Sundarbans National Park on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Sundarbans National Park is a
national park
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individual ...
, tiger reserve
Project Tiger is a tiger conservation programme launched in April 1973 by the Government of India during Prime Minister Indira Gandhi's tenure. The project aims at ensuring a viable population of the Bengal tiger in its natural habitats, protecti ...
and biosphere reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
in West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
, India. It is part of the Sundarbans on the Ganges Delta and adjacent to the Sundarban Reserve Forest in Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
. It is located to south-west of the Bangladesh. The delta is densely covered by mangrove forests, and is one of the largest reserves for the Bengal tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present i ...
. It is also home to a variety of bird, reptile and invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chorda ...
species, including the salt-water crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats and brackish wetlands from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been liste ...
. The present Sundarban National Park was declared as the core area of Sundarban Tiger Reserve in 1973 and a wildlife sanctuary in 1977. On 4 May 1984 it was declared a national park. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
inscribed in 1987, and it has been designated as a Ramsar site
A Ramsar site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention,8 ha (O)
*** Permanent 8 ha (P)
*** Seasonal Intermittent < 8 ha(Ts)
**
It is considered as a World Network of Biosphere Reserve (Man and Biosphere Reserve) from 1989.
The first forest management division to have jurisdiction over the Sundarbans was established in 1869. In 1875 a large portion of the mangrove forests was declared as reserved forests under the Forest Act, 1865 (Act VIII of 1865). The remaining portions of the forests were declared a reserve forest the following year and the forest, which was so far administered by the civil administration district, was placed under the control of the Forest Department. A forest division, which is the basic forest management and administration unit, was created in 1879 with the headquarters in
 The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of the Sundarbans. The
The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of the Sundarbans. The

 The coastal active delta of Sundarban at the mouth of Bay of Bengal in Bangladesh, having a complex geomorphologic and hydrological character with climatic hazards, has a vast area of mangrove forests with a variety of flora and diverse fauna in a unique ecosystem. The natural environment and coastal ecosystem of this Biosphere Reserve and World Heritage Site is under threat of physical disaster due to unscientific and excessive human interferences. Conservation and environmental management plan for safeguarding this unique coastal ecology and ecosystem is urgently required.
The coastal active delta of Sundarban at the mouth of Bay of Bengal in Bangladesh, having a complex geomorphologic and hydrological character with climatic hazards, has a vast area of mangrove forests with a variety of flora and diverse fauna in a unique ecosystem. The natural environment and coastal ecosystem of this Biosphere Reserve and World Heritage Site is under threat of physical disaster due to unscientific and excessive human interferences. Conservation and environmental management plan for safeguarding this unique coastal ecology and ecosystem is urgently required.


 The Sundarbans National Park houses a large number of reptiles as well, including
The Sundarbans National Park houses a large number of reptiles as well, including
Swatch of No-ground: A treasure trove of marine lives
'
 The
The
 The only means of travelling the park is by boat, down the various lanes formed by the many flowing rivers. Local boats or vessels operated by the West Bengal Tourism Development Corporation, namely ''M.V. Chitrarekha'' and ''M.V. Sarbajaya''. Accommodation on land and cruise safaris are provided by ''Sunderban Tiger Camp'', the only government-approved resort in the region. They conduct fixed departures and private tours from Kolkata throughout the year.
The only means of travelling the park is by boat, down the various lanes formed by the many flowing rivers. Local boats or vessels operated by the West Bengal Tourism Development Corporation, namely ''M.V. Chitrarekha'' and ''M.V. Sarbajaya''. Accommodation on land and cruise safaris are provided by ''Sunderban Tiger Camp'', the only government-approved resort in the region. They conduct fixed departures and private tours from Kolkata throughout the year.
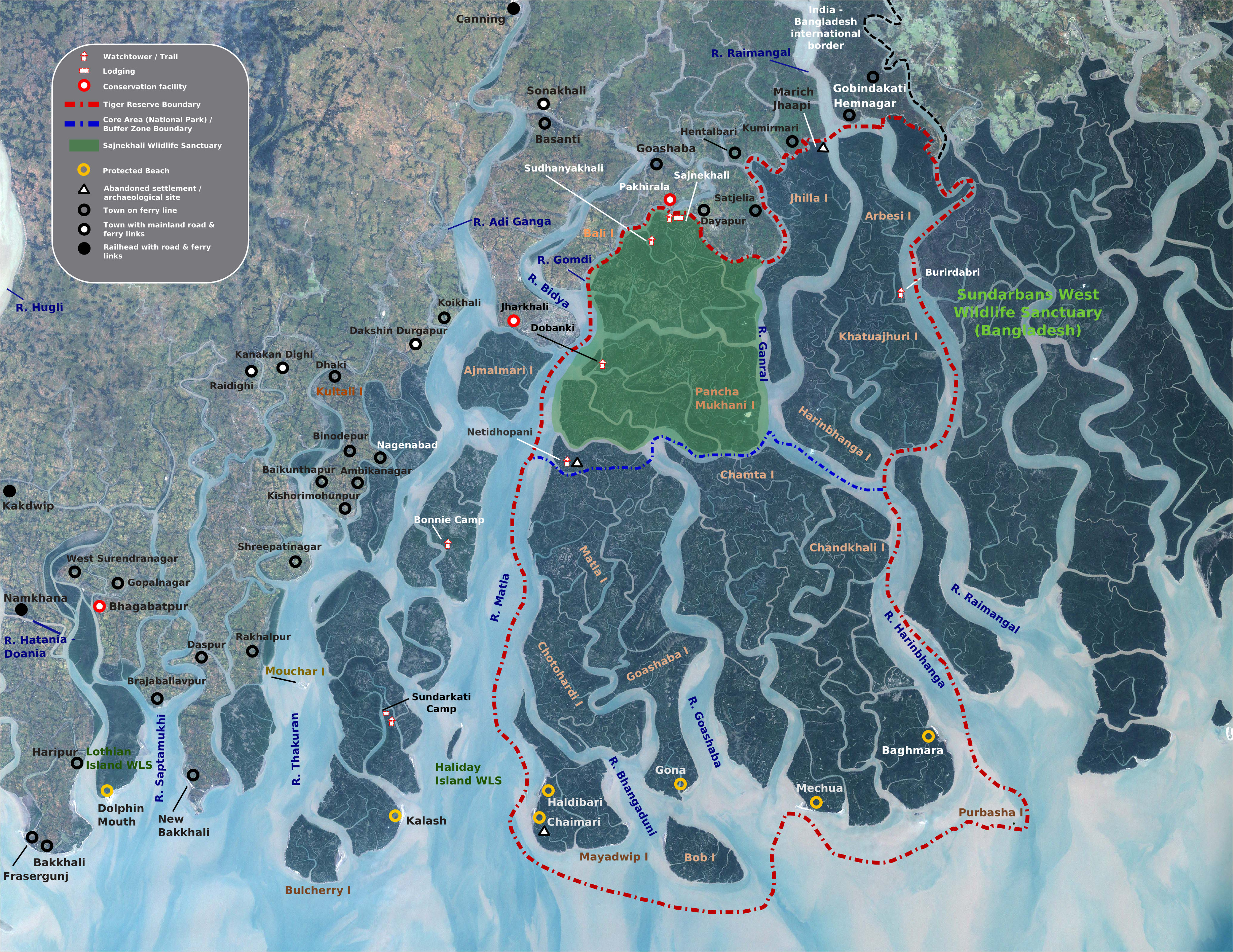
 Apart from viewing the wildlife from boat safaris, visitors also visit the Sudhanyakali Watch Tower, Dobanki Watch Tower, Burirdabri Watch Tower, Netidhopani Watch Tower, Sajnekhali Bird Sanctuary, Bhagabatpur Crocodile Project (a crocodile breeding farm),
Apart from viewing the wildlife from boat safaris, visitors also visit the Sudhanyakali Watch Tower, Dobanki Watch Tower, Burirdabri Watch Tower, Netidhopani Watch Tower, Sajnekhali Bird Sanctuary, Bhagabatpur Crocodile Project (a crocodile breeding farm),
 Cyclone Aila struck Sunderban on 25 May 2009, causing damage to field camps and fringe villages bordering the reserve. Breaches in the embankments on the village side have caused large scale flooding, leaving
Cyclone Aila struck Sunderban on 25 May 2009, causing damage to field camps and fringe villages bordering the reserve. Breaches in the embankments on the village side have caused large scale flooding, leaving
How to reach Sundarban
West Bengal, India
Sundarbans National Park
Bangladesh
Official UNESCO website entry
Bengal Wildlife Tours Sundarbans National Park
Sundarbans
UNESCO Periodic Report
* {{Authority control World Heritage Sites in India Ramsar sites in India National parks in West Bengal Protected areas of West Bengal Sundarbans Tourist attractions in South 24 Parganas district 1973 establishments in West Bengal Protected areas established in 1973
Khulna
Khulna ( bn, খুলনা, ) is the third-largest city in Bangladesh, after Dhaka and Chittagong. It is the administrative centre of Khulna District and Khulna Division. Khulna's economy is the third-largest in Bangladesh, contributing $53 ...
, Bangladesh. The first management plan was written for the period 1893–1898.
In 1911, it was described as a tract of unexamined waste country and was excluded from the census. It then stretched for about from the mouth of the Hugli to the mouth of the Meghna river and was bordered inland by the three settled districts of the 24 parganas, Khulna
Khulna ( bn, খুলনা, ) is the third-largest city in Bangladesh, after Dhaka and Chittagong. It is the administrative centre of Khulna District and Khulna Division. Khulna's economy is the third-largest in Bangladesh, contributing $53 ...
and Bakerganj. The total area (including water) was estimated at . It was a water-logged jungle, in which tigers and other wild beasts abounded. Attempts at reclamation had not been very successful. The Sundarbans was everywhere intersected by river channels and creeks, some of which afforded water communication throughout the Bengal region both for steamers and for native ships. The maximum part of the delta is located in Bangladesh.
Administration
 The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of the Sundarbans. The
The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of the Sundarbans. The Principal Chief Conservator of Forests
The Indian Forest Service (IFS) is one of the three All India Services of the Government of India. The other two All India Services being the Indian Administrative Service and the Indian Police Service. It was constituted in the year 1966 und ...
(PCCF), Wildlife & Bio-Diversity & ex-officio Chief Wildlife Warden, West Bengal, is the senior most executive officer looking over the administration of the park. The Chief Conservator of Forests (South) & Director, Sundarban Biosphere Reserve is the administrative head of the park at the local level and is assisted by a deputy field director and an assistant field director. The park area is divided into two ranges, overseen by range forest officers. Each range is further sub-divided into beats. The park also has floating watch stations and camps to protect the property from poachers.
The park receives financial aid from the state government as well as the Ministry of Environment and Forests under various plan and non-plan budgets. Additional funding is received under the Project Tiger
Project Tiger is a tiger conservation programme launched in April 1973 by the Government of India during Prime Minister Indira Gandhi's tenure. The project aims at ensuring a viable population of the Bengal tiger in its natural habitats, prote ...
from the Central Government. In 2001, a grant of US$20,000 was received as preparatory assistance for promotion between India and Bangladesh from the World Heritage Fund.
Geography
The Sundarban National Park is located between 21° 432′ – 21° 55′ N latitude and between 88° 42′ – 89° 04′ E longitude. The average altitude of the park is 7.5 m above sea level. The park is composed of 54 small islands and intersected by several distributaries of theGanges river
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
.
Climate
The average minimum and maximum temperature is 20 °C and 48 °C respectively. Rainfall is heavy with humidity as high as 80% as it is close to theBay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
. The monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
lasts from mid-June to mid-September. Prevailing wind is from the north and north-east from October to mid-March and southwest westerlies prevails from mid-March to September. Storms which sometimes develop into cyclones are common during the months of May to October.
Eco-geography, rivers and watercourses
Seven main rivers and innumerable watercourses form a network of channels at this estuarine delta. All the rivers have a southward course towards the sea. The eco-geography of this area is totally dependent on the tidal effect of two flow tides and two ebb tides occurring within 24 hours with a tidal range of 3–5 m and up to 8 m in normal spring tide, inundating the whole of Sundarban in varying depths. The tidal action deposits silts back on the channels and raising the bed, it forms new islands and creeks contributing to uncertain geomorphology. There is a great natural depression called the '' Swatch of No Ground'' in the Bay of Bengal between 21°00' to 21°22' latitude where the depth of water changes suddenly from 20 m to 500 m. This mysterious depression pushes back the silts towards south and/or further east to form new islands.
Mudflats
The Sunderbanmudflat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal f ...
s are found at the estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
and on the deltaic islands where low velocity of river and tidal current occurs. The flats are exposed in low tides and submerged in high tides, thus being changed morphologically even in one tidal cycle. The interior parts of the mudflats are the right environment for mangroves.
There are a number of mudflats outside the Sundarbans National Park is a mudflat that have the potential to be tourist spots in the Sundarbans. One can visit them and enjoy the beauty of the place during low tide. If one is lucky, one can see sea anemone
Sea anemones are a group of predatory marine invertebrates of the order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the '' Anemone'', a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemones are classified in the phylum Cnidaria, ...
s, horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to ar ...
(Nearing extinction)and small octopus.
Flora and fauna
 The coastal active delta of Sundarban at the mouth of Bay of Bengal in Bangladesh, having a complex geomorphologic and hydrological character with climatic hazards, has a vast area of mangrove forests with a variety of flora and diverse fauna in a unique ecosystem. The natural environment and coastal ecosystem of this Biosphere Reserve and World Heritage Site is under threat of physical disaster due to unscientific and excessive human interferences. Conservation and environmental management plan for safeguarding this unique coastal ecology and ecosystem is urgently required.
The coastal active delta of Sundarban at the mouth of Bay of Bengal in Bangladesh, having a complex geomorphologic and hydrological character with climatic hazards, has a vast area of mangrove forests with a variety of flora and diverse fauna in a unique ecosystem. The natural environment and coastal ecosystem of this Biosphere Reserve and World Heritage Site is under threat of physical disaster due to unscientific and excessive human interferences. Conservation and environmental management plan for safeguarding this unique coastal ecology and ecosystem is urgently required.
Flora
Sundarban has achieved its name from the Sundari tree. It is the most exquisite variety of tree that are found in this area, a special kind ofmangrove tree
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several ...
. It has specialised roots called pneumatophores which emerge above ground and help in gaseous exchange i.e. respiration. During the rainy season when the entire forest is waterlogged, the spikes rising from the ground has their peak in the air and helps in the respiration process.
Fauna
The Sundarbans forest is home to more than 400 tigers. Density of Tigers is 12 per 100 Sq. Meter area, which is 2nd highest after Jim Corbett National park in India. The royalBengal tigers
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present i ...
have developed a unique characteristic of swimming in the saline waters, and are famous for their man-eating tendencies. Tigers can be seen on the river banks sunbathing between November and February. Yearly 100-200 people, mainly fishermen get killed by Tigers in Sunderbans. Apart from the Bengal tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present i ...
, fishing cats, leopard cat
The leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') is a small wild cat native to continental South, Southeast, and East Asia. Since 2002 it has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List as it is widely distributed although threatened by hab ...
s, macaque
The macaques () constitute a genus (''Macaca'') of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and (in one instance) Gibraltar. Macaques are principall ...
s, wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species i ...
, Indian grey mongoose
The Indian grey mongoose (''Urva edwardsii'') is a mongoose species native to the Indian subcontinent and West Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
The grey mongoose inhabits open forests, scrublands and cultivated fie ...
, fox, jungle cat, flying fox, chital, etc are also found in abundance in the Sundarbans.

=Avifauna
= Some of the birds commonly found in this region are openbill storks, black-capped kingfishers, black-headed ibis, water hens,coot
Coots are medium-sized water birds that are members of the rail family, Rallidae. They constitute the genus ''Fulica'', the name being the Latin term for "coot". Coots have predominantly black plumage, and—unlike many rails—they are usually ...
s, pheasant-tailed jacanas, pariah kite
The black kite (''Milvus migrans'') is a medium-sized bird of prey in the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors. It is thought to be the world's most abundant species of Accipitridae, although some populations have ...
s, brahminy kite, marsh harriers, swamp partridges, red junglefowl, spotted doves, common mynahs, jungle crows, jungle babblers, cotton teals, herring gulls Herring gull is a common name for several birds in the genus ''Larus'', all formerly treated as a single species.
Three species are still combined in some taxonomies:
* American herring gull (''Larus smithsonianus'') - North America
* European he ...
, Caspian terns, gray heron
The grey heron (''Ardea cinerea'') is a long-legged wading bird of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more northe ...
s, common snipes, wood sandpiper
The wood sandpiper (''Tringa glareola'') is a small wader. This Eurasian species is the smallest of the shanks, which are mid-sized long-legged waders of the family Scolopacidae. The genus name ''Tringa'' is the New Latin name given to the green ...
s, green pigeons, rose ringed parakeet
The rose-ringed parakeet (''Psittacula krameri''), also known as the ring-necked parakeet (more commonly known as the Indian ringneck parrot), is a medium-sized parrot in the genus Psittacula, of the family Psittacidae. It has disjunct native ran ...
s, paradise-flycatchers, cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the IOC adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven ge ...
s, grey-headed fish eagles, white-bellied sea eagles, seagulls
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the family Laridae in the suborder Lari. They are most closely related to the terns and skimmers and only distantly related to auks, and even more distantly to waders. Until the 21st century, ...
, common kingfishers, peregrine falcons, woodpeckers
Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks, and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar, and the extreme polar regions ...
, Eurasian whimbrel
The Eurasian whimbrel or common whimbrel (''Numenius phaeopus'') is a wader in the large family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across much of subarctic Asia and Europe as far south as Scotland. This speci ...
s, black-tailed godwit
The black-tailed godwit (''Limosa limosa'') is a large, long-legged, long-billed shorebird first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. It is a member of the godwit genus, ''Limosa''. There are four subspecies, all with orange head, neck and ches ...
s, little stints, eastern knots, curlews
The curlews () are a group of nine species of birds in the genus ''Numenius'', characterised by their long, slender, downcurved bills and mottled brown plumage. The English name is imitative of the Eurasian curlew's call, but may have been i ...
, golden plover
'' Pluvialis '' is a genus of plovers, a group of wading birds comprising four species that breed in the temperate or Arctic Northern Hemisphere.
In breeding plumage, they all have largely black underparts, and golden or silvery upperparts. Th ...
s, northern pintail
The pintail or northern pintail (''Anas acuta'') is a duck species with wide geographic distribution that breeds in the northern areas of Europe and across the Palearctic and North America. It is migratory and winters south of its breeding ...
s, white-eyed pochards and whistling teals.
=Aquatic fauna
= Some of the aquatic animals found in the park are sawfish, butter fish, electric rays, silver carp,starfish
Starfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish a ...
, common carp
The Eurasian carp or European carp (''Cyprinus carpio''), widely known as the common carp, is a widespread freshwater fish of eutrophic waters in lakes and large rivers in Europe and Asia.Fishbase''Cyprinus carpio'' Linnaeus, 1758/ref>Arkive The ...
, horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to ar ...
s, prawn, shrimps
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referre ...
, Gangetic dolphins, skipping frogs, common toads and tree frogs
A tree frog (or treefrog) is any species of frog that spends a major portion of its lifespan in trees, known as an arboreal state. Several lineages of frogs among the Neobatrachia have given rise to treefrogs, although they are not closely rela ...
.
=Reptiles
=
 The Sundarbans National Park houses a large number of reptiles as well, including
The Sundarbans National Park houses a large number of reptiles as well, including gharial
The gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus''), also known as gavial or fish-eating crocodile, is a crocodilian in the family Gavialidae and among the longest of all living crocodilians. Mature females are long, and males . Adult males have a distinct ...
s, estuarine crocodiles, chameleon
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, bein ...
s, monitor lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and one species is also found in the Americas as an invasive species. About 80 species are rec ...
s, turtles
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
, including olive ridley
The olive ridley sea turtle (''Lepidochelys olivacea''), also known commonly as the Pacific ridley sea turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Cheloniidae. The species is the second-smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found in ...
, hawksbill, and green turtles, and snakes
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
, including python, king cobra, rat snake, Russell's viper, dog faced water snake, checkered keelback, red tailed bamboo pit viper, Taipan
Taipans are snakes of the genus ''Oxyuranus'' in the elapid family. They are large, fast-moving, highly venomous, and endemic to Australia and New Guinea. Three species are recognised, one of which, the coastal taipan, has two subspecies. Taipa ...
, Chinese Green viper( Trimeresurus stejnegeri), common krait, etc. Yearly 100-200 people are killed due to snake bites in Sunderbans.
=Endangered species
= Theendangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
that lives within the Sundarbans are royal Bengal tiger, saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats and brackish wetlands from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been l ...
, river terrapin, olive ridley turtle, Ganges river dolphin, hawksbill turtle
The hawksbill sea turtle (''Eretmochelys imbricata'') is a critically endangered sea turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Eretmochelys''. The species has a global distribution, that is la ...
and mangrove horseshoe crab
The mangrove horseshoe crab (''Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda''), also known as the round-tailed horseshoe crab, is a chelicerate arthropod found in tropical marine and brackish waters in India, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei, Singapore, T ...
.
=Marine mammals
= The proposed ''Sundarbans Cetacean Diversity Protected Area'', includes the coastal waters off Sundarbans that host critical habitats for endangeredcetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel th ...
s; resident groups of Bryde's whale
Bryde's whale ( Brooder's), or the Bryde's whale complex, putatively comprises three species of rorqual and maybe four. The "complex" means the number and classification remains unclear because of a lack of definitive information and research. ...
s, a newly rediscovered critical population of Irrawaddy dolphins, Spinner dolphins, Ganges river dolphins, and Chinese white dolphin
The Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin (''Sousa chinensis'') is a species of humpback dolphin inhabiting coastal waters of the eastern Indian and western Pacific Oceans. This species is often referred to as the Chinese white dolphin in mainland Chi ...
s. Indo-Pacific finless porpoise
The Indo-Pacific finless porpoise (''Neophocaena phocaenoides'') is one of eight porpoise species. The species ranges throughout most of the Indian Ocean, as well as the tropical and subtropical Pacific from Indonesia north to the Taiwan Strait. ...
s, Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin
The Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops aduncus'') is a species of bottlenose dolphin. This dolphin grows to long, and weighs up to . It lives in the waters around India, northern Australia, South China, the Red Sea, and the eastern ...
s, and Pantropical spotted dolphin
The pantropical spotted dolphin (''Stenella attenuata'') is a species of dolphin found in all the world's temperate and tropical oceans. The species was beginning to come under threat due to the killing of millions of individuals in tuna purse s ...
s are also regularly found in this area, while Minke whales and Rough-toothed dolphin
The rough-toothed dolphin (''Steno bredanensis'') is a species of dolphin that can be found in deep warm and tropical waters around the world.
The species was first described by Georges Cuvier in 1823. The genus name ''Steno'', of which this spe ...
s and False killer whales are rarer.Anisuzzaman Khan, 2017, Swatch of No-ground: A treasure trove of marine lives
'
Management and special projects
 The
The Bengal tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present i ...
is the commonly found species in the park. Having protection since its creation, the core area is free from all human disturbances such as collection of wood, honey, fishing, and other forest products. However, in the buffer area, these activities are permitted in limited form. The forest staff, using motorboats and launches, protect the park from illegal poaching and theft. Forest offices and camps are located at several important parts of the park. Under the supervision of a range officer, two or three experienced workers manage anti- poaching camps.
Habitat of wildlife is maintained through eco-conservation, eco-development, training, education and research. Ten Forest Protection Committees and 14 Eco-development Committees have been formed in the fringe of Sundarbans Tiger Reserve to help in this regard. Seminars, workshops and awareness camps are organised in the vicinity of park to educate the people on eco-conservation, eco-development, and such other issues. Mangrove and other plants are planted in the fringe area to meet the local need of fuel wood for about 1000 villages and to conserve the buffer area. Conservation of soil is done to maintain the ecological balance. Several sweet water ponds have been dug up inside the park to provide drinking water for the wild animals.
Controlling man-eating tigers is another major activity. The number of casualties has been reduced from 40 to 10 per year. The reduction in number of casualties is a result of strict control over the movement of the people inside the tiger reserve, alternative income generation and awareness building among people. It is also believed that due to use of human masks and electric human dummies the tigers will stay away from the people. Straying of tigers into nearby villages is prevented through measures such as nylon net fencing and solar illumination of villages. The youths of the villages are given training in controlling the straying of tigers into the villages.
The Mangrove Interpretation Centre is established at Sajnekhali to make the local people and tourists aware of the importance of conservation of nature in general and specially the mangrove ecosystems.
Constraints
Though protection exists in the park, there are a few loopholes. The geographical topography with hostile terrain cris-crossed by several rivers and their tributaries, long international border with Bangladesh, fishing trawlers and launches enables poaching and the cutting of wood, affecting the mangrove forests. Lack of staff, infrastructure and lack of funds exacerbate the situation.Park-specific information
Sagar Island
Sagar Island is an island in the Ganges delta, lying on the Continental Shelf of Bay of Bengal about 100 km (54 nautical miles) south of Kolkata. This island forms the Sagar CD Block in Kakdwip subdivision of South 24 Parganas district ...
, Jambudweep, Haliday Island, and Kanak.
Sunderban Tiger Reserve
Background
The Sunderban Tiger Reserve is located in theSouth 24 Parganas
South 24 Parganas (Pron: pɔrɡɔnɔs; abbr. 24 PGS (S)), or sometimes South Twenty Four Parganas and Dakshin 24 Parganas, is a district in the Indian state of West Bengal, headquartered in Alipore. It is the largest district of West Bengal by ...
district of the Indian state of West Bengal, and has a total geographical area of 2585 km2, with 1437.4 km2 consisting of populated areas and forest covering the remaining 1474 km2. The Sunderban landscape is contiguous with the mangrove habitat in Bangladesh.
Sunderban mangroves form part of the largest mangrove system of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
with a tiger population in a distinct ecological setting. These forests have saltwater crocodiles, estuarine and marine turtles, and a number of bird species. The reserve also contains species of the fishing cat, spotted deer, rhesus monkey, and wild pig.
The Sunderban is isolated with no forest connection to other tiger-occupied mainlands. Due to this, there is heavy biotic pressure for forest resources. On average, 50 metric tonnes of honey and 3 metric tonnes of wax are collected each year by locals under licence from the Indian Forest Service
The Indian Forest Service (IFS) is one of the three All India Services of the Government of India. The other two All India Services being the Indian Administrative Service and the Indian Police Service. It was constituted in the year 1966 und ...
. The habitat is traversed by many narrow tidal channel
A tidal creek or tidal channel is a narrow inlet or estuary that is affected by the ebb and flow of ocean tides. Thus, it has variable salinity and electrical conductivity over the tidal cycle, and flushes salts from inland soils. Tidal creeks a ...
s forming small to large islands. Tigers readily cross these islands and human-tiger interactions are common.
The estimation of tiger population in Sunderban, as a part of the all India tiger estimation using the refined methodology, could not be carried out owing to the unique habitat and obliteration of evidences due to high and low tides. Phase-I data collection has been completed and process is on for tiger estimation using a combination of radio telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", an ...
and pugmark deposition rate from known tigers.
Damage from Cyclone Aila
 Cyclone Aila struck Sunderban on 25 May 2009, causing damage to field camps and fringe villages bordering the reserve. Breaches in the embankments on the village side have caused large scale flooding, leaving
Cyclone Aila struck Sunderban on 25 May 2009, causing damage to field camps and fringe villages bordering the reserve. Breaches in the embankments on the village side have caused large scale flooding, leaving lakh
A lakh (; abbreviated L; sometimes written lac) is a unit in the Indian numbering system equal to one hundred thousand (100,000; scientific notation: 105). In the Indian 2,2,3 convention of digit grouping, it is written as 1,00,000. For e ...
s of people marooned in the area. The field camps were under 12 to 15 feet of water for around seven hours, resulting in soil erosion and damage to staff quarters, generators and bamboo pilling. There was a report of a tiger wandering inside an abandoned cattle shed in a village, which was captured and released back in the wild. No tiger death has been reported, apart from the mortality of two spotted deer. Several NGOs have been involved in the relief operation.
The Forest Department of the State has constituted a Committee and has assessed damage of almost Rs. 11150,000. Central assistance amounting to Rs. 10 million under Project Tiger has been provided to the State for restoring the damage done to infrastructure.
Damage from Cyclone Amphan
Cyclone Amphan made landfall near Sagar Island of South 24 Parganas district on 20 May 2020. Lives have been lost and damage has been meted out to infrastructure. The cyclone damaged "almost the entire nylon fencing" in the forest which prevents the tigers from entering the forest-fringe villages, thereby keeping a check on the man-animal conflict. Besides the fencing, the cyclone also damaged "dozens of forest camp offices, tents, watch towers and staff quarters". The West Bengal Forest Department were initially apprehensive about tigers being harmed or killed by the cyclone but the post cyclone patrolling revealed no dead bodies of the tigers and instead offered glimpses of the animals roaming around in the forest.Challenges
The Sunderban Tiger Reserve has several challenges to its future operations. Due to wandering tigers, human-tiger conflict continues to be an issue. Sunderban tigers hunt humans, and it is estimated that over a thousand of the local people have been killed by tigers over the past four decades. An estimation of the number of tigers present in the reserve using the refined method has not yet been completed. A tiger conservation plan is awaited as are constitutions for the State level Steering Committee under the Chairmanship of the Chief Minister and the reserve-specific Tiger Conservation Foundation.Transport
Air: Sundarban National Park is located 140 kilometres from Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport, which operates international flights across the world. Rail: The nearest railway station to Sundarbans National Park is Canning railway station which is located 29 km far from the Gate way of Sundarban (i.e. Godhkhali). Road: The national park can be accessed from Kolkata via West Bengal's State Highway 3.Ecosystem valuation
A 2015 economic assessment study of the Sundarbans estimated that the national park provides flow benefits worth ₹12.8 billion (approximately ₹50,000 per hectare of land) annually. Importantecosystem service
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. ...
s and their annual valuations include nursery function (₹5.17 billion), gene-pool protection (₹2.87 billion), provisioning of fish (₹1.6 billion) and waste assimilation services (₹1.5 billion). The study also mentioned services such as the generation of employment for local communities (₹36 million), moderation of cyclonic storms (₹275 million), provision of habitat and refugia for wildlife (₹360 million) and sequestration of carbon (₹462 million).
See also
*Haliday Island Wildlife Sanctuary
The Haliday Island Wildlife Sanctuary (also just known as the Haliday Wildlife Sanctuary) is one of several wildlife sanctuaries in the nation of India. Located in the state of West Bengal, the area is approximately six square kilometers in size. ...
* Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education
* Wildlife sanctuaries in India
A Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or other interest, which is reserved and managed for conservation and to provide opportunities for study or research. The Wild Life (Protection) ...
* Sangu Matamuhari
Sangu Matamuhari or Sangu Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary—IUCN category II (habitat/species management area)—situated in Bandarban District, Chittagong Division, Bangladesh. It is part of the Sangu reserve forest. It is under the Lam ...
* Sundarbans settlements
References
External links
How to reach Sundarban
West Bengal, India
Sundarbans National Park
Bangladesh
Official UNESCO website entry
Bengal Wildlife Tours Sundarbans National Park
Sundarbans
UNESCO Periodic Report
* {{Authority control World Heritage Sites in India Ramsar sites in India National parks in West Bengal Protected areas of West Bengal Sundarbans Tourist attractions in South 24 Parganas district 1973 establishments in West Bengal Protected areas established in 1973