Staphylococcus aureus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 ''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped
 ''S. aureus'' (, Greek σταφυλόκοκκος, "grape-cluster berry",
''S. aureus'' (, Greek σταφυλόκοκκος, "grape-cluster berry",
 While ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal bacterium, asymptomatically colonizing about 30% of the human population, it can sometimes cause disease. In particular, ''S. aureus'' is one of the most common causes of bacteremia and
While ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal bacterium, asymptomatically colonizing about 30% of the human population, it can sometimes cause disease. In particular, ''S. aureus'' is one of the most common causes of bacteremia and
 ;Staphylococcal pigments
Some strains of ''S. aureus'' are capable of producing
;Staphylococcal pigments
Some strains of ''S. aureus'' are capable of producing
 Depending upon the type of infection present, an appropriate specimen is obtained accordingly and sent to the laboratory for definitive identification by using biochemical or enzyme-based tests. A Gram stain is first performed to guide the way, which should show typical Gram-positive bacteria, cocci, in clusters. Second, the isolate is cultured on
Depending upon the type of infection present, an appropriate specimen is obtained accordingly and sent to the laboratory for definitive identification by using biochemical or enzyme-based tests. A Gram stain is first performed to guide the way, which should show typical Gram-positive bacteria, cocci, in clusters. Second, the isolate is cultured on
 Resistance to methicillin is mediated via the ''mec'' operon, part of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCC''mec''). SCCmec is a family of mobile genetic elements, which is a major driving force of ''S. aureus'' evolution. Resistance is conferred by the ''mecA'' gene, which codes for an altered
Resistance to methicillin is mediated via the ''mec'' operon, part of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCC''mec''). SCCmec is a family of mobile genetic elements, which is a major driving force of ''S. aureus'' evolution. Resistance is conferred by the ''mecA'' gene, which codes for an altered
guidelines
for the appropriate use of vancomycin. In situations where the incidence of MRSA infections is known to be high, the attending physician may choose to use a glycopeptide antibiotic until the identity of the infecting organism is known. After the infection is confirmed to be due to a methicillin-susceptible strain of ''S. aureus'', treatment can be changed to flucloxacillin or even penicillin, as appropriate. Vancomycin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (VRSA) is a strain of ''S. aureus'' that has become resistant to the glycopeptides. The first case of vancomycin-intermediate ''S. aureus'' (VISA) was reported in Japan in 1996; but the first case of ''S. aureus'' truly resistant to glycopeptide antibiotics was only reported in 2002. Three cases of VRSA infection had been reported in the United States as of 2005. At least in part the antimicrobial resistance in ''S. aureus'' can be explained by its ability to adapt. Multiple two component signal transduction pathways helps ''S. aureus'' to express genes that are required to survive under antimicrobial stress.
StopMRSANow.org
— Discusses how to prevent the spread of MRSA
TheMRSA.com
— Understand what the MRSA infection is all about. * *
Type strain of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' at Bac''Dive'' – the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase
{{DEFAULTSORT:Staphylococcus Aureus aureus Bacteriology Gram-positive bacteria Bacterial diseases Pathogenic bacteria Healthcare-associated infections Bacteria described in 1884

 ''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
. It is often positive for catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting t ...
and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe
A facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent.
Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are '' Staphylococ ...
that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
es, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disea ...
. Pathogenic strains often promote infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s by producing virulence factors such as potent protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA), is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practice ...
. Despite much research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existi ...
, no vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
for ''S. aureus'' has been approved.
An estimated 20% to 30% of the human population are long-term carriers of ''S. aureus'', which can be found as part of the normal skin flora, in the nostrils, and as a normal inhabitant of the lower reproductive tract of women. ''S. aureus'' can cause a range of illnesses, from minor skin infections, such as pimple
A pimple is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papules. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, antibioti ...
s, impetigo, boil
A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, which is an infection of the hair follicle. It is most commonly caused by infection by the bacterium '' Staphylococcus aureus'', resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by ...
s, cellulitis, folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.
A ...
, carbuncles, scalded skin syndrome, and abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
es, to life-threatening diseases such as pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
, meningitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
, toxic shock syndrome, bacteremia, and sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
. It is still one of the five most common causes of hospital-acquired infections and is often the cause of wound infections following surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
. Each year, around 500,000 hospital patients in the United States contract a staphylococcal infection, chiefly by ''S. aureus''. Up to 50,000 deaths each year in the U.S. are linked to ''S. aureus'' infections.
History
Discovery
In 1880, Alexander Ogston, a Scottish surgeon, discovered that ''Staphylococcus'' can cause wound infections after noticing groups of bacteria in pus from a surgical abscess during a procedure he was performing. He named it ''Staphylococcus'' after its clustered appearance evident under a microscope. Then, in 1884, German scientist Friedrich Julius Rosenbach identified ''Staphylococcus aureus'', discriminating and separating it from '' Staphylococcus albus'', a related bacterium. In the early 1930s, doctors began to use a more streamlined test to detect the presence of an ''S. aureus'' infection by the means of coagulase testing, which enables detection of an enzyme produced by the bacterium. Prior to the 1940s, ''S. aureus'' infections were fatal in the majority of patients. However, doctors discovered that the use of penicillin could cure ''S. aureus'' infections. Unfortunately, by the end of the 1940s, penicillin resistance became widespread amongst this bacterium population and outbreaks of the resistant strain began to occur.Evolution
''Staphylococcus aureus'' can be sorted into ten dominant human lineages. There are numerous minor lineages as well, but these are not seen in the population as often. Genomes of bacteria within the same lineage are mostly conserved, with the exception of mobile genetic elements. Mobile genetic elements that are common in ''S. aureus'' include bacteriophages,pathogenicity island Pathogenicity islands (PAIs), as termed in 1990, are a distinct class of genomic islands acquired by microorganisms through horizontal gene transfer. Pathogenicity islands are found in both animal and plant pathogens. Additionally, PAIs are found i ...
s, plasmids, transposons, and staphylococcal cassette chromosomes. These elements have enabled ''S. aureus'' to continually evolve and gain new traits. There is a great deal of genetic variation within the ''S. aureus'' species''.'' A study by Fitzgerald et al. (2001) revealed that approximately 22% of the ''S. aureus'' genome is non-coding and thus can differ from bacterium to bacterium. An example of this difference is seen in the species' virulence. Only a few strains of ''S. aureus'' are associated with infections in humans. This demonstrates that there is a large range of infectious ability within the species.
It has been proposed that one possible reason for the great deal of heterogeneity within the species could be due to its reliance on heterogeneous infections. This occurs when multiple different types of ''S. aureus'' cause an infection within a host. The different strains can secrete different enzymes or bring different antibiotic resistances to the group, increasing its pathogenic ability. Thus, there is a need for a large number of mutations and acquisitions of mobile genetic elements.
Another notable evolutionary process within the ''S. aureus'' species is its co-evolution with its human hosts. Over time, this parasitic relationship has led to the bacterium's ability to be carried in the nasopharynx of humans without causing symptoms or infection. This allows it to be passed throughout the human population, increasing its fitness as a species. However, only approximately 50% of the human population are carriers of ''S. aureus'', with 20% as continuous carriers and 30% as intermittent. This leads scientists to believe that there are many factors that determine whether ''S. aureus'' is carried asymptomatically in humans, including factors that are specific to an individual person. According to a 1995 study by Hofman et al., these factors may include age, sex, diabetes, and smoking. They also determined some genetic variations in humans that lead to an increased ability for ''S. aureus'' to colonize, notably a polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene that results in larger corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
production. In conclusion, there is evidence that any strain of this bacterium can become invasive, as this is highly dependent upon human factors.
Though ''S. aureus'' has quick reproductive and micro-evolutionary rates, there are multiple barriers that prevent evolution with the species. One such barrier is AGR, which is a global accessory gene regulator
Accessory gene regulator (agr) is a complex 5 gene locus that is a global regulator of virulence in ''Staphylococcus aureus''. It encodes a two-component transcriptional quorum-sensing (QS) system activated by an autoinducing, thiolactone-containi ...
within the bacteria. This such regulator has been linked to the virulence level of the bacteria. Loss of function mutations within this gene have been found to increase the fitness of the bacterium containing it. Thus, ''S. aureus'' must make a trade-off to increase their success as a species, exchanging reduced virulence for increased drug resistance. Another barrier to evolution is the Sau1 Type I restriction modification (RM) system. This system exists to protect the bacterium from foreign DNA by digesting it. Exchange of DNA between the same lineage is not blocked, since they have the same enzymes and the RM system does not recognize the new DNA as foreign, but transfer between different lineages is blocked.
Microbiology
 ''S. aureus'' (, Greek σταφυλόκοκκος, "grape-cluster berry",
''S. aureus'' (, Greek σταφυλόκοκκος, "grape-cluster berry", Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
''aureus'', "golden") is a facultative aerobic, Gram-positive coccal (round) bacterium also known as "golden staph" and "oro staphira". ''S. aureus'' is nonmotile and does not form spores. In medical literature, the bacterium is often referred to as ''S. aureus'', ''Staph aureus'' or ''Staph a.''. ''S. aureus'' appears as staphylococci (grape-like clusters) when viewed through a microscope, and has large, round, golden-yellow colonies, often with hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing ( lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents ( cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in viv ...
, when grown on blood agar plates. ''S. aureus'' reproduces asexually by binary fission. Complete separation of the daughter cells is mediated by ''S. aureus'' autolysin, and in its absence or targeted inhibition, the daughter cells remain attached to one another and appear as clusters.
''S. aureus'' is catalase-positive (meaning it can produce the enzyme catalase). Catalase converts hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
() to water and oxygen. Catalase-activity tests are sometimes used to distinguish staphylococci from enterococci and streptococci
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occu ...
. Previously, ''S. aureus'' was differentiated from other staphylococci by the coagulase test. However, not all ''S. aureus'' strains are coagulase-positive and incorrect species identification can impact effective treatment and control measures.
Natural genetic transformation is a reproductive process involving DNA transfer from one bacterium to another through the intervening medium, and the integration of the donor sequence into the recipient genome by homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may ...
. ''S. aureus'' was found to be capable of natural genetic transformation, but only at low frequency under the experimental conditions employed. Further studies suggested that the development of competence for natural genetic transformation may be substantially higher under appropriate conditions, yet to be discovered.
Role in health
In humans, ''S. aureus'' can be present in the upper respiratory tract, gut mucosa, and skin as a member of the normal microbiota. However, because ''S. aureus'' can cause disease under certain host and environmental conditions, it is characterized as a "pathobiont".Role in disease
 While ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal bacterium, asymptomatically colonizing about 30% of the human population, it can sometimes cause disease. In particular, ''S. aureus'' is one of the most common causes of bacteremia and
While ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal bacterium, asymptomatically colonizing about 30% of the human population, it can sometimes cause disease. In particular, ''S. aureus'' is one of the most common causes of bacteremia and infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complicatio ...
. Additionally, it can cause various skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and soft-tissue infections, particularly when skin or mucosal barriers have been breached.
''S. aureus'' infections can spread through contact with pus from an infected wound, skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, and contact with objects used by an infected person such as towels, sheets, clothing, or athletic equipment. Joint replacements put a person at particular risk of septic arthritis, staphylococcal endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
(infection of the heart valves), and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
.
Preventive measures include washing hands often with soap and making sure to bathe or shower daily.
''S. aureus'' is a significant cause of chronic biofilm infections on medical implants
An implant is a medical device manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. Medical implants are man-made devices, in contrast to a transplant, whi ...
, and the repressor
In molecular genetics, a repressor is a DNA- or RNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator or associated silencers. A DNA-binding repressor blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to t ...
of toxins is part of the infection pathway.
''S. aureus'' can lay dormant in the body for years undetected. Once symptoms begin to show, the host is contagious for another two weeks, and the overall illness lasts a few weeks. If untreated, though, the disease can be deadly. Deeply penetrating ''S. aureus'' infections can be severe.
Skin infections
Skin infections Skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs), also referred to as skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), or acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSIs), are infections of skin and associated soft tissues (such as loose connective ti ...
are the most common form of ''S. aureus'' infection. This can manifest in various ways, including small benign boil
A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, which is an infection of the hair follicle. It is most commonly caused by infection by the bacterium '' Staphylococcus aureus'', resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by ...
s, folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.
A ...
, impetigo, cellulitis, and more severe, invasive soft-tissue infections.
''S. aureus'' is extremely prevalent in persons with atopic dermatitis, more commonly known as eczema. It is mostly found in fertile, active places, including the armpits, hair, and scalp. Large pimples that appear in those areas may exacerbate the infection if lacerated. This can lead to staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, a severe form of which can be seen in newborns.
The presence of ''S. aureus'' in persons with atopic dermatitis is not an indication to treat with oral antibiotics, as evidence has not shown this to give benefit to the patient. However, topical antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s combined with corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s have been found to improve the condition. Colonization of ''S. aureus'' drives inflammation of atopic dermatitis; ''S. aureus'' is believed to exploit defects in the skin barrier of persons with atopic dermatitis, triggering cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
expression and therefore exacerbating symptoms.
Food poisoning
''S. aureus'' is also responsible forfood poisoning
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disea ...
and achieves this by generating toxins in the human body. Its incubation period lasts one to six hours, with the illness itself lasting from 30 minutes to 3 days.
Preventive measures one can take to help prevent the spread of the disease include washing hands thoroughly with soap and water before preparing food. Stay away from any food if ill, and wear gloves if any open wounds occur on hands or wrists while preparing food. If storing food for longer than 2 hours, keep the food below 40 or above 140 °F (4.4 or 60 °C).
Bone and joint infections
''S. aureus'' is the bacterium commonly responsible for all major bone and joint infections. This manifests in one of three forms: osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, and infection from a replacement joint surgery.Bacteremia
''S. aureus'' is a leading cause of bloodstream infections throughout much of the industrialized world. Infection is generally associated with breaks in the skin or mucosal membranes due to surgery, injury, or use of intravascular devices such as catheters, hemodialysis machines, or injected drugs. Once the bacteria have entered the bloodstream, they can infect various organs, causinginfective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complicatio ...
, septic arthritis, and osteomyelitis. This disease is particularly prevalent and severe in the very young and very old.
Without antibiotic treatment, ''S. aureus'' bacteremia has a case fatality rate around 80%. With antibiotic treatment, case fatality rates range from 15% to 50% depending on the age and health of the patient, as well as the antibiotic resistance of the ''S. aureus'' strain.
Medical implant infections
''S. aureus'' is often found inbiofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
s formed on medical devices implanted in the body or on human tissue. It is commonly found with another pathogen, '' Candida albicans'', forming multispecies biofilms. The latter is suspected to help ''S. aureus'' penetrate human tissue. A higher mortality is linked with multispecies biofilms.
''S. aureus'' biofilm is the predominant cause of orthopedic implant-related infections, but is also found on cardiac implants, vascular grafts, various catheters, and cosmetic surgical implants. After implantation, the surface of these devices becomes coated with host proteins, which provide a rich surface for bacterial attachment and biofilm formation. Once the device becomes infected, it must by completely removed, since ''S. aureus'' biofilm cannot be destroyed by antibiotic treatments.
Current therapy for ''S. aureus'' biofilm-mediated infections involves surgical removal of the infected device followed by antibiotic treatment. Conventional antibiotic treatment alone is not effective in eradicating such infections. An alternative to postsurgical antibiotic treatment is using antibiotic-loaded, dissolvable calcium sulfate beads, which are implanted with the medical device. These beads can release high doses of antibiotics at the desired site to prevent the initial infection.
Novel treatments for ''S. aureus'' biofilm involving nano silver particles, bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bac ...
s, and plant-derived antibiotic agents are being studied. These agents have shown inhibitory effects against ''S. aureus'' embedded in biofilms. A class of enzymes have been found to have biofilm matrix-degrading ability, thus may be used as biofilm dispersal agents in combination with antibiotics.
Animal infections
''S. aureus'' can survive on dogs, cats, and horses, and can cause bumblefoot in chickens. Some believe health-care workers' dogs should be considered a significant source of antibiotic-resistant ''S. aureus'', especially in times of outbreak. In a 2008 study by Boost, O’Donoghue, and James, it was found that just about 90% of ''S. aureus'' colonized within pet dogs presented as resistant to at least one antibiotic. The nasal region has been implicated as the most important site of transfer between dogs and humans. ''S. aureus'' is one of the causal agents of mastitis in dairy cows. Its largepolysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with w ...
capsule protects the organism from recognition by the cow's immune defenses.
Virulence factors
Enzymes
''S. aureus'' produces various enzymes such as coagulase (bound and free coagulases) which facilitates the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin to cause clots which is important in skin infections. Hyaluronidase (also known as spreading factor) breaks down hyaluronic acid and helps in spreading it. Deoxyribonuclease, which breaks down the DNA, protects ''S. aureus'' from neutrophil extracellular trap-mediated killing. ''S. aureus'' also produces lipase to digest lipids,staphylokinase
Staphylokinase (SAK; also known as staphylococcal fibrinolysin or Müller's factor) is a protein produced by ''Staphylococcus aureus''. It contains 136 amino acid residues and has a molecular mass of 15kDa. Synthesis of staphylokinase occurs in l ...
to dissolve fibrin and aid in spread, and beta-lactamase for drug resistance.
Toxins
Depending on the strain, ''S. aureus'' is capable of secreting severalexotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, sim ...
s, which can be categorized into three groups. Many of these toxins are associated with specific diseases.
;Superantigens
:Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s known as superantigen
Superantigens (SAgs) are a class of antigens that result in excessive activation of the immune system. Specifically it causes non-specific activation of T-cells resulting in polyclonal T cell activation and massive cytokine release. SAgs are ...
s can induce toxic shock syndrome (TSS). This group comprises 25 staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) which have been identified to date and named alphabetically (SEA - SEZ), including enterotoxin type B
In the field of molecular biology, enterotoxin type B, also known as Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), is an enterotoxin produced by the gram-positive bacteria '' Staphylococcus aureus''. It is a common cause of food poisoning, with severe ...
as well as the toxic shock syndrome toxin TSST-1 which causes TSS associated with tampon use. Toxic shock syndrome is characterized by fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, erythematous rash
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not asso ...
, low blood pressure, shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emerge ...
, multiple organ failure, and skin peeling
Desquamation occurs when the outermost layer of a tissue, such as the skin, is shed. The term is . Physiologic desquamation
Keratinocytes are the predominant cells of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Living keratinocytes reside in ...
. Lack of antibody to TSST-1 plays a part in the pathogenesis of TSS. Other strains of ''S. aureus'' can produce an enterotoxin
An enterotoxin is a protein exotoxin released by a microorganism that targets the intestines.
Enterotoxins are chromosomally encoded or plasmid encoded exotoxins that are produced and secreted from several bacterial organisms. They are heat ...
that is the causative agent of a type of gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydr ...
. This form of gastroenteritis is self-limiting, characterized by vomiting and diarrhea 1–6 hours after ingestion of the toxin, with recovery in 8 to 24 hours. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and major abdominal pain.
;Exfoliative toxins
: Exfoliative toxins are exotoxins implicated in the disease staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), which occurs most commonly in infants and young children. It also may occur as epidemics in hospital nurseries. The protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
activity of the exfoliative toxins causes peeling of the skin observed with SSSS.
;Other toxins
: Staphylococcal toxins that act on cell membranes include alpha toxin, beta toxin, delta toxin, and several bicomponent toxins. Strains of ''S. aureus'' can host phages, such as the prophage A prophage is a bacteriophage (often shortened to "phage") genome that is integrated into the circular bacterial chromosome or exists as an extrachromosomal plasmid within the bacterial cell. Integration of prophages into the bacterial host is th ...
Φ-PVL that produces Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL), to increase virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
In most, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its ability to ...
. The bicomponent toxin PVL is associated with severe necrotizing pneumonia in children. The genes encoding the components of PVL are encoded on a bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bac ...
found in community-associated MRSA strains.
Type VII Secretion system
A secretion system is a highly specialised multi-protein unit that is embedded in the cell envelope with the function of translocating effector proteins from inside of the cell to the extracellular space or into a target host cytosol. The exact structure and function of T7SS is yet to be fully elucidated. Currently, four proteins are known components of ''S. aureus'' Type VII Secretion System (T7SS); EssC is a large integral membraneATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, SV40 T-antigen, ATP hydrolase, complex V (mitochondrial electron transport), (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, HCO3−-ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase) are ...
- which most likely powers the secretion systems and has been hypothesised forming part of the translocation channel. The other proteins are EsaA, EssB, EssA, that are membrane proteins that function alongside EssC to mediate protein secretion. The exact mechanism of how substrates reach the cell surface is unknown, as is the interaction of the three membrane proteins with each other and EssC.
T7 depedent effector proteins
EsaD is DNA endonuclease
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonuclease ...
toxin secreted by ''S. aureus'', has been shown to inhibit growth of competitor ''S. aureus'' strain ''in vitro''. EsaD is cosecreted with chaperone EsaE, which stabilises EsaD structure and brings EsaD to EssC for secretion. Strains that produce EsaD also co-produce EsaG, a cytoplasmic anti-toxin that protects the producer strain from EsaD's toxicity.
TspA is another toxin that mediates intraspecies competition. It is a bacteriostatic toxin that has a membrane depolarising activity facilitated by its c-terminal domain. Tsai is a transmembrane protein that confers immunity to the producer strain of TspA, as well as the attacked strains. There is genetic variability of the c-terminal domain of TspA therefore, it seems like the strains may produce different TspA variants to increase competitiveness.
Toxins that play a role in intraspecies competition confers an advantage by promoting successful colonisation in polymicrobial communities such as the nasopharynx and lung by outcompeting lesser strains.
There are also T7 effector proteins that play role a in pathogenesis, for example mutational studies of ''S. aureus'' have suggested that EsxB and EsxC contribute to persistent infection in a murine abscess model.
EsxX is has been implicated in neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
lysis, therefore suggested as contributing to the evasion of host immune system. Deletion of ''essX'' in ''S. aureus'' resulted in significantly reduced resistance to neutrophils and reduced virulence in murine skin and blood infection models.
Altogether, T7SS and known secreted effector proteins are a strategy of pathogenesis by improving fitness against competitor ''S. aureus'' species as well as increased virulence via evading the innate immune system and optimising persistent infections.
Small RNA
The list ofsmall RNA
Small RNA (sRNA) are polymeric RNA molecules that are less than 200 nucleotides in length, and are usually non-coding. RNA silencing is often a function of these molecules, with the most common and well-studied example being RNA interference ( ...
s involved in the control of bacterial virulence in ''S. aureus'' is growing. This can be facilitated by factors such as increased biofilm formation in the presence of increased levels of such small RNAs. For example, RNAIII
RNAIII is a stable 514 nt regulatory RNA transcribed by the P3 promoter of the ''Staphylococcus aureus'' quorum-sensing '' agr'' system ). It is the major effector of the ''agr'' regulon, which controls the expression of many '' S. aureus'' gene ...
, SprD, SprC, RsaE, SprA1, SSR42, ArtR, SprX, and Teg49.
DNA repair
Hostneutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
s cause DNA double-strand breaks in ''S. aureus'' through the production of reactive oxygen species.Ha KP, Clarke RS, Kim GL, Brittan JL, Rowley JE, Mavridou DAI, Parker D, Clarke TB, Nobbs AH, Edwards AM. Staphylococcal DNA Repair Is Required for Infection. mBio. 2020 Nov 17;11(6):e02288-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02288-20. PMID: 33203752; PMCID: PMC7683395 For infection of a host to be successful, ''S. aureus'' must survive such damages caused by the hosts’ defenses. The two protein complex RexAB encoded by ''S. aureus'' is employed in the recombinational repair of DNA double-strand breaks.
Strategies for post-transcriptional regulation by 3'untranslated region
ManymRNAs
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the p ...
in ''S. aureus'' carry three prime untranslated region
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally ...
s (3'UTR) longer than 100 nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecu ...
s, which may potentially have a regulatory function.
Further investigation of i''caR'' mRNA (mRNA coding for the repressor of the main expolysaccharidic compound of the bacteria biofilm matrix) demonstrated that the 3'UTR binding to the 5' UTR can interfere with the translation initiation complex and generate a double stranded substrate for RNase III. The interaction is between the UCCCCUG motif in the 3'UTR and the Shine-Dalagarno region at the 5'UTR. Deletion of the motif resulted in IcaR repressor accumulation and inhibition of biofilm development. The biofilm formation is the main cause of ''Staphylococcus'' implant infections.
Biofilm
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
s are groups of microorganisms, such as bacteria, that attach to each other and grow on wet surfaces.Vidyasagar, A. (2016). What Are Biofilms? ''Live Science.'' The ''S. aureus'' biofilm is embedded in a glycocalyx slime layer and can consist of teichoic acids, host proteins, extracellular DNA (eDNA) and polysaccharide intercellular antigen (PIA). Not all ''S. aureus'' biofilms contain PIA. S. aureus biofilms are important in disease pathogenesis, as they can contribute to antibiotic resistance and immune system evasion. ''S. aureus'' biofilm has high resistance to antibiotic treatments and host immune response. One hypothesis for explaining this is that the biofilm matrix protects the embedded cells by acting as a barrier to prevent antibiotic penetration. However, the biofilm matrix is composed with many water channels, so this hypothesis is becoming increasingly less likely, but a biofilm matrix possibly contains antibiotic‐degrading enzymes such as β-lactamases, which can prevent antibiotic penetration. Another hypothesis is that the conditions in the biofilm matrix favor the formation of persister cells, which are highly antibiotic-resistant, dormant bacterial cells. ''S. aureus'' biofilms also have high resistance to host immune response. Though the exact mechanism of resistance is unknown, ''S. aureus'' biofilms have increased growth under the presence of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
s produced by the host immune response. Host antibodies are less effective for ''S. aureus'' biofilm due to the heterogeneous antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
distribution, where an antigen may be present in some areas of the biofilm, but completely absent from other areas.
Studies in biofilm development have shown to be related to changes in gene expression. There are specific genes that were found to be crucial in the different biofilm growth stages. Two of these genes include rocD and gudB, which encode for the enzyme's ornithine-oxo-acid transaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase, which are important for amino acid metabolism. Studies have shown biofilm development rely on amino acids glutamine and glutamate for proper metabolic functions.
Other immunoevasive strategies
;Protein A Protein A is anchored to staphylococcal peptidoglycan pentaglycine bridges (chains of five glycine residues) by the transpeptidase sortase A. Protein A, anIgG
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG an ...
-binding protein, binds to the Fc region of an antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of t ...
. In fact, studies involving mutation of genes coding for protein A resulted in a lowered virulence of ''S. aureus'' as measured by survival in blood, which has led to speculation that protein A-contributed virulence requires binding of antibody Fc regions.
Protein A in various recombinant forms has been used for decades to bind and purify a wide range of antibodies by immunoaffinity chromatography. Transpeptidases, such as the sortases responsible for anchoring factors like protein A to the staphylococcal peptidoglycan, are being studied in hopes of developing new antibiotics to target MRSA infections.
 ;Staphylococcal pigments
Some strains of ''S. aureus'' are capable of producing
;Staphylococcal pigments
Some strains of ''S. aureus'' are capable of producing staphyloxanthin
Staphyloxanthin is a carotenoid pigment that is produced by some strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus'', and is responsible for the characteristic golden color that gives ''S. aureus'' its species name. Staphyloxanthin also acts as a virulence facto ...
— a golden-coloured carotenoid pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compou ...
. This pigment acts as a virulence factor, primarily by being a bacterial antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubrica ...
which helps the microbe evade the reactive oxygen species which the host immune system uses to kill pathogens.
Mutant strains of ''S. aureus'' modified to lack staphyloxanthin are less likely to survive incubation with an oxidizing chemical, such as hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
, than pigmented strains. Mutant colonies are quickly killed when exposed to human neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
, while many of the pigmented colonies survive. In mice, the pigmented strains cause lingering abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
es when inoculated into wounds, whereas wounds infected with the unpigmented strains quickly heal.
These tests suggest the ''Staphylococcus'' strains use staphyloxanthin as a defence against the normal human immune system. Drugs designed to inhibit the production of staphyloxanthin may weaken the bacterium and renew its susceptibility to antibiotics. In fact, because of similarities in the pathways for biosynthesis of staphyloxanthin and human cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
, a drug developed in the context of cholesterol-lowering therapy was shown to block ''S. aureus'' pigmentation and disease progression in a mouse infection model.
Classical diagnosis
mannitol salt agar
Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology. It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others.
It contains a high concentration (about 7.5� ...
, which is a selective medium with 7.5% NaCl that allows ''S. aureus'' to grow, producing yellow-colored colonies as a result of mannitol fermentation and subsequent drop in the medium's pH.
Furthermore, for differentiation on the species level, catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting t ...
(positive for all ''Staphylococcus'' species), coagulase (fibrin
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin, together with pl ...
clot formation, positive for ''S. aureus''), DNAse (zone of clearance on DNase agar), lipase (a yellow color and rancid odor smell), and phosphatase (a pink color) tests are all done. For staphylococcal food poisoning, phage typing can be performed to determine whether the staphylococci recovered from the food were the source of infection.
Rapid diagnosis and typing
Recent activities and food that a patient has recently eaten will be inquired about by a physician, and a physical examination is conducted to review any symptoms. With more severe symptoms, blood tests and stool culture may be in order. Diagnostic microbiology laboratories and reference laboratories are key for identifying outbreaks and new strains of ''S. aureus''. Recent genetic advances have enabled reliable and rapid techniques for the identification and characterization of clinical isolates of ''S. aureus'' in real time. These tools support infection control strategies to limit bacterial spread and ensure the appropriate use of antibiotics. Quantitative PCR is increasingly being used to identify outbreaks of infection. When observing the evolvement of ''S. aureus'' and its ability to adapt to each modified antibiotic, two basic methods known as "band-based" or "sequence-based" are employed. Keeping these two methods in mind, other methods such as multilocus sequence typing (MLST),pulsed-field gel electrophoresis
Pulsed field gel electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of large DNA molecules by applying to a gel matrix an electric field that periodically changes direction.
Historical background
Standard gel electrophoresis techniques for s ...
(PFGE), bacteriophage typing, spa locus typing, and SCCmec typing are often conducted more than others. With these methods, it can be determined where strains of MRSA originated and also where they are currently.
With MLST, this technique of typing uses fragments of several housekeeping genes known as ''aroE, glpF, gmk, pta, tip,'' and ''yqiL''. These sequences are then assigned a number which give to a string of several numbers that serve as the allelic profile. Although this is a common method, a limitation about this method is the maintenance of the microarray which detects newly allelic profiles, making it a costly and time-consuming experiment.
With PFGE, a method which is still very much used dating back to its first success in 1980s, remains capable of helping differentiate MRSA isolates. To accomplish this, the technique uses multiple gel electrophoresis, along with a voltage gradient to display clear resolutions of molecules. The ''S. aureus'' fragments then transition down the gel, producing specific band patterns that are later compared with other isolates in hopes of identifying related strains. Limitations of the method include practical difficulties with uniform band patterns and PFGE sensitivity as a whole.
Spa locus typing is also considered a popular technique that uses a single locus zone in a polymorphic region of ''S. aureus'' to distinguish any form of mutations. Although this technique is often inexpensive and less time-consuming, the chance of losing discriminatory power making it hard to differentiate between MLST clonal complexes exemplifies a crucial limitation.
Treatment
For susceptible strains, the treatment of choice for ''S. aureus'' infection ispenicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from '' Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum usin ...
. An antibiotic derived from some '' Penicillium'' fungal species, penicillin inhibits the formation of peptidoglycan cross-linkages that provide the rigidity and strength in a bacterial cell wall. The four-membered β-lactam ring of penicillin is bound to enzyme DD-transpeptidase
DD-transpeptidase (, ''DD-peptidase'', ''DD-transpeptidase'', ''DD-carboxypeptidase'', ''D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase'', ''D-alanyl-D-alanine-cleaving-peptidase'', ''D-alanine carboxypeptidase'', ''D-alanyl carboxypeptidase'', and ''serine-t ...
, an enzyme that when functional, cross-links chains of peptidoglycan that form bacterial cell walls. The binding of β-lactam to DD-transpeptidase inhibits the enzyme's functionality and it can no longer catalyze the formation of the cross-links. As a result, cell wall formation and degradation are imbalanced, thus resulting in cell death. In most countries, however, penicillin resistance is extremely common (>90%), and first-line therapy is most commonly a penicillinase-resistant β-lactam antibiotic (for example, oxacillin or flucloxacillin, both of which have the same mechanism of action as penicillin) or vancomycin, depending on local resistance patterns. Combination therapy with gentamicin may be used to treat serious infections, such as endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
, but its use is controversial because of the high risk of damage to the kidneys. The duration of treatment depends on the site of infection and on severity. Adjunctive rifampicin has been historically used in the management of ''S aureus'' bacteraemia, but randomised controlled trial evidence has shown this to be of no overall benefit over standard antibiotic therapy.
Antibiotic resistance in ''S. aureus'' was uncommon when penicillin was first introduced in 1943. Indeed, the original Petri dish on which Alexander Fleming of Imperial College London
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cu ...
observed the antibacterial activity of the '' Penicillium'' fungus was growing a culture of ''S. aureus''. By 1950, 40% of hospital ''S. aureus'' isolates were penicillin-resistant; by 1960, this had risen to 80%.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of '' Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in human ...
(MRSA, often pronounced or ), is one of a number of greatly feared strains of ''S. aureus'' which have become resistant to most β-lactam antibiotics. For this reason, vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infection ...
, a glycopeptide antibiotic, is commonly used to combat MRSA. Vancomycin inhibits the synthesis of peptidoglycan, but unlike β-lactam antibiotics, glycopeptide antibiotics target and bind to amino acids in the cell wall, preventing peptidoglycan cross-linkages from forming. MRSA strains are most often found associated with institutions such as hospitals, but are becoming increasingly prevalent in community-acquired infections.
Minor skin infections can be treated with triple antibiotic ointment. One topical agent that is prescribed is Mupirocin, a protein synthesis inhibitor that is produced naturally by Pseudomonas fluorescens and has seen success for treatment of S. aureus nasal carriage.
Antibiotic resistance
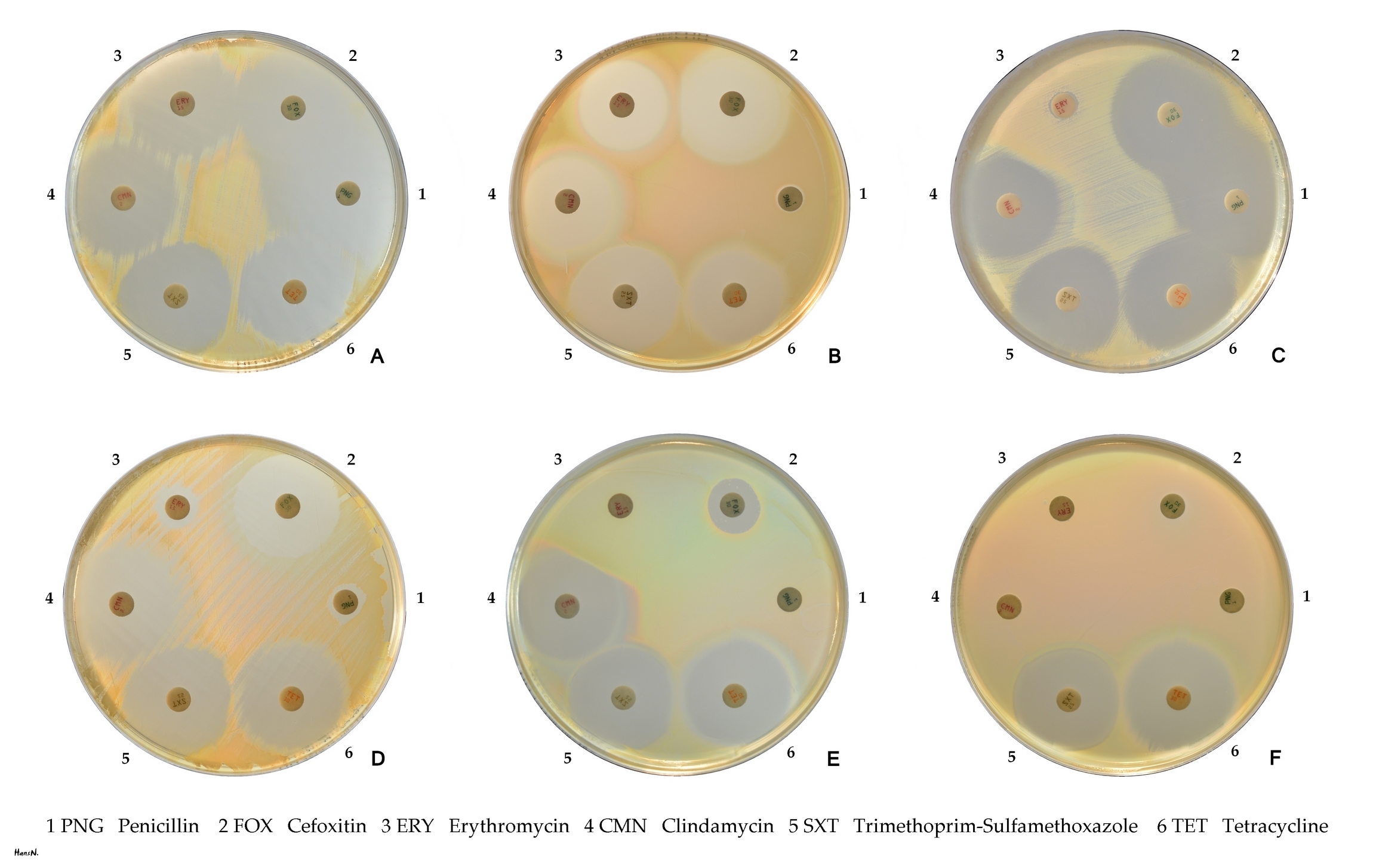
''S. aureus'' was found to be the second leading pathogen for deaths associated with Antimicrobial resistance in 2019. Staphylococcal resistance to penicillin is mediated by penicillinase (a form of beta-lactamase) production: an enzyme that cleaves the β-lactam ring of the penicillin molecule, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. Penicillinase-resistant β-lactam antibiotics, such as methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, cloxacillin, dicloxacillin, and flucloxacillin are able to resist degradation by staphylococcal penicillinase. Resistance to methicillin is mediated via the ''mec'' operon, part of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCC''mec''). SCCmec is a family of mobile genetic elements, which is a major driving force of ''S. aureus'' evolution. Resistance is conferred by the ''mecA'' gene, which codes for an altered
Resistance to methicillin is mediated via the ''mec'' operon, part of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCC''mec''). SCCmec is a family of mobile genetic elements, which is a major driving force of ''S. aureus'' evolution. Resistance is conferred by the ''mecA'' gene, which codes for an altered penicillin-binding protein
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) are a group of proteins that are characterized by their affinity for and binding of penicillin. They are a normal constituent of many bacteria; the name just reflects the way by which the protein was disc ...
(PBP2a or PBP2') that has a lower affinity for binding β-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for the treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. S ...
s). This allows for resistance to all β-lactam antibiotics, and obviates their clinical use during MRSA infections. Studies have explained that this mobile genetic element has been acquired by different lineages in separate gene transfer events, indicating that there is not a common ancestor of differing MRSA strains. Interestingly, one study suggests that MRSA sacrifices virulence, for example, toxin production and invasiveness, for survival and creation of biofilms
Aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as kanamycin, gentamicin, streptomycin, were once effective against staphylococcal infections until strains evolved mechanisms to inhibit the aminoglycosides' action, which occurs via protonated amine and/or hydroxyl interactions with the ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from riboso ...
of the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit. Three main mechanisms of aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms are currently and widely accepted: aminoglycoside modifying enzymes, ribosomal mutations, and active efflux of the drug out of the bacteria.
Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes inactivate the aminoglycoside by covalently attaching either a phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
, nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecu ...
, or acetyl moiety to either the amine or the alcohol key functional group (or both groups) of the antibiotic. This changes the charge or sterically hinders the antibiotic, decreasing its ribosomal binding affinity. In ''S. aureus'', the best-characterized aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme is aminoglycoside adenylyltransferase 4' IA (''ANT(4')IA''). This enzyme has been solved by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
. The enzyme is able to attach an adenyl moiety to the 4' hydroxyl group of many aminoglycosides, including kamamycin and gentamicin.
Glycopeptide resistance is mediated by acquisition of the ''vanA'' gene, which originates from the Tn1546 transposon found in a plasmid in enterococci and codes for an enzyme that produces an alternative peptidoglycan to which vancomycin will not bind.
Today, ''S. aureus'' has become resistant to many commonly used antibiotics. In the UK, only 2% of all ''S. aureus'' isolates are sensitive to penicillin, with a similar picture in the rest of the world. The β-lactamase-resistant penicillins (methicillin, oxacillin, cloxacillin, and flucloxacillin) were developed to treat penicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'', and are still used as first-line treatment. Methicillin was the first antibiotic in this class to be used (it was introduced in 1959), but, only two years later, the first case of methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) was reported in England.
Despite this, MRSA generally remained an uncommon finding, even in hospital settings, until the 1990s, when the MRSA prevalence in hospitals exploded, and it is now endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
. Now, methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is not only a human pathogen causing a variety of infections, such as skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), pneumonia, and sepsis, but it also can cause disease in animals, known as livestock-associated MRSA (LA-MRSA).
MRSA infections in both the hospital and community setting are commonly treated with non-β-lactam antibiotics, such as clindamycin (a lincosamine) and co-trimoxazole (also commonly known as trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole). Resistance to these antibiotics has also led to the use of new, broad-spectrum anti-Gram-positive antibiotics, such as linezolid
Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, v ...
, because of its availability as an oral drug. First-line treatment for serious invasive infections due to MRSA is currently glycopeptide antibiotics (vancomycin and teicoplanin). A number of problems with these antibiotics occur, such as the need for intravenous administration (no oral preparation is available), toxicity, and the need to monitor drug levels regularly by blood tests. Also, glycopeptide antibiotics do not penetrate very well into infected tissues (this is a particular concern with infections of the brain and meninges and in endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
). Glycopeptides must not be used to treat methicillin-sensitive ''S. aureus'' (MSSA), as outcomes are inferior.
Because of the high level of resistance to penicillins and because of the potential for MRSA to develop resistance to vancomycin, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has publisheguidelines
for the appropriate use of vancomycin. In situations where the incidence of MRSA infections is known to be high, the attending physician may choose to use a glycopeptide antibiotic until the identity of the infecting organism is known. After the infection is confirmed to be due to a methicillin-susceptible strain of ''S. aureus'', treatment can be changed to flucloxacillin or even penicillin, as appropriate. Vancomycin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (VRSA) is a strain of ''S. aureus'' that has become resistant to the glycopeptides. The first case of vancomycin-intermediate ''S. aureus'' (VISA) was reported in Japan in 1996; but the first case of ''S. aureus'' truly resistant to glycopeptide antibiotics was only reported in 2002. Three cases of VRSA infection had been reported in the United States as of 2005. At least in part the antimicrobial resistance in ''S. aureus'' can be explained by its ability to adapt. Multiple two component signal transduction pathways helps ''S. aureus'' to express genes that are required to survive under antimicrobial stress.
Efflux pumps
Among the various mechanisms that MRSA acquires to elude antibiotic resistance (e.g., drug inactivation, target alteration, reduction of permeability) there is also the overexpression of efflux pumps. Efflux pumps are membrane-integrated proteins that are physiologically needed in the cell for the exportation of xenobiotic compounds. They are divided into six families, each of which has a different structure, function, and transport of energy. The main efflux pumps of S. Aureus are the MFS (Major Facilitator Superfamily) which includes the MdeA pump as well as the NorA pump and the MATE (Multidrug and Toxin Extrusion) to which it belongs the MepA pump. For transport, these families use an electrochemical potential and an ion concentration gradient, while the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family acquires its energy from the hydrolysis of ATP. These pumps are overexpressed by MDR ''S. aureus'' (Multidrug resistant ''S. aureus)'' and the result is an excessive expulsion of the antibiotic outside the cell, which makes its action ineffective. Efflux pumps also contribute significantly to the development of impenetrable biofilms. By directly modulating efflux pumps' activity or decreasing their expression, it may be possible to modify the resistant phenotype and restore the effectiveness of existing antibiotics.Carriage
About 33% of the U.S. population are carriers of ''S. aureus'' and about 2% carry MRSA. Even healthcare providers can be MRSA colonizers. The carriage of ''S. aureus'' is an important source of hospital-acquired infection (also called nosocomial) and community-acquired MRSA. Although ''S. aureus'' can be present on the skin of the host, a large proportion of its carriage is through the anterior nares of the nasal passages and can further be present in the ears. The ability of the nasal passages to harbour ''S. aureus'' results from a combination of a weakened or defective host immunity and the bacterium's ability to evade host innate immunity. Nasal carriage is also implicated in the occurrence of staph infections.Infection control
Spread of ''S. aureus'' (including MRSA) generally is through human-to-human contact, although recently some veterinarians have discovered the infection can be spread through pets, with environmental contamination thought to play a relatively less important part. Emphasis on basic hand washing techniques are, therefore, effective in preventing its transmission. The use of disposable aprons and gloves by staff reduces skin-to-skin contact, so further reduces the risk of transmission. Recently, myriad cases of ''S. aureus'' have been reported in hospitals across America. Transmission of the pathogen is facilitated in medical settings where healthcare worker hygiene is insufficient. ''S. aureus'' is an incredibly hardy bacterium, as was shown in a study where it survived on polyester for just under three months; polyester is the main material used in hospital privacy curtains. The bacteria are transported on the hands of healthcare workers, who may pick them up from a seemingly healthy patient carrying a benign or commensal strain of ''S. aureus'', and then pass it on to the next patient being treated. Introduction of the bacteria into the bloodstream can lead to various complications, including endocarditis, meningitis, and, if it is widespread,sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
.
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
has proven to be an effective topical sanitizer against MRSA. Quaternary ammonium can be used in conjunction with ethanol to increase the duration of the sanitizing action. The prevention of nosocomial infections involves routine and terminal cleaning
Terminal cleaning is the thorough cleaning of a room after use, used in healthcare environments to control the spread of infections.
Justification
Nosocomial infections claim approximately 90,000 lives in the United States annually. When patie ...
. Nonflammable alcohol vapor in NAV-CO2 systems have an advantage, as they do not attack metals or plastics used in medical environments, and do not contribute to antibacterial resistance.
An important and previously unrecognized means of community-associated MRSA colonization and transmission is during sexual contact.
''S. aureus'' is killed in one minute at 78 °C and in ten minutes at 64 °C but is resistant to freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid ...
.
Certain strains of ''S. aureus'' have been described as being resistant to chlorine disinfection.
The use of mupirocin ointment can reduce the rate of infections due to nasal carriage of ''S. aureus.'' There is limited evidence that nasal decontamination of ''S. aureus'' using antibiotics or antiseptics can reduce the rates of surgical site infections.
Research
As of 2021, no approvedvaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
exists against ''S. aureus''. Early clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s have been conducted for several vaccines candidates such as Nabi's StaphVax and PentaStaph, Intercell's / Merck's V710, VRi's SA75, and others.
While some of these vaccines candidates have shown immune responses, others aggravated an infection by ''S. aureus''. To date, none of these candidates provides protection against a ''S. aureus'' infection. The development of Nabi's StaphVax was stopped in 2005 after phase III trials failed. Intercell's first V710 vaccine variant was terminated during phase II/III after higher mortality and morbidity were observed among patients who developed ''S. aureus'' infection.
Nabi's enhanced ''S. aureus'' vaccines candidate PentaStaph was sold in 2011 to GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals S.A. The current status of PentaStaph is unclear. A WHO document indicates that PentaStaph failed in the phase III trial stage.
In 2010, GlaxoSmithKline started a phase 1 blind study
In a blind or blinded experiment, information which may influence the participants of the experiment is withheld until after the experiment is complete. Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental biases that arise from a participants' expec ...
to evaluate its GSK2392103A vaccine. As of 2016, this vaccine is no longer under active development.
Pfizer's ''S. aureus'' four-antigen vaccine SA4Ag was granted fast track designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
in February 2014. In 2015, Pfizer has commenced a phase 2b trial regarding the SA4Ag vaccine. Phase 1 results published in February 2017 showed a very robust and secure immunogenicity of SA4Ag. The vaccine underwent clinical trial until June 2019, with results published in September 2020, that did not demonstrate a significant reduction in Postoperative Bloodstream Infection after Surgery.
In 2015, Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics, a former division of Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-lo ...
and now part of GlaxoSmithKline, published promising pre-clinical results of their four-component ''Staphylococcus aureus'' vaccine, 4C-staph.
Standard strains
A number of standard strains of ''S. aureus'' (called "type cultures") are used in research and in laboratory testing.References
Further reading
* *External links
StopMRSANow.org
— Discusses how to prevent the spread of MRSA
TheMRSA.com
— Understand what the MRSA infection is all about. * *
Type strain of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' at Bac''Dive'' – the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase
{{DEFAULTSORT:Staphylococcus Aureus aureus Bacteriology Gram-positive bacteria Bacterial diseases Pathogenic bacteria Healthcare-associated infections Bacteria described in 1884