Swimmeret on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The decapod (
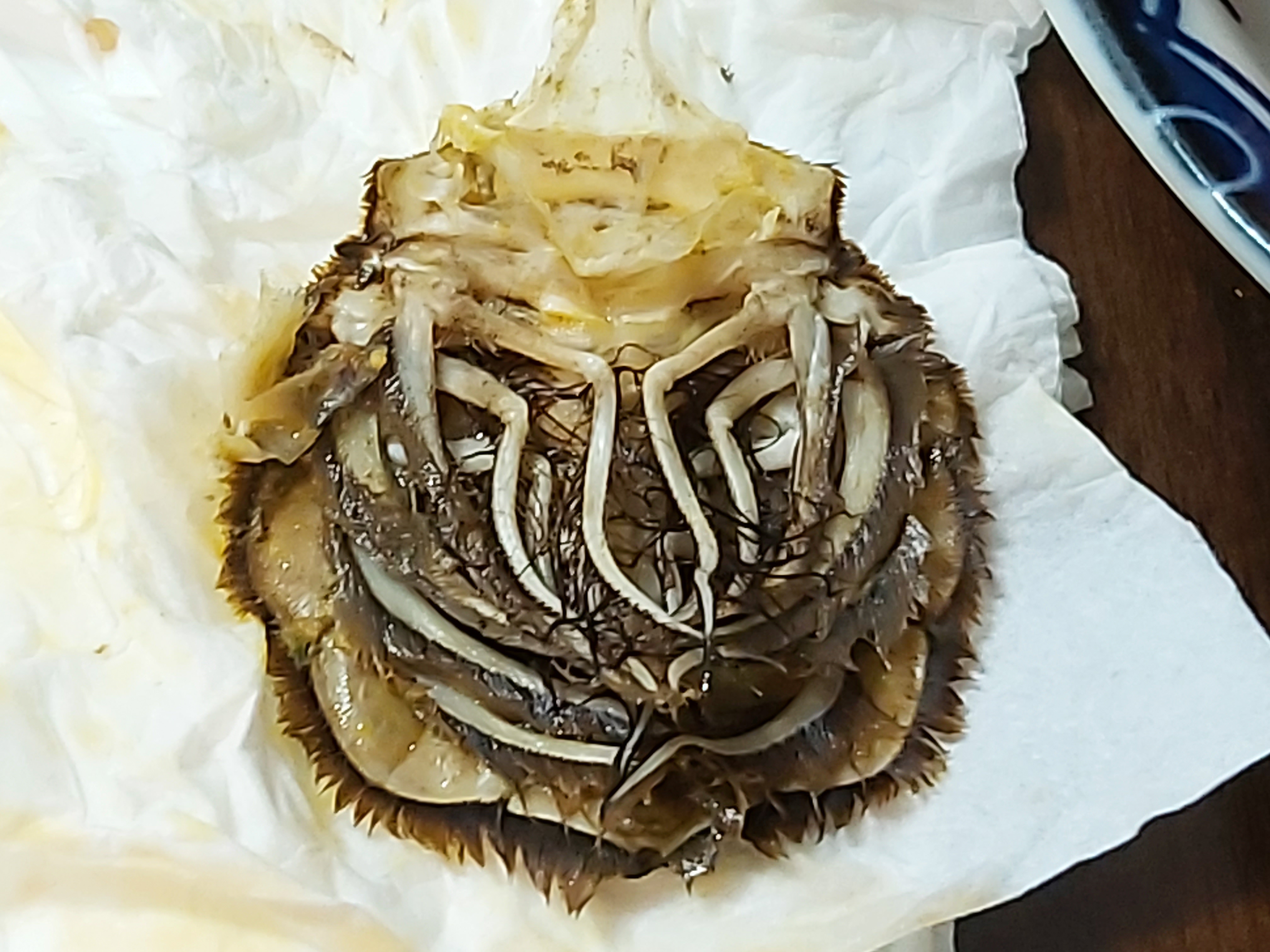 #first pleopods
#second pleopods
#third pleopods
#fourth pleopods
#fifth pleopods
#
#first pleopods
#second pleopods
#third pleopods
#fourth pleopods
#fifth pleopods
#
crustacea
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group c ...
ns such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cepha ...
and the pleon (abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
). Each segment may possess one pair of appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body.
In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including ante ...
s, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail:
Cephalothorax
Head
#antennule
Antennae ( antenna), sometimes referred to as "feelers", are paired appendages used for sensing in arthropods.
Antennae are connected to the first one or two segments of the arthropod head. They vary widely in form but are always made of one ...
s
# antennae
# mandibles
# first maxillae
# second maxillae
The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eye
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which disti ...
s. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp.
Thorax / pereon
#first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walkinglegs
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element c ...
and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods take their name. Those pereiopods which are armed with a claw ('' chela'') may be referred to as chelipeds. The moveable fingers of a claw are known as dactyls. The pereiopods bear the sexual organs, which are the third pereiopod in the female and the fifth pereiopod in the male. Each appendage from the second maxilla to the fifth pereiopod also bears a gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
. In the Anomura (hermit crab
Hermit crabs are anomuran decapod crustaceans of the superfamily Paguroidea that have adapted to occupy empty scavenged mollusc shells to protect their fragile exoskeletons. There are over 800 species of hermit crab, most of which possess an as ...
s and related animals), the fifth pair of pereiopods is often hidden inside the branchial chamber, where they are used to clean the gills. The cephalothorax is covered by a carapace
A carapace is a dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the unde ...
which protects the internal organs and the gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
s; the section of the carapace that projects in front of the eyes is called the rostrum.
Abdomen / pleon
 #first pleopods
#second pleopods
#third pleopods
#fourth pleopods
#fifth pleopods
#
#first pleopods
#second pleopods
#third pleopods
#fourth pleopods
#fifth pleopods
#uropods
Uropods are posterior appendages found on a wide variety of crustaceans. They typically have functions in locomotion.
Definition
Uropods are often defined as the appendages of the last body segment of a crustacean. An alternative definition sugg ...
Pleopods (also called ''swimmerets'') are primarily swimming legs, and are also used for brooding the eggs (except in prawns
Prawn is a common name for small aquatic crustaceans with an exoskeleton and ten legs (which is a member of the order decapoda), some of which can be eaten.
The term "prawn"Mortenson, Philip B (2010''This is not a weasel: a close look at nature ...
), catching food (then swept to the mouth), and can sometimes bear their own gills. In some taxa, the first one or two pairs of pleopods are specialised in the males for fertilisation, and are referred to as the ''gonopods
Gonopods are specialized appendages of various arthropods used in reproduction or egg-laying. In males, they facilitate the transfer of sperm from male to female during mating, and thus are a type of intromittent organ. In crustaceans and millipe ...
''.
Telson
At the end of the pleon is the tail fan, comprising a pair ofbiramous The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plu ...
uropod
Uropods are posterior appendages found on a wide variety of crustaceans. They typically have functions in locomotion.
Definition
Uropods are often defined as the appendages of the last body segment of a crustacean. An alternative definition sugge ...
s and the telson
The telson () is the posterior-most division of the body of an arthropod. Depending on the definition, the telson is either considered to be the final segment of the arthropod body, or an additional division that is not a true segment on acco ...
, which bears the anus. Together, they are used for steering while swimming, and in the caridoid escape reaction
The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.
The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfis ...
.
In crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all th ...
s and some other carcinised decapods, the abdomen is folded under the cephalothorax.
See also
*Arthropod leg The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plu ...
References
{{Anatomy Crustacean anatomy Decapods