State Duma (Russian Empire) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The State Duma, also known as the Imperial Duma, was the lower house of the Governing Senate in the
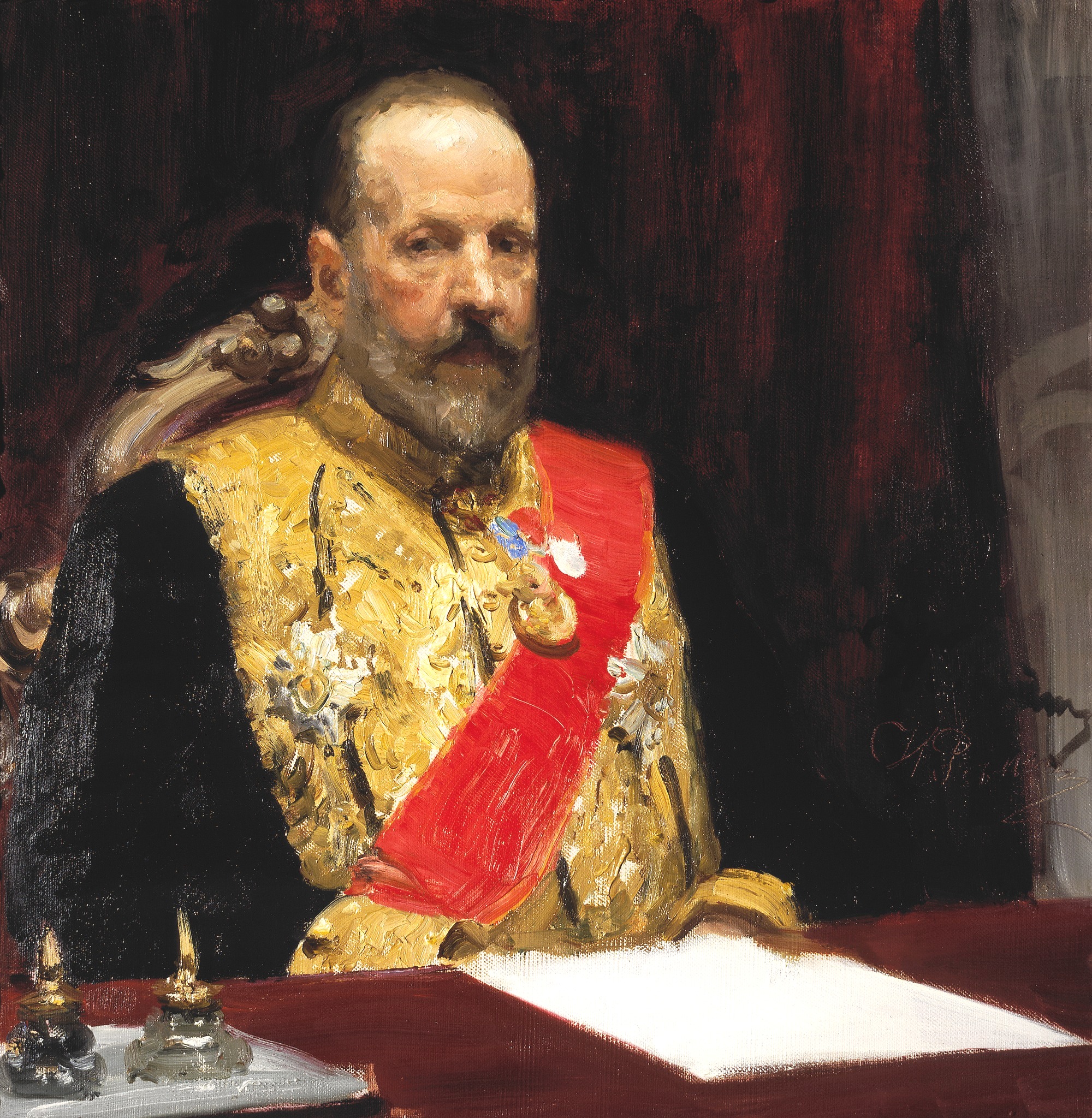 Coming under pressure from the Russian Revolution of 1905, on August 6, 1905 (O.S.), Sergei Witte (appointed by
Coming under pressure from the Russian Revolution of 1905, on August 6, 1905 (O.S.), Sergei Witte (appointed by
 The first Duma was established with around 500 deputies; most radical left parties, such as the Party of Socialist-Revolutionaries and the
The first Duma was established with around 500 deputies; most radical left parties, such as the Party of Socialist-Revolutionaries and the
 The Second Duma (from 20 February 1907 to 3 June 1907) lasted 103 days. One of the new members was Vladimir Purishkevich, strongly opposed to the October Manifesto. The
The Second Duma (from 20 February 1907 to 3 June 1907) lasted 103 days. One of the new members was Vladimir Purishkevich, strongly opposed to the October Manifesto. The

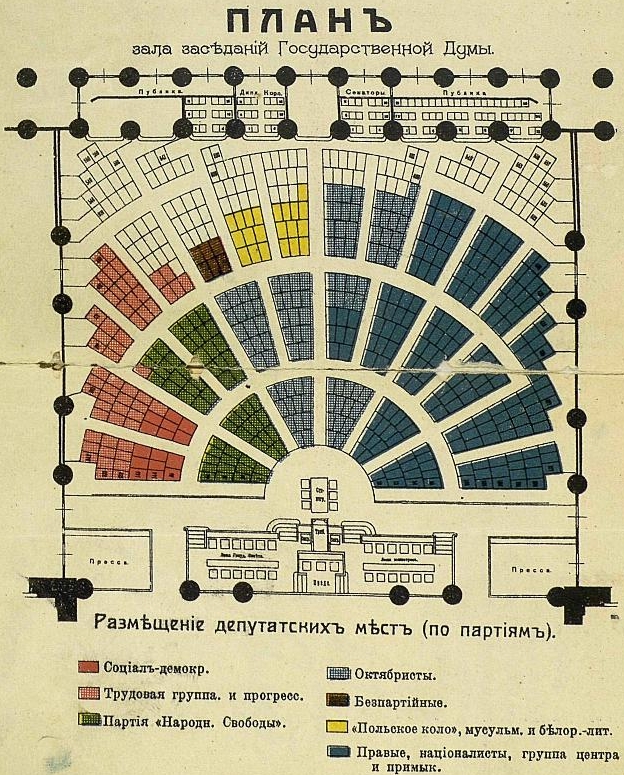 The Fourth Duma of 15 November 1912 – 6 October 1917, elected in September/October, was also of limited political influence. The first session was held from 15 November 1912 to 25 June 1913, and the second session from 15 October 1913 to 14 June 1914. On 1 July 1914 the Tsar suggested that the Duma should be reduced to merely a consultative body, but an extraordinary session was held on 26 July 1914 during the
The Fourth Duma of 15 November 1912 – 6 October 1917, elected in September/October, was also of limited political influence. The first session was held from 15 November 1912 to 25 June 1913, and the second session from 15 October 1913 to 14 June 1914. On 1 July 1914 the Tsar suggested that the Duma should be reduced to merely a consultative body, but an extraordinary session was held on 26 July 1914 during the

Speech from the Throne by Nicholas II at Opening of the State Duma, photo essay with commentaryFour Dumas of Imperial Russia
{{Authority control 1905 establishments in the Russian Empire 1917 disestablishments in Russia
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, while the upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
was the State Council. It held its meetings in the Taurida Palace
Tauride Palace (russian: Таврический дворец, translit=Tavrichesky dvorets) is one of the largest and most historically important palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
Construction and early use
Prince Grigory Potemkin of Tauride ...
in St. Petersburg. It convened four times between 27 April 1906 and the collapse of the Empire in February 1917. The first and the second dumas were more democratic and represented a greater number of national types than their successors. The third duma was dominated by gentry, landowners and businessmen. The fourth duma held five sessions; it existed until 2 March 1917, and was formally dissolved on 6 October 1917.
History
 Coming under pressure from the Russian Revolution of 1905, on August 6, 1905 (O.S.), Sergei Witte (appointed by
Coming under pressure from the Russian Revolution of 1905, on August 6, 1905 (O.S.), Sergei Witte (appointed by Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Pol ...
to manage peace negotiations with Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
after the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–1905) issued a manifesto about the convocation of the Duma, initially thought to be a purely advisory body, the so-called Bulygin
Alexander Bulygin ( – 5 September 1919) was the Minister of Interior of Russia from February 1905 until October 1905.
Biography
Graduate of the Imperial School of Law, he began work in the Tambov district court in 1871. He then held various a ...
-Duma. In the subsequent October Manifesto, the Tsar promised to introduce further civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties ma ...
, provide for broad participation in a new "State Duma", and endow the Duma with legislative and oversight powers. The State Duma was to be the lower house of a parliament, and the State Council of Imperial Russia the upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
.
However, Nicholas II was determined to retain his autocratic power (in which he succeeded). On April 23, 1906 ( O.S.), the Tsar issued the Fundamental Laws, which gave him the title of "supreme autocrat". Although no law could be made without the Duma's assent, neither could the Duma pass laws without the approval of the noble-dominated State Council (half of which was to be appointed directly by the Tsar), and the Tsar himself retained a veto. The laws stipulated that ministers could not be appointed by, and were not responsible to, the Duma, thus denying responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive br ...
at the executive level. Furthermore, the Tsar had the power to dismiss the Duma and announce new elections whenever he wished; article 87 allowed him to pass temporary (emergency) laws by decrees. All these powers and prerogatives assured that, in practice, the Government of Russia continued to be a non-official absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constituti ...
. It was in this context that the first Duma opened four days later, on April 27, 1906.
First Duma

 The first Duma was established with around 500 deputies; most radical left parties, such as the Party of Socialist-Revolutionaries and the
The first Duma was established with around 500 deputies; most radical left parties, such as the Party of Socialist-Revolutionaries and the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP; in , ''Rossiyskaya sotsial-demokraticheskaya rabochaya partiya (RSDRP)''), also known as the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party or the Russian Social Democratic Party, was a socialist pol ...
had boycotted the election, leaving the moderate Constitutional Democrats (Kadets) with the most deputies (around 184). Second came an alliance of slightly more radical leftists, the Trudoviks (Laborites) with around 100 deputies. To the right of both were a number of smaller parties, including the Octobrists. Together, they had around 45 deputies. Other deputies, mainly from peasant groups, were unaffiliated.
The Kadets were among the only political parties capable of consistently drawing voters due to their relatively moderate political stance. The Kadets drew from an especially urban population, often failing to draw the attention of rural communities who were instead committed to other parties.
The Duma ran for 73 days until 8 July 1906, with little success. The Tsar and his loyal Prime Minister Ivan Goremykin were keen to keep it in check, and reluctant to share power; the Duma, on the other hand, wanted continuing reform, including electoral reform, and, most prominently, land reform. Sergei Muromtsev
Sergey Andreevich Muromtsev (russian: Серге́й Андре́евич Му́ромцев) (October 5, Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O.S._23_September.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/> O.S._23_September">O ...
, Professor of Law at Moscow University, was elected Chairman. Lev Urusov held a famous speech. Scared by this liberalism, the Tsar dissolved the Duma, reportedly saying "curse the Duma. It is all Witte's doing". The same day, Pyotr Stolypin was named as the new Prime Minister who promoted a coalition cabinet
A coalition government is a form of government in which political parties cooperate to form a government. The usual reason for such an arrangement is that no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an election, an atypical outcome in ...
, as did Vasily Maklakov
Vasily Alekseyevich Maklakov (Russian: Васи́лий Алексе́евич Маклако́в; , Moscow – July 15, 1957, Baden, Switzerland) was a Russian student activist, a trial lawyer and liberal parliamentary deputy, an orator, and one ...
, Alexander Izvolsky
Count Alexander Petrovich Izvolsky or Iswolsky (russian: Алекса́ндр Петро́вич Изво́льский, , Moscow – 16 August 1919, Paris) was a Russian diplomat remembered as a major architect of Russia's alliance with Grea ...
, Dmitri Trepov and the Tsar.
In frustration, Paul Miliukov
Pavel Nikolayevich Milyukov ( rus, Па́вел Никола́евич Милюко́в, p=mʲɪlʲʊˈkof; 31 March 1943) was a Russian historian and liberal politician. Milyukov was the founder, leader, and the most prominent member of the Co ...
, who regarded the Russian Constitution of 1906 as a mock-constitution, and approximately 200 deputies mostly from the liberal Kadets party decamped to Vyborg, then part of Russian Finland
The Grand Duchy of Finland ( fi, Suomen suuriruhtinaskunta; sv, Storfurstendömet Finland; russian: Великое княжество Финляндское, , all of which literally translate as Grand Principality of Finland) was the predecessor ...
, to discuss the way forward. From there, they issued the Vyborg Appeal, which called for civil disobedience and a revolution. Largely ignored, it ended in their arrest and the closure of Kadet Party offices. This, among other things, helped pave the way for an alternative makeup for the second Duma.
Second Duma
 The Second Duma (from 20 February 1907 to 3 June 1907) lasted 103 days. One of the new members was Vladimir Purishkevich, strongly opposed to the October Manifesto. The
The Second Duma (from 20 February 1907 to 3 June 1907) lasted 103 days. One of the new members was Vladimir Purishkevich, strongly opposed to the October Manifesto. The Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s and Menshevik
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries.
The factions em ...
s (that is, both factions of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP; in , ''Rossiyskaya sotsial-demokraticheskaya rabochaya partiya (RSDRP)''), also known as the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party or the Russian Social Democratic Party, was a socialist pol ...
) and the Socialist Revolutionaries all abandoned their policies of boycotting elections to the Duma, and consequently won a number of seats. The election was an overall success for Russian left-wing parties: the Trudoviks won 104 seats, the Social Democrats 65 (47 Mensheviks and 18 Bolsheviks), the Socialist Revolutionaries 37 and the Popular Socialists 16.
The Kadets (by this point the most moderate and centrist party), found themselves outnumbered two-to-one by their more radical counterparts. Even so, Stolypin and the Duma could not build a working relationship, being divided on the issues of land confiscation (which the socialists and, to a lesser extent, the Kadets, supported but the Tsar and Stolypin vehemently opposed) and Stolypin's brutal attitude towards law and order.
On 1 June 1907, prime minister Pyotr Stolypin accused Social Democrats of preparing an armed uprising and demanded that the Duma exclude 55 Social Democrats from Duma sessions and strip 16 of their parliamentary immunity
Parliamentary immunity, also known as legislative immunity, is a system in which politicians such as president, vice president, governor, lieutenant governor, member of parliament, member of legislative assembly, member of legislative council, s ...
. When this ultimatum was rejected by Duma, it was dissolved on 3 June by an ukase
In Imperial Russia, a ukase () or ukaz (russian: указ ) was a proclamation of the tsar, government, or a religious leader ( patriarch) that had the force of law. "Edict" and " decree" are adequate translations using the terminology and concep ...
(imperial decree) in what became known as the Coup of June 1907.
The Tsar was unwilling to be rid of the State Duma, despite these problems. Instead, using emergency powers, Stolypin and the Tsar changed the electoral law and gave greater electoral value to the votes of landowners and owners of city properties, and less value to the votes of the peasantry, whom he accused of being "misled", and, in the process, breaking his own Fundamental Laws.
Third Duma
This ensured the third Duma (7 November 1907 – 3 June 1912) would be dominated by gentry, landowners and businessmen. The number of deputies from non-Russian regions was greatly reduced. The system facilitated better, if hardly ideal, cooperation between the Government and the Duma; consequently, the Duma lasted a full five-year term, and succeeded in 200 pieces of legislation and voting on some 2500 bills. Due to its more noble, andGreat Russian
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living Eas ...
composition, the third Duma, like the first, was also given a nickname, "The Duma of the Lords and Lackeys" or "The Master's Duma". The Octobrist party were the largest, with around one-third of all the deputies. This Duma, less radical and more conservative, left clear that the new electoral system would always generate a landowners-controlled Duma in which the tsar would have vast amounts of influence over, which in turn would be under complete submission to the Tsar, unlike the first two Dumas.
In terms of legislation, the Duma supported an improvement in Russia's military capabilities, Stolypin's plans for land reform and basic social welfare measures. The power of Nicholas' hated land captains was consistently reduced. It also supported more regressive laws, however, such as on the question of Finnish autonomy and Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cult ...
, with a fear of the Empire breaking up being prevalent. Since the dissolution of the Second Duma a very large proportion of the Empire was either under martial law, or one of the milder forms of the state of siege. It was forbidden, for instance, at various times and in various places, to refer to the dissolution of the Second Duma, to the funeral of the Speaker of the First Duma, Muromtsev, and the funeral of Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich TolstoyTolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; russian: link=no, Лев Николаевич Толстой,In Tolstoy's day, his name was written as in pre-refor ...
, to the fanatical ight-wingmonk Iliodor, or to the notorious ''agent provocateur'', Yevno Azef. Stolypin was assassinated in September 1911 and replaced by his Finance Minister Vladimir Kokovtsov. It enabled Count Kokovtsov to balance the budget regularly and even to spend on productive purposes.
Fourth Duma

 The Fourth Duma of 15 November 1912 – 6 October 1917, elected in September/October, was also of limited political influence. The first session was held from 15 November 1912 to 25 June 1913, and the second session from 15 October 1913 to 14 June 1914. On 1 July 1914 the Tsar suggested that the Duma should be reduced to merely a consultative body, but an extraordinary session was held on 26 July 1914 during the
The Fourth Duma of 15 November 1912 – 6 October 1917, elected in September/October, was also of limited political influence. The first session was held from 15 November 1912 to 25 June 1913, and the second session from 15 October 1913 to 14 June 1914. On 1 July 1914 the Tsar suggested that the Duma should be reduced to merely a consultative body, but an extraordinary session was held on 26 July 1914 during the July Crisis
The July Crisis was a series of interrelated diplomatic and military escalations among the major powers of Europe in the summer of 1914, which led to the outbreak of World War I (1914–1918). The crisis began on 28 June 1914, when Gavrilo Pri ...
. The third session gathered from 27 to 29 January 1915, the fourth from 19 July 1915 to 3 September, the fifth from 9 February to 20 June 1916, and the sixth from 1 November to 16 December 1916. No one exactly knew when they would resume their deliberations. It seems the last session was never opened (on 14 February), but kept closed on 27 February 1917.
There was one promising new member in Alexander Kerensky
Alexander Fyodorovich Kerensky, ; original spelling: ( – 11 June 1970) was a Russian lawyer and revolutionary who led the Russian Provisional Government and the short-lived Russian Republic for three months from late July to early Novem ...
, a Trudovik, but also Roman Malinovsky, a Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
who was a double agent for the secret police. In March 1913 the Octobrists, led by Alexander Guchkov
Alexander Ivanovich Guchkov (russian: Алекса́ндр Ива́нович Гучко́в) (14 October 1862 – 14 February 1936) was a Russian politician, Chairman of the Third Duma and Minister of War in the Russian Provisional Government.
...
, President of the Duma, commissioned an investigation on Grigori Rasputin to research the allegations being a Khlyst
The Khlysts or Khlysty ( rus, Хлысты, p=xlɨˈstɨ, "whips") were an underground Spiritual Christian sect, which split from the Russian Orthodox Church and existed from the 1600s until the late 20th century.
The New Israel sect that de ...
. The leading party of the Octobrists divided itself into three different sections.
The Duma "met on 8 August for three hours to pass emergency war credits, ndit was not asked to remain in session because it would only be in the way." The Duma volunteered its own dissolution until 14 February 1915. A serious conflict arose in January as the government kept information on the battlefield (in April at Gorlice) secret to the Duma. In May Guchkov initiated the War Industries Committees in order to unite industrialists who were supplying the army with ammunition and military equipment, to mobilize industry for war needs and prolonged military action, to put political pressure on the tsarist government. On 17 July 1915 the Duma reconvened for six weeks. Its former members became increasingly displeased with Tsarist control of military and governmental affairs and demanded its own reinstatement. When the Tsar refused its call for the replacement of his cabinet on 21 August with a "Ministry of National Confidence", roughly half of the deputies formed a "Progressive Bloc", which in 1917 became a focal point of political resistance. On 3 September 1915 the Duma prorogued.
On the eve of the war the government and the Duma were hovering round one another like indecisive wrestlers, neither side able to make a definite move. The war made the political parties more cooperative and practically formed into one party. When the Tsar announced he would leave for the front at Mogilev, the Progressive Bloc
The Progressive Bloc () is an electoral alliance in the Dominican Republic. The alliance is led by the Dominican Liberation Party
The Dominican Liberation Party ( Spanish: Partido de la Liberación Dominicana, referred to here by its Span ...
was formed, fearing Rasputin's influence over Tsarina Alexandra would increase.
The Duma gathered on 9 February 1916 after the 76-year-old Ivan Goremykin had been replaced by Boris Stürmer as prime minister and on the condition not to mention Rasputin. The deputies were disappointed when Stürmer held his speech. Because of the war, he said, it was not the time for constitutional reforms. For the first time in his life, the Tsar made a visit to the Taurida Palace
Tauride Palace (russian: Таврический дворец, translit=Tavrichesky dvorets) is one of the largest and most historically important palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
Construction and early use
Prince Grigory Potemkin of Tauride ...
, which made it practically impossible to hiss at the new prime minister.
On 1 November 1916 ( Old Style) the Duma reconvened and the government under Boris Stürmer was attacked by Pavel Milyukov
Pavel Nikolayevich Milyukov ( rus, Па́вел Никола́евич Милюко́в, p=mʲɪlʲʊˈkof; 31 March 1943) was a Russian historian and liberal politician. Milyukov was the founder, leader, and the most prominent member of the Co ...
in the State Duma, not gathering since February. In his speech he spoke of "Dark Forces", and highlighted numerous governmental failures with the famous question "Is this stupidity or treason?" Kerensky called the ministers "hired assassins" and "cowards" and said they were "guided by the contemptible Grishka Rasputin!" Stürmer and Protopopov asked in vain for the dissolution of the Duma. Stürmer's resignation looked like a concession to the Duma. Ivan Grigorovich and Dmitry Shuvayev declared in the Duma that they had confidence in the Russian people, the navy, and the army; the war could be won.
For the Octobrists and the Kadets, who were the liberals in the parliament, Rasputin, and his support of autocracy and absolute monarchy, was one of their main obstacles. The politicians tried to bring the government under control of the Duma. "To the Okhrana it was obvious by the end of 1916 that the liberal Duma project was superfluous, and that the only two options left were repression or a social revolution."
On 19 November Vladimir Purishkevich, one of the founders of the Black Hundreds
The Black Hundred (russian: Чёрная сотня, translit=Chornaya sotnya), also known as the black-hundredists (russian: черносотенцы; chernosotentsy), was a reactionary, monarchist and ultra-nationalist movement in Russia in t ...
, gave a speech in the Duma. He declared the monarchy had become discredited because of what he called the "ministerial leapfrog".
On 2 December, Trepov ascended the tribune in the Duma to read the government programme. The deputies shouted "down with the Ministers! Down with Protopopov!" The Prime-Minister was not allowed to speak and had to leave the rostrum three times. Trepov threatened to shut the troublesome Duma completely in her attempt to control the Tsar. The Tsar, his cabinet, Alexandra, and Rasputin discussed when to open the Duma, on 12 or 19 January, 1 or 14 February, or never. Rasputin suggested to keep the Duma closed until February; Alexandra and Protopopov supported him. On Friday, 16 December Milyukov stated in the Duma: "maybe e will bedismissed to 9 January, maybe until February", but in the evening the Duma was closed until 12 January, by a decree prepared on the day before. A military guard had been on duty at the building.
The February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and some ...
began on 22 February when the Tsar had left for the front, and strikes broke out in the Putilov workshops. On 23 February (International Women's Day
International Women's Day (IWD) is a global holiday celebrated annually on March 8 as a focal point in the women's rights movement, bringing attention to issues such as gender equality, reproductive rights, and violence and abuse against wo ...
), women in Saint Petersburg joined the strike, demanding woman suffrage, an end to Russian food shortages, and the end of World War I. Although all gathering on the streets were absolutely forbidden, on 25 February, some 250,000 people were on strike. The Tsar ordered Sergey Semyonovich Khabalov, an inexperienced and extremely indecisive commander of the Petrograd military district (and Nikolay Iudovich Ivanov) to suppress the rioting by force. On the 27th the Duma delegates received an order from his Majesty that he had decided to prorogue the Duma until April, leaving it with no legal authority to act. The Duma refused to obey, and gathered in a private meeting. According to Buchanan: "It was an act of madness to prorogue the Duma at a moment like the present." "The delegates decided to form a Provisional Committee of the State Duma. The Provisional Committee ordered the arrest of all the ex-ministers and senior officials." Orlando Figes (2006). '' A People's Tragedy: The Russian Revolution: 1891–1924'', p. 328–329. The Tauride Palace was occupied by the crowd and soldiers. "On the evening the Council of Ministers of Russia held its last meeting in the Marinsky Palace and formally submitted its resignation to the Tsar when they were cut off from the telephone. Soon a group of Duma members formed the Provisional Committee. Guchkov, along with Vasily Shulgin, came to the army headquarters near Pskov to persuade the Tsar to abdicate. The committee sent commissars to take over ministries and other government institutions, dismissing Tsar-appointed ministers and formed the Provisional Government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or ...
under Georgi Lvov.
On 2 March 1917 the Provisional government decided that the Duma would not be reconvened. Following the Kornilov Affair and the proclamation of the Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federal Republic. in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
, the State Duma was dissolved on 6 October 1917 by the Provisional government; a Provisional Council of the Russian Republic was convened on 20th October 1917 as a provisional parliament, in preparation to the election of the Russian Constituent Assembly
The All Russian Constituent Assembly (Всероссийское Учредительное собрание, Vserossiyskoye Uchreditelnoye sobraniye) was a constituent assembly convened in Russia after the October Revolution of 1917. It met fo ...
.
Seats held in Imperial Dumas

Chairmen of the State Duma
*Sergey Muromtsev
Sergey Andreevich Muromtsev (russian: Серге́й Андре́евич Му́ромцев) (October 5, Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O.S._23_September.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/> O.S._23_September">O ...
(1906)
* Fyodor Golovin (1907)
* Nikolay Khomyakov (1907–1910)
*Alexander Guchkov
Alexander Ivanovich Guchkov (russian: Алекса́ндр Ива́нович Гучко́в) (14 October 1862 – 14 February 1936) was a Russian politician, Chairman of the Third Duma and Minister of War in the Russian Provisional Government.
...
(1910–1911)
* Mikhail Rodzianko (1911–1917)
Deputy Chairmen of the State Duma
*The First Duma **PrincePavel Dolgorukov
Prince Pavel Dmitrievich Dolgorukov (russian: Князь Па́вел Дми́триевич Долгору́ков, tr. ; 1866, Tsarskoye Selo – June 9, 1927) was a Russian landowner and aristocrat who was executed by the Bolsheviks in 19 ...
( Cadet Party) 1906
**Nikolay Gredeskul
Nikolay Andreyevich Gredeskul (Russian: Николай Андреевич Гредескул; 20 April 1865 – 8 September 1941) was a Russian liberal politician.
Biography Origins
He was from an old noble family of Moldavian boyars, who emigrat ...
( Cadet Party) 1906
*The Second Duma
**N. N. Podznansky (Left) 1907
**M. E. Berezik (Trudoviki
The Trudoviks (russian: Трудова́я гру́ппа, translit=Trudovaya gruppa, lit=Labour Group) were a social-democratic political party of Russia in early 20th century.
History
The Trudoviks were a breakaway of the Socialist Revolut ...
) 1907
*The Third Duma
**Vol. V. M. Volkonsky (moderately right), bar. A. F. Meyendorff (Octobrist), C. J. Szydlowski (Octobrist), M. Kapustin (Octobrist), I. Sozonovich (right).
*The Fourth Duma
**Prince D. D. Urusov (Progressive Bloc)
***+ Prince V. M. Volkonsky (Centrum-Right) (1912–1913)
**Nikolay Nikolayevich Lvov (Progressive Bloc
The Progressive Bloc () is an electoral alliance in the Dominican Republic. The alliance is led by the Dominican Liberation Party
The Dominican Liberation Party ( Spanish: Partido de la Liberación Dominicana, referred to here by its Span ...
) (1913)
** Aleksandr Konovalov (Progressive Bloc
The Progressive Bloc () is an electoral alliance in the Dominican Republic. The alliance is led by the Dominican Liberation Party
The Dominican Liberation Party ( Spanish: Partido de la Liberación Dominicana, referred to here by its Span ...
) (1913–1914)
**S. T. Varun-Sekret ( Octobrist Party) (1913–1916)
** Alexander Protopopov (Left Wing Octobrist Party) (1914–1916)
** Nikolai Vissarionovich Nekrasov ( Cadet Party) (1916–1917)
**Count V. A. Bobrinsky (Nationalist) (1916–1917)
Notes
References
External links
*Speech from the Throne by Nicholas II at Opening of the State Duma, photo essay with commentary
{{Authority control 1905 establishments in the Russian Empire 1917 disestablishments in Russia
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
Government of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...