Strategic Missile Troops on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Strategic Rocket Forces of the Russian Federation or the Strategic Missile Forces of the Russian Federation (RVSN RF; russian: Ракетные войска стратегического назначения Российской Федерации (РВСН РФ), Raketnye voyska strategicheskogo naznacheniya Rossiyskoy Federatsii, lit. 'Strategic Purpose Rocketry Troops') are a separate-troops branch of the Russian Armed Forces that control Russia's land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).
The Strategic Rocket Forces was created on 17 December 1959 as part of the
The Strategic Rocket Forces of the Russian Federation or the Strategic Missile Forces of the Russian Federation (RVSN RF; russian: Ракетные войска стратегического назначения Российской Федерации (РВСН РФ), Raketnye voyska strategicheskogo naznacheniya Rossiyskoy Federatsii, lit. 'Strategic Purpose Rocketry Troops') are a separate-troops branch of the Russian Armed Forces that control Russia's land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).
The Strategic Rocket Forces was created on 17 December 1959 as part of the
Strategic Missile Forces
He was succeeded by General of the Army Vladimir Yakovlev, who commanded the SMT from June 1997 until April 27, 2001. Yakovlev was succeeded by Colonel General Nikolay Solovtsov. In early 2009 Solovtsov said that 96% of all Russian ICBMs were ready to be launched within a minute's notice. Solovtsov was dismissed in July–August 2009. Speculation over why Solovtsov was dismissed included opposition to further cuts in deployed nuclear ballistic missile warheads below the April 2009 figure of 1,500, the fact that he had reached the retirement age of 60, despite that he had recently been extended another year's service, or the failure of the Navy's Bulava missile). After only a year,
Russian Strategic Missile Forces
, accessed September 2010 The RVSN headquarters has a special sledgehammer that can be used to gain access to the launch codes if the commander feels the need to use it or if ordered directly, but doesn't have normal access to the safe. In 2020, the Strategic Missile Forces completed switching to digital information transmission technology.


 The main RVSN command post is at
The main RVSN command post is at
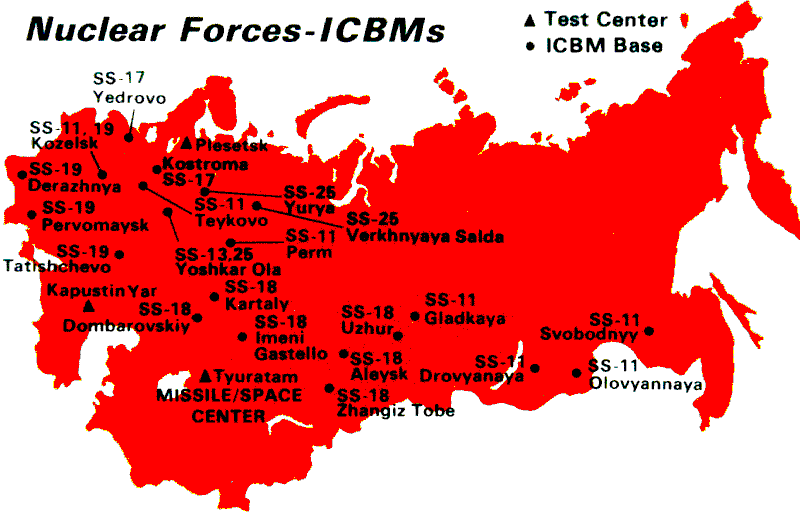
Soviet Intentions 1965–1985
'. Braddock Dunn & McDonald (BDM), 1995.
Strategic Missile Forces museum
* *"Владимирская Ракетная Стратегическая" (Vladimirskaya Strategic Missile) by I.V. Vershkov and V.G. Gagarin; Vladimir 2006; 480 pages; *"Оренбургская Стратегическая" (Orenburg Strategic) by Y.N. Feoktistov; Perm 2001; 328 pages; (also a 1997 edition). *"Читинская Ракетная Армия" (Chitinskaya Missile Army) by ??; Chita, 2002; 268 pages *"История 50-й Ракетной Армии I-IV" (History 50th Missile Army, part 1–4) by G.I. Smirnov and A.I. Yasakov; Smolensk 2008; 370+342+387+561 pages *"Стратеги" (Strategic) by V.T. Nosov; Moscow, 2008; 276 pages;
CSIS Missile Threat - Russia
''Strategic Missile Forces museum'' Official Website
Russian Nuclear Notebook 2019 - forces and Rocket Divisions
{{Strategic forces Strategic Rocket Forces Strategic forces
 The Strategic Rocket Forces of the Russian Federation or the Strategic Missile Forces of the Russian Federation (RVSN RF; russian: Ракетные войска стратегического назначения Российской Федерации (РВСН РФ), Raketnye voyska strategicheskogo naznacheniya Rossiyskoy Federatsii, lit. 'Strategic Purpose Rocketry Troops') are a separate-troops branch of the Russian Armed Forces that control Russia's land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).
The Strategic Rocket Forces was created on 17 December 1959 as part of the
The Strategic Rocket Forces of the Russian Federation or the Strategic Missile Forces of the Russian Federation (RVSN RF; russian: Ракетные войска стратегического назначения Российской Федерации (РВСН РФ), Raketnye voyska strategicheskogo naznacheniya Rossiyskoy Federatsii, lit. 'Strategic Purpose Rocketry Troops') are a separate-troops branch of the Russian Armed Forces that control Russia's land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).
The Strategic Rocket Forces was created on 17 December 1959 as part of the Soviet Armed Forces
The Soviet Armed Forces, the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union and as the Red Army (, Вооружённые Силы Советского Союза), were the armed forces of the Russian SFSR (1917–1922), the Soviet Union (1922–1991), and th ...
as the main force intended for attacking an enemy's offensive nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s, military facilities, and industrial infrastructure.
They operated all Soviet nuclear ground-based intercontinental
Intercontinental is an adjective to describe something which relates to more than one continent.
Intercontinental may also refer to:
* Intercontinental ballistic missile, a long-range guided ballistic missile
* InterContinental Hotels Group ( ...
, intermediate-range ballistic missile, and medium-range ballistic missile with ranges over 1,000 kilometers. After the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, assets of the Strategic Rocket Forces were in the territories of several new states in addition to Russia, with armed nuclear missile silos in Belarus, Kazakhstan and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. The three of them transferred their missiles to Russia for destruction and they all joined the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is an international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation ...
.
Complementary strategic forces within Russia include the Russian Aerospace Forces' Long Range Aviation and the Russian Navy's ballistic missile submarines. Together the three bodies form Russia's nuclear triad
A nuclear triad is a three-pronged military force structure that consists of land-launched nuclear missiles, nuclear-missile-armed submarines, and strategic aircraft with nuclear bombs and missiles. Specifically, these components are land-based ...
.
History
The first Soviet rocket study unit was established in June 1946, by redesignating the 92nd Guards Mortar Regiment at Bad Berka inEast Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
as the 22nd Brigade for Special Use of the Reserve of the Supreme High Command
The Reserve of the Supreme High Command (Russian: Резерв Верховного Главнокомандования; also known as the ''Stavka'' Reserve or RVGK ( ru , РВГК)) comprises reserve military formations and units; the Stav ...
. On October 18, 1947, the brigade conducted the first launch of the remanufactured former German A-4 ballistic missile, or R-1, from the Kapustin Yar
Kapustin Yar (russian: Капустин Яр) is a Russian rocket launch complex in Astrakhan Oblast, about 100 km east of Volgograd. It was established by the Soviet Union on 13 May 1946. In the beginning, Kapustin Yar used technology, material ...
Range. In the early 1950s the 77th and 90th Brigades were formed to operate the R-1 (SS-1a 'Scunner'). The 54th and 56th Brigades were formed to conduct test launches of the R-2 (SS-2 'Sibling') at Kapustin Yar on June 1, 1952.
From 1959 the Soviets introduced a number of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) into service, including the R-12 (SS-4 'Sandal'), the R-7 (SS-6 'Sapwood'), the R-16 (SS-7 'Saddler'), the R-9 (SS-8 'Sasin'), the R-26 (given the NATO reporting name SS-8 'Sasin' due to incorrect identification as the R-9), the R-36 (SS-9 'Scarp'), and the RT-21 (SS-16 'Sinner'), which was possibly never made fully operational.
By 1990 all these early types of missiles had been retired from service. In 1990 the Strategic Missile Forces were officially established as a service branch of the Armed Forces under the direct control of the Defense Ministry. The date of its formal foundation, December 17, is celebrated as Strategic Missile Forces Day.
Two rocket armies were formed in 1960. The 43rd Rocket Army
The 43rd Red Banner Rocket Army was an army of the Soviet Strategic Rocket Forces. It was formed in Vinnytsia from the 43rd Air Army of Long Range Aviation. In 1991, it came under the control of the Commonwealth of Independent States while statio ...
and the 50th Rocket Army
The 50th Red Banner Rocket Army (Military Unit Number 55135) was an army of the Soviet, later Russian Strategic Rocket Forces. It was created in 1960. Its first commander was General Lieutenant Feodor Dobish ( :ru:Добыш, Фёдор Иван� ...
were formed from the previous 43rd and 50th Air Armies of the Long Range Aviation.
During a test of the R-16 ICBM on October 24, 1960, the test missile exploded on the pad, killing the first commander of the SRF, Chief Marshal
Chief marshal of the branch (russian: Главный маршал рода войск, Glavny marshal roda voysk) was a senior military rank of the Soviet Armed Forces. It was immediately above the rank of Marshal of the branch. Both ranks were ...
of Artillery Mitrofan Ivanovich Nedelin
Mitrofan Ivanovich Nedelin (russian: Митрофа́н Ива́нович Неде́лин; – 24 October 1960) was a Soviet military commander who served as Chief marshal of the branch, Chief Marshal of the Artillery in the Soviet Armed Forc ...
. This disaster, the details of which were concealed for decades, became known as the Nedelin catastrophe. He was succeeded by Marshal of the Soviet Union
Marshal of the Soviet Union (russian: Маршал Советского Союза, Marshal sovetskogo soyuza, ) was the highest military rank of the Soviet Union.
The rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union was created in 1935 and abolished in 19 ...
Kirill Moskalenko
Kirill Semyonovich Moskalenko (russian: Кирилл Семёнович Москаленко, uk, Кирило Семенович Москаленко; May 11, 1902 – June 17, 1985) was a Marshal of the Soviet Union. A member of the Soviet Arm ...
who was in turn quickly succeeded by Marshal Sergey Biryuzov
Sergey Semyonovich Biryuzov (; 21 August 1904 – 19 October 1964) was a Marshal of the Soviet Union and Chief of the General Staff.
Early life and prewar service
Biryuzov was born in Skopin, in the Ryazan Governorate of the Russian Empire, in ...
. Under Marshal Вiryuzov the SRF deployed missiles to Cuba in 1962 as part of Operation Anadyr
Operation Anadyr (russian: Анадырь) was the code name used by the Soviet Union for its Cold War secret operation in 1962 of deploying ballistic missiles, medium-range bombers, and a division of mechanized infantry to Cuba to create an ar ...
. 36 R-12 intermediate range ballistic missile
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range of 3,000–5,500 km (1,864–3,418 miles), between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying ba ...
s were sent to Cuba, initiating the Cuban Missile Crisis. The 43rd Guards Missile Division of 43rd Rocket Army manned the missiles while in Cuba.
Marshal Nikolai Krylov took over in March 1963 and served until February 1972. During this time French President Charles de Gaulle visited the Strategic Missile Forces in 1966. Together with NI Krylov, he visited a missile division in Novosibirsk, and then at the invitation of Leonid Brezhnev participated in a demonstration missile launch at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
. Chief Marshal of Artillery Vladimir Fedorovich Tolubko commanded the SRF from April 12, 1972, to July 10, 1985. Tolubko emphasised raising the physical fitness standards within the SRF. He was succeeded by General of the Army Yury Pavlovich Maksimov, who was in command from July 10, 1985, to August 19, 1992.
According to a 1980 TIME Magazine
''Time'' (stylized in all caps) is an American news magazine based in New York City. For nearly a century, it was published weekly, but starting in March 2020 it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York City on Ma ...
article citing analysts from RAND Corporation, Soviet non-Slavs were generally barred from joining the Strategic Missile Forces because of suspicions about the loyalty of ethnic minorities to the Kremlin.
In 1989 the Strategic Missile Forces had over 1,400 ICBMs, 300 launch control centers, and twenty-eight missile bases. The SMT operated RSD-10
The RSD-10 ''Pioneer'' (russian: ракета средней дальности (РСД) «Пионер» tr.: ''raketa sredney dalnosti (RSD) "Pioner"''; en, Medium-Range Missile "Pioneer") was an intermediate-range ballistic missile with a ...
(SS-20 'Saber') intermediate-range ballistic missiles (IRBMs) and R-12 (SS-4 'Sandal') medium-range ballistic missiles (MRBMs). Two-thirds of the road-mobile Soviet RSD-10 force was based in the western Soviet Union and was aimed at Western Europe.
One-third of the force was located east of the Ural Mountains and was targeted primarily against China. Older R-12 missiles were deployed at fixed sites in the western Soviet Union. The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty
The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF Treaty, formally the Treaty Between the United States of America and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics on the Elimination of Their Intermediate-Range and Shorter-Range Missiles; / ДРСМ� ...
, signed in December 1987, called for the elimination of all 553 Soviet RSD-10 and R-12 missiles within three years. As of mid-1989, over 50% of RSD-10 and R-12 missiles had been eliminated.
By 1990 the Soviet Union had seven types of operational ICBMs. About 50% were heavy R-36M
The R-36 (russian: Р-36) is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the ...
(SS-18 'Satan') and UR-100N
The UR-100N, also known as RS-18A is an intercontinental ballistic missile in service with Soviet and Russian Strategic Missile Troops. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-19 Stiletto and carries the industry designation 15A30.
Deve ...
(SS-19 'Stiletto') ICBMs, which carried 80% of the country's land-based ICBM warheads. By this time it was producing new mobile, and hence survivable ICBMs, the RT-23 (SS-24 'Scalpel') and RT-2PM (SS-25 'Sickle').IISS Military Balance 1990–91, p.34
In 1990, with the R-12 apparently fully retired, the IISS reported that there were 350 UR-100
The UR-100 (russian: УР-100) was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed and deployed by the Soviet Union from 1966 to 1996. UR () in its designation stood for Universal Rocket (russian: links=no, Универсальная Р� ...
s (SS-11 'Sego,' Mod 2/3), 60 RT-2
The RT-2 was an intercontinental ballistic missile deployed by the Soviet Union, which was in service from December 1968 until 1976. It was assigned the NATO reporting name SS-13 Savage and carried the GRAU index 8K98. Designed by OKB-1, about 60 ...
s (SS-13 'Savage') still in service in one missile field, 75 UR-100MR
The MR-UR-100 Sotka was a MIRV-warhead intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed and deployed by the Soviet Union from 1978 to 1993. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-17 Spanker and was built under the Soviet industry des ...
s (SS-17 'Spanker,' Mod 3, with 4 MIRV), 308 R-36Ms (mostly Mod 4 with 10 MIRV), 320 UR-100Ns (mostly Mod 3 with 6 MIRV), some 60 RT-23s (silo and rail-mobile), and some 225 RT-2PMs (mobile).
Composition of the Strategic Missile Forces 1960–1991
RSVN training establishments included:
*the Order of Lenin Military Academy named for F.E. Dzerzhinskiy in Moscow;
*the Military Engineering Red Banner Institute imeni A.F. Mozhayskiy (VIKI) in Leningrad;
*the Kharkov Higher Military Command Engineering School Missile Forces imeni Marshal of the Soviet Union N.I. Krylov
*the Krasnodar Higher Military Command Engineering School Missile Forces (KVVKIU) (1982-1998)
*the Perm Higher Military Command Engineering Red Banner School Missile Forces
Perm or PERM may refer to:
Places
*Perm, Russia, a city in Russia
** Permsky District, the district
**Perm Krai, a federal subject of Russia since 2005
**Perm Oblast, a former federal subject of Russia 1938–2005
**Perm Governorate, an administra ...
( :ru:Пермский военный институт ракетных войск)
*the Riga Higher Military Political Red Banner School imeni Marshal of the Soviet Union S.S. Biryuzov (under the SRF from 1959-1993)
*the Rostov Higher Military Command Engineering School Missile Forces (RVVKIU) (1959 onwards)
*the Saratov Higher Military Command Engineering Red Banner order of the Red Star School Missile Forces imeni Major-General A.I. Lizyukov (SVVKIU) (1959-2003)
*the Serpukhov Higher Military Command Engineering School Missile Forces imeni Leninskiy Komsomol (SVVKU)
Post Soviet Union
Like most of the Russian Armed Forces, the Strategic Missile Forces had limited access to resources for new equipment in theYeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
era. However, the Russian government made a priority of ensuring that the Missile Forces received new missiles to phase out older, less-reliable systems, and to incorporate newer capabilities in the face of international threats to the viability of the nuclear deterrent effect provided by their missiles. In particular the development of missile defense systems in the United States.
In 1995, the "Strategic Missile Forces Day" and "Military Space Forces Day" were created. On July 16, 1997, President Boris Yeltsin signed a decree incorporating the Russian Space Forces
The Russian Space Forces ( rus, Космические войска России, Kosmicheskie voyska Rossii, KV) are a branch of the Russian Aerospace Forces, that provides aerospace warning, air and space sovereignty, and other related protect ...
and the Space Missile Defence Forces (Russian: Ракетно-космической обороны) into the SMT. In doing so, 'nearly 60' military units and establishments were dissolved. However, four years later, on June 1, 2001, the Russian Space Forces
The Russian Space Forces ( rus, Космические войска России, Kosmicheskie voyska Rossii, KV) are a branch of the Russian Aerospace Forces, that provides aerospace warning, air and space sovereignty, and other related protect ...
were reformed as a separate branch of service from the SMT.
Minister of Defence
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
Marshal of the Russian Federation Igor Sergeev, a former commander of the SMT from August 19, 1992 – May 22, 1997, played a major role in assuring funding for his former service.Mike HolmStrategic Missile Forces
He was succeeded by General of the Army Vladimir Yakovlev, who commanded the SMT from June 1997 until April 27, 2001. Yakovlev was succeeded by Colonel General Nikolay Solovtsov. In early 2009 Solovtsov said that 96% of all Russian ICBMs were ready to be launched within a minute's notice. Solovtsov was dismissed in July–August 2009. Speculation over why Solovtsov was dismissed included opposition to further cuts in deployed nuclear ballistic missile warheads below the April 2009 figure of 1,500, the fact that he had reached the retirement age of 60, despite that he had recently been extended another year's service, or the failure of the Navy's Bulava missile). After only a year,
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
Andrey Shvaichenko, appointed on August 3, 2009, by President Dmitry Medvedev, was replaced. The current commander of the Strategic Missile Forces, Colonel General Sergei Karakayev, was appointed to the post by a presidential decree of June 22, 2010.Pavel PodvigRussian Strategic Missile Forces
, accessed September 2010 The RVSN headquarters has a special sledgehammer that can be used to gain access to the launch codes if the commander feels the need to use it or if ordered directly, but doesn't have normal access to the safe. In 2020, the Strategic Missile Forces completed switching to digital information transmission technology.
Composition since 2010s


Kuntsevo
Kúntsevo (russian: Ку́нцево) is a district in Western Administrative Okrug of the federal city of Moscow, Russia. Population:
History
In the 18th century, a palace and a park were built; they were often visited by the Empress Catheri ...
in the suburbs of Moscow. The alternate command post is at Kosvinsky Mountain
Mount Kosvinsky Kamen, Kosvinsky Mountain, Kosvinski Mountain, Kosvinsky Rock or Rostesnoy Rock (russian: Косвинский камень, Косьвинский камень, Ростесной камень) is a mountain in the northern Ura ...
in the Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
.
Female cadets have started to join the Peter the Great Strategic Missile Forces Academy. RVSN institutes also exist at Serpukhov and Rostov-on-Don. An ICBM test impact range is located in the Far East, the Kura Test Range
Kura Missile Test Range ( rus, Ракетный полигон Кура́), originally known as ''Kama'', is a Russian intercontinental ballistic missile impact area located in northern Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East. It is the destinat ...
. This has been under Aerospace Defence Forces' command since 2010.
The Strategic Missile Forces operate four distinct missile systems. The oldest system is the silo-based R-36M2 / SS-18 ''Satan''. It carries ten warheads. The last missile will be in service until 2020.
The second system is the silo-based UR-100NUTTH / SS-19 ''Stiletto''. The last ''Stiletto'' missiles in service with six warheads each will be removed by 2019. The third system, the single warhead mobile RT-2PM Topol / SS-25 ''Sickle'' are planned to be decommissioned by 2019.
A new missile entering service is the RT-2UTTH Topol-M / SS-27 ''Sickle B'' with single warhead, of which 60 are silo-based and 18 are mobile. Some new missiles will be added in the future. The first upgraded Topol-M called RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
, carrying three warheads, was commissioned in 2010. In July 2011 the first mobile regiment with nine missiles was completed. From 2012 to 2017, about 80 ICBMs were placed in active duty. The RF Defense Minister said in December 2022 that 91.3% of the country's nuclear forces was modern.
Units
The composition of missiles and warheads of the Strategic Missile Forces previously had to be revealed as part of the START I treaty data exchange. The most recently reported (January 2020) order of battle of the forces is as follows: *27th Guards Rocket Army
27th Guards Vitebsk Red Banner Rocket Army (russian: 27-я Гвардейская Витебская Краснознамённая ракетная армия) is one of the 3 rocket armies within Russian Strategic Rocket Forces headquartered at ...
(HQ: Vladimir
Vladimir may refer to:
Names
* Vladimir (name) for the Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Macedonian, Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak and Slovenian spellings of a Slavic name
* Uladzimir for the Belarusian version of the name
* Volodymyr for the Ukr ...
)
** 98th Mixed Aviation Squadron
** 7th Guards Rocket Division
The 7th Guards Missile Rezhitskaya Red Flag division (7 GRD) – is a (military unit 14245) of the 27th Guards Missile Army, Strategic Rocket Forces located in Ozyorny, Bologovsky District, Tver region, Russia.
Abbreviated name - 7 RD
History ...
at Vypolzovo with 18+ mobile RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
** 14th Rocket Division at Yoshkar-Ola
Yoshkar-Ola ( Mari and russian: Йошкар-Ола) is the capital city of the Mari El Republic, Russia. Yoshkar-Ola means “red city” in Mari and was formerly known as Tsaryovokokshaysk () before 1919, as Krasnokokshaysk () between 1919 an ...
with 27 mobile RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
** 28th Guards Rocket Division at Kozelsk with 17 (December 2022) silo-based RS-24
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
** 54th Guards Rocket Division at Teykovo
Teykovo (russian: Те́йково) is a town in Ivanovo Oblast, Russia, located on the Vyazma River southwest of Ivanovo. Population: 42,800 (1975).
History
It was founded in the 17th century and was granted town status in 1918.
Administra ...
with 18 mobile RT-2UTTH Topol-M
The RT-2PM2 «Topol-M» (russian: РТ-2ПМ2 «Тополь-М», NATO reporting name: SS-27 "Sickle B", other designations: SS-27 Mod 1, RS-12M1, RS-12M2, formerly incorrectly RT-2UTTKh) is one of the most recent intercontinental ballistic missi ...
and 18 (December 2011) mobile RS-24
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
** 60th Rocket Division at Tatischevo with 30 silo-based UR-100N
The UR-100N, also known as RS-18A is an intercontinental ballistic missile in service with Soviet and Russian Strategic Missile Troops. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-19 Stiletto and carries the industry designation 15A30.
Deve ...
UTTH and 60 silo-based RT-2UTTH Topol-M
The RT-2PM2 «Topol-M» (russian: РТ-2ПМ2 «Тополь-М», NATO reporting name: SS-27 "Sickle B", other designations: SS-27 Mod 1, RS-12M1, RS-12M2, formerly incorrectly RT-2UTTKh) is one of the most recent intercontinental ballistic missi ...
* 31st Rocket Army
31st Rocket Army (russian: 31-я ракетная армия) is one of the three rocket armies within Russian Strategic Rocket Forces headquartered in Orenburg.
The 31st Rocket Army was formed on 8 June 1970, on the base of the 18th Separate Rock ...
(HQ: Orenburg)
** 102nd Mixed Aviation Squadron
** 8th Rocket Division at Pervomaysky, Kirov Oblast
** 13th Red Banner Rocket Division
The 13th Orenburg Red Banner Rocket Division (Military Unit Number 68545) is a military formation of the 31st Rocket Army, Strategic Missile Forces, located in Yasny, ZATO Komarovsky, Orenburg Oblast.
The deployment site for the division was c ...
at Dombarovskiy with 18 silo-based R-36M2 and 8 (December 2022) UR-100N
The UR-100N, also known as RS-18A is an intercontinental ballistic missile in service with Soviet and Russian Strategic Missile Troops. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-19 Stiletto and carries the industry designation 15A30.
Deve ...
UTTH with Avangard (hypersonic glide vehicle)s (''Project 4202''). The R-36s will be replaced with the new RS-28 Sarmat
The RS-28 Sarmat (, named after the Sarmatians; NATO reporting name: SS-X-29 or SS-X-30), known as "Satan II", is a Russian liquid-fueled, MIRV-equipped super-heavy intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) produced by the Makeyev Rocket Desig ...
when operational.
** 42nd Rocket Division The 42nd Rocket Division (v/ch 34103) is an intercontinental ballistic missile formation of the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces. It is based at Svobodny, Sverdlovsk Oblast/Nizhniy Tagil, Sverdlovsk Oblast, and it is part of the 31st Rocket Army.
...
at Nizhniy Tagil
Nizhny Tagil ( rus, Нижний Тагил, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj tɐˈgʲil) is a city in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located east of the boundary between Asia and Europe. Population:
History
The prehistory of Nizhny Tagil dates back to the mid- ...
with 27 mobile RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
* 33rd Guards Rocket Army (HQ: Omsk)
** 105th Mixed Aviation Squadron
** 29th Guards Rocket Division
The 29th Guards Rocket Division is an intercontinental ballistic missile division of the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces. The division was formerly part of the Soviet Strategic Rocket Forces and has been active since 1960. Originally based in Latvi ...
at Irkutsk with 27 mobile RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
** 35th Rocket Division
The 35th Red Banner Orders of Kutuzov and Aleksandr Nevsky Rocket Division (russian: 35-я ракетная Краснознамённая, орденов Кутузова и Александра Невского дивизия) is a strategic mi ...
at Barnaul
Barnaul ( rus, Барнау́л, p=bərnɐˈul) is the largest city and administrative centre of Altai Krai, Russia, located at the confluence of the Barnaulka and Ob Rivers in the West Siberian Plain. As of the 2021 Census, its population was ...
with mobile RT-2PM Topol
The RT-2PM Topol (russian: РТ-2ПМ Тополь ("Poplar"); NATO reporting name SS-25 Sickle; GRAU designation: 15Ж58 ("15Zh58"); START I designation: RS-12M Topol) is a mobile intercontinental ballistic missile designed in the Soviet Union a ...
and RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
** 39th Guards Rocket Division at Novosibirsk with 27 mobile RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
** 62nd Rocket Division The 62nd Red Banner Rocket Division is a formation of the 33rd Guards Rocket Army, Russian Strategic Rocket Forces, which is located near Uzhur, in Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai ( rus, Красноя́рский край, r=Krasnoyarskiy kr ...
at Uzhur with 28 silo-based R-36M2, which will also replaced with the new RS-28 Sarmat
The RS-28 Sarmat (, named after the Sarmatians; NATO reporting name: SS-X-29 or SS-X-30), known as "Satan II", is a Russian liquid-fueled, MIRV-equipped super-heavy intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) produced by the Makeyev Rocket Desig ...
when operational.
Numbers of missiles and warheads
The Strategic Missile Forces have: * 46 silo-based R-36M2 (SS-18) with up to 10 warheads, to be retired 2022 * 45 mobile RT-2PM "Topol" (SS-25) with 1 warhead, flagged for future retirement * 60 silo-based RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27) with 1 warhead * 18 mobile RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27) with 1 warhead * 17 silo-based RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29) with up to 4 warheads * 135+ mobile RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29) with up to 4 warheads Kristensen and Korda (2020) list the UR-100N (SS-19), as retired from deployment, while noting thatUR-100N
The UR-100N, also known as RS-18A is an intercontinental ballistic missile in service with Soviet and Russian Strategic Missile Troops. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-19 Stiletto and carries the industry designation 15A30.
Deve ...
UTTH being deployed with the Avangard.Hans M. Kristensen & Matt Korda (2020) Russian nuclear forces, 2020, Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, 76:2, 102-117, DOI: 10.1080/00963402.2020.1728985
Obsolete weapons and equipment

Medium-range ballistic missiles
* R-12 Dvina, SS-4 Sandel – In service from 1959 to 1993.Intermediate-range ballistic missiles
* R-14 Chusovaya, SS-5 Skean – In service from 1962 to 1984. * RSD-10 Pioneer, SS-20 Sabre, SS-23 Sabre 2 – In service from 1976 to 1988.Intercontinental-range ballistic missiles
* MR-UR-100 Sotka, SS-17 Spanker – In service from 1975 to 1995. * R-7 Semyorka, SS-6 Sapwood – In service from 1959 to 1968. * R-9 Desna, SS-8 Sasin – In service from 1964 to 1976. * R-16, SS-7 Saddler – In service from 1961 to 1976. * RT-2, SS-13 Savage – In service from 1968 to 1976. * RT-20P, SS-15 Scrooge – In service from 1961 to 1962. * RT-21 Temp 2S, SS-16 Sinner – In service from 1976 to 1986. * RT-23 Molodets, SS-24 Scalpel – In service from 1987 to 2005. * UR-100, SS-11 Sego – In service from 1967 to 1974. * UR-200, SS-10 Scrag – In service from 1963 to 1964.Ranks and rank insignia
;Officer ranks ;Other ranksFuture
According to the Federation of American Scientists, for the foreseeable future, all new Russian ICBM deployments will be ofMIRV
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with i ...
ed versions of the SS-27 "Topol-M". A “new ICBM” and a “heavy ICBM” are also being developed. By the early 2020s, according to announcements by Russian military officials, all SS-18 and SS-25 ICBMs will be retired from service following the retirements of the SS-19 systems.
This development would leave a Russian ICBM force structure based on five modifications of the solid-fuel SS-27 (silo- and mobile-based SS-27 Mod 1 (Topol-M); silo- and mobile-based SS-27 Mod 2 (RS-24 Yars
The RS-24 Yars (РС-24 Ярс– ракета стратегическая (strategic missile)) - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR (russian: PC-24 «Ярс», NATO reporting name: SS-29 or SS-27 Mod 2) is a Russian MIRV-e ...
); and the RS-26 Rubezh) and the liquid-fuel RS-28 Sarmat
The RS-28 Sarmat (, named after the Sarmatians; NATO reporting name: SS-X-29 or SS-X-30), known as "Satan II", is a Russian liquid-fueled, MIRV-equipped super-heavy intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) produced by the Makeyev Rocket Desig ...
with a large payload – either MIRV or some advanced payload to evade missile defense systems. Although the future force will be smaller, a greater portion of it will be MIRV
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with i ...
ed – up from approximately 36 percent in 2014 to roughly 70 percent by 2024.
See also
*Dead Hand
Dead Hand (russian: Система «Периметр», , lit. "Perimeter" System, with the GRAU Index 15E601, Cyrillic: 15Э601), also known as Perimeter, is a Cold War-era automatic nuclear weapons-control system (similar in concept to the A ...
*Russian Aerospace Defence Forces
The Russian Aerospace Defence Forces (VVKO) ( rus, Войска воздушно-космической обороны (ВВКО), Voyska vozdushno-kosmicheskoy oborony (VVKO)) was a branch of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation respons ...
* Awards and emblems of the Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation
*List of states with nuclear weapons
Eight sovereign states have publicly announced successful detonation of nuclear weapons. Five are considered to be nuclear-weapon states (NWS) under the terms of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). In order of acquisit ...
References
Further reading
*Дороговоз И. Г. Ракетные войска СССР. — Минск: Харвест, 2007. — 336 с. — *John G. Hines et al.Soviet Intentions 1965–1985
'. Braddock Dunn & McDonald (BDM), 1995.
Strategic Missile Forces museum
* *"Владимирская Ракетная Стратегическая" (Vladimirskaya Strategic Missile) by I.V. Vershkov and V.G. Gagarin; Vladimir 2006; 480 pages; *"Оренбургская Стратегическая" (Orenburg Strategic) by Y.N. Feoktistov; Perm 2001; 328 pages; (also a 1997 edition). *"Читинская Ракетная Армия" (Chitinskaya Missile Army) by ??; Chita, 2002; 268 pages *"История 50-й Ракетной Армии I-IV" (History 50th Missile Army, part 1–4) by G.I. Smirnov and A.I. Yasakov; Smolensk 2008; 370+342+387+561 pages *"Стратеги" (Strategic) by V.T. Nosov; Moscow, 2008; 276 pages;
External links
CSIS Missile Threat - Russia
''Strategic Missile Forces museum'' Official Website
Russian Nuclear Notebook 2019 - forces and Rocket Divisions
{{Strategic forces Strategic Rocket Forces Strategic forces