Strategic Forces Command on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Strategic Forces Command (SFC), sometimes called Strategic Nuclear Command, forms part of India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA). It is responsible for the management and administration of the country's tactical and strategic
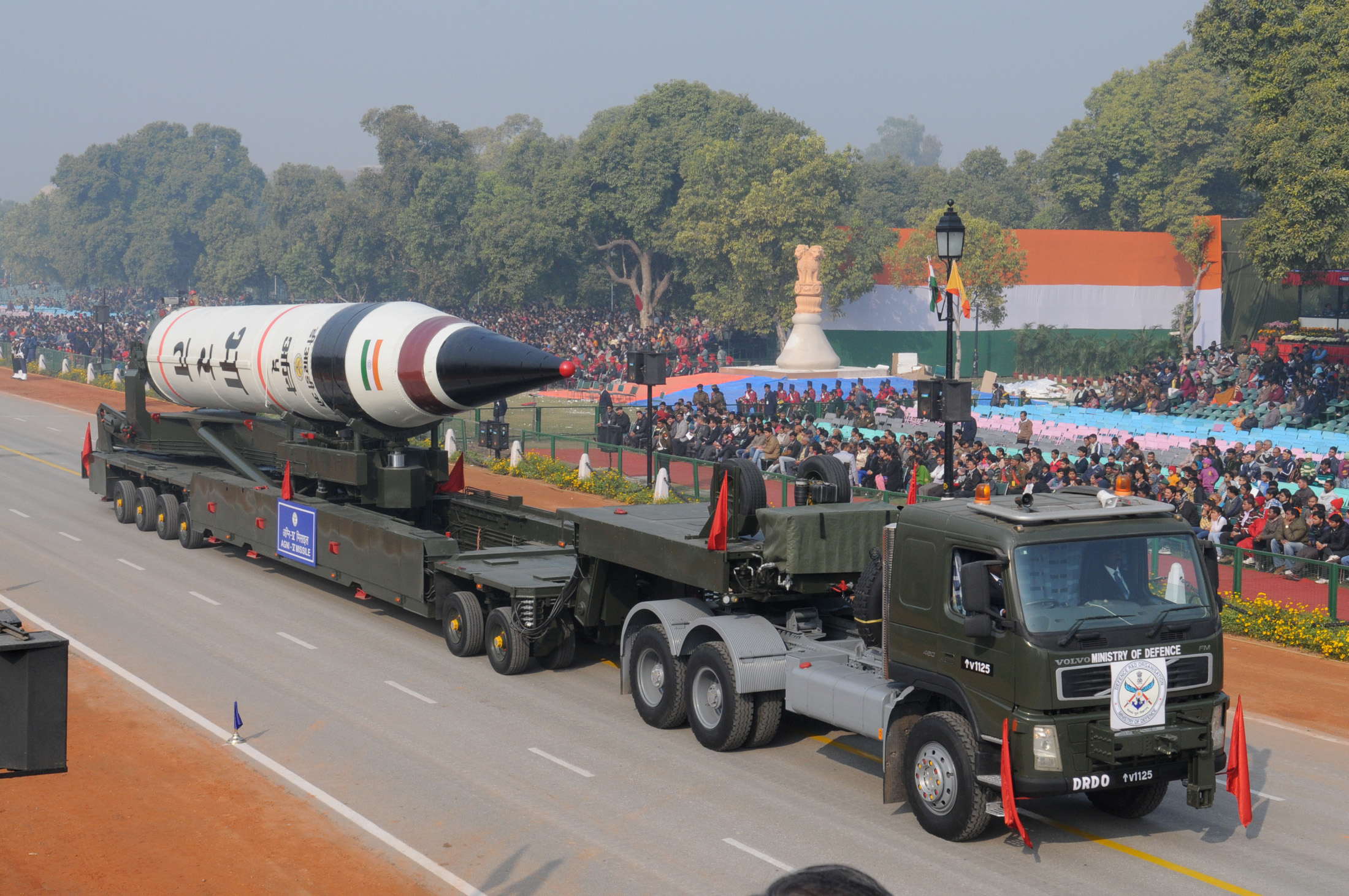 The Prithvi missile inducted into India’s Strategic Forces Command in 2003, the first missile to be developed under India’s prestigious IGMDP strengthens India’s nuclear deterrence A missile unit of the elite Strategic Forces Command (SFC) successfully launched a Prithvi missile on 7 January 2014 from the test range at Chandipur.
It was reported by ''Hindustan Times'' on 12 September 2010 that to increase its lethal power, India's tri-services strike force is planning to acquire 40 fighter planes capable of delivering nuclear weapons. The SFC has submitted a proposal to the Defence Ministry for setting up two dedicated squadrons of fighter aircraft which will act as a mini-Air Force. This will be the first time that the SFC, which at present depends on the Indian Air Force for delivering nuclear weapons under its command, will have its own aerial assets.
The Prithvi missile inducted into India’s Strategic Forces Command in 2003, the first missile to be developed under India’s prestigious IGMDP strengthens India’s nuclear deterrence A missile unit of the elite Strategic Forces Command (SFC) successfully launched a Prithvi missile on 7 January 2014 from the test range at Chandipur.
It was reported by ''Hindustan Times'' on 12 September 2010 that to increase its lethal power, India's tri-services strike force is planning to acquire 40 fighter planes capable of delivering nuclear weapons. The SFC has submitted a proposal to the Defence Ministry for setting up two dedicated squadrons of fighter aircraft which will act as a mini-Air Force. This will be the first time that the SFC, which at present depends on the Indian Air Force for delivering nuclear weapons under its command, will have its own aerial assets.
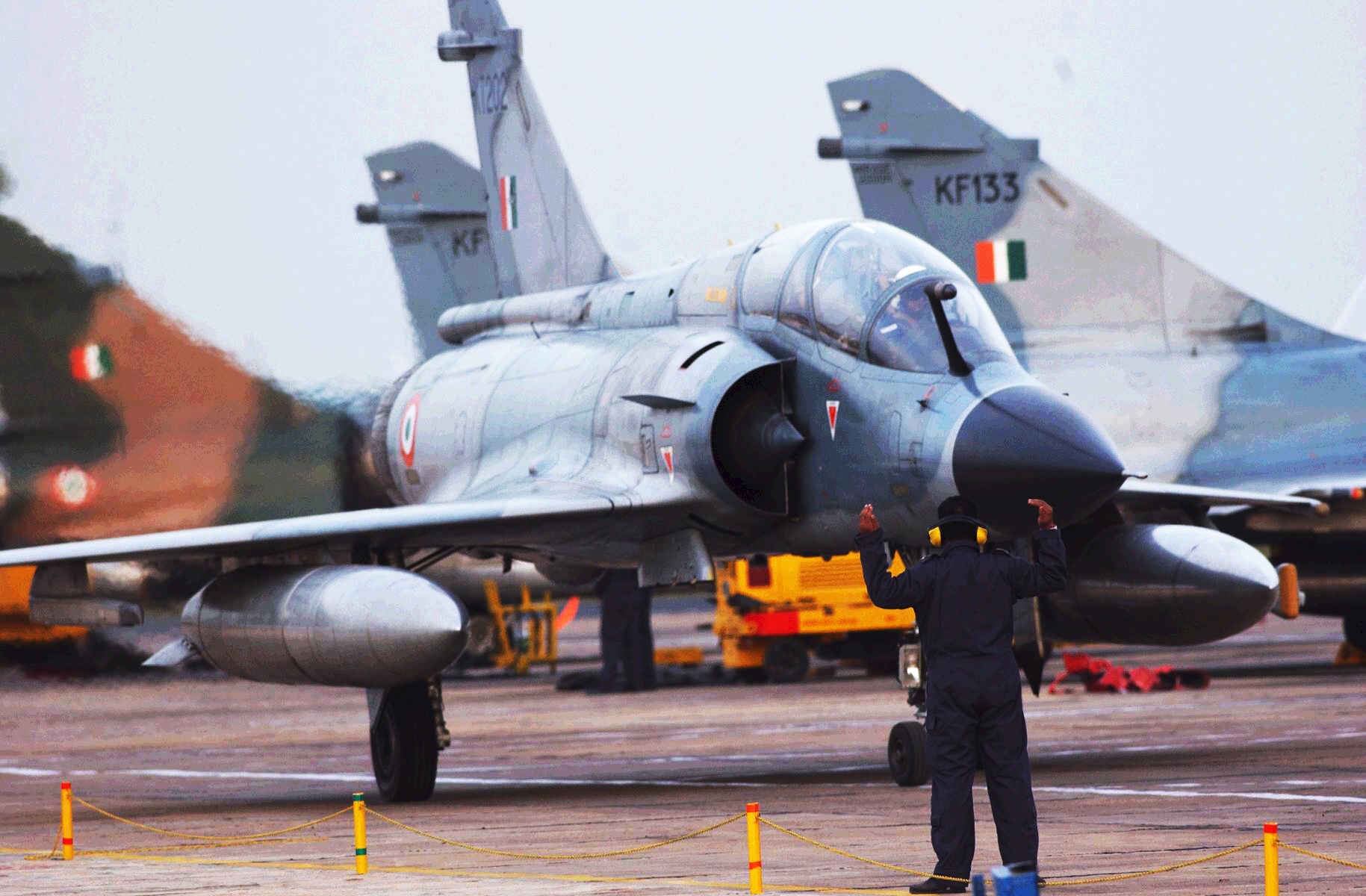 Nuclear-armed fighter-bombers were India's first and only nuclear-capable strike force until 2003, when the country's first land-based nuclear ballistic missiles were fielded.
In addition to their
Nuclear-armed fighter-bombers were India's first and only nuclear-capable strike force until 2003, when the country's first land-based nuclear ballistic missiles were fielded.
In addition to their
 The
The  The first is a submarine-launched system consisting of at least four 6,000 tonne (
The first is a submarine-launched system consisting of at least four 6,000 tonne (
nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s stockpile. It was created on 4 January 2003 by the Vajpayee Government
Atal Bihari Vajpayee was an Indian politician who served twice as Prime Minister of India, first from 16 May to 1 June 1996, and then from 19 March 1998 to 22 May 2004. A member of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), Vajpayee was the tenth Pri ...
. Air Marshal Teja Mohan Asthana became its first commander-in-chief.
Responsibility
It is the responsibility of the Strategic Forces Command to operationalize the directives of the NCA under the leadership of a Commander-in-Chief who is athree-star rank
An officer of three-star rank is a senior commander in many of the armed services holding a rank described by the NATO code of OF-8. The term is also used by some armed forces which are not NATO members. Typically, three-star officers hold the ...
officer. It will have the sole responsibility of initiating the process of delivering nuclear weapons and warheads, after acquiring explicit approval from the NCA. The exact selection of the target area shall be decided by the SFC through a calibrated, cumulative process involving various levels of decision-making, and with formal approval by the NCA.
The SFC manages and administers all strategic forces by exercising complete command and control over nuclear assets, and producing all contingency plans as needed to fulfill the required tasks. Since its inception, the SFC’s command, control and communication systems have been firmly established, and the command has attained a high state of operational readiness.
Assets
The estimated 68 nuclear warheads of land-based nuclear weapons of India are under the control of and deployed by the Strategic Forces Command, using a variety of both vehicles and launching silos. They currently consist of three different types ofballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within the ...
s, the Agni-I
Agni-I (Agni ''"Fire"'') is a medium-range ballistic missile that was developed by DRDO of India in the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program. It is a single-stage missile that was developed after the Kargil War to fill the gap between th ...
, the Agni-II
Agni-II (IAST: Agni, ), is the second strategic ballistic missile of Agni (missile) family envisaged to be the mainstay of the Indian missile-based strategic nuclear deterrence. The Agni-II is a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) with two so ...
, Agni-III
The Agni-III (IAST: Agni, ) is an Indian intermediate-range ballistic missile inducted into service in 2011 as the successor of the Agni-II. It has a range of and can reach targets deep inside neighbouring countries including China.
Introduct ...
, Shaurya and the Army's variant of the Prithvi missile
Prithvi (Sanskrit: ''"Earth"'') is a tactical surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP). ...
family – the Prithvi-I. Additional variants of the Agni missile series have recently been inducted including the most recent, the Agni-IV
Agni-IV ("Fire") is the fourth in the Agni series of missiles which was earlier known as ''Agni II prime''. It has been developed by India's DRDO and displayed a number of new technologies and significant improvement in missile technology. T ...
and the Agni-V, which is currently being deployed. Agni-VI
Agni-VI (IAST: Agni ''"Fire"'') is an MIRV-capable intercontinental ballistic missile under development by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) of the Indian Armed Forces.
Descriptio ...
is also under development, with an estimated range of 8,000–12,000 km and features such as Multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs) or Maneuverable reentry vehicle
The maneuverable reentry vehicle (abbreviated MARV or MaRV) is a type of warhead for ballistic missiles that is capable of maneuvring and changing its trajectory.
MaRV can be capable of autonomously tracking ground targets to make sure the mis ...
s (MARVs).
 The Prithvi missile inducted into India’s Strategic Forces Command in 2003, the first missile to be developed under India’s prestigious IGMDP strengthens India’s nuclear deterrence A missile unit of the elite Strategic Forces Command (SFC) successfully launched a Prithvi missile on 7 January 2014 from the test range at Chandipur.
It was reported by ''Hindustan Times'' on 12 September 2010 that to increase its lethal power, India's tri-services strike force is planning to acquire 40 fighter planes capable of delivering nuclear weapons. The SFC has submitted a proposal to the Defence Ministry for setting up two dedicated squadrons of fighter aircraft which will act as a mini-Air Force. This will be the first time that the SFC, which at present depends on the Indian Air Force for delivering nuclear weapons under its command, will have its own aerial assets.
The Prithvi missile inducted into India’s Strategic Forces Command in 2003, the first missile to be developed under India’s prestigious IGMDP strengthens India’s nuclear deterrence A missile unit of the elite Strategic Forces Command (SFC) successfully launched a Prithvi missile on 7 January 2014 from the test range at Chandipur.
It was reported by ''Hindustan Times'' on 12 September 2010 that to increase its lethal power, India's tri-services strike force is planning to acquire 40 fighter planes capable of delivering nuclear weapons. The SFC has submitted a proposal to the Defence Ministry for setting up two dedicated squadrons of fighter aircraft which will act as a mini-Air Force. This will be the first time that the SFC, which at present depends on the Indian Air Force for delivering nuclear weapons under its command, will have its own aerial assets.
Air-launched nuclear weapons
 Nuclear-armed fighter-bombers were India's first and only nuclear-capable strike force until 2003, when the country's first land-based nuclear ballistic missiles were fielded.
In addition to their
Nuclear-armed fighter-bombers were India's first and only nuclear-capable strike force until 2003, when the country's first land-based nuclear ballistic missiles were fielded.
In addition to their ground-attack
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and movem ...
role, it is believed that the Dassault Mirage 2000
The Dassault Mirage 2000 is a French multirole, single-engine, fourth-generation jet fighter manufactured by Dassault Aviation. It was designed in the late 1970s as a lightweight fighter to replace the Mirage III for the French Air Force (''A ...
s and SEPECAT Jaguars of the Indian Air Force are able to provide a secondary nuclear-strike role. The SEPECAT Jaguar was designed to be able to carry and deploy nuclear weapons and the Indian Air Force has identified the jet as being capable of delivering Indian nuclear weapons. The most likely delivery method would be the use of bombs that are free-falling and unguided.
Three airbases with four squadrons of Mirage 2000H (about 16 aircraft with 16 bombs from 1st and 7th squadrons of the 40th Wing at Maharajpur Air Force Station) and Jaguar IS/IB (about 32 aircraft with 32 bombs from one squadron each at Ambala Air Force Station and Gorakhpur Air Force Station) aircraft, are believed to be assigned the nuclear strike role.
Sea-based ballistic missile
 The
The Indian Navy
The Indian Navy is the maritime branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy. As a blue-water navy, it operates si ...
has developed two sea-based delivery systems for nuclear weapons, completing Indian ambitions for a nuclear triad
A nuclear triad is a three-pronged military force structure that consists of land-launched nuclear missiles, nuclear-missile-armed submarines, and strategic aircraft with nuclear bombs and missiles. Specifically, these components are land-based ...
, which may have been deployed in 2015.
 The first is a submarine-launched system consisting of at least four 6,000 tonne (
The first is a submarine-launched system consisting of at least four 6,000 tonne (nuclear-powered
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
) ballistic missile submarines of the Arihant class
The ''Arihant''-class ( in Sanskrit) is a class of Indian nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines being built for the Indian Navy. They were developed under the ''Advanced Technology Vessel'' (ATV) project to design and build nuclear-po ...
. The first vessel, INS ''Arihant'', has been launched and will complete extensive sea-trials before being commissioned and declared operational. She is the first nuclear-powered submarine to be built by India."Indian nuclear submarine", India Today, August 2007 edition A CIA report claimed that Russia provided technological aid to the naval nuclear propulsion program. The submarines will be armed with up to 12 Sagarika
Sagarika Mukherjee (born 4 September 1970), also known as Saag, is an Indian singer and actress. She sings mainly in Hindi, Assamese and Bengali language songs but has also sung in Tamil and Telugu languages. She is the daughter of singer ...
(K-15) missiles armed with nuclear warheads. Sagarika is a submarine-launched ballistic missile with a range of 700 km. This missile has a length of 8.5 meters, weighs seven tonnes and can carry a pay load of up to 500 kg. Sagarika has already been test-fired from an underwater pontoon, but now DRDO
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) (IAST: ''Raksā Anūsandhān Evam Vikās Sangaṭhan'') is the premier agency under the Department of Defence Research and Development in Ministry of Defence of the Government of India, ...
is planning a full-fledged test of the missile from a submarine and for this purpose may use the services of the Russian Navy. India's DRDO
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) (IAST: ''Raksā Anūsandhān Evam Vikās Sangaṭhan'') is the premier agency under the Department of Defence Research and Development in Ministry of Defence of the Government of India, ...
is also working on a submarine-launched ballistic missile version of the Agni-III missile, known as the Agni-III SL. According to Indian defence sources, the Agni-III SL will have a range of . The new missile will complement the older and less capable Sagarika submarine-launched ballistic missiles. However, the Arihant class ballistic missile submarines will be only capable of carrying a maximum of four Agni-III SL.
The second is a ship-launched system based around the short range ship-launched Dhanush ballistic missile (a variant of the Prithvi missile
Prithvi (Sanskrit: ''"Earth"'') is a tactical surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP). ...
). It has a range of around 300 km. In the year 2000 the missile was test-fired from INS ''Subhadra'' (a Sukanya class patrol craft). INS Subhadra was modified for the test and the missile was launched from the reinforced helicopter deck. The results were considered partially successful. In 2004, the missile was again tested from INS ''Subhadra'' and this time the results were reported successful. In December 2005 the missile was tested again, but this time from the destroyer INS ''Rajput''. The test was a success with the missile hitting the land based target.
List of commanders
See also
; Integrated entities * Defence Planning Committee, tri-services command at policy level with NSA as its chief *Defence Cyber Agency
The Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA) is a tri-service command of the Indian Armed Forces. Headquartered in New Delhi, the agency is tasked with handling cyber security threats. The DCyA draws personnel from all three branches of the Armed Forces. The ...
, tri-services command
* Integrated Defence Staff
The Integrated Defence Staff (IDS) is an organisation responsible for fostering coordination and enabling prioritisation across the different branches of the Indian Armed Forces. It is composed of representatives from the Indian Army, Indian Navy, ...
, tri-services command at strategic level composed of MoD, MEA and tri-services staff
* Armed Forces Special Operations Division
The Armed Forces Special Operations Division (AFSOD) is a tri-service command of the Indian Armed Forces. The division is tasked to carry out special operations. The AFSOD draws personnel from all three special warfare branches of the Armed Fo ...
, tri-services command at operational level
* Defence Space Agency, draws staff from all 3 services of Indian Armed Forces
* Strategic Forces Command, nuclear command of India
** Indian Nuclear Command Authority, Strategic Forces Command
** Special Forces of India, tri-services, RAW and internal Security each has own units
* Andaman and Nicobar Command
The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is the first and only tri-service theater command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was created in 2001 to safeguard India ...
, first operational tri-services command
; Assets
* List of Indian Air Force stations
The Indian Air Force currently operates seven Air Commands. Each command is headed by an Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of the rank of Air Marshal.
The Air Force currently has over 60 air stations all over India. These are grouped into seve ...
* List of Indian Navy bases
The Indian Navy currently operates three commands — Western Naval Command located at Mumbai, Southern Naval Command located at Kochi and Eastern Naval Command located at Visakhapatnam. The Andaman and Nicobar Command, a unified Indian Navy, ...
* List of active Indian Navy ships
List of active Indian Navy ships is a list of ships in active service with the Indian Navy. In service ships are taken from the official Indian Navy website.
* India's overseas military bases
; General concepts
* Joint warfare
Joint warfare is a military doctrine which places priority on the integration of the various service branches of a state's armed forces into one unified command. Joint warfare is in essence a form of combined arms warfare on a larger, national ...
, general concept
* Minimum Credible Deterrence
Credible minimum deterrence is the principle on which India's nuclear strategy is based.
It underlines no first use (NFU) with an assured second strike capability and falls under minimal deterrence, as opposed to mutually assured destruction. I ...
* List of cyber warfare forces
Many countries around the world maintain military units that are specifically trained to operate in a cyberwarfare environment. In several cases this units acts also as the national computer emergency response team for civilian cybersecurity threa ...
of other nations
References
{{Indian Air Force Military units and formations of India Vajpayee administration 2003 establishments in India Joint military units and formations of India Strategic forces