The Spanish American wars of independence (25 September 1808 – 29 September 1833; es, Guerras de independencia hispanoamericanas) were numerous wars in Spanish America with the aim of political independence from Spanish rule during the early 19th century. These began shortly after the start of the
French invasion of Spain during the
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
. Thus, the strict period of military campaigns would go from the battle of Chacaltaya (1809), in present-day Bolivia, to the battle of Tampico (1829), in Mexico.
In 1808, the sequestration of the
Spanish royal family by
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, the
Abdications of Bayonne, gave rise to an emergence of
liberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for c ...
and desire for liberties throughout the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
. The violent conflicts started in 1809, with short-lived
governing juntas established in
Chuquisaca,
La Paz and
Quito opposing the government of the
Supreme Central Junta of Seville. At the beginning of 1810,
numerous new juntas appeared across the Spanish domains in the Americas when the Central Junta fell to the French invasion. Although various regions of Spanish America objected to many crown policies, "there was little interest in outright independence; indeed there was widespread support for the Spanish Central Junta formed to lead the resistance against the French." While some Spanish Americans believed that independence was necessary, most who initially supported the creation of the new governments saw them as a means to preserve the region's autonomy from the French. Although there had been research on the idea of a separate Spanish American ("creole") identity separate from that of
Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, political independence was not initially the aim of most Spanish Americans, nor was it necessarily inevitable. But the conflict began as a dispute between
Liberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for c ...
movements in both hemispheres between those who wanted a unitary monarchy in Spain rather than a plural monarchy in Spanish America.
At the end of 1810,
Ferdinand VII of Spain
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Charles IV of Spain
, mother = Maria Luisa of Parma
, birth_date = 14 October 1784
, birth_place = El Escorial, Spain
, death_date =
, death_place = Madrid, Spain
, burial_p ...
, captive, was recognized by the
Cortes of Cádiz and by the governing juntas in the Americas as a subordinate king to
popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
. In agreement on this, a military conflict arose between Royalists and Patriots over the unity or independence of the empire. However, in 1814, with the defeat of Napoleon after the
treaty of Valençay
The Treaty of Valençay (11 December 1813), after the château of the same name belonging to former French foreign minister Charles Maurice de Talleyrand, was drafted by Antoine René Mathurin and José Miguel de Carvajal y Manrique on behalf of ...
, Ferdinand VII returned, and with a
coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
, reimposed
absolutism. Ferdinand was able to defeat and repress the peninsular liberals, and abolished the
liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
Constitution of Cadiz
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constituti ...
, although he could not defeat the revolutionaries, who resisted and formed their own national congresses. The Spanish navy had collapsed in the war against Napoleon, so therefore, in practice, was supporting the expeditionary forces who arrived in small groups. In 1820 the Spanish army, led by
Rafael Riego, revolted against absolutism, restored the so-called
Trienio Liberal, and ended the threat of invasion against the
Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
and
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, but did not change the position of Spain against separatism, resulting in
the defenders of the King collapsing in Americas. Over the course of the next decade, the Patriots’ armies won major victories and obtained independence in their respective countries. The political instability in Spain, without a navy, army or treasury, convinced many Spanish Americans of the need to formally establish independence from the
mother country
A homeland is a place where a cultural, national, or racial identity has formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethn ...
. In Spain, a
French army of the Holy Alliance invaded and supported the absolutists, restored Ferdinand VII, and occupied Spain until
1828
Events
January–March
* January 4 – Jean Baptiste Gay, vicomte de Martignac succeeds the Comte de Villèle, as Prime Minister of France.
* January 8 – The Democratic Party of the United States is organized.
* January 22 – Arth ...
.
These conflicts were fought both as
irregular warfare and
conventional warfare
Conventional warfare is a form of warfare conducted by using conventional weapons and battlefield tactics between two or more states in open confrontation. The forces on each side are well-defined and fight by using weapons that target primari ...
. These wars began as localized civil wars, that later spread and expanded as
secessionist
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics l ...
civil wars to promote general independence from Spanish rule.
This independence led to the development of new national boundaries based on the
colonial provinces, which would form the future independent countries that constituted contemporary Latin America during the early 19th century.
Cuba and Puerto Rico remained under
Spanish rule until the
Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
in 1898. The independence of Spanish America did not constitute an anticolonial movement. The conflict resulted in the dissolution of the Spanish Monarchy and the creation of new States. Slavery was not abolished, but the new republics immediately left the formal system of racial classification and hierarchy, the
caste system, the
Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
, and noble titles.
Criollos
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of Spanish descent born in the colonies. In different Latin American countries the word has come to have different meanings, sometimes referring to the local-born majo ...
(those of Spanish descent born in the New World) and
mestizos (those of mixed American Indigenous and Spanish blood or culture) replaced
Spanish-born appointees in most political governments. Criollos remained at the top of a social structure that retained some of its traditional features culturally, if not legally. Slavery finally ended in all of the new nations. For almost a century thereafter,
conservatives and liberals fought to reverse or to deepen the social and political changes unleashed by those rebellions.
The events in Spanish America were related to the
wars of independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars
Wars of national liberation or national liberation revolutions are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against for ...
in the former French colony of St. Domingue,
Haiti, and the transition to independence in Brazil.
Brazil's independence, in particular, shared a common starting point with that of Spanish America, since both conflicts were triggered by Napoleon's invasion of the Iberian Peninsula, which forced the Portuguese royal family
to flee to Brazil in 1807. The process of Latin American independence took place in the general political and intellectual climate of
Popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
that emerged from the
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
that influenced all of the
Atlantic Revolutions, including the earlier revolutions in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
. A more direct cause of the Spanish American wars of independence were the unique developments occurring within the
Kingdom of Spain and its
monarchy
A monarchy is a government#Forms, form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The legitimacy (political)#monarchy, political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restric ...
triggered by the
Cortes of Cadiz
Cortes, Cortés, Cortês, Corts, or Cortès may refer to:
People
* Cortes (surname), including a list of people with the name
** Hernán Cortés (1485–1547), a Spanish conquistador
Places
* Cortes, Navarre, a village in the South border of N ...
, concluding with the emergence of the new Spanish American republics in the post-Napoleonic world.
Historical context
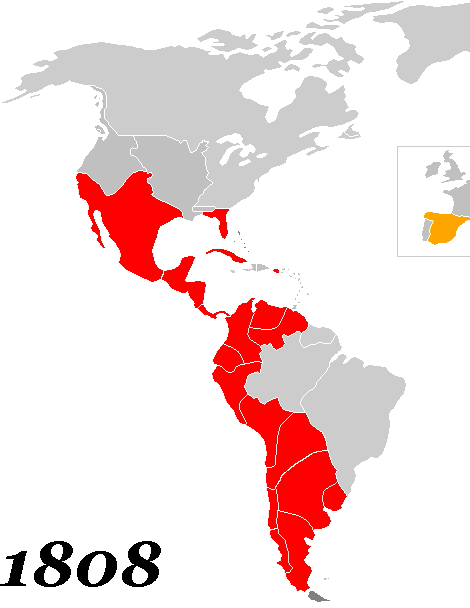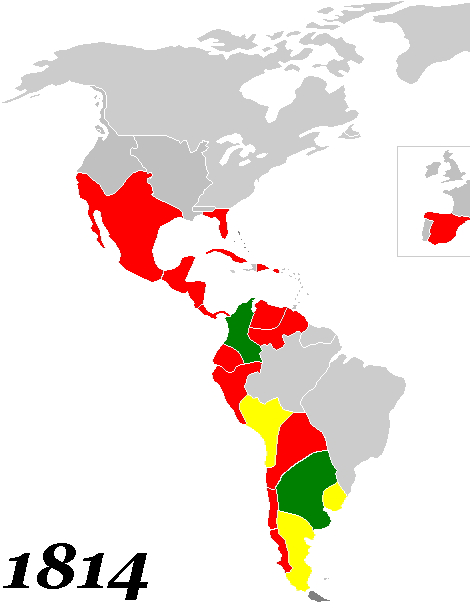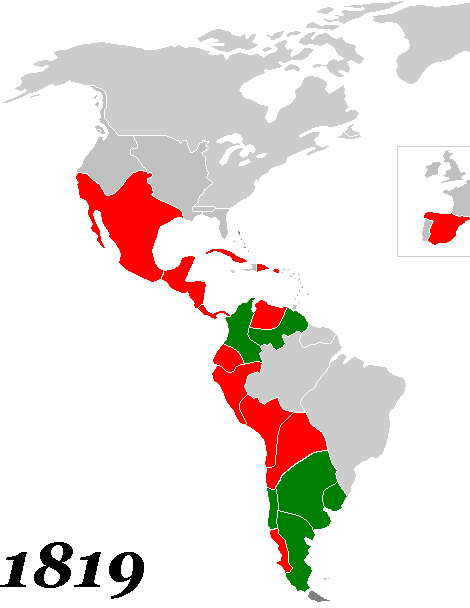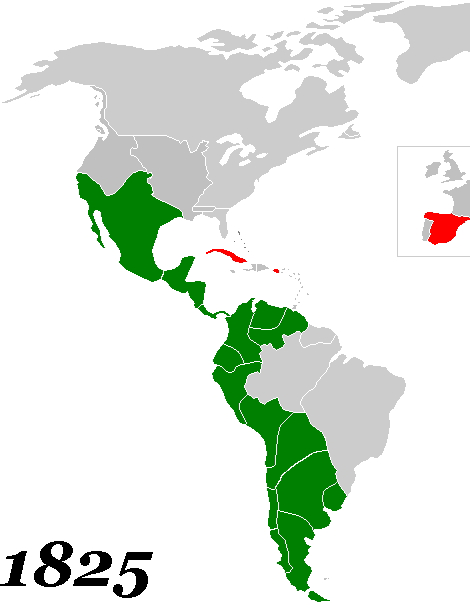
Political independence was not necessarily the foreordained outcome of the political turmoil in Spanish America. "There was little interest in outright independence." As historians
R.A. Humphreys and John Lynch note, "it is all too easy to equate the forces of discontent or even the forces of change with the forces of revolution." Since "by definition, there was no history of independence until it happened," when Spanish American independence did occur, explanations for why it came about have been sought. The Latin American Wars of Independence were essentially led by European diaspora against European empires.
Administrative and economic reforms
There are a number of factors that have been identified to have provoked the independent movements. First, increasing control by the Crown of its overseas empire via the
Bourbon Reforms of the mid-eighteenth century introduced changes to the relationship of Spanish Americans to the Crown. The language used to describe the overseas empire shifted from "kingdoms" with independent standing with the crown to "colonies" subordinate to Spain. In an effort to better control the administration and economy of the overseas possessions the Crown reintroduced the practice of appointing outsiders, almost all ''
peninsulars'', to the royal offices throughout the empire. This meant that Spanish American elites were thwarted in their expectations and ambitions by the crown's upending of long-standing practices of creole access to office holding.
The regalist and secularizing policies of the Bourbon monarchy were aimed at decreasing the power of the Roman Catholic Church. The crown had already
expelled the Jesuits in 1767, which saw many creole members of the Society of Jesus go into permanent exile. By limiting the power of the Church, the crown attempted to centralize itself within the institutions of colonial Latin America. Because of the physical and ideological proximity that the clergy had,
[Mills, Kenneth; Taylor, William B.; Lauderdale Graham, Sandra (2002). ''Colonial Latin America: A Documentary History''. Maryland: SP Books. p. 144.] they could directly influence and dictate the interactions between populations of colonial Latin America, either as legal counsel or an advisor;
[Mills, Kenneth; Taylor, William B. Taylor; Lauderdale Graham, Sandra (2002). ''Colonial Latin America: A Documentary History''. Maryland: SR Books. p. 107.] a directness which the crown would need to attempt to create the centralized, colonial state which it wanted to implement.
Later in the eighteenth century the crown sought to decrease the privileges (''fueros'') of the clergy, restricting clerical authority to spiritual matters and undermining the power of parish priests, who often acted as agents of the crown in rural parishes. By desacralizing power and frontal attacks on the clergy, the crown, according to
William B. Taylor, undermined its own legitimacy, since parish priests had been traditionally the "natural local representatives of their Catholic king."
In the economic sphere, the crown sought to gain control over church revenues. The Church functioned as one of the largest economic institutions within colonial Latin America. It owned and retained jurisdiction over large amounts of land,
which the crown wanted for itself because of the economic value which could be derived from the land. Moreover, by taking that land for itself, the Crown had the opportunity to cut down the physical presence of the Church to further weaken its ideological and social role within local colonial communities.
In a financial crisis of 1804, the crown attempted to call in debts owed the church, mainly in the form of mortgages for
haciendas owned by the elites. The Act of Consolidation simultaneously threatened the wealth of the church, whose capital was mainly lent for mortgages, as well as threatening the financial well-being of elites, who depended on mortgages for acquiring and keeping their estates. Shortening the repayment period meant many elites were faced with bankruptcy. The crown also sought to gain access to benefices elite families set aside to support a priest, often their own family members, by eliminating these endowed funds (''capellanías'') that the lower clergy depended on disproportionately. Prominently in Mexico, lower clergy participated in the insurgency for independence with priests
Miguel Hidalgo
Don Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla y Gallaga Mandarte Villaseñor (8 May 1753 – 30 July 1811), more commonly known as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or Miguel Hidalgo (), was a Catholic priest, leader of the Mexican ...
and
José María Morelos.
The reforms had mixed results. In some areas—such as
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
,
Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
and
New Spain—the reforms had positive effects, improving the local economy and the efficiency of the government. In other areas, the changes in the crown's economic and administrative policies led to tensions with locals, which at times erupted into open revolts, such as the
Revolt of the Comuneros
The Revolt of the Comuneros ( es, Guerra de las Comunidades de Castilla, "War of the Communities of Castile") was an uprising by citizens of Castile against the rule of Charles I and his administration between 1520 and 1521. At its height, th ...
in
New Granada and the
Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II
The Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II (4 November 1780 – 15 March 1783) was an uprising by ''cacique''-led Aymara, Quechua and ''mestizo'' rebels aimed at overthrowing Spanish colonial rule in Peru. The causes of the rebellion included oppositi ...
in
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
.
The loss of high offices to Peninsulars and the eighteenth-century revolts in Spanish South America were some of the direct causes of the wars of independence, which took place decades later, but they have been considered important elements of the political background in which the wars took place. Many Creoles, particularly the wealthy Creoles, were negatively impacted by the Bourbon Reforms.
This resulted in their taking action by using their wealth and positions within society, often as leaders within their communities, to spur resistance to convey their displeasure with Spanish reforms because of the negative economic impact which they had.
[Lynch, John (2001), "Spanish America's Poor Whites: Canarian Immigrants in Venezuela, 1700–1830", ''Latin America between Colony and Nation'', Palgrave Macmillan UK, pp. 58–73, , retrieved 13 January 2020] However, because of how quickly their revolts would further radicalize the lower classes, the Creoles quickly stopped supporting general violent insurrection because they benefitted from social change that occurred through the systems of the Spanish crown.
Institutional change ensured stability by supporting the political institutions that allowed for the creation of a wealthy Creole class and further adapting those institutions to meet demands, rather than propose a radical shift in the complete make-up of socioeconomic life and traditions.
However, institutional change did not come as anticipated and further spurred on the radicalization of Spanish-American social classes towards independence.
Military restructuring
Spain's international wars in the second half of the 18th century evidenced the empire's difficulties in reinforcing its colonial possessions and provide them with economic aid. This led to an increased local participation in the financing of the defense and an increased participation in the militias by the Chilean-born. Such development was at odds with the ideals of the centralized
absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism (European history), Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute pow ...
. The Spanish did also formal concessions to strengthen the defense: In
Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
Spanish authorities promised freedom from the
encomienda those
indigenous locals who settled near the new stronghold of
Ancud
Ancud () is a city in southern Chile located in the northernmost part of the island and province of Chiloé, in Los Lagos Region. It is the second largest city of Chiloé Archipelago after Castro. The city was established in 1768 to function as ...
(founded in 1768) and contributed to its defense. The increased local organization of the defenses would ultimately undermine metropolitan authority and bolster the independence movement.
Spread of Enlightment ideals
Other factors may include
Enlightenment thinking and the examples of the Atlantic Revolutions. The Enlightenment spurred the desire for social and economic reform to spread throughout Spanish America and the Iberian Peninsula. Ideas about free trade and
physiocratic economics were raised by the
Enlightenment in Spain and spread to the overseas empire and a homegrown
Spanish American Enlightenment. The political reforms implemented and the many constitutions written both in Spain and throughout the Spanish world during the wars of independence were influenced by these factors.
Creation of new ruling institutions in Spain and Americas, 1808–1810
Collapse of the Bourbon dynasty

The Peninsular War was the trigger for conflicts in Spanish America in the absence of a legitimate monarch. The Peninsular War began an extended period of instability in the worldwide Spanish monarchy that lasted until 1823. Napoleon's capture of the Bourbon monarchs precipitated a political crisis in Spain and Spanish America. Although the Spanish world almost uniformly rejected Napoleon's plan to place his brother,
Joseph, on the throne, there was no clear solution to the lack of a king. Following traditional Spanish political theories on the contractual nature of the monarchy (see
Philosophy of Law of Francisco Suárez), the peninsular provinces responded to the crisis by establishing
juntas. The move, however, led to more confusion, since there was no central authority and most juntas did not recognize the claim of some juntas to represent the monarchy as a whole. The Junta of Seville, in particular, claimed authority over the overseas empire, because of the province's historic role as the exclusive
entrepôt
An ''entrepôt'' (; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into c ...
of the empire.
This impasse was resolved through negotiations between the several juntas in Spain counted with the participation of the
Council of Castile
The Council of Castile ( es, Real y Supremo Consejo de Castilla), known earlier as the Royal Council ( es, Consejo Real), was a ruling body and key part of the domestic government of the Crown of Castile, second only to the monarch himself. It ...
, which led to the creation of a main government: the "
Supreme Central and Governmental Junta of Spain and the Indies" on 25 September 1808. It was agreed that the kingdoms of the peninsula would send two representatives to this Supreme Central Junta, and that the overseas kingdoms would send one representative each. These kingdoms were defined as "the
viceroyalties of
New Spain (Mexico),
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
,
New Granada, and
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, and the independent
captaincies general of the island of
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
,
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
,
Guatemala,
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
, Province of
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, and the
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
." This plan was criticized for providing unequal representation to Spanish America; nevertheless, throughout the end of 1808 and early 1809, the regional capitals elected candidates, whose names were forwarded to the capitals of the viceroyalties or captaincies general. Several important and large cities were left without direct representation in the Supreme Junta. In particular
Quito and
Chuquisaca, which saw themselves as the capitals of kingdoms, resented being subsumed in the larger
Viceroyalty of Peru
The Viceroyalty of Peru ( es, Virreinato del Perú, links=no) was a Spanish imperial provincial administrative district, created in 1542, that originally contained modern-day Peru and most of the Spanish Empire in South America, governed fro ...
and
Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
The Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata ( es, Virreinato del Río de la Plata or es, Virreinato de las Provincias del Río de la Plata) meaning "River of the Silver", also called " Viceroyalty of the River Plate" in some scholarly writings, i ...
respectively. This unrest led to the establishment of juntas in these cities in 1809, which were eventually quashed by the authorities within the year. An unsuccessful attempt at establishing a junta in New Spain was also stopped.
Spanish institutional revolution

The escape to
Cádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia.
Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, ...
and the dissolution of the Supreme Central Junta on 29 January 1810, because of the reverses suffered after the
Battle of Ocaña by the Spanish forces paid with Spanish American money, set off another wave of juntas being established in the Americas. French forces had taken over southern Spain and forced the Supreme Junta to seek
refuge in the island-city of Cádiz.
The Supreme Junta replaced itself with a smaller, five-man council, called the Regency, or the
Council of Regency of Spain and the Indies. Next, to establish a more legitimate government system, the Regency called for the convening of an "extraordinary and general
Cortes of the Spanish Nation": which was convened as the
Cortes of Cádiz. The plan for the election of the Cortes, based on provinces, and not kingdoms, was more equitable and provided more time to determine what would be considered an overseas province. The Cortes of Cádiz was the first national assembly to claim
sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
in Spain.
It represented the abolition of the old kingdoms. The opening session was held on 24 September 1810, in the building now known as the Real Teatro de las Cortes under the siege of French army. It met as one body and its members represented the entire Spanish empire.
[ citation: "It met as one body, and its members represented the entire Spanish world"]
Response in Spanish America
Most Spanish Americans saw no reason to recognize a rump government that was under the threat of being captured by the French at any moment, and began to work for the creation of
local juntas to preserve the region's independence from the French. Junta movements were successful in New Granada (Colombia),
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
,
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
and
Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
(Argentina). Less successful, though serious movements, also occurred in
Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
. Ultimately, Central America, along with most of New Spain, Quito (Ecuador), Peru,
Upper Peru (Bolivia), the Caribbean and the Philippine Islands remained under control of royalists for the next decade and participated in the
Cortes of Cádiz efforts to establish a liberal government for the Spanish Monarchy.
Military campaigns

Although on the battlefield the fight was to the death and without quarter, however, the recruitment of soldiers seemed to end up a common pool employed by opposing sides as cannon fodder. Socially, both apparently opposing positions, loyalist and pro-independence, had an uncertain significance for the different social strata of the monarchy. In Europe, the Spaniards made a forced recruitment for the expeditionary forces, leading to constant rebellions. Independent states relied on privateers, mercenaries, adventurers or filibusters, reliable fighters when pay or booty was at a glance. For the mobilization of the population in America, the vast majority or almost all of the troops of both sides, the indiscriminate recruitment of native American communities was used, in general in traditional confronted regions; social improvements were promised, by both sides, to the indigenous and the different mestizo colonial castes, such as mulattoes ("pardos"), cholos, etc., and even African slaves were recruited by both sides. All those recruited in America, and also the Spaniards, joined the enemy armies as combatants when they were captured. Likewise, the Creole potentates of European origin could give their support to the royalist or pro-independence cause, in relation to the commercial interests of each region. The Church was also divided, and except for the lower clergy, involved as combatants of insurgency, their position was in accordance with the political power.
Civil wars for disputed sovereignty, 1810–14
The creation of juntas in Spanish America, such as the ''
Junta Suprema de Caracas'' on 19 April 1810, set the stage for the fighting that would afflict the region for the next decade and a half. Political fault lines appeared, and were often the causes of military conflict. On the one hand the juntas challenged the authority of all royal officials, whether they recognized the Regency or not. On the other hand, royal officials and Spanish Americans who desired to keep the empire together were split between liberals, who supported the efforts of the Cortes, and conservatives (often called "
absolutists" in the historiography), who did not want to see any innovations in government. Finally, although the juntas claimed to carry out their actions in the name of the deposed king,
Ferdinand VII, their creation provided an opportunity for people who favored outright independence to promote their agenda publicly and safely. The proponents of independence called themselves patriots, a term which eventually was generally applied to them.
The idea that independence was not the initial concern is evidenced by the fact that few areas declared independence in the years after 1810. The congresses of Venezuela and New Granada did so in 1811 and also Paraguay in same year (14 and 15 May 1811). Some historians explain the reluctance to declare independence as a "mask of Ferdinand VII": that is, that patriot leaders felt that they needed to claim loyalty to the deposed monarch to prepare the masses for the radical change that full independence eventually would entail. Nevertheless, even areas such as Río de la Plata and Chile, which more or less maintained de facto independence from the peninsular authorities, did not declare independence until quite a few years later, in 1816 and 1818, respectively. Overall, despite achieving formal or de facto independence, many regions of Spanish America were marked by nearly continuous civil wars, which lasted well into the 1820s. In Mexico, where the junta movement had been stopped in its early stages by a coalition of Peninsular merchants and government officials, efforts to establish a government independent of the Regency or the French took the form of rebellion, under the leadership of
Miguel Hidalgo
Don Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla y Gallaga Mandarte Villaseñor (8 May 1753 – 30 July 1811), more commonly known as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or Miguel Hidalgo (), was a Catholic priest, leader of the Mexican ...
. Hidalgo was captured and executed in 1811, but a resistance movement continued, which
declared independence from Spain in 1813. The
Gutiérrez–Magee Expedition
The Gutiérrez–Magee Expedition was an 1812–1813 joint filibustering expedition by Mexico and the United States against Spanish Texas during the early years of the Mexican War of Independence.
Background
In 1810, Father Miguel Hidalgo y Cos ...
was a joint Tejanos-US volunteers expedition formed in
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
for Texas independence but was defeated in the
Battle of Medina. In Central America,
attempts at establishing juntas were also put down, but resulted in significantly less violence. The Caribbean islands, like the Philippines on the other side of the world, were relatively peaceful. Any plots to set up juntas were denounced to the authorities early enough to stop them before they gained widespread support.
Major cities and regional rivalries

Major cities and regional rivalry played an important role in the wars. The disappearance of a central, imperial authority—and in some cases of even a local, viceregal authority (as in the cases of New Granada and Río de la Plata)—initiated a prolonged period of
balkanization in many regions of Spanish America. It was not clear which political units should replace the empire, and there were no new national identities to replace the traditional sense of being Spaniards. The original juntas of 1810 appealed first to a sense of being Spanish, which was counterposed to the French threat; second, to a general American identity, which was counterposed to the Peninsula lost to the French; and third, to a sense of belonging to the major cities or local province, the ''
patria'' in Spanish. More often than not, juntas sought to maintain a province's independence from the capital of the former viceroyalty or captaincy general as much as from the Peninsula itself. Armed conflicts broke out between the provinces over the question of whether some cities or provinces were to be subordinate to others as they had been under the crown. This phenomenon was particularly evident in South America. This rivalry also led some regions to adopt the opposite political cause to that chosen by their rivals. Peru seems to have remained strongly royalist in large part because of its rivalry with Río de la Plata, to which it had lost control of Upper Peru when the latter was elevated to a viceroyalty in 1776. The creation of juntas in Río de la Plata allowed Peru to regain formal control of Upper Peru for the duration of the wars.
Social and racial tensions

Underlying social and racial tensions also had a great impact on the nature of the fighting. Rural areas were pitted against urban centers, as grievances against the authorities found an outlet in the political conflict. This was the case with Hidalgo's peasant revolt, which was fueled as much by discontent over several years of bad harvests as with events in the Peninsular War. Hidalgo was originally part of a circle of liberal urbanites in
Querétaro, who sought to establish a junta. After this conspiracy was discovered, Hidalgo turned to the rural people of the Mexican
Bajío to build his army, and their interests soon overshadowed those of the urban intellectuals. A similar tension existed in Venezuela, where the Spanish immigrant
José Tomás Boves formed a powerful, though irregular, royalist army out of the ''
Llaneros'', mixed-race slave and plains people, by attacking the white landowning class. Boves and his followers often disregarded the command of Spanish officials and were not concerned with actually re-establishing the toppled royal government, choosing instead to keep real power among themselves. Finally, in the back country of
Upper Peru, the ''
republiquetas'' kept the idea of independence alive by allying with disenfranchised members of rural society and native groups, but were never able to take the major population centers.
Increasingly violent confrontations developed between Spaniards and Spanish Americans, but this tension was often related to class issues or fomented by patriot leaders to create a new sense of nationalism. After being incited to rid the country of the ''gachupines'' (a disparaging term for ''Peninsulares''), Hidalgo's forces indiscriminately massacred hundreds of Criollos and ''Peninsulares'' who had taken refuge at the
Alhóndiga de Granaditas
The Alhóndiga de Granaditas (Regional Museum of Guanajuato) ( public grain exchange) is an old grain storage building in Guanajuato City, Mexico. This historic building was created to replace an old grain exchange near the city's river. The name ...
in Guanajuato. In Venezuela during his
Admirable Campaign
The Admirable Campaign () was a military action led by Simón Bolívar in which the provinces of Mérida, Barinas, Trujillo and Caracas were conquered by the Patriot Governments (Spanish American independence), Patriots.Arana, M., 2013, Bolivar, ...
,
Simón Bolívar instituted a policy of a
war to the death, in which royalist Spanish Americans would be purposely spared but even neutral ''Peninsulares'' would be killed, to drive a wedge between the two groups. This policy laid the ground for the violent royalist reaction under Boves. Often though, royalism or patriotism simply provided a banner to organize the aggrieved, and the political causes could be discarded just as quickly as they were picked up. The Venezuelan ''Llaneros'' switched to the patriot banner once the elites and the urban centers became securely royalist after 1815, and it was the royal army in Mexico that ultimately brought about that nation's independence.
King's war against independence, 1814–20
At the first years of war, during Spanish constitutional period, the main military effort of Spain was aimed at preserving the island of Cuba and the
viceroyalty of Mexico in North America. But in 1814, with the restoration of Ferdinand VII, the strategic line of the war changed drastically, directing the major Spanish military effort towards South America. By 1815 the general outlines of which areas were controlled by royalists and pro-independence forces were established and a general stalemate set in the war. In areas where royalists controlled the main population centers, most of the fighting by those seeking independence was done by isolated
guerrilla bands. In New Spain, the two main guerrilla groups were led by
Guadalupe Victoria in Puebla and
Vicente Guerrero in Oaxaca. In northern South America, New Granadan and Venezuelan patriots, under leaders such as
Simón Bolívar,
Francisco de Paula Santander,
Santiago Mariño,
Manuel Piar
Manuel Carlos María Francisco Piar Gómez (April 28, 1774 – October 16, 1817) was General-in-Chief of the army fighting Spain during the Venezuelan War of Independence.
Heritage and early life
The son of Fernando Alonso Piar y Lottyn, a Spani ...
and
José Antonio Páez, carried out campaigns in the vast
Orinoco River basin and along the Caribbean coast, often with material aid coming from
Curaçao and
Haiti. Also, as mentioned above, in Upper Peru, guerrilla bands controlled the isolated, rural parts of the country.
Restoration of Ferdinand VII
In March 1814, following the collapse of the
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental E ...
, Ferdinand VII was restored to the Spanish throne. This signified an important change, since most of the political and legal changes made on both sides of the Atlantic—the myriad of juntas, the Cortes in Spain and several of the congresses in the Americas, and many of the constitutions and new legal codes—had been made in his name. Before entering Spanish territory, Ferdinand made loose promises to the Cortes that he would uphold the Spanish Constitution. But once in Spain he realized that he had significant support from
conservatives
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
in the general population and the hierarchy of the
Spanish Catholic Church; so, on 4 May, he repudiated the Constitution and ordered the arrest of liberal leaders on 10 May. Ferdinand justified his actions by stating that the Constitution and other changes had been made by a Cortes assembled in his absence and without his consent. He restored the former legal codes and political institutions and promised to convene a new Cortes under its traditional form (with separate chambers for the clergy and the nobility), a promise never fulfilled. News of the events arrived through Spanish America during the next three weeks to nine months, depending on time it took
goods and people to travel from Spain.
Ferdinand's actions constituted a definitive de facto break both with the autonomous governments, which had not yet declared formal independence, and with the effort of Spanish liberals to create a representative government that would fully include the overseas possessions. Such a government was seen as an alternative to independence by many in New Spain, Central America, the Caribbean, Quito, Peru, Upper Peru and Chile. Yet the news of the restoration of the "
Ancien Régime" did not initiate a new wave of juntas, as had happened in 1809 and 1810, with the notable exception of the establishment of a junta in
Cuzco
Cusco, often spelled Cuzco (; qu, Qusqu ()), is a city in Southeastern Peru near the Urubamba Valley of the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cusco Region and of the Cusco Province. The city is the seventh most populous in Peru; ...
demanding the implementation of the Spanish Constitution. Instead most Spanish Americans were moderates who decided to wait and see what would come out of the restoration of normalcy. In fact, in areas of New Spain, Central America and Quito, governors found it expedient to leave the elected constitutional ''
ayuntamientos'' in place for several years to prevent conflict with the local society. Liberals on both sides of the Atlantic, nevertheless, continued to conspire to bring back a constitutional monarchy, ultimately succeeding in 1820. The most dramatic example of transatlantic collaboration is perhaps
Francisco Javier Mina's expedition to Texas and northern Mexico in 1816 and 1817.
Spanish Americans in royalist areas who were committed to independence had already joined the guerrilla movements. However, Ferdinand's actions did set areas outside of the control of the crown on the path to full independence. The governments of these regions, which had their origins in the juntas of 1810, and even moderates there, who had entertained a reconciliation with the crown, now saw the need to separate from Spain if they were to protect the reforms they had enacted.
Royalist military

During this period, royalist forces made advances into New Granada, which they controlled from 1815 to 1819, and into Chile, which they controlled from 1814 to 1817. Except for royalist areas in the northeast and south, the provinces of New Granada had maintained independence from Spain since 1810, unlike neighboring Venezuela, where royalists and pro-independence forces had exchanged control of the region several times. To pacify Venezuela and to retake New Granada, Spain organized in 1815 the largest armed force it ever sent to the New World, consisting of 10,500 troops and nearly sixty ships. (See,
Spanish reconquest of New Granada.) Although this force was crucial in retaking a solidly pro-independence region like New Granada, its soldiers were eventually spread out throughout Venezuela, New Granada, Quito, and Peru and were lost to tropical diseases, diluting their impact on the war. More importantly, the majority of the royalist forces were composed, not of soldiers sent from the peninsula, but of Spanish Americans.
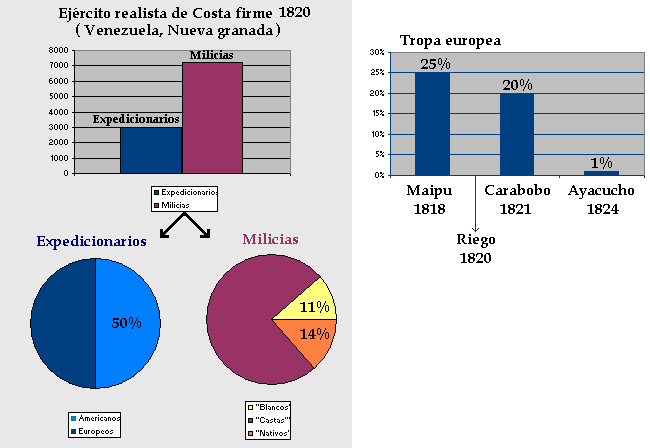
Overall, Europeans formed only about a tenth of the royalist armies in Spanish America, and only about half of the expeditionary units, once they were deployed in the Americas. Since each European soldier casualty was replaced by a Spanish American soldier, over time, there were more and more Spanish American soldiers in the expeditionary units. For example,
Pablo Morillo, commander in chief of the expeditionary force sent to South America, reported that he had only 2,000 European soldiers under his command in 1820; in other words, only half the soldiers of his expeditionary force were European. It is estimated that in the
Battle of Maipú only a quarter of the royalist forces were European soldiers, in the
Battle of Carabobo about a fifth, and in the
Battle of Ayacucho
The Battle of Ayacucho ( es, Batalla de Ayacucho, ) was a decisive military encounter during the Peruvian War of Independence. This battle secured the independence of Peru and ensured independence for the rest of South America. In Peru it is co ...
less than 1% was European.
The American militias reflected the racial make-up of the local population. For example, in 1820 the royalist army in Venezuela had 843 white (''español''), 5,378
Casta and 980
Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
soldiers.
Pro-independence advances
Towards the end of this period the pro-independence forces made two important advances. In the
Southern Cone, a veteran of the Spanish army with experience in the Peninsular War,
José de San Martín
José Francisco de San Martín y Matorras (25 February 177817 August 1850), known simply as José de San Martín () or '' the Liberator of Argentina, Chile and Peru'', was an Argentine general and the primary leader of the southern and centr ...
, became the governor of the
Province of Cuyo. He used this position to begin organizing an army as early as 1814 in preparation for an invasion of Chile. This was an important change in strategy after
three United Provinces campaigns had been defeated in
Upper Peru. San Martín's army became the nucleus of the
Army of the Andes
The Army of the Andes ( es, Ejército de los Andes) was a military force created by the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (Argentina) and mustered by general José de San Martín in his campaign to free Chile from the Spanish Empire. In 181 ...
, which received crucial political and material support in 1816 when
Juan Martín de Pueyrredón
Juan Martín de Pueyrredón y O'Dogan (December 18, 1777 – March 13, 1850) was an Argentine general and politician of the early 19th century. He was appointed Supreme Director of the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata after the Argentine ...
became
Supreme Director of the
United Provinces. In January 1817, San Martín was finally ready to advance against the royalists in Chile. Ignoring an injunction from the congress of the Río de la Plata not to move against Chile, San Martín together with General
Bernardo O'Higgins Riquelme, later Supreme Director of Chile, led the Army over the Andes in a move that turned the tables on the royalists. By 10 February, San Martín had control of northern and central Chile, and a year later, after a
war with no quarter, the south. With the aid of a fleet under the command of former British naval officer
Thomas Cochrane, Chile was secured from royalist control and independence was declared that year. San Martín and his allies spent the next two years planning an invasion of Peru, which began in 1820.
In northern South America, after several failed campaigns to take Caracas and other urban centers of Venezuela,
Simón Bolívar devised a similar plan in 1819 to cross the Andes and liberate New Granada from the royalists. Like San Martín, Bolívar personally undertook the efforts to create an army to invade a neighboring country, collaborated with pro-independence exiles from that region, and lacked the approval of the
Venezuelan congress. Unlike San Martín, however, Bolívar did not have a professionally trained army, but rather a quickly assembled mix of ''Llanero'' guerrillas, New Granadan exiles led by Santander and
British recruits. From June to July 1819, using the
rainy season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs.
Rainy Season may also refer to:
* ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King
* "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni
* '' ...
as cover, Bolívar led his army across the flooded plains and over the cold, forbidding passes of the Andes, with heavy losses—a quarter of the British Legion perished, as well as many of his ''Llanero'' soldiers, who were not prepared for the nearly 4,000-meter altitudes—but the gamble paid off. By August Bolívar was in control of
Bogotá and its treasury, and gained the support of many in New Granada, which still resented the harsh reconquest carried out under Morillo. Nevertheless, Santander found it necessary to continue the policy of the "war to the death" and carried out the execution of thirty-eight royalist officers who had surrendered. With the resources of New Granada, Bolívar became the undisputed leader of the patriots in Venezuela and orchestrated the union of the two regions in a new state called
Colombia (Gran Colombia).
Independence consolidated, 1820–25

To counter the advances the pro-independence forces had made in South America, Spain prepared a second, large, expeditionary force in 1819. This force, however, never left Spain. Instead, it became the means by which liberals were finally able to reinstate a constitutional regime. On 1 January 1820,
Rafael Riego, commander of the Asturias Battalion, headed a rebellion among the troops, demanding the return of the 1812 Constitution. His troops marched through the cities of
Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The t ...
with the hope of extending the uprising to the civilian population, but locals were mostly indifferent. An uprising, however, did occur in
Galicia in northern Spain, and from there it quickly spread throughout the country. On 7 March, the royal palace in Madrid was surrounded by soldiers under the command of General
Francisco Ballesteros, and three days later, on 10 March, the besieged Ferdinand VII, now a virtual prisoner, agreed to restore the Constitution.
Riego's Revolt had two significant effects on the war in the Americas. Militarily, the large numbers of reinforcements, which were especially needed to retake New Granada and defend the Viceroyalty of Peru, would never arrive. Furthermore, as the royalists' situation became more desperate in region after region, the army experienced wholesale defections of units to the patriot side. Politically, the reinstitution of a liberal regime changed the terms under which the Spanish government sought to engage the insurgents. The new government naively assumed that the insurgents were fighting for Spanish liberalism and that the Spanish Constitution could still be the basis of reconciliation between the two sides. The government implemented the Constitution and held elections in the overseas provinces, just as in Spain. It also ordered military commanders to begin armistice negotiations with the insurgents with the promise that they could participate in the restored representative government.
New Spain and Central America
In effect, the
Spanish Constitution of 1812
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constitut ...
adopted by the
Cortes of Cádiz served as the basis for independence in New Spain and Central America, since in both regions it was a coalition of conservative and liberal royalist leaders who led the establishment of new states. The Spanish Constitution of 1812 attempted to return to the policies that the Spanish government had implemented under Habsburg rule.
These policies gave recognized Spanish colonial territory as fellow kingdoms with equal standing to Spain.
The policies under the Habsburgs, moreover, allowed for constant revisionism, through corruption and the sale of office, that provided the opportunity to grant more rights and change policy to respond to the demands of the populations. The restoration of the Spanish Constitution and representative government was enthusiastically welcomed in New Spain and Central America. Elections were held, local governments formed and
deputies
A legislator (also known as a deputy or lawmaker) is a person who writes and passes laws, especially someone who is a member of a legislature. Legislators are often elected by the people of the state. Legislatures may be supra-national (for ex ...
sent to the Cortes. The Spanish Constitution of 1812 could have been an opportunity to enact social change slowly and without the threat of a radicalized uprising from the lower social classes by offering an opportunity to enact change that those in power would believe would best benefit their respective territories.
Among liberals, however, there was fear that the new regime would not last; and conservatives and the Church worried that the new liberal government would expand its reforms and anti-clerical legislation. Yet, because the Cortes of Cádiz was located in Spain, political and economic power and decisions were localized in Spain, effectively giving them control over all of colonial Latin America.
These tensions further frustrated many Spanish-Americans because of their inability to control the politics that directly affected their economic and sociopolitical wellbeing, further leading them towards independence.
This climate of instability created the conditions for the two sides to forge an alliance. This alliance coalesced towards the end of 1820 behind
Agustín de Iturbide, a
colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge o ...
in the royal army, who at the time was assigned to destroy the guerrilla forces led by
Vicente Guerrero.
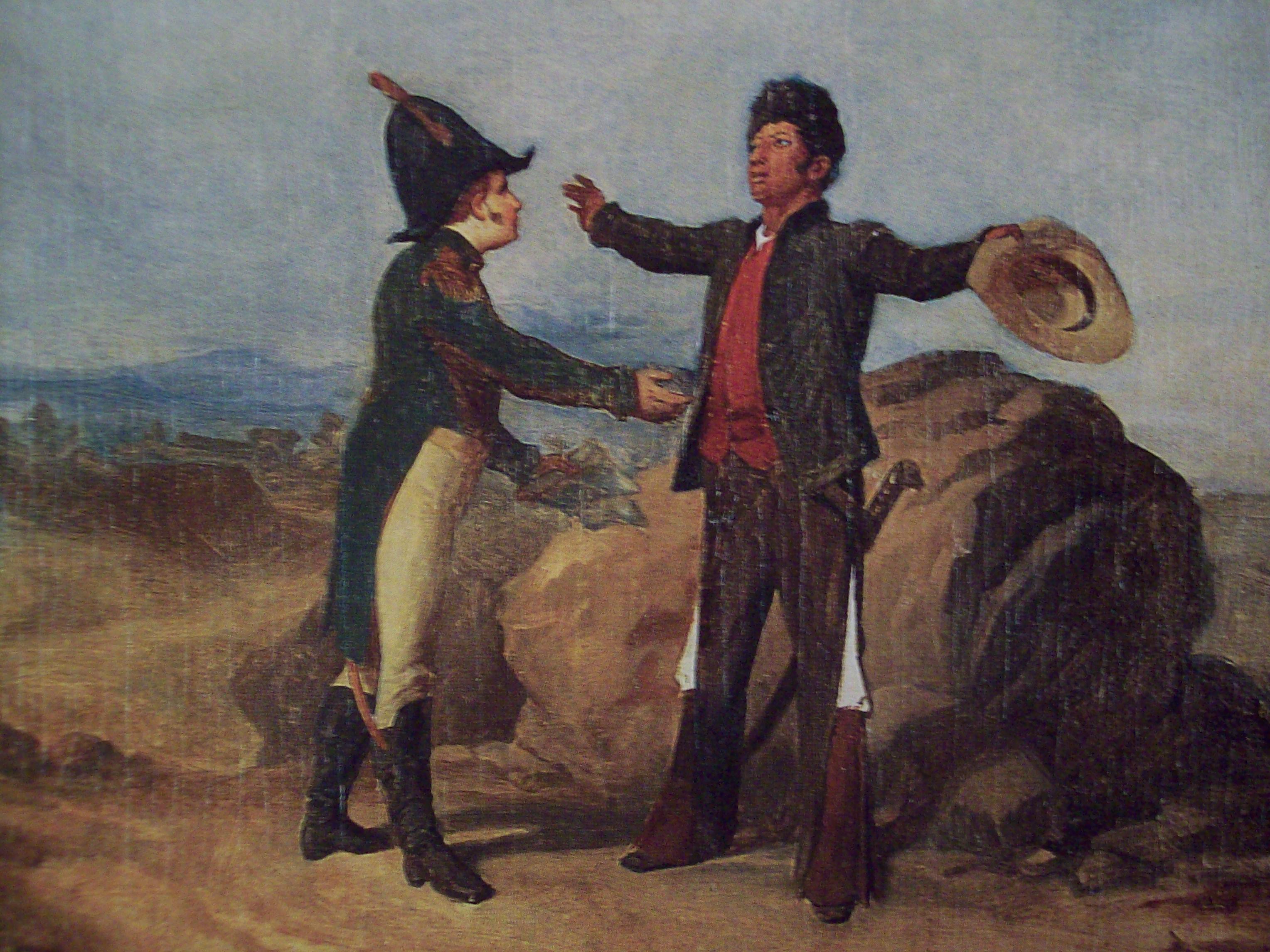

In January 1821, in expectation of the abolition in Spain of the Constitution of 1812, Iturbide was chosen and was sent by the officials of New Spain with Guerrero, the leader of the rebellions. He began so-called "peace" negotiations, suggesting the parties unite to establish an independent New Spain. Later, Iturbide was dethroned and quietly captured to be executed. The simple terms that Iturbide proposed became the basis of the
Plan of Iguala
The Plan of Iguala, also known as The Plan of the Three Guarantees ("Plan Trigarante") or Act of Independence of North America, was a revolutionary proclamation promulgated on 24 February 1821, in the final stage of the Mexican War of Independenc ...
: the independence of New Spain (now to be called the Mexican Empire) with Ferdinand VII or another Bourbon as emperor; the retention of the Catholic Church as the official state religion and the protection of its
existing privileges; and the equality of all New Spaniards, whether immigrants or native-born. Many of that laws was abolished decades later or are in present-day Mexico. The following month the other important guerrilla leader,
Guadalupe Victoria, joined the alliance, and on 1 March Iturbide was proclaimed head of a new
Army of the Three Guarantees
At the end of the Mexican War of Independence, the Army of the Three Guarantees ( es, Ejército Trigarante or ) was the name given to the army after the unification of the Spanish troops led by Agustín de Iturbide and the Mexican insurgent troo ...
. The representative of the new Spanish government, Superior Political Chief
Juan O'Donojú, who replaced the previous viceroys, arrived in
Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
on 1 July 1821, but he found that royalists held the entire country except for Veracruz, Mexico City and
Acapulco. Since at the time that O'Donojú had left Spain, the Cortes was considering greatly expanding the autonomy of the overseas Spanish possessions, O'Donojú proposed to negotiate a treaty with Iturbide on the terms of the Plan of Iguala. The resulting
Treaty of Córdoba
The Treaty of Córdoba established Mexican independence from Spain at the conclusion of the Mexican War of Independence. It was signed on August 24, 1821 in Córdoba, Veracruz, Mexico. The signatories were the head of the Army of the Three Guara ...
, which was signed on 24 August, kept all existing laws, including the 1812 Constitution, in force until a new constitution for Mexico could be written. O'Donojú became part of the provisional governing junta until his death on 8 October. Both the Spanish Cortes and Ferdinand VII rejected the Treaty of Córdoba, and the final break with the mother country came on 19 May 1822, when the Mexican Congress conferred the throne on Iturbide. Spain recognized Mexico's independence in 1836.
Central America gained its independence along with New Spain. On 15 September 1821, an
Act of Independence was signed in Guatemala City which declared Central America (Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica) independent from Spain. The regional elites supported the terms of the Plan of Iguala and
orchestrated the union of Central America with the Mexican Empire in January 1822. One years later, following Iturbide's downfall, the region, with the exception of Chiapas, peacefully seceded from Mexico on 1 July 1823, establishing the Federal Republic of Central America. The new state existed for seventeen years, centrifugal forces pulling the individual provinces apart by 1840.
South America

Unlike in New Spain and Central America, in South America independence was spurred by the pro-independence fighters who had held out for the past half-decade.
José de San Martín
José Francisco de San Martín y Matorras (25 February 177817 August 1850), known simply as José de San Martín () or '' the Liberator of Argentina, Chile and Peru'', was an Argentine general and the primary leader of the southern and centr ...
and
Simón Bolívar inadvertently led a continent-wide
pincer movement
The pincer movement, or double envelopment, is a military maneuver in which forces simultaneously attack both flanks (sides) of an enemy formation. This classic maneuver holds an important foothold throughout the history of warfare.
The pin ...
from southern and northern South America that liberated most of the
Spanish American nations on that continent. After securing the
independence of Chile in 1818, San Martín concentrated on building a naval fleet in the Pacific to counter
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
control of those waters and reach the
royalist stronghold of
Lima
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of ...
. By mid-1820 San Martín had assembled a fleet of eight warships and sixteen transport ships under the command of Admiral Cochrane. The fleet set sail from
Valparaíso to
Paracas in southern
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
. On 7 September, the army landed at Paracas and successfully took
Pisco
Pisco is a colorless or yellowish-to-amber colored brandy produced in winemaking regions of Peru and Chile. Made by distilling fermented grape juice into a high-proof spirit, it was developed by 16th-century Spanish settlers as an alternative ...
. After this, San Martín, waiting for a generalized Peruvian revolt, chose to avoid direct military confrontation. San Martín hoped that his presence would initiate an authentic
Peruvian revolt against Spanish rule, believing that otherwise any liberation would be ephemeral. In the meantime, San Martín engaged in diplomacy with Viceroy
Joaquín de la Pezuela, who was under orders from the constitutional government to negotiate on the basis of the
1812 Constitution and to maintain the unity of the
Spanish Monarchy
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
. However, these efforts proved fruitless, since independence and unity of the monarchy could not be reconciled, so the army sailed in late October to a better strategic position in
Huacho
Huacho () is a city in Peru, capital of the Huaura Province and capital of the Lima Region. Also is the most populated city of the Lima Region and Norte Chico. It is located 223 feet (68 metres) above sea level and 148 km north of the city of ...
, in northern Peru. During the next few months, successful land and naval campaigns against the royalists secured the new foothold, and it was at Huacho that San Martín learned that
Guayaquil
, motto = Por Guayaquil Independiente en, For Independent Guayaquil
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Ecuador#South America
, pushpin_re ...
(in
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
) had declared independence on 9 October.
Bolívar, learning about the
collapse of the Cádiz expedition, spent the year 1820 preparing a liberating campaign in
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. Bolívar was aided by Spain's new policy of seeking engagement with the insurgents, which Morillo implemented, renouncing to the command in chief, and returning to Spain. Although Bolívar rejected the Spanish proposal that the patriots rejoin Spain under the Spanish Constitution, the two sides established a six-month
truce and the regularization of the
rules of engagement
Rules of engagement (ROE) are the internal rules or directives afforded military forces (including individuals) that define the circumstances, conditions, degree, and manner in which the use of force, or actions which might be construed as pro ...
under the
law of nations on 25 and 26 November. The truce did not last six months. It was apparent to all that the royalist cause had been greatly weakened by the lack of reinforcements. Royalist soldiers and whole units began to desert or defect to the patriots in large numbers. On 28 January 1821, the ''
ayuntamiento
''Ayuntamiento'' ()In other languages of Spain:
* ca, ajuntament ().
* gl, concello ().
* eu, udaletxea (). is the general term for the town council, or ''cabildo'', of a municipality or, sometimes, as is often the case in Spain and Latin Amer ...
'' of
Maracaibo declared the province an independent republic that chose to join the new
nation-state of
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central Ameri ...
.
Miguel de la Torre, who had replaced Morillo as head of the army, took this to be a violation of the truce, and although the republicans argued that Maracaibo had switched sides of its own volition, both sides began to prepare for renewed war. The fate of Venezuela was sealed when Bolívar returned there in April leading an army of 7,000 from New Granada. At the
Battle of Carabobo on 24 June, the Gran Colombian forces decisively defeated the royalist forces, assuring control of Venezuela save for
Puerto Cabello and guaranteeing Venezuelan independence. Bolívar could now concentrate on Gran Colombia's claims to southern New Granada and Quito.

In Peru, on 29 January 1821, Viceroy Pezuela was deposed in a coup d'état by
José de la Serna, but it would be two months before San Martín moved his army closer to Lima by sailing it to
Ancón. During the next few months
San Martín once again engaged in negotiations, offering the creation of an independent monarchy; but La Serna insisted on the unity of the Spanish monarchy, so the negotiations came to nothing. By July La Serna judged his hold on Lima to be weak, and on 8 July the royal army abandoned the coastal city to reinforce positions in the highlands, with
Cuzco
Cusco, often spelled Cuzco (; qu, Qusqu ()), is a city in Southeastern Peru near the Urubamba Valley of the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cusco Region and of the Cusco Province. The city is the seventh most populous in Peru; ...
as new capital of the viceroyalty. On the 12th
San Martín entered Lima, where he was declared "Protector of the Country" on 28 July, an office which allowed him to rule the newly independent state.

To ensure that the Presidency of Quito became a part of Gran Colombia and did not remain a collection of small, divided republics, Bolívar sent aid in the form of supplies and an army under
Antonio José de Sucre
Antonio José de Sucre y Alcalá (; 3 February 1795 – 4 June 1830), known as the "Gran Mariscal de Ayacucho" ( en, "Grand Marshal of Ayacucho"), was a Venezuelan independence leader who served as the president of Peru and as the second p ...
to Guayaquil in February 1821. For a year Sucre was unable to take Quito, and by November both sides, exhausted, signed a ninety-day armistice. The following year, at the
Battle of Pichincha on 24 May 1822, Sucre's Venezuelan forces finally conquered Quito; Gran Colombia's hold on the territory was secure. The following year, after a Peruvian patriot army was destroyed in the
Battle of Ica, San Martín met with Simón Bolívar in
Guayaquil
, motto = Por Guayaquil Independiente en, For Independent Guayaquil
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Ecuador#South America
, pushpin_re ...
on 26 and 27 July. Thereafter San Martín decided to retire from the scene. For the next two years, two armies of ''Rioplatense'' (Argentinian), Chilean, Colombian and Peruvian patriots were destroyed trying to penetrate the royalist bastion in the
Andean
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S l ...
regions of Peru and
Upper Peru. A year later a Peruvian congress resolved to make Bolívar head of the patriot forces in the country. An internecine conflict between La Serna and General Pedro Antonio Olañeta, which was an extension of the
Liberal Triennium, proved to be the royalists' undoing. La Serna lost control of half of his best army by the beginning of 1824, giving the patriots an opportunity.
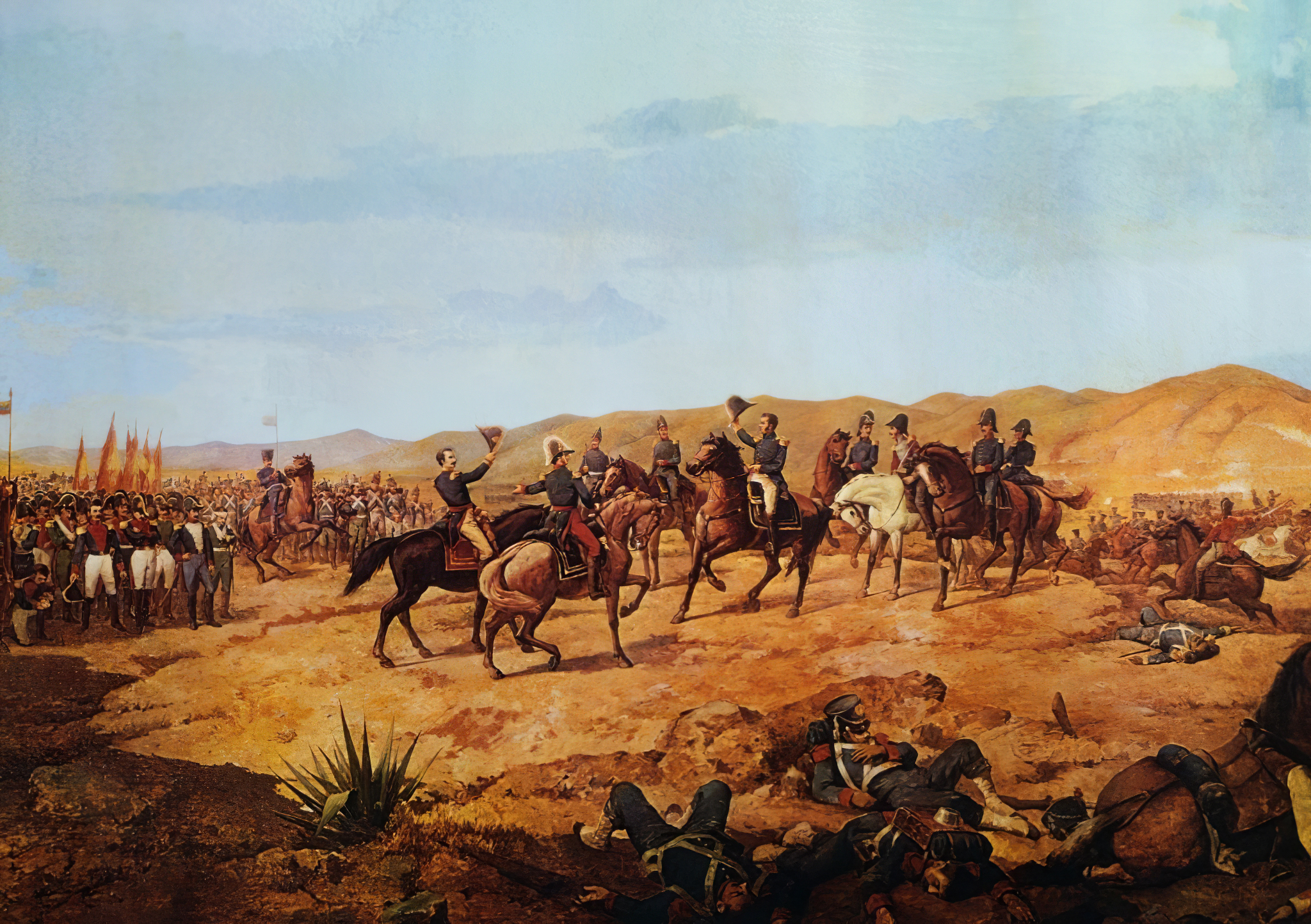

Under the command of Bolívar and Sucre, the experienced veterans of the combined army, mainly Colombians, destroyed a royalist army under La Serna's command in the
Battle of Ayacucho
The Battle of Ayacucho ( es, Batalla de Ayacucho, ) was a decisive military encounter during the Peruvian War of Independence. This battle secured the independence of Peru and ensured independence for the rest of South America. In Peru it is co ...
on 9 December 1824. La Serna's army was numerically superior but consisted of mostly new recruits. The only significant royalist area remaining on the continent was the highland country of
Upper Peru. Following the Battle of Ayacucho, the royalist troops of Upper Peru under the command of Olañeta surrendered after he died in
Tumusla on 2 April 1825. Bolívar tended to favor maintaining the unity of Upper Peru with Peru, but the Upper Peruvian leaders—many former royalists, like Casimiro Olañeta, nephew of General Olañeta—gathered in a congress under Sucre's auspices supported the country's independence. Bolívar left the decision to Sucre, who went along with the congress. Sucre proclaimed Upper Peru's independence in the
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
which now bears his name on 6 August, bringing the main wars of independence to an end.
As it became clear that there was to be no reversal of Spanish American independence, several of the new states began to receive international recognition. Early, in 1822, the United States recognized Chile, the
United Provinces of the Río de la Plata
The United Provinces of the Río de la Plata ( es, link=no, Provincias Unidas del Río de la Plata), earlier known as the United Provinces of South America ( es, link=no, Provincias Unidas de Sudamérica), was a name adopted in 1816 by the Co ...
, Peru,
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central Ameri ...
, and Mexico. Britain waited until 1825, after the Battle of Ayacucho, to recognize Mexico, Gran Colombia, and Río de la Plata. Both nations recognized more Spanish American states in the next few years.
Last royalist bastions, 1825-33

The Spanish coastal fortifications in
Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
,
Callao and
Chiloé were the footholds that resisted until 1825 and 1826 respectively. In the following decade, royalist guerrillas continued to operate in several countries and Spain launched a few attempts to retake parts of the Spanish American mainland. In 1827 Colonel
José Arizabalo started an irregular war with Venezuelan guerrillas, and Brigadier
Isidro Barradas led the last attempt with regular troops to
reconquer Mexico in 1829. The
Pincheira brothers
The Pincheira brothers (Spanish: ''Hermanos Pincheira'') was an infamous royalist outlaw group in Chile and Argentina active from 1818 to 1832. The gang fought initially in the Chilean War of Independence as royalist guerrillas during the Guer ...
moved to Patagonia and remained there as
multiethnic royalist outlaws gang until defeated in 1832. But efforts like these did not reverse the new political situation.
The increasing irrelevance of the
Holy Alliance
The Holy Alliance (german: Heilige Allianz; russian: Священный союз, ''Svyashchennyy soyuz''; also called the Grand Alliance) was a coalition linking the monarchist great powers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia. It was created after ...
after 1825 and the fall of the Bourbon dynasty in France in 1830 during the
July Revolution
The French Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution (french: révolution de Juillet), Second French Revolution, or ("Three Glorious ays), was a second French Revolution after the first in 1789. It led to the overthrow of King ...
eliminated the principal support of Ferdinand VII in Europe, but it was not until the king's death in 1833 that Spain finally abandoned all plans of military reconquest, and in 1836 its government went so far as to renounce sovereignty over all of continental America. During the course of the 19th century, Spain would recognize each of the new states. Only Cuba and Puerto Rico remained under Spanish rule, until the
Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
in 1898.
Effects of independence
Economics
The nearly decade and a half of wars greatly weakened the Spanish American economies and political institutions, which hindered the region's potential
economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and ...
for most of the nineteenth century and resulted in the enduring instability the region experienced. Independence destroyed the de facto
trade bloc
A trade bloc is a type of intergovernmental agreement, often part of a regional intergovernmental organization, where barriers to trade (tariffs and others) are reduced or eliminated among the participating states.
Trade blocs can be stand-alone ...
that was the Spanish Empire –
Manila galleon
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire ...
s and
Spanish treasure fleet
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to ...
s in particular. After independence, trade ''among'' the new Spanish American nations was less than it had been in the colonial period. Once the ties were broken, the small populations of most of the new nations provided little incentive to entice Spanish American producers to recreate the old trade patterns. In addition, the protection against European competition, which the Spanish monopoly had provided to the manufacturing sectors of the economy, ended. Due to expediency, protective tariffs for these sectors, in particular textile production, were permanently dropped and foreign imports beat out local production. This greatly affected Native communities, which in many parts of Spanish America, specialized in supplying finished products to the urban markets, albeit using pre-industrial-quarters in Mexico. Cities dependent on seaborne trade like
Valdivia plunged into depression as the intracolonial trade system collapsed.
Foreign trade policies varied among the new countries, some like the
United Provinces of the Río de la Plata
The United Provinces of the Río de la Plata ( es, link=no, Provincias Unidas del Río de la Plata), earlier known as the United Provinces of South America ( es, link=no, Provincias Unidas de Sudamérica), was a name adopted in 1816 by the Co ...
and
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
applied initially
protectionist
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. ...
policies while Chile was more open to foreign trade while still applying a kind of
neomercantilism.
[ Salazar, Gabriel; Pinto, Julio (2002). ''Historia contemporánea de Chile III. La economía: mercados empresarios y trabajadores.'' ]LOM Ediciones LOM Ediciones («Lom», means in yaghan language: «sun») is a Chilean press based in Santiago. It was established in 1990. Several Chileans and Latin American writers published in this press, like Pedro Lemebel, Tomas Moulian and Enrique Lihn
...
. pp. 19–21.
The new states that began to take root in Latin America, particularly Mexico, often courted foreign financial support from European nations.
[Ávila, Alfredo; Tutino, John, "Becoming MexicoThe Conflictive Search for a North American Nation", ''New CountriesCapitalism, Revolutions, and Nations in the Americas, 1750–1870'', Duke University Press, , retrieved 2020-01-13] This foreign investment often came via loans, which only continued to cripple economies that had been destroyed or left alone during conflict.
This investment was not enough to support economic recovery and can be considered to have only further negatively impacted economic growth in these newly developing states by pushing them further into debt in an attempt to recover and grow their economies.
As the newly independent nations finally entered the world economy after the end of the
French Revolutionary and
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, when the economies of Europe and the United States were recovering and aggressively seeking new markets to sell their products after more than two decades of disruption. Ultimately Spanish America could only connect to the world markets as an exporter of raw materials and a consumer of finished products.
Society
Independence from the Spanish crown required solidarity across all social classes. However, each social faction had their ideas of what local society should and would look like after independence.
This impacted the ability for societies to easily integrate because of the disunity of their ideas of future political systems and ideologies, which resulted in more conflict when it came to state consolidation.
The power which the elite Creole class commanded allowed them to control state and national development to ensure that they remained in power.
As a result, the newly forming Latin American states would fulfill some of the demands of other social factions to ensure the stability and integration of all into the social fabric of a new state while guaranteeing the continual reproduction of the Creole elite into position of power and control over the rest of society.
The political debate seeking answers to these questions was marked by a clash between liberalism and conservatism. Conservatives sought to maintain the traditional social structures to ensure stability; liberals sought to create a more dynamic society and economy by ending ethnically-based social distinctions and freeing property from economic restrictions. In its quest to transform society, liberals often adopted policies that were not welcome by Native communities, who had benefited from unique protections afforded to them by traditional Spanish law.
Independence, however, did initiate the
abolition of slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
in Spanish America, as it was seen as part of the independence struggle, since many slaves had gained their manumission by joining the patriot armies. In areas where slavery was not a major source of labor (Mexico, Central America, Chile), emancipation occurred almost immediately after independence was achieved. In areas where slavery was a main labor source (Colombia, Venezuela, Peru, Argentina), emancipation was carried out in steps over the next three decades, usually first with the creation of free-womb laws and programs for
compensated emancipation. By the early 1850s, slavery had been abolished in the independent nations of Spanish America.
Role of women

Women were not simply spectators throughout the Independence Wars of Latin America. Many women took sides on political issues and joined independence movements to participate on many different levels. Women could not help but act as caring relatives either as mother, sister, wives or daughters of the men who were fighting. Women created political organizations and organized meetings and groups to donate food and supplies to the soldiers.
Some women supported the wars as spies, informants and combatants.
Manuela Sáenz
Doña Manuela Sáenz de Vergara y Aizpuru (27 December 1797 – 23 November 1856) was an Ecuadorian revolutionary heroine of South America who supported the revolutionary cause by gathering information, distributing leaflets and protesting for ...
was a long term lover of
Simón Bolívar and acted as his spy and confidante and was secretary of his archive. She saved his life on two occasions, nursed wounded soldiers and has even been believed some historians to have fought in a few battles. Sáenz followed Bolívar and his army through the independence wars and became known in Latin America as the "mother of feminism and women's emancipation and equal rights."
Bolívar himself was a supporter of women's rights and suffrage in Latin America. It was Bolívar who allowed for Sáenz to become the great pioneer of women's freedom. He wanted to set the women of Latin America free from the oppression and inferiority of what the Spanish regime had established. Bolívar even made Sáenz a Colonel of the Colombian Army due to her heroics which caused controversy because there were no women in the army at the time. Another woman who gained prominence in the fight for independence was
Juana Azurduy de Padilla, a mixed-race woman who fought for independence in the Río de la Plata region. Argentine President
Cristina Fernández de Kirchner
Cristina Elisabet Fernández de Kirchner (; born 19 February 1953), often referred to by her initials CFK, is an Argentine lawyer and politician who has served as the Vice President of Argentina since 2019. She also served as the President o ...
posthumously promoted her to the rank of general.
According to gender stereotypes, women were not meant to be soldiers; only men were supposed to engage in fighting and conflict. There were still plenty of women present on the battlefields to help rescue and nurse soldiers. Some women fought alongside their husbands and sons on the battlefield. The majority of women assumed supportive and non-competitive roles such as fundraising and caring for the sick. Revolution for women meant something different than for men. Women saw revolution as a way to earn equal rights, such as voting, and to overcome the suppression of subordination of women to men.
Women were usually identified as victims during the independence wars since the women of Latin America were forced to sacrifice for the cause. The ideals of womanhood meant that women must sacrifice what the situation required such as a mother sacrificing her son or a virgin knowing she might be sacrificing motherhood or marriage due to the loss of many young men. This view meant that women were meant to contribute to independence in a supportive role while leaving the combat and politics in the hands of the men.
Government and politics

Independence also did not result in stable political regimes, save in a few countries. First, the new nations did not have well-defined identities, but rather the process of creating identities was only beginning. This would be carried out through newspapers and the creation of national symbols, including new names for the countries ("Mexico", "Colombia", "Ecuador", "Bolivia", "Argentina"), that broke with the past. In addition, the borders were not firmly established, and the struggle between
federalism and
centralism, which began in independence, continued throughout the rest of the century. Two large states that emerged from the wars—
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central Ameri ...
and the
Federal Republic of Central America
The Federal Republic of Central America ( es, República Federal de Centroamérica), originally named the United Provinces of Central America ( es, Provincias Unidas del Centro de América), and sometimes simply called Central America, in it ...
—collapsed after a decade or two, and Argentina would not
consolidate politically until the 1860s.
The wars destroyed the old civilian bureaucracy that had governed the region for centuries, as institutions such as the
audiencias were eliminated and many ''Peninsular'' officials fled to Spain. The Catholic Church, which had been an important social and political institution during the colonial period, initially came out weakened by the end of the conflicts. As with government officials, many ''Peninsular'' bishops abandoned their dioceses and their posts were not filled for decades until new prelates could be created and relations between the new nations and the
Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
were regularized. Then as the Church recovered, its economic and political power was attacked by liberals.
Despite the fact that the period of the wars of independence itself was marked by a rapid expansion of
representative government, for several of the new nations the nineteenth century was marked by militarism because of the lack of well-defined political and national institutions. The armies and officers that came into existence during the process of independence wanted to ensure that they got their rewards once the struggle was over. Many of these armies did not fully disband once the wars were over and they proved to be one of the stabler institutions in the first decades of national existence. These armies and their leaders effectively influenced the course of political development. Out of this new tradition came the
caudillo
A ''caudillo'' ( , ; osp, cabdillo, from Latin , diminutive of ''caput'' "head") is a type of personalist leader wielding military and political power. There is no precise definition of ''caudillo'', which is often used interchangeably with " ...
s, strongmen who amassed formal and informal economic, military and political power in themselves.
Foreign support
United Kingdom

Britain wanted to see an end to Spanish rule in South America and ultimately tap the monopoly of the important potential markets there. At the same time they wanted Spain as an ally to keep the balance of power in post Napoleonic Europe.
To fulfil this, Britain went covert in support of the Revolutionaries in South America. In a kind of private free enterprise going by the law, she sent men, financial and material support to help the insurgents fight against Spain.
[Baeza Ruz, Andrés (2017). "Imperio, Estado y Nación en las relaciones entre chilenos y británicos durante el proceso de independencia hispanoamericano, 1806-1831", pp 71-72]
One of the most significant contributions were the
British Legions
The British Legion () or British Legions were foreign volunteer units that fought under Simón Bolívar against Spain for the independence of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador and José de San Martín for the independence of Peru in the Spanish Ameri ...
, a
volunteer
Volunteering is a voluntary act of an individual or group freely giving time and labor for community service. Many volunteers are specifically trained in the areas they work, such as medicine, education, or emergency rescue. Others serve ...
unit that fought under
Simón Bolívar. This force numbered upwards of 6,000 men – the majority of whom were composed of veterans of the Napoleonic wars.
[Arana, M., 2013, Bolivar, New York: Simon & Schuster, ] In combat their greatest achievements were at
Boyacá (1819),
Carabobo (1821),
Pichincha (1822) and
Ayacucho (1824) which secured independence for Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador and Peru from Spanish rule respectively. Bolívar described the Legions and all who served in them as "the saviours of my country".
Many members of the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
also volunteered for the revolutionary forces. The most famous being
Thomas Cochrane who reorganised the
Chilean navy
The Chilean Navy ( es, Armada de Chile) is the naval warfare service branch of the Chilean Armed Forces. It is under the Ministry of National Defense. Its headquarters are at Edificio Armada de Chile, Valparaiso.
History
Origins and the War ...
, most of whom were composed of Royal Navy veterans. Amongst many feats
he captured the Spanish fortress of
Valdivia in 1820; and in the same year he
captured the flagship of the Spanish South American fleet, the
''Esmeralda'', in the port of
Callao. As well as helping Chile gain independence from Spain Cochrane did the same for Peru too by mounting an effective blockade and transporting troops. He then moved on to Brazil in their fight for independence from Portugal.
At their peak by 1819 around 10,000 men from the
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
served in South America to fight against the Spanish.
British diplomacy also played a key role; in particular the role of foreign secretaries
Viscount Castlereagh and later
George Canning both of whom wanted to see the demise of Spain's South American colonies. Castlereagh's greatest achievement was to settle a deal with the European powers at the
Congress of Aix-La-Chapelle in 1818 and the
Congress of Verona
The Congress of Verona met at Verona on 20 October 1822 as part of the series of international conferences or congresses that opened with the Congress of Vienna in 1814–15, which had instituted the Concert of Europe at the close of the Napol ...
four years later. This blocked aid to Spain which inhibited her reconquest of South America. With the Royal Navy in command of the oceans this set the precedence - they were also a decisive factor in the struggle for independence of certain Latin American countries.
United States
The intervention of the United States was due to two distinct causes; a territorial annexation and a revolts within the Spanish territories itself.
The Republic of West Florida was a short-lived republic in 1810 in the westernmost region of Spanish West Florida, which after less than three months was annexed and occupied by the United States a little later in 1810, and then became part of the territory of Louisiana. The Republic of East Florida was another republic declared against Spanish rule of East Florida by insurgents who wanted its annexation by the United States without success. In 1819, the
Treaty of Florida was signed between Spain and the United States, and Spain ceded all of Florida to the United States.
In 1811, the Spanish crushed the San Antonio (Texas) revolt during the revolution against the royalists in the Mexican War of Independence. The remaining rebels then turned to the United States for help. Bernardo Gutiérrez de Lara traveled to Washington, D.C. Gutierrez gained the support of
Augustus Magee and formed a U.S. filibuster force in Louisiana. A green flag from the expedition represented the rebels. The Northern Republican Army was defeated in the bloodiest battle in Texas, the Battle of Medina. Thus, Texas was incorporated into the Mexican Independence, and later Texas Independence and its annexation to the United States took place.
The United States remained neutral. Thus, for the rest of Madison's term, until 1817, the theoretical neutrality pending the development of events in the Old World. The point is, Madison's policy of neutrality favored insurgents and this, along with the border-line problems in North America, led to a situation of pre-war tension with Spain. This situation forced the United States to act very cautiously in the Spanish-American issue, since it was trying to avoid at all costs to give an excuse for European intervention. At the end, the recognition in 1822 also was very delicate, at the international level the North American position against European powers.
Russia
The Spanish navy had been totally dismantled by a disastrous naval policy and relegated to the background by the urgency of the war against Napoleon itself. To 1817, Tsar Alexander supported reactionary governments. Ferdinand VII applied to the Tsar to purchase vessels. The Tsar agreed to this request with the offer of the sale of some of his own vessels. The agreement was finally negotiated at Madrid, between
Dmitry Tatishchev, Russian ambassador, and Eguia, Minister of war. It was apparently known only to these two, and to the king himself. The text of the treaty of sale has not been found in the Spanish Naval archives. This diplomatic transaction was veiled in the deepest secrecy against Spanish Navy and Minister of Navy.
The requested fleet would consist of 5 warships and 3 frigates. The squadron would be delivered to Cadiz, duly armed, and supplied. The arrival of the Russian fleet in Cadiz in February 1818 was not to the liking of the Spanish navy, which was dissatisfied with the state of deterioration in which some supposedly new ships were found: between 1820 and 1823 all the Warships were scrapped as being useless. This fiasco put an end to the whole plan to reconquer the Rio de la Plata, which would end with the uprising of the Spanish Army in Cadiz (
Trienio Liberal). In 1818 one of the frigates (Maria Isabel aka Patrikki) was captured in the Pacific, after the uprising of one of the Spanish troop transports that went over to the side of the American rebels delivering all the keys, routes and signals for the capture of the frigate. Only two of the Russian frigates provided important services in the Caribbean in defense of the island of Cuba, although they only made the one-way trip, they got lost, sunk when they arrived in Havana.
Portuguese Empire
After a long colonial dispute between Spain, and to avoid insurgency in this disputed territory, the Portuguese government organized an Army to defend the city of Montevideo against the revolutionaries (1811) and to annexed the disputed territory of
Banda Oriental
Banda Oriental, or more fully Banda Oriental del Uruguay (Eastern Bank), was the name of the South American territories east of the Uruguay River and north of Río de la Plata that comprise the modern nation of Uruguay; the modern state of Rio Gra ...
against Spain (1816).
In 1811, the first Portuguese invasion took place in support of the besieged city of Montevideo. The Portuguese invasion forces were commanded by the governor and captain general of the Captaincy of Río Grande de San Pedro, Diego de Souza (Diogo de Souza), and their declared objective was to help Montevideo and the viceroy of the Río de la Plata, Francisco Javier de Elío, who was besieged by revolutionary forces from the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata. The invasion included clashes with eastern forces led by José Gervasio Artigas. After an ephemeral agreement, the Portuguese did not completely abandon the occupied territory.
In 1816, the second Portuguese Invasion or War against Artigas, giving rise to the armed conflict that took place between 1816 and 1820 in the entire territory of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, in the Argentine Mesopotamia and southern Brazil, and which resulted in the annexation of the Banda Oriental to the
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
, with the name of
Cisplatina
Cisplatina () was a Brazilian province in existence from 1821 to 1828 created by the Luso-Brazilian invasion of the Banda Oriental. From 1815 until 1822 Brazil was a constituent kingdom of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algar ...
Province. This annexation broke relations with Spain, which prepared an army in Spain to recover Montevideo and invade the Río de la Plata, but this project ended up in rebellion of entire Army in 1820 in Cádiz.
Portugal tries to ensure its annexation by being the first country to grant international recognition of the independence of Latin American Republics on 1821.
Overview
Wars, battles, and revolts
Pro-independence
Royalists
See also
*
Age of Revolution
The Age of Revolution is a period from the late-18th to the mid-19th centuries during which a number of significant revolutionary movements occurred in most of Europe and the Americas. The period is noted for the change from absolutist monarc ...
*
British Legions
The British Legion () or British Legions were foreign volunteer units that fought under Simón Bolívar against Spain for the independence of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador and José de San Martín for the independence of Peru in the Spanish Ameri ...
*
List of foreign volunteers
*
Insurgent privateer
Insurgent privateers ( es, corsarios insurgentes) were private armed vessels recruited by the insurgent governments during the Spanish American wars of independence to destroy Spanish trade and capture Spanish merchant vessels.
Privateering star ...
*
Philippine Revolution
*
Spanish reconquest of Mexico
*
Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
*
Latin American wars of independence
The Spanish American wars of independence (25 September 1808 – 29 September 1833; es, Guerras de independencia hispanoamericanas) were numerous wars in Spanish America with the aim of political independence from Spanish rule during the early ...
*
Wars of national liberation
Wars of national liberation or national liberation revolutions are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against foreign powers (or at least those perceived as foreign) to establish separa ...
*
History of South America
The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of South America. The continent continues to be home to indigeno ...
*
History of Mexico
The written history of Mexico spans more than three millennia. First populated more than 13,000 years ago, central and southern Mexico (termed Mesoamerica) saw the rise and fall of complex indigenous civilizations. Mexico would later develop ...
*
New Spain
*
Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales españolas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madri ...
*
Decolonization of the Americas
*
Timeline of the Spanish American wars of independence
*
Timeline of Mexican War of Independence
*
Panhispanism
Notes
References
Further reading
Spanish America and Spain
* Adelman, Jeremy. ''Sovereignty and Revolution in the Iberian Atlantic''. Princeton University Press 2006.
* Andrews, George Reid. "Spanish American independence: A structural analysis." ''Latin American Perspectives'' (1985): 105–132
online* Andrien, Kenneth J. and Lyman L. Johnson. ''The Political Economy of Spanish America in the Age of Revolution, 1750–1850''. Albuquerque, University of New Mexico Press, 1994.
* Anna, Timothy.. ''Spain & the Loss of Empire''. Lincoln, University of Nebraska Press, 1983.
* Archer, Christon I., ed.. ''The Wars of Independence in Spanish America''. Willmington, SR Books, 2000.
* Benson, Nettie Lee. ''Mexico and the Spanish Cortes, 1810–1822''. Austin: University of Texas Press 1966.
* Brading, D.A. ''The First America: The Spanish Monarchy, Creole Patriots and the Liberal State, 1492–1867''. Cambridge University Press, 1991.
*
Chasteen, John Charles. ''Americanos: Latin America's Struggle for Independence''. Oxford University Press, 2008.
* Costeloe, Michael P. ''Response to Revolution: Imperial Spain and the Spanish American Revolutions, 1810–1840''. Cambridge University Press, 1986.
* Domínguez, Jorge I. ''Insurrection or Loyalty: The Breakdown of the Spanish American Empire''. Cambridge, Harvard University Press, 1980.
* Graham, Richard. ''Independence in Latin America: A Comparative Approach'' (2nd edition). McGraw-Hill, 1994.
* Hamnett, Brian. ''The End of Iberian Rule on the American Continent, 1770–1830''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 2017.
* Harvey, Robert. ''Liberators: Latin America's Struggle For Independence, 1810–1830''. John Murray, London (2000).
* Higgins, James (editor). ''The Emancipation of Peru: British Eyewitness Accounts'', 2014. Online at https://sites.google.com/site/jhemanperu
* Humphreys, R. A., and John Lynch (editors). ''The Origins of the Latin American Revolutions, 1808–1826''. New York, Alfred A. Knopf, 1965.
* Kinsbruner, Jay. ''The Spanish-American Independence Movement''. (Krieger Publishing Company, 1976).
* Kinsbruner, Jay. ''Independence in Spanish America: Civil Wars, Revolutions, and Underdevelopment'' (2nd ed. University of New Mexico Press, 2000).
* Ladd, Doris M. ''The Mexican Nobility at Independence, 1780–1826''. Austin: University of Texas Press 1976.
* Lynch, John. ''Caudillos in Spanish America, 1800–1850''. Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1992.
* Lynch, John. ''The Spanish American Revolutions, 1808–1826'' (2nd edition). New York, W. W. Norton & Company, 1986.
* Lynch, John, ed. ''Latin American Revolutions, 1808–1826: Old and New World Origins '' (1995) 424pp; essays by scholars
* McFarlane, Anthony. ''War and Independence in Spanish America''. Routledge, 2014.
* Méndez, Cecilia. "Incas si, Indios no: Notes on Peruvian Creole Nationalism and Its Contemporary Crisis." ''Journal of Latin American Studies'', 28 (1) (Feb. 1996) pp. 197–225.
* Ossa Santa Cruz, Juan Luis. ''Armies, Politics, and Revolution: Chile 1808–1826''. Liverpool 2014.
* Rodríguez O., Jaime E. ''The Independence of Spanish America''. (Cambridge UP, 1998).
* Scheina, Robert L.. ''Latin America's Wars: The Age of the Caudillo, 1791–1899''. (Potomac Books, 2003).
Foreign involvement
* Bartley, Russell H. ''Imperial Russia and the Struggle for Latin American Independence, 1808–1828''. Austin: University of Texas Press 1978.
* Brown, Matthew. ''Adventuring through Spanish Colonies: Simón Bolívar, Foreign Mercenaries and the Birth of New Nations''. Liverpool University Press, 2006.
* Hasbrouck, Alfred. ''Foreign Legionaries in the Liberation of Spanish South America''. New York: Octagon Books, 1969.
* Hughes, Ben. ''Conquer or Die!: Wellington's Veterans and the Liberation of the New World'', Osprey 2010.
* Kaufman, William W. ''British Policy and the Independence of Latin America, 1804–1828''. New Haven, Yale UP, 1951.
* Robertson, William Spence. ''France and Latin American Independence''. (1939
online free to borrow* Rodríguez, Moises Enrique. ''Freedom's Mercenaries: British Volunteers in the Wars of Independence of Latin America'', 2 vols. Lanham, Hamilton Books, University Press of America, 2006.
* Whitaker, Arthur P. ''The United States and the Independence of Latin America, 1800–1830''. Johns Hopkins UP, 1941
online
Historiography
*
Adelman, Jeremy. "Independence in Latin America" in ''The Oxford Handbook of Latin American History'', José C. Moya, ed. New York: Oxford University Press 2011, pp. 153–180.
* Hensel, Silke. "Was There an Age of Revolution in Latin America?: New Literature on Latin American Independence." ''Latin American Research Review'' (2003) 38#3 pp: 237–249
online* Racine, Karen. "Simón Bolívar and friends: Recent biographies of independence figures in Colombia and Venezuela" ''History Compass'' 18#3 (Feb 2020) https://doi.org/10.1111/hic3.12608
* Uribe, Victor M. "The Enigma of Latin American Independence: Analyses of the Last Ten Years," ''Latin American Research Review'' (1997) 32#1 pp. 236–25
in JSTOR
{{Use dmy dates, date=May 2021
19th-century revolutions
Spanish colonization of the Americas
Rebellions against the Spanish Empire
Wars involving the states and peoples of North America
Aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars
Military emancipation
Age of Revolution
 Political independence was not necessarily the foreordained outcome of the political turmoil in Spanish America. "There was little interest in outright independence." As historians R.A. Humphreys and John Lynch note, "it is all too easy to equate the forces of discontent or even the forces of change with the forces of revolution." Since "by definition, there was no history of independence until it happened," when Spanish American independence did occur, explanations for why it came about have been sought. The Latin American Wars of Independence were essentially led by European diaspora against European empires.
Political independence was not necessarily the foreordained outcome of the political turmoil in Spanish America. "There was little interest in outright independence." As historians R.A. Humphreys and John Lynch note, "it is all too easy to equate the forces of discontent or even the forces of change with the forces of revolution." Since "by definition, there was no history of independence until it happened," when Spanish American independence did occur, explanations for why it came about have been sought. The Latin American Wars of Independence were essentially led by European diaspora against European empires.
 The Peninsular War was the trigger for conflicts in Spanish America in the absence of a legitimate monarch. The Peninsular War began an extended period of instability in the worldwide Spanish monarchy that lasted until 1823. Napoleon's capture of the Bourbon monarchs precipitated a political crisis in Spain and Spanish America. Although the Spanish world almost uniformly rejected Napoleon's plan to place his brother, Joseph, on the throne, there was no clear solution to the lack of a king. Following traditional Spanish political theories on the contractual nature of the monarchy (see Philosophy of Law of Francisco Suárez), the peninsular provinces responded to the crisis by establishing juntas. The move, however, led to more confusion, since there was no central authority and most juntas did not recognize the claim of some juntas to represent the monarchy as a whole. The Junta of Seville, in particular, claimed authority over the overseas empire, because of the province's historic role as the exclusive
The Peninsular War was the trigger for conflicts in Spanish America in the absence of a legitimate monarch. The Peninsular War began an extended period of instability in the worldwide Spanish monarchy that lasted until 1823. Napoleon's capture of the Bourbon monarchs precipitated a political crisis in Spain and Spanish America. Although the Spanish world almost uniformly rejected Napoleon's plan to place his brother, Joseph, on the throne, there was no clear solution to the lack of a king. Following traditional Spanish political theories on the contractual nature of the monarchy (see Philosophy of Law of Francisco Suárez), the peninsular provinces responded to the crisis by establishing juntas. The move, however, led to more confusion, since there was no central authority and most juntas did not recognize the claim of some juntas to represent the monarchy as a whole. The Junta of Seville, in particular, claimed authority over the overseas empire, because of the province's historic role as the exclusive  The escape to
The escape to  Although on the battlefield the fight was to the death and without quarter, however, the recruitment of soldiers seemed to end up a common pool employed by opposing sides as cannon fodder. Socially, both apparently opposing positions, loyalist and pro-independence, had an uncertain significance for the different social strata of the monarchy. In Europe, the Spaniards made a forced recruitment for the expeditionary forces, leading to constant rebellions. Independent states relied on privateers, mercenaries, adventurers or filibusters, reliable fighters when pay or booty was at a glance. For the mobilization of the population in America, the vast majority or almost all of the troops of both sides, the indiscriminate recruitment of native American communities was used, in general in traditional confronted regions; social improvements were promised, by both sides, to the indigenous and the different mestizo colonial castes, such as mulattoes ("pardos"), cholos, etc., and even African slaves were recruited by both sides. All those recruited in America, and also the Spaniards, joined the enemy armies as combatants when they were captured. Likewise, the Creole potentates of European origin could give their support to the royalist or pro-independence cause, in relation to the commercial interests of each region. The Church was also divided, and except for the lower clergy, involved as combatants of insurgency, their position was in accordance with the political power.
Although on the battlefield the fight was to the death and without quarter, however, the recruitment of soldiers seemed to end up a common pool employed by opposing sides as cannon fodder. Socially, both apparently opposing positions, loyalist and pro-independence, had an uncertain significance for the different social strata of the monarchy. In Europe, the Spaniards made a forced recruitment for the expeditionary forces, leading to constant rebellions. Independent states relied on privateers, mercenaries, adventurers or filibusters, reliable fighters when pay or booty was at a glance. For the mobilization of the population in America, the vast majority or almost all of the troops of both sides, the indiscriminate recruitment of native American communities was used, in general in traditional confronted regions; social improvements were promised, by both sides, to the indigenous and the different mestizo colonial castes, such as mulattoes ("pardos"), cholos, etc., and even African slaves were recruited by both sides. All those recruited in America, and also the Spaniards, joined the enemy armies as combatants when they were captured. Likewise, the Creole potentates of European origin could give their support to the royalist or pro-independence cause, in relation to the commercial interests of each region. The Church was also divided, and except for the lower clergy, involved as combatants of insurgency, their position was in accordance with the political power.
 Underlying social and racial tensions also had a great impact on the nature of the fighting. Rural areas were pitted against urban centers, as grievances against the authorities found an outlet in the political conflict. This was the case with Hidalgo's peasant revolt, which was fueled as much by discontent over several years of bad harvests as with events in the Peninsular War. Hidalgo was originally part of a circle of liberal urbanites in Querétaro, who sought to establish a junta. After this conspiracy was discovered, Hidalgo turned to the rural people of the Mexican Bajío to build his army, and their interests soon overshadowed those of the urban intellectuals. A similar tension existed in Venezuela, where the Spanish immigrant José Tomás Boves formed a powerful, though irregular, royalist army out of the '' Llaneros'', mixed-race slave and plains people, by attacking the white landowning class. Boves and his followers often disregarded the command of Spanish officials and were not concerned with actually re-establishing the toppled royal government, choosing instead to keep real power among themselves. Finally, in the back country of Upper Peru, the '' republiquetas'' kept the idea of independence alive by allying with disenfranchised members of rural society and native groups, but were never able to take the major population centers.
Increasingly violent confrontations developed between Spaniards and Spanish Americans, but this tension was often related to class issues or fomented by patriot leaders to create a new sense of nationalism. After being incited to rid the country of the ''gachupines'' (a disparaging term for ''Peninsulares''), Hidalgo's forces indiscriminately massacred hundreds of Criollos and ''Peninsulares'' who had taken refuge at the
Underlying social and racial tensions also had a great impact on the nature of the fighting. Rural areas were pitted against urban centers, as grievances against the authorities found an outlet in the political conflict. This was the case with Hidalgo's peasant revolt, which was fueled as much by discontent over several years of bad harvests as with events in the Peninsular War. Hidalgo was originally part of a circle of liberal urbanites in Querétaro, who sought to establish a junta. After this conspiracy was discovered, Hidalgo turned to the rural people of the Mexican Bajío to build his army, and their interests soon overshadowed those of the urban intellectuals. A similar tension existed in Venezuela, where the Spanish immigrant José Tomás Boves formed a powerful, though irregular, royalist army out of the '' Llaneros'', mixed-race slave and plains people, by attacking the white landowning class. Boves and his followers often disregarded the command of Spanish officials and were not concerned with actually re-establishing the toppled royal government, choosing instead to keep real power among themselves. Finally, in the back country of Upper Peru, the '' republiquetas'' kept the idea of independence alive by allying with disenfranchised members of rural society and native groups, but were never able to take the major population centers.
Increasingly violent confrontations developed between Spaniards and Spanish Americans, but this tension was often related to class issues or fomented by patriot leaders to create a new sense of nationalism. After being incited to rid the country of the ''gachupines'' (a disparaging term for ''Peninsulares''), Hidalgo's forces indiscriminately massacred hundreds of Criollos and ''Peninsulares'' who had taken refuge at the  During this period, royalist forces made advances into New Granada, which they controlled from 1815 to 1819, and into Chile, which they controlled from 1814 to 1817. Except for royalist areas in the northeast and south, the provinces of New Granada had maintained independence from Spain since 1810, unlike neighboring Venezuela, where royalists and pro-independence forces had exchanged control of the region several times. To pacify Venezuela and to retake New Granada, Spain organized in 1815 the largest armed force it ever sent to the New World, consisting of 10,500 troops and nearly sixty ships. (See, Spanish reconquest of New Granada.) Although this force was crucial in retaking a solidly pro-independence region like New Granada, its soldiers were eventually spread out throughout Venezuela, New Granada, Quito, and Peru and were lost to tropical diseases, diluting their impact on the war. More importantly, the majority of the royalist forces were composed, not of soldiers sent from the peninsula, but of Spanish Americans.
Overall, Europeans formed only about a tenth of the royalist armies in Spanish America, and only about half of the expeditionary units, once they were deployed in the Americas. Since each European soldier casualty was replaced by a Spanish American soldier, over time, there were more and more Spanish American soldiers in the expeditionary units. For example, Pablo Morillo, commander in chief of the expeditionary force sent to South America, reported that he had only 2,000 European soldiers under his command in 1820; in other words, only half the soldiers of his expeditionary force were European. It is estimated that in the Battle of Maipú only a quarter of the royalist forces were European soldiers, in the Battle of Carabobo about a fifth, and in the
During this period, royalist forces made advances into New Granada, which they controlled from 1815 to 1819, and into Chile, which they controlled from 1814 to 1817. Except for royalist areas in the northeast and south, the provinces of New Granada had maintained independence from Spain since 1810, unlike neighboring Venezuela, where royalists and pro-independence forces had exchanged control of the region several times. To pacify Venezuela and to retake New Granada, Spain organized in 1815 the largest armed force it ever sent to the New World, consisting of 10,500 troops and nearly sixty ships. (See, Spanish reconquest of New Granada.) Although this force was crucial in retaking a solidly pro-independence region like New Granada, its soldiers were eventually spread out throughout Venezuela, New Granada, Quito, and Peru and were lost to tropical diseases, diluting their impact on the war. More importantly, the majority of the royalist forces were composed, not of soldiers sent from the peninsula, but of Spanish Americans.
Overall, Europeans formed only about a tenth of the royalist armies in Spanish America, and only about half of the expeditionary units, once they were deployed in the Americas. Since each European soldier casualty was replaced by a Spanish American soldier, over time, there were more and more Spanish American soldiers in the expeditionary units. For example, Pablo Morillo, commander in chief of the expeditionary force sent to South America, reported that he had only 2,000 European soldiers under his command in 1820; in other words, only half the soldiers of his expeditionary force were European. It is estimated that in the Battle of Maipú only a quarter of the royalist forces were European soldiers, in the Battle of Carabobo about a fifth, and in the 
 Unlike in New Spain and Central America, in South America independence was spurred by the pro-independence fighters who had held out for the past half-decade.
Unlike in New Spain and Central America, in South America independence was spurred by the pro-independence fighters who had held out for the past half-decade.  To ensure that the Presidency of Quito became a part of Gran Colombia and did not remain a collection of small, divided republics, Bolívar sent aid in the form of supplies and an army under
To ensure that the Presidency of Quito became a part of Gran Colombia and did not remain a collection of small, divided republics, Bolívar sent aid in the form of supplies and an army under  Under the command of Bolívar and Sucre, the experienced veterans of the combined army, mainly Colombians, destroyed a royalist army under La Serna's command in the
Under the command of Bolívar and Sucre, the experienced veterans of the combined army, mainly Colombians, destroyed a royalist army under La Serna's command in the  The Spanish coastal fortifications in
The Spanish coastal fortifications in  Women were not simply spectators throughout the Independence Wars of Latin America. Many women took sides on political issues and joined independence movements to participate on many different levels. Women could not help but act as caring relatives either as mother, sister, wives or daughters of the men who were fighting. Women created political organizations and organized meetings and groups to donate food and supplies to the soldiers.
Some women supported the wars as spies, informants and combatants.
Women were not simply spectators throughout the Independence Wars of Latin America. Many women took sides on political issues and joined independence movements to participate on many different levels. Women could not help but act as caring relatives either as mother, sister, wives or daughters of the men who were fighting. Women created political organizations and organized meetings and groups to donate food and supplies to the soldiers.
Some women supported the wars as spies, informants and combatants.  Independence also did not result in stable political regimes, save in a few countries. First, the new nations did not have well-defined identities, but rather the process of creating identities was only beginning. This would be carried out through newspapers and the creation of national symbols, including new names for the countries ("Mexico", "Colombia", "Ecuador", "Bolivia", "Argentina"), that broke with the past. In addition, the borders were not firmly established, and the struggle between federalism and centralism, which began in independence, continued throughout the rest of the century. Two large states that emerged from the wars—
Independence also did not result in stable political regimes, save in a few countries. First, the new nations did not have well-defined identities, but rather the process of creating identities was only beginning. This would be carried out through newspapers and the creation of national symbols, including new names for the countries ("Mexico", "Colombia", "Ecuador", "Bolivia", "Argentina"), that broke with the past. In addition, the borders were not firmly established, and the struggle between federalism and centralism, which began in independence, continued throughout the rest of the century. Two large states that emerged from the wars—