Antarctic Treaty System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике
es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in '' The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate
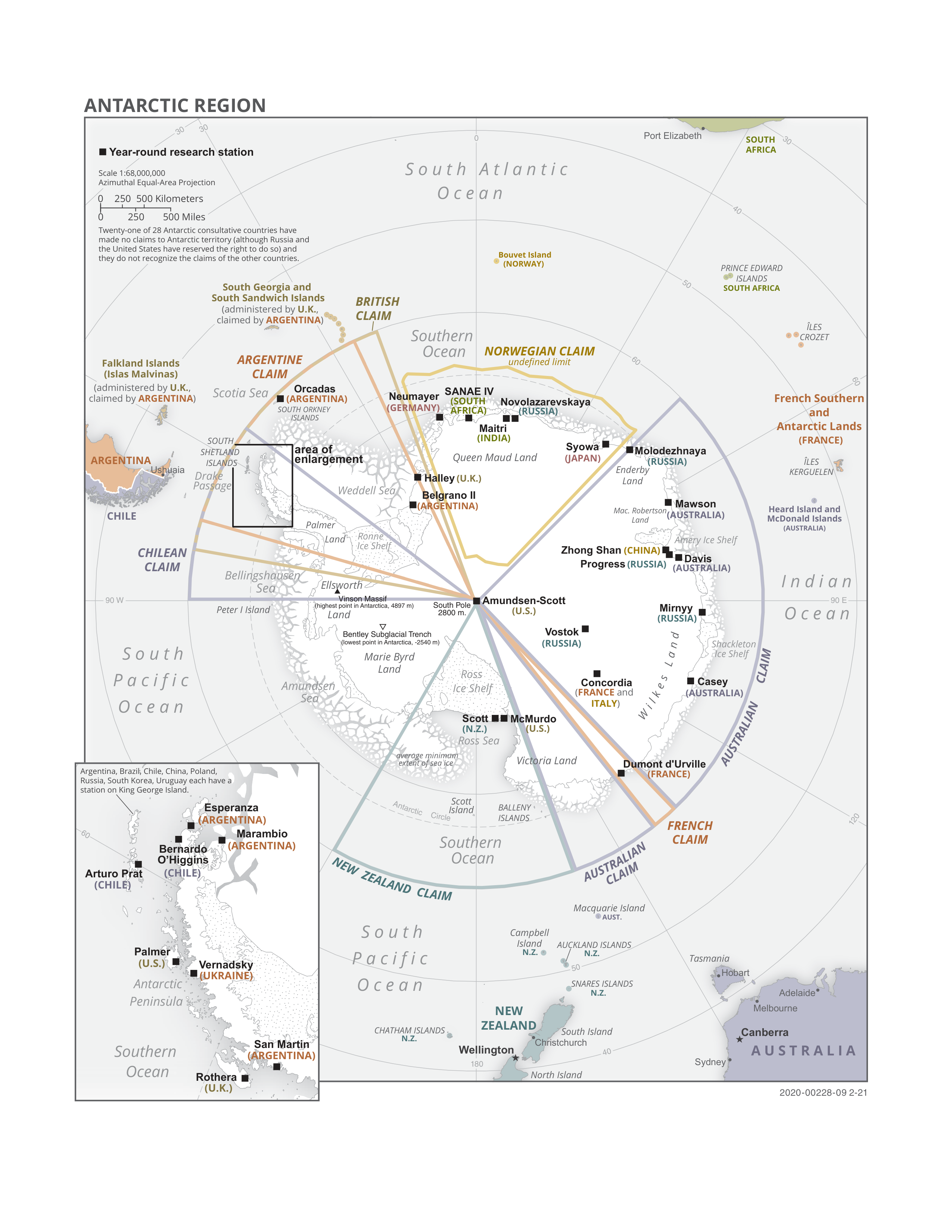
 * Has an overlapping claim with another one or two claimants.
* Has an overlapping claim with another one or two claimants.
† Reserved the right to make a claim.
 Since the designation of the Australian Antarctic Territory pre-dated the signing of the Antarctic Treaty, Australian laws that relate to Antarctica date from more than two decades before the Antarctic Treaty era. In terms of criminal law, the laws that apply to the Jervis Bay Territory (which follows the laws of the
Since the designation of the Australian Antarctic Territory pre-dated the signing of the Antarctic Treaty, Australian laws that relate to Antarctica date from more than two decades before the Antarctic Treaty era. In terms of criminal law, the laws that apply to the Jervis Bay Territory (which follows the laws of the
"South Pole death file still open".
''Sunday Star Times'', December 17, 2006. Retrieved December 19, 2006.Deutsche Presse-Agentur.
"Death of Australian astrophysicist an Antarctic whodunnit".
''Monstersandcritics.com'', December 14, 2006. Retrieved December 19, 2006. Dr. Marks died while wintering over at the United States' Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station located at the geographic South Pole. Prior to autopsy, the death was attributed to natural causes by the
"New Zealand Probes What May Be First South Pole Murder".
''The Daily Telegraph'', (December 14, 2006), reprinted i
''The New York Sun''
(December 19, 2006). Retrieved December 19, 2006.Booker, Jarrod
"South Pole scientist may have been poisoned".
''The New Zealand Herald'', (December 14, 2006). Retrieved December 19, 2006.
''Sunday Star Times'' (January 21, 2007)
Antarctic Treaty Secretariat
Full Text of the Antarctic Treaty
Original facsimile of Antarctic Treaty
Australian Antarctic Territory
National Science Foundation – Office of Polar Programs
List of all Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings
San Diego Union-Tribune, August 25, 2005 (Both South Korea and North Korea are members of the Antarctic Treaty)
Emblem of the Antarctic Treaty
{{Authority control Antarctica agreements 1959 in Antarctica 1959 in Washington, D.C. December 1959 events 1961 in Antarctica 1961 in the environment Arms control treaties Cold War treaties Territorial claims in Antarctica Treaties concluded in 1959 Treaties entered into force in 1961 Treaties establishing nuclear-weapon-free zones Treaties of Argentina Treaties of Australia Treaties of Austria Treaties of Belarus Treaties of Belgium Treaties of the military dictatorship in Brazil Treaties of the People's Republic of Bulgaria Treaties of Canada Treaties of Chile Treaties of the People's Republic of China Treaties of Colombia Treaties of Cuba Treaties of Denmark Treaties of the Czech Republic Treaties of Czechoslovakia Treaties of Ecuador Treaties of Estonia Treaties of Finland Treaties of France Treaties of West Germany Treaties of East Germany Treaties of Greece Treaties of Guatemala Treaties of the Hungarian People's Republic Treaties of Italy Treaties of India Treaties of Japan Treaties of Malaysia Treaties of Monaco Treaties of the Netherlands Treaties of New Zealand Treaties of North Korea Treaties of Norway Treaties of Pakistan Treaties of Papua New Guinea Treaties of Peru Treaties of the Polish People's Republic Treaties of Portugal Treaties of the Socialist Republic of Romania Treaties of the Soviet Union Treaties of Slovakia Treaties of South Africa Treaties of South Korea Treaties of Spain Treaties of Sweden Treaties of Switzerland Treaties of Turkey Treaties of Ukraine Treaties of the United Kingdom Treaties of the United States Treaties of Uruguay Treaties of Venezuela History of the Ross Dependency December 1959 events in the United States
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике
es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''
The New Encyclopædia Britannica
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the ...
''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc.
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article ...
, 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439.
, location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States
, date_sealed =
, date_effective = June 23, 1961
, condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories
, date_expiration =
, signatories = 12
, parties = 55
, depositor = Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
, languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish
, wikisource = Antarctic Treaty
 The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations
International relations (IR), sometimes referred to as international studies and international affairs, is the scientific study of interactions between sovereign states. In a broader sense, it concerns all activities between states—such ...
with respect to Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
, Earth's only continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
without a native human population. It was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, setting aside the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which implements the treaty system, is headquartered in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, Argentina.
The main treaty was opened for signature on December 1, 1959, and officially entered into force
In law, coming into force or entry into force (also called commencement) is the process by which legislation, regulations, treaties and other legal instruments come to have legal force and effect. The term is closely related to the date of ...
on June 23, 1961. The original signatories were the 12 countries active in Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year (IGY) of 1957–58: Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. These countries had established over 55 Antarctic research stations for the IGY, and the subsequent promulgation of the treaty was seen as a diplomatic expression of the operational and scientific cooperation that had been achieved. , the treaty has 55 parties.
History

1940s
After the Second World War, the U.S. considered establishing a claim in Antarctica. From August 26, 1946, and until the beginning of 1947, it carried out Operation Highjump, the largest military expeditionary force that the United States had ever sent to Antarctica, consisting of 13 ships, 4,700 men, and numerous aerial devices. Its goals were to train military personnel and to test materiel in conditions of extreme cold for a hypothetical war in the Antarctic. On September 2, 1947, the quadrant of Antarctica in which the United States was interested (between 24° W and 90° W) was included as part of the security zone of theInter-American Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance
The Inter-American Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance (commonly known as the Rio Treaty, the Rio Pact, the Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance, or by the Spanish-language acronym TIAR from ''Tratado Interamericano de Asistencia Recíproca'') is an agree ...
, committing its members to defend it in case of external aggression.
In August 1948, the United States proposed that Antarctica be under the guardianship of the United Nations, as a trust territory administered by Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, the United States, the United Kingdom, and New Zealand. This idea was rejected by Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, and Norway. Before the rejection, on August 28, 1948, the United States proposed to the claimant countries some form of internationalization of Antarctica, and this was supported by the United Kingdom. Chile responded by presenting a plan to suspend all Antarctic claims for five to ten years, while negotiating a final solution, but this did not find acceptance.
In 1950, the interest of the United States to keep the Soviet Union away from Antarctica was frustrated, when the Soviets informed the claimant states that they would not accept any Antarctic agreement in which they were not represented. The fear that the USSR would react by making a territorial claim, bringing the Cold War to Antarctica, led the United States to make none.
International conflicts
Various international conflicts motivated the creation of an agreement for the Antarctic. Some incidents had occurred during theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, and a new one occurred in Hope Bay on February 1, 1952, when the Argentine military fired warning shots at a group of Britons. The response of the United Kingdom was to send a warship that landed marines at the scene on February 4. In 1949, Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom signed a Tripartite Naval Declaration committing not to send warships south of the 60th parallel south, which was renewed annually until 1961 when it was deemed unnecessary when the treaty entered into force. This tripartite declaration was signed after the tension generated when Argentina sent a fleet of eight warships to Antarctica in February 1948.
On January 17, 1953, Argentina reopened the Lieutenant Lasala refuge on Deception Island
Deception Island is an island in the South Shetland Islands close to the Antarctic Peninsula with a large and usually "safe" natural harbor, which is occasionally troubled by the underlying active volcano. This island is the caldera of an ac ...
, leaving a sergeant and a corporal in the Argentine Navy. On February 15, in the incident on Deception Island, 32 royal marines landed from the British frigate HMS ''Snipe'' armed with Sten machine guns, rifles, and tear gas capturing the two Argentine sailors. The Argentine refuge and a nearby uninhabited Chilean shelter were destroyed, and the Argentine sailors were delivered to a ship from that country on February 18 in the South Georgia Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in United Kingdom.svg
, map_caption = Location of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in the southern Atlantic Oce ...
. A British detachment remained three months on the island while the frigate patrolled its waters until April.
On May 4, 1955, the United Kingdom filed two lawsuits, against Argentina and Chile respectively, before the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordan ...
to declare the invalidity of the claims of the sovereignty of the two countries over Antarctic and sub-Antarctic areas. On July 15, 1955, the Chilean government rejected the jurisdiction of the court in that case, and on August 1, the Argentine government also did so, so on March 16, 1956, the claims were closed.
In 1956 and 1958, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
tried unsuccessfully to bring the Antarctic issue to the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
.
International Geophysical Year
In 1950 theInternational Council of Scientific Unions
The International Council for Science (ICSU, after its former name, International Council of Scientific Unions) was an international non-governmental organization devoted to international cooperation in the advancement of science. Its members ...
(ICSU) had discussed the possibility of holding a third International Polar Year
The International Polar Years (IPY) are collaborative, international efforts with intensive research focus on the polar regions. Karl Weyprecht, an Austro-Hungarian naval officer, motivated the endeavor in 1875, but died before it first occurred i ...
. At the suggestion of the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Inter ...
, the idea of the International Polar Year was extended to the entire planet, thus creating the International Geophysical Year that took place between July 1, 1957, and December 31, 1958. In this event, 66 countries participated. At the ICSU meeting in Stockholm from September 9 to 11, 1957, the creation of a Special Committee for Antarctic Research (SCAR) was approved, inviting the twelve countries conducting Antarctic investigations to send delegates to integrate the committee, with the purpose of exchanging scientific information among its members regarding Antarctica. The SCAR was later renamed to the Scientific Committee for Research in Antarctica.
Both Argentina and Chile stated that research carried out on the continent during the International Geophysical Year would not give any territorial rights to the participants, and that the facilities that were erected during that year should be dismantled at the end of it. However, in February 1958 the United States proposed that the Antarctic investigations should be extended for another year, and the Soviet Union reported that it would maintain its scientific bases until the studies being carried out had been completed.
Negotiation of the treaty
Scientific bases increased international tension concerning Antarctica. The danger of the Cold War spreading to that continent caused the President of the United States, Dwight D. Eisenhower, to convene an Antarctic Conference of the twelve countries active in Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year, to sign a treaty. In the first phase, representatives of the twelve nations met in Washington, who met in sixty sessions between June 1958 and October 1959 to define a basic negotiating framework. However, no consensus was reached on a preliminary draft. In the second phase, a conference at the highest diplomatic level was held from October 15 to December 1, 1959, when the Treaty was signed. The central ideas with full acceptance were the freedom of scientific research in Antarctica and the peaceful use of the continent. There was also a consensus for demilitarization and the maintenance of the status quo. The positions of the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and New Zealand coincided in the establishment of an international administration for Antarctica, proposing that it should be within the framework of the United Nations. Australia and the United Kingdom expressed the need for inspections by observers, and the British also proposed the use of military personnel for logistical functions. Argentina proposed that all atomic explosions be banned in Antarctica, which caused a crisis that lasted until the last day of the conference, since the United States, along with other countries, intended to ban only those that were made without prior notice and without prior consultation. The support of the USSR and Chile for the Argentine proposal finally caused the United States to retract its opposition. The signing of the treaty was the first arms control agreement that occurred in the framework of the Cold War, and the participating countries managed to avoid the internationalization of Antarcticsovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
.
Other agreements
Other agreements – some 200 recommendations adopted at treaty consultative meetings and ratified by governments – include: * Agreed Measures for the Conservation of Antarctic Fauna and Flora (1964) (entered into force in 1982) * TheConvention for the Conservation of Antarctic Seals
The Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Seals (CCAS) is part of the Antarctic Treaty System. It was signed at the conclusion of a multilateral conference in London on February 11, 1972.
Contents
CCAS had the objective "to promote and ac ...
(1972)
* The Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (1982)
* The Convention on the Regulation of Antarctic Mineral Resource Activities (1988) (signed in 1988, not in force)
* The Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty
The Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty, also known as the Madrid Protocol, is a complementary legal instrument to the Antarctic Treaty signed in Madrid on October 4, 1991. It entered into force on January 14, 1998.
The ...
was signed October 4, 1991, and entered into force January 14, 1998; this agreement prevents development and provides for the protection of the Antarctic environment through five specific annexes on marine pollution, fauna and flora, environmental impact assessments, waste management, and protected areas. It prohibits all activities relating to mineral resources except scientific. A sixth annex on liability arising from environmental emergencies was adopted in 2005, but is yet to enter into force.
Bilateral treaties
* Exchange of Notes constituting an Agreement between the Governments of Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, and the Government of the French Republic, regarding Aerial Navigation in the Antarctic (Paris, October 25, 1938) * Treaty Between the Government of Australia and the Government of the French Republic on Cooperation in the Maritime Areas Adjacent to the French Southern and Antarctic Territories (TAAF), Heard Island and the McDonald Islands (Canberra, November 24, 2003) * Agreement on Cooperative Enforcement of Fisheries Laws between the Government of Australia and the Government of the French Republic in the Maritime Areas Adjacent to the French Southern and Antarctic Territories, Heard Island and the McDonald Islands (Paris, January 8, 2007)Meetings
The Antarctic Treaty System's yearly ''Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings (ATCM)'' are the international forum for the administration and management of the region. Only 29 of the 55 parties to the agreements have the right to participate in decision-making at these meetings, though the other 26 are still allowed to attend. The decision-making participants are the ''Consultative Parties'' and, in addition to the 12 original signatories, including 17 countries that have demonstrated their interest in Antarctica by carrying out substantial scientific activity there. The Antarctic Treaty also has ''Special Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings (SATCM)'', which are generally summoned to treat more important topics but are less frequents and Meetings of Experts.Parties
As of 2022, there are 55 states party to the treaty, 29 of which, including all 12 original signatories to the treaty, have consultative (voting) status. The consultative members include the 7 countries that claim portions of Antarctica as their territory. The 48 non-claimant countries do not recognize the claims of others. 40 parties to the Antarctic Treaty have also ratified the "Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty".† Reserved the right to make a claim.
Antarctic Treaty Secretariat
The ''Antarctic Treaty Secretariat'' was established in Buenos Aires, Argentina in September 2004 by the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM). Jan Huber (the Netherlands) served as the first Executive Secretary for five years until August 31, 2009. He was succeeded on September 1, 2009, by Manfred Reinke (Germany). Reinke was succeeded by Albert Lluberas (Uruguay), who was elected in June 2017 at the 40th Antarctic Consultative Treaty Meeting in Beijing, China. The tasks of the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat can be divided into the following areas: * Supporting the annual Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) and the meeting of the Committee for Environmental Protection (CEP). * Facilitating the exchange of information between the Parties required in the Treaty and the Environment Protocol. * Collecting, storing, arranging and publishing the documents of the ATCM. * Providing and disseminating public information about the Antarctic Treaty system and Antarctic activities.Legal system
Antarctica currently has no permanent population and therefore it has no citizenship nor government. Personnel present on Antarctica at any time are always citizens or nationals of some sovereignty outside Antarctica, as there is no Antarctic sovereignty. The majority of Antarctica is claimed by one or more countries, but most countries do not explicitly recognize those claims. The area on the mainland between 90 degrees west and 150 degrees west is the only major land on Earth not claimed by any country. Until 2015 the interior of the Norwegian Sector, the extent of which had never been officially defined, was considered to be unclaimed. That year, Norway formally laid claim to the area between its Queen Maud Land and the South Pole. Governments that are party to the Antarctic Treaty and its Protocol on Environmental Protection implement the articles of these agreements, and decisions taken under them, through national laws. These laws generally apply only to their own citizens, wherever they are in Antarctica, and serve to enforce the consensus decisions of the consultative parties: about which activities are acceptable, which areas require permits to enter, what processes of environmental impact assessment must precede activities, and so on. The Antarctic Treaty is often considered to represent an example of the common heritage of mankind principle.Australia
 Since the designation of the Australian Antarctic Territory pre-dated the signing of the Antarctic Treaty, Australian laws that relate to Antarctica date from more than two decades before the Antarctic Treaty era. In terms of criminal law, the laws that apply to the Jervis Bay Territory (which follows the laws of the
Since the designation of the Australian Antarctic Territory pre-dated the signing of the Antarctic Treaty, Australian laws that relate to Antarctica date from more than two decades before the Antarctic Treaty era. In terms of criminal law, the laws that apply to the Jervis Bay Territory (which follows the laws of the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding township#Aust ...
) apply to the Australian Antarctic Territory. Key Australian legislation applying Antarctic Treaty System decisions include the ''Antarctic Treaty Act 1960'', the ''Antarctic Treaty (Environment Protection) Act 1980'' and the ''Antarctic Marine Living Resources Conservation Act 1981''.
United States
Thelaw of the United States
The law of the United States comprises many levels of codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the most important is the nation's Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the federal government of the United States, as well as ...
, including certain criminal offences by or against U.S. nationals, such as murder, may apply to areas not under jurisdiction of other countries. To this end, the United States now stations special deputy U.S. Marshals in Antarctica to provide a law enforcement presence.
Some U.S. laws directly apply to Antarctica. For example, the Antarctic Conservation Act, Public Law 95-541, ''et seq.'', provides civil and criminal penalties for the following activities, unless authorized by regulation or statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by ...
:
* the taking of native Antarctic mammals or birds
* the introduction into Antarctica of non-indigenous plants and animals
* entry into specially protected or scientific areas
* the discharge or disposal of pollutants into Antarctica or Antarctic waters
* the importation into the U.S. of certain items from Antarctica
Violation of the Antarctic Conservation Act carries penalties of up to US$10,000 in fines and one year in prison. The Departments of the Treasury, Commerce
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions directly and indirectly related to the exchange (buying and selling) of goods and services among two or more parties within local, regional, natio ...
, Transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
, and the Interior share enforcement responsibilities. The Act requires expeditions from the U.S. to Antarctica to notify, in advance, the Office of Oceans and Polar Affairs of the State Department, which reports such plans to other nations as required by the Antarctic Treaty. Further information is provided by the Office of Polar Programs of the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
.
New Zealand
In 2006, the New Zealand police reported that jurisdictional issues prevented them issuing warrants for potential American witnesses who were reluctant to testify during theChristchurch
Christchurch ( ; mi, Ōtautahi) is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Canterbury Region. Christchurch lies on the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula on Pegasus Bay. The Avon Rive ...
Coroner's investigation into the death by poisoning of Australian astrophysicist Rodney Marks
Rodney David Marks (13 March 1968 – 12 May 2000) was an Australian astrophysicist who died from methanol poisoning while working in Antarctica.
Early life
Marks was born in Geelong, Victoria in Australia and received his education from the ...
at the South Pole base in May 2000.Hotere, Andrea."South Pole death file still open".
''Sunday Star Times'', December 17, 2006. Retrieved December 19, 2006.Deutsche Presse-Agentur.
"Death of Australian astrophysicist an Antarctic whodunnit".
''Monstersandcritics.com'', December 14, 2006. Retrieved December 19, 2006. Dr. Marks died while wintering over at the United States' Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station located at the geographic South Pole. Prior to autopsy, the death was attributed to natural causes by the
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
and the contractor administering the base. However, an autopsy in New Zealand revealed that Dr. Marks died from methanol poisoning. The New Zealand Police launched an investigation. In 2006, frustrated by lack of progress, the Christchurch Coroner said that it was unlikely that Dr. Marks ingested the methanol knowingly, although there is no certainty that he died as the direct result of the act of another person. During media interviews, the police detective in charge of the investigation criticized the National Science Foundation and contractor Raytheon for failing to co-operate with the investigation.Chapman, Paul"New Zealand Probes What May Be First South Pole Murder".
''The Daily Telegraph'', (December 14, 2006), reprinted i
''The New York Sun''
(December 19, 2006). Retrieved December 19, 2006.Booker, Jarrod
"South Pole scientist may have been poisoned".
''The New Zealand Herald'', (December 14, 2006). Retrieved December 19, 2006.
''Sunday Star Times'' (January 21, 2007)
South Africa
Under the South African Citizens in Antarctica Act, 1962, South African law applies to all South African citizens inAntarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
, and they are subject to the jurisdiction of the magistrate's court in Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. The Antarctic Treaties Act, 1996 incorporates the Antarctic Treaty and related agreements into South African law. In regard to violations of these treaties, South Africa also asserts jurisdiction over South African residents and members of expeditions organised in South Africa.Antarctic Treaties Act, No. 60 of 1996.
See also
* Antarctic and Southern Ocean Coalition (ASOC) * Antarctic Protected Areas * Antarctic Treaty issue *Arctic Council
The Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum that addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic. At present, eight countries exercise sovereignty over the lands within the Arctic Circle, ...
* Arctic sanctuary
Arctic sanctuary was a proposed marine protected area around the North Pole. As of 2016, 4.7% of the Arctic marine area is protected. The marine sanctuary is seen to be an important aspect of an international treaty that can act for the protection ...
* Crime in Antarctica
* ''Endurance'' – lost ship of Ernest Shackleton
Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton (15 February 1874 – 5 January 1922) was an Anglo-Irish Antarctic explorer who led three British expeditions to the Antarctic. He was one of the principal figures of the period known as the Heroic Age o ...
, found in 2022 and protected by the treaty
* International Seabed Authority
* Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force ...
* Moon treaty
* Multilateral treaty
* National Antarctic Program
* Outposts of Antarctica
* Research stations in Antarctica
* Solar radiation management
Solar geoengineering, or solar radiation modification (SRM), is a type of climate engineering in which sunlight (solar radiation) would be reflected back to outer space to limit or reverse human-caused climate change. It is not a substitute for ...
* Svalbard Treaty
The Svalbard Treaty (originally the Spitsbergen Treaty) recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and ...
References
External links
Antarctic Treaty Secretariat
Full Text of the Antarctic Treaty
Original facsimile of Antarctic Treaty
Australian Antarctic Territory
National Science Foundation – Office of Polar Programs
List of all Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings
San Diego Union-Tribune, August 25, 2005 (Both South Korea and North Korea are members of the Antarctic Treaty)
Emblem of the Antarctic Treaty
{{Authority control Antarctica agreements 1959 in Antarctica 1959 in Washington, D.C. December 1959 events 1961 in Antarctica 1961 in the environment Arms control treaties Cold War treaties Territorial claims in Antarctica Treaties concluded in 1959 Treaties entered into force in 1961 Treaties establishing nuclear-weapon-free zones Treaties of Argentina Treaties of Australia Treaties of Austria Treaties of Belarus Treaties of Belgium Treaties of the military dictatorship in Brazil Treaties of the People's Republic of Bulgaria Treaties of Canada Treaties of Chile Treaties of the People's Republic of China Treaties of Colombia Treaties of Cuba Treaties of Denmark Treaties of the Czech Republic Treaties of Czechoslovakia Treaties of Ecuador Treaties of Estonia Treaties of Finland Treaties of France Treaties of West Germany Treaties of East Germany Treaties of Greece Treaties of Guatemala Treaties of the Hungarian People's Republic Treaties of Italy Treaties of India Treaties of Japan Treaties of Malaysia Treaties of Monaco Treaties of the Netherlands Treaties of New Zealand Treaties of North Korea Treaties of Norway Treaties of Pakistan Treaties of Papua New Guinea Treaties of Peru Treaties of the Polish People's Republic Treaties of Portugal Treaties of the Socialist Republic of Romania Treaties of the Soviet Union Treaties of Slovakia Treaties of South Africa Treaties of South Korea Treaties of Spain Treaties of Sweden Treaties of Switzerland Treaties of Turkey Treaties of Ukraine Treaties of the United Kingdom Treaties of the United States Treaties of Uruguay Treaties of Venezuela History of the Ross Dependency December 1959 events in the United States