Spread of the Latin script on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This article discusses the geographic spread of the Latin script throughout history, from its archaic beginnings in
This article discusses the geographic spread of the Latin script throughout history, from its archaic beginnings in
 The Latin script originated in archaic antiquity in the
The Latin script originated in archaic antiquity in the
 Along with the Latin language, the Latin writing system first spread over the Italian Peninsula with the rise of the
Along with the Latin language, the Latin writing system first spread over the Italian Peninsula with the rise of the
 The
The
 In Western Europe, the
In Western Europe, the
 From the 1830s to the 1880s,
From the 1830s to the 1880s,
 Croatian linguist Ljudevit Gaj devised a uniform Latin alphabet for Croatian in 1835, while in 1818, Serbian linguist
Croatian linguist Ljudevit Gaj devised a uniform Latin alphabet for Croatian in 1835, while in 1818, Serbian linguist
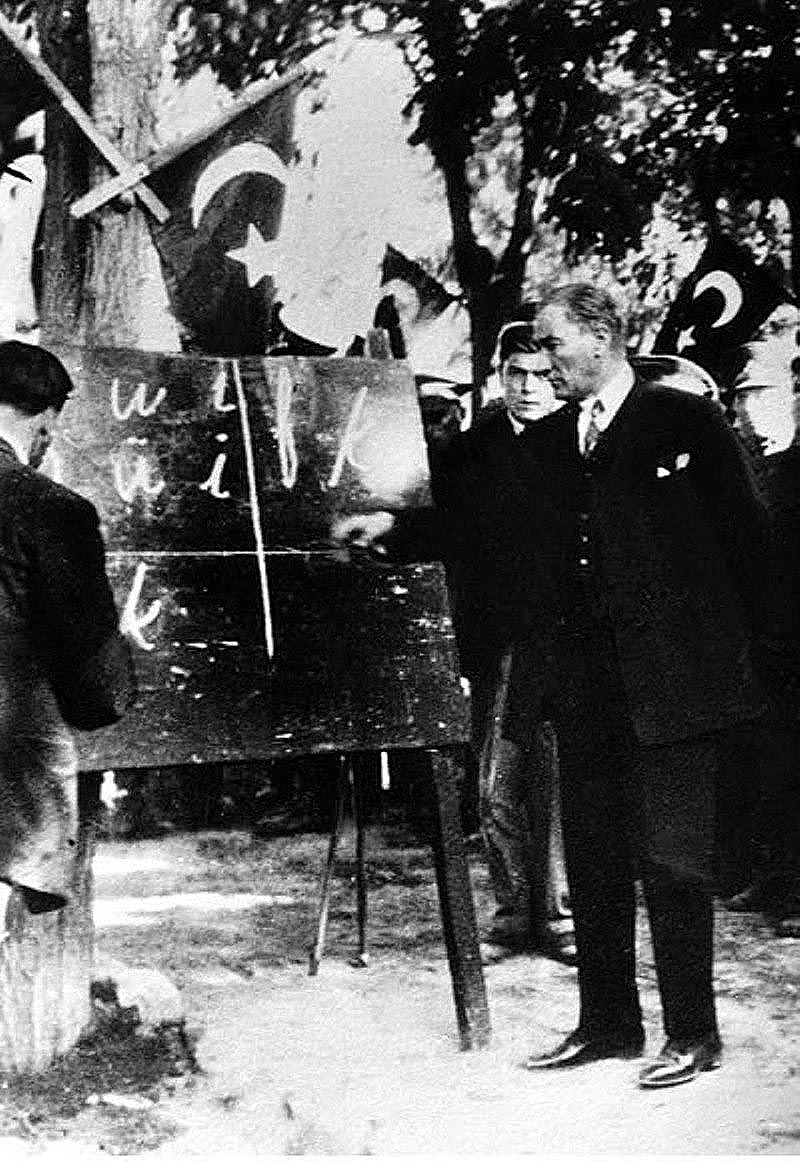 In 1928, as part of Mustafa Kemal Atat├╝rk's reforms, the new Republic of Turkey adopted the
In 1928, as part of Mustafa Kemal Atat├╝rk's reforms, the new Republic of Turkey adopted the

 Under the Constitution of Serbia of 2006, Cyrillic script is the only one in official use. Nonetheless the Latin script is widely used. In May 2017, Minister of Culture and Information Vladan Vukosavljevi─ć proposed several measures to better support the Cyrillic script, which was "in danger of falling into disuse". He said there wasn't any kind of conspiracy going on against the Cyrillic alphabet, but rather that the spirit of the times, historical circumstances and the decades-long process of globalisation had gradually made Latin the world's dominant script. "Especially young people in Serbia are now mostly turning to Latin characters because of the media, the Internet and the logos of world
Under the Constitution of Serbia of 2006, Cyrillic script is the only one in official use. Nonetheless the Latin script is widely used. In May 2017, Minister of Culture and Information Vladan Vukosavljevi─ć proposed several measures to better support the Cyrillic script, which was "in danger of falling into disuse". He said there wasn't any kind of conspiracy going on against the Cyrillic alphabet, but rather that the spirit of the times, historical circumstances and the decades-long process of globalisation had gradually made Latin the world's dominant script. "Especially young people in Serbia are now mostly turning to Latin characters because of the media, the Internet and the logos of world
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil ( Old Latium) on w ...
to the dominant writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable fo ...
on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
in modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular socio-cultural norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the Renaissancein the "Age of Reas ...
.
The Latin letters' ancestors are found in the Phoenician, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Etruscan alphabet
The Etruscan alphabet was the alphabet used by the Etruscans, an ancient civilization of central and northern Italy, to write their language, from about 700 BC to sometime around 100 AD.
The Etruscan alphabet derives from the Euboean alphabet u ...
s. As the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, ╬Æ╬▒Žā╬╣╬╗╬Ą╬»╬▒ Žäß┐Č╬Į ß┐¼Žē╬╝╬▒╬»Žē╬Į, Basile├Ła t├┤n Rh┼Źma├Ł┼Źn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
expanded in classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, the Latin script and language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
spread along with its conquests, and remained in use in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: P├®ninsule Ib├®rique
* mwl, Pen├Łnsula Eib├®rica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
and Western Europe after the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
's disappearance. During the early and high Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the script was spread by Christian missionaries and rulers, replacing earlier writing systems in Central and Northern Europe, and the remainder of the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
.
In the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
, the first wave of European colonisation saw the adoption of Latin alphabets primarily in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
and Australia, whereas sub-Sahara Africa, maritime Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
and the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
were Latinised in the period of New Imperialism
In historical contexts, New Imperialism characterizes a period of colonial expansion by European powers, the United States, and Japan during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Com
The period featured an unprecedented pursuit of ove ...
. Realising that Latin was now the most widely used script on Earth, the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: ąæąŠą╗čīčłąĄą▓ąĖą║ąĖ╠ü, from ą▒ąŠą╗čīčłąĖąĮčüčéą▓ąŠ╠ü ''bol'shinstv├│'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstv├│'' (ą▒ąŠą╗čīčłąĖąĮčüčéą▓ąŠ╠ü), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
made efforts to develop and establish Latin alphabets for all languages in the lands they controlled in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
, North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. However, after the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
's first three decades, these were gradually abandoned in the 1930s in favour of Cyrillic. Some post-Soviet Turkic-majority states decided to reintroduce the Latin script in the 1990s, following the 1928 example of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, T├╝rkiye ), officially the Republic of T├╝rkiye ( tr, T├╝rkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
. In the early 21st century, non-Latin writing systems were only still prevalent in most parts of the Middle East and North Africa
MENA, an acronym in the English language, refers to a grouping of countries situated in and around the Middle East and North Africa. It is also known as WANA, SWANA, or NAWA, which alternatively refers to the Middle East as Western Asia (or a ...
and former Soviet regions, South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ŌĆśGeoŌĆÖ (The Earth) and ŌĆśGraphienŌĆÖ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
, most countries in mainland Southeast Asia, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ßŖóßēĄßŗ«ßīĄßŗ½, ├Źtiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Eritrea and some Balkan countries in Europe.
Protohistory
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil ( Old Latium) on w ...
region in central Italy
Central Italy ( it, Italia centrale or just ) is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first-level NUTS region, and a European Parliament constituency.
Regions
Central I ...
. It is generally held that the Latins, one of many ancient Italic tribes, adopted the western variant of the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as w ...
in the 7th century BCE from Cumae
Cumae ( grc, ╬ÜŽŹ╬╝╬Ę, (Kum─ō) or or ; it, Cuma) was the first ancient Greek colony on the mainland of Italy, founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BC and soon becoming one of the strongest colonies. It later became a rich Ro ...
, a Greek colony
Greek colonization was an organised colonial expansion by the Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8thŌĆō6th centuries BC.
This colonization differed from the migrations of the Greek Dark Ages in that i ...
in southern Italy ŌĆō making the early Latin alphabet one among several Old Italic scripts
The Old Italic scripts are a family of similar ancient writing systems used in the Italian Peninsula between about 700 and 100 BC, for various languages spoken in that time and place. The most notable member is the Etruscan alphabet, which ...
emerging at the time. The early Latin script was heavily influenced by the then regionally dominant Etruscan civilization
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
;Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993ŌĆō2002) s.v. "Etrusken. ┬¦2. Taal en schrift". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. the Latins ultimately adopted 22 of the original 26 Etruscan letters, which derived from Western Greek as well. It is highly probable that the Latins received their alphabet via the Etruscans rather than directly from the Greek colonists.
Antiquity
Latinisation of Italy
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
from the 4th to the 1st century BCE. By the 4th century, the Latin alphabet had been standardised by the city of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and begun to dominate Latium. Other local alphabets in Latium fell into disuse, particularly after the Latin War
The (Second) Latin War (340ŌĆō338 BC)The Romans customarily dated events by noting the consuls who held office that year. The Latin War broke out in the year that Titus Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus and Publius Decius Mus were consuls and ended ...
(340ŌĆō338 BCE). There is evidence for a phase of bilingualism and digraphia
In sociolinguistics, digraphia refers to the use of more than one writing system for the same language. Synchronic digraphia is the coexistence of two or more writing systems for the same language, while diachronic digraphia (or sequential digra ...
in the late 4th and 3rd centuries in Etruria, Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
, Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
and most other Central Italian regions that were conquered by the Romans (primarily during the Samnite Wars
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343ŌĆō341 BC, 326ŌĆō304 BC, and 298ŌĆō290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe. ...
of 343ŌĆō290 BCE), or maintained frequent contact with the Romans and other Latins, who set up numerous ''coloniae
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Characteri ...
'' in annexed and allied territories. The participation of Italic peoples in the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500ŌĆō31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BCŌĆō395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
accelerated the Romanisation and Latinisation process.
Umbria seems to have switched from its own script in the 2nd century BCE to Latin in the 1st. After the subjugation of Southern Italy in the Pyrrhic War
The Pyrrhic War (280ŌĆō275 BC) was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans.
A sk ...
(280ŌĆō275 BCE), Messapic (using a Greek-derived alphabet) disappeared completely, and with the exception of the two Griko enclaves that still exist in the 21st century, Latin replaced all Greek in Magna Graecia. Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC ŌĆō AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
reports that the local government of Cumae
Cumae ( grc, ╬ÜŽŹ╬╝╬Ę, (Kum─ō) or or ; it, Cuma) was the first ancient Greek colony on the mainland of Italy, founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BC and soon becoming one of the strongest colonies. It later became a rich Ro ...
ŌĆō the Greek colony that may have originally spread its alphabet to the Latins via the Etruscans ŌĆō made an unsolicited request in the 2nd century BCE to henceforth use Latin in public affairs. After the First Punic War (264ŌĆō241 BCE), the Latin script gradually took over written communication on Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
from Paleo-Sardinian (also termed "Nuragic"), on Corsica from Paleo-Corsican, and on Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
from Greek and the local Sicula, Sicani
The Sicani (Ancient Greek ╬Żß┐É╬║ߊ▒╬Į╬┐╬» ''Sik─üno├Ł'') or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, ...
, and Elymian
The Elymians ( grc-gre, ß╝£╬╗Žģ╬╝╬┐╬╣, ''├ēlymoi''; Latin: ''Elymi'') were an ancient tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity.
Origins
According to Hellanicus of Lesbos, the Elymians ...
languages. The Roman conquest of Mediolanum
Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in northern Italy. The city was settled by the Insubres around 600 BC, conquered by the Romans in 222 BC, and ...
(Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
) in 222 BCE commenced the Latinisation of the Po Valley.
The Latinisation of Italy was resisted by various ethnic groups, however, most notably the Samnites, who regarded their Oscan language
Oscan is an extinct Indo-European language of southern Italy. The language is in the Osco-Umbrian or Sabellic branch of the Italic languages. Oscan is therefore a close relative of Umbrian.
Oscan was spoken by a number of tribes, including the ...
and script as part of their identity, and employed it in clear opposition to Rome, for example in coinage during the Social War (91ŌĆō87 BCE). The Veneti, though steadfast allies of the Romans for centuries, retained their own alphabet until the end of the Roman Republic (27 BCE). According to Lomas (2004), the crucial factor in Latinising these remaining groups that resisted full integration was granting them Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
(most notably by the '' Lex Iulia de Civitate Latinis et Sociis Danda'' in 90 BCE), thereby leading them to participate in RomanŌĆōLatin society and gradually abandon their Italic, Etruscan, Celtic etc. cultural independence.
Western Mediterranean and Gaul
 The
The Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula
The Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula was a process by which the Roman Republic seized territories in the Iberian Peninsula that were previously under the control of native Celtic, Iberian, Celtiberian and Aquitanian tribes and the Ca ...
(206ŌĆō19 BCE) drove all indigenous writing systems such as the Iberian scripts
The Iberian scripts are the Paleohispanic scripts that were used to represent the extinct Iberian language. Most of them are typologically unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic.Ferrer, J., Moncunill, N., V ...
extinct. Likewise, Caesar's
Caesar's is a restaurant on Avenida Revoluci├│n in Tijuana, Mexico, famous as the home of the Caesar salad. Restaurateur Caesar Cardini, an Italian immigrant, opened the restaurant in 1923,
and it is now under chef Javier Plascencia, leading ...
conquest of Gaul
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
(58ŌĆō50 BCE) sealed the fate of the Greek-derived alphabets used by various Gallic tribes. According to Miles (2013) 'there was a sudden and complete disappearance of Iberian and Gallo-Greek scripts by the mid first century AD.' The Iberian language was spoken until at least the 1st century CE; the Basque language is still spoken in the 21st century, but uses a 27-letter Latin alphabet for writing. The new Gallo-Roman elite used the Latin script to write texts in Celtic languages, and 'Gallo-Latin inscriptions flourished alongside Latin texts'. Gregory of Tours (6th century CE) claimed that Gaulish was still spoken in some countrysides.
After the defeat of Ancient Carthage
Carthage () was a settlement in modern Tunisia that later became a city-state and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians in the ninth century BC, Carthage reached its height in the fourth century BC as one of the largest metropolises in t ...
(Third Punic War
The Third Punic War (149ŌĆō146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in modern northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 ...
149ŌĆō146 BCE), the urban centres of North Africa were Latinised, while the rural areas remained Berber-speaking. Bilingual inscriptions emerged in the 1st century CE, and Punic
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' ŌĆō the Latin equivalent of t ...
inscriptions have been found on public buildings in Africa Proconsularis until the late 2nd century CE. Although the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb
The Muslim conquest of the Maghreb ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘Æ┘ü┘Äž¬┘ÆžŁ┘Å ž¦┘äžźž│┘ä┘Äž¦┘ģ┘É┘Ŗ┘Å┘æ ┘ä┘É┘ä┘Æ┘ģ┘Äž║ž▒┘Éž©) continued the century of rapid Muslim conquests following the death of Muhammad in 632 and into the Byzantine-controlled territories of ...
(7thŌĆō8th centuries CE) led to the eventual Arabisation
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, ž¬ž╣ž▒┘Ŗž©, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, aft ...
of North Africa, an account by geographer Muhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abdullah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani as-Sabti, or simply al-Idrisi ( ar, žŻž©┘ł ž╣ž©ž» ž¦┘ä┘ä┘ć ┘ģžŁ┘ģž» ž¦┘äžźž»ž▒┘Ŗž│┘Ŗ ž¦┘ä┘éž▒žĘž©┘Ŗ ž¦┘䞣ž│┘å┘Ŗ ž¦┘äž│ž©ž¬┘Ŗ; la, Dreses; 1100 ŌĆō 1165), was a Muslim geographer, cartogra ...
about 'the African Latin language' spoken by most inhabitants of the Tunisian city of Gafsa
Gafsa ( aeb, ┌©┘üžĄž® '; ar, ┘é┘üžĄž® qafß╣Żah), originally called Capsa in Latin, is the capital of Gafsa Governorate of Tunisia. It lends its Latin name to the Mesolithic Capsian culture. With a population of 111,170, Gafsa is the ninth-la ...
(Latin: ''Capsa'') may be evidence that the Latin script was still used there in the 12th century.
There were similar events during the early period of expansion of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, ╬Æ╬▒Žā╬╣╬╗╬Ą╬»╬▒ Žäß┐Č╬Į ß┐¼Žē╬╝╬▒╬»Žē╬Į, Basile├Ła t├┤n Rh┼Źma├Ł┼Źn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
(c. 27 BCE ŌĆō 117 CE) in regions such as Numidia, Rhaetia, Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, ...
, Belgica, and western Germania. On the other hand, the Roman conquest of Britain (42ŌĆō87 CE) never led to deep Latinisation of the local population; although most inscriptions found are in Latin, the tribes continued to speak Brittonic dialects.
Eastern Mediterranean and the Roman legacy
The eastern half of the Empire, includingGreece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, Macedonia, Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yar─▒madas─▒), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
, and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, ┘ģžĄž▒ , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, continued to use Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
as a lingua franca after the Macedonian Wars
The Macedonian Wars (214ŌĆō148 BC) were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Greece ...
(214ŌĆō148 BCE) due to the superiority of Ancient Greek culture; Latin was restricted to administrative and military purposes in the Eastern Mediterranean. Only in the western half was Latin widely spoken and written, and as the western Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
evolved out of Latin, they continued to use and adapt the Latin alphabet. There were two major exceptions to this "Greek East and Latin West
Greek East and Latin West are terms used to distinguish between the two parts of the Greco-Roman world and of Medieval Christendom, specifically the eastern regions where Greek was the ''lingua franca'' (Greece, Anatolia, the southern Balkans, the ...
" rule:
* Illyria, which was annexed as the province of Dalmatia, fully Latinised, and after Rome's fall evolved the Dalmatian language which lasted until 1898.
*After Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
subdued the lower Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
region in the Dacian Wars (101ŌĆō106), the Dacian and Thracian language
The Thracian language () is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it wa ...
s were abandoned in favour of Latin, out of which developed modern Romanian.
Despite the loss of the Latin-speaking Western provinces in the 5th and 6th centuries, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
maintained Latin as its legal language, under 6th-century emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, ß╝Ė╬┐ŽģŽāŽä╬╣╬Į╬╣╬▒╬ĮŽīŽé ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renova ...
producing the vast Corpus Juris Civilis
The ''Corpus Juris'' (or ''Iuris'') ''Civilis'' ("Body of Civil Law") is the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, issued from 529 to 534 by order of Justinian I, Byzantine Emperor. It is also sometimes referred ...
that would have a major impact on Western European legal history from c. 1100 to 1900. The use of Latin as the Byzantine language of administration persisted until the adoption of Middle Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5thŌĆō6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Fall of Co ...
as the sole official language by Heraclius in the 7th century. Scholarly Latin rapidly fell into disuse among the educated classes, although the language continued to be at least a ceremonial part of the Empire's culture for some time.;
Middle Ages
Migration Period
TheGermanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
that invaded and gradually settled the Western Roman Empire between the 5th and 8th centuries originally had little written culture to speak of; apart from some runic inscriptions
A runic inscription is an inscription made in one of the various runic alphabets. They generally contained practical information or memorials instead of magic or mythic stories. The body of runic inscriptions falls into the three categories of E ...
amongst most tribes, there was no written administration or literature, and oral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication wherein knowledge, art, ideas and cultural material is received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another. Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (1985) ...
prevailed instead. After the Migration Period (c. 300ŌĆō800), the Germanic elite not only adopted the Latin script and spread it further, but usually also employed the Latin language for early medieval politics and literature. A slight exception to this is Anglo-Saxon England, where apart from Latin itself, the Latin-derived Insular script
Insular script was a medieval script system originating from Ireland that spread to Anglo-Saxon England and continental Europe under the influence of Irish Christianity. Irish missionaries took the script to continental Europe, where they found ...
gave rise to the Old English Latin alphabet The Old English Latin alphabet generally consisted of about 24 letters, and was used for writing Old English from the 8th to the 12th centuries. Of these letters, most were directly adopted from the Latin alphabet, two were modified Latin letters ( ...
that was also regularly used for writing in the vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
from the 7th century.
 In Western Europe, the
In Western Europe, the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
were instrumental in spreading and developing the majuscule uncial and half-uncial scripts (used for Greek and Latin texts from the 4th to the 9th centuries), first into the Merovingian script
Merovingian script or Gallo-Roman script ( la, Scriptura Merovingica/Francogallica) was a medieval variant of the Latin script so called because it was developed in Gaul during the Merovingian dynasty. It was used in the 7th and 8th centuries bef ...
(7thŌĆō8th century), later the Carolingian minuscule
Carolingian minuscule or Caroline minuscule is a script which developed as a calligraphic standard in the medieval European period so that the Latin alphabet of Jerome's Vulgate Bible could be easily recognized by the literate class from one reg ...
(9thŌĆō12th centuries). Most of this work was done on parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared untanned skins of animalsŌĆöprimarily sheep, calves, and goats. It has been used as a writing medium for over two millennia. Vellum is a finer quality parchment made from the skins o ...
codices
The codex (plural codices ) was the historical ancestor of the modern book. Instead of being composed of sheets of paper, it used sheets of vellum, papyrus, or other materials. The term ''codex'' is often used for ancient manuscript books, with ...
(replacing the earlier papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
scrolls) by Frankish monk
A monk (, from el, ╬╝╬┐╬Į╬▒ŽćŽīŽé, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
s in scriptoria
Scriptorium (), literally "a place for writing", is commonly used to refer to a room in medieval European monasteries devoted to the writing, copying and illuminating of manuscripts commonly handled by monastic scribes.
However, lay scribes and ...
of monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
, with a focus on preserving classical Greek and Latin texts as well as Biblical books and patristic commentaries through copying.
Many Central European regions south of the ''limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a ...
'' that were never fully Latinised in Roman times, including modern Austria
Austria, , bar, Ûstareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
, Baden-W├╝rttemberg
Baden-W├╝rttemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaW├╝, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
, the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rh├®nanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
, Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Els├Āss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
( Alsatian and Lorraine Franconian), and Alemannic Switzerland, all (re-)Germanised at different points in late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rdŌĆō7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
due to the large influx of Germanic-speaking groups from the north. While there are a few Germanic runic inscriptions from before the mid-8th century, all Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
texts are written with the Latin alphabet. However, because it was ill-suited for representing some of the sounds of Old High German, this led to considerable variations in spelling conventions, as individual scribes and scriptoria had to develop their own solutions to these problems.
Christianisation
The spread ofWestern Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity ( Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic ...
during the early Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
strongly contributed to spreading the Latin script across Europe, especially in areas beyond the old Roman ''limes'' that barely had any written culture up to that point, such as Scandinavia
Scandinavia; S├Īmi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
and East Central Europe. Western Christian missionaries associated the non-Latin scripts with paganism, and therefore insisted on their abandonment. The European peoples who were gradually converted to Latin Christianity and carved their own alphabets out of it spoke Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
(displacing the Ogham
Ogham ( Modern Irish: ; mga, ogum, ogom, later mga, ogam, label=none ) is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the early Irish language (in the "orthodox" inscriptions, 4th to 6th centuries AD), and later the Old Irish langu ...
alphabet since the 5th century), Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, E ...
(displacing the earlier runic alphabets 'fu├Šark' and 'fu├Šorc' since the 8th century), Baltic languages, Uralic languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (w ...
such as Hungarian, Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
and Estonian, and Slavic languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the ...
. The Carolingian minuscule was extensively used in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
from 800 to 1200. The blackletter or Gothic script evolved from it in the 12th and 13th centuries, and was commonplace in Germany as ''Fraktur
Fraktur () is a calligraphic hand of the Latin alphabet and any of several blackletter typefaces derived from this hand. The blackletter lines are broken up; that is, their forms contain many angles when compared to the curves of the Antiqu ...
'' from the 16th up to the 20th centuries. In the rest of Latin Christendom, the Gothic script was restricted to the Church, and disappeared centuries earlier.
The Latin script was introduced to Scandinavia in the 9th century, first in Denmark. It reached Norway during the 11th-century Christianisation, but in two different forms: the Anglo-Saxon Insular script
Insular script was a medieval script system originating from Ireland that spread to Anglo-Saxon England and continental Europe under the influence of Irish Christianity. Irish missionaries took the script to continental Europe, where they found ...
in Western Norway and the Carolingian minuscule in Eastern Norway. Scandinavia went through a phase of digraphia between Latin letters and Norse runes before abandoning the latter, with some individuals being proficient in both during this transition. It was not until the early 14th century that the Scandinavian vernaculars developed into fully-fledged written languages, and literature became more dominant than oral culture.
The spread of the Latin and Cyrillic scripts in Eastern Europe was closely connected to the competing missionary efforts of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, ┘éž│žĘ┘åžĘ┘Ŗ┘å┘Ŗ┘ć
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. In areas where both were proselytising to pagan Europeans, such as the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
, the Croatian Duchy and the Principality of Serbia
The Principality of Serbia ( sr-Cyrl, ąÜčÜą░ąČąĄčüčéą▓ąŠ ąĪčĆą▒ąĖčśą░, Knja┼Šestvo Srbija) was an autonomous state in the Balkans that came into existence as a result of the Serbian Revolution, which lasted between 1804 and 1817. Its creation wa ...
, mixtures of languages, scripts and alphabets emerged, and the lines between Latin Catholic (''Latinitas'') and Cyrillic Orthodox literacy (''Slavia Orthodoxa'') were blurred. The administrative literacy of Lithuania, for example, was gradually Latinised after it united with the Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Kr├│lestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
in the late 14th century, but the realm retained the Ruthenian language and Cyrillic script for pragmatic literature, and some local books of terrestrial tribunals used Latin and Cyrillic on the same page.
Generally speaking, the Latin script came into use for writing the West Slavic languages
The West Slavic languages are a subdivision of the Slavic language group. They include Polish, Czech, Slovak, Kashubian, Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian. The languages have traditionally been spoken across a mostly continuous region encom ...
and several South Slavic languages such as Slovene and Croatian, as the people who spoke them adopted Roman Catholicism. The speakers of East Slavic languages
The East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of the Slavic languages, distinct from the West and South Slavic languages. East Slavic languages are currently spoken natively throughout Eastern Europe, and eastwards to Siber ...
generally adopted Cyrillic along with Orthodox Christianity
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Chur ...
. Modern Serbian, Bosnian and Montenegrin have come to use both scripts, whilst the Eastern South Slavic Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
and Macedonian languages have maintained Cyrillic only.
Early modern period
As late as 1500, the Latin script was limited primarily to the languages spoken inWestern
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
, South Western, Northern and Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618ŌĆō1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
. The Orthodox Christian
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Churche ...
Slavs of Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
and Southeastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (a ...
mostly used Cyrillic, and Greek speakers around the eastern Mediterranean used the Greek alphabet. The Arabic script was widespread in the Islamic world, among both Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, ž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©┘É┘Ŗ┘ī┘æ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, ž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s and non-Arab nations like the Iranians, Indonesians, Malays, and Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
, as well as amongst Arab Christians. Most of the rest of Asia used a variety of Brahmic alphabets or the Chinese script
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji' ...
.
Since the 15th and especially 16th centuries, European colonisation has spread the Latin script around the world, to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, and parts of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
(until about 1880 mostly limited to the coastal areas) and the Pacific, along with the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, French, and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
languages.
Americas
In an effort to Christianise and 'civilise' theMayans
The Maya peoples () are an ethnolinguistic group of indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived within that historical reg ...
, the Roman Catholic bishop Diego de Landa
Diego de Landa Calder├│n, O.F.M. (12 November 1524 – 29 April 1579) was a Spanish Franciscan bishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Yucat├Īn. Many historians criticize his campaign against idolatry. In particular, he burned almost a ...
of Yucat├Īn
Yucat├Īn (, also , , ; yua, Y├║ukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucat├Īn,; yua, link=no, X├│ot' Noj Lu'umil Y├║ukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
ordered the burning of most Maya codices
Maya codices (singular ''codex'') are folding books written by the pre-Columbian Maya civilization in Maya hieroglyphic script on Mesoamerican bark paper. The folding books are the products of professional scribes working under the patronage of ...
in July 1562, and with it the near destruction of the Mayan hieroglyphic script. He then rewrote the history of the Mayans in Spanish, and the Mayan language was romanised, leading to an enormous loss in culture.
Latin letters served as an inspiration for the forms of the Cherokee syllabary
The Cherokee syllabary is a syllabary invented by Sequoyah in the late 1810s and early 1820s to write the Cherokee language. His creation of the syllabary is particularly noteworthy as he was illiterate until the creation of his syllabary. He ...
developed by Sequoyah in the late 1810s and early 1820s; however, Latin influence is mainly skin deep with Sequoyah having freely created new syllabograms.
South Asia
The only South Asian language that has widely adopted the Latin script is Konkani (in the 16th century), spoken on the midwestern Indian coast. Attempts to introduce Latin alphabets instead of Brahmi-derived scripts for other Indian languages have so far been unsuccessful. Nevertheless,British colonialism
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts est ...
introduced the widespread use of the Latin-lettered English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the ...
in the subcontinent, which has retained and even expanded its prominence in the post-independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
era in both India and Pakistan.
Southeast Asia and Pacific
The Latin script was introduced for many Austronesian languages, including thelanguages of the Philippines
There are some 120 to 187 languages spoken in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called C ...
and the Malaysian
Malaysian may refer to:
* Something from or related to Malaysia, a country in Southeast Asia
* Malaysian Malay, a dialect of Malay language spoken mainly in Malaysia
* Malaysian people, people who are identified with the country of Malaysia regard ...
and Indonesian language
Indonesian ( ) is the official and national language of Indonesia. It is a standardized variety of Malay, an Austronesian language that has been used as a lingua franca in the multilingual Indonesian archipelago for centuries. Indonesia ...
s, replacing earlier Arabic and indigenous Brahmic alphabets. The Latin script fits the phonology of Austronesian languages very well, which helped speed up its adoption, as well as helping it to mostly displace the Arabic-based Jawi script
Jawi (; ace, Jawoë; Kelantan-Pattani: ''Yawi''; ) is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese, Banjarese, Kerinci, Maguindanaon, Malay, Minangkabau, Tausūg, and Ternate. Jawi is based ...
in Muslim countries. (This is in contrast to other languages in mainland Asia, where Latin script is a much poorer fit and would require heavy use of diacritics, as with Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
, which actually did adopt Latin script.)
During the Dutch rule on Formosa (1624ŌĆō1662), the island currently known as Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, the Siraya language
Siraya is a Formosan language spoken until the end of the 19th century by the indigenous Siraya people of Taiwan, derived from Proto-Siraya. Some scholars believe Taivoan and Makatao are two dialects of Siraya, but now more evidence shows that ...
was given a Sinckan Latin alphabet by the Dutch, which lasted until the 19th century.
19th century
US
There was an attempt at simplifying English spelling by promoting the Deseret alphabet, but it failed to achieve success.Africa
The Scramble for Africa (1881ŌĆō1914), meaning the rapid occupation, colonisation and annexation of inland Africa by European powers, went hand in hand with the spread of literacy amongst native Africans, as the Latin script was introduced where there were other writing systems or none. Until the early 19th century, theBerber peoples
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
in North Africa had two systems: originally Tifinagh
Tifinagh ( Tuareg Berber language: or , ) is a script used to write the Berber languages. Tifinagh is descended from the ancient Libyco-Berber alphabet. The traditional Tifinagh, sometimes called Tuareg Tifinagh, is still favored by the Tuar ...
, and, following the spread of Islam, the Arabic script as well. French colonists, particularly missionaries and army linguists, developed a Berber Latin alphabet to make communication easier, especially for the Kabyle people
The Kabyle people ( kab, Izwawen or ''Leqbayel'' or ''Iqbayliyen'', ) are a Berber ethnic group indigenous to Kabylia in the north of Algeria, spread across the Atlas Mountains, east of Algiers. They represent the largest Berber-speaking populat ...
in French Algeria. Since no great body of Berber literature existed, and the colonisers greatly helped improve literacy rates, the romanisation received much support, more so after Algerian independence (1962) when the French-educated Kabyle intelligentsia began to stimulate the transition and especially since the establishment of a standard transcription for Kabylie in 1970. Similar French attempts to Latinise the Arabic language met much more resistance, were unsuccessful and eventually abandoned.
Galicia
 From the 1830s to the 1880s,
From the 1830s to the 1880s, Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, ąŻą║čĆą░茹Įčåč¢, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
in Galicia (then divided between the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
and Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
) were engaged in a linguistics controversy known as the Alphabetical War
The Alphabet War ( uk, ąÉąĘą▒čāčćąĮą░ ą▓č¢ą╣ąĮą░, Azbuchna viina), also called the Alphabet Blizzard ( uk, ąÉąĘą▒čāčćąĮą░ ąĘą░ą▓č¢čĆčÄčģą░, Azbuchna zaviriukha), was a controversy in the 19th century among Galician Ukrainians. It concerned attemp ...
. They discussed whether the Ukrainian language
Ukrainian ( uk, čāą║čĆą░čŚ╠üąĮčüčīą║ą░ ą╝ąŠ╠üą▓ą░, translit=ukrainska mova, label=native name, ) is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family. It is the native language of about 40 million people and the official state lan ...
(then known as "Ruthenian") was best written in the Latin script (based on the Czech model) against perceived Russification, or in the Cyrillic script against perceived Polonisation. In the end, Cyrillic prevailed.
Romania
As aRomance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language f ...
, Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
*** Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
** Romanian cuisine, tradition ...
continued to be written in Latin script until the Council of Florence in 1439. Increasingly influenced by Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
as the Greek Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
declined and was gradually conquered by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ą×╬ĖŽē╬╝╬▒╬Į╬╣╬║╬« ╬æŽģŽä╬┐╬║Žü╬▒Žä╬┐Žü╬»╬▒, Oth┼Źmanik─ō Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in the 15th century, the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
had begun promoting the Slavic Cyrillic. In the 19th century, the Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
returned to the Latin alphabet under the influence of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
. The linguist Ion Heliade R─ādulescu
Ion Heliade R─ādulescu or Ion Heliade (also known as ''Eliade'' or ''Eliade R─ādulescu''; ; January 6, 1802 ŌĆō April 27, 1872) was a Wallachian, later Romanian academic, Romantic and Classicist poet, essayist, memoirist, short story writ ...
first proposed a simplified version of Cyrillic in 1829, but in 1838, he introduced a mixed alphabet containing 19 Cyrillic and 10 Latin letters, and an and that could be both. This 'transitional orthography' was widely used until the official adoption of a completely Latin Romanian alphabet in Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, ╚Üara Rom├óneasc─ā, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
(1860) and Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, ąŚąĄą╝ą╗č¦ ą£ąŠą╗ą┤ą░ą▓čüą║ą░č¦; el, ß╝®╬│╬Ą╬╝╬┐╬Į╬»╬▒ Žäß┐åŽé ╬£╬┐╬╗╬┤╬▒╬▓╬»╬▒Žé) is a historical region and for ...
(1863), that were gradually united since 1859 to become the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
in 1881. Romanian intellectuals in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erd├®ly; german: Siebenb├╝rgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, then still part of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, and scholars in Wallachia-Moldavia agreed to cleanse the language from all non-Latin elements (Greek, Magyar, Slavic, and Ottoman), and to emulate French wherever needed.
Russian Empire
Russian and Polish are both Slavic languages and have many similarities, thus from the 1840s on, Russia considered introducing the Cyrillic script for spelling thePolish language
Polish (Polish: ''j─Özyk polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In a ...
, with the first school books printed in the 1860s. The idea was quickly abandoned due to Polish being completely substituted by Russian in education as part of Russification process.
The initially successfully enacted Lithuanian press ban (1865ŌĆō1904) outlawed the use of Latin script, whilst encouraging writing Lithuanian texts in Cyrillic. Resistance grew as time went on: Lithuanian books were smuggled into the country, mainly from Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor ( lt, Ma┼Šoji Lietuva; german: Kleinlitauen; pl, Litwa Mniejsza; russian: ą£ą░╠üą╗ą░čÅ ąøąĖčéą▓ą░╠ü), or Prussian Lithuania ( lt, Pr┼½s┼│ Lietuva; german: Preu├¤isch-Litauen, pl, Litwa Pruska), is a historical ethnographic re ...
in East Prussia. Although the Russian authorities tried to seize them, they could not stop the rapid increase in forbidden titles from crossing the border. The Lithuanian ban, lifted in 1904, is widely felt to have stimulated the Lithuanian national movement and embracing the Latin script, rather than discouraging it.
Vietnam
Aromanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, a ...
of Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
was codified in the 17th century by the French Jesuit missionary Alexandre de Rhodes
Alexandre de Rhodes (15 March 1593 ŌĆō 5 November 1660) was an Avignonese Jesuit missionary and lexicographer who had a lasting impact on Christianity in Vietnam. He wrote the '' Dictionarium Annamiticum Lusitanum et Latinum'', the first triling ...
(1591ŌĆō1660), based on works of the early 16th-century Portuguese missionaries Gaspar do Amaral and Ant├│nio Barbosa. This Vietnamese alphabet
The Vietnamese alphabet ( vi, chữ Quốc ngữ, lit=script of the National language) is the modern Latin writing script or writing system for Vietnamese. It uses the Latin script based on Romance languages originally developed by Portuguese m ...
(''chữ quốc ngữ'' or "national script") was gradually expanded from its initial domain in Christian writing to become more popular among the general public, which had previously used Chinese-based characters.
During the French protectorate (1883ŌĆō1945), colonial rulers made an effort to educate all Vietnamese, and a simpler writing system was found more expedient for teaching and communication with the general population. It was not until the beginning of the 20th century that the romanized script came to predominate written communication. To further the process, Vietnamese written with the alphabet was made obligatory for all public documents in 1910 by issue of a decree by the French R├®sident Sup├®rieur of the protectorate of Tonkin in northern Vietnam.
20th century
Albanian
Albanian had used a variety of writing systems since its first attestation in the 12th century, especially Latin (in the north), Greek (in the south), Ottoman and Arabic (favoured by many Muslims). There were attempts at standardisation throughout the 19th century, from 1879 led by the Society for the Publication of Albanian Writings, culminating in the 1908Congress of Manastir
The Congress of Manastir ( sq, Kongresi i Manastirit) was an academic conference held in the city of Manastir (now Bitola) from November 14 to 22, 1908, with the goal of standardizing the Albanian alphabet. November 22 is now a commemorative da ...
when a single Latin script, Bashkimi, was chosen for the whole language. Although the newly adopted Albanian Latin alphabet symbolised a break with Ottoman rule, some Islamist Kosovo Albanians objected strongly against it, preferring to maintain the Arabic script that was found in the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
, which they held sacred. However, nationalists maintained that the Latin alphabet was 'above religion' and therefore also acceptable to non-Islamic and secular Albanians; and they won the argument.
China
After the establishment of thePeopleŌĆÖs Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
in 1949, Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 ŌĆō 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
initially considered Latinizing written Chinese, but during his first official visit to the Soviet Union in that year Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; ŌĆō 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
, who stopped the Latinizing of all languages in the Soviet Union in 1930, convinced Mao to maintain the existing Chinese writing system. Instead Zhou Youguang
Zhou Youguang (; 13 January 1906 ŌĆō 14 January 2017), also known as Chou Yu-kuang or Chou Yao-ping, was a Chinese economist, banker, linguist, sinologist, Esperantist, publisher, and supercentenarian, known as the "father of Pinyin", a system f ...
created the pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally writte ...
system and Chinese characters were simplified.
As a remnant of the romanization era, for official writing of the Zhuang language
The Zhuang languages (; autonym: , pre-1982: , Sawndip: Ķ®▒Õā«, from ''vah'', 'language' and ''Cuengh'', 'Zhuang'; ) are any of more than a dozen Tai languages spoken by the Zhuang people of Southern China in the province of Guangxi and adjac ...
the Latin alphabet was chosen over some form of standardised centuries-old Sawndip
Zhuang characters or ''Sawndip'' (Sawndip: ; ) are logograms derived from Chinese characters and used by the Zhuang people of Guangxi and Yunnan provinces in China to write the Zhuang languages for more than one thousand years. The script is used ...
script based on Chinese characters. The practical consequences of this are limited though, since most Zhuang speakers still use Sawndip.
The Uyghur language
The Uyghur or Uighur language (; , , , or , , , , CTA: Uy─¤ur├¦├ż; formerly known as Eastern Turki), is a Turkic language written in a Uyghur Perso-Arabic script with 8-11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xi ...
in China used a Latin-derived alphabet created upon Pinyin spelling conventions, but it was abolished in 1982 and the Arabic script was restored.
Serbo-Croatian
 Croatian linguist Ljudevit Gaj devised a uniform Latin alphabet for Croatian in 1835, while in 1818, Serbian linguist
Croatian linguist Ljudevit Gaj devised a uniform Latin alphabet for Croatian in 1835, while in 1818, Serbian linguist Vuk Karad┼Ši─ć
Vuk Stefanovi─ć Karad┼Ši─ć ( sr-Cyrl, ąÆčāą║ ąĪč鹥čäą░ąĮąŠą▓ąĖčø ąÜą░čĆą░褹Ėčø, ; 6 November 1787 (26 October OS)7 February 1864) was a Serbian philologist, anthropologist and linguist. He was one of the most important reformers of the moder ...
had developed a Serbian Cyrillic alphabet
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karad┼Ši─ć. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, t ...
. In the first half of the 19th century, the Illyrian movement
The Illyrian movement ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Ilirski pokret, ąśą╗ąĖčĆčüą║ąĖ ą┐ąŠą║čĆąĄčé; sl, Ilirsko gibanje) was a pan-South-Slavic cultural and political campaign with roots in the early modern period, and revived by a group of young Croatian inte ...
to unite all Southern Slavs (Yugoslavs) culturally, and perhaps also politically, was quite strong, and efforts were made to create a unified literary language that would set the standard for all Yugoslav dialects. The Vienna Literary Agreement
The Vienna Literary Agreement (Serbo-Croatian: ''Be─Źki knji┼Ševni dogovor'', ąæąĄčćą║ąĖ ą║čÜąĖąČąĄą▓ąĮąĖ ą┤ąŠą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆ) was the result of a meeting held in March 1850, when writers from Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia, Principality ...
(March 1850) between writers from Croatia, Serbia and one from Slovenia was the most significant attempt, where some basic rules were agreed upon. In the 1860s, Vuk's orthography gained acceptance in Serbia, while a Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts
The Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts ( la, Academia Scientiarum et Artium Croatica, hr, Hrvatska akademija znanosti i umjetnosti, abbrev. HAZU) is the national academy of Croatia.
HAZU was founded under patronage of the Croatian bishop Jo ...
was founded in 1866 in Zagreb
Zagreb ( , , , ) is the capital and largest city of Croatia. It is in the northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slopes of the Medvednica mountain. Zagreb stands near the international border between Croatia and Slov ...
and the first 'Serbo-Croatian' grammar book by Pero Budmani
Petar "Pero" Budmani ( sr-Cyrl, ą¤ąĄčĆąŠ ąæčāą┤ą╝ą░ąĮąĖ; 27 October 1835 ŌĆō 27 December 1914) was a writer, linguist, grammarian, and philologist from Dubrovnik and a renowned polyglot.
Biography
Budmani was born in Dubrovnik/Ragusa, at the time ...
was published in Croatia in 1867. In 1913, Jovan Skerli─ć
Jovan Skerli─ć (, ; 20 August 1877 ŌĆō 15 May 1914) was a Serbian writer and literary critic.''Jovan Skerli─ć u srpskoj knji┼Ševnosti 1877ŌĆō1977: Zbornik radova''. Posebna izdanja, Institut za knjizevnost i umetnost, Belgrade. He is seen as one ...
proposed a compromise for a single writing system and dialect to create true language unity. After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, political unity was realised in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, ąÜčĆą░čÖąĄą▓ąĖąĮą░ ąłčāą│ąŠčüą╗ą░ą▓ąĖčśą░; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
, but an agreement on scriptural unity for its population was never reached. The post-war Titoist
Titoism is a political philosophy most closely associated with Josip Broz Tito during the Cold War. It is characterized by a broad Yugoslav identity, workers' self-management, a political separation from the Soviet Union, and leadership in the ...
Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
made another attempt at achieving linguistic unity, but the 1954 Novi Sad Agreement only managed to get equality of Latin and Cyrillic, and an obligation for all citizens to learn both alphabets. With the return of ethnic nationalism in the 1980s, the two again became heavily associated with particular variants of the Serbo-Croatian language and thus with national identities. Exacerbated by the Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
that led to the disintegration of Yugoslavia in the 1990s, nationalists on all sides resumed insisting Croatian, Bosnian, Serbian and Montenegrin were distinct languages in their own right, undermining the project of Serbo-Croatian linguistic unity.
The Bosnian language was originally primarily expressed in the Cyrillic-type '' Bosan─Źica'' since the 11th century (originally alongside the older '' Glagoljica''), but it was gradually driven extinct in the 18th century after the Ottoman introduction of the Perso-Arabic script
The Persian alphabet ( fa, ž¦┘ä┘üž©ž¦█ī ┘üž¦ž▒ž│█ī, Alefb├óye F├órsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran ( Western Persian) and Afghanistan (Dari Persian) since the 7th cen ...
-type ''Arebica
Arebica () is a variant of the Arabic script used to write the Serbo-Croatian language. It was used mainly between the 15th and 19th centuries and is frequently categorized as part of Aljamiado literature. Before World War I there were unsuccess ...
'' (15thŌĆō20th century). Eventually, most Bosnians adopted the Croatian-derived '' Latinica'' or Latin script ŌĆōoriginally introduced by the Catholic Franciscans
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
ŌĆō in the course of the 20th century, standardised in the 1990s.
Middle East and North Africa
 In 1928, as part of Mustafa Kemal Atat├╝rk's reforms, the new Republic of Turkey adopted the
In 1928, as part of Mustafa Kemal Atat├╝rk's reforms, the new Republic of Turkey adopted the Turkish Latin alphabet
The Turkish alphabet ( tr, ) is a Latin-script alphabet used for writing the Turkish language, consisting of 29 letters, seven of which ( ├ć, ─×, I, ─░, ├¢, ┼× and ├£) have been modified from their Latin originals for the phonetic requirem ...
for the Turkish language
Turkish ( , ), also referred to as Turkish of Turkey (''T├╝rkiye T├╝rk├¦esi''), is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, with around 80 to 90 million speakers. It is the national language of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. Significant sma ...
, replacing a modified Arabic script.
In the 1930s and 1940s, the majority of Kurds ug:┘ā█ćž▒ž»┘䞦ž▒
Kurds ( ku, ┌®┘łž▒ž» ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Ira ...
replaced the Arabic script with two Latin alphabets. Although the only official Kurdish government, the Kurdistan Regional Government
The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) ( ku, žŁ┌®┘ł┘ł┘ģ█Ģž¬█ī ┘ć█Ģž▒█Ä┘ģ█ī ┌®┘łž▒ž»ž│ž¬ž¦┘å, ''Hik├╗met├« Her├¬m├« Kurdistan'') is the official executive body of the autonomous Kurdistan Region of northern Iraq.
The cabinet is selected by the m ...
in northern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é, translit=├Ŗraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, ┌®█å┘ģž¦ž▒█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é, translit=Komar├« ├Ŗraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, uses an Arabic script for public documents, the Latin Kurdish alphabet remains widely used throughout the region by the majority of Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish languages
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern Kurdistan
**Eastern Kurdistan
**Northern Kurdistan
**Western Kurdistan
See also
* Kurd (dis ...
speakers, especially in Turkey and Syria.
During the late 20th century decolonisation
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on independence m ...
, Pan-Arabism and Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘é┘ł┘ģ┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž©┘Ŗž®, al-Qawm─½ya al-╩┐Arab─½ya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language a ...
expressed themselves in anti-Western tendencies, including hostility towards the Latin script. It was banned in some places such as Libya after Moammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi, . Due to the lack of standardization of transcribing written and regionally pronounced Arabic, Gaddafi's name has been romanized in various ways. A 1986 column by ''The Straight Dope'' lists 32 spellin ...
's 1969 coup, in favour of exclusive Arabic script.
Soviet Union
Since at least 1700, Russian intellectuals have sought to Latinise the Russian language in their desire for close relations with the West. TheBolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: ąæąŠą╗čīčłąĄą▓ąĖą║ąĖ╠ü, from ą▒ąŠą╗čīčłąĖąĮčüčéą▓ąŠ╠ü ''bol'shinstv├│'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstv├│'' (ą▒ąŠą╗čīčłąĖąĮčüčéą▓ąŠ╠ü), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
had four goals: to break with Tsarism
Tsarist autocracy (russian: čåą░čĆčüą║ąŠąĄ čüą░ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄčƹȹ░ą▓ąĖąĄ, transcr. ''tsarskoye samoderzhaviye''), also called Tsarism, was a form of autocracy (later absolute monarchy) specific to the Grand Duchy of Moscow and its successor states th ...
, to spread socialism
Socialism is a left-wing Economic ideology, economic philosophy and Political movement, movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to Private prop ...
to the whole world, to isolate the Muslim inhabitants of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
from the Arabic-Islamic world and religion, and eradicate illiteracy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in Writing, written form in some specific context of use. In other wo ...
through simplification. They concluded the Latin alphabet was the right tool to do so, and after seizing power during the Russian Revolution of 1917, they made plans to realise these ideals.
Although progress was slow at first, in 1926 the Turkic-majority republics of the Soviet Union adopted the Latin script, giving a major boost to reformers in neighbouring Turkey. Z├╝rcher, Erik Jan. ''Turkey: a modern history'', p. 188. I.B.Tauris, 2004. When Mustafa Kemal Atat├╝rk adopted the new Turkish Latin alphabet
The Turkish alphabet ( tr, ) is a Latin-script alphabet used for writing the Turkish language, consisting of 29 letters, seven of which ( ├ć, ─×, I, ─░, ├¢, ┼× and ├£) have been modified from their Latin originals for the phonetic requirem ...
in 1928, this in turn encouraged the Soviet leaders to proceed. The Commission to romanise the Russian alphabet completed its work in mid-January 1930. But on 25 January 1930, General Secretary Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; ŌĆō 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
ordered the stop of the romanisation of Russian. The Latinisation of non-Slavic languages within the USSR continued until the late 1930s, however. Most of the Turkic-speaking peoples of the Soviet Union, including Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Bashkirs
, native_name_lang = bak
, flag = File:Bashkirs of Baymak rayon.jpg
, flag_caption = Bashkirs of Baymak in traditional dress
, image =
, caption =
, population = approx. 2 million
, popplace ...
, Azerbaijani or Azeri, Kazakh (1929ŌĆō40), Kyrgyz and others, used the Latin-based Uniform Turkic alphabet
A uniform is a variety of clothing worn by members of an organization while participating in that organization's activity. Modern uniforms are most often worn by armed forces and paramilitary organizations such as police, emergency services, ...
in the 1930s; but, in the 1940s, all were replaced by Cyrillic.
Post-Soviet states
The Russian conquest ofTranscaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
in the 19th century split the Azerbaijani language community across two states, the other being Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The Soviet Union promoted development of the language, but set it back considerably with two successive script changes ŌĆō from the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
to Latin and then to the Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
ŌĆō while Iranian Azerbaijanis continued to use the Persian as they always had. Despite the wide use of Azerbaijani in the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, it did not become the official language of Azerbaijan until 1956. After achieving independence from the Soviet Union 1991, the new Republic of Azerbaijan decided to switch back to the Latin script.
Two other newly independent Turkic-speaking republics, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: ąŻąĘą▒ąĄą║ąĖčüčéą░ąĮ), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░ ąŻąĘą▒ąĄą║ąĖčüčéą░ąĮ), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, T├╝rkmenistan / ąóę»čĆą║ą╝ąĄąĮąĖčüčéą░ąĮ, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
, as well as Romanian-speaking Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
on 31 August 1989, Horia C. Matei, "State lumii. Enciclopedie de istorie." Meronia, Bucure╚Öti, 2006, pp. 292ŌĆō294 officially adopted Latin alphabets for their languages. In 1995, Uzbekistan ordered the Uzbek alphabet
The Uzbek language has been written in various scripts: Latin, Cyrillic and Arabic. The language traditionally used Arabic script, but the official Uzbek government under the Soviet Union started to use Cyrillic in 1940, which is when widesprea ...
changed from a Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
-based Cyrillic script to a modified Latin alphabet, and in 1997, Uzbek became the sole language of state administration. However, the government's implementation of the transition to Latin has been rather slow, suffered several setbacks and as of 2017 has not yet been completed. In 2021, the country expressed its ambition to complete the transition process by 2023.
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
-speaking Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, ąóąŠęĘąĖą║ąĖčüč鹊ąĮ, Tojikiston; russian: ąóą░ą┤ąČąĖą║ąĖčüčéą░ąĮ, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, ęČčāą╝ę│čāčĆąĖąĖ ąóąŠęĘąĖą║ąĖčüč鹊ąĮ, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, and the breakaway region of Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
kept the Cyrillic alphabet, chiefly due to their close ties with Russia. Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, however, is planning to start a transition process to the Latin alphabet in 2023.
21st century
Kazakhstan
Unlike its Turkic neighbours, Kazakhstan did not immediately move towards Latinisation after obtaining statehood in 1991. This was motivated by pragmatic reasons: the government was wary to alienate the country's large Russian-speaking minority (who wrote Russian in Cyrillic), and due to the economic crisis in the early 1990s, a transition was considered fiscally unfeasible at the time. It was not until 2017 that Latin became the official script for the Kazakh language in Kazakhstan, replacing Cyrillic. In 2006, PresidentNursultan Nazarbayev
Nursultan Abishuly Nazarbayev ( kk, ąØę▒čĆčüę▒ą╗čéą░ąĮ ėśą▒č¢čłę▒ą╗čŗ ąØą░ąĘą░čĆą▒ą░ąĄą▓, N┼½rs┼½ltan ├äbi┼¤┼½l─▒ Nazarbaev, ; born 6 July 1940) is a Kazakh politician and military officer who served as the first President of Kazakhstan, in off ...
requested the Ministry of Education and Science to examine the experiences of Turkey, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, which had all switched to Latin script in the 20th century. The ministry reported in the summer of 2007 that a six-step plan, based primarily on the Uzbekistan model, should be implemented over a 12-to-15-year period at the cost of about $300 million. Aside from integrating Kazakhstan into the global economy, officials have argued it would help the development of a Kazakh national identity separate from Russia. In 2007, Nazarbayev said the transformation of the Kazakh alphabet from Cyrillic to Latin should not be rushed, as he noted: "For 70 years, the Kazakhstanis read and wrote in Cyrillic. More than 100 nationalities live in our state. Thus we need stability and peace. We should be in no hurry in the issue of alphabet transformation".
In 2015, the Kazakh government
The Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan ( kk, ęÜą░ąĘą░ęøčüčéą░ąĮ ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░čüčŗąĮčŗęŻ ę«ą║č¢ą╝ąĄčéč¢, tr, ''Qazaqstan Respublikasyny├▒ ├£k─▒met─▒'') oversees a presidential republic. The President of Kazakhstan, currently Kassym- ...
announced that the Latin script would replace Cyrillic as the writing system for the Kazakh language by 2025. In 2017, Nazarbayev said that "by the end of 2017, after consultation with academics and representatives of the public, a single standard for the new Kazakh alphabet
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
*Kazakh cuisine
*Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative distr ...
and script should be developed." Education specialists were to be trained to teach the new alphabet and provide textbooks beginning in 2018. The romanisation policy is intended to modernise Kazakhstan and increase international cooperation. On 19 February 2018, president Nazarbayev signed an amendment to the decree of 26 October 2017 No. 569 "On translating the Kazakh alphabet from Cyrillic alphabet to the Latin script." The amended alphabet uses "Sh" and "Ch" for the Kazakh sounds "ą©" and "ą¦" and eliminates the use of apostrophes.
Turkmenistan
TheTurkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
The Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic (, ; russian: ąóčāčĆą║ą╝ąĄąĮčüą║ą░čÅ ąĪąŠą▓ąĄčéčüą║ą░čÅ ąĪąŠčåąĖą░ą╗ąĖčüčéąĖč湥čüą║ą░čÅ ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░, ''Turkmenskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika''), also commonly known as Turkmenistan o ...
employed a Latin alphabet from 1928 to 1940, when it was decreed that all languages in the Soviet Union be written in Cyrillic. After gaining independence in 1991, Turkmenistan was amongst several ex-Soviet states seeking to reintroduce the Latin script. Although totalitarian dictator Saparmurat Niyazov, ruling Turkmenistan from 1985 to his death in 2006, announced a decree on 12 April 1993 that formalised a new Turkmen Latin alphabet, the ''de facto'' implementation has been slow and incomplete. The original 1993 alphabet had 30 letters, but missed several sounds and did not fit the Turkmen language, so several amendments were made in 1996. The first book in Latin script was printed in 1995, but Turkmen language and literature manuals were not available until 1999; Cyrillic manuals had been banned before Latin ones were available. Although by 2011 the younger generations were well-versed in the Turkmen Latin alphabet through the education system, adults, including teachers, were not given any official training programme and were expected to learn it by themselves without state support.
Canada
In October 2019, the organization National Representational Organization for Inuit inCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
(ITK) announced that they will introduce a unified writing system for the Inuit languages
The Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and adjacent subarctic, reaching farthest south in Labrador. The related Yupik languages (spoken in weste ...
in the country. The writing system is based on the Latin alphabet and is modeled after the one used in the Greenlandic language.
Oklahoma (United States)
From 2006, a newwriting system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable fo ...
was developed for the Native American Osage language
Osage (; Osage: ''Wa┼Š├Ī┼Še ie'') is a Siouan language that is spoken by the Osage people of Oklahoma. Their original territory was in present-day Missouri and Kansas but they were gradually pushed west by European-American pressure and treati ...
, challenging the dominance of the Latin script for writing that language.
Debates and proposals
Bulgaria
In 2001, Austrian slavistics professor Otto Kronsteiner recommended that Bulgaria adopt the Latin script in order to facilitate the country's accession to theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
. This caused such a scandal that the Veliko Tarnovo University
The St. Cyril and St. Methodius University of Veliko Tarnovo ( Bulgarian ''ąÆąĄą╗ąĖą║ąŠčéčŖčĆąĮąŠą▓čüą║ąĖ čāąĮąĖą▓ąĄčĆčüąĖč鹥čé ŌĆ׹Īą▓. čüą▓. ąÜąĖčĆąĖą╗ ąĖ ą£ąĄč鹊ą┤ąĖą╣ŌĆ£'') is a Bulgarian university based in Veliko Tarnovo.
History
...
revoked the honorary degree it had previously awarded him (for supporting the Bulgarian viewpoint on the Macedonian language
Macedonian (; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around two million ...
). For many Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, ąæčŖą╗ą│ą░čĆąĖčÅ, BŪÄlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
ns, the Cyrillic alphabet has become an important component of their national identity, and great pride is taken in having introduced Cyrillic into the EU in 2007.With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
, following the Latin and Greek scripts.
However, in digital communication using computers and writing email
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" mean ...
s and SMS
Short Message/Messaging Service, commonly abbreviated as SMS, is a text messaging service component of most telephone, Internet and mobile device systems. It uses standardized communication protocols that let mobile devices exchange short text ...
, the Latin script has been proposed to replace the Cyrillic. A Bulgarian Latin alphabet, the so-called ''shlyokavitsa'', is already often employed for convenience for emails and SMS messages. Ciphers are used to denote Bulgarian sounds that cannot be represented with a single Latin character (for example, a " 4" represents a " čć" because they look alike and the Bulgarian word for the cardinal number four, čćčÉčéąĖčĆąĖ ''─ŹčÉtiri'', starts with a "čć").
Kosovo
Despite initial resistance from Islamist Kosovo Albanians (who favoured the Arabic script) against the 1908Congress of Manastir
The Congress of Manastir ( sq, Kongresi i Manastirit) was an academic conference held in the city of Manastir (now Bitola) from November 14 to 22, 1908, with the goal of standardizing the Albanian alphabet. November 22 is now a commemorative da ...
's resolution to adopt the Latin script to write the Albanian language in, Kosovo Albanians
The Albanians of Kosovo ( sq, Shqiptarët e Kosovës, ), also commonly called Kosovo Albanians, Kosovar/Kosovan Albanians or Kosovars/Kosovans, constitute the largest ethnic group in Kosovo.
Kosovo Albanians belong to the ethnic Albanian sub-gr ...
came to accept the Albanian Latin alphabet over the course of the early 20th century. Literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
amongst Kosovo Albanians increased from 26% in 1948 to 96.6% (men) and 87.5% (women) in 2007. The Kosovo Serbs
Kosovo Serbs are one of the ethnic groups of Kosovo. There are around 100,000 Kosovo Serbs as of 2014 and about half of them live in North Kosovo. Other Serb communities live in southern Kosovo. After Albanians, they form the largest ethnic com ...
have followed the practice of Cyrillic/Latin digraphia in the Republic of Serbia and continued to use both alphabets after the Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the wa ...
(1998ŌĆō9) and the 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence. Article 2 of the 2006 Law on the Use of Languages states that ŌĆ£Albanian and Serbian and their alphabets are official languages of Kosovo and have equal status in Kosovo institutions,ŌĆØ but fails to specify which alphabets these are, as neither Latin nor Cyrillic is mentioned. This has often led the (ethnic Albanian-dominated) Kosovo authorities to exclusively use the Serbo-Croatian Latin alphabet in its communication with the Serb minority, as it does with the country's other five officially recognised minorities, especially the Bosniaks whose language is very similar to Serbian, but always written in Latin. Although Kosovo Serbs may use either or both alphabets in everyday life, some claim they've got the right to demand the authorities to communicate with them in their preferred alphabet, and accuse the government of violating the law. The present attitudes of the Kosovar authorities have raised concerns over the Latinisation of the Kosovo Serbs against their will, while the government maintains it respects the legal rights of minorities.
Kyrgyzstan
Adopting the Latin script for the Kyrgyz language has been the subject of discussions inKyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
since attaining independence in the 1990s. However, unlike in the other Turkic-dominated former Soviet republics in Central Asia, the issue did not become prominent until its great neighbour Kazakhstan in September 2015 and April 2017 confirmed its previous announcements to Latinise the closely related Kazakh language. Before then, the largely Russian-speaking elite of the country saw no reason to, nor did it seek to endanger its good-standing political and economic relations with the Russian Federation. Amongst others, deputy Kanybek Imanaliyev advocated a shift to Latin for 'the development of contemporary technology, communication, education and science.' On the other hand, due to financial constraints, he proposed to postpone the transition to the 2030s or even 2040s. Because Russia is still a very important financial supporter of Kyrgyzstan, other experts agreed it would be unwise for Bishkek to make a move that would culturally alienate Moscow. President Almazbek Atambayev
Almazbek Sharshen uluu Atambayev ( ky, ąÉą╗ą╝ą░ąĘą▒ąĄą║ ą©ą░čĆčłąĄąĮ čāčāą╗čā ąÉčéą░ą╝ą▒ą░ąĄą▓, translit=Almazbek ┼×ar┼¤en uulu Atambayev; born 17 September 1956) is a Kyrgyz politician who served as the President of Kyrgyzstan from 1 December 2 ...
stated in October 2017 that the country would not Latinise any time soon. In 2019, the then-Minister of Education and Science Kanybek Isakov
Kanybek Abdouvassitovitch Isakov ( ky, ąÜą░ąĮčŗą▒ąĄą║ ąÉą▒ą┤čāą▓ą░čüąĖč鹊ą▓ąĖčć ąśčüą░ą║ąŠą▓, 4 June 1969 ŌĆō 12 November 2020) was a Kyrgyz politician and academic.
Biography
Isakov became a professor of philology at Osh State University in 199 ...
expressed support for a switch to the Latin alphabet, which restarted a public debate about the benefits and drawbacks of such a change.
Uyghur
To the east of Kyrgyz language there it is a western China's language that historically was linked to the Kyrgyzstan's language: the Uighur language. Here recently has been created the ''Uyghur Latin script'' or ULY. This "Uyghur Latin Yëziqi" (ULY) is an auxiliary alphabet for the Uighur language based on the Latin script.North Macedonia
TheMacedonian language
Macedonian (; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around two million ...
in its Cyrillic alphabet has been the official language of the Republic of Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
throughout the country and in its foreign relations since 1991. However, since the 2001 Albanian insurgency was ended by the Ohrid Agreement
The Ohrid Framework Agreement ( mk, ą×čģčĆąĖą┤čüą║ąĖ čĆą░ą╝ą║ąŠą▓ąĄąĮ ą┤ąŠą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆ, Ohridski ramkoven dogovor) was the peace deal signed by the government of the Republic of Macedonia (now North Macedonia) and representatives of the Albanian ...
, the Constitution of Macedonia has been amended (Amendment V) to mandate the co-official use of the six minority languages and their respective alphabets in municipalities in which more than 20% of an ethnic minority resides. The six minority languages ŌĆō Albanian, Turkish, Romani, Serbian, Bosnian and Aromanian ŌĆō are (with the exception of Serbian) always officially written in Latin script in the municipalities where their speakers constitute a significant minority or even majority. In addition, Macedonian is occasionally written in Latin, especially in advertising.
Montenegro
There is ongoing discussion inMontenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
about how to label the majority language of Montenegro, which is mutually intelligible with the other standardised versions of Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () ŌĆō also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) ŌĆō is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia an ...
: Serbian, Croatian and Bosnian. These debates focus on the perceived linguistic differences between Montenegrin and related variants, but also on national and political identification. Montenegro practices digraphia
In sociolinguistics, digraphia refers to the use of more than one writing system for the same language. Synchronic digraphia is the coexistence of two or more writing systems for the same language, while diachronic digraphia (or sequential digra ...
: there are two official Montenegrin alphabet
The Montenegrin alphabet is the collective name given to "''Abeceda''" (Montenegrin Latin alphabet) and "''ąÉąĘą▒čāą║ą░''" ( Montenegrin Cyrillic alphabet), the writing systems used to write the Montenegrin language. It was adopted on 9 June 200 ...
s, one Latin and one Cyrillic. In electoral campaigns after 2000, especially the 2006 independence referendum, Latin has come to symbolise closeness to Western countries, including Montenegro's historical ties to Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
, and independence from Serbia; on the other hand, Cyrillic is taken to signify unity with Serbia and closeness to the East.
In general, proponents of calling the language "Montenegrin" ŌĆō including the DPS-led governments (1990ŌĆō2020) ŌĆō tend to favour the Latin script, whereas supporters of "Serbian" prefer Cyrillic. In June 2016, an incident in which top students in primary and secondary schools for the first time since World War II received their "Luca" diplomas ŌĆō named after Njego┼Ī's poem ŌĆō printed in the Latin alphabet, sparked political controversy. The opposition Socialist People's Party (SNP) accused Education Minister Predrag Bo┼Īkovi─ć
Predrag Bo┼Īkovi─ć (; born 12 March 1972) is a Montenegrin politician and sports administrator. Currently he is a member of the Parliament of Montenegro, and the former Minister of Defence of Montenegro.
Bo┼Īkovi─ć is an economist and has been i ...
of "persecuting Cyrillic" and discriminating against pupils who use this script. The SNP was unsuccessful in forcing the minister to resign. The annual June reception of Latin-printed pupil's diplomas in schools continued to cause pro-Serbian organisations including new small opposition party True Montenegro
The True Montenegro (; abbr. ą¤čĆą░ą▓ą░ / Prava or ą¤ą”ąō / PCG) is a right-wing populist political party in Montenegro, formed in January 2018 from the political movement ''Resistance to Hopelessness'' (OB), prior to the March 2018 presidential ...
to claim Cyrillic users were being 'discriminated' against, while Education Minister Damir ┼Āehovi─ć stated that schools are obliged to issue Cyrillic diplomas, but only at the request of pupilsŌĆÖ parents.
Serbia
brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create ...
s." In August 2018, the Ministry of Culture proposed a law to that effect, obliging government institutions to use Cyrillic under the threat of fines Fines may refer to:
* Fines, Andalusia, Spanish municipality
* Fine (penalty)
* Fine, a dated term for a premium on a lease of land, a large sum the tenant pays to commute (lessen) the rent throughout the term
*Fines, ore or other products with a s ...
, and setting up a Council for the Serbian Language to implement this suggested language policy. The ministry claimed that indifference towards which script to use was not ŌĆ£a culturally responsible positionŌĆØ, and complained that some people had come to ŌĆ£use the Latin script as a symbol of heiropenness and European affiliationŌĆØ, arguing that Cyrillic was also one of the European Union's official writing systems and that "the EU is a community of peoples with their peculiarities."
Tatarstan (Russia)
In 1999, the RussianRepublic of Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░ ąóą░čéą░čĆčüčéą░ąĮ, Respublika Tatarstan, p=r╩▓╔¬s╦łpubl╩▓╔¬k╔Ö t╔Öt╔Ér╦łstan; tt-Cyrl, ąóą░čéą░čĆčüčéą░ąĮ ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░čüčŗ), or simply Tatarstan (russian: ąóą░čéą░čĆčüčéą░ąĮ, tt ...
proposed to convert the Turkic Tatar language to Latin script in order to bring it into the modern world of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
. There was opposition from both inside and outside Tatarstan, with Tatars arguing it would threaten their national identity and to sever their ties to the past. The Russian State Duma rejected the proposal. President Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
said that a Tatar move from Cyrillic to Latin would 'threaten the unity of the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
'. In 2002, Putin enacted a law that made Cyrillic the default script for all languages in all autonomous republics of Russia. Adoption of a different script is possible, but requires a separate law.
Ukraine
Ideas about Latinisation of theUkrainian language
Ukrainian ( uk, čāą║čĆą░čŚ╠üąĮčüčīą║ą░ ą╝ąŠ╠üą▓ą░, translit=ukrainska mova, label=native name, ) is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family. It is the native language of about 40 million people and the official state lan ...
can be traced as far back as the 17th century, when Ukrainian lands in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth were under the influence of Polonisation
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in ąĪą╝ą░ą╗čÅąĮčćčāą║ ąÉ. ąż. (Smalyanchuk 2001) ą¤ą░ą╝č¢ąČ ą║čĆą░čæą▓ą░čüčåčÄ č¢ ąĮą░čåčŗčÅąĮą░ą╗čīąĮą░ą╣ č¢ą┤čŹčÅą ...
. In the 19th century, the so-called Alphabet War occurred amongst linguists in Galicia, during which pro-Polish Ukrainophile
Ukrainophilia is the love of or identification with Ukraine and Ukrainians; its opposite is Ukrainophobia. The term is used primarily in a political and cultural context. "Ukrainophilia" and "Ukrainophile" are the terms used to denote pro-Ukrainia ...
scholars argued for Latinisation of Ukrainian (then called " Ruthenian"), while anti-Polish Galician Russophiles (or Muscovites) sought closer cultural attachment to the Russian language and favoured the continued use of Cyrillic. In the 1920s and 1930s, Ukrainian was also part of the Latinisation in the Soviet Union
In the USSR, latinisation or latinization (russian: ą╗ą░čéąĖąĮąĖąĘą░╠üčåąĖčÅ, ') was the name of the campaign during the 1920sŌĆō1930s which aimed to replace traditional writing systems for all languages of the Soviet Union with systems that wo ...
, although this early internationalist Bolshevik policy would be reversed by Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; ŌĆō 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
.
In 2014, the city of Lviv
Lviv ( uk, ąøčīą▓č¢ą▓) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
in Western Ukraine began promoting transition to the Latin script. In 2017, Kyiv-based journalist Stanislav Rechinsky reinvigorated the topic of Latinisation under the slogan "The more we differ from Russia - the better". In March 2018, Foreign Minister of Ukraine Pavlo Klimkin
Pavlo Anatoliiovych Klimkin ( uk, ą¤ą░ą▓ą╗ąŠ ąÉąĮą░č鹊ą╗č¢ą╣ąŠą▓ąĖčć ąÜą╗č¢ą╝ą║č¢ąĮ; born 25 December 1967) is a Ukrainian diplomat who from 19 June 2014 until 29 August 2019 served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Ukraine. A Moscow-educated p ...
called for a discussion on the introduction of the Latin alphabet in parallel usage with the traditional Cyrillic one in Ukraine. He did so in response to the suggestion of Polish historian Ziemowit Szczerek. Ukraine's parliamentary committee on science and education responded, with first deputy chair Oleksandr Spivakovsky saying that today in Ukraine there are other, more important issues to work on than a transition to the Latin script. Similarly, philology professor Oleksandr Ponomariv was skeptical whether a full transition to Latin would benefit Ukraine, but did not rule out the parallel use of two alphabets. He pointed to the fact that the Serbian language
Serbian (, ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and co-official in Montenegro and K ...
is also expressed in both a Cyrillic and a Latin alphabet. Ukrainian philologist Oleksandr Polishchuk (2020) said that in the long term, it would be desirable 'to withdraw the Ukrainian
language from the Kremlin's cultural space. However, now is not the best time for this.' He pointed to the rapid growth of Ukrainian-language books published in the 2010s, and that a switch to Latin would threaten this nascent and still vulnerable book market, as it 'may take decades for people to get used to the new alphabet.' In 2021, Oleksiy Danilov
Oleksiy Miacheslavovych Danilov ( uk, ą×ą╗ąĄą║čüč¢ą╣ ą£čÅč湥čüą╗ą░ą▓ąŠą▓ąĖčć ąöą░ąĮč¢ą╗ąŠą▓; born 7 September 1962) is a Ukrainian politician. He is the current Secretary of the National Security and Defense Council (since 3 October 2019).
...
, the Ukrainian Secretary of the National Security and Defense Council
The National Security and Defense Council of Ukraine (NSDC; uk, ąĀą░ą┤ą░ ąĮą░čåč¢ąŠąĮą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčŚ ą▒ąĄąĘą┐ąĄą║ąĖ č¢ ąŠą▒ąŠčĆąŠąĮąĖ ąŻą║čĆą░茹ĮąĖ, RNBO or RNBOU) is the coordinating state body of the executive power under the President of Ukrai ...
, also called for the country to switch to the Latin alphabet.
Linguist I.I. ą£č¢nkovska (2019) stated: "Currently, in the world there are more than 20 Ukrainian-Latin alphabet transliteration standards that are used to a greater or lesser extent", "but none of them is approved at the Ukrainian official level." She argued that the government-used "Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine 2010" standard "does not meet the basic principles of transliteration in the best way", and other systems had other flaws. On 1 April 2022, the "Cyrillic-Latin transliteration and Latin-Cyrillic retransliteration of Ukrainian texts. Writing rules" (SSOU 9112:2021), jointly proposed and developed by the State Scientific and Technical Library of Ukraine and the Technical Committee 144 ŌĆ£Information and DocumentationŌĆØ, came into force as the national standard of the Ukrainian Latin alphabet
The Ukrainian Latin alphabet (Ukrainian: ąŻą║čĆą░茹Įčüčīą║ą░ ą╗ą░čéąĖąĮąĖčåčÅ, tr. ''Ukrainska latynytsia'' or ąøą░čéąĖąĮą║ą░, tr. ''Latynka'') is the form of the Latin script used for writing, transliteration and retransliteration of Ukrainia ...
. It would be used in future cooperation between the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and Ukraine, in which "Ukrainian will soon, along with other European languages, take its rightful place in multilingual natural language processing scenarios, including machine translation."
Crimean Tatar
In September 2021, the Ukrainian Cabinet of Ministers announced that it intends to approve a new alphabet of the Crimean Tatar language which would be based on the Latin script.See also
* Latinisation of names *Metrication
Metrication or metrification is the act or process of converting to the metric system of measurement. All over the world, countries have transitioned from local and traditional units of measurement to the metric system. This process began in ...
*Romanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, a ...
, conversion of a text in Latin (or Roman) letters
References
{{Latin script Latin script History of writing Language geography