Syringe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a
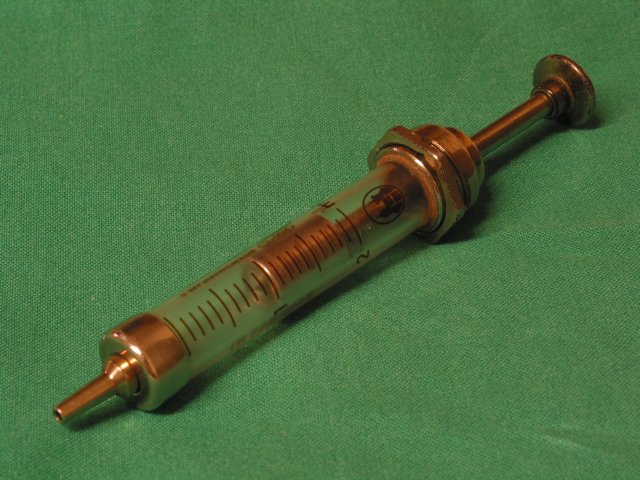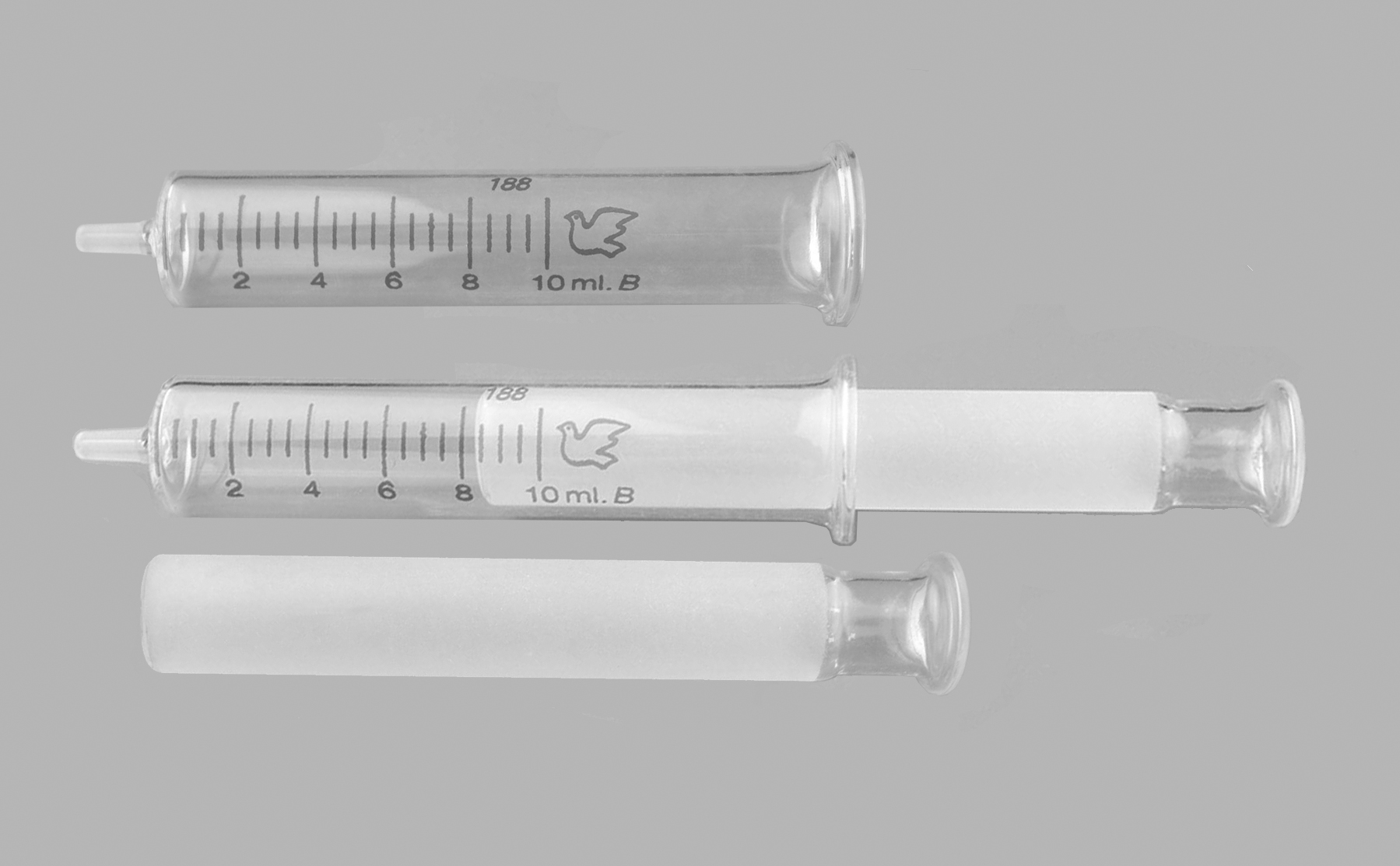
 Sectors in the syringe and needle market include disposable and safety syringes, injection pens, needleless injectors, insulin pumps, and specialty needles. Hypodermic syringes are used with
Sectors in the syringe and needle market include disposable and safety syringes, injection pens, needleless injectors, insulin pumps, and specialty needles. Hypodermic syringes are used with
 A dose-sparing syringe is one which minimises the amount of liquid remaining in the barrel after the plunger has been depressed. These syringes feature a combined needle and syringe, and a protrusion on the face of the plunger to expel liquid from the needle hub. Such syringes were particularly popular during the
A dose-sparing syringe is one which minimises the amount of liquid remaining in the barrel after the plunger has been depressed. These syringes feature a combined needle and syringe, and a protrusion on the face of the plunger to expel liquid from the needle hub. Such syringes were particularly popular during the
 Medical-grade disposable hypodermic syringes are often used in research laboratories for convenience and low cost. Another application is to use the needle tip to add liquids to very confined spaces, such as washing out some scientific apparatus. They are often used for measuring and transferring solvents and reagents where a high precision is not required. Alternatively, microliter syringes can be used to measure and dose chemicals very precisely by using a small diameter capillary as the syringe barrel.
The
Medical-grade disposable hypodermic syringes are often used in research laboratories for convenience and low cost. Another application is to use the needle tip to add liquids to very confined spaces, such as washing out some scientific apparatus. They are often used for measuring and transferring solvents and reagents where a high precision is not required. Alternatively, microliter syringes can be used to measure and dose chemicals very precisely by using a small diameter capillary as the syringe barrel.
The
Inventors of the hypodermic syringeMedical syringe patentsYouTube video
of a juvenile

 A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)), one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps, is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. It is commonly used ...
, a nozzle or tubing to direct the flow into and out of the barrel. Syringes are frequently used in clinical medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practice ...
to administer injections, infuse intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
into the bloodstream, apply compounds such as glue
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
or lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, t ...
, and draw/measure liquids. There are also prefilled syringes (disposable syringes marketed with liquid inside).
The word "syringe" is derived from the Greek σύριγξ ('' syrinx'', meaning "Pan flute", "tube").
Medical syringes

 Sectors in the syringe and needle market include disposable and safety syringes, injection pens, needleless injectors, insulin pumps, and specialty needles. Hypodermic syringes are used with
Sectors in the syringe and needle market include disposable and safety syringes, injection pens, needleless injectors, insulin pumps, and specialty needles. Hypodermic syringes are used with hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)), one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps, is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. It is commonly used ...
s to inject liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, ...
or gases into body tissues, or to remove from the body. Injecting of air into a blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide awa ...
is hazardous, as it may cause an air embolism; preventing embolisms by removing air from the syringe is one of the reasons for the familiar image of holding a hypodermic syringe pointing upward, tapping it, and expelling a small amount of liquid before an injection into the bloodstream.
The barrel of a syringe is made of plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adapta ...
or glass
Glass is a non- crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenchin ...
, usually has graduated marks indicating the volume of fluid in the syringe, and is nearly always transparent. Glass syringes may be sterilized in an autoclave. Plastic syringes can be constructed as either two-part or three-part designs. A three-part syringe contains a plastic plunger/ piston with a rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
tip to create a seal between the piston and the barrel, where a two-part syringe is manufactured to create a perfect fit between the plastic plunger and the barrel to create the seal without the need for a separate synthetic rubber piston. Two-part syringes have been traditionally used in European countries
The list below includes all entities falling even partially under any of the various common definitions of Europe, geographical or political. Fifty generally recognised sovereign states, Kosovo with limited, but substantial, international rec ...
to prevent introduction of additional materials such as silicone oil needed for lubricating three-part plungers. Most modern medical syringes are plastic because they are cheap enough to dispose of after being used only once, reducing the risk of spreading blood-borne diseases. Reuse of needles and syringes has caused spread of diseases, especially HIV and hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
, among intravenous drug users. Syringes are also commonly reused by diabetics, as they can go through several in a day with multiple daily insulin injections, which becomes an affordability issue for many. Even though the syringe and needle are only used by a single person, this practice is still unsafe as it can introduce bacteria from the skin into the bloodstream and cause serious and sometimes lethal infections. In medical settings, single-use needles and syringes effectively reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
Medical syringes are sometimes used without a needle for orally administering liquid medicines to young children or animals, or milk to small young animals, because the dose can be measured accurately and it is easier to squirt the medicine into the subject's mouth instead of coaxing the subject to drink out of a measuring spoon.
Tip designs
Syringes come with a number of designs for the area in which the blade locks to the syringe body. Perhaps the most well known of these is theLuer lock
The Luer taper is a standardized system of small-scale fluid fittings used for making leak-free connections between a male-taper fitting and its mating female part on medical and laboratory instruments, including hypodermic syringe tips and need ...
, which simply twists the two together.
Bodies featuring a small, plain connection are known as slip tips and are useful for when the syringe is being connected to something not featuring a screw lock mechanism.
Similar to this is the catheter tip, which is essentially a slip tip but longer and tapered, making it good for pushing into things where there the plastic taper can form a tight seal. These can also be used for rinsing out wounds or large abscesses in veterinary use.
There is also an eccentric tip, where the nozzle at the end of the syringe is not in the centre of the syringe but at the side. This causes the blade attached to the syringe to lie almost in line with the walls of the syringe itself and they are used when the blade needs to get very close to parallel with the skin (when injecting into a surface vein or artery for example).
Standard U-100 insulin syringes
Syringes forinsulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
users are designed for standard U-100 insulin. The dilution of insulin is such that 1 mL of insulin fluid has 100 standard "units" of insulin. Since insulin vials are typically 10 mL, each vial has 1000 units.
Insulin syringes are made specifically for self injections and have friendly features:
*shorter needles, as insulin injections are subcutaneous (under the skin) rather than intramuscular,
*finer gauge needles, for less pain,
*markings in insulin units to simplify drawing a measured dose of insulin, and
* low dead space to reduce complications caused by improper drawing order of different insulin strengths.
Multishot needle syringes
There are needle syringes designed to reload from a built-in tank (container) after each injection, so they can make several or many injections on a filling. These are not used much in human medicine because of the risk of cross-infection via the needle. An exception is the personalinsulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
autoinjector
An autoinjector (or auto-injector) is a medical device designed to deliver a dose of a particular drug. The injectors were initially designed to overcome the hesitation associated with self-administration of the needle-based drug delivery devic ...
used by diabetic
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
patients and in dual-chambered syringe designs intended to deliver a prefilled saline flush solution after the medication.
Venom extraction syringes
Venom extraction syringes are different from standard syringes, because they usually do not puncture the wound. The most common types have a plastic nozzle which is placed over the affected area, and then the syringe piston is pulled back, creating a vacuum that allegedly sucks out the venom. Attempts to treat snakebites in this way are specifically advised against, as they are ineffective and can cause additional injury. Syringes of this type are sometimes used for extractinghuman botfly
The human botfly, ''Dermatobia hominis'' ( Greek δέρμα, skin + βίος, life, and Latin '' hominis'', of a human), is a species of botfly whose larvae parasitise humans (in addition to a wide range of other animals, including other primat ...
larvae from the skin.
Oral
An oral syringe is ameasuring instrument
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Est ...
used to accurately measure doses of liquid medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
, expressed in millilitres
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). ...
(mL). They do not have threaded tips, because no needle or other device needs to be screwed onto them. The contents are simply squirted or sucked from the syringe directly into the mouth of the person or animal.
Oral syringes are available in various sizes, from 1–10 mL and larger. The sizes most commonly used are 1 mL, 2.5 mL and 5 mL.
Dental syringes
A dental syringe is a used bydentist
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry (the diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the oral cavity and other aspects of the craniofacial c ...
s for the injection of an anesthetic. It consists of a breech-loading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition ( cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally breec ...
syringe fitted with a sealed cartridge containing an anesthetic solution.
In 1928, Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceutic ...
Dental developed, coined and produced a sealed cartridge system under the registered trademark Carpule®. The current trademark owner is Kulzer Dental GmbH.
The carpules have long been reserved for anesthetic products for dental use. It is practically a bottomless flask. The latter is replaced by an elastomer plug that can slide in the body of the cartridge. This plug will be pushed by the plunger of the syringe. The neck is closed with a rubber cap. The dentist places the cartridge directly into a stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's r ...
syringe, with a double-pointed (single-use) needle. The tip placed on the cartridge side punctures the capsule and the piston will push the product. There is therefore no contact between the product and the ambient air during use.
The ancillary tool (generally part of a dental engine) used to supply water, compressed air or mist (formed by combination of water and compressed air) to the oral cavity for the purpose of irrigation (cleaning debris away from the area the dentist is working on), is also referred to as a dental syringe or a dental irrigation nozzle.
A 3-way syringe/nozzle has separate internal channels supplying air, water or a mist created by combining the pressurized air with the waterflow. The syringe tip can be separated from the main body and replaced when necessary.
In the UK and Ireland, manually operated hand syringes are used to inject lidocaine into patients' gums.
Dose-sparing syringes
 A dose-sparing syringe is one which minimises the amount of liquid remaining in the barrel after the plunger has been depressed. These syringes feature a combined needle and syringe, and a protrusion on the face of the plunger to expel liquid from the needle hub. Such syringes were particularly popular during the
A dose-sparing syringe is one which minimises the amount of liquid remaining in the barrel after the plunger has been depressed. These syringes feature a combined needle and syringe, and a protrusion on the face of the plunger to expel liquid from the needle hub. Such syringes were particularly popular during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
as vaccines were in short supply.
Regulation
In some jurisdictions, the sale or possession of hypodermic syringes may be controlled or prohibited without a prescription, due to its potential use with illegalintravenous drug
Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenously, but also at an intramuscular or subcutaneous location). Intravenous t ...
s.
Non-medical uses
The syringe has many non-medical applications.Laboratory applications
 Medical-grade disposable hypodermic syringes are often used in research laboratories for convenience and low cost. Another application is to use the needle tip to add liquids to very confined spaces, such as washing out some scientific apparatus. They are often used for measuring and transferring solvents and reagents where a high precision is not required. Alternatively, microliter syringes can be used to measure and dose chemicals very precisely by using a small diameter capillary as the syringe barrel.
The
Medical-grade disposable hypodermic syringes are often used in research laboratories for convenience and low cost. Another application is to use the needle tip to add liquids to very confined spaces, such as washing out some scientific apparatus. They are often used for measuring and transferring solvents and reagents where a high precision is not required. Alternatively, microliter syringes can be used to measure and dose chemicals very precisely by using a small diameter capillary as the syringe barrel.
The polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including b ...
construction of these disposable syringes usually makes them rather chemically resistant. There is, however, a risk of the contents of the syringes leaching plasticizers from the syringe material. Non-disposable glass syringes may be preferred where this is a problem. Glass syringes may also be preferred where a very high degree of precision is important (i.e. quantitative chemical analysis), because their engineering tolerances are lower and the plungers move more smoothly. In these applications, the transfer of pathogens is usually not an issue.
Used with a long needle or cannula, syringes are also useful for transferring fluids through rubber septa
The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly 4 million people in five c ...
when atmospheric oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
or moisture are being excluded. Examples include the transfer of air-sensitive or pyrophoric
A substance is pyrophoric (from grc-gre, πυροφόρος, , 'fire-bearing') if it ignites spontaneously in air at or below (for gases) or within 5 minutes after coming into contact with air (for liquids and solids). Examples are organolith ...
reagents such as phenylmagnesium bromide
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula , is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is ...
and ''n''-butyllithium respectively. Glass syringes are also used to inject small samples for gas chromatography (1 μl) and mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is u ...
(10 μl). Syringe drivers may be used with the syringe as well.
Cooking
Some culinary uses of syringes are injecting liquids (such asgravy
Gravy is a sauce often made from the juices of meats that run naturally during cooking and often thickened with wheat flour or corn starch for added texture. The gravy may be further coloured and flavoured with gravy salt (a simple mix of sa ...
) into other foods, or for the manufacture of some candies.
Syringes may also be used when cooking
Cooking, cookery, or culinary arts is the art, science and craft of using heat to prepare food for consumption. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire to using electric stoves, to baking in vario ...
meat to enhance flavor and texture by injecting juices inside the meat, and in baking to inject filling inside a pastry
Pastry is baked food made with a dough of flour, water and shortening (solid fats, including butter or lard) that may be savoury or sweetened. Sweetened pastries are often described as '' bakers' confectionery''. The word "pastries" suggests ...
. It is common for these syringes to be made of stainless steel components, including the barrel. Such facilitates easy disassembly and cleaning.
Others
Syringes are used to refill ink cartridges with ink infountain pen
A fountain pen is a writing instrument which uses a metal nib (pen), nib to apply a Fountain pen ink, water-based ink to paper. It is distinguished from earlier dip pens by using an internal reservoir to hold ink, eliminating the need to repeat ...
s.
Common workshop applications include injecting glue
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
into tight spots to repair joints where disassembly is impractical or impossible; and injecting lubricants onto working surfaces without spilling.
Sometimes a large hypodermic syringe is used without a needle for very small baby mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s to suckle from in artificial rearing.
Historically, large pumps that use reciprocating motion to pump water were referred to as syringes. Pumps of this type were used as early firefighting
Firefighting is the act of extinguishing or preventing the spread of unwanted fires from threatening human lives and destroying property and the environment. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter.
Firefighters typically ...
equipment.
There are fountain syringes where the liquid is in a bag or can and goes to the nozzle via a pipe. In earlier times, clyster
An enema, also known as a clyster, is an injection of fluid into the lower bowel by way of the rectum.Cullingworth, ''A Manual of Nursing, Medical and Surgical'':155 The word enema can also refer to the liquid injected, as well as to a device ...
syringes were used for that purpose.
Loose snus
Snus ( , ) is a tobacco product, originating from a variant of dry snuff in early 18th-century Sweden. It is placed between the upper lip and gum for extended periods, as a form of sublabial administration. Snus is not fermented. Although use ...
is often applied using modified syringes. The nozzle is removed so the opening is the width of the chamber. The snus can be packed tightly into the chamber and plunged into the upper lip. Syringes, called portioners, are also manufactured for this particular purpose.
Historical timeline
*Piston syringes were used in ancient times. During the 1st century AD Aulus Cornelius Celsus mentioned the use of them to treat medical complications in his ''De Medicina
''De Medicina'' is a 1st-century medical treatise by Aulus Cornelius Celsus, a Roman encyclopedist and possibly (but not likely) a practicing physician. It is the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia; only small parts still survi ...
''.
*9th century: The Iraqi/ Egyptian surgeon Ammar ibn 'Ali al-Mawsili' created a syringe in the 9th century using a hollow glass tube, and suction to remove cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble ...
from patients' eyes, a practice that remained in use until at least the 13th century.
*Pre-Columbian Native Americans created early hypodermic needles and syringes using "hollow bird bones and small animal bladders".
*1650: Blaise Pascal invented a syringe (not necessarily hypodermic) as an application of what is now called Pascal's law.
*1844: Irish physician Francis Rynd invented the hollow needle and used it to make the first recorded subcutaneous injections, specifically a sedative to treat neuralgia.
*1853: Charles Pravaz
Charles Gabriel Pravaz (24 March 1791 – 24 June 1853), a French orthopedic surgeon, pioneered the hypodermic syringe.
While the concept dated to Galen, the modern syringe is thought to have originated in 15th-century Italy, although it took se ...
and Alexander Wood independently developed medical syringes with a needle fine enough to pierce the skin. Pravaz's syringe was made of silver and used a screw mechanism to dispense fluids. Wood's syringe was made of glass, enabling its contents to be seen and measured, and used a plunger to inject them. It is effectively the syringe that is used today.
*1865: Charles Hunter coined the term "hypodermic", and developed an improvement to the syringe that locked the needle into place so that it would not be ejected from the end of the syringe when the plunger was depressed, and published research indicating that injections of pain relief could be given anywhere in the body, not just in the area of pain, and still be effective.
*1867: The Medical and Chirurgical Society of London
The Medical and Chirurgical Society of London was a learned society of physicians and surgeons which was founded in 1805 by 26 personalities in these fields who had left the Medical Society of London (founded 1773) because of disagreement with the ...
investigated whether injected narcotics had a general effect (as argued by Hunter) or whether they only worked locally (as argued by Wood). After conducting animal tests and soliciting opinions from the wider medical community, they firmly sided with Hunter.
*1899: Letitia Mumford Geer patented a syringe which could be operated with one hand and which could be used for self-administered rectal injections.
*1946: Chance Brothers in Smethwick
Smethwick () is an industrial town in Sandwell, West Midlands, England. It lies west of Birmingham city centre. Historically it was in Staffordshire.
In 2019, the ward of Smethwick had an estimated population of 15,246, while the wider b ...
, West Midlands, England, produced the first all-glass syringe with interchangeable barrel and plunger, thereby allowing mass-sterilisation of components without the need for matching them.
*1949: Australian inventor Charles Rothauser created the world's first plastic, disposable hypodermic syringe at his Adelaide factory.
*1951: Rothauser produced the first injection-moulded syringes made of polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins a ...
, a plastic that can be heat-sterilised. Millions were made for Australian and export markets.
*1956: New Zealand pharmacist and inventor Colin Murdoch
Colin Albert Murdoch (6 February 1929 – 4 May 2008) was a New Zealand pharmacist and veterinarian who made a number of significant inventions, in particular the tranquilliser gun, the disposable hypodermic syringe and the child-pro ...
was granted New Zealand and Australian patents for a disposable plastic syringe.
See also
*Fire syringe has two meanings: **Afire piston
A fire piston, sometimes called a fire syringe or a slam rod fire starter, is a device of ancient Southeast Asian origin which is used to kindle fire. It uses the principle of the heating of a gas (in this case air) by rapid and adiabatic compress ...
, a fire starting
Fire making, fire lighting or fire craft is the process of artificially starting a fire. It requires completing the fire triangle, usually by heating tinder above its autoignition temperature.
Fire is an essential tool for human survival an ...
device
**A squirt, in the form of a large syringe, one of the first firefighting
Firefighting is the act of extinguishing or preventing the spread of unwanted fires from threatening human lives and destroying property and the environment. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter.
Firefighters typically ...
devices in history used to squirt water onto the burning fuel.Walford, Cornelius. ''The insurance cyclopaedia: being a dictionary of the definitions of terms used in connexion with the theory and practice of insurance in all its branches: a biographical summary ... a bibliographical repertory of all works written upon the subject'' ... an . London: C. and E. Layton ;, 1871,1880. 337 Print.
*Autoinjector
An autoinjector (or auto-injector) is a medical device designed to deliver a dose of a particular drug. The injectors were initially designed to overcome the hesitation associated with self-administration of the needle-based drug delivery devic ...
, a device to ease injection, e.g. by the patient or other untrained personnel.
* Hippy Sippy
* Jet injector, injects without a needle, by squirting the injection fluid so fast that it makes a hole in the skin.
* Luer Taper, a standardized fitting system used for making leak-free connections between syringe tips and needles.
* Needle exchange programme, is a social policy based on the philosophy of harm reduction where injecting drug users (IDUs) can obtain hypodermic needles and associated injection equipment at little or no cost.
*Trypanophobia
Fear of needles, known in medical literature as needle phobia, is the extreme fear of medical procedures involving injections or hypodermic needles. This can lead to avoidance of medical care, including vaccine hesitancy.
It is occasionally refe ...
, a fairly common extreme fear of hypodermic syringes
* Syrette, similar to a syringe except that it has a closed flexible tube (like that used for toothpaste) instead of a rigid tube and piston.
* Syringing the ear to remove excess ear wax.
* Syrinx, the nymph from classical mythology after which syringes were supposedly named.
* Safety syringe, with features to prevent accidental needlesticks and reuse
*Vaginal syringe
A vaginal syringe was an object used in the 19th century in the Western world for douching, treating diseases and for birth control. Vaginal syringes were fairly common at the time, but were not openly discussed because of taboos about discussing ...
References
Further reading
* Hans-Jürgen Bässler und Frank Lehmann : ''Containment Technology: Progress in the Pharmaceutical and Food Processing Industry.'' Springer, Berlin 2013,External links
Inventors of the hypodermic syringe
of a juvenile
red squirrel
The red squirrel (''Sciurus vulgaris'') is a species of tree squirrel in the genus ''Sciurus'' common throughout Europe and Asia. The red squirrel is an arboreal, primarily herbivorous rodent.
In Great Britain, Ireland, and in Italy numbe ...
suckling milk from a hypodermic syringe without a needle
{{Dosage forms, state=expanded
Medical equipment
Drug delivery devices
Drug paraphernalia
Arab inventions
Egyptian inventions
New Zealand inventions