Table of organization and equipment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
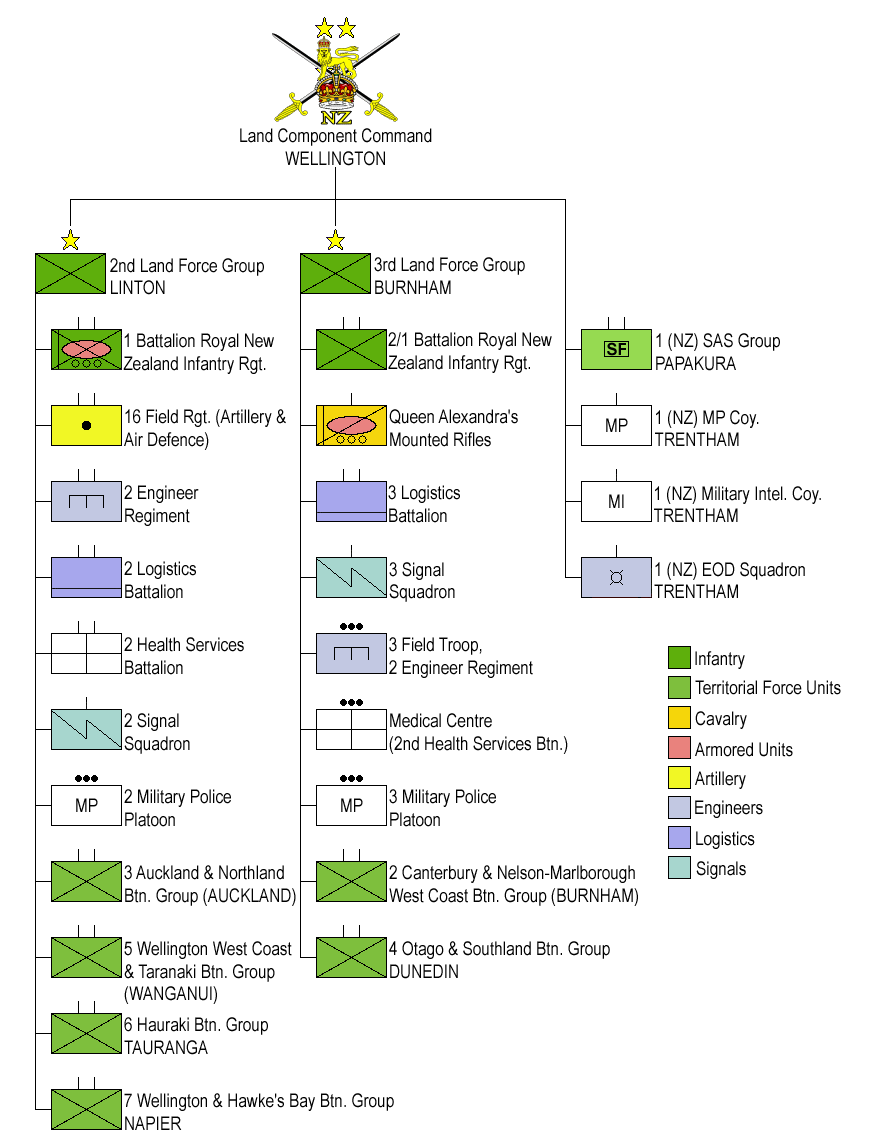
A table of organization and equipment (TOE or TO&E) is the specified organization, staffing, and equipment of units. Also used in acronyms as 'T/O' and 'T/E'. It also provides information on the mission and capabilities of a unit as well as the unit's current status.
A general TOE is applicable to a type of unit (for instance, an
 *
*
U.S. Army TOE
United States Department of Defense publications United States Army doctrine
infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
battalion) rather than a specific unit (the 2nd Battalion, 4th Infantry Regiment). Sometimes, all units of the same branch (such as Infantry) follow the same structural guidelines; much more often, there are a wide variety of TOEs to suit specific circumstances (Modified Tables of Organization and Equipment (MTOEs), in the United States Army, for example).
Soviet Union and Russia
In theSoviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and the Russian Armed Forces
The Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (, ), commonly referred to as the Russian Armed Forces, are the military forces of Russia. In terms of active-duty personnel, they are the world's fifth-largest military force, with at least two m ...
the term used for TO&E since the 1930s is ''"Shtatnoe raspisanie"'' (''Штатное расписание'', literally translated as Shtat Prescription). It originates from the term ''"Shtat"'' (''штат'') which is used primarily to denote manpower and in a secondary meaning as the synonym for TO&E itself. Note that in the Soviet Union and modern day Russia the term ''"Shtatnoe raspisanie"'' applied not only to military unit, but also to state organisations such as ministries, agencies, universities, hospitals etc. and even to the corporate structure of private companies.
Many of the Red Army's rifle divisions at the beginning of Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
were operating on Shtat 04/400 of 5 April 1941. This Shtat stipulated that an infantry division should consist of three infantry regiments, a light and a howitzer artillery regiment, other artillery units, a reconnaissance battalion, a combat engineer battalion, signals, chemical company (decontamination/flamethrower), transport, medical, and logistics train units, an aviation flight, and a division staff seemingly consisting of the division commander (1/0/0), division staff (70, including 12 horses and 13 vehicles), a quartermaster
Quartermaster is a military term, the meaning of which depends on the country and service. In land armies, a quartermaster is generally a relatively senior soldier who supervises stores or barracks and distributes supplies and provisions. In ...
section of five officers (5/0/0), a military tribunal (military justice
Military justice (also military law) is the legal system (bodies of law and procedure) that governs the conduct of the active-duty personnel of the armed forces of a country. In some nation-states, civil law and military law are distinct bod ...
) of two officers, and a political section of 11 officers.
Soviet rifle divisions were often forced to operate at far below their authorised strengths. For example, in the middle of the fighting on the Eastern Front, on July 20, 1942, a report on the 284th Rifle Division lamented:
The commissar, Tkachenko, went on to urgently request vehicles (including ambulances, of which there were none), small arms and support weapons, draught horses, and a closer supply base. After the first day of fighting he further reported that the lack of high-explosive shells forced the artillery to fire armor-piercing rounds at enemy firing points and troops; there were no cartridges for the submachine guns; many of the men's uniforms and footwear were worn out; and it was impossible to commit the replacements into the fighting because of the lack of weapons.
United States
Army
In the U.S. Army, there are four basic types of TOEs: *The Base Table of Organization and Equipment (BTOE) **An organizational design document based on current doctrine and available equipment. It shows the basics of a unit's structure and their wartime requirements (both for personnel and equipment). *The Objective Table of Organization and Equipment (OTOE) **An updated form of the BTOE, usually formed within the last year. It is a fully modern document and is up to date with current policies and initiatives. *A Modified Table of Organization and Equipment (MTOE) **A document that modifies a BTOE in regard to a specific unit. Used when a unit's needs are substantially different from the BTOE. *A Table of Distribution and Allowances (TDA) **A type of temporary TOE that is applicable to a specific mission. Used in an instance when there is no applicable TOE. Each TOE has a unique number that identifies it. When changes are needed, a table is not modified, instead, a new table is drafted from scratch. An example of an overall T/O change can be seen when the " Pentomic" organization was superseded by the Reorganization Objective Army Division (ROAD). During the 1950s, the Pentomic reorganization shifted the basic tactical unit from the regiment to the five-company battle group. Instead of brigades, an armored division had three Combat Commands designated: CCA, CCB, and CCC. On 16 December 1960, the Army Chief of Staff directed a reappraisal of division organization. Resulting studies were carried out between January and April 1961, and fully implemented by 1965.Wilson, John B. (1997). ''Maneuver and Firepower: The Evolution of Divisions and Separate Brigades''. Washington, DC: Center of Military History. The resulting Reorganization of Army Divisions (ROAD) changed all division types (Mechanized, Airborne, Armor, Infantry and Cavalry) to an identical structure of three brigades of three (sometimes four) battalions. The ROAD division consisted of a mix of nine to twelve armor and infantry battalions based on its Mission, the likely Enemy, the Terrain/weather, and other forces available or Troops (METT). Each brigade would be assigned or attached the mix of battalions and companies based on the division commanders estimate based on METT. As operations continued, the division commander could task organize subordinate units as needed by the flow of the battle.Marine Corps
{{Unreferenced section, date=February 2019Marine
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean.
Marine or marines may refer to:
Ocean
* Maritime (disambiguation)
* Marine art
* Marine biology
* Marine debris
* Marine habitats
* Marine life
* Marine pollution
Military ...
T/O&Es are based on a generic template for each specific type and size of unit, for example, a weapons company A weapons company, sometimes called a manoeuvre support company, is a company-sized military unit attached to an infantry battalion to support the rifle companies of the battalion. It usually possesses some combination of machine-guns, mortars, anti ...
of an infantry battalion, or a heavy helicopter squadron. These templates are then modified as needed by the individual unit. The Marine Corps also relies on other documents to report what personnel and equipment a unit actually possesses.
The T/O section denotes every authorized billet
A billet is a living-quarters to which a soldier is assigned to sleep. Historically, a billet was a private dwelling that was required to accept the soldier.
Soldiers are generally billeted in barracks or garrisons when not on combat duty, alth ...
within a unit by rank and Military Occupational Specialty
A United States military occupation code, or a military occupational specialty code (MOS code), is a nine-character code used in the United States Army and United States Marine Corps to identify a specific job. In the United States Air Force, a sy ...
required to fulfill the necessary duties. The T/E section denotes authorized equipment by Line Item Number and quantity.
See also
 *
*Military organization
Military organization or military organisation is the structuring of the armed forces of a state so as to offer such military capability as a national defense policy may require. In some countries paramilitary forces are included in a nati ...
*Military doctrine
Military doctrine is the expression of how military forces contribute to campaigns, major operations, battles, and engagements.
It is a guide to action, rather than being hard and fast rules. Doctrine provides a common frame of reference acros ...
*Military science
Military science is the study of military processes, institutions, and behavior, along with the study of warfare, and the theory and application of organized coercive force. It is mainly focused on theory, method, and practice of producing mi ...
*Military unit
Military organization or military organisation is the structuring of the armed forces of a state so as to offer such military capability as a national defense policy may require. In some countries paramilitary forces are included in a natio ...
*Order of battle
In modern use, the order of battle of an armed force participating in a military operation or campaign shows the hierarchical organization, command structure, strength, disposition of personnel, and equipment of units and formations of the armed ...
References
External links and sources
U.S. Army TOE
United States Department of Defense publications United States Army doctrine