Tear of meniscus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A tear of a meniscus is a rupturing of one or more of the
Anatomy
Meniscal Tear. The larger semilunar medial meniscus is attached more firmly than the loosely fixed, more circular lateral meniscus. The anterior and posterior horns of both menisci are secured to the tibial plateaus. Anteriorly, the transverse
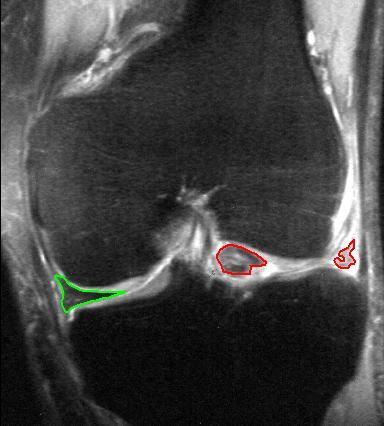
 A meniscal tear can be classified in various ways, such as by anatomic location or by proximity to blood supply. Various tear patterns and configurations have been described.Classification of meniscal tear
A meniscal tear can be classified in various ways, such as by anatomic location or by proximity to blood supply. Various tear patterns and configurations have been described.Classification of meniscal tear
sportsmd. These include: * Radial tears * Flap or parrot-beak tears * Peripheral, longitudinal tears * Bucket-handle tears * Horizontal cleavage tears * Complex, degenerative tears These tears can then be further classified by their proximity to the meniscus blood supply, namely whether they are located in the “red-red,” “red-white,” or “white-white” zones. The functional importance of these classifications, however, is to ultimately determine whether a meniscus is repairable. The repairability of a meniscus depends on a number of factors. These include: * Age/strength * Activity level * Tear pattern * Chronicity of the tear * Associated injuries (anterior cruciate ligament injury) * Healing potential

 Presently, treatments make it possible for quicker recovery. If the tear is not serious, physical therapy, compression, elevation and icing the knee can heal the meniscus. Meniscus tears are more likely to heal on their own if they are in what physicians call the "red zone," or the outer edge of the meniscus where blood supply is present. More serious tears may require surgical procedures. Surgery, however, does not appear to be better than non-surgical care. In the long term, degenerative meniscal tears are often associated with
Presently, treatments make it possible for quicker recovery. If the tear is not serious, physical therapy, compression, elevation and icing the knee can heal the meniscus. Meniscus tears are more likely to heal on their own if they are in what physicians call the "red zone," or the outer edge of the meniscus where blood supply is present. More serious tears may require surgical procedures. Surgery, however, does not appear to be better than non-surgical care. In the long term, degenerative meniscal tears are often associated with
 After a successful surgery for treating the destroyed part of the meniscus, patients must follow a rehabilitation program to have the best result. The rehabilitation following a meniscus surgery depends on whether the entire meniscus was removed or repaired.
If the destroyed part of the meniscus was removed, patients can usually start walking using a crutch a day or two after surgery. Although each case is different, patients return to their normal activities on average after a few weeks (2 or 3). Still, a completely normal walk will resume gradually, and it's not unusual to take 2–3 months for the recovery to reach a level where a patient will walk totally smoothly. Many meniscectomy patients don't ever feel a 100% functional recovery, but even years after the procedure they sometimes feel tugging or tension in a part of their knee. There is little medical follow-up after meniscectomy and official medical documentation tends to ignore the imperfections and side-effects of this procedure.
If the meniscus was repaired, the
After a successful surgery for treating the destroyed part of the meniscus, patients must follow a rehabilitation program to have the best result. The rehabilitation following a meniscus surgery depends on whether the entire meniscus was removed or repaired.
If the destroyed part of the meniscus was removed, patients can usually start walking using a crutch a day or two after surgery. Although each case is different, patients return to their normal activities on average after a few weeks (2 or 3). Still, a completely normal walk will resume gradually, and it's not unusual to take 2–3 months for the recovery to reach a level where a patient will walk totally smoothly. Many meniscectomy patients don't ever feel a 100% functional recovery, but even years after the procedure they sometimes feel tugging or tension in a part of their knee. There is little medical follow-up after meniscectomy and official medical documentation tends to ignore the imperfections and side-effects of this procedure.
If the meniscus was repaired, the 

 People who work in physically demanding jobs such as construction or professional sports are more at risk of a meniscal tear because of the different stresses to which their knees are subjected.
According to the
People who work in physically demanding jobs such as construction or professional sports are more at risk of a meniscal tear because of the different stresses to which their knees are subjected.
According to the
fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
strips in the knee called menisci. When doctors and patients refer to "torn cartilage" in the knee, they actually may be referring to an injury to a meniscus at the top of one of the tibiae
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
. Menisci can be torn during innocuous activities such as walking or squatting
Squatting is the action of occupying an abandoned or unoccupied area of land or a building, usually residential, that the squatter does not own, rent or otherwise have lawful permission to use. The United Nations estimated in 2003 that there ...
. They can also be torn by traumatic force encountered in sports or other forms of physical exertion. The traumatic action is most often a twisting movement at the knee while the leg is bent. In older adults, the meniscus can be damaged following prolonged 'wear and tear'. Especially acute injuries (typically in younger, more active patients) can lead to displaced tears which can cause mechanical symptoms such as clicking, catching, or locking during motion of the joint. The joint will be in pain when in use, but when there is no load, the pain goes away.
A tear of the medial meniscus can occur as part of the unhappy triad
The unhappy triad, also known as a blown knee among other names, is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and meniscus. Analysis during the 1990s indicated that this 'classic' O'Donoghue triad is actually an un ...
, together with a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee. The two ligaments are also called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formati ...
and medial collateral ligament
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), or tibial collateral ligament (TCL), is one of the four major ligaments of the knee. It is on the medial (inner) side of the knee joint in humans and other primates. Its primary function is to resist outwar ...
.
Signs and symptoms
The common signs and symptoms of a torn meniscus are knee pain, particularly along the joint line, and swelling. These are worse when the knee bears more weight (for example, when running). Another typical complaint is joint locking, when the affected person is unable to straighten the leg fully. This can be accompanied by a clicking feeling. Sometimes, a meniscal tear also causes a sensation that the knee gives way. A person with a torn meniscus can sometimes remember a specific activity during which the injury was sustained. A tear of the meniscus commonly follows a trauma that involves rotation of the knee while it was slightly bent. These maneuvers also exacerbate the pain after the injury; for example, getting out of a car is often reported as painful.Causes
There are two menisci in the knee. They sit between thethigh bone
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
and the shin bone
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
. While the ends of the thigh bone and the shin bone have a thin covering of soft hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and h ...
, the menisci are made of tough fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
and conform to the surfaces of the bones they rest on. One meniscus rests on the medial tibial plateau; this is the medial meniscus. The other meniscus rests on the lateral tibial plateau; this is the lateral meniscus.
These menisci act to distribute body weight across the knee joint
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the human leg, leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest join ...
. Without the menisci, the weight of the body would be unevenly applied to the bones in the legs (the femur and tibia). This uneven weight distribution would cause the development of abnormal excessive forces leading to early damage of the knee joint. The menisci also contribute to the stability of the joint.
The menisci are nourished by small blood vessels but have a large area in the center with no direct blood supply (avascular). This presents a problem when there is an injury to the meniscus, as the avascular areas tend not to heal. Without the essential nutrients supplied by blood vessels, healing cannot take place.
The two most common causes of a meniscal tear are traumatic injury (often seen in athletes) and degenerative processes, which are the most common tear seen in all ages of patients. Meniscal tears can occur in all age groups. Traumatic tears are most common in active people aged 10–45. Traumatic tears are usually radial or vertical in the meniscus and more likely to produce a moveable fragment that can catch in the knee and therefore require surgical treatment.
A meniscus can tear due to an internally or externally rotated knee in a flexed position, with the foot in a flexed position. It is not uncommon for a meniscal tear to occur along with injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament ACL and the medial collateral ligament MCL — these three problems occurring together are known as the "unhappy triad
The unhappy triad, also known as a blown knee among other names, is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and meniscus. Analysis during the 1990s indicated that this 'classic' O'Donoghue triad is actually an un ...
," which is seen in sports such as football when the player is hit on the outside of the knee. Individuals who experience a meniscal tear usually experience pain and swelling as their primary symptoms. Another common complaint is joint locking, or the inability to completely straighten the joint. This is due to a piece of the torn cartilage preventing the normal functioning of the knee joint.
Degenerative tears are most common in people from age 40 upward but can be found at any age, especially with obesity. Degenerative meniscal tears are thought to occur as part of the aging process when the collagen fibers within the meniscus start to break down and lend less support to the structure of the meniscus. Degenerative tears are usually horizontal, producing both an upper and a lower segment of the meniscus. These segments do not usually move out of place and are therefore less likely to produce mechanical symptoms of catching or locking.
Risk factors
The meniscus is made ofcartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck ...
, a viscoelastic material, which makes it more susceptible to rate of loading injuries. Repetitive loading can also lead to injury. Recent studies have shown people who experience rapid rate of loading and/or repetitive loading to be the most susceptible to meniscus tears. People over the age of 60 who have working conditions in which squatting
Squatting is the action of occupying an abandoned or unoccupied area of land or a building, usually residential, that the squatter does not own, rent or otherwise have lawful permission to use. The United Nations estimated in 2003 that there ...
and kneeling are common are more susceptible to degenerative meniscal tears. Athletes who constantly experience a high rate of loading (e.g. soccer, rugby) are also susceptible to meniscus tears. Studies have also shown with increasing time between ACL injury and ACL reconstruction, there is an increasing chance of meniscus tears. This study showed meniscus tears occurring at a rate of 50–70% depending on how long after the ACL injury the surgery occurred. Meniscal ramp lesions (tears of the medial meniscus posterior horn at the menisco-capsular junction) occur in approximately 25% of ACL-injured knees. Lateral meniscal root tears occur in approximately 7% of ACL injured knees
Pathophysiology
The force distribution is across the knee joint, increasing force concentration on the cartilage and other joint structures. Damage to the meniscus due to rotational forces directed to a flexed knee (as may occur with twisting sports) is the usual underlying mechanism of injury. A valgus force applied to a flexed knee with the foot planted and thefemur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates ...
rotated externally can result in a lateral meniscus tear. A varus force applied to the flexed knee when the foot is planted and the femur rotated internally result in a tear of the medial meniscus.
Tears produce rough surfaces inside the knee, which cause catching, locking, buckling, pain, or a combination of these symptoms. Abnormal loading patterns and rough surfaces inside the knee, especially when coupled with return to sports, significantly increase the risk of developing arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
if not already present.
Anatomy
The menisci are C-shaped wedges offibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
located between the tibial plateau Tibial may refer to:
* Tibia bone
* Tibial nerve
* Anterior tibial artery
* Posterior tibial artery
* Anterior tibial vein
* Posterior tibial vein
The posterior tibial veins are veins of the leg in humans. They drain the posterior compartment o ...
and femoral condyle
The lower extremity of femur (or distal extremity) is the lower end of the femur (thigh bone) in human and other animals, closer to the knee. It is larger than the upper extremity of femur, is somewhat cuboid in form, but its transverse diameter is ...
s. The menisci contain 70% type I collagen."Anatomy of Meniscus" 1994. May. 21011Anatomy
Meniscal Tear. The larger semilunar medial meniscus is attached more firmly than the loosely fixed, more circular lateral meniscus. The anterior and posterior horns of both menisci are secured to the tibial plateaus. Anteriorly, the transverse
ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal l ...
connects the 2 menisci; posteriorly, the meniscofemoral ligament helps stabilize the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus to the femoral condyle. The coronary ligaments connect the peripheral meniscal rim loosely to the tibia. Although the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) passes in close proximity, the lateral meniscus has no attachment to this structure.
The joint capsule attaches to the entire periphery of each meniscus but adheres more firmly to the medial meniscus. An interruption in the attachment of the joint capsule to the lateral meniscus, forming the popliteal hiatus, allows the popliteus tendon to pass through to its femoral attachment site. Contraction by the popliteus during knee flexion pulls the lateral meniscus posteriorly, avoiding entrapment within the joint space. The medial meniscus does not have a direct muscular connection. The medial meniscus may shift a few millimeters, while the less stable lateral meniscus may move at least 1 cm.
In 1978, Shrive ''et al.'' reported that the collagen fibers of the menisci are oriented in a circumferential pattern. When a compressive force is applied in the knee joint, a tensile force is transmitted to the menisci. The femur attempts to spread the menisci anteroposteriorly in extension and mediolaterally in flexion. Shrive ''et al.'' further studied the effects of a radial cut in the peripheral rim of the menisci during loading. In joints with intact menisci, the force was applied through the menisci and articular cartilage; however, a lesion in the peripheral rim disrupted the normal mechanics of the menisci and allowed it to spread when a load was applied. The load now was distributed directly to the articular cartilage. In light of these findings, it is essential to preserve the peripheral rim during partial meniscectomy to avoid irreversible disruption of the structure's hoop tension capability.
Diagnosis
Physical examination
After noting symptoms, aphysician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
can perform clinical tests to determine if the pain is caused by compression and impingement of a torn meniscus. The knee is examined for swelling. In meniscal tears, pressing on the joint line on the affected side typically produces tenderness. The McMurray test The McMurray test, also known as the McMurray circumduction test is used to evaluate individuals for tears in the meniscus of the knee. A tear in the meniscus may cause a pedunculated tag of the meniscus which may become jammed between the joint sur ...
involves pressing on the joint line while stressing the meniscus (using flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
–extension
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate
* Ext ...
movements and varus or valgus stress). Similar tests are the Steinmann test (with the patient sitting) and the Apley grind test (a grinding maneuver while the person lies prone and the knee is bent 90°) and the Thessaly test (flexing the affected knee to 20 degrees, pivoting on the knee to see if the pain is reproduced). Bending the knee (into hyperflexion if tolerable), and especially squatting, is typically a painful maneuver if the meniscus is torn. The range of motion
Range of motion (or ROM), is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another. It is also called range of travel (or ROT), particularly when talking about mechanical devices and in mechanic ...
of the joint is often restricted.
Cooper's sign is present in over 92% of tears. It is a subjective symptom of pain in the affected knee when turning over in bed at night. Osteoarthritic pain is present with weightbearing, but the meniscal tear causes pain with a twisting motion of the knee as the meniscal fragment gets pinched, and the capsular attachment gets stretched causing the complaint of pain.
Radiology

X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
images (normally during weightbearing) can be obtained to rule out other conditions or to see if the patient also has osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
. The menisci themselves cannot be visualised with plain radiographs. If the diagnosis is not clear from the history and examination, the menisci can be imaged with magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(an MRI scan). This technique has replaced previous arthrography
An arthrogram is a series of images of a joint after injection of a contrast medium, usually done by fluoroscopy or MRI. The injection is normally done under a local anesthetic such as Novocain or lidocaine. The radiologist or radiographer perfor ...
, which involved injecting contrast medium
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radio ...
into the joint space. In straightforward cases, knee arthroscopy
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic or keyhole surgery) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted into the ...
allows quick diagnosis and simultaneous treatment. Recent clinical data shows that MRI and clinical testing are comparable in sensitivity and specificity when looking for a meniscal tear.
Classification
sportsmd. These include: * Radial tears * Flap or parrot-beak tears * Peripheral, longitudinal tears * Bucket-handle tears * Horizontal cleavage tears * Complex, degenerative tears These tears can then be further classified by their proximity to the meniscus blood supply, namely whether they are located in the “red-red,” “red-white,” or “white-white” zones. The functional importance of these classifications, however, is to ultimately determine whether a meniscus is repairable. The repairability of a meniscus depends on a number of factors. These include: * Age/strength * Activity level * Tear pattern * Chronicity of the tear * Associated injuries (anterior cruciate ligament injury) * Healing potential
Prevention
Tear of a meniscus is a commoninjury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
in many sports. The menisci hold 30–50% of the body load in standing position. Some sports
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, ...
where a meniscus tear is common are American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
, association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
, ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
and tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball cov ...
. Regardless of what the activity is, it is important to take the correct precautions to prevent a meniscus tear from happening.
Footwear
There are three major ways of preventing a meniscus tear. The first of these is wearing the correct footwear for the sport and surface that the activity is taking place on. This means that if the sport being played isassociation football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
, cleats are an important item in reducing the risk of a meniscus tear. The proper footwear
Footwear refers to garments worn on the feet, which typically serves the purpose of protection against adversities of the environment such as wear from ground textures and temperature. Footwear in the manner of shoes therefore primarily serves ...
is imperative when engaging in physical activity because one off-balanced step could mean a meniscus tear.
It is highly advised that cleats contain a sole that molds around the foot, no fewer than fourteen cleats per shoe, no lower than a half inch diameter of the cleat tip, and at most, a three-eighths inch of cleat length.
Stretches
The second way to prevent a meniscus tear is to strengthen and stretch the major leg muscles. Those muscles include the hamstrings, quadriceps, and calf muscles. One popular exercise used to strengthen the hamstrings is the leg curl. It is also important to properly stretch the hamstrings; doing standing toe touches can do this. Seated leg extensions strengthen the quadriceps and doing the quadriceps stretch will help loosen the muscles. Toe raises are used to strengthen and stretch the calves. Adequate muscle mass and strength may also aid in maintaining healthy knees. The use of the parallel squat increases much needed stability in the knee if executed properly. Execution of the parallel squat will develop the lower body muscles that will strengthen the hips, knees, and ankles.
Technique
The last major way to prevent a tear in the meniscus is learning proper technique for the movement that is taking place. For the sports involving quick powerful movements it is important to learn how to cut, turn, land from ajump
Jumping is a form of locomotion or movement in which an organism or non-living (e.g., robotic) mechanical system propels itself through the air along a ballistic trajectory.
Jump or Jumping also may refer to:
Places
* Jump, Kentucky or Jump S ...
, and stop correctly. It is important to take the time out to perfect these techniques when used. These three major techniques will significantly prevent and reduce the risk of a meniscus tear.
Treatment
 Presently, treatments make it possible for quicker recovery. If the tear is not serious, physical therapy, compression, elevation and icing the knee can heal the meniscus. Meniscus tears are more likely to heal on their own if they are in what physicians call the "red zone," or the outer edge of the meniscus where blood supply is present. More serious tears may require surgical procedures. Surgery, however, does not appear to be better than non-surgical care. In the long term, degenerative meniscal tears are often associated with
Presently, treatments make it possible for quicker recovery. If the tear is not serious, physical therapy, compression, elevation and icing the knee can heal the meniscus. Meniscus tears are more likely to heal on their own if they are in what physicians call the "red zone," or the outer edge of the meniscus where blood supply is present. More serious tears may require surgical procedures. Surgery, however, does not appear to be better than non-surgical care. In the long term, degenerative meniscal tears are often associated with osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
. This leads to poor outcomes regardless of treatment type. In the short term, studies have shown arthroscopic partial meniscectomy (APM) is a more effective treatment with regards to function and pain management.
Conservative treatments
Initial treatment may includephysical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, pat ...
, bracing, anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as o ...
drugs, or corticosteroid injections to increase flexibility, endurance, and strength., which cites
*
Common anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers prescribed for meniscus tears include acetaminophen, non-steroidal inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroids.
Exercises can strengthen the muscles around the knee, especially the quadriceps. Stronger and bigger muscles will protect the meniscus cartilage by absorbing a part of the weight. The patient may be given paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferio ...
or anti-inflammatory medications.
For patients selecting non-surgical treatment, physical therapy may reduce symptoms of pain and swelling. This type of rehabilitation focuses on maintenance of full range of motion and functional progression without aggravating symptoms. Physical therapists can employ electric stimulation
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is a technique that uses low-energy electrical pulses to artificially generate body movements in individuals who have been paralyzed due to injury to the central nervous system. More specifically, FES can ...
, cold therapy, and ultrasonography.
Accelerated rehabilitation programs can be as successful as the conservative program. The program reduces the time the patient spends using crutches and allows weight bearing activities. The less conservative approach allows the patient to apply a small amount of stress while protecting range of motion. It is likely that a patient with a peripheral tear can pursue the accelerated program, while a patient with a larger tear adopts the conservative program.
The use of platelet rich plasma ( PRP) to aid in the healing process has become widely accepted among US athletes. Although the procedure has grown in popularity, studies assessing the efficacy of PRP treatment have yielded contradictory results.
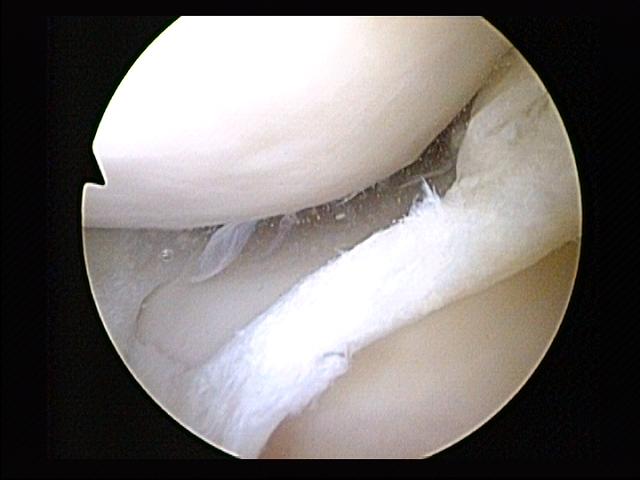
Surgery
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic or keyhole surgery) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted into the ...
is a surgical technique in which a joint is operated on using an endoscopic camera as opposed to open surgery on the joint. The meniscus can either be repaired or completely removed. Surgery is not appropriate for a degenerative meniscus tear, absent locking or catching of the knee, recurrent effusion or persistent pain. Evidence suggests that it is no better than conservative management in those with and without osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
. Surgery appears to offer no benefit to adults who have mild arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
.
An independent international guideline panel recommended against arthroscopy for degenerative meniscus tears; this conclusion derived from evidence of no lasting benefit and that less than 15% of patients experience even a short-term benefit. Disadvantages include a two to six week recovery time and rare but serious adverse effects that can occur, including blood clots in the legs, surgical site infections, and nerve damage
Nerve injury is an injury to nervous tissue. There is no single classification system that can describe all the many variations of nerve injuries. In 1941, Seddon introduced a classification of nerve injuries based on three main types of nerve f ...
. The BMJ Rapid Recommendation includes infographics and shared decision-making tools to facilitate a conversation between doctors and patients about the risks and benefits of arthroscopic surgery.
If the injury is isolated, then the knee would be relatively stable. However, if an injury such as an anterior cruciate ligament injury
An anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is either stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. The most common injury is a complete tear. Symptoms include pain, an audible cracking sound during inju ...
(torn ACL) is coupled with a torn meniscus, then an arthroscopy is recommended. A meniscal repair has a higher success rate given an adequate blood supply to the peripheral rim. The interior of the meniscus is avascular, but the blood supply can penetrate up to about . Therefore, meniscus tears that occur near the peripheral rim are able to heal after a meniscal repair. One study found that repair is better than removal (meniscectomy). The amount of rehabilitation time required for a repair is longer, but removing the meniscus can induce osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
. Meniscectomy rehab requires four to six weeks. Repair requires four to six months. If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention may be required. Younger patients are typically more resilient and respond well to this treatment, while older, more sedentary patients do not have a favorable outcome after a repair.
Transplants
Meniscus transplants are regularly successful, although the procedure is not common and many questions surrounding its use remain. Side effects of meniscectomy include: * The knee loses its ability to transmit and distribute load and absorb mechanical shock. * Persistent and significant swelling and stiffness in the knee. * The knee may be not be fully mobile; there may be the sensation of knee locking or buckling in the knee. * The full knee may be in full motion after tear of meniscus. * Increases progression of arthritis and time to knee replacement.Implants
Another treatment approach in development is a meniscus implant or "artificial meniscus." While many artificial joints and bionic body parts are available, including arms, legs, joints and other body parts, a prosthetic meniscus replacement. The first to be implanted in humans is called the NUsurface Meniscus Implant. The implant is made from medical grade plastic and is designed not to require fixation to bone or soft tissue. The implant could be a good option for younger, active patients who are considered too young for knee replacement because that surgery lasts only about 10 years. The implant has been used in clinical trials in Europe since 2008. The first surgery as part of US clinical trials took place in January 2015 atOhio State University
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best pub ...
's Wexner Medical Center. Two FDA-approved clinical trials evaluating the implant completed enrollment in June 2018. In September 2019, the manufacturer received breakthrough designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and the company expected to file for regulatory approval within the following year. In November 2019, the implant became commercially available in Israel.
Other implants include TRAMMPOLIN and Orthonika.
Scientists are working to grow an artificial meniscus in the lab. Scientists from Cornell
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to tea ...
and Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region i ...
universities grew a meniscus inside the knee joint of a sheep using a 3-D printer and the sheep's stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
s. Similarly, researchers at Scripps Research
Scripps Research, previously known as The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI), is a nonprofit American medical research facility that focuses on research and education in the biomedical sciences. Headquartered in San Diego, California, the institu ...
Shiley Center for Orthopaedic Research and Education reported growing a meniscus.
Post-surgical rehabilitation
rehabilitation
Rehabilitation or Rehab may refer to:
Health
* Rehabilitation (neuropsychology), therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
* Rehabilitation (wildlife), treatment of injured wildlife so they can be retur ...
program that follows is a lot more intensive. After the surgery, a hinged knee brace is sometimes placed on the patient. This brace allows controlled movement of the knee. The patient is encouraged to walk using crutches from the first day, and most of the times can put partial weight on the knee.
Improving symptoms, restoring function, and preventing further injuries are the main goals when rehabilitating. By the end of rehabilitation, normal range of motion, function of muscles and coordination of the body are restored. Personalized rehabilitation programs are designed considering the patient's surgery type, location repaired (medial or lateral), simultaneous knee injuries, type of meniscal tear, age of patient, condition of the knee, loss of strength and ROM, and the expectations and motivations of the patient.

Phase I
There are three phases that follow meniscal surgery. Each phase consists of rehabilitation goals, exercises, and criteria to move on to the next phase. Phase I starts immediately following surgery to 4–6 weeks or until the patient is able meet progression criteria. The goals are to restore normal knee extension, reduce and eliminate swelling, regain leg control, and protect the knee (Fowler, PJ and D. Pompan, 1993). During the first 5 days following the surgery, a passive continuous motion machine is used to prevent a prolonged period of immobilization which leads to muscular atrophy and delays functional recovery. During the 4–6 weeks post-surgical, active and passive non-weight bearing motions which flex the knee up to 90° are recommended. For patients with meniscal transplantation, further knee flexion can damage the allograft because of the increased shear forces and stresses. If any weight-bearing exercises are applied, a controlled brace should be worn on the knee to keep the knee at near (<10°) or full extension. The suggested exercises target increasing the patient's ROM, muscular and neuromuscular strength, andcardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
endurance
Endurance (also related to sufferance, resilience, constitution, fortitude, and hardiness) is the ability of an organism to exert itself and remain active for a long period of time, as well as its ability to resist, withstand, recover from an ...
. Aquatic therapy
Aquatic therapy refers to treatments and exercises performed in water for relaxation, fitness, physical rehabilitation, and other therapeutic benefit. Typically a qualified aquatic therapist gives constant attendance to a person receiving treat ...
, or swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
, can be used to rehab patients because it encompasses ROM, strength, and cardiovascular exercises while relieving stress on the body. It has also been shown to significantly improve dependent edema and pain symptoms. No pain gait without crutches, swelling and 4–6 weeks after surgery are the criteria to begin the next phase (Ulrich G.S., and S Aroncyzk, 1993).
Phase II
This phase of the rehabilitation program is 6 to 14 weeks after the surgery. The goals for Phase II include being able to restore full ROM, normalized gait, and performing functional movements with control and no pain (Fowler, PJ and D. Pompan, 1993). Also, muscular strengthening and neuromuscular training are emphasized using progressive weight bearing and balance exercises. Exercises in this phase can increase knee flexion for more than 90°. Advised exercises includestationary bicycle
A stationary bicycle (also known as exercise bicycle, exercise bike, spinning bike, spin bike, or exercycle) is a device used as exercise equipment for indoor cycling. It includes a saddle, pedals, and some form of handlebars arranged as on ...
, standing on foam surface with two and one leg, abdominal and back strengthening, and quadriceps strengthening. The proposed criteria include normal gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. ...
on all surfaces and single leg balance longer than 15 seconds (Ulrich G.S., and S Aroncyzk, 1993). 
Phase III
Patients begin exercises in phase III 14 to 22 weeks after surgery. Phase III's goal and final criterion is to perform sport/work specific movements with no pain or swelling (Fowler, PJ and D. Pompan, 1993). Drills for maximal muscle control, strength, flexibility, movements specific to patient's work/sport, low to high rate exercises, andabdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
and back strengthening exercises are all recommended exercises (Ulrich G.S., and S Aroncyzk, 1993). Exercises to increase cardiovascular fitness are also applied to fully prepare the patients to return to their desired activities.
If the progression criteria are met, the patient can gradually return to "high-impact" activities (like running). However, "heavier activities", like running, skiing, basketball etc., generally any activities where knees bear sudden changes of the direction of movement can lead to repeated injuries. When planning sport activities it makes sense to consult a physical therapist and check how much impact the sport will have on the knee.
Epidemiology
The meniscal tear is the most common knee injury. It tends to be more frequent in sports that have rough contact or pivoting sports such assoccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
. It is more common in males than females, with a ratio of about two and a half males to one female. Males between the ages of 31 and 40 tend to tear their meniscus more frequently than younger men. Females seem to be more likely to tear their meniscus between the ages of 11 and 20.
 People who work in physically demanding jobs such as construction or professional sports are more at risk of a meniscal tear because of the different stresses to which their knees are subjected.
According to the
People who work in physically demanding jobs such as construction or professional sports are more at risk of a meniscal tear because of the different stresses to which their knees are subjected.
According to the United States National Library of Medicine
The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), operated by the United States federal government, is the world's largest medical library.
Located in Bethesda, Maryland, the NLM is an institute within the National Institutes of Health. Its ...
, the isolated medial meniscal tear occurs more frequently than any other tear associated with the meniscus. The prevalence of meniscus tears is the same for both knees. In a few studies the having a higher BMI puts more weight on the joints, which can cause the knee to be non-aligned, resulting in an easier tear.
In 2008 the U.S Department of Health and Human Services reported a combined total of 2,295 discharges for the principal diagnosis of tear of lateral cartilage/meniscus (836.0), tear of medial cartilage/meniscus (836.1), and tear of cartilage/meniscus (836.2). Females had a total of 53.49% discharges, while males had 45.72%. Individuals between the ages of 45 and 68 had an average of 31.73% discharges followed by age group 65–84, with 28.82%. The average length of stay for a patient diagnosed with torn menisci was 2.7 days for males and 3.7 days for females. There was a report of 6,941 hospital discharges for knee repair. Individuals between age 18 and 44 were among the highest with 37.37% total of discharges, followed by the age group 45–64, with a percentage of 36.34%. Males had a slightly higher number of discharges (50.78%) than females (48.66%). The average length of stay for both male and female patients in a hospital setting was 3.1.
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Meniscus (tear) Dislocations, sprains and strains Knee injuries