Szaloncukor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Szaloncukor'' ( Slovak: ''salónka'', plural ''salónky''; literally: "parlour candy",
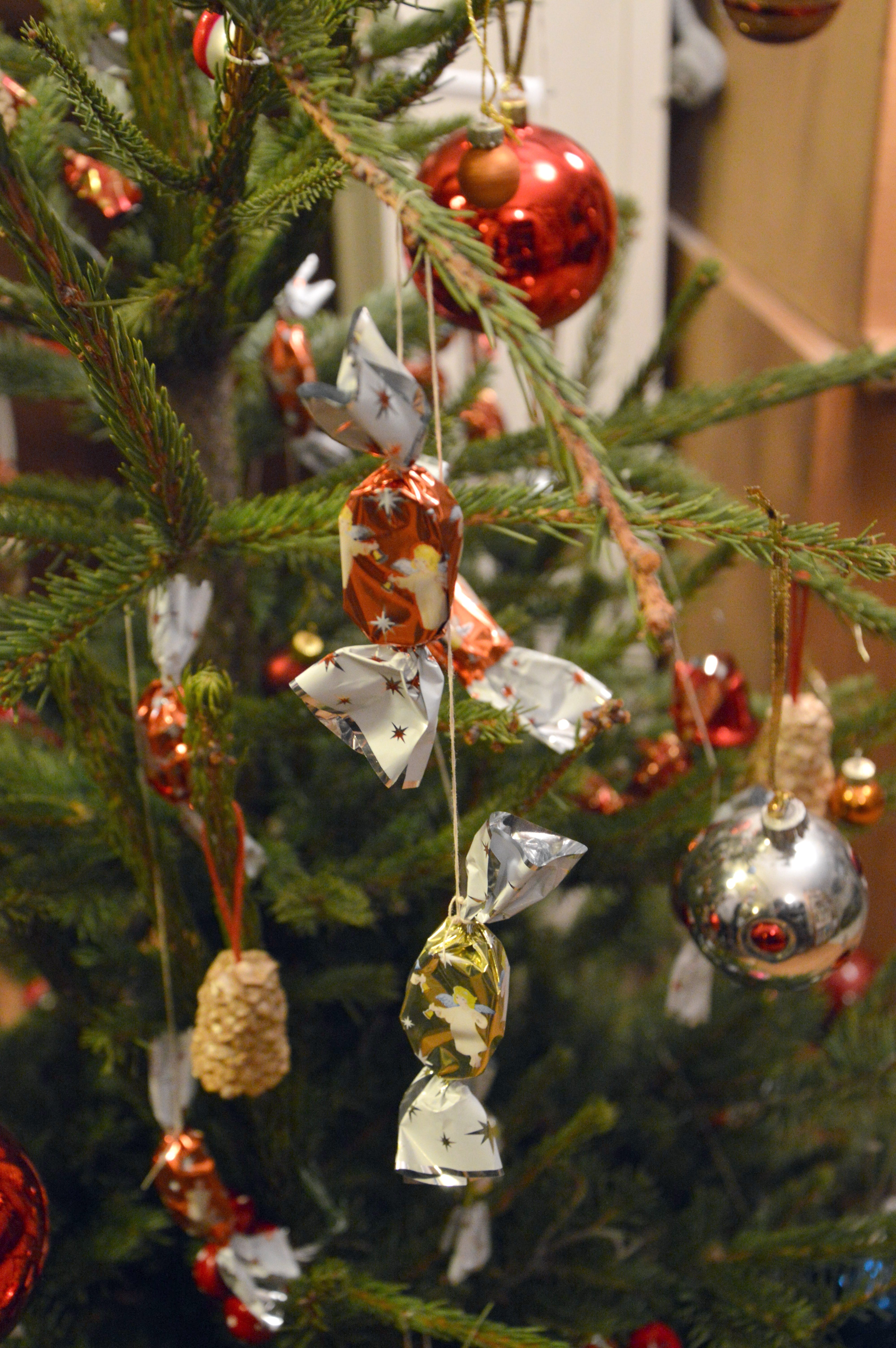 The earliest version of this fondant dessert emerged during the 14th century in France and was called ''fondantcukor''. The recipe was altered through the years of European confectionery history. French pastry chef Pierre-Andre Manion in the 17th century introduced ''fondantcukor'' recipe in Germany.
The popularity of the fondant candies reached Hungary when German craftsmen migrated there in the 19th century. German wealthy families would erect Christmas trees in the entrance halls of their homes (called salons) and decorate them with sweets wrapped in shiny paper.
Such candies were made first in the 14th century in
The earliest version of this fondant dessert emerged during the 14th century in France and was called ''fondantcukor''. The recipe was altered through the years of European confectionery history. French pastry chef Pierre-Andre Manion in the 17th century introduced ''fondantcukor'' recipe in Germany.
The popularity of the fondant candies reached Hungary when German craftsmen migrated there in the 19th century. German wealthy families would erect Christmas trees in the entrance halls of their homes (called salons) and decorate them with sweets wrapped in shiny paper.
Such candies were made first in the 14th century in About the company
Trebišov: ChocoSuc Partner. Retrieved December 29, 2014. Note
Slovak version's
"Trebišovské vianočné kolekcie, ''salónky'' a dezerty... " translated to English as "The Trebišov Christmas collection, sweets and desserts". See als
Business Register of the District Court Košice I
Insert No. 18398/V.
Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
** Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditiona ...
: ''bomboane de pom'') is a type of sweet traditionally associated with Christmas in Hungary, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
. It is a typical imported and adapted Hungarikum. It is assumed that almost the whole quantity consumed in Romania are of Hungarian production, as Romanian chocolate production decreased substantially after the fall of communism. It is usually made of fondant, covered by chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec ci ...
and wrapped in shiny coloured foil, then hung on the Christmas tree
A Christmas tree is a decorated tree, usually an evergreen conifer, such as a spruce, pine or fir, or an artificial tree of similar appearance, associated with the celebration of Christmas. The custom was further developed in early modern ...
as decoration.
Every year, almost a kilo and a half of it are consumed per household during Christmas season.
The tradition of hanging these candies on the Christmas tree started in the 19th century. It was named ''szaloncukor'' because the tree usually stood in the parlour (''szalon'' in Hungarian; ''Cukor'' means "sugar" or "candy"; in Slovak ''salón'' is "parlour" and ''-ka'' is diminutive
A diminutive is a root word that has been modified to convey a slighter degree of its root meaning, either to convey the smallness of the object or quality named, or to convey a sense of intimacy or endearment. A ( abbreviated ) is a word-form ...
suffix).
The name comes from the German-Austrian ''Salonzuckerl'', this is why the original name was ''szalonczukkedli''.
Manufacturing
The whole procedure was manual until the first fondant-machines have appeared. These were made by Stühmer chocolate factory for the famous sweet-shop, Gerbaud. The last part of the procedure to be mechanized was the thrumming of the end of the paper cover. Considering that it has such a typical shape to keep, this part was not to be omitted. Fondant candies originally came in a few flavours (vanilla and strawberry for example), but now there is a variety of candies, including jelly, coconut, hazelnut and many other flavors. It is usually hung on the tree with strings or small metal hooks. It is considered traditional on children's part, no matter how adults may frown, to empty all the wrappers on the tree before the season is out.History
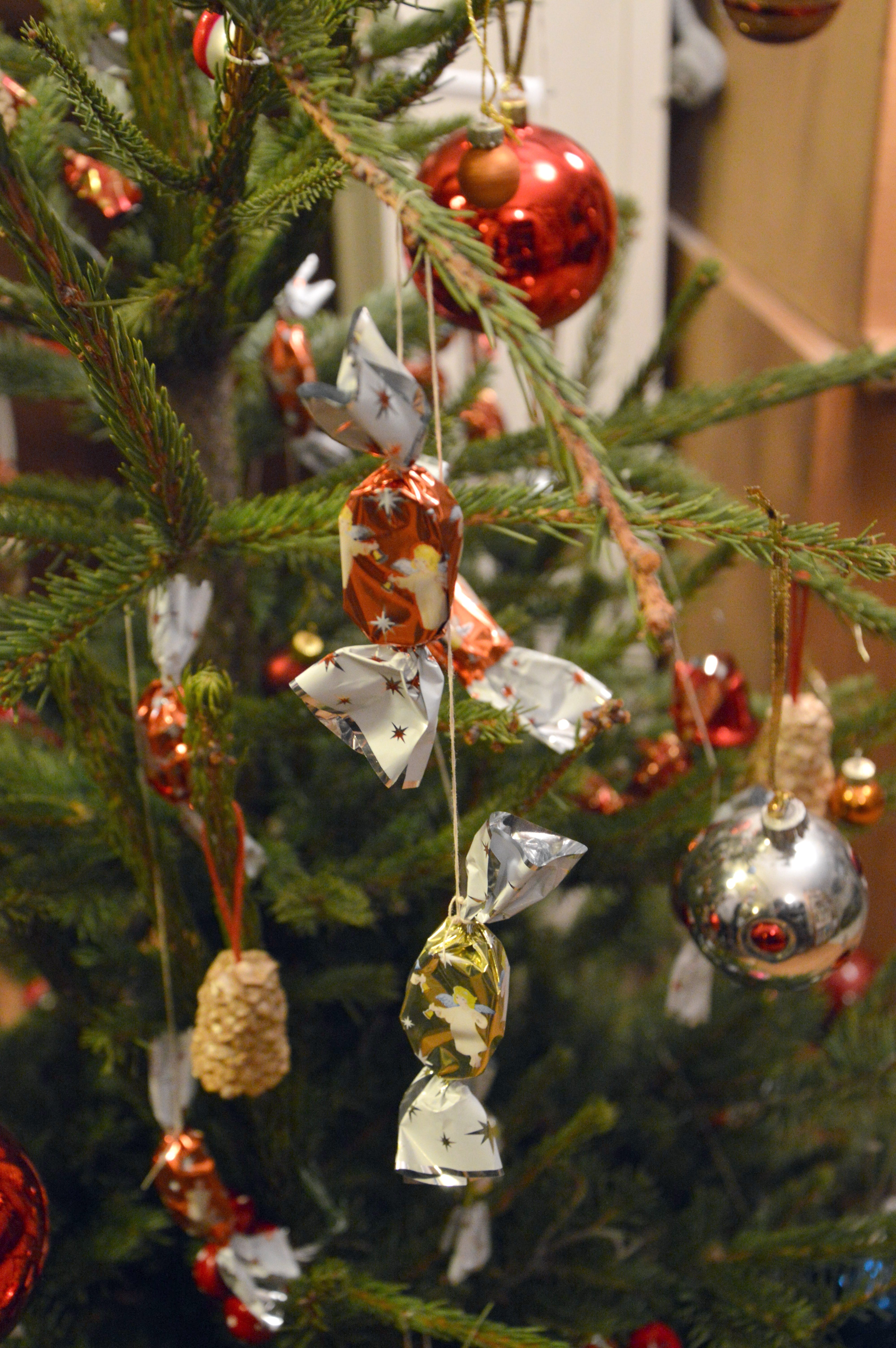 The earliest version of this fondant dessert emerged during the 14th century in France and was called ''fondantcukor''. The recipe was altered through the years of European confectionery history. French pastry chef Pierre-Andre Manion in the 17th century introduced ''fondantcukor'' recipe in Germany.
The popularity of the fondant candies reached Hungary when German craftsmen migrated there in the 19th century. German wealthy families would erect Christmas trees in the entrance halls of their homes (called salons) and decorate them with sweets wrapped in shiny paper.
Such candies were made first in the 14th century in
The earliest version of this fondant dessert emerged during the 14th century in France and was called ''fondantcukor''. The recipe was altered through the years of European confectionery history. French pastry chef Pierre-Andre Manion in the 17th century introduced ''fondantcukor'' recipe in Germany.
The popularity of the fondant candies reached Hungary when German craftsmen migrated there in the 19th century. German wealthy families would erect Christmas trees in the entrance halls of their homes (called salons) and decorate them with sweets wrapped in shiny paper.
Such candies were made first in the 14th century in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. By the beginning of the 19th century it came through German intermediates to Hungary. In 1891, Hungarian-French chef and entrepreneur Hegyesi Joseph coined the name Szaloncukor which is derived from German fondant candy called "Salonzuckerl" which mean "Sugar in Salons".
The mass production of fondant candies wrapped in foil packaging was manufactured by steam-powered engines in 1883 in Hungary, mostly dedicated for creating traditional cakes of the Gerbeaud brand.
Following Gerbeaud as inspiration, the family of Geza Kugler founded a chocolate factory in 1886. The Gerbeauds and Kuglers each adopted their own version of the recipe and published 19th-century recipe books of Hungarian confectionery. By the end of the 1800s, the candies were packed in tinfoil balls and colored tissue papers.
In 1941, the Kuglers opened the largest chocolate factory in Hungary.
In 1951 chocolate factory DEVA was founded in Trebišov, Czechoslovakia (today Slovakia), which has been producing one of the best known chocolate Christmas candy in Slovakia, including "parlour candy" (''salónky''). Today, DEVA is brand owned by company ChocoSuc Partner s.r.o.Trebišov: ChocoSuc Partner. Retrieved December 29, 2014. Note
Slovak version's
"Trebišovské vianočné kolekcie, ''salónky'' a dezerty... " translated to English as "The Trebišov Christmas collection, sweets and desserts". See als
Business Register of the District Court Košice I
Insert No. 18398/V.
See also
*Christmas trees
A Christmas tree is a decorated tree, usually an evergreen conifer, such as a spruce, pine or fir, or an artificial tree of similar appearance, associated with the celebration of Christmas. The custom was further developed in early modern G ...
References
{{Christmas Hungarian cuisine Confectionery Christmas food Christmas decorations Chocolate