Taklamakan Desert on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Taklimakan or Taklamakan Desert (; zh, s=塔克拉玛干沙漠, p=Tǎkèlāmǎgān Shāmò, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Такәламаган Шамә; ug, تەكلىماكان قۇملۇقى, Täklimakan qumluqi; also spelled Taklimakan and Teklimakan) is a

 The Taklamakan Desert has an area of , making it slightly smaller than Germany. The desert is part of the
The Taklamakan Desert has an area of , making it slightly smaller than Germany. The desert is part of the

 Because it lies in the
Because it lies in the
 The Taklamakan Desert has very little water, therefore it is hazardous to cross. Merchant caravans on the
The Taklamakan Desert has very little water, therefore it is hazardous to cross. Merchant caravans on the
Photos of area in China
{{Authority control Deserts of China Deserts and xeric shrublands Ecoregions of China Ergs Geography of Xinjiang Sites along the Silk Road Physiographic provinces Ecoregions of Asia Palearctic ecoregions World Heritage Tentative List
desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
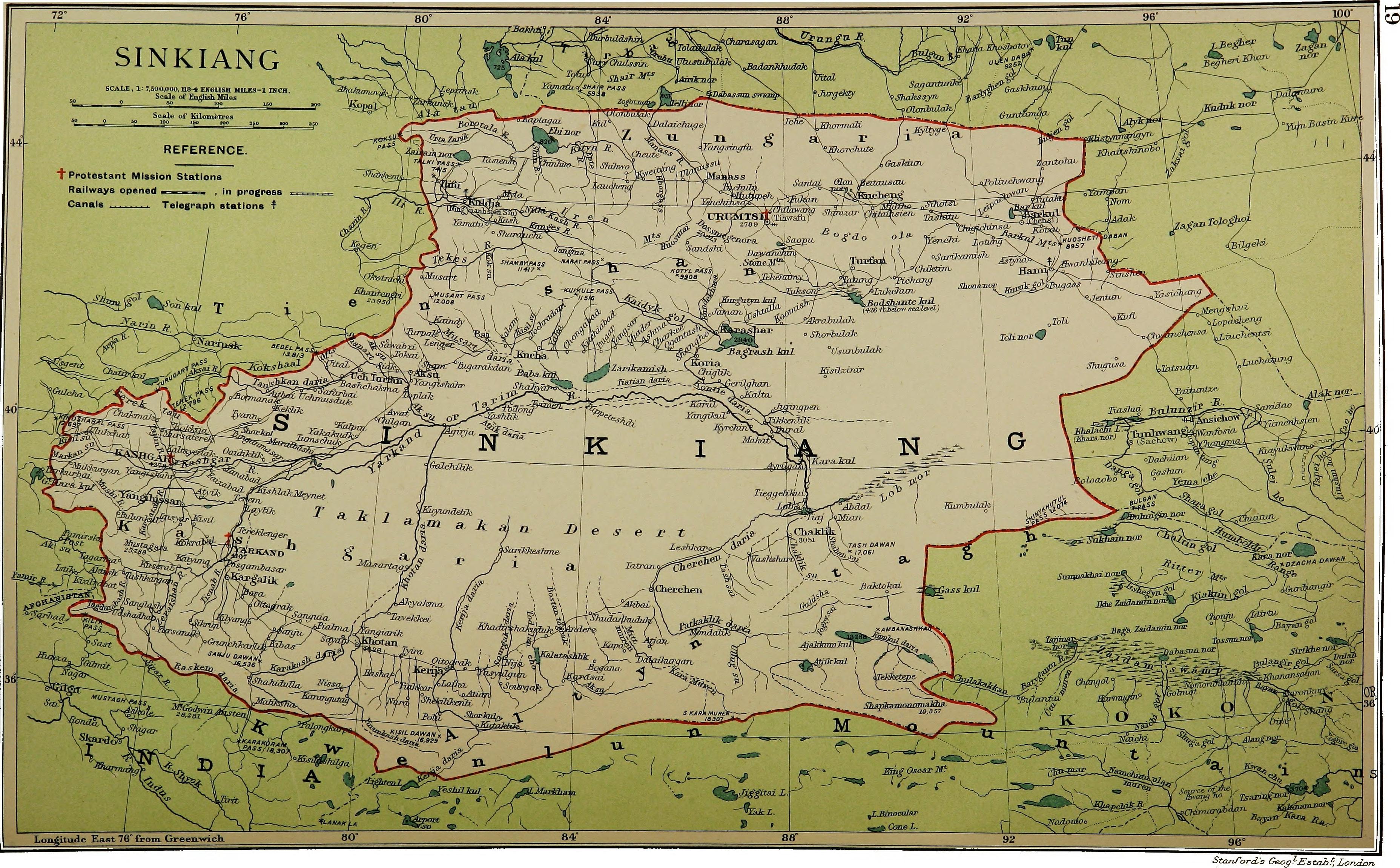
in Southwestern Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
in Northwest China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. It is bounded by the Kunlun Mountains
The Kunlun Mountains ( zh, s=昆仑山, t=崑崙山, p=Kūnlún Shān, ; ug, كۇئېنلۇن تاغ تىزمىسى / قۇرۇم تاغ تىزمىسى ) constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the bro ...
to the south, the Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the wor ...
to the west, the Tian Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘ ...
range to the north, and the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert ( Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast a ...
to the east.
Etymology
While most researchers agree on being the Persian word for "place", etymology of ''Takla'' is less clear. The word may be a Uyghur borrowing of the Persian , "to leave alone/out/behind, relinquish, abandon" + ''makan''. Another plausible explanation suggests it is derived fromTurki
Chagatai (چغتای, ''Čaġatāy''), also known as ''Turki'', Eastern Turkic, or Chagatai Turkic (''Čaġatāy türkīsi''), is an extinct Turkic literary language that was once widely spoken across Central Asia and remained the shared literar ...
''taqlar makan'', describing "the place of ruins". Chinese scholars Wang Guowei
Wang Guowei (; 2 December 18772 June 1927) or Wang Kuo-wei, courtesy name Jing'an () or Boyu (), was a Chinese historian and poet. A versatile and original scholar, he made important contributions to the studies of ancient history, epigraphy, ph ...
and Huang Wenbi
Huang Wenbi (; April 23, 1893 – December 18, 1966) was a Chinese archaeologist specializing in Xinjiang.
Huang was born in Hanchuan, Hubei Province. After graduating from Peking University in 1918, he became a faculty member of the university. ...
linked the name to the Tocharians
The Tocharians, or Tokharians ( US: or ; UK: ), were speakers of Tocharian languages, Indo-European languages known from around 7600 documents from around 400 to 1200 AD, found on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (modern Xinjiang, China). ...
, a historical people of the Tarim Basin, making the meaning of "Taklamakan" similar to "Tocharistan". According to Uyghur scholar Turdi Mettursun Kara, the name Taklamakan comes from the expression Terk-i Mekan. The name is first mentioned as Terk-i Makan (ترك مكان / trk mkan) in the book called Tevarih-i Muskiyun, which was written in 1867 in the Hotan Prefecture of Xinjiang.
In folk etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more famili ...
, it is said to mean "Place of No Return" or "get in and you'll never get out".
Geography

 The Taklamakan Desert has an area of , making it slightly smaller than Germany. The desert is part of the
The Taklamakan Desert has an area of , making it slightly smaller than Germany. The desert is part of the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
, which is long and wide. It is crossed at its northern and at its southern edge by two branches of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
, by which travellers sought to avoid the arid wasteland.
It is the world's second-largest shifting sand desert, with about 85% made up of shifting sand dunes, ranking 17th in size in a ranking of the world's largest deserts.
Dunes range in height from up to as much as . The few breaks in this sea of sand are small patches of alluvial clay. Generally, the steeper sides of the dunes face away from the prevailing winds.
The People's Republic of China has constructed two cross-desert highways. The Tarim Desert Highway 200px, Vegetation on either side of the highway to prevent shifting sand dunes from covering it, as well as a blue pump house in the distance. 200px, PetroChina gas station on the highway route
The Tarim Desert Highway (), also known as the Cross- ...
links the cities of Hotan (on the southern edge) and Luntai
Bügür County ( transliterated from Mongolian), also known from Mandarin Chinese as Luntai County, is a county in central Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region and is under the administration of the Bayin'gholin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture. It con ...
(on the northern edge) and the Bayingol
Bayingolin (; often abbreviated to Bayingol; also as Bayinguoleng) is an autonomous prefecture for Mongol people in the southeast of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Western China. It borders Gansu to the east, Qinghai to the southeast and ...
to Ruoqiang road crosses the desert to the east.
In recent years, the desert has expanded in some areas, its sands enveloping farms and villages as a result of desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused ...
.
The Golmud-Korla Railway crosses the Taklamakan as well.
Named areas in the desert include Ha-la-ma, A-lang-ha and Mai-k'o-tsa-k'o. The Mazartag mountains are located in the western part of the desert.
Climate

 Because it lies in the
Because it lies in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is ca ...
of the Himalayas, Taklamakan has a cold desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in deser ...
. Given its relative proximity with the cold to frigid air masses in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
, extreme temperatures are recorded in wintertime, sometimes well below , while in summer they can rise up to . During the 2008 Chinese winter storms
The 2008 Chinese winter storms () were a series of winter storm events that affected large portions of southern and central China, where it does not usually snow severely or extensively, starting on 25 January 2008 until 6 February 2008. The syst ...
episode, the Taklamakan was reported to be covered, for the first time in its recorded history, entirely with a thin layer of snow reaching , with a temperature of in some observatories.
Its extreme inland position, virtually in the very heartland of Asia and thousands of kilometres from any open body of water, accounts for the somewhat wide diurnal temperature variation.
Oasis
 The Taklamakan Desert has very little water, therefore it is hazardous to cross. Merchant caravans on the
The Taklamakan Desert has very little water, therefore it is hazardous to cross. Merchant caravans on the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
would stop for relief at the thriving oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
towns. It was in close proximity to many of the ancient civilizations—to the Northwest is the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
basin, to the southwest the Afghanistan mountain passes lead to Iran and India, to the east is China, and even to the north ancient towns such as Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to 1936 as an autonomous republic as part of ...
can be found.
The key oasis towns, watered by rainfall from the mountains, were Kashgar, Miran
Miran may refer to:
Places
* Miran (Xinjiang), an ancient oasis town in Ruoqiang County, Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, southeastern Xinjiang, western China
* Miran fort, a ruined defensive structure built by the Tibetan Empire, located ...
, Niya, Yarkand
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous ...
, and Khotan (Hetian) to the south, Kuqa and Turpan
Turpan (also known as Turfan or Tulufan, , ug, تۇرپان) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 632,000 (2015).
Geonyms
The original name of the cit ...
in the north, and Loulan and Dunhuang in the east. Now, many, such as Miran and Gaochang, are ruined cities in sparsely inhabited areas in the Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
.
The archaeological treasures found in its sand-buried ruins point to Tocharian, early Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
, Indian, and Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
influences. Its treasures and dangers have been vividly described by Aurel Stein
Sir Marc Aurel Stein,
( hu, Stein Márk Aurél; 26 November 1862 – 26 October 1943) was a Hungarian-born British archaeologist, primarily known for his explorations and archaeological discoveries in Central Asia. He was also a professor at ...
, Sven Hedin, Albert von Le Coq
Albert von Le Coq (; 8 September 1860 Berlin, Prussia – 21 April 1930 Berlin, Germany) was a Prussian/German brewery owner and wine merchant, who at the age of 40 began to study archaeology.''Schatzjagd an der Seidenstraße.'' A film by Susann ...
, and Paul Pelliot.
Mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
, some 4000 years old, have been found in the region.
Later, the Taklamakan was inhabited by Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
. Starting with the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
, the Chinese sporadically extended their control to the oasis cities of the Taklamakan Desert to control the important silk route trade across Central Asia. Periods of Chinese rule were interspersed with rule by Turkic, Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
and Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken diale ...
peoples. The present population consists largely of Turkic Uyghur people
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghu ...
and ethnic Han people.
Scientific exploration
This desert was explored by several scholars, includingXuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
, a 7th-century Buddhist monk, and, in the 20th century, the archaeologist Aurel Stein
Sir Marc Aurel Stein,
( hu, Stein Márk Aurél; 26 November 1862 – 26 October 1943) was a Hungarian-born British archaeologist, primarily known for his explorations and archaeological discoveries in Central Asia. He was also a professor at ...
.
Atmospheric studies have shown that dust originating from the Taklamakan is blown over the Pacific, where it contributes to cloud formation over the Western United States. Further, the traveling dust redistributes minerals from the Taklamakan to the western U.S.A. via rainfall. Studies have shown that a specific class of mineral found in the dust, known as K-feldspar
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar (endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angles ...
, triggers ice formation particularly well. K-feldspar is particularly susceptible to corrosion by acidic atmospheric pollution, such as nitrates and phosphates; exposure to these constituents reduces the ability of the dust to trigger water droplet formation.
In popular culture
The desert is the main setting for Chinese film series '' Painted Skin'' and '' Painted Skin: The Resurrection''. The Chinese TV series '' Candle in the Tomb'' is mostly spent in this desert as they are searching for the ancient city of Jinjue (see Niya (Tarim Basin)). The issue No. 39 'Soft Places' of Neil Gaiman's '' The Sandman'' takes place in the desert, whenMarco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in '' The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
gets lost in the desert.
A portion of the Korean quasi-historical TV drama series '' Queen Seondeok'' takes place in the Taklamakan Desert. Sohwa escapes from Silla with baby Deokman and raises her in the desert. As a teenager, Deokman returns to Silla and uses the knowledge and experience gained from life among international traders in the Taklamakan trading centers to gain the throne of Silla.
The desert is showcased in the Japanese animation '' Mobile Suit Gundam 00'', set in the year 2307. On the series, the Taklamakan Desert is the setting of a large-scale military joint operation performed by all the world's blocks of power, and interdicted by the paramilitary organization Celestial Being.
The Japanese anime '' Code Geass'' depicts a fictionalized version of Taklamakan Desert within the Chinese Federation, one of three superstates in the series. It serves as the setting of a key battle between the Holy Britannian Empire and Japanese insurrectionists backed by the Chinese Federation. Later, the presence of an underground city is revealed, where members of the Geass Order are being used by Emperor Charles zi Britannia and his consort Marianne vi Britannia to bring about the Ragnarök Connection.
See also
* * * * *'' Taklamakania'', named for the desert * * *References
Citations
Sources
* Jarring, Gunnar (1997). "Thetoponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
Takla-makan", ''Turkic Languages'', Vol. 1, pp. 227–240.
* Hopkirk, Peter
Peter Stuart Hopkirk (15 December 1930 – 22 August 2014) was a British journalist, author and historian who wrote six books about the British Empire, Russia and Central Asia.
Biography
Peter Hopkirk was born in Nottingham, the son of Frank St ...
(1980). ''Foreign Devils on the Silk Road: The Search for the Lost Cities and Treasures of Chinese Central Asia''. Amherst: The University of Massachusetts Press
The University of Massachusetts Press is a university press that is part of the University of Massachusetts Amherst
The University of Massachusetts Amherst (UMass Amherst, UMass) is a public research university in Amherst, Massachusetts a ...
. .
* Hopkirk, Peter (1994). '' The Great Game: The Struggle for Empire in Central Asia''. .
* Tamm, Eric Enno (2010). ''The Horse That Leaps Through Clouds''. Vancouver/Toronto/Berkeley: Douglas & McIntyre. (cloth); (ebook).
* Warner, Thomas T. (2004). ''Desert Meteorology''. Cambridge University Press, 612 pages. .
Further reading
* *Videography
* ''Treasure seekers : China's frozen desert'', National Geographic Society (2001)External links
Photos of area in China
{{Authority control Deserts of China Deserts and xeric shrublands Ecoregions of China Ergs Geography of Xinjiang Sites along the Silk Road Physiographic provinces Ecoregions of Asia Palearctic ecoregions World Heritage Tentative List