The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an
imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an
interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the
Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
and followed by the
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen conc ...
. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a
golden age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the '' Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the G ...
of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
.
The
Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress
Wu Zetian
Wu Zetian (17 February 624 – 16 December 705), personal name Wu Zhao, was the ''de facto'' ruler of the Tang dynasty from 665 to 705, ruling first through others and then (from 690) in her own right. From 665 to 690, she was first empres ...
seized the throne, proclaiming the
Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese
empress regnant. The devastating
An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general off ...
(755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynasty's latter half. Like the previous
Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
, the Tang maintained a civil-service system by recruiting
scholar-official
The scholar-officials, also known as literati, scholar-gentlemen or scholar-bureaucrats (), were government officials and prestigious scholars in Chinese society, forming a distinct social class.
Scholar-officials were politicians and governmen ...
s through
standardized examinations and recommendations to office. The rise of regional military governors known as ''
jiedushi
The ''jiedushi'' (), or jiedu, was a title for regional military governors in China which was established in the Tang dynasty and abolished in the Yuan dynasty. The post of ''jiedushi'' has been translated as "military commissioner", "legate ...
'' during the 9th century undermined this civil order. The dynasty and central government went into decline by the latter half of the 9th century; agrarian rebellions resulted in mass population loss and displacement, widespread poverty, and further government dysfunction that ultimately ended the dynasty in 907.
The Tang capital at
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
(present-day
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
) was then the world's most populous city. Two censuses of the 7th and 8th centuries estimated the empire's population at about 50 million people, which grew to an estimated 80 million by the dynasty's end. From its numerous subjects, the dynasty raised professional and conscripted armies of hundreds of thousands of troops to contend with nomadic powers for
control
Control may refer to:
Basic meanings Economics and business
* Control (management), an element of management
* Control, an element of management accounting
* Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization
* Controlli ...
of
Inner Asia
Inner Asia refers to the northern and landlocked regions spanning North, Central and East Asia. It includes parts of western and northeast China, as well as southern Siberia. The area overlaps with some definitions of 'Central Asia', mostly the ...
and the lucrative trade-routes along the
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
.
Far-flung kingdoms and states paid tribute to the Tang court, while the Tang also indirectly controlled several regions through a
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its in ...
system. In addition to its political
hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
, the Tang exerted a powerful cultural influence over neighboring
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
n nations such as
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
and
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
.
Chinese culture
Chinese culture () is one of the world's oldest cultures, originating thousands of years ago. The culture prevails across a large geographical region in East Asia and is extremely diverse and varying, with customs and traditions varying grea ...
flourished and further matured during the Tang era. It is traditionally considered the greatest age for
Chinese poetry
Chinese poetry is poetry written, spoken, or chanted in the Chinese language. While this last term comprises Classical Chinese, Standard Chinese, Mandarin Chinese, Yue Chinese, and other historical and vernacular forms of the language, its poetry ...
. Two of China's most famous poets,
Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), also pronounced as Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet, acclaimed from his own time to the present as a brilliant and romantic figure who took traditional poetic forms to new heights. He and his friend Du F ...
and
Du Fu
Du Fu (; 712–770) was a Tang dynasty poet and politician. Along with his elder contemporary and friend Li Bai (Li Po), he is frequently called the greatest of the Chinese poets.Ebrey, 103. His greatest ambition was to serve his country ...
, belonged to this age, contributing with poets such as
Wang Wei to the monumental ''
Three Hundred Tang Poems
The ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'' () is an anthology of poems from the Chinese Tang dynasty (618–907). It was first compiled around 1763 by Sun Zhu (1722–1778Yu, 64–65), who was a Qing Dynasty scholar and was also known as Hengtang Tuishi ( ...
''. Many famous painters such as
Han Gan
Han Gan (Chinese: 韩干/韓幹) (c. 706–783) was a Chinese painter during the Tang Dynasty.
He came from a poor family in either Chang'an, modern-day Xi'an, Shaanxi; Lantian, modern-day Shaanxi; or Daliang, modern-day Kaifeng, Henan. ...
,
Zhang Xuan
Zhang Xuan () (713–755) was a Chinese painter who lived during the Tang Dynasty (618–907).
Zhang Xuan painted many pieces of art, one of his best-known paintings is '' Court Ladies Preparing Newly Woven Silk'', of which a single copy survi ...
, and
Zhou Fang were active, while Chinese court music flourished with instruments such as the popular
pipa
The pipa, pípá, or p'i-p'a () is a traditional Chinese musical instrument, belonging to the plucked category of instruments. Sometimes called the "Chinese lute", the instrument has a pear-shaped wooden body with a varying number of frets ran ...
. Tang scholars compiled a rich variety of
historical literature
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as wel ...
, as well as encyclopedias and geographical works. Notable innovations included the development of
woodblock printing
Woodblock printing or block printing is a technique for printing text, images or patterns used widely throughout East Asia and originating in China in antiquity as a method of printing on textiles and later paper. Each page or image is crea ...
.
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
became a major influence in Chinese culture, with
native Chinese sects gaining prominence. However, in the 840s,
Emperor Wuzong enacted policies to
suppress Buddhism, which subsequently declined in influence.
History
Establishment and early reign

The
Li family had ethnic
Han origins, and it belonged to the northwest military aristocracy prevalent during the
Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
. According to official Tang records, they were
paternally descended from the founder of
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
,
Lao Tzu
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state ...
(whose personal name was Li Dan or Li Er), the
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
general
Li Guang
Li Guang (184-119 BC) was a Chinese military general of the Western Han dynasty. Nicknamed "Flying General" by the Xiongnu, he fought primarily in the campaigns against the nomadic Xiongnu tribes to the north of China. He was known to the Xiong ...
, and
Li Gao, the founder of the Han-ruled
Western Liang kingdom. This family was known as the
Longxi Li lineage (; ), and it included the prominent Tang poet
Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), also pronounced as Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet, acclaimed from his own time to the present as a brilliant and romantic figure who took traditional poetic forms to new heights. He and his friend Du F ...
. Aside from traditional historiography, some modern historians have suggested that the Tang imperial family might have modified its genealogy to conceal
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
heritage. The Tang Emperors had part-
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
maternal ancestry, from
Emperor Gaozu of Tang
Emperor Gaozu of Tang (7 April 566 – 25 June 635, born Li Yuan, courtesy name Shude) was the founding emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 618 to 626. Under the Sui dynasty, Li Yuan was the governor in the area of modern-day ...
's part-Xianbei mother,
Duchess Dugu.
 Li Yuan
Li Yuan, the founder of the Tang dynasty, was Duke of Tang and governor of
Taiyuan
Taiyuan (; ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; also known as (), ()) is the capital and largest city of Shanxi Province, People's Republic of China. Taiyuan is the political, economic, cultural and international exchange center of Shanxi Province. ...
, the capital of modern
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-leve ...
, during the collapse of the
Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
. He had prestige and military experience, and was a first cousin of
Emperor Yang of Sui
Emperor Yang of Sui (隋煬帝, 569 – 11 April 618), personal name Yang Guang (), alternative name Ying (), Xianbei name Amo (), also known as Emperor Ming of Sui () during the brief reign of his grandson Yang Tong, was the second emperor ...
(their mothers were both one of the
Dugu sisters). Li Yuan rose in rebellion in 617, along with his son and his equally militant daughter
Princess Pingyang (d. 623), who raised and commanded her own troops. In winter 617, Li Yuan occupied
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
, relegated Emperor Yang to the position of ''
Taishang Huang
In Chinese history, a ''Taishang Huang'' or ''Taishang Huangdi'' is an honorific and institution of a retired emperor. The former emperor had, at least in name, abdicated in favor of someone else. Although no longer the reigning sovereign, ther ...
'' or retired emperor, and acted as
regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
to the puppet child-emperor,
Yang You
Emperor Gong of Sui (隋恭帝) (605 – 14 September 619), personal name Yang You (楊侑), was an emperor of the Chinese Sui dynasty. He was installed as a puppet emperor by Li Yuan, and after Emperor Yang of Sui died, Li then became the fou ...
. On the news of Emperor Yang's murder by General
Yuwen Huaji
Yuwen Huaji (; died March 22, 619) was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician of the Sui Dynasty who, in 618, led a coup against and murdered Emperor Yang of Sui. He subsequently declared Emperor Yang's nephew Yang Hao emperor and ...
on June 18, 618, Li Yuan declared himself the emperor of a new dynasty, the Tang.
Li Yuan, known as
Emperor Gaozu of Tang
Emperor Gaozu of Tang (7 April 566 – 25 June 635, born Li Yuan, courtesy name Shude) was the founding emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 618 to 626. Under the Sui dynasty, Li Yuan was the governor in the area of modern-day ...
, ruled until 626, when he was forcefully deposed by his son
Li Shimin
Emperor Taizong of Tang (28January 59810July 649), previously Prince of Qin, personal name Li Shimin, was the second emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649. He is traditionally regarded as a co-founder of the dynasty ...
, the Prince of Qin. Li Shimin had commanded troops since the age of 18 years old, had prowess with
bow and arrow
The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles (arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the practice was common ...
,
sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
and
lance
A lance is a spear designed to be used by a mounted warrior or cavalry soldier (lancer). In ancient and medieval warfare, it evolved into the leading weapon in cavalry charges, and was unsuited for throwing or for repeated thrusting, unlike s ...
and was known for his effective
cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in ...
charges. Fighting a numerically superior army, he defeated
Dou Jiande
Dou Jiande (; 573 – 3 August 621) was a leader of the agrarian rebels who rose against the rule of Emperor Yang of Sui near the end of the Chinese Sui dynasty. Generally considered the kindest and most able of the agrarian rebel leaders ...
(573–621) at
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
in the
Battle of Hulao
The Battle of Hulao () or Battle of Sishui (汜水之戰, Wade–Giles: Ssŭ Shui), on 28 May 621 was the main and final battle of the Luoyang–Hulao campaign between the rival Tang, Zheng, and Xia regimes during the transition from Sui to Ta ...
on May 28, 621. In a violent elimination of royal family due to fear of assassination, Li Shimin ambushed and killed two of his brothers,
Li Yuanji
Li Yuanji (李元吉) (603 – 2 July 626The date of the incident at Xuanwu Gate was the fourth day of the sixth month of the ''Wude'' era, which translates to July 2, 626, according to the Academia Sinicabr>), formally Prince La of Chao (巢剌� ...
(b. 603) and
Crown prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the w ...
Li Jiancheng
Li Jiancheng (; 589 – July 2, 626, formally Crown Prince Yin (, literally, "the hidden crown prince"), nickname Vaishravana (; Sanskrit: Vaiśravaṇa), was the first crown prince of the Chinese Tang Dynasty. He was the oldest son of the foun ...
(b. 589), in the
Xuanwu Gate Incident
The Xuanwu Gate Incident was a palace coup for the throne of the Tang dynasty on 2 July 626, when Prince Li Shimin (Prince of Qin) and his followers assassinated Crown Prince Li Jiancheng and Prince Li Yuanji (Prince of Qi). Li Shimin, the seco ...
on July 2, 626. Shortly thereafter, his father abdicated in his favor and Li Shimin ascended the throne. He is conventionally known by his
temple name
Temple names are posthumous titles accorded to monarchs of the Sinosphere for the purpose of ancestor worship. The practice of honoring monarchs with temple names began during the Shang dynasty in China and had since been adopted by other dyna ...
Taizong.
Although killing two brothers and deposing his father contradicted the
Confucian value of
filial piety
In Confucianism, Chinese Buddhism, and Daoist ethics, filial piety (, ''xiào'') (Latin: pietas) is a virtue of respect for one's parents, elders, and ancestors. The Confucian '' Classic of Filial Piety'', thought to be written around the lat ...
, Taizong showed himself to be a capable leader who listened to the advice of the wisest members of his council. In 628, Emperor Taizong held a Buddhist memorial service for the casualties of war, and in 629 he had Buddhist monasteries erected at the sites of major battles so that monks could pray for the fallen on both sides of the fight.
During the
Tang campaign against the Eastern Turks, the
Eastern Turkic Khaganate
The Eastern Turkic Khaganate () was a Turkic khaganate formed as a result of the internecine wars in the beginning of the 7th century (AD 581–603) after the First Turkic Khaganate (founded in the 6th century in the Mongolian Plateau by ...
was destroyed after the capture of its ruler,
Illig Qaghan by the famed Tang military officer
Li Jing (571–649), who later became a
Chancellor of the Tang dynasty
The chancellor () was a semi-formally designated office position for a number of high-level officials at one time during the Tang dynasty of China. This list also includes chancellors of the short-lived Wu Zhou dynasty, which is typically trea ...
. With this victory, the Turks accepted Taizong as their
khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, 𐰴𐰍𐰣 ), or , tr, Kağan or ; ug, قاغان, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاقان ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
, a title rendered as
Tian Kehan Khan of Heaven or Tian Kehan, Celestial Kha(ga)n, Heavenly Kha(ga)n, Tengri Kha(ga)n (; Old Turkic: 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃𐰴𐰍𐰣) was a title addressed to the Emperor Taizong of Tang by various Turkic nomads. It was first mentioned in accounts on ...
in addition to his rule as
emperor of China
''Huangdi'' (), translated into English as Emperor, was the superlative title held by monarchs of China who ruled various imperial regimes in Chinese history. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was considered the Son of Heav ...
under the traditional title "
Son of Heaven
Son of Heaven, or ''Tianzi'' (), was the sacred monarchical title of the Chinese sovereign. It originated with the Zhou dynasty and was founded on the political and spiritual doctrine of the Mandate of Heaven. Since the Qin dynasty, the secu ...
". Taizong was succeeded by his son Li Zhi (as
Emperor Gaozong) in 649 CE.
The Tang dynasty further led the
Tang campaigns against the Western Turks
The Tang campaigns against the Western Turks, known as the Western Tujue in Chinese sources, were a series of military campaigns conducted by the Tang dynasty against the Western Turkic Khaganate in the 7th century AD. Early military conflicts we ...
. Early military conflicts were a result of the Tang interventions in the rivalry between the
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and
Eastern Turks in order to weaken both. Under
Emperor Taizong, campaigns were dispatched in the Western Regions against
Gaochang in 640,
Karasahr
Karasahr or Karashar ( ug, قاراشەھەر, Qarasheher, 6=Қарашәһәр), which was originally known, in the Tocharian languages as ''Ārśi'' (or Arshi) and Agni or the Chinese derivative Yanqi ( zh, s=焉耆, p=Yānqí, w=Yen-ch'i), is an ...
in 644 and 648, and
Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road ...
in 648. The wars against the Western Turks continued under
Emperor Gaozong, and the
Western Turkic Khaganate
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after ...
was finally annexed after General
Su Dingfang
Su Dingfang () (591–667), formal name Su Lie () but went by the courtesy name of Dingfang, formally Duke Zhuang of Xing (), was a Chinese military general of the Tang Dynasty who succeeded in destroying the Western Turkic Khaganate in 657. He wa ...
's defeat of
Qaghan Ashina Helu in 657 CE.
Around that time, the Tang court enjoyed the visit of numerous dignitaries from foreign lands. These were portraited in ''
The Gathering of Kings'' (, ''Wanghuitu''), probably painted by
Yan Liben
Yan may refer to:
Chinese states
* Yan (state) (11th century – 222 BC), a major state in northern China during the Zhou dynasty
* Yan (Han dynasty kingdom), first appearing in 206 BC
* Yan (Three Kingdoms kingdom), officially claimed indep ...
(, 601–673 CE). From right to left, the countries are
Lu (魯國) which is a reference to the
Eastern Wei,
Rouran
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organizat ...
(),
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(),
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
(),
Kumedh (),
Baiti
Baitsi, formerly known as Baiti and previously as Beidi, is a district in the Pacific nation of Nauru. It belongs to Ubenide Constituency.
Geography Location
The district is located in the northwest of the island. It covers an area of 1.2 ...
(),
Mohe people
The Mohe, Malgal, or Mogher, or Mojie, were an East Asian Tungusic people who lived primarily in the modern geographical region of Northeast Asia. The two most powerful Mohe groups were known as the Heishui Mohe, located along the Amur Rive ...
(), Central
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
(),
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
(), Northern
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
(),
Tashkurgan
Tashkurgan ( ug, تاشقورغان بازىرى; zh, s=塔什库尔干镇, p=Tǎshíkù'ěrgān Zhèn; ) is a town in the far northwest of China, close to the country's border with Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. It is the principal to ...
(), Wuxing City of the
Chouchi (武興國),
Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road ...
(龜茲國),
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
(),
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
(),
Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
(),
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
(),
Dangchang (),
Langkasuka
Langkasuka was an ancient Hindu-Buddhist kingdom located in the Malay Peninsula. The name is Sanskrit in origin; it is thought to be a combination of ''langkha'' for "resplendent land" -'' sukkha'' for "bliss". The kingdom, along with Old K ...
(),
Dengzhi (),
Yarkand
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous ...
(),
Kabadiyan (), Barbarians of Jianping (), Nudan ().
Wu Zetian's usurpation

Although she entered
Emperor Gaozong's court as the lowly consort,
Wu Zetian
Wu Zetian (17 February 624 – 16 December 705), personal name Wu Zhao, was the ''de facto'' ruler of the Tang dynasty from 665 to 705, ruling first through others and then (from 690) in her own right. From 665 to 690, she was first empres ...
rose to the highest seat of power in 690, establishing the short-lived Wu Zhou. Empress Wu's rise to power was achieved through cruel and calculating tactics: a popular conspiracy theory stated that she killed her own baby girl and blamed it on Gaozong's empress so that the empress would be demoted. Emperor Gaozong suffered a
stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
in 655, and Wu began to make many of his court decisions for him, discussing affairs of state with his councilors, who took orders from her while she sat behind a screen. When Empress Wu's eldest son, the crown prince, began to assert his authority and advocate policies opposed by Empress Wu, he suddenly died in 675. Many suspected he was poisoned by Empress Wu. Although the next heir apparent kept a lower profile, in 680 he was accused by Wu of plotting a rebellion. He was then banished and later obliged to commit suicide.
In 683, Emperor Gaozong died. He was succeeded by
Emperor Zhongzong, his eldest surviving son by Wu. Zhongzong tried to appoint his wife's father as chancellor: after only six weeks on the throne, he was deposed by Empress Wu in favor of his younger brother,
Emperor Ruizong. This provoked a group of Tang princes to rebel in 684. Wu's armies suppressed them within two months. She proclaimed the Tianshou
era of Wu Zhou on October 16, 690, and three days later demoted Emperor Ruizong to
crown prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the w ...
. He was also forced to give up his father's surname Li in favor of the Empress Wu. She then ruled as China's only
empress regnant.
A
palace coup
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
on February 20, 705, forced Empress Wu to yield her position on February 22. The next day, her son Zhongzong was restored to power; the Tang was formally restored on March 3. She died soon after. To legitimize her rule, she circulated a document known as the ''Great Cloud Sutra'', which predicted that a
reincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the philosophical or religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new life in a different physical form or body after biological death. Resurrectio ...
of the
Maitreya
Maitreya (Sanskrit: ) or Metteyya (Pali: ), also Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha, is regarded as the future Buddha of this world in Buddhist eschatology. As the 5th and final Buddha of the current kalpa, Maitreya's teachings will be aimed a ...
Buddha would be a female monarch who would dispel illness, worry, and disaster from the world. She even introduced numerous revised
written characters to
the written language, which reverted to the originals after her death. Arguably the most important part of her legacy was diminishing the hegemony of the Northwestern aristocracy, allowing people from other clans and regions of China to become more represented in Chinese politics and government.
Emperor Xuanzong's reign
There were many prominent women at court during and after Wu's reign, including
Shangguan Wan'er
Shangguan Wan'er (664–21 July 710) was a Chinese politician, poet, and imperial consort of the Wu Zhou and Tang dynasties. Described as a "female prime minister," Shangguan rose from modest origins as a palace servant to become secretary and ...
(664–710), a poet, writer, and trusted official in charge of Wu's private office. In 706 the wife of Emperor Zhongzong of Tang,
Empress Wei (d. 710), persuaded her husband to staff government offices with his sister and her daughters, and in 709 requested that he grant women the right to bequeath hereditary privileges to their sons (which before was a male right only). Empress Wei eventually poisoned Zhongzong, whereupon she placed his fifteen-year-old son upon the throne in 710. Two weeks later,
Li Longji
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (; 8 September 685 – 3 May 762), personal name Li Longji, was the seventh emperor of the Tang dynasty in China, reigning from 712 to 756 CE. His reign of 44 years was the longest during the Tang dynasty. In the ear ...
(the later Emperor Xuanzong) entered the palace with a few followers and slew Empress Wei and her faction. He then installed his father
Emperor Ruizong (r. 710–712) on the throne. Just as Emperor Zhongzong was dominated by Empress Wei, so too was Ruizong dominated by
Princess Taiping. This was finally ended when Princess Taiping's coup failed in 712 (she later hanged herself in 713) and Emperor Ruizong abdicated to
Emperor Xuanzong.
During the 44-year reign of Emperor Xuanzong, the Tang dynasty reached its height, a golden age with low economic inflation and a toned down lifestyle for the imperial court. Seen as a progressive and benevolent ruler, Xuanzong even abolished the death penalty in the year 747; all executions had to be approved beforehand by the emperor himself (these were relatively few, considering that there were only 24 executions in the year 730). Xuanzong bowed to the consensus of his ministers on policy decisions and made efforts to staff government ministries fairly with different political factions. His staunch Confucian chancellor
Zhang Jiuling (673–740) worked to reduce
deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% (a negative inflation rate). Inflation reduces the value of currency over time, but sudden deflatio ...
and increase the money supply by upholding the use of private coinage, while his aristocratic and
technocratic successor
Li Linfu (d. 753) favored government monopoly over the issuance of coinage. After 737, most of Xuanzong's confidence rested in his long-standing chancellor
Li Linfu, who championed a more aggressive foreign policy employing non-Chinese generals. This policy ultimately created the conditions for a massive rebellion against Xuanzong.
An Lushan Rebellion and catastrophe

The Tang Empire was at its height of power up until the middle of the 8th century, when the
An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general off ...
(December 16, 755 – February 17, 763) destroyed the prosperity of the empire.
An Lushan
An Lushan (; 20th day of the 1st month 19 February 703 – 29 January 757) was a general in the Tang dynasty and is primarily known for instigating the An Lushan Rebellion.
An Lushan was of Sogdian and Göktürk origin,Yang, Zhijiu, "An Lush ...
was a half-
Sogdian, half-
Turk
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic o ...
Tang commander since 744, who had experience fighting the
Khitans
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
As a people desce ...
of
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
with a victory in 744, yet most of his campaigns against the Khitans were unsuccessful. He was given great responsibility in
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
, which allowed him to rebel with an army of more than 100,000 troops. After capturing Luoyang, he named himself emperor of a new, but short-lived,
Yan state. Despite early victories scored by Tang General
Guo Ziyi
Guo Ziyi (Kuo Tzu-i; Traditional Chinese: 郭子儀, Simplified Chinese: 郭子仪, Hanyu Pinyin: Guō Zǐyí, Wade-Giles: Kuo1 Tzu3-i2) (697 – July 9, 781), posthumously Prince Zhōngwǔ of Fényáng (), was a Chinese military general and po ...
(697–781), the newly recruited troops of the army at the capital were no match for An Lushan's frontier veterans, so the court fled Chang'an. While the heir apparent raised troops in
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-leve ...
and Xuanzong fled to
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
province, they called upon the help of the
Uyghur Khaganate
The Uyghur Khaganate (also Uyghur Empire or Uighur Khaganate, self defined as Toquz-Oghuz country; otk, 𐱃𐰆𐰴𐰕:𐰆𐰍𐰕:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Toquz Oγuz budun, Tang-era names, with modern Hanyu Pinyin: or ) was a Turkic empire that e ...
in 756. The
Uyghur khan
Moyanchur was greatly excited at this prospect, and married his own daughter to the Chinese diplomatic envoy once he arrived, receiving in turn a Chinese princess as his bride.
The Uyghurs helped recapture the Tang capital from the rebels, but they refused to leave until the Tang paid them an enormous sum of tribute in silk. Even
Abbasid Arabs assisted the Tang in putting down An Lushan's rebellion. A massacre of foreign Arab and Persian Muslim merchants by
Tian Shengong happened during the An Lushan rebellion in the
Yangzhou massacre (760)
In the Yangzhou massacre, Chinese forces under Tian Shengong killed thousands of foreign merchants in Yangzhou in 760 CE during the Tang dynasty.
Yangzhou, at the junction of the Yangtze River and the Grand Canal, was a center of commerce, fina ...
. The
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
ans took hold of the opportunity and raided many areas under Chinese control, and even after the
Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the 3 ...
had fallen apart in 842 (and
the Uyghurs soon after) the Tang were in no position to
reconquer Central Asia after 763. So significant was this loss that half a century later ''jinshi'' examination candidates were required to write an essay on the causes of the Tang's decline. Although An Lushan was killed by one of his eunuchs in 757, this time of troubles and widespread insurrection continued until rebel
Shi Siming
Shi Siming () (19th day of the 1st month, 703? – 18 April 761), or Shi Sugan (), was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician during the Tang Dynasty who followed his childhood friend An Lushan in rebelling against Tang, and who la ...
was killed by his own son in 763.


One of the legacies that the Tang government left since 710 was the gradual rise of regional military governors, the
jiedushi
The ''jiedushi'' (), or jiedu, was a title for regional military governors in China which was established in the Tang dynasty and abolished in the Yuan dynasty. The post of ''jiedushi'' has been translated as "military commissioner", "legate ...
, who slowly came to challenge the power of the central government. After the An Lushan Rebellion, the autonomous power and authority accumulated by
the jiedushi in Hebei went beyond the central government's control. After a series of rebellions between 781 and 784 in today's Hebei,
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in His ...
, Hubei and
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is a ...
provinces, the government had to officially acknowledge the jiedushi's hereditary ruling without accreditation. The Tang government relied on these governors and their armies for protection and to suppress locals that would take up arms against the government. In return, the central government would acknowledge the rights of these governors to maintain their army, collect taxes and even to pass on their title to heirs. As time passed, these military governors slowly phased out the prominence of civil officials drafted by exams, and became more autonomous from central authority. The rule of these powerful military governors lasted until 960, when a new civil order under the
Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
was established. Also, the abandonment of the equal-field system meant that people could buy and sell land freely. Many poor fell into debt because of this, forced to sell their land to the wealthy, which led to the exponential growth of large estates. With the breakdown of the land allocation system after 755, the central Chinese state barely interfered in agricultural management and acted merely as tax collector for roughly a millennium, save a few instances such as the Song's failed land nationalization during the 13th-century war with the
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
.
With the central government collapsing in authority over the various regions of the empire, it was recorded in 845 that bandits and river pirates in parties of 100 or more began plundering settlements along the Yangtze River with little resistance. In 858, massive floods along the
Grand Canal inundated vast tracts of land and terrain of the
North China Plain
The North China Plain or Huang-Huai-Hai Plain () is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin formed in the late Paleogene and Neogene and then modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. It is the largest alluvial plain of China. The plain is border ...
, which drowned tens of thousands of people in the process.
The Chinese belief in the
Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven () is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven (天, '' Tian'') – which embodies the nat ...
granted to the ailing Tang was also challenged when natural calamities occurred, forcing many to believe that the Tang had lost their right to rule. Furthermore, in 873 a disastrous harvest shook the foundations of the empire; in some areas only half of all agricultural produce was gathered, and tens of thousands faced famine and starvation. In the earlier period of the Tang, the central government was able to meet crises in the harvest, as it was recorded from 714 to 719 that the Tang government responded effectively to natural disasters by extending the price-regulation
granary
A granary is a storehouse or room in a barn for threshed grain or animal feed. Ancient or primitive granaries are most often made of pottery. Granaries are often built above the ground to keep the stored food away from mice and other animals ...
system throughout the country. The central government was able then to build a large surplus stock of foods to ward off the rising danger of famine and increased agricultural productivity through
land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamat ...
. In the 9th century, however, the Tang government was nearly helpless in dealing with any calamity.
Rebuilding and recovery

Although these natural calamities and rebellions stained the reputation and hampered the effectiveness of the central government, the early 9th century is nonetheless viewed as a period of recovery for the Tang dynasty. The government's withdrawal from its role in managing the economy had the unintended effect of stimulating trade, as more markets with fewer bureaucratic restrictions were opened up. By 780, the old grain tax and labor service of the 7th century was replaced by a semiannual tax paid in cash, signifying the shift to a money economy boosted by the merchant class. Cities in the
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
region to the south, such as
Yangzhou
Yangzhou, postal romanization Yangchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu Province (Suzhong), East China. Sitting on the north bank of the Yangtze, it borders the provincial capital Nanjing to the southwest, Huai'an to the north, ...
,
Suzhou
Suzhou (; ; Suzhounese: ''sou¹ tseu¹'' , Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Soochow, is a major city in southern Jiangsu province, East China. Suzhou is the largest city in Jiangsu, and a major economic center and focal point of trad ...
, and
Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also Chinese postal romanization, romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the prov ...
prospered the most economically during the late Tang period. The
government monopoly on the production of salt, weakened after the
An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general off ...
, was placed under the
Salt Commission, which became one of the most powerful state agencies, run by capable ministers chosen as specialists. The commission began the practice of selling merchants the rights to buy monopoly salt, which they would then transport and sell in local markets. In 799 salt accounted for over half of the government's revenues. S.A.M. Adshead writes that this salt tax represents "the first time that an indirect tax, rather than tribute, levies on land or people, or profit from state enterprises such as mines, had been the primary resource of a major state." Even after the power of the central government was in decline after the mid 8th century, it was still able to function and give out imperial orders on a massive scale. The ''Tangshu'' (
Old Book of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingd ...
) compiled in the year 945 recorded that in 828 the Tang government issued a decree that standardized
irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
al square-pallet
chain pump
The chain pump is type of a water pump in which several circular discs are positioned on an endless chain. One part of the chain dips into the water, and the chain runs through a tube, slightly bigger than the diameter of the discs. As the chain i ...
s in the country:
In the second year of the Taihe reign period 28 in the second month... a standard model of the chain pump was issued from the palace, and the people of Jingzhao Fu Jingzhao ( zh, 京兆) was a historical region centered on the ancient Chinese capital of Chang'an.
Han dynasty
In early Han dynasty, the governor of the capital Chang'an and its vicinities was known as ''You Neishi'' (), and the region was also ...
(d footnote: the capital) were ordered by the emperor to make a considerable number of machines, for distribution to the people along the Zheng Bai Canal, for irrigation purposes.,
The last great ambitious ruler of the Tang dynasty was
Emperor Xianzong (r. 805–820), whose reign was aided by the fiscal reforms of the 780s, including a government monopoly on the salt industry. He also had an effective and well-trained imperial army stationed at the capital led by his court eunuchs; this was the Army of Divine Strategy, numbering 240,000 in strength as recorded in 798. Between the years 806 and 819, Emperor Xianzong conducted seven major military campaigns to quell the rebellious provinces that had claimed autonomy from central authority, managing to subdue all but two of them. Under his reign there was a brief end to the hereditary jiedushi, as Xianzong appointed his own military officers and staffed the regional bureaucracies once again with civil officials. However, Xianzong's successors proved less capable and more interested in the leisure of hunting, feasting, and playing outdoor sports, allowing eunuchs to amass more power as drafted scholar-officials caused strife in the bureaucracy with factional parties. The eunuchs' power became unchallenged after
Emperor Wenzong's (r. 826–840) failed
plot to have them overthrown; instead the allies of Emperor Wenzong were publicly executed in the
West Market of Chang'an, by the eunuchs' command.

However, the Tang did manage to restore at least indirect control over former Tang territories as far west as the
Hexi Corridor
The Hexi Corridor (, Xiao'erjing: حْسِ ظِوْلاْ, IPA: ), also known as the Gansu Corridor, is an important historical region located in the modern western Gansu province of China. It refers to a narrow stretch of traversable and rela ...
and
Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major s ...
in
Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
. In 848 the ethnic Han Chinese general
Zhang Yichao Zhang may refer to:
Chinese culture, etc.
* Zhang (surname) (張/张), common Chinese surname
** Zhang (surname 章), a rarer Chinese surname
* Zhang County (漳县), of Dingxi, Gansu
* Zhang River (漳河), a river flowing mainly in Henan
* ''Zh ...
(799–872) managed to wrestle control of the region from the
Tibetan Empire during its civil war. Shortly afterwards
Emperor Xuānzong of Tang
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (July 27, 810 – September 7, 859) (reigned April 25, 846 – September 7, 859) was an emperor in the latter part of the Tang dynasty of China. Personally named Li Yi, later renamed Li Chen (), and known before his rei ...
(r. 846–859) acknowledged Zhang as the protector (防禦使, ''Fangyushi'') of Sha Prefecture and ''jiedushi'' military governor of the new
Guiyi Circuit
The Guiyi Circuit, also known as the Guiyi Army (, 848–1036 AD), was a Chinese regional military command and later an autonomous regime nominally subordinate to the Tang dynasty, the Five Dynasties, and the Northern Song dynasty. The Guiyi Ci ...
.
['']Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynast ...
'', vol. 249.
The Tang dynasty recovered its power decades after the An Lushan rebellion and was still able to launch offensive conquests and campaigns like its
destruction of the Uyghur Khaganate in Mongolia in 840–847.
End of the dynasty
In addition to natural calamities and ''jiedushi'' amassing autonomous control, the
Huang Chao Rebellion (874–884) resulted in the sacking of both Chang'an and Luoyang, and took an entire decade to suppress. It was the Huang Chao rebellion by the native Han rebel Huang Chao that permanently destroyed the power of the Tang dynasty since Huang Chao not only devastated the north but marched into southern China which An Lushan failed to do due to the Battle of Suiyang. Huang Chao's army in southern China committed the
Guangzhou massacre
The Guangzhou massacre was a massacre of the inhabitants of the prosperous port city of Guangzhou in 878–879 by the rebel army of Huang Chao. Arab sources indicate that foreign victims, including Muslims, Jews, Christians, and Zoroastrians, num ...
against foreign Arab and Persian Muslim, Zoroastrian, Jewish and Christian merchants in 878–879 at the seaport and trading port of
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, sou ...
, and captured both Tang dynasty capitals, Luoyang and Chang'an. A medieval Chinese source claimed that Huang Chao killed 8 million people. The Tang never recovered from this rebellion, weakening it for future military powers to replace it. Large groups of bandits in the size of small armies ravaged the countryside in the last years of the Tang. They smuggled illicit salt, ambushed merchants and convoys, and even besieged several walled cities. Amid the sacking of cities and murderous factional strife among eunuchs and officials, the top tier of aristocratic families, which had amassed a large fraction of the landed wealth and official positions, was largely destroyed or marginalized.
During the last two decades of the Tang dynasty, the gradual collapse of central authority led to the rise of two prominent rival military figures over
northern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions within China. The exact boundary between these two regions is not precisely defined and only serve to depict where there appears to be regional differences between the climate ...
:
Li Keyong
Li Keyong () (October 24, 856 – February 24, 908) was a Chinese military general and politician of Shatuo ethnicity, and from January 896 a Prince of Jin (, ''Jin Wang''), which would become an independent state after the fall of the Tang dyn ...
and
Zhu Wen
Emperor Taizu of Later Liang (), personal name Zhu Quanzhong () (December 5, 852 – July 18, 912), né Zhu Wen (), name later changed to Zhu Huang (), nickname Zhu San (朱三, literally, "the third Zhu"), was a Chinese military general, mona ...
. Tang forces had defeated Huang Chao's rebellion with the crucial aid of allied
Shatuo
The Shatuo, or the Shatuo Turks (; also transcribed as Sha-t'o, Sanskrit SartZuev Yu.A., ''"Horse Tamgas from Vassal Princedoms (Translation of Chinese composition "Tanghuyao" of 8-10th centuries)"'', Kazakh SSR Academy of Sciences, Alma-Ata, ...
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
of what is now
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-leve ...
led by Li Keyong. He was made a jiedushi governor and later
Prince of Jin, bestowed with the imperial surname Li by the Tang court. Zhu Wen, originally a salt smuggler who served as a lieutenant under the rebel Huang Chao, surrendered to Tang forces. By helping to defeat Huang, he was
renamed Zhu Quanzhong ("Zhu of Perfect Loyalty") and granted a series of rapid military promotions to military governor of Xuanwu Circuit.
In 901, from his powerbase of
Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the Nort ...
, Zhu Wen seized control of the Tang capital Chang'an and with it the imperial family. By 903 he forced
Emperor Zhaozong of Tang
Emperor Zhaozong of Tang (March 31, 867 – September 22, 904), né Li Jie, name later changed to Li Min and again to Li Ye, was the penultimate emperor of the Tang dynasty of China. He reigned from 888 to 904 (although he was briefly deposed ...
to move the capital to Luoyang, preparing to take the throne for himself. In 904 Zhu assassinated Emperor Zhaozong to replace him with the emperor's young son
Emperor Ai of Tang
Emperor Ai of Tang (27 October 89226 March 908), also known as Emperor Zhaoxuan of Tang (), born Li Zuo, later known as Li Chu (), was the last emperor of the Tang dynasty of China. He reigned—as but a puppet ruler—from 904 to 907. Empe ...
. In 905 Zhu executed the brothers of Emperor Ai as well as many officials and
Empress Dowager He. In 907 the Tang dynasty was ended when Zhu deposed Ai and took the throne for himself (known posthumously as Emperor Taizu of Later Liang). He established the
Later Liang, which inaugurated the
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen conc ...
. A year later Zhu had the deposed Emperor Ai poisoned to death.
Zhu Wen's hated nemesis Li Keyong died in 908 but, out of loyalty to Tang, Li never claimed the
title of emperor. His son
Li Cunxu
Emperor Zhuangzong of Later Tang (), personal name Li Cunxu (), nickname Yazi (), stage name Li Tianxia (), was the ruling prince of the Former Jin dynasty (r. 908–923) and later became the founding emperor of the Later Tang dynasty (r. 923 ...
(Emperor Zhuangzong) inherited his title Prince of Jin along with his father's rivalry against Zhu. In 923 Li Cunxu declared a "restored" Tang dynasty, the
Later Tang
Tang, known in historiography as the Later Tang, was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China and the second of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in Chinese history.
The first three of the Later Tang's four ...
, before toppling the Later Liang dynasty the same year. However,
southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
would remain splintered into various small kingdoms until most of China was reunified under the
Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
(960–1279). Control over parts of
northeast China
Northeast China or Northeastern China () is a geographical region of China, which is often referred to as "Manchuria" or "Inner Manchuria" by surrounding countries and the West. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of ...
and
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
by the
Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü ...
of the
Khitan people
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
As a people desc ...
also stemmed from this period. In 905 their leader
Abaoji formed a military alliance with Li Keyong against Zhu Wen but the Khitans eventually turned against the Later Tang, helping another Shatuo leader
Shi Jingtang
Shi Jingtang ( zh, 石敬瑭; 30 March 892 – 28 July 942'' Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 283.), also known by his temple name Gaozu (), was the founding emperor of imperial China's short-lived Later Jin during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
of
Later Jin to overthrow Later Tang in 936.
Administration and politics
Initial reforms

Taizong set out to solve internal problems within the government which had constantly plagued past dynasties. Building upon the Sui
legal code
A code of law, also called a law code or legal code, is a systematic collection of statutes. It is a type of legislation that purports to exhaustively cover a complete system of laws or a particular area of law as it existed at the time the cod ...
, he issued
a new legal code that subsequent Chinese dynasties would model theirs upon, as well as neighboring polities in
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
,
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
, and
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
. The earliest law code to survive was the one established in the year 653, which was divided into 500 articles specifying different crimes and penalties ranging from ten blows with a light stick, one hundred blows with a heavy rod, exile, penal servitude, or execution.
The legal code distinguished different levels of severity in meted punishments when different members of the social and political hierarchy committed the same crime. For example, the severity of punishment was different when a servant or nephew killed a master or an uncle than when a master or uncle killed a servant or nephew.

The Tang Code was largely retained by later codes such as the early
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
(1368–1644) code of 1397, yet there were several revisions in later times, such as
improved property rights for women during the
Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
(960–1279).
The Tang had three departments (), which were obliged to draft, review, and implement policies respectively. There were also six ministries () under the administrations that implemented policy, each of which was assigned different tasks. These
Three Departments and Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) a ...
included the personnel administration, finance, rites, military, justice, and public works—an administrative model which would last until the fall of the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
(1644–1912).
Although the founders of the Tang related to the glory of the earlier
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(3rd century BC–3rd century AD), the basis for much of their administrative organization was very similar to the previous
Northern and Southern dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered a ...
. The
Northern Zhou
Zhou (), known in historiography as the Northern Zhou (), was a Xianbei-led dynasty of China that lasted from 557 to 581. One of the Northern dynasties of China's Northern and Southern dynasties period, it succeeded the Western Wei dynasty a ...
(6th century)
fubing system of divisional militia was continued by the Tang, along with farmer-soldiers serving in rotation from the capital or frontier in order to receive appropriated farmland. The
equal-field system
The equal-field system () or land-equalization system was a system of land ownership and distribution in China used from the Northern Wei to the mid-Tang dynasty.
By the Han dynasty, the well-field system of land distribution had fallen out of ...
of the
Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during t ...
(4th–6th centuries) was also kept, although there were a few modifications.
Although the central and local governments kept an enormous number of records about land property in order to assess taxes, it became common practice in the Tang for literate and affluent people to create their own private documents and signed contracts. These had their own signature and that of a witness and scribe in order to prove in court (if necessary) that their claim to property was legitimate. The prototype of this actually existed since the ancient Han dynasty, while contractual language became even more common and embedded into Chinese literary culture in later dynasties.
The center of the political power of the Tang was the capital city of
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
(modern
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
), where the emperor maintained his large palace quarters and entertained political emissaries with music, sports,
acrobatic
Acrobatics () is the performance of human feats of balance, agility, and motor coordination. Acrobatic skills are used in performing arts, sporting events, and martial arts. Extensive use of acrobatic skills are most often performed in acro ...
stunts, poetry, paintings, and
dramatic theater performances. The capital was also filled with incredible amounts of riches and resources to spare. When the Chinese
prefectural
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
government officials traveled to the capital in the year 643 to give the annual report of the affairs in their districts, Emperor Taizong discovered that many had no proper quarters to rest in and were renting rooms with merchants. Therefore, Emperor Taizong ordered the government agencies in charge of
municipal
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
construction to build every visiting official his own private
mansion
A mansion is a large dwelling house. The word itself derives through Old French from the Latin word ''mansio'' "dwelling", an abstract noun derived from the verb ''manere'' "to dwell". The English word '' manse'' originally defined a property l ...
in the capital.
Imperial examinations

Students of
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
studies were candidates for the
imperial examination
The imperial examination (; lit. "subject recommendation") refers to a civil-service examination system in Imperial China, administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the state bureaucracy. The concept of choosing bureaucrats by ...
s, which qualified their graduates for appointment to the local, provincial, and central government bureaucracies. Two types of exams given, ''mingjing'' (; "illuminating the classics") and ''jinshi'' (; "presented scholar"). The ''mingjing'' was based upon the
Confucian classics
Chinese classic texts or canonical texts () or simply dianji (典籍) refers to the Chinese texts which originated before the imperial unification by the Qin dynasty in 221 BC, particularly the "Four Books and Five Classics" of the Neo-Confucian ...
and tested the student's knowledge of a broad variety of texts. The ''jinshi'' tested a student's literary abilities in writing essays in response to questions on governance and politics, as well as in composing
poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek '' poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meani ...
. Candidates were also judged on proper deportment, appearance, speech, and
calligraphy
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined ...
, all subjective criteria that favored the wealthy over those of more modest means who were unable to pay tutors of
rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate par ...
and writing. Although a disproportionate number of civil officials came from aristocratic families, wealth and noble status were not prerequisites, and the exams were open to all male subjects whose fathers were not of the
artisan or merchant classes. To promote widespread Confucian education, the Tang government established state-run schools and issued standard versions of the
Five Classics
The Four Books and Five Classics () are the authoritative books of Confucianism, written in China before 300 BCE. The Four Books and the Five Classics are the most important classics of Chinese Confucianism.
Four Books
The Four Books () are ...
with commentaries.
Open competition was designed to draw the best talent into government. But perhaps an even greater consideration for the Tang rulers was to avoid imperial dependence on powerful aristocratic families and
warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
s by recruiting a body of career officials having no family or local
power base. The Tang law code ensured equal division of inherited property amongst legitimate heirs, encouraging
social mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given society ...
by preventing powerful families from becoming
landed nobility Landed nobility or landed aristocracy is a category of nobility in the history of various countries, for which landownership was part of their noble privileges. Their character depends on the country.
*The notion of landed gentry in the United Kin ...
through
primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
. The competition system proved successful, as
scholar-officials
The scholar-officials, also known as literati, scholar-gentlemen or scholar-bureaucrats (), were government officials and prestigious scholars in Chinese society, forming a distinct social class.
Scholar-officials were politicians and governmen ...
acquired status in their local communities while developing an
esprit de corps
Morale, also known as esprit de corps (), is the capacity of a group's members to maintain belief in an institution or goal, particularly in the face of opposition or hardship. Morale is often referenced by authority figures as a generic value ...
that connected them to the imperial court. From Tang times until the end of the Qing dynasty in 1912, scholar-officials served as intermediaries between the
people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
and the government.
Yet the potential of a widespread examination system was not fully realized until the succeeding Song dynasty, when the merit-driven scholar official largely shed his aristocratic habits and defined his social status through the examination system.
Religion and politics
From the outset, religion played a role in Tang politics. In his bid for power, Li Yuan had attracted a following by claiming descent from the
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
sage
Lao Tzu
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state ...
( 6th century BC). People bidding for office would request the prayers of Buddhist monks, with successful aspirants making donations in return. Before the persecution of Buddhism in the 9th century, Buddhism and Taoism were both accepted.
Religion was central in the reign of
Emperor Xuanzong (r. 712–756). The Emperor invited Taoist and Buddhist monks and clerics to his court, exalted the Taoist ancient Lao Tzu with grand titles, wrote commentary on the ''Lao Tzu'' scriptures, and set up a school to prepare candidates for Taoist examinations. In 726 he called upon the Indian monk
Vajrabodhi
Vajrabodhi ( sa, वज्रबोधि, , 671–741) was an Indian esoteric Buddhist monk from Kerala and teacher in Tang China. He is one of the eight patriarchs in Shingon Buddhism. He is notable for introducing Vajrayana Buddhism in the ...
(671–741) to perform
Tantric rites to avert a drought. In 742 he personally held the incense burner while
Amoghavajra
Amoghavajra ( sa, अमोघवज्र ; , 705–774) was a prolific translator who became one of the most politically powerful Buddhist monks in Chinese history and is acknowledged as one of the Eight Patriarchs of the Doctrine in Shingo ...
(705–774, patriarch of the
Shingon school) recited "mystical incantations to secure the victory of Tang forces."
Emperor Xuanzong closely regulated religious finances. Near the beginning of his reign in 713, he liquidated the
Inexhaustible Treasury of a prominent Buddhist monastery in Chang'an which had collected vast riches as multitudes of anonymous repentants left money, silk, and treasure at its doors. Although the monastery used its funds generously, the Emperor condemned it for fraudulent
banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
practices, and distributed its wealth to other Buddhist and Taoist monasteries, and to repair local statues, halls, and bridges. In 714, he forbade Chang'an shops from selling copied Buddhist sutras, giving a monopoly of this trade to the Buddhist clergy.
Taxes and the census
The Tang dynasty government attempted to create an accurate census of the empire's population, mostly for effective taxation and military conscription. The early Tang government established modest grain and cloth taxes on each household, persuading households to register and provide the government with accurate demographic information. In the official census of 609, the population was tallied at 9 million households, about 50 million people, and this number did not increase in the census of 742.
Patricia Ebrey writes that nonwithstanding census undercounting, China's population had not grown significantly since the earlier
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
, which recorded 58 million people in the year 2. S.A.M. Adshead disagrees, estimating about 75 million people by 750.
In the Tang census of 754, there were 1,859 cities, 321
prefectures
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
, and 1,538
counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
throughout the empire. Although there were many large and prominent cities, the rural and agrarian areas comprised some 80 to 90% of the population. There was also a dramatic migration from
northern to southern China, as the North held 75% of the overall population at the dynasty's inception, which by its end was reduced to 50%.
Chinese population would not dramatically increase until the Song dynasty, when it doubled to 100 million because of extensive rice cultivation in central and southern China, coupled with higher yields of grain sold in a growing market.
Military and foreign policy

Protectorates and tributaries
The 7th and first half of the 8th century are generally considered to be the era in which the Tang reached the zenith of its power. In this period, Tang control extended further west than any previous dynasty, stretching from north Vietnam in the south, to a point north of
Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
bordering Persia in the west, to northern Korea in the north-east.
Some of the kingdoms paying tribute to the Tang dynasty included
Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
, Nepal,
Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
,
Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road ...
,
Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. ...
,
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
,
Champa
Champa ( Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd ...
, and kingdoms located in
Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
and
Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
valley. Turkic nomads addressed the Emperor of Tang China as ''
Tian Kehan Khan of Heaven or Tian Kehan, Celestial Kha(ga)n, Heavenly Kha(ga)n, Tengri Kha(ga)n (; Old Turkic: 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃𐰴𐰍𐰣) was a title addressed to the Emperor Taizong of Tang by various Turkic nomads. It was first mentioned in accounts on ...
''. After the widespread Göktürk revolt of
Shabolüe Khan (d. 658) was put down at
Issyk Kul in 657 by
Su Dingfang
Su Dingfang () (591–667), formal name Su Lie () but went by the courtesy name of Dingfang, formally Duke Zhuang of Xing (), was a Chinese military general of the Tang Dynasty who succeeded in destroying the Western Turkic Khaganate in 657. He wa ...
(591–667), Emperor Gaozong established several protectorates governed by a Protectorate General or Grand Protectorate General, which extended the Chinese
sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
as far as
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
in Western Afghanistan. Protectorate Generals were given a great deal of autonomy to handle local crises without waiting for central admission. After Xuanzong's reign, military governors (jiedushi) were given enormous power, including the ability to maintain their own armies, collect taxes, and pass their titles on hereditarily. This is commonly recognized as the beginning of the fall of Tang's central government.
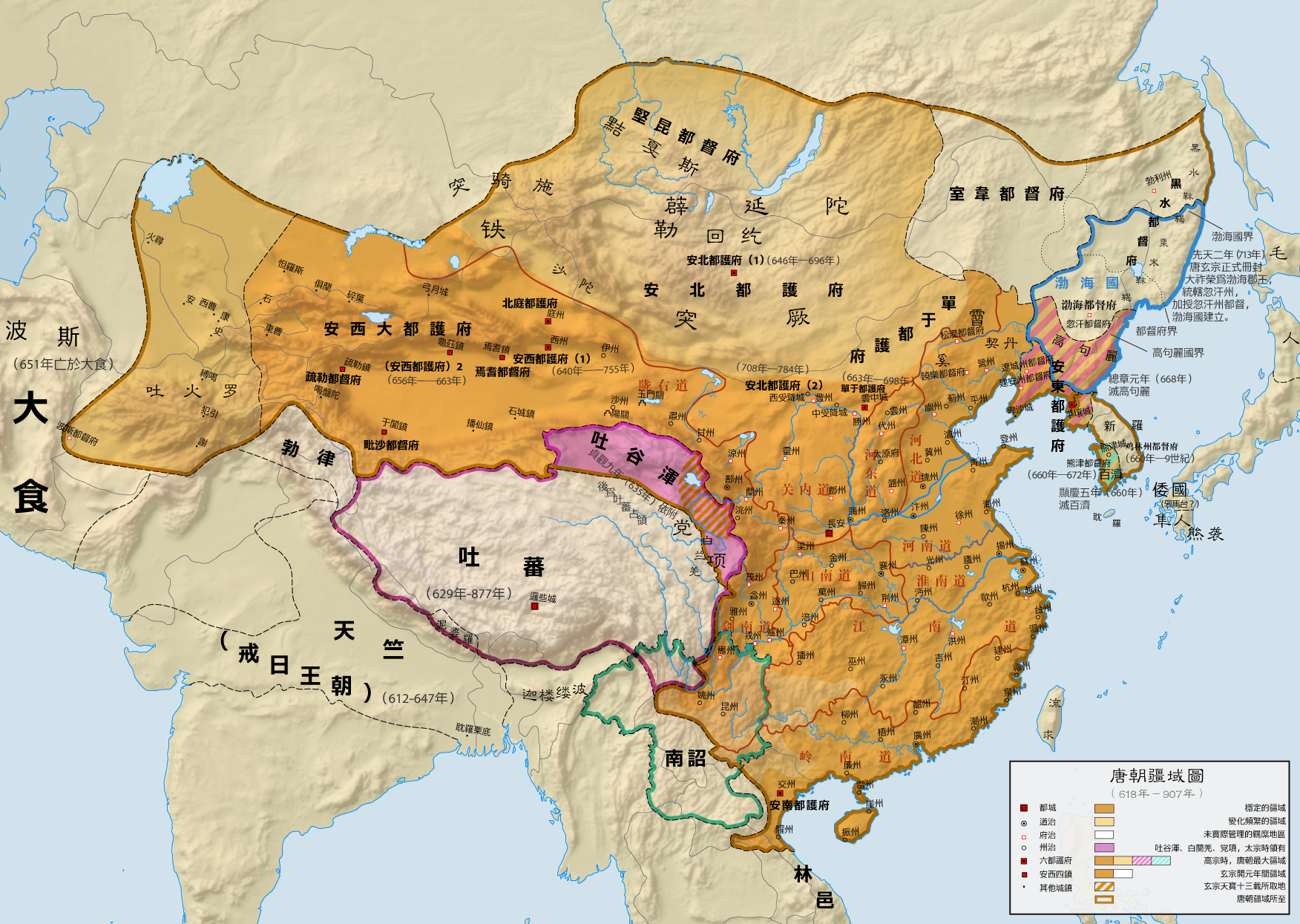
Soldiers and conscription
By the year 737, Emperor Xuanzong discarded the policy of conscripting soldiers that were replaced every three years, replacing them with long-service soldiers who were more battle-hardened and efficient. It was more economically feasible as well, since training new recruits and sending them out to the frontier every three years drained the treasury. By the late 7th century, the ''
fubing'' troops began abandoning military service and the homes provided to them in the equal-field system. The supposed standard of 100 ''
mu'' of land allotted to each family was in fact decreasing in size in places where population expanded and the wealthy bought up most of the land. Hard-pressed peasants and vagrants were then induced into military service with benefits of exemption from both taxation and corvée labor service, as well as provisions for farmland and dwellings for dependents who accompanied soldiers on the frontier. By the year 742 the total number of enlisted troops in the Tang armies had risen to about 500,000 men.
Eastern regions
In East Asia, Tang Chinese military campaigns were less successful elsewhere than in previous imperial Chinese dynasties.
Like the emperors of the Sui dynasty before him, Taizong established a military campaign in 644 against the Korean kingdom of
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
in the
Goguryeo–Tang War
The Goguryeo–Tang War occurred from 645 to 668 and was fought between Goguryeo and the Tang dynasty. During the course of the war, the two sides allied with various other states. Goguryeo successfully repulsed the invading Tang armies dur ...
; however, this led to its withdrawal in the
first campaign because they failed to overcome the successful defense led by General
Yeon Gaesomun.
Allying with the Korean Silla Kingdom, the Chinese fought against
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
and their
Yamato Japanese allies in the
Battle of Baekgang
The Battle of Baekgang or Battle of Baekgang-gu, also known as Battle of Hakusukinoe ( ja, 白村江の戦い, Hakusuki-no-e no Tatakai / Hakusonkō no Tatakai) in Japan, as Battle of Baijiangkou ( zh, c=白江口之战, p=Bāijiāngkǒu Zhīzh ...
in August 663, a decisive Tang–Silla victory. The Tang dynasty navy had
several different ship types at its disposal to engage in
naval warfare
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river. Mankind has fought battles on the sea for more than 3,000 years. Even in the interior of large la ...
, these ships described by Li Quan in his ''Taipai Yinjing'' (Canon of the White and Gloomy Planet of War) of 759. The Battle of Baekgang was actually a restoration movement by remnant forces of Baekje, since their kingdom was toppled in 660 by a joint Tang–Silla invasion, led by Chinese general Su Dingfang and Korean general
Kim Yushin
Gim Yu-sin (sometimes romanized Kim Yu-shin, Gim Yu-sin, or Gim Yu-shin) (595 – 18 August 673) was a Korean military general and politician in 7th-century Silla. He led the unification of the Korean Peninsula by Silla under the reign of King ...
(595–673). In another joint invasion with Silla, the Tang army severely weakened the Goguryeo Kingdom in the north by taking out its outer forts in the year 645. With joint attacks by Silla and Tang armies under commander
Li Shiji
Li Shiji (594?The ''Old Book of Tang'' indicated that Li Shiji was 75 at the time of his death, while the ''New Book of Tang'' indicated that Li Shiji was 85 at the time of his death. Compare ''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 67 with ''New Book of Tang ...
(594–669), the Kingdom of Goguryeo was destroyed by 668.

Although they were formerly enemies, the Tang accepted officials and generals of Goguryeo into their administration and military, such as the brothers
Yeon Namsaeng
Yeon Namsaeng (연남생, 淵男生) (634–679) was the eldest son of the Goguryeo '' Dae Magniji'' (대막리지, 大莫離支; highest ranking official or dictator; "prime minister") Yeon Gaesomun (603?-665). In 665, Yeon Namsaeng succeeded h ...
(634–679) and
Yeon Namsan
Yeon Namsan (淵男産, 연남산) (639–701) was the third son of the Goguryeo military leader and dictator Yeon Gaesomun (603?–665).
The course of his career shadowed closely that of his elder brother Yeon Namsaeng. From an early age he wa ...
(639–701). From 668 to 676, the Tang Empire would control northern Korea. However, in 671 Silla broke the alliance and began the
Silla–Tang War to expel the Tang forces. At the same time the Tang faced threats on its western border when a large Chinese army was defeated by the Tibetans on the Dafei River in 670. By 676, the Tang army was expelled out of Korea by
Unified Silla
Unified Silla, or Late Silla (, ), is the name often applied to the Korean kingdom of Silla, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, after 668 CE. In the 7th century, a Silla–Tang alliance conquered Baekje and the southern part of Goguryeo in the ...
. Following a revolt of the Eastern Turks in 679, the Tang abandoned its Korean campaigns.
Although the Tang had fought the Japanese, they still held cordial relations with Japan. There were numerous
Imperial embassies to China from Japan, diplomatic missions that were not halted until 894 by
Emperor Uda
was the 59th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 宇多天皇 (59)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession.
Uda's reign spanned the years from 887 through 897.
Traditional narrative
Name and legacy
Befor ...
(r. 887–897), upon persuasion by
Sugawara no Michizane
was a scholar, poet, and politician of the Heian Period of Japan. He is regarded as an excellent poet, particularly in Kanshi poetry, and is today revered in Shinto as the god of learning, . In the poem anthology '' Hyakunin Isshu'', he is know ...
(845–903). The Japanese
Emperor Tenmu
was the 40th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 天武天皇 (40) retrieved 2013-8-22. according to the traditional order of succession. Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', p. 53.
Tenmu's rei ...
(r. 672–686) even established his conscripted army on that of the Chinese model, based his state ceremonies on the Chinese model, and constructed his palace at
Fujiwara Fujiwara (, written: 藤原 lit. "''Wisteria'' field") is a Japanese surname. (In English conversation it is likely to be rendered as .) Notable people with the surname include:
; Families
* The Fujiwara clan and its members
** Fujiwara no Kamatari ...
on the
Chinese model of architecture.
Many Chinese Buddhist monks came to Japan to help further the spread of Buddhism as well. Two 7th-century monks in particular, Zhi Yu and Zhi You, visited the court of
Emperor Tenji
, also known as Emperor Tenchi, was the 38th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'')天智天皇 (38)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession.Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', p. 52 ...
(r. 661–672), whereupon they presented a gift of a
south-pointing chariot
The south-pointing chariot (or carriage) was an ancient Chinese two-wheeled vehicle that carried a movable pointer to indicate the south, no matter how the chariot turned. Usually, the pointer took the form of a doll or figure with an outstretch ...
that they had crafted. This 3rd century mechanically driven directional-
compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
vehicle (employing a
differential gear
A differential is a gear train with three drive shafts that has the property that the rotational speed of one shaft is the average of the speeds of the others, or a fixed multiple of that average.
Functional description
The following descri ...
) was again reproduced in several models for Tenji in 666, as recorded in the ''
Nihon Shoki'' of 720. Japanese monks also visited China; such was the case with
Ennin
, better known in Japan by his posthumous name, Jikaku Daishi (), was a priest of the Tendai school of Buddhism in Japan, and its third . Ennin was instrumental in expanding the Tendai Order's influence, and bringing back crucial training and re ...
(794–864), who wrote of his travel experiences including travels along
China's Grand Canal. The Japanese monk
Enchin
(814–891) was a Japanese Buddhist monk who founded of the Jimon school of Tendai Buddhism and Chief Abbot of Mii-dera at the foot of Mount Hiei. After succeeding to the post of Tendai , in 873, a strong rivalry developed between his followers ...
(814–891) stayed in China from 839 to 847 and again from 853 to 858, landing near
Fuzhou, Fujian and setting sail for Japan from
Taizhou, Zhejiang
Tāizhōu (pronunciation in PRC Standard Mandarin: , Taizhou dialect: Thecieu), alternately known as Taichow, is a city located at the middle of the East China Sea coast of Zhejiang province. It is located south of Shanghai and southeast o ...
during his second trip to China.
Western and Northern regions

The Sui and Tang carried out successful military campaigns against the steppe nomads. Chinese foreign policy to the north and west now had to deal with
Turkic nomads, who were becoming the most dominant ethnic group in Central Asia. To handle and avoid any threats posed by the Turks, the Sui government repaired fortifications and received their trade and tribute missions. They sent four royal princesses to form
marriage alliances with Turkic clan leaders, in 597, 599, 614, and 617. The Sui stirred trouble and conflict amongst ethnic groups against the Turks. As early as the Sui dynasty, the Turks had become
a major militarized force employed by the Chinese. When the
Khitans
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
As a people desce ...
began raiding northeast China in 605, a Chinese general led 20,000 Turks against them, distributing Khitan livestock and women to the Turks as a reward. On two occasions between 635 and 636, Tang royal princesses were married to Turk mercenaries or generals in Chinese service. Throughout the Tang dynasty until the end of 755, there were approximately ten Turkic generals serving under the Tang. While most of the Tang army was made of ''fubing'' Chinese conscripts, the majority of the troops led by Turkic generals were of non-Chinese origin, campaigning largely in the western frontier where the presence of ''fubing'' troops was low. Some "Turkic" troops were tribalized Han Chinese, a
desinicized people.
Civil war in China was almost totally diminished by 626, along with the defeat in 628 of the
Ordos Chinese warlord
Liang Shidu
Liang Shidu (梁師都) (died June 3, 628) was an agrarian leader who rebelled against the rule of the Chinese dynasty Sui Dynasty near the end of the reign of Emperor Yang of Sui. He, claiming the title of Emperor of Liang with the aid from Ea ...
; after these internal conflicts, the Tang began an offensive against the Turks. In the year 630, Tang armies captured areas of the Ordos Desert, modern-day
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
province, and southern
Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
from the Turks. After this military victory, On June 11, 631, Emperor Taizong also sent envoys to the
Xueyantuo
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and khaganate in Northeast Asia who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Göktürks.
Names Xue
''Xue'' 薛 appeared earlier as ' ...
bearing gold and silk in order to persuade the release of enslaved Chinese prisoners who were captured during the
transition from Sui to Tang
The transition from Sui to Tang (613–628) was the period of Chinese history between the end of the Sui dynasty and the start of the Tang dynasty. The Sui dynasty's territories were carved into a handful of short-lived states by its officials, ...
from the northern frontier; this embassy succeeded in freeing 80,000 Chinese men and women who were then returned to China.

While the Turks were settled in the Ordos region (former territory of the
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
), the Tang government took on the military policy of dominating the central
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
. Like the earlier Han dynasty, the Tang dynasty (along with Turkic allies) conquered and subdued Central Asia during the 640s and 650s. During Emperor Taizong's reign alone, large campaigns were launched against not only the
Göktürks, but also separate campaigns against the
Tuyuhun
Tuyuhun (; LHC: *''tʰɑʔ-jok-guənʔ''; Wade-Giles: ''T'u-yühun''), also known as Henan () and Azha (; ), was a dynastic kingdom established by the nomadic peoples related to the Xianbei in the Qilian Mountains and upper Yellow River valle ...
, the
oasis city-states, and the
Xueyantuo
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and khaganate in Northeast Asia who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Göktürks.
Names Xue
''Xue'' 薛 appeared earlier as ' ...
. Under Emperor Gaozong, a campaign led by the general
Su Dingfang
Su Dingfang () (591–667), formal name Su Lie () but went by the courtesy name of Dingfang, formally Duke Zhuang of Xing (), was a Chinese military general of the Tang Dynasty who succeeded in destroying the Western Turkic Khaganate in 657. He wa ...
was
launched against the Western Turks ruled by Ashina Helu.
The Tang Empire competed with the
Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the 3 ...
for control of areas in Inner and Central Asia, which was at times settled with
marriage alliances such as the marrying of
Princess Wencheng (d. 680) to
Songtsän Gampo (d. 649). A Tibetan tradition mentions that Chinese troops captured Lhasa after Songtsän Gampo's death, but no such invasion is mentioned in either Chinese annals or the Tibetan manuscripts of
Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major s ...
.
There was a long string of conflicts with Tibet over territories in the
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
between 670 and 692, and in 763 the Tibetans even captured the capital of China,
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
, for fifteen days during the
An Shi Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general office ...
. In fact, it was during this rebellion that the Tang withdrew its western garrisons stationed in what is now
Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
and
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
, which the Tibetans then occupied along with the territory of what is now
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
. Hostilities between the Tang and Tibet continued until they signed a formal peace treaty in 821. The terms of this treaty, including the fixed borders between the two countries, are recorded in a bilingual inscription on
a stone pillar outside the
Jokhang
The Jokhang (, ), also known as the Qoikang Monastery, Jokang, Jokhang Temple, Jokhang Monastery and Zuglagkang ( or Tsuklakang), is a Buddhist temple in Barkhor Square in Lhasa, the capital city of Tibet Autonomous Region of China. Tibetans, in ...
temple in Lhasa.
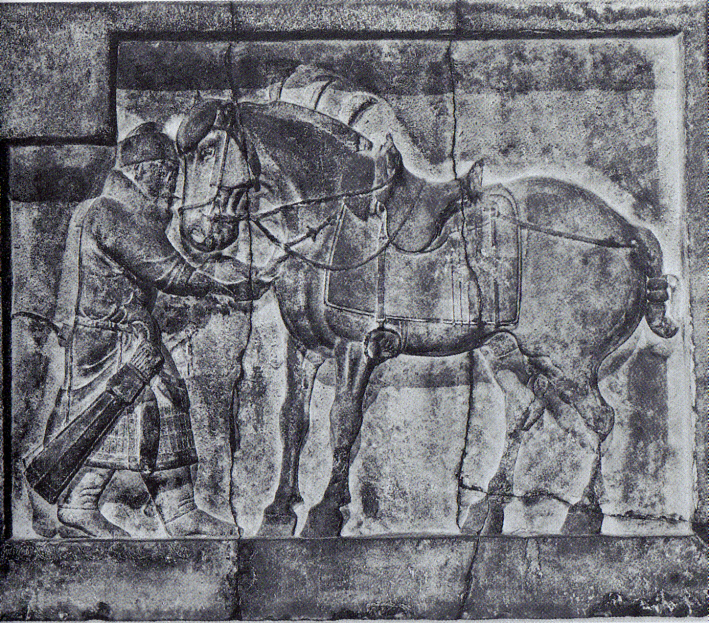

During the
Islamic conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
The r ...
(633–656), the son of the last ruler of the
Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
,
Prince Peroz and his court moved to Tang China. According to the ''
Old Book of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingd ...
'', Peroz was made the head of a Governorate of Persia in what is now
Zaranj
Zaranj or Zarang ( Persian/Pashto/ bal, زرنج) is a city in southwestern Afghanistan, near the border with Iran, which has a population of 160,902 people as of 2015. It is the capital of Nimruz Province and is linked by highways with Lashkarga ...
, Afghanistan. During this conquest of Persia, the
Rashidun
, image = تخطيط كلمة الخلفاء الراشدون.png
, caption = Calligraphic representation of Rashidun Caliphs
, birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia present-day Saudi Arabia
, known_for = Companions of ...
Caliph
Uthman Ibn Affan (r. 644–656) sent an embassy to the Tang court at Chang'an. Arab sources claim Umayyad commander
Qutayba ibn Muslim
Abū Ḥafṣ Qutayba ibn Abī Ṣāliḥ Muslim ibn ʿAmr al-Bāhilī ( ar, أبو حفص قتيبة بن أبي صالح مسلم بن عمرو الباهلي; 669–715/6) was an Arab commander of the Umayyad Caliphate who became governor of ...
briefly took
Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. ...
from China and withdrew after an agreement,
but modern historians entirely dismiss this claim. The Arab
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
in 715 deposed
Ikhshid
''Ikhshid'' ( sog, xšyδ, ) was the princely title of the Iranian rulers of Soghdia and the Ferghana Valley in Transoxiana during the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods. The title is of Iranian origin; scholars have derived it variously from ...
, the king the
Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
, and installed a new king Alutar on the throne. The deposed king fled to
Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road ...
(seat of
Anxi Protectorate
The Protectorate General to Pacify the West (Anxi Grand Protectorate), initially the Protectorate to Pacify the West (Anxi Protectorate), was a protectorate (640 – ) established by the Chinese Tang dynasty in 640 to control the Tarim Basin. Th ...
), and sought Chinese intervention. The Chinese sent 10,000 troops under
Zhang Xiaosong to
Ferghana
Fergana ( uz, Fargʻona/Фарғона, ), or Ferghana, is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 420 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km west of Andijan, and less than 20 km fr ...
. He defeated Alutar and the Arab occupation force at
Namangan
Namangan (; ) is a city in eastern Uzbekistan. It is the administrative, economic, and cultural center of Namangan Region. Administratively, it is a district-level city. Namangan is located in the northern edge of the Fergana Valley, less than ...
and reinstalled Ikhshid on the throne.
[ Bai, Shouyi et al. (2003). ''A History of Chinese Muslim (Vol.2)''. Beijing: Zhonghua Book Company. . pp. 235–236] The Tang dynasty Chinese defeated the Arab
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
invaders at the
Battle of Aksu (717)
The Battle of Aksu () was fought between Arabs of the Umayyad Caliphate and their Turgesh and Tibetan Empire allies against the Tang dynasty of China. In 717 AD, the Arabs, guided by their Turgesh allies, besieged Buat-ɦuɑn (Aksu) and Dai-d ...
. The Arab Umayyad commander Al-Yashkuri and his army fled to Tashkent after they were defeated.
The Turgesh then
crushed the Arab Umayyads and drove them out. By the 740s, the
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
under the
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
in
Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
had reestablished a presence in the
Ferghana
Fergana ( uz, Fargʻona/Фарғона, ), or Ferghana, is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 420 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km west of Andijan, and less than 20 km fr ...
basin and in
Sogdiana
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empi ...
. At the
Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas or Battle of Artlakh (; ar, معركة نهر طلاس, translit=Maʿrakat nahr Ṭalās, Persian: Nabard-i Tarāz) was a military encounter and engagement between the Abbasid Caliphate along with its ally, the Tibetan Empi ...
in 751,
Karluk mercenaries under the Chinese defected, helping the Arab armies of the Caliphate to defeat the Tang force under commander
Gao Xianzhi. Although the battle itself was not of the greatest significance militarily, this was a pivotal moment in history, as it marks the spread of Chinese
papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a speciali ...
into regions west of China as captured Chinese soldiers shared the technique of papermaking to the Arabs. These techniques ultimately reached Europe by the 12th century through
Arab-controlled Spain.
[
] Although they had fought at Talas, on June 11, 758, an
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
embassy arrived at Chang'an simultaneously with the Uighur Turks bearing gifts for the Tang Emperor. In 788–789 the Chinese concluded a military alliance with the
Uighur Turks who twice defeated the Tibetans, in 789 near the town of
Gaochang in
Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang". Bounded by the ...
, and in 791 near
Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1 ...
on the Yellow River.

Joseph Needham
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (; 9 December 1900 – 24 March 1995) was a British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science and technology, i ...
writes that a
tributary embassy came to the court of Emperor Taizong in 643 from the
Patriarch of Antioch
Patriarch of Antioch is a traditional title held by the bishop of Antioch (modern-day Antakya, Turkey). As the traditional "overseer" (ἐπίσκοπος, ''episkopos'', from which the word ''bishop'' is derived) of the first gentile Christian c ...
. However,
Friedrich Hirth and other
sinologists
Sinology, or Chinese studies, is an academic discipline that focuses on the study of China primarily through Chinese philosophy, language, literature, culture and history and often refers to Western scholarship. Its origin "may be traced to the ex ...
such as S.A.M. Adshead have identified ''Fu lin'' (拂菻) in the ''
Old
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
* Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, M ...
'' and ''
New Book of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the So ...
'' as the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, which those histories directly associated with ''
Daqin'' (i.e. the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
).
The embassy sent in 643 by ''Boduoli'' (波多力) was identified as Byzantine ruler
Constans II Pogonatos (''Kōnstantinos Pogonatos'', or "Constantine the Bearded") and
further embassies were recorded as being sent into the 8th century.
S.A.M. Adshead offers a different transliteration stemming from "
patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in c ...
" or "
patrician", possibly a reference to one of the acting
regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
s for the young Byzantine monarch. The ''Old'' and ''New Book of Tang'' also provide a description of the Byzantine capital
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, including
how it was besieged by the ''Da shi'' (大食, i.e.
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
) forces of
Muawiyah I
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
, who forced them to pay tribute to the Arabs.
The 7th-century Byzantine historian
Theophylact Simocatta
Theophylact Simocatta (Byzantine Greek: Θεοφύλακτος Σιμοκάτ(τ)ης ''Theophýlaktos Simokát(t)ēs''; la, Theophylactus Simocatta) was an early seventh-century Byzantine historiographer, arguably ranking as the last historian o ...
wrote about the reunification of
northern and southern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions within China. The exact boundary between these two regions is not precisely defined and only serve to depict where there appears to be regional differences between the climates ...
by the Sui dynasty (dating this to the time of
Emperor Maurice
Maurice ( la, Mauricius or ''Mauritius''; ; 539 – 27 November 602) was Eastern Roman emperor from 582 to 602 and the last member of the Justinian dynasty. A successful general, Maurice was chosen as heir and son-in-law by his predecessor Tib ...
); the capital city ''Khubdan'' (from
Old Turkic
Old Turkic (also East Old Turkic, Orkhon Turkic language, Old Uyghur) is the earliest attested form of the Turkic languages, found in Göktürk and Uyghur Khaganate inscriptions dating from about the eighth to the 13th century. It is the old ...
''Khumdan'', i.e. Chang'an); the basic
geography of China including its previous political division around the
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
; the name of China's ruler ''Taisson'' meaning "
Son of God", but possibly derived from the name of the contemporaneous ruler Emperor Taizong.
Economy
Through use of the land trade along the
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
and
maritime trade by sail at sea, the Tang were able to acquire and gain many new technologies, cultural practices, rare luxury, and contemporary items. From Europe, the Middle East, Central and South Asia, the Tang dynasty were able to acquire new ideas in fashion, new types of ceramics, and improved silver-smithing techniques. The Tang Chinese also gradually adopted the foreign concept of stools and chairs as seating, whereas the Chinese beforehand always sat on mats placed on the floor. People of the Middle East coveted and purchased in bulk Chinese goods such as silks,
lacquerware
Lacquerware are objects decoratively covered with lacquer. Lacquerware includes small or large containers, tableware, a variety of small objects carried by people, and larger objects such as furniture and even coffins painted with lacquer. Befor ...
s, and
porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
wares. Songs, dances, and musical instruments from foreign regions became popular in China during the Tang dynasty. These musical instruments included
oboe
The oboe ( ) is a type of double reed woodwind instrument. Oboes are usually made of wood, but may also be made of synthetic materials, such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The most common oboe plays in the treble or soprano range.
...
s,
flute
The flute is a family of classical music instrument in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, meaning they make sound by vibrating a column of air. However, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is a reedles ...
s, and small lacquered drums from
Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road ...
in the
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
, and percussion instruments from India such as
cymbal
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs soun ...
s. At the court there were nine musical ensembles (expanded from seven in the Sui dynasty) that played ecletic Asian music.

There was great interaction with India, a hub for Buddhist knowledge, with famous travelers such as
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
(d. 664) visiting the South Asian state. After a 17-year-long trip, Xuanzang managed to bring back valuable
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
texts to be translated into Chinese. There was also a
Turkic–Chinese dictionary available for serious scholars and students, while Turkic folk songs gave inspiration to some Chinese poetry. In the interior of China, trade was facilitated by the
Grand Canal and the Tang government's rationalization of the greater canal system that reduced costs of transporting grain and other commodities. The state also managed roughly of
postal service
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal syst ...
routes by horse or boat.
Silk Road
Although the
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
from China to
Europe and the Western World was initially formulated during the reign of
Emperor Wu (141–87 BC) during the
Han, it was reopened by the Tang in 639 when
Hou Junji ( 643) conquered the West, and remained open for almost four decades. It was closed after the Tibetans captured it in 678, but in 699, during Empress Wu's period, the Silk Road reopened when the Tang reconquered the
Four Garrisons of Anxi
The Four Garrisons of Anxi were Chinese military garrisons installed by the Tang dynasty between 648 and 658. They were stationed at the Indo-European city-states of Qiuci (Kucha), Yutian (Hotan), Shule (Kashgar) and Yanqi ( Karashahr). The ...
originally installed in 640, once again connecting China directly to the West for land-based trade.
The Tang captured the vital route through the
Gilgit Valley
Gilgit Valley () is a valley located in Gilgit District in Gilgit-Baltistan, northern Pakistan. The Gilgit River flows through the valley. 375 km of road connects it to the town of Chitral via the Shandur Pass (3,800 m).
The town of Gilgit
...
from Tibet in 722, lost it to the Tibetans in 737, and regained it under the command of the Goguryeo-Korean General Gao Xianzhi. When the An Lushan Rebellion ended in 763, the Tang Empire withdrew its troops from its western lands, allowing the Tibetan Empire to largely cut off China's direct access to the Silk Road. An internal rebellion in 848 ousted the Tibetan rulers, and Tang China regained its northwestern prefectures from Tibet in 851. These lands contained crucial grazing areas and pastures for raising horses that the Tang dynasty desperately needed.
Despite the many expatriate European travelers coming into China to live and trade, many travelers, mainly religious monks and missionaries, recorded China's stringent immigrant laws. As the monk Xuanzang and many other monk travelers attested to, there were many Chinese government
checkpoints
Checkpoint may refer to:
Places
* Border checkpoint, a place on the land border between two states where travellers and/or goods are inspected
* Security checkpoint, erected and enforced within contiguous areas under military or paramilitary cont ...
along the Silk Road that examined travel permits into the Tang Empire. Furthermore,
banditry
Banditry is a type of organized crime committed by outlaws typically involving the threat or use of violence. A person who engages in banditry is known as a bandit and primarily commits crimes such as extortion, robbery, and murder, either as an ...
was a problem along the checkpoints and
oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
towns, as Xuanzang also recorded that his group of travelers were assaulted by bandits on multiple occasions.
The
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
also affected
Tang dynasty art. Horses became a significant symbol of prosperity and power as well as an instrument of military and diplomatic policy. Horses were also revered as a relative of the dragon.
Seaports and maritime trade

Chinese envoys had been sailing through the Indian Ocean to states of
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
since perhaps the 2nd century BC, yet it was during the Tang dynasty that a strong Chinese maritime presence could be found in the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
and
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
, into
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
,
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
(sailing up the
Euphrates River
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
in modern-day
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
),
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Pl ...
, Egypt in the Middle East and
Aksum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole regio ...
(
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
), and
Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
in the
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004 ...
.
During the Tang dynasty, thousands of foreign expatriate merchants came and lived in numerous Chinese cities to do business with China, including
Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
,
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
,
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
Indians,
Malays,
Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of ...
,
Sinhalese,
Khmers
The Khmer people ( km, ជនជាតិខ្មែរ, ) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Cambodia. They comprise over 90% of Cambodia's population of 17 million. ,
Chams
The Cham ( Cham: ''Čaṃ'') or Champa people ( Cham: , ''Urang Campa''; vi, Người Chăm or ; km, ជនជាតិចាម, ) are an Austronesian ethnic group. From the 2nd century to 1832 the Cham populated Champa, a contiguous territ ...
,
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and
Nestorian Christians of the
Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
, among many others. In 748, the Buddhist monk Jian Zhen described
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, sou ...
as a bustling mercantile business center where many large and impressive foreign ships came to dock. He wrote that "many large ships came from
Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
, Persia, Qunglun (
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
/
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
)... with... spices, pearls, and jade piled up mountain high", as written in the ''Yue Jue Shu'' (Lost Records of the State of Yue). Relations with the Arabs were often strained: When the imperial government was attempting to quell the
An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general off ...
, Arab and Persian
pirate
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
s burned and looted Canton on October 30, 758. The Tang government reacted by shutting the port of Canton down for roughly five decades; thus, foreign vessels docked at
Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi i ...
instead. However, when the port reopened, it continued to thrive. In 851 the Arab merchant
Sulaiman al-Tajir observed the manufacturing of Chinese
porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
in Guangzhou and admired its transparent quality. He also provided a description of Guangzhou's landmarks, granaries, local government administration, some of its written records, treatment of travelers, along with the use of
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
s, rice, wine, and tea. Their presence
came to an end under the revenge of Chinese rebel Huang Chao in 878, who purportedly slaughtered thousands regardless of ethnicity. Huang's rebellion was eventually suppressed in 884.
Vessels from other East Asian states such as
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
,
Bohai and the
Hizen Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of the Saga and Nagasaki prefectures. It was sometimes called , with Higo Province. Hizen bordered on the provinces of Chikuzen and Chikugo. The province was included in Saikaidō. It did not incl ...
of Japan were all involved in the
Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea. It is one of four seas named after common colour ter ...
trade, which Silla of Korea dominated. After Silla and Japan reopened renewed hostilities in the late 7th century, most Japanese maritime merchants chose to set sail from
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
towards the mouth of the
Huai River, the Yangtze River, and even as far south as the
Hangzhou Bay
Hangzhou Bay, or the Bay of Hangzhou (), is a funnel-shaped inlet of the East China Sea, bordered by the province of Zhejiang and the municipality of Shanghai, which lies north of the Bay. The Bay extends from the East China Sea to its head ...
in order to avoid Korean ships in the Yellow Sea. In order to sail back to Japan in 838, the Japanese embassy to China procured nine ships and sixty Korean sailors from the Korean wards of Chuzhou and Lianshui cities along the Huai River. It is also known that Chinese trade ships traveling to Japan set sail from the various ports along the coasts of
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Ji ...
and
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its ...
provinces.
The Chinese engaged in large-scale production for overseas export by at least the time of the Tang. This was proven by the discovery of the
Belitung shipwreck
The Belitung shipwreck (also called the Tang shipwreck or Batu Hitam shipwreck) is the wreck of an Arabian dhow which sank around 830 AD. The ship completed the outward journey from Arabia to China, but sank on the return journey from China, app ...
, a silt-preserved shipwrecked Arabian
dhow
Dhow ( ar, داو, translit=dāwa; mr, script=Latn, dāw) is the generic name of a number of traditional sailing vessels with one or more masts with settee or sometimes lateen sails, used in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean region. Typically spo ...
in the
Gaspar Strait
The Gaspar Strait ( id, Selat Gaspar) is a strait separating the Indonesian islands Belitung ( en, Billiton, link=no) and Bangka. It connects the Java Sea with the South China Sea.
Etymology
The strait is named after a Spanish captain, who p ...
near
Belitung
Belitung ( Belitung Malay: ''Belitong'', formerly Billiton) is an island on the east coast of Sumatra, Indonesia in the Java Sea. It covers , and had a population of 309,097 at the 2020 Census. Administratively, it forms two regencies ( Beli ...
, which had 63,000 pieces of Tang ceramics, silver, and gold (including a
Changsha
Changsha (; ; ; Changshanese pronunciation: (), Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is the capital and the largest city of Hunan Province of China. Changsha is the 17th most populous city in China with a population of over 10 million, and ...
bowl inscribed with a date: "16th day of the seventh month of the second year of the Baoli reign", or 826, roughly confirmed by
radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
of
star anise
''Illicium verum'' is a medium-sized evergreen tree native to northeast Vietnam and southwest China. A spice commonly called star anise, staranise, star anise seed, star aniseed, star of anise, Chinese star anise, or badian that closely resemb ...
at the wreck).
Beginning in 785, the Chinese began to call regularly at
Sufala on the East African coast in order to cut out Arab middlemen, with various contemporary Chinese sources giving detailed descriptions of trade in Africa. The official and geographer
Jia Dan (730–805) wrote of two common sea trade routes in his day: one from the coast of the
Bohai Sea
The Bohai Sea () is a marginal sea approximately in area on the east coast of Mainland China. It is the northwestern and innermost extension of the Yellow Sea, to which it connects to the east via the Bohai Strait. It has a mean depth of ...
towards Korea and another from Guangzhou through
Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has bee ...
towards the
Nicobar Islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located southeast of the Indian ...
, Sri Lanka and India, the eastern and northern shores of the Arabian Sea to the Euphrates River. In 863 the Chinese author
Duan Chengshi
Duan Chengshi () (died 863) was a Chinese poet and writer of the Tang Dynasty. He was born to a wealthy family in present-day Zibo, Shandong. A descendant of the early Tang official Duan Zhixuan (, ''Duàn Zhìxuán'') (-642), and the son of Duan ...
(d. 863) provided a detailed description of the
slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
,
ivory trade
The ivory trade is the commercial, often illegal trade in the ivory tusks of the hippopotamus, walrus, narwhal, mammoth, and most commonly, African and Asian elephants.
Ivory has been traded for hundreds of years by people in Africa and Asia ...
, and
ambergris
Ambergris ( or , la, ambra grisea, fro, ambre gris), ''ambergrease'', or grey amber is a solid, waxy, flammable substance of a dull grey or blackish colour produced in the digestive system of sperm whales. Freshly produced ambergris has a mari ...
trade in a country called
Bobali, which historians suggest was
Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. I ...
in Somalia. In
Fustat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by t ...
(old
Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metr ...
), Egypt, the fame of Chinese ceramics there led to an enormous demand for Chinese goods; hence Chinese often traveled there (this continued into later periods such as
Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyna ...
Egypt). From this time period, the Arab merchant Shulama once wrote of his admiration for Chinese seafaring
junks
A junk (Chinese: 船, ''chuán'') is a type of Chinese sailing ship with fully battened sails. There are two types of junk in China: northern junk, which developed from Chinese river boats, and southern junk, which developed from Austronesian ...
, but noted that their draft was too deep for them to enter the Euphrates River, which forced them to ferry passengers and cargo in small boats. Shulama also noted that Chinese ships were often very large, with capacities up to 600–700 passengers.
Culture and society
Art
Both the Sui and Tang Dynasties had turned away from the more
feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
culture of the preceding Northern Dynasties, in favor of staunch civil
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, ...
. The governmental system was supported by a large class of Confucian intellectuals selected through either civil service examinations or recommendations. In the Tang period,
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
and
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
were commonly practiced ideologies that played a large role in people's daily lives. The Tang Chinese enjoyed feasting, drinking, holidays, sports, and all sorts of entertainment, while
Chinese literature blossomed and was more widely accessible with new
printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
methods.
Chang'an, the Tang capital

Although Chang'an was the capital of the earlier Han and Jin dynasties, after subsequent destruction in warfare, it was the Sui dynasty model that comprised the Tang era capital. The roughly square dimensions of the city had six miles (10 km) of outer walls running east to west, and more than five miles (8 km) of outer walls running north to south. The royal palace, the Taiji Palace, stood north of the city's central axis. From the large Mingde Gates located mid-center of the main southern wall, a wide city avenue stretched from there all the way north to the central administrative city, behind which was the Chentian Gate of the royal palace, or Imperial City. Intersecting this were fourteen main streets running east to west, while eleven main streets ran north to south. These main intersecting roads formed 108 rectangular wards with walls and four gates each, and each ward filled with multiple
city block
A city block, residential block, urban block, or simply block is a central element of urban planning and urban design.
A city block is the smallest group of buildings that is surrounded by streets, not counting any type of thoroughfare within t ...
s. The city was made famous for this checkerboard pattern of main roads with walled and gated districts, its layout even mentioned in one of Du Fu's poems. During the
Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japan ...
, the city of
Heian kyō (present-day
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the c ...
) of Japan like many cities was arranged in the checkerboard street grid pattern of the Tang capital and in accordance with traditional geomancy following the model of Chang'an. Of these 108 wards in Chang'an, two of them (each the size of two regular city wards) were designated as government-supervised markets, and other space reserved for temples, gardens, ponds, etc. Throughout the entire city, there were 111 Buddhist monasteries, 41 Taoist abbeys, 38 family shrines, 2 official temples, 7 churches of foreign religions, 10 city wards with provincial transmission offices, 12 major inns, and 6 graveyards. Some city wards were literally filled with open public playing fields or the backyards of lavish mansions for playing horse polo and
cuju
''Cuju'' or ''Ts'u-chü'' (蹴鞠) is an ancient Chinese football game. Cuju is the earliest known recorded game of football. It is a competitive game that involves kicking a ball through an opening into a net without the use of hands. Descripti ...
(Chinese soccer). In 662,
Emperor Gaozong moved the imperial court to the
Daming Palace, which became the political center of the empire and served as the royal residence of the Tang emperors for more than 220 years.

The Tang capital was the largest city in the world at its time, the population of the city wards and its suburban countryside reaching two million inhabitants. The Tang capital was very cosmopolitan, with ethnicities of
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Central Asia, Japan, Korea,
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
, Tibet, India, and many other places living within. Naturally, with this plethora of different ethnicities living in Chang'an, there were also many different practiced religions, such as
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
,
Nestorian Christianity
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
, and
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
, among others. With the open access to China that the
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
to the west facilitated, many foreign settlers were able to move east to China, while the city of Chang'an itself had about 25,000 foreigners living within. Exotic green-eyed, blond-haired
Tocharian ladies serving wine in
agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Anci ...
and
amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
cups, singing, and dancing at taverns attracted customers. If a foreigner in China pursued a Chinese woman for marriage, he was required to stay in China and was unable to take his bride back to his homeland, as stated in a law passed in 628 to protect women from temporary marriages with foreign envoys. Several laws enforcing segregation of foreigners from Chinese were passed during the Tang dynasty. In 779 the Tang dynasty issued an edict which forced
Uighurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghu ...
in the capital, Chang'an, to wear their ethnic dress, stopped them from marrying Chinese females, and banned them from passing off as Chinese.

Chang'an was the center of the central government, the home of the imperial family, and was filled with splendor and wealth. However, incidentally it was not the economic hub during the Tang dynasty. The city of
Yangzhou
Yangzhou, postal romanization Yangchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu Province (Suzhong), East China. Sitting on the north bank of the Yangtze, it borders the provincial capital Nanjing to the southwest, Huai'an to the north, ...
along the
Grand Canal and close to the
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
was the greatest economic center during the Tang era.
Yangzhou was the headquarters for the Tang government's salt monopoly, and was the greatest industrial center of China. It acted as a midpoint in shipping of foreign goods that would be organized and distributed to the major cities of the north. Much like the seaport of
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, sou ...
in the south, Yangzhou boasted thousands of foreign traders from all across Asia.
There was also the secondary capital city of
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
, which was the favored capital of the two by
Empress Wu. In the year 691 she had more than 100,000 families (more than 500,000 people) from around the region of Chang'an move to populate Luoyang instead. With a population of about a million, Luoyang became the second largest city in the empire, and with its closeness to the Luo River it benefited from southern agricultural fertility and trade traffic of the Grand Canal. However, the Tang court eventually demoted its capital status and did not visit Luoyang after the year 743, when Chang'an's problem of acquiring adequate supplies and stores for the year was solved. As early as 736, granaries were built at critical points along the route from Yangzhou to Chang'an, which eliminated shipment delays, spoilage, and pilfering. An artificial lake used as a transshipment pool was dredged east of Chang'an in 743, where curious northerners could finally see the array of boats found in southern China, delivering tax and tribute items to the imperial court.
Literature
The Tang period was a
golden age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the '' Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the G ...
of Chinese literature and
art. Over 48,900 poems penned by some 2,200 Tang authors have survived to the present day. Skill in the composition of poetry became a required study for those wishing to pass imperial examinations, while poetry was also heavily competitive; poetry contests amongst guests at banquets and courtiers were common. Poetry styles that were popular in the Tang included
''gushi'' and
''jintishi'', with the renowned poet
Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), also pronounced as Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet, acclaimed from his own time to the present as a brilliant and romantic figure who took traditional poetic forms to new heights. He and his friend Du F ...
(701–762) famous for the former style, and poets like
Wang Wei (701–761) and
Cui Hao
Cui Hao () (died 450 CE), courtesy name Boyuan (伯淵), was a ''shangshu'' of the Xianbei-led Northern Wei dynasty of China. Largely because of Cui's counsel, Emperor Taiwu of Northern Wei was able to unify northern China, ending the Sixteen Ki ...
(704–754) famous for their use of the latter. ''Jintishi'' poetry, or regulated verse, is in the form of eight-line
stanza
In poetry, a stanza (; from Italian ''stanza'' , "room") is a group of lines within a poem, usually set off from others by a blank line or indentation. Stanzas can have regular rhyme and metrical schemes, but they are not required to have ei ...
s or seven
characters per line with a fixed pattern of tones that required the second and third couplets to be antithetical (although the
antithesis
Antithesis ( Greek for "setting opposite", from "against" and "placing") is used in writing or speech either as a proposition that contrasts with or reverses some previously mentioned proposition, or when two opposites are introduced together ...
is often lost in translation to other languages). Tang poems remained popular and great emulation of Tang era poetry began in the Song dynasty; in that period, Yan Yu (嚴羽; active 1194–1245) was the first to confer the poetry of the High Tang (c. 713–766) era with "canonical status within the classical poetic tradition." Yan Yu reserved the position of highest esteem among all Tang poets for
Du Fu
Du Fu (; 712–770) was a Tang dynasty poet and politician. Along with his elder contemporary and friend Li Bai (Li Po), he is frequently called the greatest of the Chinese poets.Ebrey, 103. His greatest ambition was to serve his country ...
(712–770), who was not viewed as such in his own era, and was branded by his peers as an anti-traditional rebel.
The
Classical Prose Movement
The Classical Prose Movement () of the late Tang dynasty and the Song dynasty in China advocated clarity and precision rather than the florid '' pianwen'' () or parallel prose style that had been popular since the Han dynasty. Parallel prose had ...
was spurred in large part by the writings of Tang authors
Liu Zongyuan
Liu Zongyuan (; 77328 November 819) was a Chinese philosopher, poet, and politician who lived during the Tang Dynasty. Liu was born in present-day Yongji, Shanxi. Along with Han Yu, he was a founder of the Classical Prose Movement. He has been ...
(773–819) and
Han Yu
Han Yu (; 76825 December 824), courtesy name Tuizhi (), and commonly known by his posthumous name Han Wengong (韓文公), was a Chinese essayist, poet, philosopher, and politician during the Tang dynasty who significantly influenced the devel ...
(768–824). This new prose style broke away from the poetry tradition of the ''piantiwen'' (, "parallel prose") style begun in the Han dynasty. Although writers of the Classical Prose Movement imitated ''piantiwen'', they criticized it for its often vague content and lack of colloquial language, focusing more on clarity and precision to make their writing more direct. This ''guwen'' (archaic prose) style can be traced back to Han Yu, and would become largely associated with
orthodox Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lǐxué'' 理學, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, and originated with Han Yu (768–824) and Li Ao (772–841) ...
.
Short story fiction and tales were also popular during the Tang, one of the more famous ones being ''Yingying's Biography'' by
Yuan Zhen (779–831), which was widely circulated in his own time and by the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
(1279–1368) became the basis for plays in
Chinese opera
Traditional Chinese opera (), or ''Xiqu'', is a form of musical theatre in China with roots going back to the early periods in China. It is an amalgamation of various art forms that existed in ancient China, and evolved gradually over more tha ...
. Timothy C. Wong places this story within the wider context of Tang love tales, which often share the plot designs of quick passion, inescapable societal pressure leading to the abandonment of romance, followed by a period of
melancholy. Wong states that this scheme lacks the undying vows and total self-commitment to love found in Western romances such as ''
Romeo and Juliet
''Romeo and Juliet'' is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare early in his career about the romance between two Italian youths from feuding families. It was among Shakespeare's most popular plays during his lifetime and, along with ''Ham ...
'', but that underlying traditional Chinese values of inseparableness of self from one's environment (including human society) served to create the necessary fictional device of romantic tension.

There were large
encyclopedia
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles ...
s published in the Tang. The ''
Yiwen Leiju
The ''Yiwen Leiju'' is a Chinese ''leishu'' encyclopedia completed by Ouyang Xun in 624 under the Tang. Its other contributors included Linghu Defen and Chen Shuda.
It is divided into 47 sections and many subsections. It covers a vast number ...
'' encyclopedia was compiled in 624 by the chief editor
Ouyang Xun
Ouyang Xun (; 557–641), courtesy name Xinben (), was a Chinese calligrapher, politician, and writer of the early Tang dynasty. He was born in Hunan, Changsha, to a family of government officials; and died in modern Anhui province.
Achievements ...
(557–641) as well as
Linghu Defen (582–666) and
Chen Shuda (d. 635). The encyclopedia ''
Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era'' was fully compiled in 729 by
Gautama Siddha (fl. 8th century), an ethnic Indian astronomer, astrologer, and scholar born in the capital Chang'an.
Chinese geographers
China has great physical diversity. The eastern plains and southern coasts of the country consist of fertile lowlands and foothills. They are the location of most of China's agricultural output and human population. The southern areas of th ...
such as
Jia Dan wrote accurate descriptions of places far abroad. In his work written between 785 and 805, he described the sea route going into the mouth of the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
, and that the medieval
Iranians (whom he called the people of Luo-He-Yi) had erected 'ornamental pillars' in the sea that acted as
lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses m ...
beacons for ships that might go astray. Confirming Jia's reports about lighthouses in the Persian Gulf, Arabic writers a century after Jia wrote of the same structures, writers such as
al-Mas'udi and
al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
. The Tang dynasty Chinese diplomat
Wang Xuance traveled to
Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was rul ...
(modern northeastern
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
) during the 7th century. Afterwards he wrote the book ''Zhang Tianzhu Guotu'' (Illustrated Accounts of Central India), which included a wealth of geographical information.
Many histories of previous dynasties were compiled between 636 and 659 by court officials during and shortly after the reign of
Emperor Taizong of Tang
Emperor Taizong of Tang (28January 59810July 649), previously Prince of Qin, personal name Li Shimin, was the second emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649. He is traditionally regarded as a co-founder of the dynasty ...
. These included the ''
Book of Liang'', ''
Book of Chen'', ''
Book of Northern Qi'', ''
Book of Zhou'', ''
Book of Sui
The ''Book of Sui'' (''Suí Shū'') is the official history of the Sui dynasty. It ranks among the official Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written by Yan Shigu, Kong Yingda, and Zhangsun Wuji, with Wei Zheng as the lead author. ...
'', ''
Book of Jin
The ''Book of Jin'' is an official Chinese historical text covering the history of the Jin dynasty from 266 to 420. It was compiled in 648 by a number of officials commissioned by the imperial court of the Tang dynasty, with chancellor Fang ...
'', ''
History of Northern Dynasties
The ''History of the Northern Dynasties'' () is one of the official Chinese historical works in the ''Twenty-Four Histories'' canon. The text contains 100 volumes and covers the period from 386 to 618, the histories of Northern Wei, Western We ...
'' and the ''
History of Southern Dynasties''. Although not included in the official ''
Twenty-Four Histories
The ''Twenty-Four Histories'' (), also known as the ''Orthodox Histories'' (), are the Chinese official dynastic histories covering from the earliest dynasty in 3000 BC to the Ming dynasty in the 17th century.
The Han dynasty official Sima Qia ...
'', the ''
Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang Dynasty. The book was written by Du You from 766 ...
'' and ''
Tang Huiyao'' were nonetheless valuable written historical works of the Tang period. The ''
Shitong
The ''Shitong'' () is the first Chinese-language work about historiography compiled by Liu Zhiji between 708 and 710. The book describes the general pattern of the past official dynastic historiography on structure, method, order of arrangement, s ...
'' written by
Liu Zhiji
Liu Zhiji (; 661–721), courtesy name Zixuan (), was a Chinese historian and politician of the Tang dynasty. Well known as the author of ''Shitong'', he was born in present-day Xuzhou, Jiangsu, during the Tang dynasty. Liu's father Liu Zangqi and ...
in 710 was a meta-history, as it covered the history of
Chinese historiography
Chinese historiography is the study of the techniques and sources used by historians to develop the recorded history of China.
Overview of Chinese history
The recording of events in Chinese history dates back to the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 ...
in past centuries until his time. The ''
Great Tang Records on the Western Regions
The ''Great Tang Records on the Western Regions'' is a narrative of Xuanzang's nineteen-year journey from Chang'an in central China to the Western Regions of Chinese historiography. The Buddhist scholar traveled through the Silk Road regions of ...
'', compiled by
Bianji
Bianji (fl. 7th century) was a Buddhist monk who lived in the Tang Dynasty. He was also the translator and author of '' Great Tang Records on the Western Regions''. Little is known about his life, apart from that he translated several Buddhist scr ...
, recounted the journey of
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
, the Tang era's most renowned
Buddhist monk.
Other important literary offerings included
Duan Chengshi
Duan Chengshi () (died 863) was a Chinese poet and writer of the Tang Dynasty. He was born to a wealthy family in present-day Zibo, Shandong. A descendant of the early Tang official Duan Zhixuan (, ''Duàn Zhìxuán'') (-642), and the son of Duan ...
's (d. 863) ''
Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang
The ''Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang'' () is a book written by Duan Chengshi in the 9th century. It focuses on miscellany of Chinese and foreign legends and hearsay, reports on natural phenomena, short anecdotes, and tales of the wondrous a ...
'', an entertaining collection of foreign legends and hearsay, reports on natural phenomena, short
anecdote
An anecdote is "a story with a point", such as to communicate an abstract idea about a person, place, or thing through the concrete details of a short narrative or to characterize by delineating a specific quirk or trait. Occasionally humorous ...
s, mythical and mundane tales, as well as notes on various subjects. The exact literary category or classification that Duan's large informal narrative would fit into is still debated amongst scholars and historians.
Religion and philosophy


Since ancient times, some Chinese had believed in
folk religion
In religious studies and folkloristics, folk religion, popular religion, traditional religion or vernacular religion comprises various forms and expressions of religion that are distinct from the official doctrines and practices of organized re ...
and
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
that incorporated many deities. Practitioners believed the
Tao and the afterlife was a reality parallel to the living world, complete with its own bureaucracy and afterlife currency needed by dead ancestors. Funerary practices included providing the deceased with everything they might need in the afterlife, including animals, servants, entertainers, hunters, homes, and officials. This ideal is reflected in
Tang dynasty art. This is also reflected in many short stories written in the Tang about people accidentally winding up in the realm of the dead, only to come back and report their experiences.
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, originating in India around the time of
Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=Kǒng Fūzǐ, "Master Kǒng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=Kǒngzǐ, labels=no; – ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. C ...
, continued its influence during the Tang period and was accepted by some members of imperial family, becoming thoroughly sinicized and a permanent part of Chinese traditional culture. In an age before
Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lǐxué'' 理學, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, and originated with Han Yu (768–824) and Li Ao (772–841) ...
and figures such as
Zhu Xi
Zhu Xi (; ; October 18, 1130 – April 23, 1200), formerly romanized Chu Hsi, was a Chinese calligrapher, historian, philosopher, poet, and politician during the Song dynasty. Zhu was influential in the development of Neo-Confucianism. He con ...
(1130–1200), Buddhism had begun to flourish in China during the
Northern and Southern dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered a ...
, and became the dominant ideology during the prosperous Tang. Buddhist monasteries played an integral role in Chinese society, offering lodging for travelers in remote areas, schools for children throughout the country, and a place for urban literati to stage social events and gatherings such as going-away parties. Buddhist monasteries were also engaged in the economy, since their land property and serfs gave them enough revenues to set up mills, oil presses, and other enterprises. Although the monasteries retained 'serfs', these monastery dependents could actually own property and employ others to help them in their work, including their own slaves.
The prominent status of Buddhism in Chinese culture began to decline as the dynasty and central government declined as well during the late 8th century to 9th century. Buddhist
convent
A convent is a community of monks, nuns, religious brothers or, sisters or priests. Alternatively, ''convent'' means the building used by the community. The word is particularly used in the Catholic Church, Lutheran churches, and the Angl ...
s and
temples that were exempt from state taxes beforehand were targeted by the state for taxation. In 845
Emperor Wuzong of Tang
Emperor Wuzong of Tang (July 2, 814 – April 22, 846), né Li Chan, later changed to Li Yan just before his death, was an emperor of the Tang Dynasty of China, reigning from 840 to 846. Emperor Wuzong is mainly known in modern times for the r ...
finally shut down 4,600 Buddhist monasteries along with 40,000 temples and shrines, forcing 260,000 Buddhist monks and nuns to return to
secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
life; this episode would later be dubbed one of the
Four Buddhist Persecutions in China
The Four Buddhist Persecutions in China were the wholesale suppression of Buddhism carried out on four occasions from the 5th through the 10th century by four Chinese emperors, during the Northern Wei, Northern Zhou, Tang and Later Zhou dynasties ...
. Although the ban would be lifted just a few years after, Buddhism never regained its once dominant status in Chinese culture. This situation also came about through a revival of interest in native Chinese philosophies such as Confucianism and Taoism.
Han Yu
Han Yu (; 76825 December 824), courtesy name Tuizhi (), and commonly known by his posthumous name Han Wengong (韓文公), was a Chinese essayist, poet, philosopher, and politician during the Tang dynasty who significantly influenced the devel ...
(786–824)—who
Arthur F. Wright stated was a "brilliant
polemicist
Polemic () is contentious rhetoric intended to support a specific position by forthright claims and to undermine the opposing position. The practice of such argumentation is called ''polemics'', which are seen in arguments on controversial topic ...
and ardent
xenophobe"—was one of the first men of the Tang to denounce Buddhism. Although his contemporaries found him crude and obnoxious, he would foreshadow the later persecution of Buddhism in the Tang, as well as the revival of Confucian theory with the rise of Neo-Confucianism of the Song dynasty. Nonetheless,
Chán Buddhism gained popularity amongst the educated elite. There were also many famous Chan monks from the Tang era, such as
Mazu Daoyi
Mazu Daoyi (709–788) (, Japanese: Baso Dōitsu) was an influential abbot of Chan Buddhism during the Tang dynasty. The earliest recorded use of the term "Chan school" is from his ''Extensive Records''. Master Ma's teaching style of "strange wo ...
,
Baizhang, and
Huangbo Xiyun
Huángbò Xīyùn (, ja, Ōbaku Kiun) (died 850) was an influential master of Zen Buddhism during the Tang dynasty.
Huángbò was a disciple of Baizhang Huaihai (720–840), and the teacher of Linji Yixuan (died 866) (Wade–Giles: Lin-chi I- ...
. The sect of
Pure Land Buddhism
Pure Land Buddhism (; ja, 浄土仏教, translit=Jōdo bukkyō; , also referred to as Amidism in English,) is a broad branch of Mahayana Buddhism focused on achieving rebirth in a Buddha's Buddha-field or Pure Land. It is one of the most wid ...
initiated by the Chinese monk
Huiyuan (334–416) was also just as popular as Chan Buddhism during the Tang.

Rivaling Buddhism was Taoism, a native Chinese philosophical and religious belief system that found its roots in the ''
Tao Te Ching
The ''Tao Te Ching'' (, ; ) is a Chinese classic text written around 400 BC and traditionally credited to the sage Laozi, though the text's authorship, date of composition and date of compilation are debated. The oldest excavated portion ...
'' (a text attributed to a 6th-century BC figure named
Lao Tzu
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state ...
) and the ''
Zhuangzi''. The ruling Li family of the Tang dynasty actually claimed descent from the ancient Lao Tzu. On numerous occasions where Tang princes would become crown prince or Tang princesses taking vows as Taoist priestesses, their lavish former mansions would be converted into Taoist
abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns.
The c ...
s and places of worship. Many Taoists were associated with
alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim wo ...
in their pursuits to find an
elixir of immortality
The elixir of life, also known as elixir of immortality, is a potion that supposedly grants the drinker eternal life and/or eternal youth. This elixir was also said to cure all diseases. Alchemists in various ages and cultures sought the means ...
and a means to create gold from concocted mixtures of many other elements. Although they never achieved their goals in either of these futile pursuits, they did contribute to the discovery of new metal alloys, porcelain products, and new dyes. The historian Joseph Needham labeled the work of the Taoist alchemists as "protoscience rather than pseudoscience." However, the close connection between Taoism and alchemy, which some
sinologists
Sinology, or Chinese studies, is an academic discipline that focuses on the study of China primarily through Chinese philosophy, language, literature, culture and history and often refers to Western scholarship. Its origin "may be traced to the ex ...
have asserted, is refuted by
Nathan Sivin
Nathan Sivin (11 May 1931 – 24 June 2022), also known as Xiwen (), was an American sinologist, historian, essayist, educator, and writer. He taught first at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, then at the University of Pennsylvania until his r ...
, who states that alchemy was just as prominent (if not more so) in the secular sphere and practiced more often by laymen.
The Tang dynasty also officially recognized various foreign religions. The
Assyrian Church of the East
The Assyrian Church of the East,, ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية sometimes called Church of the East, officially the Holy Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East,; ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية الرسول� ...
, otherwise known as the
Nestorian Church
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
or the
Church of the East in China
The Church of the East (also known as the Nestorian Church) historically had a presence in China during two periods: first from the 7th through the 10th century in the Tang dynasty, when it was known as ''Jingjiao'' ( zh, t=景教, w=Ching3-chiao4 ...
, was given recognition by the Tang court. In 781, the
Nestorian Stele was created in order to honor the achievements of their community in China. A Christian monastery was established in Shaanxi province where the
Daqin Pagoda still stands, and inside the pagoda there is Christian-themed artwork. Although the religion largely died out after the Tang, it was revived in China following the
Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation ...
of the 13th century.
Although the
Sogdia
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Emp ...
ns had been responsible for transmitting Buddhism to China from India during the 2nd to 4th centuries, soon afterwards they largely converted to
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
due to their links to
Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
Persia. Sogdian merchants and their families living in cities such as Chang'an, Luoyang, and Xiangyang usually built a Zoroastrian temple once their local communities grew larger than 100 households. Sogdians were also responsible for spreading
Manicheism
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani (AD ...
in Tang China and the
Uighur Khaganate. The Uighurs built the first Manichean monastery in China in 768, yet in 843 the Tang government ordered that the property of all Manichean monasteries be confiscated in response to the outbreak of war with the Uighurs. With the blanket ban on foreign religions two years later, Manicheism was driven underground and never flourished in China again.
Leisure
Much more than earlier periods, the Tang era was renowned for the time reserved for leisure activity, especially for those in the upper classes. Many outdoor sports and activities were enjoyed during the Tang, including
archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In ...
, hunting, horse
polo
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small ha ...
,
cuju
''Cuju'' or ''Ts'u-chü'' (蹴鞠) is an ancient Chinese football game. Cuju is the earliest known recorded game of football. It is a competitive game that involves kicking a ball through an opening into a net without the use of hands. Descripti ...
(soccer),
cockfighting
A cockfight is a blood sport, held in a ring called a cockpit. The history of raising fowl for fighting goes back 6,000 years. The first documented use of the ''word'' gamecock, denoting use of the cock as to a "game", a sport, pastime or ente ...
, and even
tug of war
Tug of war (also known as tug o' war, tug war, rope war, rope pulling, or tugging war) is a sport that pits two teams against each other in a test of strength: teams pull on opposite ends of a rope, with the goal being to bring the rope a certa ...
. Government officials were granted
vacations during their tenure in office. Officials were granted 30 days off every three years to visit their parents if they lived away, or 15 days off if the parents lived more than away (travel time not included). Officials were granted nine days of vacation time for weddings of a son or daughter, and either five, three, or one days/day off for the
nuptials of close relatives (travel time not included). Officials also received a total of three days off for their son's capping initiation rite into manhood, and one day off for the ceremony of initiation rite of a close relative's son.

Traditional Chinese holidays
The traditional Chinese holidays are an essential part of harvests or prayer offerings. The most important Chinese holiday is the Chinese New Year (Spring Festival), which is also celebrated in overseas ethnic Chinese communities (for example in ...
such as
Chinese New Year
Chinese New Year is the festival that celebrates the beginning of a new year on the traditional lunisolar and solar Chinese calendar. In Chinese and other East Asian cultures, the festival is commonly referred to as the Spring Festival () a ...
,
Lantern Festival
The Lantern Festival ( zh, t=元宵節, s=元宵节, first=t, hp=Yuánxiāo jié), also called Shangyuan Festival ( zh, t=上元節, s=上元节, first=t, hp=Shàngyuán jié), is a Chinese traditional festival celebrated on the fifteenth d ...
,
Cold Food Festival
The Cold Food or Hanshi Festival is a traditional Chinese holiday which developed from the local commemoration of the death of the Jin nobleman Jie Zitui in the 7thcenturyBC under the Zhou dynasty, into an occasion across East Asia for the com ...
, and others were universal holidays. In the capital city of
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
there was always lively celebration, especially for the
Lantern Festival
The Lantern Festival ( zh, t=元宵節, s=元宵节, first=t, hp=Yuánxiāo jié), also called Shangyuan Festival ( zh, t=上元節, s=上元节, first=t, hp=Shàngyuán jié), is a Chinese traditional festival celebrated on the fifteenth d ...
since the city's nighttime
curfew
A curfew is a government order specifying a time during which certain regulations apply. Typically, curfews order all people affected by them to ''not'' be in public places or on roads within a certain time frame, typically in the evening and ...
was lifted by the government for three days straight. Between the years 628 and 758, the imperial throne bestowed a total of sixty-nine grand
carnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival t ...
s nationwide, granted by the emperor in the case of special circumstances such as important military victories, abundant
harvest
Harvesting is the process of gathering a ripe crop from the fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most l ...
s after a long
drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
or
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
, the granting of
amnesties, the installment of a new
crown prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the w ...
, etc. For special celebration in the Tang era, lavish and gargantuan-sized feasts were sometimes prepared, as the imperial court had staffed agencies to prepare the meals. This included a prepared feast for 1,100 elders of Chang'an in 664, a feast for 3,500 officers of the Divine Strategy Army in 768, and a feast for 1,200 women of the palace and members of the imperial family in the year 826. Drinking wine and alcoholic beverages was heavily ingrained into Chinese culture, as people drank for nearly every social event. A court official in the 8th century allegedly had a serpentine-shaped structure called the 'Ale Grotto' built with 50,000 bricks on the groundfloor that each featured a bowl from which his friends could drink.
Status in clothing
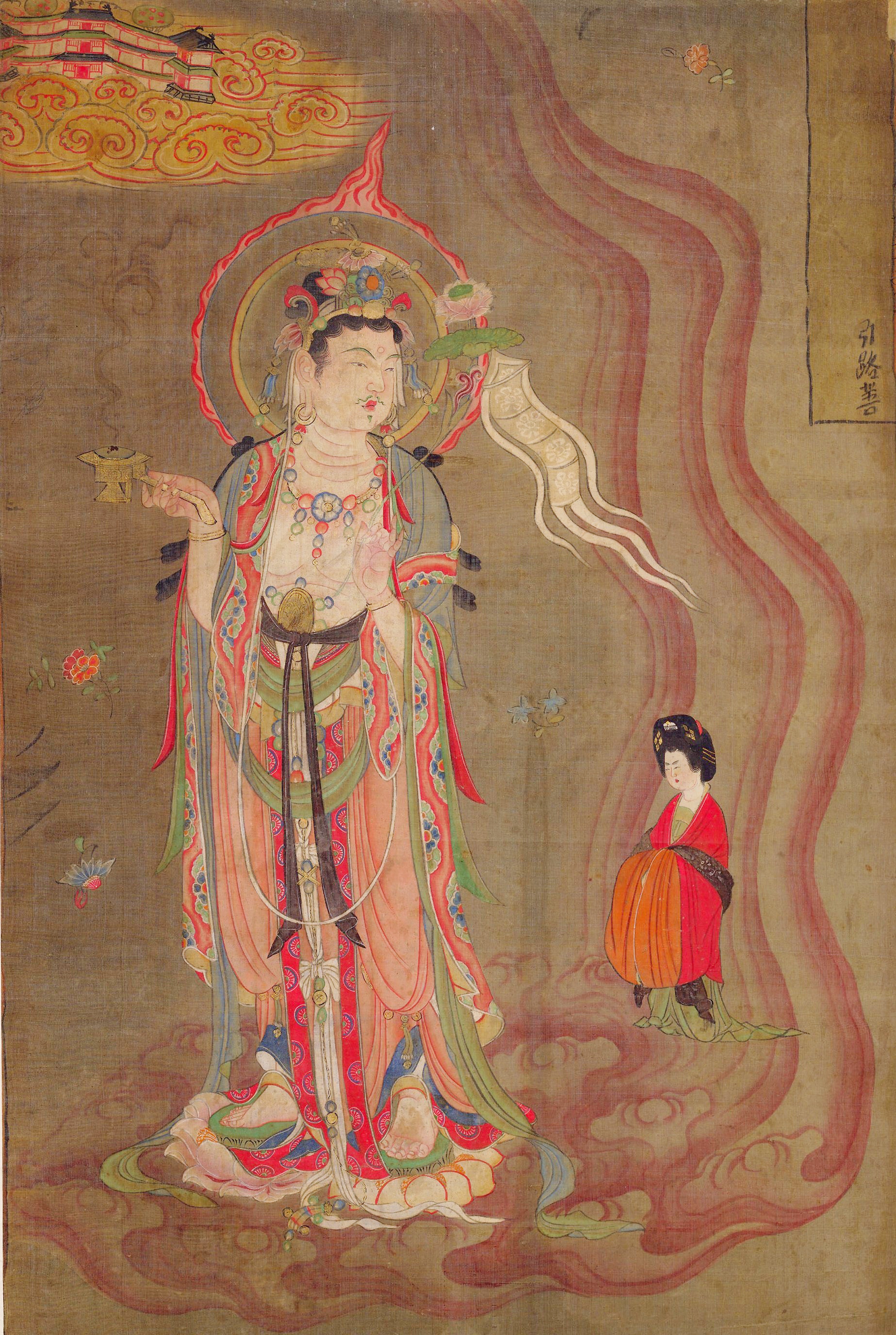

In general, garments were made from silk, wool, or linen depending on your social status and what you could afford. Furthermore, there were laws that specified what kinds of clothing could be worn by whom. The color of the clothing also indicated rank. During this period, China's power, culture, economy, and influence were thriving. As a result, women could afford to wear loose-fitting, wide-sleeved garments. Even lower-class women's robes would have sleeves four to five feet in width.
Position of women

Concepts of women's social rights and social status during the Tang era were notably liberal-minded for the period. However, this was largely reserved for urban women of elite status, as men and women in the rural countryside labored hard in their different set of tasks; with wives and daughters responsible for more domestic tasks of weaving textiles and rearing of
silk worms, while men tended to farming in the fields.
There were many women in the Tang era who gained access to religious authority by taking vows as Taoist priestesses. The head mistresses of high-class
courtesan
Courtesan, in modern usage, is a euphemism for a "kept" mistress or prostitute, particularly one with wealthy, powerful, or influential clients. The term historically referred to a courtier, a person who attended the court of a monarch or othe ...
s in the
North Hamlet of the capital Chang'an acquired large amounts of wealth and power. Such
courtesan
Courtesan, in modern usage, is a euphemism for a "kept" mistress or prostitute, particularly one with wealthy, powerful, or influential clients. The term historically referred to a courtier, a person who attended the court of a monarch or othe ...
s, who likely influenced the Japanese
geisha
{{Culture of Japan, Traditions, Geisha
{{nihongo, Geisha, 芸者 ({{IPAc-en, ˈ, ɡ, eɪ, ʃ, ə; {{IPA-ja, ɡeːɕa, lang), also known as {{nihongo, , 芸子, geiko (in Kyoto and Kanazawa) or {{nihongo, , 芸妓, geigi, are a class of female J ...
s, were well respected. These courtesans were known as great singers and poets, supervised banquets and feasts, knew the rules to all the
drinking game
Drinking games are games which involve the consumption of alcoholic beverages and often enduring the subsequent intoxication resulting from them. Evidence of the existence of drinking games dates back to antiquity. Drinking games have been banned ...
s, and were trained to have the utmost respectable
table manners.
Although they were renowned for their polite behavior, the courtesans were known to dominate the conversation among elite men, and were not afraid to openly castigate or criticize prominent male guests who talked too much or too loudly, boasted too much of their accomplishments, or had in some way ruined dinner for everyone by rude behavior (on one occasion a courtesan even beat up a drunken man who had insulted her). When singing to entertain guests, courtesans not only composed the lyrics to their own songs, but they popularized a new form of lyrical verse by singing lines written by various renowned and famous men in Chinese history.
It was fashionable for women to be full-figured (or plump). Men enjoyed the presence of assertive, active women. The foreign horse-riding sport of
polo
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small ha ...
from Persia became a wildly popular trend among the Chinese elite, and women often played the sport (as glazed
earthenware
Earthenware is glazed or unglazed nonvitreous pottery that has normally been fired below . Basic earthenware, often called terracotta, absorbs liquids such as water. However, earthenware can be made impervious to liquids by coating it with a c ...
figurines from the time period portray). The preferred hairstyle for women was to bunch their hair up like "an elaborate edifice above the forehead", while affluent ladies wore extravagant head ornaments, combs, pearl necklaces, face powders, and perfumes. A law was passed in 671 which attempted to force women to wear hats with veils again in order to promote decency, but these laws were ignored as some women started wearing caps and even no hats at all, as well as men's riding clothes and boots, and tight-sleeved bodices.
There were some prominent court women after the era of
Empress Wu, such as
Yang Guifei
Yang Yuhuan (; 26 June, 719 – 15 July 756Volume 218 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' recorded that Yang was killed on the ''bingshen'' day of the 6th month of the 1st year of the Zhide era of Tang Suzong's reign. This date corresponds to 15 Jul 756 on t ...
(719–756), who had Emperor Xuanzong appoint many of her relatives and cronies to important ministerial and martial positions.
Cuisine
During the earlier
Northern and Southern dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered a ...
(420–589), and perhaps even earlier, the drinking of tea (''
Camellia sinensis
''Camellia sinensis'' is a species of evergreen shrub or small tree in the flowering plant family Theaceae. Its leaves and leaf buds are used to produce the popular beverage, tea. Common names include tea plant, tea shrub, and tea tree (not t ...
'') became popular in southern China. Tea was viewed then as a beverage of tasteful pleasure and with pharmacological purpose as well. During the Tang dynasty, tea became synonymous with everything sophisticated in society. The poet
Lu Tong (790–835) devoted most of his poetry to his love of tea. The 8th-century author
Lu Yu (known as the Sage of Tea) even wrote a treatise on the art of drinking tea, called ''
The Classic of Tea
''The Classic of Tea'' or ''Tea Classic'' () is the first known monograph on tea in the world, by Chinese writer Lu Yu between 760 CE and 762 CE, during the Tang dynasty. Lu Yu's original manuscript is lost; the earliest editions available date ...
''. Although
wrapping paper
Gift wrapping is the act of enclosing a gift in some sort of material. Wrapping paper is a kind of paper designed for gift wrapping. An alternative to gift wrapping is using a gift box or bag. A wrapped or boxed gift may be held closed with ri ...
had been used in China since the 2nd century BC, during the Tang dynasty the Chinese were using wrapping paper as folded and sewn square bags to hold and preserve the flavor of tea leaves. This followed many other uses for paper such as the first recorded use of
toilet paper
Toilet paper (sometimes called toilet tissue or bathroom tissue) is a tissue paper product primarily used to clean the anus and surrounding anal region of feces after defecation, and to clean the perineal area and external genitalia of ur ...
made in 589 by the scholar-official
Yan Zhitui (531–591), confirmed in 851 by an Arab traveler who remarked that Tang Chinese lacked cleanliness because they relied on toilet paper instead of washing themselves with water.
In ancient times, the Chinese had outlined the five most basic foodstuffs known as the five grains:
sesamum,
legume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock for ...
s, wheat,
panicle
A panicle is a much-branched inflorescence. (softcover ). Some authors distinguish it from a compound spike inflorescence, by requiring that the flowers (and fruit) be pedicellate (having a single stem per flower). The branches of a panicle are of ...
d
millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets a ...
, and
glutinous millet. The
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
encyclopedist Song Yingxing
Song Yingxing (Traditional Chinese: 宋應星; Simplified Chinese: 宋应星; Wade Giles: Sung Ying-Hsing; 1587-1666 AD) was a Chinese scientist and encyclopedist who lived during the late Ming Dynasty (1368–1644). He was the author of ''Tian ...
(1587–1666) noted that rice was not counted amongst the five grains from the time of the legendary and deified Chinese sage
Shennong
Shennong (), variously translated as "Divine Farmer" or "Divine Husbandman", born Jiang Shinian (), was a mythological Chinese ruler known as the first Yan Emperor who has become a deity in Chinese and Vietnamese folk religion. He is vene ...
(the existence of whom Yingxing wrote was "an uncertain matter") into the 2nd millenniums BC, because the properly wet and humid climate in southern China for growing rice was not yet fully settled or cultivated by the Chinese. Song Yingxing also noted that in the Ming dynasty, seven tenths of civilians' food was rice. During the Tang dynasty rice was not only the most important staple in southern China, but had also become popular in the north where central authority resided.
During the Tang dynasty, wheat replaced the position of millet and became the main staple crop. As a consequence, wheat cake shared a considerable amount in the staple of Tang. There were four main kinds of cake: steamed cake, boiled cake, pancake, and Hu cake. Steamed cake was consumed commonly by both civilians and aristocrats. Like ''
rougamo'' in modern Chinese cuisine, steamed cake was usually stuffed with meat and vegetables. Shops and packmen regularly sold inexpensive steamed cake on the streets of Chang’an.
Boiled cake was the staple of the Northern Dynasties, and it kept its popularity in the Tang dynasty. It included a wide variety of dishes similar to modern
wonton
A wonton () is a type of Chinese dumpling commonly found across regional styles of Chinese cuisine. It is also spelled wantan or wuntun in transliteration from Cantonese () and wenden from Shanghainese (). There are many different styles o ...
, noodles, and many other kinds of food that soak wheat in water. While aristocrats favored wonton, civilians usually consumed noodles and noodle slice soup that were easier to produce. Pancakes was rare in China before the Tang, when it gained popularity. Food shops in Tang cities such as Chang'an commonly sold both pancakes and
dumpling
Dumpling is a broad class of dishes that consist of pieces of dough (made from a variety of starch sources), oftentimes wrapped around a filling. The dough can be based on bread, flour, buckwheat or potatoes, and may be filled with meat, ...
s.
Hu cake, which means "foreign cake", was extremely popular during the Tang. Hu cake was toasted in the oven, covered with
sesame seed
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus '' Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cu ...
s, and served at taverns, inns and shops. Japanese Buddhist monk Ennin observed that Hu cake was popular among all of China's civilians.
During the Tang, the many common foodstuffs and cooking ingredients in addition to those already listed were barley, garlic, salt, turnips, soybeans, pears, apricots, peaches, apples, pomegranates, jujubes, rhubarb, hazelnuts, pine nuts, chestnuts, walnuts, yams, taro, etc. The various meats that were consumed included pork, chicken,
lamb (especially preferred in the north),
sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smal ...
, bear (which was hard to catch, but there were recipes for steamed, boiled, and
marinated
Marinating is the process of soaking foods in a seasoned, often acidic, liquid before cooking. The origin of the word alludes to the use of brine (''aqua marina'' or sea water) in the pickling process, which led to the technique of adding flavor b ...
bear), and even
Bactrian camel
The Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''), also known as the Mongolian camel or domestic Bactrian camel, is a large even-toed ungulate native to the steppes of Central Asia. It has two humps on its back, in contrast to the single-humped dro ...
s. In the south along the coast meat from seafood was by default the most common, as the Chinese enjoyed eating cooked
jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbre ...
with
cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus '' Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakf ...
,
Sichuan pepper,
cardamom
Cardamom (), sometimes cardamon or cardamum, is a spice made from the seeds of several plants in the genera '' Elettaria'' and '' Amomum'' in the family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to the Indian subcontinent and Indonesia. They ar ...
, and
ginger
Ginger (''Zingiber officinale'') is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or ginger, is widely used as a spice and a folk medicine. It is a herbaceous perennial which grows annual pseudostems (false stems made of the rolled bases of ...
, as well as
oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not ...
s with wine, fried
squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fittin ...
with ginger and vinegar,
horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to ar ...
s and
red swimming crabs,
shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are ref ...
and
pufferfish
Tetraodontidae is a family of primarily marine and estuarine fish of the order Tetraodontiformes. The family includes many familiar species variously called pufferfish, puffers, balloonfish, blowfish, blowies, bubblefish, globefish, swellfis ...
, which the Chinese called "river piglet".
From the trade overseas and over land, the Chinese acquired peaches from
Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, date palms, pistachios, and figs from
Greater Iran
Greater Iran ( fa, ایران بزرگ, translit=Irān-e Bozorg) refers to a region covering parts of Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Xinjiang, and the Caucasus, where both Iranian culture and Iranian languages have had a s ...
,
pine nut
Pine nuts, also called piñón (), pinoli (), pignoli or chilgoza (), are the edible seeds of pines (family Pinaceae, genus ''Pinus''). According to the Food and Agriculture Organization, only 29 species provide edible nuts, while 20 are trad ...
s and
ginseng
Ginseng () is the root of plants in the genus '' Panax'', such as Korean ginseng ('' P. ginseng''), South China ginseng ('' P. notoginseng''), and American ginseng ('' P. quinquefolius''), typically characterized by the presence of ginsenosides ...
roots from
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
and
mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It is believed to have originated in the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in Sout ...
es from
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
. In China, there was a great demand for sugar; during the reign of
Harsha
Harshavardhana ( IAST Harṣa-vardhana; c. 590–647 CE) was a Pushyabhuti emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 CE. He was the son of Prabhakaravardhana who had defeated the Alchon Huna invaders, and the younger brother of Rajy ...
over
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
(r. 606–647), Indian envoys to the Tang brought two makers of sugar who successfully taught the Chinese how to cultivate sugarcane. Cotton also came from India as a finished product from Bengal, although it was during the Tang that the Chinese began to grow and process cotton, and by the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
it became the prime textile fabric in China.
Some foods were also food taboo, off-limits, as the Tang court encouraged people beef taboo#China, not to eat beef. This was due to the role of the bull as a valuable working animal. From 831 to 833 Emperor Wenzong of Tang even banned the slaughter of cattle on the grounds of his religious convictions to
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
.
Methods of food preservation were important, and practiced throughout China. The common people used simple methods of preservation, such as digging deep ditches and trenches, brining, and salting their foods. The emperor had large ice pits located in the parks in and around Chang'an for preserving food, while the wealthy and elite had their own smaller ice pits. Each year the emperor had laborers carve 1000 blocks of ice from frozen creeks in mountain valleys, each block with the dimension of by 3 ft by . Frozen delicacies such as chilled melon were enjoyed during the summer.
File:鸳鸯莲瓣纹金碗 20091112.jpg, Tang era gilding, gilt-gold bowl with lotus and animal motifs
File:Plat à offrandes Chine Musée Guimet 2418 3.jpg, A Tang sancai-glazed lobed dish with incised decorations, 8th century
File:Dame Chine Guimet 291003.jpg, Tang dynasty tomb figures, Tomb figure of a lady attendant, 7th- to 8th-century; during the Tang era, female hosts prepared feasts, tea parties, and played drinking games with their guests.
File:Plat à offrandes Chine Musée Guimet 2418 1.jpg, A rounded "offering plate" with design in "three colors" (sancai) glaze, 8th-century
File:Chajing.jpeg, A page of Lu Yu's ''The Classic of Tea
''The Classic of Tea'' or ''Tea Classic'' () is the first known monograph on tea in the world, by Chinese writer Lu Yu between 760 CE and 762 CE, during the Tang dynasty. Lu Yu's original manuscript is lost; the earliest editions available date ...
''
Science and technology
Engineering

Technology during the Tang period was built also upon the precedents of the past. Previous advancements in clockworks and timekeeping included the mechanical gear systems of Zhang Heng (78–139) and Ma Jun (mechanical engineer), Ma Jun (fl. 3rd century), which gave the Tang mathematician, mechanical engineer, astronomer, and monk Yi Xing (683–727) inspiration when he invented the world's first clockwork escapement mechanism in 725. This was used alongside a Water clock, clepsydra clock and waterwheel to power a rotating armillary sphere in representation of astronomical observation. Yi Xing's device also had a mechanically timed bell that was struck automatically every hour, and a drum that was struck automatically every quarter-hour; essentially, a striking clock. Yi Xing's astronomical clock and water-powered armillary sphere became well known throughout the country, since students attempting to pass the imperial examinations by 730 had to write an essay on the device as an exam requirement. However, the most common type of public and palace timekeeping device was the inflow clepsydra. Its design was improved c. 610 by the Sui-dynasty engineers Geng Xun and Yuwen Kai. They provided a steelyard balance that allowed seasonal adjustment in the pressure head of the compensating tank and could then control the rate of flow for different lengths of day and night.
There were many other mechanical inventions during the Tang era. These included a 3 ft (0.91 m) tall mechanical wine server of the early 8th century that was in the shape of an artificial mountain, carved out of iron and rested on a lacquered-wooden tortoise frame. This intricate device used a hydraulic pump that siphoned wine out of metal Chinese dragon, dragon-headed faucets, as well as tilting bowls that were timed to dip wine down, by force of gravity when filled, into an artificial lake that had intricate iron leaves popping up as trays for placing party treats. Furthermore, as the historian Charles Benn describes it:
Yet the use of a teasing mechanical puppet in this wine-serving device wasn't exactly a novel invention of the Tang, since the use of mechanical puppets in China date back to the Qin dynasty (221–207 BC). In the 3rd century Ma Jun (mechanical engineer), Ma Jun had an entire mechanical puppet theater operated by the rotation of a waterwheel. There was also an automatic wine-server known in the ancient Greco-Roman world, a design of the Greek inventor Heron of Alexandria that employed an urn with an inner valve and a lever device similar to the one described above. There are many stories of automatons used in the Tang, including general Yang Wulian's wooden statue of a monk who stretched his hands out to collect contributions; when the number of coins reached a certain weight, the mechanical figure moved his arms to deposit them in a satchel. This weight-and-lever mechanism was exactly like Heron's penny slot machine. Other devices included one by Wang Ju, whose "wooden otter" could allegedly catch fish; Needham suspects a Spring (device), spring trap of some kind was employed here.
In the realm of structural engineering and technical Chinese architecture, there were also government standard building codes, outlined in the early Tang book of the ''Yingshan Ling'' (National Building Law). Fragments of this book have survived in the ''Tang Lü'' (The Tang Code), while the Song dynasty architectural manual of the ''Yingzao Fashi'' (State Building Standards) by Architecture of the Song dynasty#Literature, Li Jie (1065–1101) in 1103 is the oldest existing technical treatise on Chinese architecture that has survived in full. During the reign of Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (712–756) there were 34,850 registered Artisan, craftsmen serving the state, managed by the Agency of Palace Buildings (Jingzuo Jian).
Woodblock printing

Woodblock printing made the written word available to vastly greater audiences. One of the world's oldest surviving printed documents is a miniature Buddhist ''dharani'' sutra unearthed at Xi'an in 1974 and dated roughly from 650 to 670. The ''Diamond Sutra'' is the first full-length book printed at regular size, complete with illustrations embedded with the text and dated precisely to 868. Among the earliest documents to be printed were Buddhist texts as well as calendars, the latter essential for calculating and marking which days were auspicious and which days were not. With so many books coming into circulation for the general public, literacy rates could improve, along with the lower classes being able to obtain cheaper sources of study. Therefore, there were more lower-class people seen entering the Imperial Examinations and passing them by the later Song dynasty. Although the later Bi Sheng's movable type
printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
in the 11th century was innovative for his period, woodblock printing that became widespread in the Tang would remain the dominant History of typography in East Asia, printing type in China until the more advanced printing press from Europe became widely accepted and used in East Asia. The first use of the playing card during the Tang dynasty was an auxiliary invention of the new age of printing.
Cartography

In the realm of cartography, there were further advances beyond the map-makers of the Han dynasty. When the Tang chancellor Pei Ju (547–627) was working for the Sui dynasty as a Commercial Commissioner in 605, he created a well-known gridded map with a Scale (map), graduated scale in the tradition of Pei Xiu (224–271). The Tang chancellor Xu Jingzong (592–672) was also known for his map of China drawn in the year 658. In the year 785 the Emperor Dezong of Tang, Emperor Dezong had the geographer and cartographer
Jia Dan (730–805) complete a map of China and her former colonies in Central Asia. Upon its completion in 801, the map was 9.1 m (30 ft) in length and 10 m (33 ft) in height, mapped out on a grid scale of one inch equaling one hundred ''li (unit), li'' (Chinese unit of measuring distance). A Chinese map of 1137 is similar in complexity to the one made by Jia Dan, carved on a stone stele with a grid scale of 100 li. However, the only type of map that has survived from the Tang period are star charts. Despite this, Chinese cartography, the earliest extant terrain maps of China come from the ancient Qin (state), State of Qin; maps from the 4th century BC that were excavated in 1986.
Medicine
The Chinese of the Tang era were also very interested in the benefits of officially classifying all of the Traditional Chinese medicine, medicines used in pharmacology. In 657, Emperor Gaozong of Tang (r. 649–683) commissioned the literary project of publishing an official ''materia medica'', complete with text and illustrated drawings for 833 different medicinal substances taken from different stones, minerals, metals, History of opium in China, plants, herbs, animals, vegetables, fruits, and cereal crops. In addition to compiling pharmacopeias, the Tang fostered learning in medicine by upholding imperial medical colleges, state examinations for doctors, and publishing forensic manuals for physicians. Authors of medicine in the Tang include Zhen Chuan (d. 643) and Sun Simiao (581–682), the former who first identified in writing that patients with diabetes had an excess of sugar in their urine, and the latter who was the first to recognize that diabetic patients should avoid consuming alcohol and starchy foods. As written by Zhen Chuan and others in the Tang, the thyroid glands of sheep and pigs were successfully used to treat goiters; thyroid extracts were not used to treat patients with goiter in the West until 1890. The use of the Amalgam (dentistry), dental amalgam, manufactured from tin and silver, was first introduced in the medical text ''Xinxiu bencao'' written by Su Gong in 659.
Alchemy, gas cylinders, and air conditioning
Chinese scientists of the Tang period employed complex chemical formulas for an array of different purposes, often found through experiments of
alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim wo ...
. These included a waterproof and dust-repelling cream or varnish for clothes and weapons, fireproof cement for glass and porcelain wares, a waterproof cream applied to silk clothes of underwater diving, underwater divers, a cream designated for polishing bronze mirrors, and many other useful formulas. The vitrified, translucent ceramic known as
porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
was invented in China during the Tang, although many types of glazed ceramics preceded it.
Ever since the
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(202 BC – 220 AD), the Chinese had drilled deep boreholes to transport natural gas from Pipeline transport, bamboo pipelines to stoves where cast iron evaporation pans boiled brine to extract salt. During the Tang dynasty, a gazetteer of Sichuan province stated that at one of these 182 m (600 ft) 'fire wells', men collected natural gas into portable bamboo tubes which could be carried around for dozens of km (mi) and still produce a flame. These were essentially the first gas cylinders; Robert Temple assumes Tap (valve), some sort of tap was used for this device.
The inventor Ding Huan (floruit, fl. 180 AD) of the Han dynasty invented a Fan (mechanical), rotary fan for air conditioning, with seven wheels 3 m (10 ft) in diameter and manually powered. In 747,
Emperor Xuanzong had a "Cool Hall" built in the imperial palace, which the ''Tang Yulin'' () describes as having water-powered fan wheels for air conditioning as well as rising jet streams of water from fountains. During the subsequent Song dynasty, written sources mentioned the air conditioning rotary fan as even more widely used.
Historiography
The first classic work about the Tang is the ''
Old Book of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingd ...
'' by Liu Xu (887–946) et al. of the
Later Jin, who redacted it during the last years of his life. This was edited into another history (labeled the ''
New Book of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the So ...
'') in order to distinguish it, which was a work by the Song historians Ouyang Xiu (1007–1072), Song Qi (998–1061), et al. of the Song dynasty (between the years 1044 and 1060). Both of them were based upon earlier annals, yet those are now lost.
Both of them also rank among the ''
Twenty-Four Histories
The ''Twenty-Four Histories'' (), also known as the ''Orthodox Histories'' (), are the Chinese official dynastic histories covering from the earliest dynasty in 3000 BC to the Ming dynasty in the 17th century.
The Han dynasty official Sima Qia ...
'' of China. One of the surviving sources of the ''Old Book of Tang'', primarily covering up to 756, is the ''
Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang Dynasty. The book was written by Du You from 766 ...
'', which Du You presented to the emperor in 801. The Tang period was again placed into the enormous universal history text of the ''
Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynast ...
'', edited, compiled, and completed in 1084 by a team of scholars under the Song dynasty Chancellor Sima Guang (1019–1086). This historical text, written with three million Chinese characters in 294 volumes, covered the history of China from the beginning of the Warring States (403 BC) until the beginning of the Song dynasty (960).
Notes
References
Citations
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* (paperback).
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
excerpt
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
External links
at the Metropolitan Museum of Art
University of Virginia
Tang art with video commentary from the Minneapolis Institute of Arts
* ''
Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynast ...
'', vols. :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷182, 182, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷183, 183, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷184, 184, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷185, 185, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷186, 186, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷187, 187, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷188, 188, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷189, 189, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷190, 190, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷191, 191, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷192, 192, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷193, 193, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷194, 194, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷195, 195, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷196, 196, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷197, 197, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷198, 198, :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷199, 199.
{{authority control
Tang dynasty,
7th-century establishments in China
7th century in China
8th century in China
9th century in China
10th-century disestablishments in China
10th century in China
618 establishments
907 disestablishments
Dynasties in Chinese history
Former countries in Chinese history
Imperial China
Medieval Asia
States and territories disestablished in 907
States and territories established in the 610s
 The Li family had ethnic Han origins, and it belonged to the northwest military aristocracy prevalent during the
The Li family had ethnic Han origins, and it belonged to the northwest military aristocracy prevalent during the  Li Yuan, the founder of the Tang dynasty, was Duke of Tang and governor of
Li Yuan, the founder of the Tang dynasty, was Duke of Tang and governor of  The Tang Empire was at its height of power up until the middle of the 8th century, when the
The Tang Empire was at its height of power up until the middle of the 8th century, when the  Although these natural calamities and rebellions stained the reputation and hampered the effectiveness of the central government, the early 9th century is nonetheless viewed as a period of recovery for the Tang dynasty. The government's withdrawal from its role in managing the economy had the unintended effect of stimulating trade, as more markets with fewer bureaucratic restrictions were opened up. By 780, the old grain tax and labor service of the 7th century was replaced by a semiannual tax paid in cash, signifying the shift to a money economy boosted by the merchant class. Cities in the
Although these natural calamities and rebellions stained the reputation and hampered the effectiveness of the central government, the early 9th century is nonetheless viewed as a period of recovery for the Tang dynasty. The government's withdrawal from its role in managing the economy had the unintended effect of stimulating trade, as more markets with fewer bureaucratic restrictions were opened up. By 780, the old grain tax and labor service of the 7th century was replaced by a semiannual tax paid in cash, signifying the shift to a money economy boosted by the merchant class. Cities in the  However, the Tang did manage to restore at least indirect control over former Tang territories as far west as the
However, the Tang did manage to restore at least indirect control over former Tang territories as far west as the  Taizong set out to solve internal problems within the government which had constantly plagued past dynasties. Building upon the Sui
Taizong set out to solve internal problems within the government which had constantly plagued past dynasties. Building upon the Sui  The Tang Code was largely retained by later codes such as the early
The Tang Code was largely retained by later codes such as the early  Students of
Students of 

 Although they were formerly enemies, the Tang accepted officials and generals of Goguryeo into their administration and military, such as the brothers
Although they were formerly enemies, the Tang accepted officials and generals of Goguryeo into their administration and military, such as the brothers  The Sui and Tang carried out successful military campaigns against the steppe nomads. Chinese foreign policy to the north and west now had to deal with Turkic nomads, who were becoming the most dominant ethnic group in Central Asia. To handle and avoid any threats posed by the Turks, the Sui government repaired fortifications and received their trade and tribute missions. They sent four royal princesses to form marriage alliances with Turkic clan leaders, in 597, 599, 614, and 617. The Sui stirred trouble and conflict amongst ethnic groups against the Turks. As early as the Sui dynasty, the Turks had become a major militarized force employed by the Chinese. When the
The Sui and Tang carried out successful military campaigns against the steppe nomads. Chinese foreign policy to the north and west now had to deal with Turkic nomads, who were becoming the most dominant ethnic group in Central Asia. To handle and avoid any threats posed by the Turks, the Sui government repaired fortifications and received their trade and tribute missions. They sent four royal princesses to form marriage alliances with Turkic clan leaders, in 597, 599, 614, and 617. The Sui stirred trouble and conflict amongst ethnic groups against the Turks. As early as the Sui dynasty, the Turks had become a major militarized force employed by the Chinese. When the  While the Turks were settled in the Ordos region (former territory of the
While the Turks were settled in the Ordos region (former territory of the  During the
During the 
 There was great interaction with India, a hub for Buddhist knowledge, with famous travelers such as
There was great interaction with India, a hub for Buddhist knowledge, with famous travelers such as  Chinese envoys had been sailing through the Indian Ocean to states of
Chinese envoys had been sailing through the Indian Ocean to states of  Although Chang'an was the capital of the earlier Han and Jin dynasties, after subsequent destruction in warfare, it was the Sui dynasty model that comprised the Tang era capital. The roughly square dimensions of the city had six miles (10 km) of outer walls running east to west, and more than five miles (8 km) of outer walls running north to south. The royal palace, the Taiji Palace, stood north of the city's central axis. From the large Mingde Gates located mid-center of the main southern wall, a wide city avenue stretched from there all the way north to the central administrative city, behind which was the Chentian Gate of the royal palace, or Imperial City. Intersecting this were fourteen main streets running east to west, while eleven main streets ran north to south. These main intersecting roads formed 108 rectangular wards with walls and four gates each, and each ward filled with multiple
Although Chang'an was the capital of the earlier Han and Jin dynasties, after subsequent destruction in warfare, it was the Sui dynasty model that comprised the Tang era capital. The roughly square dimensions of the city had six miles (10 km) of outer walls running east to west, and more than five miles (8 km) of outer walls running north to south. The royal palace, the Taiji Palace, stood north of the city's central axis. From the large Mingde Gates located mid-center of the main southern wall, a wide city avenue stretched from there all the way north to the central administrative city, behind which was the Chentian Gate of the royal palace, or Imperial City. Intersecting this were fourteen main streets running east to west, while eleven main streets ran north to south. These main intersecting roads formed 108 rectangular wards with walls and four gates each, and each ward filled with multiple  The Tang capital was the largest city in the world at its time, the population of the city wards and its suburban countryside reaching two million inhabitants. The Tang capital was very cosmopolitan, with ethnicities of
The Tang capital was the largest city in the world at its time, the population of the city wards and its suburban countryside reaching two million inhabitants. The Tang capital was very cosmopolitan, with ethnicities of  There were large
There were large  Since ancient times, some Chinese had believed in
Since ancient times, some Chinese had believed in  Rivaling Buddhism was Taoism, a native Chinese philosophical and religious belief system that found its roots in the ''
Rivaling Buddhism was Taoism, a native Chinese philosophical and religious belief system that found its roots in the '' In general, garments were made from silk, wool, or linen depending on your social status and what you could afford. Furthermore, there were laws that specified what kinds of clothing could be worn by whom. The color of the clothing also indicated rank. During this period, China's power, culture, economy, and influence were thriving. As a result, women could afford to wear loose-fitting, wide-sleeved garments. Even lower-class women's robes would have sleeves four to five feet in width.
In general, garments were made from silk, wool, or linen depending on your social status and what you could afford. Furthermore, there were laws that specified what kinds of clothing could be worn by whom. The color of the clothing also indicated rank. During this period, China's power, culture, economy, and influence were thriving. As a result, women could afford to wear loose-fitting, wide-sleeved garments. Even lower-class women's robes would have sleeves four to five feet in width.
 Concepts of women's social rights and social status during the Tang era were notably liberal-minded for the period. However, this was largely reserved for urban women of elite status, as men and women in the rural countryside labored hard in their different set of tasks; with wives and daughters responsible for more domestic tasks of weaving textiles and rearing of silk worms, while men tended to farming in the fields.
There were many women in the Tang era who gained access to religious authority by taking vows as Taoist priestesses. The head mistresses of high-class
Concepts of women's social rights and social status during the Tang era were notably liberal-minded for the period. However, this was largely reserved for urban women of elite status, as men and women in the rural countryside labored hard in their different set of tasks; with wives and daughters responsible for more domestic tasks of weaving textiles and rearing of silk worms, while men tended to farming in the fields.
There were many women in the Tang era who gained access to religious authority by taking vows as Taoist priestesses. The head mistresses of high-class  Technology during the Tang period was built also upon the precedents of the past. Previous advancements in clockworks and timekeeping included the mechanical gear systems of Zhang Heng (78–139) and Ma Jun (mechanical engineer), Ma Jun (fl. 3rd century), which gave the Tang mathematician, mechanical engineer, astronomer, and monk Yi Xing (683–727) inspiration when he invented the world's first clockwork escapement mechanism in 725. This was used alongside a Water clock, clepsydra clock and waterwheel to power a rotating armillary sphere in representation of astronomical observation. Yi Xing's device also had a mechanically timed bell that was struck automatically every hour, and a drum that was struck automatically every quarter-hour; essentially, a striking clock. Yi Xing's astronomical clock and water-powered armillary sphere became well known throughout the country, since students attempting to pass the imperial examinations by 730 had to write an essay on the device as an exam requirement. However, the most common type of public and palace timekeeping device was the inflow clepsydra. Its design was improved c. 610 by the Sui-dynasty engineers Geng Xun and Yuwen Kai. They provided a steelyard balance that allowed seasonal adjustment in the pressure head of the compensating tank and could then control the rate of flow for different lengths of day and night.
There were many other mechanical inventions during the Tang era. These included a 3 ft (0.91 m) tall mechanical wine server of the early 8th century that was in the shape of an artificial mountain, carved out of iron and rested on a lacquered-wooden tortoise frame. This intricate device used a hydraulic pump that siphoned wine out of metal Chinese dragon, dragon-headed faucets, as well as tilting bowls that were timed to dip wine down, by force of gravity when filled, into an artificial lake that had intricate iron leaves popping up as trays for placing party treats. Furthermore, as the historian Charles Benn describes it:
Yet the use of a teasing mechanical puppet in this wine-serving device wasn't exactly a novel invention of the Tang, since the use of mechanical puppets in China date back to the Qin dynasty (221–207 BC). In the 3rd century Ma Jun (mechanical engineer), Ma Jun had an entire mechanical puppet theater operated by the rotation of a waterwheel. There was also an automatic wine-server known in the ancient Greco-Roman world, a design of the Greek inventor Heron of Alexandria that employed an urn with an inner valve and a lever device similar to the one described above. There are many stories of automatons used in the Tang, including general Yang Wulian's wooden statue of a monk who stretched his hands out to collect contributions; when the number of coins reached a certain weight, the mechanical figure moved his arms to deposit them in a satchel. This weight-and-lever mechanism was exactly like Heron's penny slot machine. Other devices included one by Wang Ju, whose "wooden otter" could allegedly catch fish; Needham suspects a Spring (device), spring trap of some kind was employed here.
In the realm of structural engineering and technical Chinese architecture, there were also government standard building codes, outlined in the early Tang book of the ''Yingshan Ling'' (National Building Law). Fragments of this book have survived in the ''Tang Lü'' (The Tang Code), while the Song dynasty architectural manual of the ''Yingzao Fashi'' (State Building Standards) by Architecture of the Song dynasty#Literature, Li Jie (1065–1101) in 1103 is the oldest existing technical treatise on Chinese architecture that has survived in full. During the reign of Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (712–756) there were 34,850 registered Artisan, craftsmen serving the state, managed by the Agency of Palace Buildings (Jingzuo Jian).
Technology during the Tang period was built also upon the precedents of the past. Previous advancements in clockworks and timekeeping included the mechanical gear systems of Zhang Heng (78–139) and Ma Jun (mechanical engineer), Ma Jun (fl. 3rd century), which gave the Tang mathematician, mechanical engineer, astronomer, and monk Yi Xing (683–727) inspiration when he invented the world's first clockwork escapement mechanism in 725. This was used alongside a Water clock, clepsydra clock and waterwheel to power a rotating armillary sphere in representation of astronomical observation. Yi Xing's device also had a mechanically timed bell that was struck automatically every hour, and a drum that was struck automatically every quarter-hour; essentially, a striking clock. Yi Xing's astronomical clock and water-powered armillary sphere became well known throughout the country, since students attempting to pass the imperial examinations by 730 had to write an essay on the device as an exam requirement. However, the most common type of public and palace timekeeping device was the inflow clepsydra. Its design was improved c. 610 by the Sui-dynasty engineers Geng Xun and Yuwen Kai. They provided a steelyard balance that allowed seasonal adjustment in the pressure head of the compensating tank and could then control the rate of flow for different lengths of day and night.
There were many other mechanical inventions during the Tang era. These included a 3 ft (0.91 m) tall mechanical wine server of the early 8th century that was in the shape of an artificial mountain, carved out of iron and rested on a lacquered-wooden tortoise frame. This intricate device used a hydraulic pump that siphoned wine out of metal Chinese dragon, dragon-headed faucets, as well as tilting bowls that were timed to dip wine down, by force of gravity when filled, into an artificial lake that had intricate iron leaves popping up as trays for placing party treats. Furthermore, as the historian Charles Benn describes it:
Yet the use of a teasing mechanical puppet in this wine-serving device wasn't exactly a novel invention of the Tang, since the use of mechanical puppets in China date back to the Qin dynasty (221–207 BC). In the 3rd century Ma Jun (mechanical engineer), Ma Jun had an entire mechanical puppet theater operated by the rotation of a waterwheel. There was also an automatic wine-server known in the ancient Greco-Roman world, a design of the Greek inventor Heron of Alexandria that employed an urn with an inner valve and a lever device similar to the one described above. There are many stories of automatons used in the Tang, including general Yang Wulian's wooden statue of a monk who stretched his hands out to collect contributions; when the number of coins reached a certain weight, the mechanical figure moved his arms to deposit them in a satchel. This weight-and-lever mechanism was exactly like Heron's penny slot machine. Other devices included one by Wang Ju, whose "wooden otter" could allegedly catch fish; Needham suspects a Spring (device), spring trap of some kind was employed here.
In the realm of structural engineering and technical Chinese architecture, there were also government standard building codes, outlined in the early Tang book of the ''Yingshan Ling'' (National Building Law). Fragments of this book have survived in the ''Tang Lü'' (The Tang Code), while the Song dynasty architectural manual of the ''Yingzao Fashi'' (State Building Standards) by Architecture of the Song dynasty#Literature, Li Jie (1065–1101) in 1103 is the oldest existing technical treatise on Chinese architecture that has survived in full. During the reign of Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (712–756) there were 34,850 registered Artisan, craftsmen serving the state, managed by the Agency of Palace Buildings (Jingzuo Jian).
 Woodblock printing made the written word available to vastly greater audiences. One of the world's oldest surviving printed documents is a miniature Buddhist ''dharani'' sutra unearthed at Xi'an in 1974 and dated roughly from 650 to 670. The ''Diamond Sutra'' is the first full-length book printed at regular size, complete with illustrations embedded with the text and dated precisely to 868. Among the earliest documents to be printed were Buddhist texts as well as calendars, the latter essential for calculating and marking which days were auspicious and which days were not. With so many books coming into circulation for the general public, literacy rates could improve, along with the lower classes being able to obtain cheaper sources of study. Therefore, there were more lower-class people seen entering the Imperial Examinations and passing them by the later Song dynasty. Although the later Bi Sheng's movable type
Woodblock printing made the written word available to vastly greater audiences. One of the world's oldest surviving printed documents is a miniature Buddhist ''dharani'' sutra unearthed at Xi'an in 1974 and dated roughly from 650 to 670. The ''Diamond Sutra'' is the first full-length book printed at regular size, complete with illustrations embedded with the text and dated precisely to 868. Among the earliest documents to be printed were Buddhist texts as well as calendars, the latter essential for calculating and marking which days were auspicious and which days were not. With so many books coming into circulation for the general public, literacy rates could improve, along with the lower classes being able to obtain cheaper sources of study. Therefore, there were more lower-class people seen entering the Imperial Examinations and passing them by the later Song dynasty. Although the later Bi Sheng's movable type  In the realm of cartography, there were further advances beyond the map-makers of the Han dynasty. When the Tang chancellor Pei Ju (547–627) was working for the Sui dynasty as a Commercial Commissioner in 605, he created a well-known gridded map with a Scale (map), graduated scale in the tradition of Pei Xiu (224–271). The Tang chancellor Xu Jingzong (592–672) was also known for his map of China drawn in the year 658. In the year 785 the Emperor Dezong of Tang, Emperor Dezong had the geographer and cartographer Jia Dan (730–805) complete a map of China and her former colonies in Central Asia. Upon its completion in 801, the map was 9.1 m (30 ft) in length and 10 m (33 ft) in height, mapped out on a grid scale of one inch equaling one hundred ''li (unit), li'' (Chinese unit of measuring distance). A Chinese map of 1137 is similar in complexity to the one made by Jia Dan, carved on a stone stele with a grid scale of 100 li. However, the only type of map that has survived from the Tang period are star charts. Despite this, Chinese cartography, the earliest extant terrain maps of China come from the ancient Qin (state), State of Qin; maps from the 4th century BC that were excavated in 1986.
In the realm of cartography, there were further advances beyond the map-makers of the Han dynasty. When the Tang chancellor Pei Ju (547–627) was working for the Sui dynasty as a Commercial Commissioner in 605, he created a well-known gridded map with a Scale (map), graduated scale in the tradition of Pei Xiu (224–271). The Tang chancellor Xu Jingzong (592–672) was also known for his map of China drawn in the year 658. In the year 785 the Emperor Dezong of Tang, Emperor Dezong had the geographer and cartographer Jia Dan (730–805) complete a map of China and her former colonies in Central Asia. Upon its completion in 801, the map was 9.1 m (30 ft) in length and 10 m (33 ft) in height, mapped out on a grid scale of one inch equaling one hundred ''li (unit), li'' (Chinese unit of measuring distance). A Chinese map of 1137 is similar in complexity to the one made by Jia Dan, carved on a stone stele with a grid scale of 100 li. However, the only type of map that has survived from the Tang period are star charts. Despite this, Chinese cartography, the earliest extant terrain maps of China come from the ancient Qin (state), State of Qin; maps from the 4th century BC that were excavated in 1986.