Ténéré on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ténéré ( Tuareg: Tenere, literally: "desert") is a desert region in the south central Sahara. It comprises a vast plain of
sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
stretching from northeastern Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesChad, occupying an area of over . The Ténéré's boundaries are said to be the
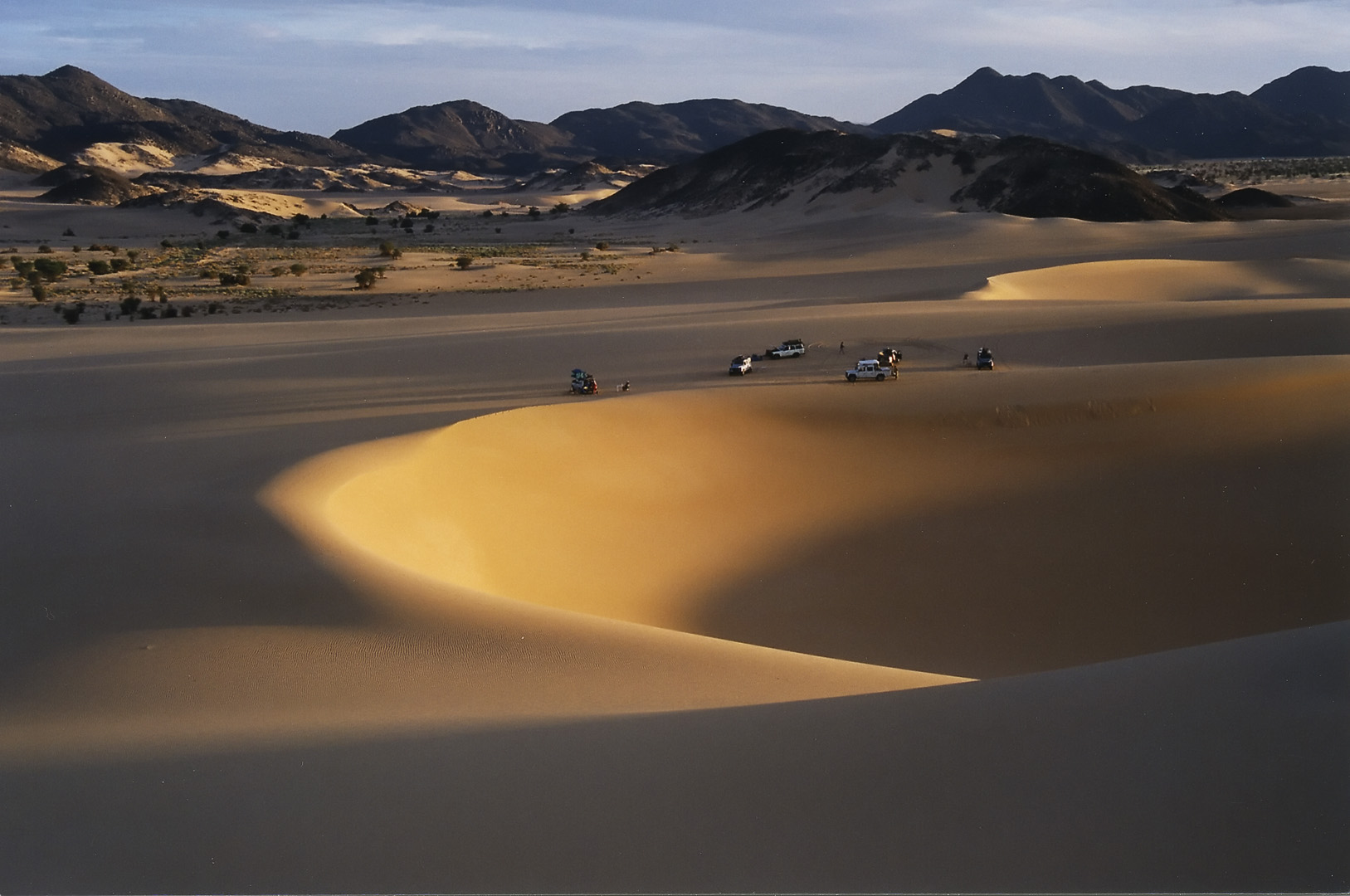 Most of the Ténéré is a flat basin, once the bed of the prehistoric Lake Chad. In the north, the Ténéré is a vast sand sheet - the true, featureless 'Ténéré' of legend reaching up to the low hills of the Tassili du Hoggar along the Algerian border. In the centre, the Bilma Erg forms rows of easily navigable low dunes whose corridors make regular byways for the azalai or salt caravans. To the west, the
Most of the Ténéré is a flat basin, once the bed of the prehistoric Lake Chad. In the north, the Ténéré is a vast sand sheet - the true, featureless 'Ténéré' of legend reaching up to the low hills of the Tassili du Hoggar along the Algerian border. In the centre, the Bilma Erg forms rows of easily navigable low dunes whose corridors make regular byways for the azalai or salt caravans. To the west, the

Aïr Mountains
The Aïr Mountains or Aïr Massif ( tmh, Ayăr; Hausa: Eastern ''Azbin'', Western ''Abzin'') is a triangular massif, located in northern Niger, within the Sahara. Part of the West Saharan montane xeric woodlands ecoregion, the ...
in the west, the Hoggar Mountains
The Hoggar Mountains ( ar, جبال هقار, Berber: ''idurar n Ahaggar'') are a highland region in the central Sahara in southern Algeria, along the Tropic of Cancer. The mountains cover an area of approximately 550,000 km.
Geography
This ...
in the north, the Djado Plateau in the northeast, the Tibesti Mountains
The Tibesti Mountains are a mountain range in the central Sahara, primarily located in the extreme north of Chad, with a small portion located in southern Libya. The highest peak in the range, Emi Koussi, lies to the south at a height of and i ...
in the east, and the basin of Lake Chad in the south. The central part of the desert, the Erg du Bilma, is centred at approximately . It is the locus of the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Tenerian culture.
Name
The name ''Ténéré'' comes from the Tuareg language, meaning "desert", in much the same way that theArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
word for "desert", '' Sahara'', came to be applied to the region as a whole.
Climate
The Ténéré has ahot desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''BWh''), typical of the large Sahara Desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
. The climate is hyper-arid, extremely hot, sunny and dry year-round and there is virtually no plant life. The average high temperatures are above 40 °C (104 °F) for about 5 months and more in the hottest regions, and record high temperatures as high as 50 °C (122 °F) are highly possible during summer. The annual average high temperature is around 35 °C (95 °F) and even more. During "winter" months, the average high temperatures stay above 25 °C (77 °F) and generally hover around 30 °C (86 °F).
The annual precipitation amount is extremely low—one of the lowest annual rainfall amounts found on Earth—around 10 mm (0.39 in) to 15 mm (0.59 in), and frequently several years may pass without seeing any rainfall at all. Water is notoriously difficult to find, even underground, and wells may be hundreds of miles apart.
The sunshine duration is also one of the highest results on the planet at around 4,000 hours, that is about 91% of the daylight hours between sunrise and sunset. This part of the Sahara Desert has one of the harshest climates in the world. According to a NASA study, the sunniest spot in the world would be a ruined fort in Agadem in the southeastern Ténéré, and has even clearer skies than the polar deserts overall. The Ténéré, as well as the rest of the Great Desert, is among the most extreme environments on Earth.
Topography
 Most of the Ténéré is a flat basin, once the bed of the prehistoric Lake Chad. In the north, the Ténéré is a vast sand sheet - the true, featureless 'Ténéré' of legend reaching up to the low hills of the Tassili du Hoggar along the Algerian border. In the centre, the Bilma Erg forms rows of easily navigable low dunes whose corridors make regular byways for the azalai or salt caravans. To the west, the
Most of the Ténéré is a flat basin, once the bed of the prehistoric Lake Chad. In the north, the Ténéré is a vast sand sheet - the true, featureless 'Ténéré' of legend reaching up to the low hills of the Tassili du Hoggar along the Algerian border. In the centre, the Bilma Erg forms rows of easily navigable low dunes whose corridors make regular byways for the azalai or salt caravans. To the west, the Aïr Mountains
The Aïr Mountains or Aïr Massif ( tmh, Ayăr; Hausa: Eastern ''Azbin'', Western ''Abzin'') is a triangular massif, located in northern Niger, within the Sahara. Part of the West Saharan montane xeric woodlands ecoregion, the ...
rise up. To the southeast, the Ténéré is bordered by the Kaouar cliffs running 100 km north to south. At the base, lies a string of oases including the famous Bilma.
Periodic outcrops, such as the unusual marble Blue Mountains in the northwest near Adrar Chiriet, or the Agram hills near the oasis of Fachi and Adrar Madet to the north, are rare but notable landmarks.
History
During the Carboniferous period, the region was beneath the sea; later it was a tropical forest. A majordinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
cemetery lies southeast of Agadez at Gadoufaoua
The Elrhaz Formation is a geological formation in Niger, central Africa.
Its strata date back to the Early Cretaceous, about 125 to 112 million years ago. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, alongsi ...
; many fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s have been found there, having eroded out from the ground. An almost complete specimen of the crocodile-like reptile '' Sarcosuchus imperator'', nicknamed the '' SuperCroc'', was discovered there by paleontologists.
During early human history, this was a fertile land much more congenial to human life than it is now. The region was inhabited by modern humans as long ago as the Paleolithic period some 60,000 years ago. They hunted wild animals and left evidence of their presence in the form of stone tools including tiny, finely carved arrow heads. During the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
period about 10,000 years ago, ancient hunters, the early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
Kiffian people, created rock engravings and cave paintings that can still be found across the region.
The Neolithic Subpluvial
The African humid period (AHP) (also known by other names) is a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grasses, ...
was an extended meteorological period, from about 7,500-7,000 BC to about 3,500-3,000 BC, of relatively wet and rainy conditions in the climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
history of northern Africa. It was both preceded and followed by much drier periods. Several archaeological sites that date from this time, often identified as part of the Tenerian culture, are dotted across the deserts along the borders of Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesAlgeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
. The human population dwindled as the Sahara dried out, and by 2500 BC, it had largely become as dry as it is today.
In recent times, Ténéré has been a crossing route for African migrants looking to immigrate to Europe.
Population
The Ténéré is very sparsely populated. Fachi and Bilma are the only settlements that are not on the edge of the Tenéré. While the well-known Tuareg occupy theAïr Mountains
The Aïr Mountains or Aïr Massif ( tmh, Ayăr; Hausa: Eastern ''Azbin'', Western ''Abzin'') is a triangular massif, located in northern Niger, within the Sahara. Part of the West Saharan montane xeric woodlands ecoregion, the ...
and Agadez
Agadez ( Air Tamajeq: ⴰⴶⴰⴷⴰⵣ, ''Agadaz''), formerly spelled Agadès, is the fifth largest city in Niger, with a population of 110,497 based on the 2012 census. The capital of Agadez Region, it lies in the Sahara desert, and is also ...
to the west, and still operate the salt caravans for Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
...
merchants, other inhabitants of the Ténéré, found from oases like Fachi eastwards, are the non-Berber Kanuri and Toubou
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an ethnic group native to the Tibesti Mountains that inhabit the central Sahara in northern Chad, southern Libya and northeastern Niger. They live either as herders and nomads or as ...
, the latter thought to be descended from among the original inhabitants of the Sahara.
Governance
In 1960, the Tuareg territory became part of the independent republic of Niger. It has been divided into seven ''départments''. The central part of the Ténéré is a protected area, under the auspices of the Aïr and Ténéré Natural Reserve.Cities
The administrative centre of the Ténéré is the town ofAgadez
Agadez ( Air Tamajeq: ⴰⴶⴰⴷⴰⵣ, ''Agadaz''), formerly spelled Agadès, is the fifth largest city in Niger, with a population of 110,497 based on the 2012 census. The capital of Agadez Region, it lies in the Sahara desert, and is also ...
, south of the Aïr Mountains and west of the Tenere. There are also various oasis settlements, some like Bilma and Séguedine based on salt production.
Settlements and villages of Ténéré:
* Fachi
*
*Bilma
Bilma is an oasis town and commune in north east Niger with, as of the 2012 census, a total population of 4,016 people.
It lies protected from the desert dunes under the Kaouar Cliffs and is the largest town along the Kaouar escarpment. It ...
*Dirkou
Dirkou is a town in the Bilma Department, Agadez Region of north-eastern Niger. It lies in the northern Kaouar escarpment, a north–south line of cliffs which form an isolated oasis in the Sahara desert. As of 2011, the commune had a total po ...
*
*
* Séguedine
Landmarks
The desert is also known for the celebrated Tree of Ténéré, once thought to be among the most remote in the world. Situated by the last well before entering the Grand Erg du Bilma on the way to Fachi, salt caravans relied on the tree as a landmark until it was allegedly knocked down by a truck driver in 1973. It was replaced by a metal sculpture and the remains are enshrined at the museum in Niamey (capital of Niger). New trees were planted but, because of the very low water table (the adjacent well is some 40m deep), irregular watering by passing travellers saw them fail to survive. Despite this unfortunate mishap, the tree is still often indicated on maps of the region as a notable landmark, as is the less well-known Arbre Perdu (Lost Tree) situated in the true Tenere to the north, west of Chirfa. A monument toUTA Flight 772
UTA Flight 772 was a scheduled international passenger flight of the French airline Union de Transports Aériens (UTA) operating from Brazzaville in the People's Republic of the Congo, via N'Djamena in Chad, to Charles de Gaulle Airport in Pari ...
, a 200-foot diameter circle of dark stones and 170 broken mirrors which represent each victim of the 1989 terrorist attack which brought down the aircraft, was built in May and June 2007 at 16°51′53″N 11°57′13″E.
View


See also
*Aïr and Ténéré National Nature Reserve
The Aïr and Ténéré National Nature Reserve is a national nature reserve in Niger. It includes several overlapping reserve designations, and is designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It covers both the eastern half of the Aïr Mountains and ...
*Germa
Germa ( ar, جرمة), known in ancient times as Garama, is an archaeological site in Libya. It was the capital of the Garamantian Kingdom.
The Garamantes were a Berber people living in the Fezzan in the northeastern Sahara Desert. Garamantian p ...
* Green Sahara
* The Ténéré motorbike
* Missions Berliet-Ténéré
References
* Samuel Decalo. Historical Dictionary of Niger. Scarecrow Press, London and New Jersey (1979). * Jolijn Geels. Niger. Bradt London and Globe Pequot New York (2006). . * Chris Scott. Sahara Overland. Trailblazer (2004). . {{DEFAULTSORT:Tenere Natural regions Deserts of Niger Ergs of Africa Tuareg World Heritage Sites in Niger