language or if an urban centre has at least 5,000 francophones.
Other languages spoken by residents include Arabic, Bengali, Cantonese, Dutch, German, Greek, Gujarati, Hindi, Hebrew, Italian, Korean, Malayalam, Mandarin, Marathi, Persian, Polish, Portuguese, Punjabi, Russian, Sinhalese, Somali, Spanish, Tagalog, Telugu, Tamil, Tibetan, Ukrainian, Urdu, and Vietnamese.
As of the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 Canadian Census, the ten most spoken languages in the province included English (13,650,230 or 97.28%), French (1,550,545 or 11.05%), Mandarin (467,420 or 3.33%), Hindi (436,125 or 3.11%), Spanish (401,205 or 2.86%), Punjabi (397,865 or 2.84%), Cantonese (352,135 or 2.51%), Arabic (342,860 or 2.44%), Italian (312,800 or 2.23%), and Urdu (295,175 or 2.1%). The question on knowledge of languages allows for multiple responses.
The principal language of Ontario is English, the province's ''de facto'' official language, with approximately 97.2 per cent of Ontarians having proficiency in the language, although only 69.5 per cent of Ontarians reported English as their mother tongue in the 2016 Census. English is one of two official languages of Canada, with the other being French. English and French are the official languages of the courts in Ontario. Approximately 4.6 per cent of the population identified as francophone, and a total of 11.5 per cent of Ontarians reported having proficiency in French. Approximately 11.2 per cent of Ontarians reported being bilingual in both English and French. Approximately 2.5 per cent of Ontarians have no proficiency in either English or French.
Franco-Ontarians are concentrated in the northeastern, eastern, and extreme southern parts of the province, where under the ''French Language Services Act'', provincial government services are required to be available in French if at least 10 per cent of a designated area's population report French as their native language or if an urban centre has at least 5,000 francophones.
Other languages spoken by residents include Arabic, Bengali, Cantonese, Dutch, German, Greek, Gujarati, Hindi, Hebrew, Italian, Korean, Malayalam, Mandarin, Marathi, Persian, Polish, Portuguese, Punjabi, Russian, Sinhalese, Somali, Spanish, Tagalog, Telugu, Tamil, Tibetan, Ukrainian, Urdu, and Vietnamese.
 Mining and the forest products industry, notably pulp and paper industry in Canada, pulp and paper, are vital to the economy of Northern Ontario. As of 2011, roughly 200,000 ha are clearcut each year; herbicides for hardwood suppression are applied to a third of the total. There has been controversy over the Northern Ontario Ring of Fire, Ring of Fire mineral deposit, and whether the province can afford to spend CAD$2.25 billion on a road from the Trans-Canada Highway near Kenora to the deposit, currently valued at CAD$60 billion.
An abundance of natural resources, excellent transportation links to the North American heartland and the inland Great Lakes making ocean access possible via container ships, have all contributed to making manufacturing the principal industry of the province, found mainly in the Golden Horseshoe region, which is the largest industrialized area in Canada, the southern end of the region being part of the North American Rust Belt. Important products include motor vehicles, iron, steel, food, electrical appliances, machinery, chemicals, and paper.
Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton is the largest steel manufacturing city in Canada followed closely by Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste. Marie, and Sarnia is the centre for petrochemical production. Construction employed more than 6.5% of the province's work force in June 2011. Ontario's steel industry was once centred in Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton. Hamilton harbour, which can be seen from the QEW Skyway bridge, is an industrial wasteland; U.S. Steel-owned Stelco announced in the autumn of 2013 that it would close in 2014, with the loss of 875 jobs. The move flummoxed a union representative, who seemed puzzled why a plant with capacity of 2 million tons per annum would be shut while Canada imported 8 million tons of steel the previous year. Algoma Steel maintains a plant in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste Marie.
Mining and the forest products industry, notably pulp and paper industry in Canada, pulp and paper, are vital to the economy of Northern Ontario. As of 2011, roughly 200,000 ha are clearcut each year; herbicides for hardwood suppression are applied to a third of the total. There has been controversy over the Northern Ontario Ring of Fire, Ring of Fire mineral deposit, and whether the province can afford to spend CAD$2.25 billion on a road from the Trans-Canada Highway near Kenora to the deposit, currently valued at CAD$60 billion.
An abundance of natural resources, excellent transportation links to the North American heartland and the inland Great Lakes making ocean access possible via container ships, have all contributed to making manufacturing the principal industry of the province, found mainly in the Golden Horseshoe region, which is the largest industrialized area in Canada, the southern end of the region being part of the North American Rust Belt. Important products include motor vehicles, iron, steel, food, electrical appliances, machinery, chemicals, and paper.
Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton is the largest steel manufacturing city in Canada followed closely by Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste. Marie, and Sarnia is the centre for petrochemical production. Construction employed more than 6.5% of the province's work force in June 2011. Ontario's steel industry was once centred in Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton. Hamilton harbour, which can be seen from the QEW Skyway bridge, is an industrial wasteland; U.S. Steel-owned Stelco announced in the autumn of 2013 that it would close in 2014, with the loss of 875 jobs. The move flummoxed a union representative, who seemed puzzled why a plant with capacity of 2 million tons per annum would be shut while Canada imported 8 million tons of steel the previous year. Algoma Steel maintains a plant in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste Marie.
 Ontario surpassed Michigan in car production, assembling more than 2,696,000 vehicles in 2004. Ontario has Chrysler plants in Windsor, Ontario, Windsor and Bramalea, two General Motors, GM plants in Oshawa and one in Ingersoll, a Honda assembly plant in Alliston, Ford Motor Company, Ford plants in Oakville and St. Thomas and Toyota assembly plants in Cambridge and Woodstock. However, as a result of steeply declining sales, in 2005, General Motors announced massive layoffs at production facilities across North America, including two large GM plants in Oshawa and a Powertrain, drive train facility in St. Catharines, that resulted in 8,000 job losses in Ontario alone. In 2006, Ford Motor Company announced between 25,000 and 30,000 layoffs phased until 2012; Ontario was spared the worst, but job losses were announced for the St. Thomas, Ontario, St Thomas facility and the Windsor Casting plant. However, these losses will be offset by Ford's recent announcement of a hybrid vehicle facility slated to begin production in 2007 at its Oakville, Ontario, Oakville plant and GM's re-introduction of the Chevrolet Camaro, Camaro which will be produced in Oshawa. On December 4, 2008, Toyota announced the grand opening of the Toyota RAV4, RAV4 plant in Woodstock, Ontario, Woodstock, and Honda also plans to add an engine plant at its facility in Alliston. Despite these new plants coming online, Ontario has not yet fully recovered following massive layoffs caused by the Financial crisis of 2007–2010, global recession; its unemployment rate was 7.3% in May 2013, compared to 8.7 percent in January 2010 and approximately 6% in 2007. In September 2013, the Ontario government committed CAD$70.9 million to the Ford plant in Oakville, Ontario, Oakville, while the federal government committed CAD$71.1mn, to secure 2,800 jobs. The province has lost 300,000 manufacturing jobs in the decade from 2003, and the Bank of Canada noted that "while the energy and mining industries have benefitted from these movements, the pressure on the manufacturing sector has intensified, since many firms in this sector were already dealing with growing competition from low-cost economies such as China."
Ontario surpassed Michigan in car production, assembling more than 2,696,000 vehicles in 2004. Ontario has Chrysler plants in Windsor, Ontario, Windsor and Bramalea, two General Motors, GM plants in Oshawa and one in Ingersoll, a Honda assembly plant in Alliston, Ford Motor Company, Ford plants in Oakville and St. Thomas and Toyota assembly plants in Cambridge and Woodstock. However, as a result of steeply declining sales, in 2005, General Motors announced massive layoffs at production facilities across North America, including two large GM plants in Oshawa and a Powertrain, drive train facility in St. Catharines, that resulted in 8,000 job losses in Ontario alone. In 2006, Ford Motor Company announced between 25,000 and 30,000 layoffs phased until 2012; Ontario was spared the worst, but job losses were announced for the St. Thomas, Ontario, St Thomas facility and the Windsor Casting plant. However, these losses will be offset by Ford's recent announcement of a hybrid vehicle facility slated to begin production in 2007 at its Oakville, Ontario, Oakville plant and GM's re-introduction of the Chevrolet Camaro, Camaro which will be produced in Oshawa. On December 4, 2008, Toyota announced the grand opening of the Toyota RAV4, RAV4 plant in Woodstock, Ontario, Woodstock, and Honda also plans to add an engine plant at its facility in Alliston. Despite these new plants coming online, Ontario has not yet fully recovered following massive layoffs caused by the Financial crisis of 2007–2010, global recession; its unemployment rate was 7.3% in May 2013, compared to 8.7 percent in January 2010 and approximately 6% in 2007. In September 2013, the Ontario government committed CAD$70.9 million to the Ford plant in Oakville, Ontario, Oakville, while the federal government committed CAD$71.1mn, to secure 2,800 jobs. The province has lost 300,000 manufacturing jobs in the decade from 2003, and the Bank of Canada noted that "while the energy and mining industries have benefitted from these movements, the pressure on the manufacturing sector has intensified, since many firms in this sector were already dealing with growing competition from low-cost economies such as China."

 Once the dominant industry, agriculture now uses a small percentage of the workforce. However, much of the land in southern Ontario is given over to agriculture. As the following table shows, while the number of individual farms has steadily decreased and their overall size has shrunk at a lower rate, greater mechanization has supported increased supply to satisfy the ever-increasing demands of a growing population base; this has also meant a gradual increase in the total amount of land used for growing crops.
Once the dominant industry, agriculture now uses a small percentage of the workforce. However, much of the land in southern Ontario is given over to agriculture. As the following table shows, while the number of individual farms has steadily decreased and their overall size has shrunk at a lower rate, greater mechanization has supported increased supply to satisfy the ever-increasing demands of a growing population base; this has also meant a gradual increase in the total amount of land used for growing crops.
 Common types of farms reported in the 2001 census include those for cattle, small grains and dairy. The fruit- and Ontario wine, wine industry is primarily on the Niagara Peninsula, Prince Edward County Wine, Prince Edward County, and along the northern shore of Lake Erie, where tobacco farms are also situated. Market vegetables grow in the rich soils of the Holland Marsh near Newmarket, Ontario, Newmarket. The area near Windsor, Ontario, Windsor is also very fertile. The Heinz plant in Leamington, Ontario, Leamington was taken over in these autumn of 2013 by Warren Buffett and a Brazilian partner, following which it put 740 people out of work. Government subsidies followed shortly; Premier Kathleen Wynne offered CAD$200,000 to cushion the blow, and promised that another processed-food operator would soon be found. On December 10, 2013, Kellogg's announced layoffs for more than 509 workers at a cereal manufacture plant in London, Ontario, London.
The area defined as the Corn Belt covers much of the southwestern area of the province, extending as far north as close to Goderich, but corn and soy are grown throughout the southern portion of the province. Apple orchards are a common sight along the southern shore of Nottawasaga Bay (part of Georgian Bay) near Collingwood and along the northern shore of Lake Ontario near Cobourg. Tobacco production, centred in Norfolk County, Ontario, Norfolk County, has decreased, allowing an increase in alternative crops such as Corylus avellana, hazelnuts and ginseng. The Ontario origins of Massey Ferguson, once one of the largest Agricultural machinery, farm-implement manufacturers in the world, indicate the importance agriculture once had to the Canadian economy.
Common types of farms reported in the 2001 census include those for cattle, small grains and dairy. The fruit- and Ontario wine, wine industry is primarily on the Niagara Peninsula, Prince Edward County Wine, Prince Edward County, and along the northern shore of Lake Erie, where tobacco farms are also situated. Market vegetables grow in the rich soils of the Holland Marsh near Newmarket, Ontario, Newmarket. The area near Windsor, Ontario, Windsor is also very fertile. The Heinz plant in Leamington, Ontario, Leamington was taken over in these autumn of 2013 by Warren Buffett and a Brazilian partner, following which it put 740 people out of work. Government subsidies followed shortly; Premier Kathleen Wynne offered CAD$200,000 to cushion the blow, and promised that another processed-food operator would soon be found. On December 10, 2013, Kellogg's announced layoffs for more than 509 workers at a cereal manufacture plant in London, Ontario, London.
The area defined as the Corn Belt covers much of the southwestern area of the province, extending as far north as close to Goderich, but corn and soy are grown throughout the southern portion of the province. Apple orchards are a common sight along the southern shore of Nottawasaga Bay (part of Georgian Bay) near Collingwood and along the northern shore of Lake Ontario near Cobourg. Tobacco production, centred in Norfolk County, Ontario, Norfolk County, has decreased, allowing an increase in alternative crops such as Corylus avellana, hazelnuts and ginseng. The Ontario origins of Massey Ferguson, once one of the largest Agricultural machinery, farm-implement manufacturers in the world, indicate the importance agriculture once had to the Canadian economy.

 Despite its diverse range of power options, problems related to increasing consumption, lack of energy efficiency and aging nuclear reactors, Ontario has been forced in recent years to purchase power from its neighbours Quebec and Michigan to supplement its power needs during peak consumption periods. Ontario's basic domestic rate in 2010 was 11.17 cents per kWh; by contrast. Quebec's was 6.81. In December 2013, the government projected a 42 percent hike by 2018, and 68 percent by 2033. Industrial rates are projected to rise by 33% by 2018, and 55% in 2033.
The ''Green Energy and Green Economy Act'', 2009 (GEA), takes a two-pronged approach to commercializing renewable energy; first, it aims to bring more Renewable resource, renewable energy sources to the province; and secondly, it aims to adopt more efficient energy use, energy-efficiency measures to help energy conservation, conserve energy. The bill envisaged appointing a Renewable Energy Facilitator to provide "one-window" assistance and support to project developers to facilitate project approvals.
The approvals process for transmission projects would also be wikt:streamline, streamlined and (for the first time in Ontario) the bill would enact standards for renewable energy projects. Homeowners would have access to incentives to develop small-scale renewables such as low- or no-interest loans to finance the capital cost of renewable energy generating facilities like solar panels.
Despite its diverse range of power options, problems related to increasing consumption, lack of energy efficiency and aging nuclear reactors, Ontario has been forced in recent years to purchase power from its neighbours Quebec and Michigan to supplement its power needs during peak consumption periods. Ontario's basic domestic rate in 2010 was 11.17 cents per kWh; by contrast. Quebec's was 6.81. In December 2013, the government projected a 42 percent hike by 2018, and 68 percent by 2033. Industrial rates are projected to rise by 33% by 2018, and 55% in 2033.
The ''Green Energy and Green Economy Act'', 2009 (GEA), takes a two-pronged approach to commercializing renewable energy; first, it aims to bring more Renewable resource, renewable energy sources to the province; and secondly, it aims to adopt more efficient energy use, energy-efficiency measures to help energy conservation, conserve energy. The bill envisaged appointing a Renewable Energy Facilitator to provide "one-window" assistance and support to project developers to facilitate project approvals.
The approvals process for transmission projects would also be wikt:streamline, streamlined and (for the first time in Ontario) the bill would enact standards for renewable energy projects. Homeowners would have access to incentives to develop small-scale renewables such as low- or no-interest loans to finance the capital cost of renewable energy generating facilities like solar panels.
 Ontario is home to Niagara Falls, which supplies a large amount of electricity to the province. The Bruce Nuclear Generating Station, the largest operational nuclear power plant in the world, is also in Ontario and uses 8 CANDU reactors to generate electricity for the province.
Ontario had the most wind energy capacity of the country with 4,900 MW of power (41% of Canada's capacity).
Ontario is home to Niagara Falls, which supplies a large amount of electricity to the province. The Bruce Nuclear Generating Station, the largest operational nuclear power plant in the world, is also in Ontario and uses 8 CANDU reactors to generate electricity for the province.
Ontario had the most wind energy capacity of the country with 4,900 MW of power (41% of Canada's capacity).
 Ontario has grown, from its roots in Upper Canada, into a modern jurisdiction. The old titles of the chief law officers, the Attorney-General and the Solicitor-General, remain in use. They both are responsible to the Legislature. The Attorney-General drafts the laws and is responsible for criminal prosecutions and the administration of justice, while the Solicitor-General is responsible for law enforcement and the police services of the province.
The Municipal Act, 2001 (Ontario) is the main statute governing the creation, administration and government of municipality, municipalities in the Canada, Canadian province of Ontario, other than the City of Toronto government, City of Toronto. After being passed in 2001, it came into force on January 1, 2003, replacing the previous ''Municipal Act''. Effective January 1, 2007, the Municipal Act, 2001 (the Act) was significantly amended by the Municipal Statute Law Amendment Act, 2006 (Bill 130).
Ontario has grown, from its roots in Upper Canada, into a modern jurisdiction. The old titles of the chief law officers, the Attorney-General and the Solicitor-General, remain in use. They both are responsible to the Legislature. The Attorney-General drafts the laws and is responsible for criminal prosecutions and the administration of justice, while the Solicitor-General is responsible for law enforcement and the police services of the province.
The Municipal Act, 2001 (Ontario) is the main statute governing the creation, administration and government of municipality, municipalities in the Canada, Canadian province of Ontario, other than the City of Toronto government, City of Toronto. After being passed in 2001, it came into force on January 1, 2003, replacing the previous ''Municipal Act''. Effective January 1, 2007, the Municipal Act, 2001 (the Act) was significantly amended by the Municipal Statute Law Amendment Act, 2006 (Bill 130).
 Ontario has numerous political parties which run for election. The four main parties are the centre-right Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, the Social democracy, social democratic Ontario New Democratic Party (NDP), the centre to centre-left Ontario Liberal Party, and Green Party of Ontario. The Progressive Conservatives, Liberals and New Democrats have each governed the province, while the Greens elected their first member to the Legislative Assembly in 2018 Ontario general election, 2018.
The 2018 Ontario general election, 2018 provincial election resulted in a Progressive Conservative majority government under party leader Doug Ford, who was sworn in as Premier of Ontario, Premier on June 29. Ontario NDP leader Andrea Horwath was sworn in as the leader of her Majesty's Loyal Opposition.
Ontario has numerous political parties which run for election. The four main parties are the centre-right Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, the Social democracy, social democratic Ontario New Democratic Party (NDP), the centre to centre-left Ontario Liberal Party, and Green Party of Ontario. The Progressive Conservatives, Liberals and New Democrats have each governed the province, while the Greens elected their first member to the Legislative Assembly in 2018 Ontario general election, 2018.
The 2018 Ontario general election, 2018 provincial election resulted in a Progressive Conservative majority government under party leader Doug Ford, who was sworn in as Premier of Ontario, Premier on June 29. Ontario NDP leader Andrea Horwath was sworn in as the leader of her Majesty's Loyal Opposition.
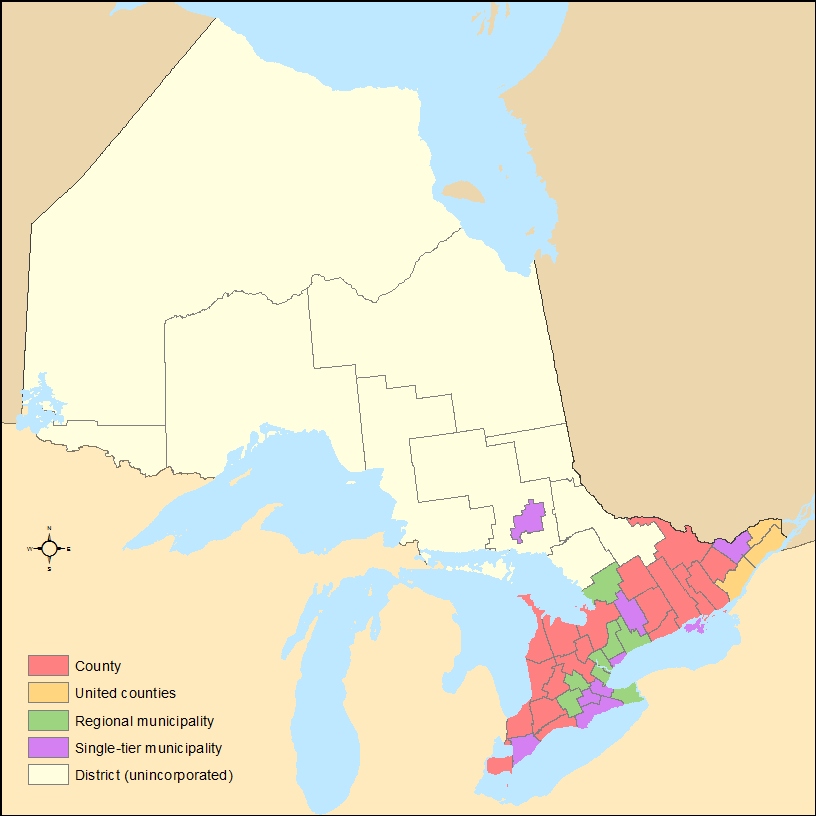 Ontario has three types of List of census divisions of Ontario, first-level administrative divisions. They include List of census divisions of Ontario#Single-tier municipalities, single-tier municipalities, upper-tier municipalities (which may be in the form of either List of regional municipalities in Ontario, regional municipalities or United counties, counties), and Districts of Ontario, districts. Upper-tier municipalities and districts are made up of smaller municipalities and other types of administrative divisions.
Administrative divisions differ primarily in the services that they provide to their residents, with the differing structures of these administrative regions resulting in disparities among Ontario's different regions. The administrative regions of Ontario are roughly coterminous with the List of census divisions of Ontario, census divisions used by Statistics Canada, although some exceptions do exist.
Ontario has three types of List of census divisions of Ontario, first-level administrative divisions. They include List of census divisions of Ontario#Single-tier municipalities, single-tier municipalities, upper-tier municipalities (which may be in the form of either List of regional municipalities in Ontario, regional municipalities or United counties, counties), and Districts of Ontario, districts. Upper-tier municipalities and districts are made up of smaller municipalities and other types of administrative divisions.
Administrative divisions differ primarily in the services that they provide to their residents, with the differing structures of these administrative regions resulting in disparities among Ontario's different regions. The administrative regions of Ontario are roughly coterminous with the List of census divisions of Ontario, census divisions used by Statistics Canada, although some exceptions do exist.
* Parts of Quebec (including Gatineau) are included in the Ottawa CMA. The population of the Ottawa CMA, in both provinces, is shown.
;Ten largest municipalities by population
 In 1973, the first slogan to appear on Vehicle registration plates of Ontario, licence plates in Ontario was "Keep It Beautiful". This was replaced by "Yours to Discover" in 1982, apparently inspired by a tourism slogan, "Discover Ontario", dating back to 1927. Plates with the French equivalent, , were made available to the public beginning in May 2008. (From 1988 to 1990, "Ontario Incredible" gave "Yours to Discover" a brief respite.)
A Place to Stand, a Place to Grow is a song commissioned by the government of Ontario for its pavilion in Expo 67, and an unofficial anthem of the province. As a part of the Canada 150 celebrations in 2017, the provincial government released an updated rendition. In 2007, the provincial tourism agency commissioned a new song, "There's No Place Like This" is featured in television advertisement, television advertising, performed by Ontario artists including Molly Johnson, Brian Byrne, Keshia Chanté, as well as Tomi Swick and Arkells.
In 1973, the first slogan to appear on Vehicle registration plates of Ontario, licence plates in Ontario was "Keep It Beautiful". This was replaced by "Yours to Discover" in 1982, apparently inspired by a tourism slogan, "Discover Ontario", dating back to 1927. Plates with the French equivalent, , were made available to the public beginning in May 2008. (From 1988 to 1990, "Ontario Incredible" gave "Yours to Discover" a brief respite.)
A Place to Stand, a Place to Grow is a song commissioned by the government of Ontario for its pavilion in Expo 67, and an unofficial anthem of the province. As a part of the Canada 150 celebrations in 2017, the provincial government released an updated rendition. In 2007, the provincial tourism agency commissioned a new song, "There's No Place Like This" is featured in television advertisement, television advertising, performed by Ontario artists including Molly Johnson, Brian Byrne, Keshia Chanté, as well as Tomi Swick and Arkells.
 Important airports in the province include Toronto Pearson International Airport, which is the List of the busiest airports in Canada, busiest airport in Canada, handling nearly 50 million passengers in 2018. Ottawa Macdonald–Cartier International Airport is Ontario's second largest airport. Toronto/Pearson and Ottawa/Macdonald-Cartier form two of the three points in Canada's busiest set of air routes (the third point being Montréal–Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport). In addition to airports in Ottawa, and Toronto, the province also operates three other international airports, the John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport in Hamilton, the Thunder Bay International Airport in Thunder Bay and the London International Airport in London. John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport serves as cargo hub, reliever for Pearson, and a hub for ULCC Swoop (airline), Swoop.
Most Ontario cities have regional airports, many of which have scheduled commuter flights from Air Canada Jazz or smaller airlines and charter companies – flights from the mid-size cities such as Thunder Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, Sudbury, North Bay, Timmins, Windsor, London, and Kingston feed directly into larger airports in Toronto and Ottawa. Bearskin Airlines also runs flights along the northerly east–west route, connecting Ottawa, North Bay, Sudbury, Sault Ste. Marie, Kitchener and Thunder Bay directly.
Isolated towns and settlements in the northern areas of the province rely partly or entirely on airline, air service for travel, goods, and even air ambulance, ambulance services (Medical evacuation, MEDIVAC), since much of the far northern area of the province cannot be reached by road or rail.
Important airports in the province include Toronto Pearson International Airport, which is the List of the busiest airports in Canada, busiest airport in Canada, handling nearly 50 million passengers in 2018. Ottawa Macdonald–Cartier International Airport is Ontario's second largest airport. Toronto/Pearson and Ottawa/Macdonald-Cartier form two of the three points in Canada's busiest set of air routes (the third point being Montréal–Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport). In addition to airports in Ottawa, and Toronto, the province also operates three other international airports, the John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport in Hamilton, the Thunder Bay International Airport in Thunder Bay and the London International Airport in London. John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport serves as cargo hub, reliever for Pearson, and a hub for ULCC Swoop (airline), Swoop.
Most Ontario cities have regional airports, many of which have scheduled commuter flights from Air Canada Jazz or smaller airlines and charter companies – flights from the mid-size cities such as Thunder Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, Sudbury, North Bay, Timmins, Windsor, London, and Kingston feed directly into larger airports in Toronto and Ottawa. Bearskin Airlines also runs flights along the northerly east–west route, connecting Ottawa, North Bay, Sudbury, Sault Ste. Marie, Kitchener and Thunder Bay directly.
Isolated towns and settlements in the northern areas of the province rely partly or entirely on airline, air service for travel, goods, and even air ambulance, ambulance services (Medical evacuation, MEDIVAC), since much of the far northern area of the province cannot be reached by road or rail.
 400-series highways make up the primary vehicular network in the south of province, and they connect at a number of points to border crossings to the United States, and
400-series highways make up the primary vehicular network in the south of province, and they connect at a number of points to border crossings to the United States, and
Virtual Vault
, an online exhibition of Canadian historical art at Library and Archives Canada.
online review
* Chambers, Lori, and Edgar-Andre Montigny, eds. ''Ontario Since Confederation: A Reader'' (2000), articles by scholars * Winfield, Mark S. ''Blue-Green Province: The Environment and the Political Economy of Ontario'' (University of British Columbia Press; 2012) 296 pages; environmental policies since 1945
Government of Ontario
Tourism Ontario
*
Ontario Visual Heritage Project
nbsp;– Non-profit documentary project about Ontario's history {{Authority control Ontario, 1867 establishments in Canada Provinces and territories of Canada States and territories established in 1867 Eastern Canada
provinces and territories of Canada
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British Nort ...
.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, which is Ontario's provincial capital.
Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay
James Bay (french: Baie James; cr, ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, Wînipekw, dirty water) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost pa ...
to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
s of (from west to east) Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
, Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States follows inland waterways: from the westerly Lake of the Woods, eastward along the major rivers and lakes of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
/Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connectin ...
drainage system. There is only about of actual land border, made up of portages including Height of Land Portage
Height of Land Portage is a portage along the historic Boundary Waters route between Canada and the United States. Located at the border of the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Minnesota, the path is a relatively easy crossing ...
on the Minnesota border.
The great majority of Ontario's population and arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for th ...
is in Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
. In contrast, Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Pro ...
is sparsely populated with cold winters and heavy forestation.
Etymology
Ontario is a term thought to be derived from Indigenous origins, either , aHuron
Huron may refer to:
People
* Wyandot people (or Wendat), indigenous to North America
* Wyandot language, spoken by them
* Huron-Wendat Nation, a Huron-Wendat First Nation with a community in Wendake, Quebec
* Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawatomi ...
(Wyandot
Wyandot may refer to:
Native American ethnography
* Wyandot people, also known as the Huron
* Wyandot language
Wyandot (sometimes spelled Wandat) is the Iroquoian language traditionally spoken by the people known variously as Wyandot or Wya ...
) word meaning "great lake", or possibly , which means "beautiful water" or "sparkling water" in the Iroquoian languages
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian ...
. Ontario has about 250,000 freshwater lakes. The first mention of the name Ontario was in 1641, when "Ontario" was used to describe the land on the north shore of the easternmost part of the Great Lakes. It was adopted as the official name of the new province at Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
in 1867.
Geography
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s, partly covered by the Central and Midwestern Canadian Shield forests
The Midwestern Canadian Shield forests ecoregion, in the Taiga and Boreal forests Biome, are of northern Canada.
Setting
This is an area of rolling hills with lakes both small and large, wetlands, and rocky outcrops on the Canadian Shield in no ...
, and studded with lakes and rivers. Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Pro ...
is subdivided into two sub-regions: Northwestern Ontario and Northeastern Ontario
Northeastern Ontario is a secondary region of Northern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario, which lies north of Lake Huron and east of Lake Superior.
Northeastern Ontario consists of the districts of Algoma, Sudbury, Cochrane, Timiskami ...
.
The virtually unpopulated Hudson Bay Lowlands
The Hudson Bay Lowlands is a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec. Many wid ...
in the extreme north and northeast, mainly swampy and sparsely forested.
Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
, which is further sub-divided into four sub-regions: Central Ontario
Central Ontario is a secondary region of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario that lies between Georgian Bay and the eastern end of Lake Ontario.
The population of the region was 1,123,307 in 2016; however, this number does not in ...
(although not actually the province's geographic centre), Eastern Ontario
Eastern Ontario (census population 1,763,186 in 2016) (french: Est de l'Ontario) is a secondary region of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario which lies in a wedge-shaped area between the Ottawa River and St. Lawrence River. It s ...
, Golden Horseshoe
The Golden Horseshoe is a secondary region of Southern Ontario, Canada, which lies at the western end of Lake Ontario, with outer boundaries stretching south to Lake Erie and north to Lake Scugog, Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay of Lake Huron. The ...
and Southwestern Ontario (parts of which were formerly referred to as Western Ontario).
Despite the absence of any mountainous terrain in the province, there are large areas of uplands, particularly within the Canadian Shield which traverses the province from northwest to southeast and also above the Niagara Escarpment which crosses the south. The highest point is Ishpatina Ridge
Ishpatina Ridge is the highest point of land in the Canadian province of Ontario, at an estimated above sea level. Ishpatina Ridge rises approximately above the immediate area. It was only truly recognized as Ontario's highest point after topog ...
at above sea level in Temagami
Temagami, formerly spelled as Timagami, is a municipality in northeastern Ontario, Canada, in the Nipissing District with Lake Temagami at its heart.
The Temagami region is known as ''n'Daki Menan'', the homeland of the area's First Nations c ...
, Northeastern Ontario. In the south, elevations of over are surpassed near Collingwood, above the Blue Mountains in the Dundalk Highlands and in hilltops near the Madawaska River in Renfrew County
Renfrew County is a county in the Canadian province of Ontario. It stands on the west bank of the Ottawa River. There are 17 municipalities in the county.
History Bathurst District
When Carleton County was withdrawn from Bathurst District in 1 ...
.
The Carolinian forest zone covers most of the southwestern region of the province. The temperate and fertile Great Lakes-Saint Lawrence Valley in the south is part of the Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests ecoregion where the forest has now been largely replaced by agriculture, industrial and urban development. A well-known geographic feature is Niagara Falls, part of the Niagara Escarpment. The Saint Lawrence Seaway allows navigation to and from the Atlantic Ocean as far inland as Thunder Bay in Northwestern Ontario. Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Pro ...
covers approximately 87% of the province's surface area; conversely Southern Ontario contains 94% of the population.
Point Pelee National Park, Point Pelee is a peninsula of Lake Erie in southwestern Ontario (near Windsor, Ontario, Windsor and Detroit, Detroit, Michigan) that is the southernmost extent of Canada's mainland. Pelee, Ontario, Pelee Island and Middle Island (Lake Erie), Middle Island in Lake Erie extend slightly farther. All are south of 42nd parallel north, 42°N – slightly farther south than the northern border of California.
Climate
 Ontario's climate varies by season and location. Three air sources affect it: cold, dry, arctic air from the north (dominant factor during the winter months, and for a longer part of the year in far northern Ontario); Pacific polar air crossing in from the western Canadian Prairies/US Northern Plains; and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. The effects of these major air masses on temperature and precipitation depend mainly on latitude, proximity to major bodies of water and to a small extent, terrain relief. In general, most of Ontario's climate is classified as humid continental.
Ontario has four main climatic regions:
* The surrounding Great Lakes greatly influence the climatic region of southern Ontario. During the fall and winter, the release of heat stored by the lakes moderates the climate near the shores. This gives parts of southern Ontario milder winters than mid-continental areas at lower latitudes. Parts of Southwestern Ontario (generally south of a line from Sarnia–Toronto) have a moderate humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification ''Dfa''), similar to the inland Mid-Atlantic states and the
Ontario's climate varies by season and location. Three air sources affect it: cold, dry, arctic air from the north (dominant factor during the winter months, and for a longer part of the year in far northern Ontario); Pacific polar air crossing in from the western Canadian Prairies/US Northern Plains; and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. The effects of these major air masses on temperature and precipitation depend mainly on latitude, proximity to major bodies of water and to a small extent, terrain relief. In general, most of Ontario's climate is classified as humid continental.
Ontario has four main climatic regions:
* The surrounding Great Lakes greatly influence the climatic region of southern Ontario. During the fall and winter, the release of heat stored by the lakes moderates the climate near the shores. This gives parts of southern Ontario milder winters than mid-continental areas at lower latitudes. Parts of Southwestern Ontario (generally south of a line from Sarnia–Toronto) have a moderate humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification ''Dfa''), similar to the inland Mid-Atlantic states and the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
portion of the Midwestern United States. The region has warm to hot, humid summers and cold winters. Annual precipitation ranges from and is well distributed throughout the year. Most of this region lies in the lee of the Great Lakes, making for abundant snow in some areas. In December 2010, the snowbelt set a new record when it was hit by more than a metre of snow within 48 hours.
* The next climatic region is Central and Eastern Ontario, which has a moderate humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dfb''). This region has warm and sometimes hot summers with colder, longer winters, ample snowfall (even in regions not directly in the snowbelts) and annual precipitation similar to the rest of Southern Ontario.
*The smallest climatic region is located at the most northeastern part of the Niagara Peninsula, which has a Humid subtropical climate, temperate humid climate (Köppen Cfa), due to moderating effects by Lake Ontario, the Niagara River and battling air masses from the Gulf of Mexico during the winter months. It is one of the most temperate regions in the entire province.
In the northeastern parts of Ontario, extending south as far as Kirkland Lake, the cold waters of Hudson Bay depress summer temperatures, making it cooler than other locations at similar latitudes. The same is true on the northern shore of Lake Superior, which cools hot, humid air from the south, leading to cooler summer temperatures. Along the eastern shores of Lake Superior and Lake Huron winter temperatures are slightly moderated but come with frequent heavy lake-effect snow squalls that increase seasonal snowfall totals to upwards of in some places. These regions have higher annual precipitation, in some places over .
 * The northernmost parts of Ontario – primarily north of 50°N – have a subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfc'') with long, severely cold winters and short, cool to warm summers with dramatic temperature changes possible in all seasons. With no major mountain ranges blocking sinking Arctic air masses, temperatures of are not uncommon; snow remains on the ground for sometimes over half the year. Snow accumulation can be high in some areas. Precipitation is generally less than and peaks in the summer months in the form of rain or thunderstorms.
Severe thunderstorms peak in summer. Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, in Southern Ontario, Southern Southwestern Ontario, (Southwestern) Ontario, has the most lightning strikes per year in Canada, averaging 33 days of thunderstorm activity per year. In a typical year, Ontario averages 11 confirmed tornado touchdowns. However, over the last 4 years, it has had upwards of 20 tornado touchdowns per year, with the highest frequency in the Windsor-Essex – Chatham Kent area, though few are very destructive (the majority between F0 to F2 on the Fujita scale). Ontario had a record 29 tornadoes in both 2006 and 2009. Tropical cyclone, Tropical depression remnants occasionally bring heavy rains and winds in the south, but are rarely deadly. A notable exception was Hurricane Hazel which struck Southern Ontario centred on Toronto, in October 1954.
* The northernmost parts of Ontario – primarily north of 50°N – have a subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfc'') with long, severely cold winters and short, cool to warm summers with dramatic temperature changes possible in all seasons. With no major mountain ranges blocking sinking Arctic air masses, temperatures of are not uncommon; snow remains on the ground for sometimes over half the year. Snow accumulation can be high in some areas. Precipitation is generally less than and peaks in the summer months in the form of rain or thunderstorms.
Severe thunderstorms peak in summer. Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, in Southern Ontario, Southern Southwestern Ontario, (Southwestern) Ontario, has the most lightning strikes per year in Canada, averaging 33 days of thunderstorm activity per year. In a typical year, Ontario averages 11 confirmed tornado touchdowns. However, over the last 4 years, it has had upwards of 20 tornado touchdowns per year, with the highest frequency in the Windsor-Essex – Chatham Kent area, though few are very destructive (the majority between F0 to F2 on the Fujita scale). Ontario had a record 29 tornadoes in both 2006 and 2009. Tropical cyclone, Tropical depression remnants occasionally bring heavy rains and winds in the south, but are rarely deadly. A notable exception was Hurricane Hazel which struck Southern Ontario centred on Toronto, in October 1954.
History
Indigenous habitation (pre-1610)
Paleo-Indians were the first people to settle on the lands of Ontario, arriving there after the Laurentide Ice Sheet melted roughly 11,000 years ago. From them, many ethnocultural groups emerged and came to exist on the lands of Ontario: the Algonquin people, Algonquins, Mississaugas, Ojibway, Cree, Odawa, Potawatomi, Pottowatomi, and Iroquois.Pays d'en Haut (1610–1763)
In the 15th century, the Fall of Constantinople, Byzantine Empire fell, prompting Western Europeans to search for new sea lane, sea routes to the Far East. Around 1522–1523, Giovanni da Verrazzano persuaded King Francis I of France to commission an expedition to find a western route to Cathay (China) via a Northwest Passage. Though this expedition was unsuccessful, it established the name "New France" for northeastern North America. After a few expeditions, France mostly abandoned North America for 50 years because of its financial crisis; France was involved in the Italian Wars and there were religious wars between Protestants and Catholics. Around 1580 however, the rise of the fur trade (particularly the demand for beaver pelts), reignited French interest. In 1608, Samuel de Champlain established France's first colonial settlement in New France, the Habitation de Québec (now Quebec City), in the Canada (New France), colony of Canada (now southern Quebec). Afterwards, French explorers continued to travel west, establishing new villages along the coasts of the Saint Lawrence River. French explorers, the first of which was Étienne Brûlé who explored the Georgian Bay area in 1610–1612, mappedSouthern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
and called the region the Pays d'en Haut ("Upper Country"), in reference to the region being upstream of the Saint Lawrence River. The colony of the Pays d'en Haut was formally established in 1610 as an administrative dependency of Canada, and was for defence and business rather than a settlement colony. The territory of the Pays-d'en-Haut was quite large and would today include the province of Ontario, as well as, in whole or in part, the American states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania and New York. Indigenous peoples were the vast majority of the Pays d'en Haut population. As for Northern Ontario, the English explorer Henry Hudson sailed into Hudson Bay in 1611 and claimed its drainage basin for England. The area would become known as Rupert's Land.
Samuel de Champlain reached Lake Huron in 1615, and French missionaries, such as the Jésuites and Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice, Supliciens, began to establish posts along the Great Lakes. The French allied with most Indigenous groups of Ontario, all for the fur trade and for defence against Iroquois attacks (which would later be called the Iroquois Wars). The French would declare their Indigenous allies to be subjects of the King of France and would often act as mediators between different groups. The Iroquois later allied themselves with the British.
From 1634 to 1640, the Huron were devastated by European infectious diseases, such as measles and smallpox, to which they had no immunity. By 1700, the Iroquois had been driven out or left the area that would become Ontario and the Mississaugas of the Ojibwa had settled the north shore of Lake Ontario. The remaining Huron settled north of Quebec.
During the French and Indian War, the North American theater of the Seven Years' War of 1754 to 1763, the British defeated the armies of New France and its Indigenous allies. In the Treaty of Paris 1763 France ceded most of its possessions in North America to Britain. Using the Quebec Act, Britain re-organised the territory into the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Province of Quebec.
As for Northern Ontario, the English explorer Henry Hudson sailed into Hudson Bay in 1611 and claimed its drainage basin for England. The area would become known as Rupert's Land.
Samuel de Champlain reached Lake Huron in 1615, and French missionaries, such as the Jésuites and Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice, Supliciens, began to establish posts along the Great Lakes. The French allied with most Indigenous groups of Ontario, all for the fur trade and for defence against Iroquois attacks (which would later be called the Iroquois Wars). The French would declare their Indigenous allies to be subjects of the King of France and would often act as mediators between different groups. The Iroquois later allied themselves with the British.
From 1634 to 1640, the Huron were devastated by European infectious diseases, such as measles and smallpox, to which they had no immunity. By 1700, the Iroquois had been driven out or left the area that would become Ontario and the Mississaugas of the Ojibwa had settled the north shore of Lake Ontario. The remaining Huron settled north of Quebec.
During the French and Indian War, the North American theater of the Seven Years' War of 1754 to 1763, the British defeated the armies of New France and its Indigenous allies. In the Treaty of Paris 1763 France ceded most of its possessions in North America to Britain. Using the Quebec Act, Britain re-organised the territory into the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Province of Quebec.
Province of Quebec (1763–1791)
 In 1782–1784, 5,000 United Empire Loyalists entered what is now Ontario following the American Revolution. The Kingdom of Great Britain granted them land and other items with which to rebuild their lives. The British also set up reserves in Ontario for the Mohawk people, Mohawks who had fought for the British and had lost their land in New York state. Other Iroquois, also displaced from New York were resettled in 1784 at the Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations reserve at the west end of Lake Ontario. The Mississaugas, displaced by European settlements, would later move to Six Nations also.
After the American War of Independence, the first reserves for First Nations were established. These are situated at Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations (1784), Tyendinaga Mohawk Territory, Tyendinaga (1793) and Akwesasne (1795). Six Nations and Tyendinaga were established by the British for those Indigenous groups who had fought on the side of the British, and were expelled from the new United States. Akwesasne was a pre-existing Mohawk community and its borders were formalized under the 1795 Jay Treaty.
In 1788, while part of the Province of Quebec, southern Ontario was divided into four District#Ontario, districts: Western District, Upper Canada, Hesse, Eastern District, Upper Canada, Lunenburg, Midland District, Upper Canada, Mecklenburg, and Home District, Nassau. In 1792, the four districts were renamed: Hesse became the Western District, Lunenburg became the Eastern District, Mecklenburg became the Midland District, and Nassau became the Home District. Counties were created within the districts.
The population of Canada west of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence substantially increased during this period, a fact recognized by the Constitutional Act 1791, ''Constitutional Act'' of 1791, which split Quebec into the Canadas: Upper Canada southwest of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence, and Lower Canada east of it.
In 1782–1784, 5,000 United Empire Loyalists entered what is now Ontario following the American Revolution. The Kingdom of Great Britain granted them land and other items with which to rebuild their lives. The British also set up reserves in Ontario for the Mohawk people, Mohawks who had fought for the British and had lost their land in New York state. Other Iroquois, also displaced from New York were resettled in 1784 at the Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations reserve at the west end of Lake Ontario. The Mississaugas, displaced by European settlements, would later move to Six Nations also.
After the American War of Independence, the first reserves for First Nations were established. These are situated at Six Nations of the Grand River, Six Nations (1784), Tyendinaga Mohawk Territory, Tyendinaga (1793) and Akwesasne (1795). Six Nations and Tyendinaga were established by the British for those Indigenous groups who had fought on the side of the British, and were expelled from the new United States. Akwesasne was a pre-existing Mohawk community and its borders were formalized under the 1795 Jay Treaty.
In 1788, while part of the Province of Quebec, southern Ontario was divided into four District#Ontario, districts: Western District, Upper Canada, Hesse, Eastern District, Upper Canada, Lunenburg, Midland District, Upper Canada, Mecklenburg, and Home District, Nassau. In 1792, the four districts were renamed: Hesse became the Western District, Lunenburg became the Eastern District, Mecklenburg became the Midland District, and Nassau became the Home District. Counties were created within the districts.
The population of Canada west of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence substantially increased during this period, a fact recognized by the Constitutional Act 1791, ''Constitutional Act'' of 1791, which split Quebec into the Canadas: Upper Canada southwest of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence, and Lower Canada east of it.
Upper Canada (1791–1841)
 John Graves Simcoe was appointed Upper Canada's first Lieutenant governor (Canada), Lieutenant governor in 1793. A second wave of Americans, not all of them necessarily loyalists moved to Upper Canada after 1790 until the pre-war of 1812, many seeking available cheap land, and at the time, lower taxation.
By 1798, there were eight districts: Eastern, Home, Johnstown District, Upper Canada, Johnstown, London District, Upper Canada, London, Midland, Newcastle District, Newcastle, Niagara District, Niagara, and Western. By 1826, there were eleven districts: Bathurst District, Bathurst, Eastern, Gore District, Upper Canada, Gore, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa District, Ottawa, and Western. By 1838, there were twenty districts: Bathurst, Brock, Colbourne, Dalhousie District, Dalhousie, Eastern, Gore, Home, Huron, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, Prince Edward, Simcoe County, Simcoe, Talbot, Victoria, Wellington District, Upper Canada, Wellington, and Western.
American troops in the War of 1812 invaded Upper Canada across the Niagara River and the Detroit River, but were defeated and pushed back by the British, Canadian fencibles and militias, and First Nations in Canada, First Nations warriors. However, the Americans eventually gained control of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario. The 1813 Battle of York saw American troops defeat the garrison at the Upper Canada capital of York, Upper Canada, York. The Americans looted the town and burned the Upper Canada Parliament Buildings during their brief occupation. The British would Burning of Washington, burn the American capital of Washington, D.C. in 1814.
John Graves Simcoe was appointed Upper Canada's first Lieutenant governor (Canada), Lieutenant governor in 1793. A second wave of Americans, not all of them necessarily loyalists moved to Upper Canada after 1790 until the pre-war of 1812, many seeking available cheap land, and at the time, lower taxation.
By 1798, there were eight districts: Eastern, Home, Johnstown District, Upper Canada, Johnstown, London District, Upper Canada, London, Midland, Newcastle District, Newcastle, Niagara District, Niagara, and Western. By 1826, there were eleven districts: Bathurst District, Bathurst, Eastern, Gore District, Upper Canada, Gore, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa District, Ottawa, and Western. By 1838, there were twenty districts: Bathurst, Brock, Colbourne, Dalhousie District, Dalhousie, Eastern, Gore, Home, Huron, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, Prince Edward, Simcoe County, Simcoe, Talbot, Victoria, Wellington District, Upper Canada, Wellington, and Western.
American troops in the War of 1812 invaded Upper Canada across the Niagara River and the Detroit River, but were defeated and pushed back by the British, Canadian fencibles and militias, and First Nations in Canada, First Nations warriors. However, the Americans eventually gained control of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario. The 1813 Battle of York saw American troops defeat the garrison at the Upper Canada capital of York, Upper Canada, York. The Americans looted the town and burned the Upper Canada Parliament Buildings during their brief occupation. The British would Burning of Washington, burn the American capital of Washington, D.C. in 1814.
 After the War of 1812, relative stability allowed for increasing numbers of immigrants to arrive from Europe rather than from the United States. As was the case in the previous decades, this immigration shift was encouraged by the colonial leaders. Despite affordable and often free land, many arriving newcomers, mostly from Britain and Ireland, found frontier life with the harsh climate difficult, and some of those with the means eventually returned home or went south. However, population growth far exceeded emigration in the following decades. It was a mostly agrarian-based society, but canal projects and a new network of plank roads spurred greater trade within the colony and with the United States, thereby improving previously damaged relations over time.
Meanwhile, Ontario's numerous waterways aided travel and transportation into the interior and supplied Hydropower, water power for development. As the population increased, so did the industries and transportation networks, which in turn led to further development. By the end of the century, Ontario vied with Quebec as the nation's leader in terms of growth in population, industry, arts and communications.
Unrest in the colony began to chafe against the aristocratic Family Compact who governed while benefiting economically from the region's resources, and who did not allow elected bodies power. This resentment spurred republican ideals and sowed the seeds for early Canadian nationalism. Accordingly, rebellion in favour of responsible government rose in both regions; Louis-Joseph Papineau led the Lower Canada Rebellion and William Lyon Mackenzie, first
After the War of 1812, relative stability allowed for increasing numbers of immigrants to arrive from Europe rather than from the United States. As was the case in the previous decades, this immigration shift was encouraged by the colonial leaders. Despite affordable and often free land, many arriving newcomers, mostly from Britain and Ireland, found frontier life with the harsh climate difficult, and some of those with the means eventually returned home or went south. However, population growth far exceeded emigration in the following decades. It was a mostly agrarian-based society, but canal projects and a new network of plank roads spurred greater trade within the colony and with the United States, thereby improving previously damaged relations over time.
Meanwhile, Ontario's numerous waterways aided travel and transportation into the interior and supplied Hydropower, water power for development. As the population increased, so did the industries and transportation networks, which in turn led to further development. By the end of the century, Ontario vied with Quebec as the nation's leader in terms of growth in population, industry, arts and communications.
Unrest in the colony began to chafe against the aristocratic Family Compact who governed while benefiting economically from the region's resources, and who did not allow elected bodies power. This resentment spurred republican ideals and sowed the seeds for early Canadian nationalism. Accordingly, rebellion in favour of responsible government rose in both regions; Louis-Joseph Papineau led the Lower Canada Rebellion and William Lyon Mackenzie, first Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
mayor, led the Upper Canada Rebellion. In Upper Canada, the rebellion was quickly a failure. William Lyon Mackenzie escaped to the United States, where he declared the Republic of Canada on Navy Island on the Niagara River.
Canada West (1841–1867)
Although both rebellions were put down in short order, the British government sent John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, Lord Durham to investigate the causes. He recommended self-government be granted and Lower and Upper Canada be re-joined in an attempt to assimilate the French Canadians. Accordingly, the two colonies were merged into the Province of Canada by the ''Act of Union 1840'', with the capital at Kingston, Ontario, Kingston, and Upper Canada becoming known as Province of Canada, Canada West. Parliamentary Self-governance, self-government was granted in 1848. There were heavy waves of immigration in the 1840s, and the population of Canada West more than doubled by 1851 over the previous decade. As a result, for the first time, the English-speaking population of Canada West surpassed the French-speaking population of Canada East, tilting the representative balance of power. In 1849, the districts of southern Ontario were abolished by the Province of Canada, and county governments took over certain municipal responsibilities. The Province of Canada also began creating ''districts'' in sparsely populated Northern Ontario with the establishment of Algoma District and Nipissing District in 1858.
An economic boom in the 1850s coincided with railway expansion across the province, further increasing the economic strength of Central Canada. With the repeal of the Corn Laws and a reciprocity agreement in place with the United States, various industries such as timber, mining, farming and alcohol distilling benefited tremendously.
A political stalemate between the Canadian French, French- and Canadian English, English-speaking legislators, as well as fear of aggression from the United States during and immediately after the American Civil War, led the political elite to hold a series of conferences in the 1860s to effect a broader federal union of all British North American colonies. The ''Constitution Act, 1867, British North America Act'' took effect on July 1, 1867, establishing the Dominion of Canada, initially with four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. The Province of Canada was divided into Ontario and Quebec so that each linguistic group would have its own province. Both Quebec and Ontario were required by section 93 of the ''British North America Act'' to safeguard existing educational rights and privileges of the Protestant and Catholic minorities. Thus, separate Catholic schools and board of education, school boards were permitted in Ontario. However, neither province had a constitutional requirement to protect its French- or English-speaking minority. Toronto was formally established as Ontario's provincial capital.
In 1849, the districts of southern Ontario were abolished by the Province of Canada, and county governments took over certain municipal responsibilities. The Province of Canada also began creating ''districts'' in sparsely populated Northern Ontario with the establishment of Algoma District and Nipissing District in 1858.
An economic boom in the 1850s coincided with railway expansion across the province, further increasing the economic strength of Central Canada. With the repeal of the Corn Laws and a reciprocity agreement in place with the United States, various industries such as timber, mining, farming and alcohol distilling benefited tremendously.
A political stalemate between the Canadian French, French- and Canadian English, English-speaking legislators, as well as fear of aggression from the United States during and immediately after the American Civil War, led the political elite to hold a series of conferences in the 1860s to effect a broader federal union of all British North American colonies. The ''Constitution Act, 1867, British North America Act'' took effect on July 1, 1867, establishing the Dominion of Canada, initially with four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. The Province of Canada was divided into Ontario and Quebec so that each linguistic group would have its own province. Both Quebec and Ontario were required by section 93 of the ''British North America Act'' to safeguard existing educational rights and privileges of the Protestant and Catholic minorities. Thus, separate Catholic schools and board of education, school boards were permitted in Ontario. However, neither province had a constitutional requirement to protect its French- or English-speaking minority. Toronto was formally established as Ontario's provincial capital.
Canadian province (1867–present)
 The borders of Ontario, its new name in 1867, were provisionally expanded north and west. When the Province of Canada was formed, its borders were not entirely clear, and Ontario claimed eventually to reach all the way to the Rocky Mountains and Arctic Ocean. With Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land, Ontario was interested in clearly defining its borders, especially since some of the new areas in which it was interested were rapidly growing. After the federal government asked Ontario to pay for construction in the new disputed area, the province asked for an elaboration on its limits, and its boundary was moved north to the 51st parallel north.
The borders of Ontario, its new name in 1867, were provisionally expanded north and west. When the Province of Canada was formed, its borders were not entirely clear, and Ontario claimed eventually to reach all the way to the Rocky Mountains and Arctic Ocean. With Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land, Ontario was interested in clearly defining its borders, especially since some of the new areas in which it was interested were rapidly growing. After the federal government asked Ontario to pay for construction in the new disputed area, the province asked for an elaboration on its limits, and its boundary was moved north to the 51st parallel north.
 Once constituted as a province, Ontario proceeded to assert its economic and legislative power. In 1872, the lawyer Oliver Mowat became Premier of Ontario and remained as premier until 1896. He fought for provincial rights, weakening the power of the Government of Canada, federal government in provincial matters, usually through well-argued appeals to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. His battles with the federal government greatly Decentralization, decentralized Canada, giving the provinces far more power than John A. Macdonald had intended. He consolidated and expanded Ontario's educational and provincial institutions, created districts in Northern Ontario, and fought to ensure that those parts of Northwestern Ontario not historically part of Upper Canada (the vast areas north and west of the Lake Superior-Hudson Bay watershed, known as the District of Keewatin) would become part of Ontario, a victory embodied in the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889''. He also presided over the emergence of the province into the economic powerhouse of Canada. Mowat was the creator of what is often called ''Empire Ontario''.
Beginning with Macdonald's National Policy (1879) and the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway (1875–1885) through Northern Ontario and the Canadian Prairies to British Columbia, Ontario manufacturing and industry flourished. However, population increases slowed after a large recession hit the province in 1893, thus slowing growth drastically but for only a few years. Many newly arrived immigrants and others moved west along the railway to the Prairie Provinces and British Columbia, sparsely settling Northern Ontario.
The northern and western boundaries of Ontario were in dispute after Canadian Confederation. Ontario's right to Northwestern Ontario was determined by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in 1884 and confirmed by the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889'' of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. By 1899, there were seven northern districts: Algoma, Manitoulin, Muskoka, Nipissing, Parry Sound, Rainy River, and Thunder Bay. Four more northern districts were created between 1907 and 1912: Cochrane, Kenora, Sudbury and Timiskaming.
Mineral exploitation accelerated in the late 19th century, leading to the rise of important mining centres in the northeast, such as Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, Cobalt, Ontario, Cobalt and Timmins. The province harnessed its water power to generate hydro-electric power and created the state-controlled Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, later Ontario Hydro. The availability of cheap electric power further facilitated the development of industry. The Ford Motor Company of Canada was established in 1904 and the McLaughlin Motor Car Company (later General Motors Canada) was founded in 1907. The motor vehicle industry became the most lucrative industry for the Ontario economy during the 20th century.
In July 1912, the Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, Conservative government of James Whitney (politician), James Whitney issued Regulation 17 which severely limited the availability of French-language schooling to the province's French-speaking minority. French Canadians reacted with outrage, journalist Henri Bourassa denouncing the "Prussians of Ontario". The regulation was eventually repealed in 1927.
Once constituted as a province, Ontario proceeded to assert its economic and legislative power. In 1872, the lawyer Oliver Mowat became Premier of Ontario and remained as premier until 1896. He fought for provincial rights, weakening the power of the Government of Canada, federal government in provincial matters, usually through well-argued appeals to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. His battles with the federal government greatly Decentralization, decentralized Canada, giving the provinces far more power than John A. Macdonald had intended. He consolidated and expanded Ontario's educational and provincial institutions, created districts in Northern Ontario, and fought to ensure that those parts of Northwestern Ontario not historically part of Upper Canada (the vast areas north and west of the Lake Superior-Hudson Bay watershed, known as the District of Keewatin) would become part of Ontario, a victory embodied in the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889''. He also presided over the emergence of the province into the economic powerhouse of Canada. Mowat was the creator of what is often called ''Empire Ontario''.
Beginning with Macdonald's National Policy (1879) and the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway (1875–1885) through Northern Ontario and the Canadian Prairies to British Columbia, Ontario manufacturing and industry flourished. However, population increases slowed after a large recession hit the province in 1893, thus slowing growth drastically but for only a few years. Many newly arrived immigrants and others moved west along the railway to the Prairie Provinces and British Columbia, sparsely settling Northern Ontario.
The northern and western boundaries of Ontario were in dispute after Canadian Confederation. Ontario's right to Northwestern Ontario was determined by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in 1884 and confirmed by the ''Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889'' of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. By 1899, there were seven northern districts: Algoma, Manitoulin, Muskoka, Nipissing, Parry Sound, Rainy River, and Thunder Bay. Four more northern districts were created between 1907 and 1912: Cochrane, Kenora, Sudbury and Timiskaming.
Mineral exploitation accelerated in the late 19th century, leading to the rise of important mining centres in the northeast, such as Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, Cobalt, Ontario, Cobalt and Timmins. The province harnessed its water power to generate hydro-electric power and created the state-controlled Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, later Ontario Hydro. The availability of cheap electric power further facilitated the development of industry. The Ford Motor Company of Canada was established in 1904 and the McLaughlin Motor Car Company (later General Motors Canada) was founded in 1907. The motor vehicle industry became the most lucrative industry for the Ontario economy during the 20th century.
In July 1912, the Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, Conservative government of James Whitney (politician), James Whitney issued Regulation 17 which severely limited the availability of French-language schooling to the province's French-speaking minority. French Canadians reacted with outrage, journalist Henri Bourassa denouncing the "Prussians of Ontario". The regulation was eventually repealed in 1927.
 Influenced by events in the United States, the government of William Howard Hearst, William Hearst introduced Prohibition in Canada, prohibition of alcoholic drinks in 1916 with the passing of the ''Ontario Temperance Act''. However, residents could distil and retain their own personal supply, and liquor producers could continue distillation and export for sale, allowing this already sizeable industry to strengthen further. Ontario became a hotbed for the illegal smuggling of liquor and the biggest supplier into the United States, which was under complete Prohibition in the United States, prohibition. Prohibition in Ontario came to an end in 1927 with the establishment of the Liquor Control Board of Ontario under the government of Howard Ferguson. The sale and consumption of liquor, wine, and beer are still controlled by some of the most extreme laws in North America to ensure strict community standards and revenue generation from the alcohol retail monopoly are upheld.
The post-World War II period was one of exceptional prosperity and growth. Ontario has been the recipients of most immigration to Canada, largely immigrants from war-torn Europe in the 1950s and 1960s and following changes in federal immigration law, a massive influx of non-Europeans since the 1970s. From a largely ethnic group, ethnically British province, Ontario has rapidly become culturally very diverse.
The nationalist movement in Quebec, particularly after the election of the ''Parti Québécois'' in 1976, contributed to driving many businesses and English-speaking people out of Quebec to Ontario, and as a result, Toronto surpassed Montreal as the largest city and economic centre of Canada. Depressed economic conditions in the Atlantic Canada, Maritime Provinces have also resulted in de-population of those provinces in the 20th century, with heavy migration into Ontario.
Ontario's official language is English, although there exists a number of List of francophone communities in Ontario, French-speaking communities across Ontario. French-language services are made available for communities with a sizeable French-speaking population; a service that is ensured under the ''French Language Services Act'' of 1989.
Influenced by events in the United States, the government of William Howard Hearst, William Hearst introduced Prohibition in Canada, prohibition of alcoholic drinks in 1916 with the passing of the ''Ontario Temperance Act''. However, residents could distil and retain their own personal supply, and liquor producers could continue distillation and export for sale, allowing this already sizeable industry to strengthen further. Ontario became a hotbed for the illegal smuggling of liquor and the biggest supplier into the United States, which was under complete Prohibition in the United States, prohibition. Prohibition in Ontario came to an end in 1927 with the establishment of the Liquor Control Board of Ontario under the government of Howard Ferguson. The sale and consumption of liquor, wine, and beer are still controlled by some of the most extreme laws in North America to ensure strict community standards and revenue generation from the alcohol retail monopoly are upheld.
The post-World War II period was one of exceptional prosperity and growth. Ontario has been the recipients of most immigration to Canada, largely immigrants from war-torn Europe in the 1950s and 1960s and following changes in federal immigration law, a massive influx of non-Europeans since the 1970s. From a largely ethnic group, ethnically British province, Ontario has rapidly become culturally very diverse.
The nationalist movement in Quebec, particularly after the election of the ''Parti Québécois'' in 1976, contributed to driving many businesses and English-speaking people out of Quebec to Ontario, and as a result, Toronto surpassed Montreal as the largest city and economic centre of Canada. Depressed economic conditions in the Atlantic Canada, Maritime Provinces have also resulted in de-population of those provinces in the 20th century, with heavy migration into Ontario.
Ontario's official language is English, although there exists a number of List of francophone communities in Ontario, French-speaking communities across Ontario. French-language services are made available for communities with a sizeable French-speaking population; a service that is ensured under the ''French Language Services Act'' of 1989.
Demographics

Population
In the 2021 Canadian Census, 2021 census, Ontario had a population of 14,223,942 living in 5,491,201 of its 5,929,250 total dwellings, a 5.8 percent change from its 2016 population of 13,448,494. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021. The largest List of population centres in Ontario, population centres in Ontario areToronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, Ottawa, Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton, Kitchener, Ontario, Kitchener, London, Ontario, London and Oshawa, which all have more than 300,000 inhabitants.
Ethnicity
The percentages given below add to more than 100 per cent because of dual responses (e.g., "French and Canadian" response generates an entry both in the category "French Canadian" and in the category "Canadian"). The majority of Ontarians are of English Canadians, English or other European Canadians, European descent including large Scottish, Irish and Italian communities. Slightly less than 5 per cent of the population of Ontario is Franco-Ontarian, that is those whose native tongue is French, although those with French ancestry account for 11 per cent of the population. In relation to natural increase or inter-provincial migration, Immigration to Canada, immigration is a huge population growth force in Ontario, as it has been over the last two centuries. More recent sources of immigrants with large or growing communities in Ontario include East Asian Canadians, East Asians, South Asian Canadians, South Asians, Caribbeans, Latin Americans, Europeans, and Africans. Most populations have settled in the larger urban centres. In 2011, 25.9 per cent of the population consisted of visible minorities and 2.4 per cent of the population was Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous, mostly of First Nations in Canada, First Nations and Métis in Canada, Métis descent. There was also a small number of Inuit in the province. The number of Indigenous people and visible minorities has been increasing at a faster rate than the general population of Ontario.Religion
In 2021, 52.1% of the population was Christian, with the largest religious denominations being the Catholic Church in Canada, Roman Catholic Church (with 26.0% of the population), Islam (6.7%), Hinduism (4.1%), and the United Church of Canada (4.1 %). 31.6% of Ontarians had no religious affiliation. The major religious groups in Ontario in 2021 were: In Ontario, Catholics are represented by the Assembly of Catholic Bishops of Ontario and the Anglican Protestants by the Ecclesiastical Province of Ontario. The Ecclesiastical Province covers most of the geographical province of OntarioLanguage
Economy
Ontario is Canada's leading manufacturing province, accounting for 52% of the total national manufacturing shipments in 2004. Ontario's largest trading partner is the American state ofMichigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
. , Moody's Corporation, Moody's bond-rating agency rated Canadian public debt, Ontario debt at AA2/stable, while S&P rated it AA-. Dominion Bond Rating Service rated it AA(low) in January 2013. Long known as a bastion of Canadian manufacturing and financial solvency, Ontario's public debt-to-GDP ratio is projected to be 38.4% in fiscal year 2023–2024.
 Mining and the forest products industry, notably pulp and paper industry in Canada, pulp and paper, are vital to the economy of Northern Ontario. As of 2011, roughly 200,000 ha are clearcut each year; herbicides for hardwood suppression are applied to a third of the total. There has been controversy over the Northern Ontario Ring of Fire, Ring of Fire mineral deposit, and whether the province can afford to spend CAD$2.25 billion on a road from the Trans-Canada Highway near Kenora to the deposit, currently valued at CAD$60 billion.
An abundance of natural resources, excellent transportation links to the North American heartland and the inland Great Lakes making ocean access possible via container ships, have all contributed to making manufacturing the principal industry of the province, found mainly in the Golden Horseshoe region, which is the largest industrialized area in Canada, the southern end of the region being part of the North American Rust Belt. Important products include motor vehicles, iron, steel, food, electrical appliances, machinery, chemicals, and paper.
Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton is the largest steel manufacturing city in Canada followed closely by Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste. Marie, and Sarnia is the centre for petrochemical production. Construction employed more than 6.5% of the province's work force in June 2011. Ontario's steel industry was once centred in Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton. Hamilton harbour, which can be seen from the QEW Skyway bridge, is an industrial wasteland; U.S. Steel-owned Stelco announced in the autumn of 2013 that it would close in 2014, with the loss of 875 jobs. The move flummoxed a union representative, who seemed puzzled why a plant with capacity of 2 million tons per annum would be shut while Canada imported 8 million tons of steel the previous year. Algoma Steel maintains a plant in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste Marie.
Mining and the forest products industry, notably pulp and paper industry in Canada, pulp and paper, are vital to the economy of Northern Ontario. As of 2011, roughly 200,000 ha are clearcut each year; herbicides for hardwood suppression are applied to a third of the total. There has been controversy over the Northern Ontario Ring of Fire, Ring of Fire mineral deposit, and whether the province can afford to spend CAD$2.25 billion on a road from the Trans-Canada Highway near Kenora to the deposit, currently valued at CAD$60 billion.
An abundance of natural resources, excellent transportation links to the North American heartland and the inland Great Lakes making ocean access possible via container ships, have all contributed to making manufacturing the principal industry of the province, found mainly in the Golden Horseshoe region, which is the largest industrialized area in Canada, the southern end of the region being part of the North American Rust Belt. Important products include motor vehicles, iron, steel, food, electrical appliances, machinery, chemicals, and paper.
Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton is the largest steel manufacturing city in Canada followed closely by Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste. Marie, and Sarnia is the centre for petrochemical production. Construction employed more than 6.5% of the province's work force in June 2011. Ontario's steel industry was once centred in Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton. Hamilton harbour, which can be seen from the QEW Skyway bridge, is an industrial wasteland; U.S. Steel-owned Stelco announced in the autumn of 2013 that it would close in 2014, with the loss of 875 jobs. The move flummoxed a union representative, who seemed puzzled why a plant with capacity of 2 million tons per annum would be shut while Canada imported 8 million tons of steel the previous year. Algoma Steel maintains a plant in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste Marie.
 Ontario surpassed Michigan in car production, assembling more than 2,696,000 vehicles in 2004. Ontario has Chrysler plants in Windsor, Ontario, Windsor and Bramalea, two General Motors, GM plants in Oshawa and one in Ingersoll, a Honda assembly plant in Alliston, Ford Motor Company, Ford plants in Oakville and St. Thomas and Toyota assembly plants in Cambridge and Woodstock. However, as a result of steeply declining sales, in 2005, General Motors announced massive layoffs at production facilities across North America, including two large GM plants in Oshawa and a Powertrain, drive train facility in St. Catharines, that resulted in 8,000 job losses in Ontario alone. In 2006, Ford Motor Company announced between 25,000 and 30,000 layoffs phased until 2012; Ontario was spared the worst, but job losses were announced for the St. Thomas, Ontario, St Thomas facility and the Windsor Casting plant. However, these losses will be offset by Ford's recent announcement of a hybrid vehicle facility slated to begin production in 2007 at its Oakville, Ontario, Oakville plant and GM's re-introduction of the Chevrolet Camaro, Camaro which will be produced in Oshawa. On December 4, 2008, Toyota announced the grand opening of the Toyota RAV4, RAV4 plant in Woodstock, Ontario, Woodstock, and Honda also plans to add an engine plant at its facility in Alliston. Despite these new plants coming online, Ontario has not yet fully recovered following massive layoffs caused by the Financial crisis of 2007–2010, global recession; its unemployment rate was 7.3% in May 2013, compared to 8.7 percent in January 2010 and approximately 6% in 2007. In September 2013, the Ontario government committed CAD$70.9 million to the Ford plant in Oakville, Ontario, Oakville, while the federal government committed CAD$71.1mn, to secure 2,800 jobs. The province has lost 300,000 manufacturing jobs in the decade from 2003, and the Bank of Canada noted that "while the energy and mining industries have benefitted from these movements, the pressure on the manufacturing sector has intensified, since many firms in this sector were already dealing with growing competition from low-cost economies such as China."
Ontario surpassed Michigan in car production, assembling more than 2,696,000 vehicles in 2004. Ontario has Chrysler plants in Windsor, Ontario, Windsor and Bramalea, two General Motors, GM plants in Oshawa and one in Ingersoll, a Honda assembly plant in Alliston, Ford Motor Company, Ford plants in Oakville and St. Thomas and Toyota assembly plants in Cambridge and Woodstock. However, as a result of steeply declining sales, in 2005, General Motors announced massive layoffs at production facilities across North America, including two large GM plants in Oshawa and a Powertrain, drive train facility in St. Catharines, that resulted in 8,000 job losses in Ontario alone. In 2006, Ford Motor Company announced between 25,000 and 30,000 layoffs phased until 2012; Ontario was spared the worst, but job losses were announced for the St. Thomas, Ontario, St Thomas facility and the Windsor Casting plant. However, these losses will be offset by Ford's recent announcement of a hybrid vehicle facility slated to begin production in 2007 at its Oakville, Ontario, Oakville plant and GM's re-introduction of the Chevrolet Camaro, Camaro which will be produced in Oshawa. On December 4, 2008, Toyota announced the grand opening of the Toyota RAV4, RAV4 plant in Woodstock, Ontario, Woodstock, and Honda also plans to add an engine plant at its facility in Alliston. Despite these new plants coming online, Ontario has not yet fully recovered following massive layoffs caused by the Financial crisis of 2007–2010, global recession; its unemployment rate was 7.3% in May 2013, compared to 8.7 percent in January 2010 and approximately 6% in 2007. In September 2013, the Ontario government committed CAD$70.9 million to the Ford plant in Oakville, Ontario, Oakville, while the federal government committed CAD$71.1mn, to secure 2,800 jobs. The province has lost 300,000 manufacturing jobs in the decade from 2003, and the Bank of Canada noted that "while the energy and mining industries have benefitted from these movements, the pressure on the manufacturing sector has intensified, since many firms in this sector were already dealing with growing competition from low-cost economies such as China."

Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, the capital of Ontario, is the centre of Canada's financial services and banking industry. Neighbouring cities are home to product distribution, IT centres, and manufacturing industries. Canada's Federal Government is the largest single employer in the National Capital Region (Canada), National Capital Region, which centres on the border cities of Ontario's Ottawa and Quebec's Gatineau.
The information technology sector is important, particularly in the ''Silicon Valley North'' section of Ottawa, home to Canada's largest technology park. IT is also important in the Regional Municipality of Waterloo, Waterloo Region, where the headquarters of BlackBerry is located.
Tourism contributes heavily to the economy of Central Ontario, peaking during the summer months owing to the abundance of fresh water recreation and wilderness found there in reasonable proximity to the major urban centres. At other times of the year, hunting, skiing and snowmobile, snowmobiling are popular. This region has some of the most vibrant fall colour displays anywhere on the continent, and tours directed at overseas visitors are organized to see them. Tourism also plays a key role in border cities with large casinos, among them Windsor, Cornwall, Ontario, Cornwall, Sarnia and Niagara Falls, Ontario, Niagara Falls, the latter of which attracts millions of US and other international visitors.
Agriculture
 Once the dominant industry, agriculture now uses a small percentage of the workforce. However, much of the land in southern Ontario is given over to agriculture. As the following table shows, while the number of individual farms has steadily decreased and their overall size has shrunk at a lower rate, greater mechanization has supported increased supply to satisfy the ever-increasing demands of a growing population base; this has also meant a gradual increase in the total amount of land used for growing crops.
Once the dominant industry, agriculture now uses a small percentage of the workforce. However, much of the land in southern Ontario is given over to agriculture. As the following table shows, while the number of individual farms has steadily decreased and their overall size has shrunk at a lower rate, greater mechanization has supported increased supply to satisfy the ever-increasing demands of a growing population base; this has also meant a gradual increase in the total amount of land used for growing crops.
 Common types of farms reported in the 2001 census include those for cattle, small grains and dairy. The fruit- and Ontario wine, wine industry is primarily on the Niagara Peninsula, Prince Edward County Wine, Prince Edward County, and along the northern shore of Lake Erie, where tobacco farms are also situated. Market vegetables grow in the rich soils of the Holland Marsh near Newmarket, Ontario, Newmarket. The area near Windsor, Ontario, Windsor is also very fertile. The Heinz plant in Leamington, Ontario, Leamington was taken over in these autumn of 2013 by Warren Buffett and a Brazilian partner, following which it put 740 people out of work. Government subsidies followed shortly; Premier Kathleen Wynne offered CAD$200,000 to cushion the blow, and promised that another processed-food operator would soon be found. On December 10, 2013, Kellogg's announced layoffs for more than 509 workers at a cereal manufacture plant in London, Ontario, London.
The area defined as the Corn Belt covers much of the southwestern area of the province, extending as far north as close to Goderich, but corn and soy are grown throughout the southern portion of the province. Apple orchards are a common sight along the southern shore of Nottawasaga Bay (part of Georgian Bay) near Collingwood and along the northern shore of Lake Ontario near Cobourg. Tobacco production, centred in Norfolk County, Ontario, Norfolk County, has decreased, allowing an increase in alternative crops such as Corylus avellana, hazelnuts and ginseng. The Ontario origins of Massey Ferguson, once one of the largest Agricultural machinery, farm-implement manufacturers in the world, indicate the importance agriculture once had to the Canadian economy.
Common types of farms reported in the 2001 census include those for cattle, small grains and dairy. The fruit- and Ontario wine, wine industry is primarily on the Niagara Peninsula, Prince Edward County Wine, Prince Edward County, and along the northern shore of Lake Erie, where tobacco farms are also situated. Market vegetables grow in the rich soils of the Holland Marsh near Newmarket, Ontario, Newmarket. The area near Windsor, Ontario, Windsor is also very fertile. The Heinz plant in Leamington, Ontario, Leamington was taken over in these autumn of 2013 by Warren Buffett and a Brazilian partner, following which it put 740 people out of work. Government subsidies followed shortly; Premier Kathleen Wynne offered CAD$200,000 to cushion the blow, and promised that another processed-food operator would soon be found. On December 10, 2013, Kellogg's announced layoffs for more than 509 workers at a cereal manufacture plant in London, Ontario, London.
The area defined as the Corn Belt covers much of the southwestern area of the province, extending as far north as close to Goderich, but corn and soy are grown throughout the southern portion of the province. Apple orchards are a common sight along the southern shore of Nottawasaga Bay (part of Georgian Bay) near Collingwood and along the northern shore of Lake Ontario near Cobourg. Tobacco production, centred in Norfolk County, Ontario, Norfolk County, has decreased, allowing an increase in alternative crops such as Corylus avellana, hazelnuts and ginseng. The Ontario origins of Massey Ferguson, once one of the largest Agricultural machinery, farm-implement manufacturers in the world, indicate the importance agriculture once had to the Canadian economy.

Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
's limited supply of agricultural land is going out of production at an increasing rate. Urban sprawl and farmland Severance (land), severances contribute to the loss of thousands of acres of productive agricultural land in Ontario each year. Over 2,000 farms and of farmland in the GTA alone were lost to production in the two decades between 1976 and 1996. This loss represented approximately 18%". of Ontario's Class 1 farmland being converted to urban purposes. In addition, increasing rural severances provide ever-greater interference with agricultural production. In an effort to protect the farmland and green spaces of the National Capital Region, and Greater Toronto Area, the Federal and Provincial Governments introduced green belt#Canada, greenbelts around Ottawa and the Golden Horseshoe
The Golden Horseshoe is a secondary region of Southern Ontario, Canada, which lies at the western end of Lake Ontario, with outer boundaries stretching south to Lake Erie and north to Lake Scugog, Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay of Lake Huron. The ...
, limiting urban development in these areas.
Energy
Ontario's rivers make it rich in hydroelectric energy. In 2009, Ontario Power Generation generated 70 percent of the province's electricity, of which 51 percent is nuclear power, nuclear, 39% is hydroelectricity, hydroelectric and 10% is fossil-fuel derived. By 2025, nuclear power is projected to supply 42%, while fossil-fuel-derived generation is projected to decrease slightly over the next 20 years. Much of the newer power generation coming online in the last few years is natural gas or combined-cycle natural gas plants. OPG is not, however, responsible for the transmission of power, which is under the control of Hydro One. Despite its diverse range of power options, problems related to increasing consumption, lack of energy efficiency and aging nuclear reactors, Ontario has been forced in recent years to purchase power from its neighbours Quebec and Michigan to supplement its power needs during peak consumption periods. Ontario's basic domestic rate in 2010 was 11.17 cents per kWh; by contrast. Quebec's was 6.81. In December 2013, the government projected a 42 percent hike by 2018, and 68 percent by 2033. Industrial rates are projected to rise by 33% by 2018, and 55% in 2033.
The ''Green Energy and Green Economy Act'', 2009 (GEA), takes a two-pronged approach to commercializing renewable energy; first, it aims to bring more Renewable resource, renewable energy sources to the province; and secondly, it aims to adopt more efficient energy use, energy-efficiency measures to help energy conservation, conserve energy. The bill envisaged appointing a Renewable Energy Facilitator to provide "one-window" assistance and support to project developers to facilitate project approvals.
The approvals process for transmission projects would also be wikt:streamline, streamlined and (for the first time in Ontario) the bill would enact standards for renewable energy projects. Homeowners would have access to incentives to develop small-scale renewables such as low- or no-interest loans to finance the capital cost of renewable energy generating facilities like solar panels.
Despite its diverse range of power options, problems related to increasing consumption, lack of energy efficiency and aging nuclear reactors, Ontario has been forced in recent years to purchase power from its neighbours Quebec and Michigan to supplement its power needs during peak consumption periods. Ontario's basic domestic rate in 2010 was 11.17 cents per kWh; by contrast. Quebec's was 6.81. In December 2013, the government projected a 42 percent hike by 2018, and 68 percent by 2033. Industrial rates are projected to rise by 33% by 2018, and 55% in 2033.
The ''Green Energy and Green Economy Act'', 2009 (GEA), takes a two-pronged approach to commercializing renewable energy; first, it aims to bring more Renewable resource, renewable energy sources to the province; and secondly, it aims to adopt more efficient energy use, energy-efficiency measures to help energy conservation, conserve energy. The bill envisaged appointing a Renewable Energy Facilitator to provide "one-window" assistance and support to project developers to facilitate project approvals.
The approvals process for transmission projects would also be wikt:streamline, streamlined and (for the first time in Ontario) the bill would enact standards for renewable energy projects. Homeowners would have access to incentives to develop small-scale renewables such as low- or no-interest loans to finance the capital cost of renewable energy generating facilities like solar panels.
 Ontario is home to Niagara Falls, which supplies a large amount of electricity to the province. The Bruce Nuclear Generating Station, the largest operational nuclear power plant in the world, is also in Ontario and uses 8 CANDU reactors to generate electricity for the province.
Ontario had the most wind energy capacity of the country with 4,900 MW of power (41% of Canada's capacity).
Ontario is home to Niagara Falls, which supplies a large amount of electricity to the province. The Bruce Nuclear Generating Station, the largest operational nuclear power plant in the world, is also in Ontario and uses 8 CANDU reactors to generate electricity for the province.
Ontario had the most wind energy capacity of the country with 4,900 MW of power (41% of Canada's capacity).
Government, law and politics
The ''British North America Act 1867'' section 69 stipulated "There shall be a Legislature for Ontario consisting of the Lieutenant Governor and of One House, styled the Legislative Assembly of Ontario." The assembly currently has 124 seats (increased from 107 as of the 42nd Ontario general election) representing electoral district (Canada), ridings elected in a Plurality voting, first-past-the-post system across the province. The legislative buildings at Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park are the seat of government. Following the Westminster system, the leader of the party holding the most seats in the assembly is known as the "Premier and President of the Council" (Executive Council Act R.S.O. 1990). The Premier chooses the cabinet (government), cabinet or Executive Council of Ontario, Executive Council whose members are deemed ministers of the Crown. Although the ''Legislative Assembly Act (R.S.O. 1990)'' refers to "members of the assembly", the legislators are now commonly called MPPs (Member of Provincial Parliament (Ontario), Members of the Provincial Parliament) in English and ''députés de l'Assemblée législative'' in French, but they have also been called MLAs (Member of the Legislative Assembly, Members of the Legislative Assembly), and both are acceptable. The title of Prime Minister of Ontario, correct in French (''le Premier ministre''), is permissible in English but now generally avoided in favour of the title "Premier" to avoid confusion with the Prime Minister of Canada.Law
 Ontario has grown, from its roots in Upper Canada, into a modern jurisdiction. The old titles of the chief law officers, the Attorney-General and the Solicitor-General, remain in use. They both are responsible to the Legislature. The Attorney-General drafts the laws and is responsible for criminal prosecutions and the administration of justice, while the Solicitor-General is responsible for law enforcement and the police services of the province.
The Municipal Act, 2001 (Ontario) is the main statute governing the creation, administration and government of municipality, municipalities in the Canada, Canadian province of Ontario, other than the City of Toronto government, City of Toronto. After being passed in 2001, it came into force on January 1, 2003, replacing the previous ''Municipal Act''. Effective January 1, 2007, the Municipal Act, 2001 (the Act) was significantly amended by the Municipal Statute Law Amendment Act, 2006 (Bill 130).
Ontario has grown, from its roots in Upper Canada, into a modern jurisdiction. The old titles of the chief law officers, the Attorney-General and the Solicitor-General, remain in use. They both are responsible to the Legislature. The Attorney-General drafts the laws and is responsible for criminal prosecutions and the administration of justice, while the Solicitor-General is responsible for law enforcement and the police services of the province.
The Municipal Act, 2001 (Ontario) is the main statute governing the creation, administration and government of municipality, municipalities in the Canada, Canadian province of Ontario, other than the City of Toronto government, City of Toronto. After being passed in 2001, it came into force on January 1, 2003, replacing the previous ''Municipal Act''. Effective January 1, 2007, the Municipal Act, 2001 (the Act) was significantly amended by the Municipal Statute Law Amendment Act, 2006 (Bill 130).
Politics
 Ontario has numerous political parties which run for election. The four main parties are the centre-right Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, the Social democracy, social democratic Ontario New Democratic Party (NDP), the centre to centre-left Ontario Liberal Party, and Green Party of Ontario. The Progressive Conservatives, Liberals and New Democrats have each governed the province, while the Greens elected their first member to the Legislative Assembly in 2018 Ontario general election, 2018.
The 2018 Ontario general election, 2018 provincial election resulted in a Progressive Conservative majority government under party leader Doug Ford, who was sworn in as Premier of Ontario, Premier on June 29. Ontario NDP leader Andrea Horwath was sworn in as the leader of her Majesty's Loyal Opposition.
Ontario has numerous political parties which run for election. The four main parties are the centre-right Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario, the Social democracy, social democratic Ontario New Democratic Party (NDP), the centre to centre-left Ontario Liberal Party, and Green Party of Ontario. The Progressive Conservatives, Liberals and New Democrats have each governed the province, while the Greens elected their first member to the Legislative Assembly in 2018 Ontario general election, 2018.
The 2018 Ontario general election, 2018 provincial election resulted in a Progressive Conservative majority government under party leader Doug Ford, who was sworn in as Premier of Ontario, Premier on June 29. Ontario NDP leader Andrea Horwath was sworn in as the leader of her Majesty's Loyal Opposition.
Administrative divisions
 Ontario has three types of List of census divisions of Ontario, first-level administrative divisions. They include List of census divisions of Ontario#Single-tier municipalities, single-tier municipalities, upper-tier municipalities (which may be in the form of either List of regional municipalities in Ontario, regional municipalities or United counties, counties), and Districts of Ontario, districts. Upper-tier municipalities and districts are made up of smaller municipalities and other types of administrative divisions.
Administrative divisions differ primarily in the services that they provide to their residents, with the differing structures of these administrative regions resulting in disparities among Ontario's different regions. The administrative regions of Ontario are roughly coterminous with the List of census divisions of Ontario, census divisions used by Statistics Canada, although some exceptions do exist.
Ontario has three types of List of census divisions of Ontario, first-level administrative divisions. They include List of census divisions of Ontario#Single-tier municipalities, single-tier municipalities, upper-tier municipalities (which may be in the form of either List of regional municipalities in Ontario, regional municipalities or United counties, counties), and Districts of Ontario, districts. Upper-tier municipalities and districts are made up of smaller municipalities and other types of administrative divisions.
Administrative divisions differ primarily in the services that they provide to their residents, with the differing structures of these administrative regions resulting in disparities among Ontario's different regions. The administrative regions of Ontario are roughly coterminous with the List of census divisions of Ontario, census divisions used by Statistics Canada, although some exceptions do exist.
Urban areas
Statistics Canada's measure of a "metro area", the Census Metropolitan Area (CMA), roughly bundles together population figures from the core municipality with those from "commuter" municipalities.Education
In Canada, education falls under provincial jurisdiction. Publicly funded elementary and secondary schools are administered by the Ministry of Education (Ontario), Ontario Ministry of Education, while colleges and universities are administered by the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities, Ontario Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities. The Minister of Education is Stephen Lecce, the Minister of Colleges and Universities is Ross Romano, and the Minister of Labour, Training and Skills Development Monte McNaughton.Higher education
Higher education in Ontario includes post-secondary education and skills training regulated by the Ministry of Education (Ontario), Ministry of Training, Colleges, and Universities and provided by universities, colleges of applied arts and technology, and private career colleges. The minister is Merrilee Fullerton. The ministry administers laws covering 22 public universities, 24 public colleges (21 Colleges of Applied Arts and Technology (CAATs) and three Institutes of Technology and Advanced Learning (ITALs)), 17 privately funded religious universities, and over 500 private career colleges. The Canadian constitution provides each province with the responsibility for higher education and there is no corresponding national federal ministry of higher education. Within Canadian federalism the division of responsibilities and taxing powers between the Ontario and Canadian governments creates the need for co-operation to fund and deliver higher education to students. Each higher education system aims to improve participation, access, and mobility for students. There are two central organizations that assist with the process of applying to Ontario universities and colleges: the Ontario Universities' Application Centre and Ontario College Application Service. While application services are centralized, admission and selection processes vary and are the purview of each institution. Admission to many Ontario postsecondary institutions can be highly competitive. Upon admission, students may get involved with regional student representation with the Canadian Federation of Students, the Canadian Alliance of Student Associations, the Ontario Undergraduate Student Alliance, or through the College Student Alliance in Ontario.Culture
In 2019, the government of Ontario passed legislation that established the Poet Laureate of Ontario.Songs and slogans
 In 1973, the first slogan to appear on Vehicle registration plates of Ontario, licence plates in Ontario was "Keep It Beautiful". This was replaced by "Yours to Discover" in 1982, apparently inspired by a tourism slogan, "Discover Ontario", dating back to 1927. Plates with the French equivalent, , were made available to the public beginning in May 2008. (From 1988 to 1990, "Ontario Incredible" gave "Yours to Discover" a brief respite.)
A Place to Stand, a Place to Grow is a song commissioned by the government of Ontario for its pavilion in Expo 67, and an unofficial anthem of the province. As a part of the Canada 150 celebrations in 2017, the provincial government released an updated rendition. In 2007, the provincial tourism agency commissioned a new song, "There's No Place Like This" is featured in television advertisement, television advertising, performed by Ontario artists including Molly Johnson, Brian Byrne, Keshia Chanté, as well as Tomi Swick and Arkells.
In 1973, the first slogan to appear on Vehicle registration plates of Ontario, licence plates in Ontario was "Keep It Beautiful". This was replaced by "Yours to Discover" in 1982, apparently inspired by a tourism slogan, "Discover Ontario", dating back to 1927. Plates with the French equivalent, , were made available to the public beginning in May 2008. (From 1988 to 1990, "Ontario Incredible" gave "Yours to Discover" a brief respite.)
A Place to Stand, a Place to Grow is a song commissioned by the government of Ontario for its pavilion in Expo 67, and an unofficial anthem of the province. As a part of the Canada 150 celebrations in 2017, the provincial government released an updated rendition. In 2007, the provincial tourism agency commissioned a new song, "There's No Place Like This" is featured in television advertisement, television advertising, performed by Ontario artists including Molly Johnson, Brian Byrne, Keshia Chanté, as well as Tomi Swick and Arkells.
Professional sports
The province has professional sports teams in baseball, basketball, Canadian football, ice hockey, lacrosse, rugby league, rugby union and Association football, soccer.Notable residents
Museums
Transportation
Transportation routes in Ontario evolved from early waterway travel and First Nations paths followed by European explorers. Ontario has two major east–west routes, both starting from Montreal in the neighbouring province of Quebec. The northerly route, which was a major fur trade route, travels west from Montreal along the Ottawa River, then continues northwestward towards Manitoba. Major cities on or near the route include Ottawa, North Bay, Sudbury, Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Sault Ste. Marie, and Thunder Bay. The southerly route, which was driven by growth in settlements originated by the United Empire Loyalists and later other European immigrants, travels southwest from Montreal along the St. Lawrence River, Lake Ontario, and Lake Erie before entering the United States in Michigan. Major cities on or near the route include Kingston, Belleville, Peterborough, Oshawa, Toronto, Mississauga, Regional Municipality of Waterloo, Kitchener-Waterloo, Hamilton, London, Sarnia, and Windsor. This route was also heavily used by immigrants to the Midwestern US particularly in the late 19th century.Air travel
Railways
Via Rail operates the inter-regional passenger train service on the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor (Via Rail), Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, along with ''Canadian (train), The Canadian'', a transcontinental rail service from Southern Ontario to Vancouver, and the Sudbury–White River train. Additionally, Amtrak rail connects Ontario with key New York cities including Buffalo, New York, Buffalo, Albany, New York, Albany, and New York City. Ontario Northland Railway, Ontario Northland provides rail service to destinations as far north as Moosonee nearJames Bay
James Bay (french: Baie James; cr, ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, Wînipekw, dirty water) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost pa ...
, connecting them with the south.
Rail freight transport, Freight rail is dominated by the founding cross-country Canadian National Railway and Canadian Pacific Railway, CP Rail companies, which during the 1990s sold many Shortline railroad, short rail lines from their vast network to private companies operating mostly in the south.
Regional commuter rail is limited to the provincially owned GO Transit, and serves a train-bus network spanning the Golden Horseshoe region, with Union Station (Toronto), Union Station in Toronto serving as the transport hub.
There are several city rail-transit systems in the Province. The Toronto Transit Commission operates Toronto subway, subways, as well as Toronto streetcar system, streetcars (being one of the busiest streetcar systems in North America). OC Transpo operates a O-Train, light rail metro system in Ottawa. In addition, Regional Municipality of Waterloo, Waterloo region operates a surface light rail system. Plans to build a light rail line is also underway in the Regional Municipality of Peel.
Roads
 400-series highways make up the primary vehicular network in the south of province, and they connect at a number of points to border crossings to the United States, and
400-series highways make up the primary vehicular network in the south of province, and they connect at a number of points to border crossings to the United States, and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, the busiest being the Detroit–Windsor Tunnel and Ambassador Bridge and the Blue Water Bridge (via Ontario Highway 402, Highway 402). Some of the primary highways along the southern route are Ontario Highway 401, Highway 401, Ontario Highway 417, Highway 417, and Ontario Highway 400, Highway 400, Highway 401 being the busiest highway in North America. Other List of provincial highways in Ontario, provincial highways and regional roads inter-connect the remainder of the province.
Waterways
The Saint Lawrence Seaway, which extends across most of the southern portion of the province and connects to the Atlantic Ocean, is the primary water transportation route for cargo, particularly iron ore and grain. In the past, the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence River were also a major passenger transportation route, but over the past half century passenger travel has been reduced to ferry services and sightseeing cruises. Ontario's three largest ports are the Hamilton-Oshawa Port Authority, Port of Hamilton, Thunder Bay Port Authority, Port of Thunder Bay and the Port of Windsor. Ontario's only saltwater port is located in the town of Moosonee onJames Bay
James Bay (french: Baie James; cr, ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, Wînipekw, dirty water) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost pa ...
.
See also
* Outline of Ontario * Index of Ontario-related articlesNotes
References
Sources
* Michael Sletcher, "Ottawa", in James Ciment, ed., ''Colonial America: An Encyclopedia of Social, Political, Cultural, and Economic History'', (5 vols., M. E. Sharpe, New York, 2006).Virtual Vault
, an online exhibition of Canadian historical art at Library and Archives Canada.
Further reading
* * * * ''Celebrating One Thousand Years of Ontario's History: Proceedings of the Celebrating One Thousand Years of Ontario's History Symposium, April 14, 15 and 16, 2000.'' Ontario Historical Society, 2000. 343 pp. * Baskerville, Peter A. ''Sites of Power: A Concise History of Ontario.'' Oxford U. Press., 2005. 296 pp. (first edition was ''Ontario: Image, Identity and Power,'' 2002)online review
* Chambers, Lori, and Edgar-Andre Montigny, eds. ''Ontario Since Confederation: A Reader'' (2000), articles by scholars * Winfield, Mark S. ''Blue-Green Province: The Environment and the Political Economy of Ontario'' (University of British Columbia Press; 2012) 296 pages; environmental policies since 1945
External links
Government of Ontario
Tourism Ontario
*
Ontario Visual Heritage Project
nbsp;– Non-profit documentary project about Ontario's history {{Authority control Ontario, 1867 establishments in Canada Provinces and territories of Canada States and territories established in 1867 Eastern Canada