T-12 antitank gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
2A19 or T-12 was a revolutionary
 The T-12 used the carriage of the
The T-12 used the carriage of the
 ;3BM-2
;3BM-2
 *: 10
*: 126
*: 80
*: 16
*: 68
*: 18
*: 37
*
*: 20+
*
*: 10
*: 126
*: 80
*: 16
*: 68
*: 18
*: 37
*
*: 20+
*
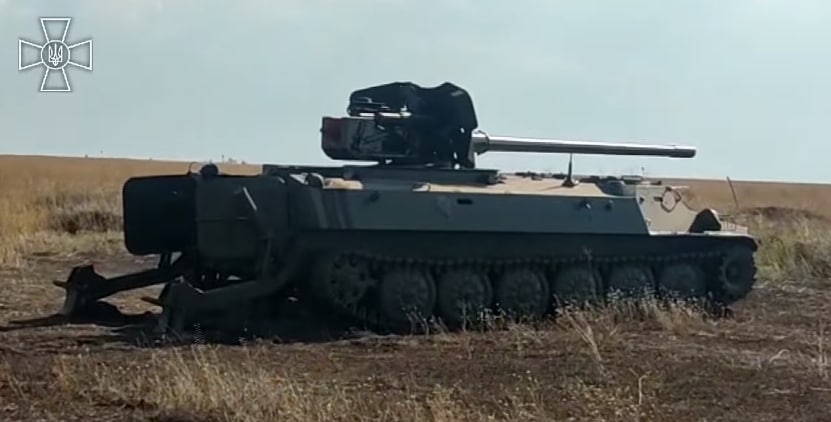 In August 2022, videos of a Ukrainian T-12 mounted on top of an MT-LB began to circulate online. While the combination was widely reported as mounting an MT-12, these same publications consistently showed photographs of a T-12 being mounted. The conversion was done by local infantrymen. These were even so clever as to mount hydraulic supports at the back of the MT-LB. This would stabilize the shot, and lessen the effort to re-aim after each shot. In effect it does not matter whether the gun is a T-12 or an MT-12, because the gun itself is identical. What is far more interesting are the pictures of this self propelled variant firing at elevations of about 35 degrees.
The usefulness of this first "T-12 on MT-LB" idea made that more Ukrainian units sought to acquire such a combination.
In August 2022, videos of a Ukrainian T-12 mounted on top of an MT-LB began to circulate online. While the combination was widely reported as mounting an MT-12, these same publications consistently showed photographs of a T-12 being mounted. The conversion was done by local infantrymen. These were even so clever as to mount hydraulic supports at the back of the MT-LB. This would stabilize the shot, and lessen the effort to re-aim after each shot. In effect it does not matter whether the gun is a T-12 or an MT-12, because the gun itself is identical. What is far more interesting are the pictures of this self propelled variant firing at elevations of about 35 degrees.
The usefulness of this first "T-12 on MT-LB" idea made that more Ukrainian units sought to acquire such a combination.
T-12 walkaround on DishModels.ru
* http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/russia/t-12.htm
part of
' a publication of the
Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
100-mm anti-tank gun. It was the first (anti-) tank gun to adopt a smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.
History
Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without signi ...
barrel, and to introduce modern armor piercing shot, like the APFSDS
Armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS), long dart penetrator, or simply dart ammunition, is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition used to attack modern vehicle armour. As an armament for main battle tanks, it succeeds A ...
. It uses long projectiles that are more powerful than its caliber suggests. The T-12 served as the primary towed anti-tank artillery in the Soviet and Bulgarian armies from the early 1960s to the late 1980s.
History
The T-12 was designed by the construction bureau of theYurga Machine-Building Plant
Yurga Machine-Building Plant (russian: Юргинский машиностроительный завод) is a company based in Yurga, Russia. Since 2015 it is part of Uralvagonzavod.
Yurga Machine-Building Plant produces missile launchers for Ru ...
as a replacement for the BS-3 100 mm gun. The first serial examples were produced in 1955, but the T-12 entered service only in 1961. Its special feature was the use of a smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.
History
Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without signi ...
gun. The T-12 was typically deployed in the anti-tank units of armored and motor rifle regiments to protect flanks against counter-attacks during rapid advances.
In 1971 a new variant was introduced, T-12A or MT-12 "Rapira" (2A29). This has the same barrel, but has a redesigned carriage and gun shield. This allows the MT-12 to be towed by the MT-LB
The MT-LB (russian: Многоцелевой Тягач Легкий Бронированный, translit=Mnogotselevoy tyagach legky bronirovanny, literally "multi-purpose towing vehicle light armored") is a Soviet multi-purpose, fully amphibi ...
, giving greater mobility. The 2A29R "Ruta" or MT-12R is an MT-12 version with a radar system. From 1981, the gun could fire the laser beam-riding guided missile 9M117 Kastet (weapon system 9K116) and carried the new designator 2A29K "Kastet" or MT-12K.
By the mid-1990s modern western tanks' frontal armor protection could no longer be penetrated by a 100 mm gun. The 100 mm caliber ammunition had reached the limits of what could be achieved with it. For a static anti-tank that cannot move to attack the sides of an opponent this is extra problematic. Today, the T-12 is applied mostly in the role of ordinary artillery, using FRAG-HE shells. The T-12 was planned to be superseded by the 2A45 Sprut-B
2A45 and 2A45M are the respective GRAU designations of the Sprut-A and Sprut-B (Russian for ''octopus'' or ''kraken'') Soviet smoothbore 125 mm anti-tank guns.
Development
The 2A45M was created in the late 1980s by the Petrov Design Bure ...
125 mm smooth bore anti-tank gun.
Description
A revolutionary smoothbore gun
On introduction, the T-12's gun differed from all existing artillery by employing asmoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.
History
Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without signi ...
barrel instead of a rifled one. The reasons to introduce a smoothbore barrel primarily relate to armor piercing shot. This kind of shot relies on mechanically penetrating armor. It is most effective if it has the form of a long narrow diameter rod fired at very high speed. In flight it can be stabilized by a rifled gun barrel having given it rotation when it was fired, but this becomes less effective if the projectile becomes longer. The T-12 gun overcame the stabilization problem by applying fins to the projectile. This started the replacement of the armour-piercing discarding sabot
Armour-piercing discarding sabot (APDS) is a type of spin-stabilized kinetic energy projectile for anti-armour warfare. Each projectile consists of a sub-calibre round fitted with a sabot. The combination of a lighter sub-calibre projectile wi ...
(APDS) fired by rifled guns by the armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot
Armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS), long dart penetrator, or simply dart ammunition, is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition used to attack modern vehicle armour. As an armament for main battle tanks, it succeeds ...
(APFSDS) shot fired by smoothbore guns.
Another reason to use a smoothbore barrel for armor piercing shot, is that smoothbore guns allow for higher pressures, and thus higher projectile speeds. The result is that the T-12 fired a conspicuously long APFSDS projectile. This BM2 shot (see picture) had a diameter of 38 mm and used 8.75kg of propellant instead of less than 6kg for the existing Soviet tank gun. It was fired at a muzzle velocity of 1,540 m/s as opposed to only 900 m/s for the usual armor piercing shot. At 1,000 m this improved armor penetration from 185 mm to 230 mm, enough to penetrate most NATO tanks of the period.
High-explosive anti-tank
High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity ...
(HEAT) shells do not rely on high speed to penetrate armor, but on the explosion of the projectile on impact. The problem of using a rifled gun to fire a HEAT shot was that the stabilizing spin degraded the penetrating power by as much as half. Combined with other challenges HEAT shots were not effective for tank guns in the mid-1950s. The T-12 overcame most problems by firing a HEAT shot that was stabilized by pop-out fins. However, it was still not ideal as it was slow and therefore had to be fired in a higher arc. This was complicated by the Soviet scarcity of good rangefinders.
In 1958 Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev s ...
saw the T-12 and was so enthusiastic about the gun, that he wanted it placed in the T55. However, the long ammunition would not fit in the existing Soviet medium-tank turrets. Therefore, the 115 mm U-5TS
The U-5TS (production designation 2A20) tank gun is a 115 mm- calibre weapon that was fitted exclusively to the Soviet Union's T-62 main battle tank. It was the first smoothbore weapon designed for tanks and heralded the change in main armam ...
gun of the T-62
The T-62 is a Soviet main battle tank that was first introduced in 1961. As a further development of the T-55 series, the T-62 retained many similar design elements of its predecessor including low profile and thick turret armour. In contras ...
was developed with a larger caliber, so it could use more propellant while not requiring the very long T-12 projectiles.
The T-12's breech is semi-automatic, meaning that it needs to be opened only before the first shot. After the first shot the breech opens by itself, so a new projectile can immediately be loaded.
Other charactertistics
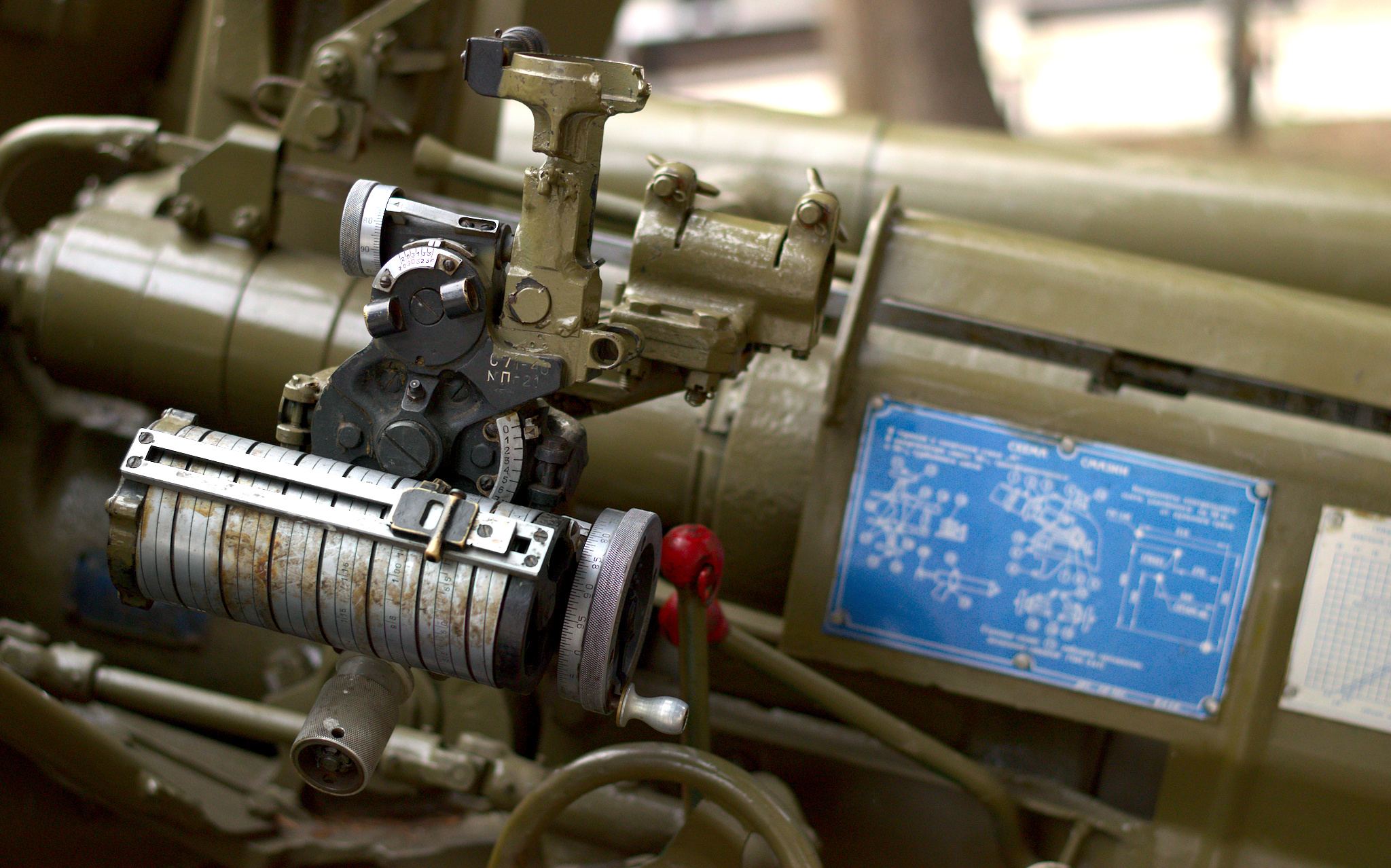
 The T-12 used the carriage of the
The T-12 used the carriage of the 85 mm anti-tank gun D-48
The 85-mm antitank gun D-48 (russian: 85-мм противотанковая пушка Д-48) was a Soviet 85-mm calibre anti-tank gun used after World War II. It was designed as the replacement for the 100 mm field gun M1944 (BS-3). Distinguish ...
. In fact the only difference between the T-12 and the D-48 was the barrel. Both can be told apart by the muzzle brake
A muzzle brake or recoil compensator is a device connected to, or a feature integral to the construction of, the muzzle or barrel of a firearm or cannon that is intended to redirect a portion of propellant gases to counter recoil and unwanted ...
, which becomes wider towards the end of the D-48's barrel, but has the same width throughout for the T-12 and MT-12. The wheels of both D-48 and T-12 are secured by six bolts. The carriage of the T-12 did not allow it to be towed cross-country by fast tracked vehicles. It was therefore usually towed by trucks. This limited the T-12's cross country movement to only 15 km/h.
The gun can be fitted with the LO-7 ski gear for travel across snow or swampy ground. This is a metal welded structure with wide runners. The wheels are rolled up to the runners and fastened with a coupling chain. The gun can fire directly from the skis.
The principal difference between the upper part of the T-12 and that of the MT-12 is in the equilibrator that is used. That of the T-12 is hardly visible, whereas that of the MT-12 is a huge tube lying on top of the right rear part of the gun. Standing behind the gun, a barrel that has two short tubes on top of the gun barrel between the breech and the gun shield, is a T-12. If a third misaligned tube is present on the right side, the gun is an MT-12.
The gun requires a crew of six: commander, driver of the towing vehicle, gun layer, loader, and two ammunition crewmen. Since the weapon is a smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.
History
Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without signi ...
, all the ammunition is finned for accuracy during flight.
The standard equipment of the T-12 includes multiple sight
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflecte ...
s. The indirect aiming mechanism consists of the S71-40 mechanism with panoramic PG-1M sight. The OP4M-40U sight is used for direct fire. The APN-5-40 or APN-6-40 are used for direct fire by night.
Ammunition
''Note: penetration numbers for RHA at 90 degrees.''APFSDS
APFSDS
Armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS), long dart penetrator, or simply dart ammunition, is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition used to attack modern vehicle armour. As an armament for main battle tanks, it succeeds A ...
-T Tungsten
* Round weight:
* Projectile weight:
* Muzzle velocity:
* Maximum range:
* Penetration:
**230 mm at 500 m (9 in at 550 yd)
**180 mm at 2,000 m (7 in at 2,200 yd)
**140 mm at 3,000 m (5.5 in at 3,300 yd)
;3BM23/3UBM10
APFSDS
* Round weight:
* Projectile weight:
* Muzzle velocity:
* Maximum range:
* Penetration: 225 mm at 1000 m (8.8 in at 1100 yd)
HEAT
;3BK16M/3UBK8 * Round weight: * Projectile weight: * Muzzle velocity: * Maximum range: * Penetration:HE-FRAG
;3OF12/3OF35 * Round weight: * Projectile weight: * Muzzle velocity: * Maximum range (indirect):Guided projectile
;9K117 Kastet 3UBK10/3UBK10M Beam riding laser guided projectile. * Round weight: * Projectile weight: * Average speed: * Range: * Penetration:Operators
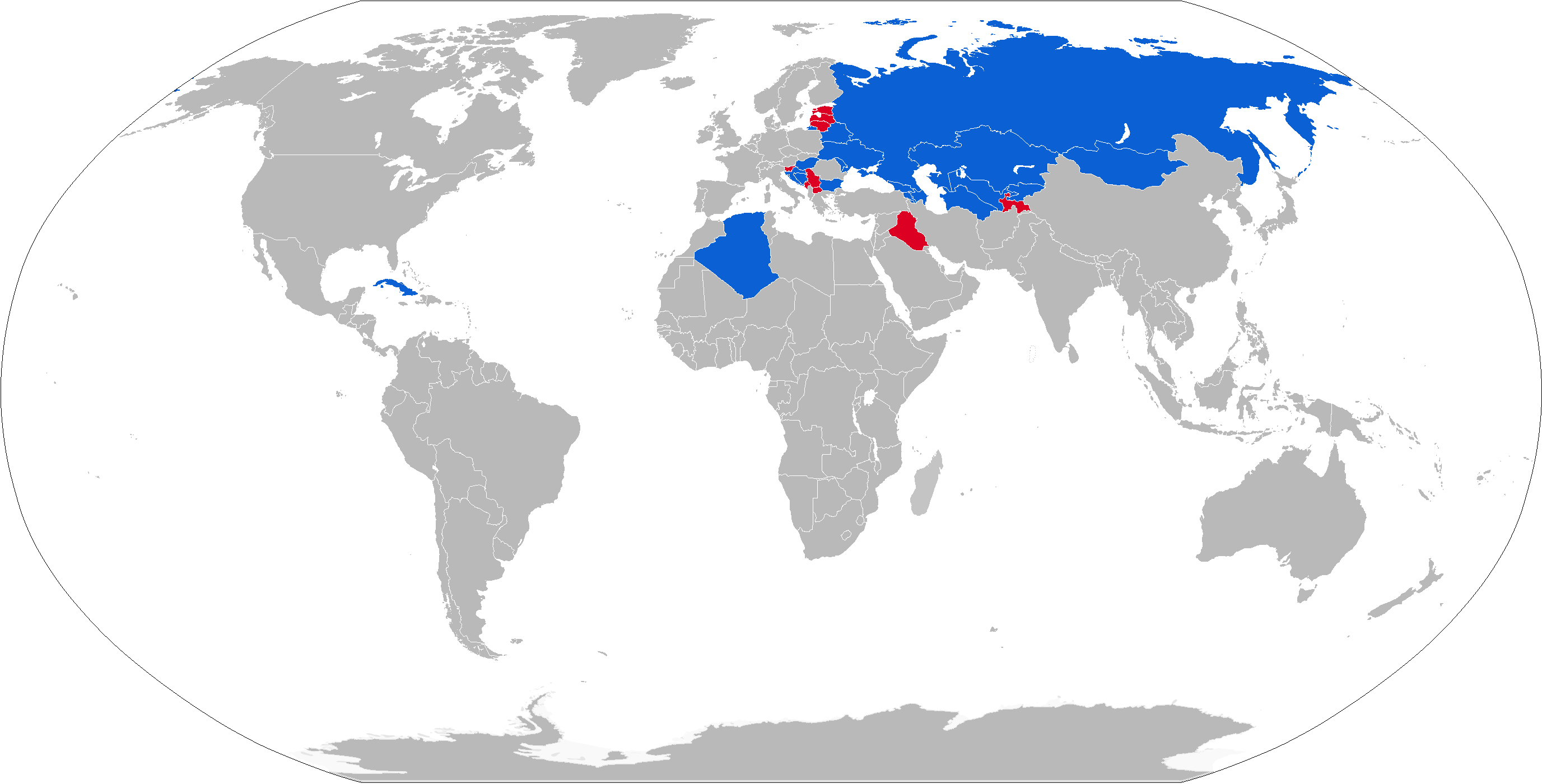
 *: 10
*: 126
*: 80
*: 16
*: 68
*: 18
*: 37
*
*: 20+
*
*: 10
*: 126
*: 80
*: 16
*: 68
*: 18
*: 37
*
*: 20+
* Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
*: 60
*: 500
*: 36
*
Former operators
* * * *: 267 *: 100 *: 50 * *: 100 *People's Republic of Kampuchea
The People's Republic of Kampuchea (PRK), UNGEGN: , ALA-LC: ; vi, Cộng hòa Nhân dân Campuchia was a partially recognised state in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as So ...
: 15
*: 25
*: 25
*: 72
*
*: 350
Combat history
Russo-Ukrainian War
During theRusso-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Rev ...
(2014-present) the T-12's successor, the MT-12 is known to have been widely used on both sides. During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. ...
, Ukrainian forces have also been observed using the MT-12, see MT-12. Use of the T-12 is not known to have been reported. However, the two Ukrainian self propelled 100 mm T-12's are undoubtedly T-12's, not MT-12's.
Second Nagorno-Karabakh War
During theSecond Nagorno-Karabakh War
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of an unresolved conflict over the region, involving Azerbai ...
(2020), the T-12 was used on the Armenian side.
Transnistria conflict
During the 1992 Battle for Tighina/Bender, part of theTransnistria conflict
The Transnistria conflict ( ro, Conflictul din Transnistria; russian: Приднестровский конфликт, Pridnestrovskiy konflikt) is an ongoing frozen conflict between Moldova and the unrecognized state of Transnistria. Its m ...
, the Moldovan military utilized MT-12s to engage T-64BV
The T-64 is a Soviet Union, Soviet tank manufactured in Kharkiv, and designed by Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau. The tank was introduced in the early 1960s. It was a more advanced counterpart to the T-62: the T-64 served in tank di ...
tanks of the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR).
Other conflicts
Incomplete, and stil requiring thorough check whether T-12 or MT-12 was used: *Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen (alongside smaller groups of anti-Sovie ...
* Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Ba'athist Iraq, Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations S ...
* Persian Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
* War of Dagestan
The Dagestan War (russian: Дагестанская война), also known as the Invasion of Militants in Dagestan (russian: Вторжение боевиков в Дагестан) began when the Chechnya-based Islamic International Peacekeep ...
* Russo-Georgian War
The 2008 Russo-Georgian WarThe war is known by a variety of other names, including Five-Day War, August War and Russian invasion of Georgia. was a war between Georgia, on one side, and Russia and the Russian-backed self-proclaimed republics of Sou ...
* Syrian civil war
Variants
Ukraine
 In August 2022, videos of a Ukrainian T-12 mounted on top of an MT-LB began to circulate online. While the combination was widely reported as mounting an MT-12, these same publications consistently showed photographs of a T-12 being mounted. The conversion was done by local infantrymen. These were even so clever as to mount hydraulic supports at the back of the MT-LB. This would stabilize the shot, and lessen the effort to re-aim after each shot. In effect it does not matter whether the gun is a T-12 or an MT-12, because the gun itself is identical. What is far more interesting are the pictures of this self propelled variant firing at elevations of about 35 degrees.
The usefulness of this first "T-12 on MT-LB" idea made that more Ukrainian units sought to acquire such a combination.
In August 2022, videos of a Ukrainian T-12 mounted on top of an MT-LB began to circulate online. While the combination was widely reported as mounting an MT-12, these same publications consistently showed photographs of a T-12 being mounted. The conversion was done by local infantrymen. These were even so clever as to mount hydraulic supports at the back of the MT-LB. This would stabilize the shot, and lessen the effort to re-aim after each shot. In effect it does not matter whether the gun is a T-12 or an MT-12, because the gun itself is identical. What is far more interesting are the pictures of this self propelled variant firing at elevations of about 35 degrees.
The usefulness of this first "T-12 on MT-LB" idea made that more Ukrainian units sought to acquire such a combination.
Romania
* A407 - This artillery system was designed by Arsenal-Resita and is very similar to the MT-12. It can fire the same range of ammunition as the T-54/55 tank and has a maximum range of 2,200 m (HEAT) or 4,000 m (APC-T). Subversions are the A407M1 and the A407M2. InRomanian Army
The Romanian Land Forces ( ro, Forțele Terestre Române) is the army of Romania, and the main component of the Romanian Armed Forces. In recent years, full professionalisation and a major equipment overhaul have transformed the nature of the Lan ...
service, the A407 is known as the 100 mm anti-tank gun M1977 ( ro, Tun antitanc calibrul 100-mm Model 1977) and is normally towed by the DAC 887R truck.Jane's Armour and Artillery 2003-2004 It can also be towed with the DAC 665T truck. The Model 2002 is an improved version, fitted with the automatic fire control system TAT-100.http://www.arsenal.ro/Arsenal/
People's Republic of China
* Type 73 - This appears to be a copy of the Soviet T-12. * Type 86 - This is a 100mm smoothbore anti-tank gun that has some similarities with the 85mm Type 56 (D-44). It fires ammunition of the fixed type, including the Type 73 HE, Type 73 HEAT, Type 73 APFSDS and Type 86 APFSDS to a maximum range of 1,800 m.See also
* List of anti-tank guns *List of military equipment of Croatia
The List of military equipment of Croatia is an alphabetical listing of all types used by or produced in Croatia since independence in 1991.
A
* Agram 2000/2002: 9 mm weapon made in Croatia.
* APS-95: 5.56 mm rifle made in Cro ...
* List of artillery of the Soviet Union and Russia
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * USA Today article - https://www.usatoday.com/news/world/iraq/2003-03-25-war-zone_x.htm * 100 mm Ammunition https://web.archive.org/web/20070927080509/http://www.milparade.com/catalog/pdf/698.pdf * 100 mm Ammunition https://web.archive.org/web/20070927080621/http://www.milparade.com/catalog/pdf/697.pdf * 100 mm Ammunition https://web.archive.org/web/20041223234049/http://www.milparade.com/catalog/pdf/696.pdf * MT-12 https://web.archive.org/web/20041214105425/http://www.milparade.com/catalog/pdf/99.pdf * ''Jane's Armour and Artillery 2005-2006'' * http://rbase.new-factoria.ru/missile/wobb/bastion/bastion.shtmlExternal links
T-12 walkaround on DishModels.ru
* http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/russia/t-12.htm
part of
' a publication of the
United States Army Center of Military History
The United States Army Center of Military History (CMH) is a directorate within the United States Army Training and Doctrine Command. The Institute of Heraldry remains within the Office of the Administrative Assistant to the Secretary of the Ar ...
* https://web.archive.org/web/20041223150348/http://www.milparade.com/catalog/part5/tank_rounds.shtml
* http://www.arsenal.ro/Arsenal/
{{SovArtyColdWar
100 mm artillery
Anti-tank guns of the Soviet Union
Cold War artillery of the Soviet Union
Anti-tank guns of the Cold War
Military equipment introduced in the 1960s