Super-resolution imaging on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that enhance (increase) the resolution of an


"Fast and Robust Multi-frame Super-resolution"
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 1327–1344, October 2004.), the presence of aliasing is still a necessary condition for SR reconstruction.
Image processing Signal processing Imaging
imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
system. In optical SR the diffraction limit
The resolution of an optical imaging system a microscope, telescope, or camera can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to t ...
of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital imaging sensors is enhanced.
In some radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
and sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
imaging applications (e.g. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), high-resolution computed tomography
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing t ...
), subspace decomposition-based methods (e.g. MUSIC
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
) and compressed sensing
Compressed sensing (also known as compressive sensing, compressive sampling, or sparse sampling) is a signal processing technique for efficiently acquiring and reconstructing a signal, by finding solutions to underdetermined linear systems. This ...
-based algorithms (e.g., SAMV) are employed to achieve SR over standard periodogram In signal processing, a periodogram is an estimate of the spectral density of a signal. The term was coined by Arthur Schuster in 1898. Today, the periodogram is a component of more sophisticated methods (see spectral estimation). It is the most ...
algorithm.
Super-resolution imaging techniques are used in general image processing and in super-resolution microscopy
Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have resolutions higher than those imposed by the diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techni ...
.
Basic concepts
Because some of the ideas surrounding super-resolution raise fundamental issues, there is need at the outset to examine the relevant physical and information-theoretical principles: *Diffraction limit
The resolution of an optical imaging system a microscope, telescope, or camera can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to t ...
: The detail of a physical object that an optical instrument can reproduce in an image has limits that are mandated by laws of physics, whether formulated by the diffraction equations in the wave theory of light or equivalently the uncertainty principle
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle (also known as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle) is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physic ...
for photons in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistr ...
. Information transfer can never be increased beyond this boundary, but packets outside the limits can be cleverly swapped for (or multiplexed with) some inside it. One does not so much “break” as “run around” the diffraction limit. New procedures probing electro-magnetic disturbances at the molecular level (in the so-called near field) remain fully consistent with Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.
...
.
** Spatial-frequency domain: A succinct expression of the diffraction limit is given in the spatial-frequency domain. In Fourier optics Fourier optics is the study of classical optics using Fourier transforms (FTs), in which the waveform being considered is regarded as made up of a combination, or '' superposition'', of plane waves. It has some parallels to the Huygens–Fresnel pri ...
light distributions are expressed as superpositions of a series of grating light patterns in a range of fringe widths, technically spatial frequencies
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, spatial frequency is a characteristic of any structure that is periodic across position in space. The spatial frequency is a measure of how often sinusoidal components (as determined by the Fourier tra ...
. It is generally taught that diffraction theory stipulates an upper limit, the cut-off spatial-frequency, beyond which pattern elements fail to be transferred into the optical image, i.e., are not resolved. But in fact what is set by diffraction theory is the width of the passband, not a fixed upper limit. No laws of physics are broken when a spatial frequency band beyond the cut-off spatial frequency is swapped for one inside it: this has long been implemented in dark-field microscopy. Nor are information-theoretical rules broken when superimposing several bands,Lukosz, W., 1966. Optical systems with resolving power exceeding the classical limit. J. opt. soc. Am. 56, 1463–1472.Gustaffsson, M., 2000. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microscopy 198, 82–87. disentangling them in the received image needs assumptions of object invariance during multiple exposures, i.e., the substitution of one kind of uncertainty for another.
* Information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random ...
: When the term super-resolution is used in techniques of inferring object details from statistical treatment of the image within standard resolution limits, for example, averaging multiple exposures, it involves an exchange of one kind of information (extracting signal from noise) for another (the assumption that the target has remained invariant).
* Resolution and localization: True resolution involves the distinction of whether a target, e.g. a star or a spectral line, is single or double, ordinarily requiring separable peaks in the image. When a target is known to be single, its location can be determined with higher precision than the image width by finding the centroid (center of gravity) of its image light distribution. The word ''ultra-resolution'' had been proposed for this process but it did not catch on, and the high-precision localization procedure is typically referred to as super-resolution.
The technical achievements of enhancing the performance of imaging-forming and –sensing devices now classified as super-resolution utilize to the fullest but always stay within the bounds imposed by the laws of physics and information theory.
Techniques
Optical or diffractive super-resolution
Substituting spatial-frequency bands: Though the bandwidth allowable by diffraction is fixed, it can be positioned anywhere in the spatial-frequency spectrum. Dark-field illumination in microscopy is an example. See alsoaperture synthesis
Aperture synthesis or synthesis imaging is a type of interferometry that mixes signals from a collection of telescopes to produce images having the same angular resolution as an instrument the size of the entire collection. At each separation and ...
.

Multiplexing spatial-frequency bands
An image is formed using the normal passband of the optical device. Then some known light structure, for example a set of light fringes that need not even be within the passband, is superimposed on the target. The image now contains components resulting from the combination of the target and the superimposed light structure, e.g. moiré fringes, and carries information about target detail which simple unstructured illumination does not. The “superresolved” components, however, need disentangling to be revealed. For an example, see structured illumination (figure to left).Multiple parameter use within traditional diffraction limit
If a target has no special polarization or wavelength properties, two polarization states or non-overlapping wavelength regions can be used to encode target details, one in a spatial-frequency band inside the cut-off limit the other beyond it. Both would utilize normal passband transmission but are then separately decoded to reconstitute target structure with extended resolution.Probing near-field electromagnetic disturbance
The usual discussion of super-resolution involved conventional imagery of an object by an optical system. But modern technology allows probing the electromagnetic disturbance within molecular distances of the source which has superior resolution properties, see alsoevanescent waves
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillati ...
and the development of the new Super lens.
Geometrical or image-processing super-resolution

Multi-exposure image noise reduction
When an image is degraded by noise, there can be more detail in the average of many exposures, even within the diffraction limit. See example on the right.Single-frame deblurring
Known defects in a given imaging situation, such asdefocus
In optics, defocus is the aberration in optical systems, aberration in which an image is simply out of focus (optics), focus. This aberration is familiar to anyone who has used a camera, videocamera, microscope, telescope, or binoculars. Opti ...
or aberrations, can sometimes be mitigated in whole or in part by suitable spatial-frequency filtering of even a single image. Such procedures all stay within the diffraction-mandated passband, and do not extend it.

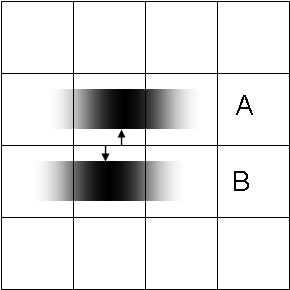
Sub-pixel image localization
The location of a single source can be determined by computing the "center of gravity" (centroid
In mathematics and physics, the centroid, also known as geometric center or center of figure, of a plane figure or solid figure is the arithmetic mean position of all the points in the surface of the figure. The same definition extends to any ...
) of the light distribution extending over several adjacent pixels (see figure on the left). Provided that there is enough light, this can be achieved with arbitrary precision, very much better than pixel width of the detecting apparatus and the resolution limit for the decision of whether the source is single or double. This technique, which requires the presupposition that all the light comes from a single source, is at the basis of what has become known as super-resolution microscopy
Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have resolutions higher than those imposed by the diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techni ...
, e.g. stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM), where fluorescent probes attached to molecules give nanoscale
The nanoscopic scale (or nanoscale) usually refers to structures with a length scale applicable to nanotechnology, usually cited as 1–100 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a billionth of a meter. The nanoscopic scale is (roughly speaking) a lo ...
distance information. It is also the mechanism underlying visual hyperacuity.
Bayesian induction beyond traditional diffraction limit
Some object features, though beyond the diffraction limit, may be known to be associated with other object features that are within the limits and hence contained in the image. Then conclusions can be drawn, using statistical methods, from the available image data about the presence of the full object. The classical example is Toraldo di Francia's proposition of judging whether an image is that of a single or double star by determining whether its width exceeds the spread from a single star. This can be achieved at separations well below the classical resolution bounds, and requires the prior limitation to the choice "single or double?" The approach can take the form ofextrapolating
In mathematics, extrapolation is a type of estimation, beyond the original observation range, of the value of a variable on the basis of its relationship with another variable. It is similar to interpolation, which produces estimates between know ...
the image in the frequency domain, by assuming that the object is an analytic function
In mathematics, an analytic function is a function that is locally given by a convergent power series. There exist both real analytic functions and complex analytic functions. Functions of each type are infinitely differentiable, but complex ...
, and that we can exactly know the function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
values in some interval. This method is severely limited by the ever-present noise in digital imaging systems, but it can work for radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, microscopy or magnetic resonance imaging. More recently, a fast single image super-resolution algorithm based on a closed-form solution to '''' problems has been proposed and demonstrated to accelerate most of the existing Bayesian super-resolution methods significantly.
Aliasing
Geometrical SR reconstructionalgorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
s are possible if and only if the input low resolution images have been under-sampled and therefore contain aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable (or ''aliases'' of one another) when sampled. It also often refers to the distortion or artifact that results when ...
. Because of this aliasing, the high-frequency content of the desired reconstruction image is embedded in the low-frequency content of each of the observed images. Given a sufficient number of observation images, and if the set of observations vary in their phase (i.e. if the images of the scene are shifted by a sub-pixel amount), then the phase information can be used to separate the aliased high-frequency content from the true low-frequency content, and the full-resolution image can be accurately reconstructed.
In practice, this frequency-based approach is not used for reconstruction, but even in the case of spatial approaches (e.g. shift-add fusionS. Farsiu, D. Robinson, M. Elad, and P. Milanfar"Fast and Robust Multi-frame Super-resolution"
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 1327–1344, October 2004.), the presence of aliasing is still a necessary condition for SR reconstruction.
Technical implementations
There are very both single-frame and multiple-frame variants of SR. Multiple-frame SR uses the sub- pixel shifts between multiple low resolution images of the same scene. It creates an improved resolution image fusing information from all low resolution images, and the created higher resolution images are better descriptions of the scene. Single-frame SR methods attempt to magnify the image without producing blur. These methods use other parts of the low resolution images, or other unrelated images, to guess what the high-resolution image should look like. Algorithms can also be divided by their domain:frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
or space domain. Originally, super-resolution methods worked well only on grayscale images, but researchers have found methods to adapt them to color camera images. Recently, the use of super-resolution for 3D data has also been shown.
Research
There is promising research on using deep convolutional networks to perform super-resolution. In particular work has been demonstrated showing the transformation of a 20xmicroscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
image of pollen grains into a 1500x scanning electron microscope image using it. While this technique can increase the information content of an image, there is no guarantee that the upscaled features exist in the original image and deep convolutional upscalers should not be used in analytical applications with ambiguous inputs. These methods can hallucinate image features, which can make them unsafe for medical use.
See also
* Optical resolution *Oversampling
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling a signal at a sampling frequency significantly higher than the Nyquist rate. Theoretically, a bandwidth-limited signal can be perfectly reconstructed if sampled at the Nyquist rate o ...
* Video super-resolution
*Single-particle trajectory
Single-particle trajectories (SPTs) consist of a collection of successive discrete points causal in time. These trajectories are acquired from images in experimental data. In the context of cell biology, the trajectories are obtained by the tran ...
* Superoscillation
References
Other related work
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ; * * ; * ; * {{Video processingImage processing Signal processing Imaging