Southern Australia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The term Southern Australia is generally considered to refer to the
 Whilst
Whilst
 The effect of large-scale extreme events such as prolonged heat waves not only impacts human activities but mortality rates; this presenting critical reasons to address climate change.
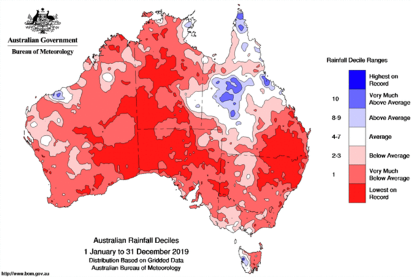
Whilst Australian rainfall has always been variable and influenced by weather patterns such as La Ninã and El Niño, there are underlying trends that implicate global warming as the cause of drier winter seasons across south-eastern and south-western Australia. Since 1970, the region has experienced 20% less rainfall than in the period of 1900–1969, and now since 1999 that has increased to 26% less rainfall. Although southern Australia has experienced declining rainfall in the colder months of April to October, the northern counterpart has seen increasing rainfall since the 1970s. The prevalence of flash flooding is set to continue to intensify, brought by a 7% increase in short-duration extreme rainfall events.
The effect of large-scale extreme events such as prolonged heat waves not only impacts human activities but mortality rates; this presenting critical reasons to address climate change.
Whilst Australian rainfall has always been variable and influenced by weather patterns such as La Ninã and El Niño, there are underlying trends that implicate global warming as the cause of drier winter seasons across south-eastern and south-western Australia. Since 1970, the region has experienced 20% less rainfall than in the period of 1900–1969, and now since 1999 that has increased to 26% less rainfall. Although southern Australia has experienced declining rainfall in the colder months of April to October, the northern counterpart has seen increasing rainfall since the 1970s. The prevalence of flash flooding is set to continue to intensify, brought by a 7% increase in short-duration extreme rainfall events.
 An increase in the simultaneous occurrence of two or more extreme events, known as compound extreme events, has largely impacted Southern Australia's agricultural industry. In each year of dry conditions and synchronous heatwaves, a typical cropping farm will experience a substantial loss of approximately $125,000 whilst in a regular year profit exceeds $230,000. Simultaneously, drought years lead to reduction of
An increase in the simultaneous occurrence of two or more extreme events, known as compound extreme events, has largely impacted Southern Australia's agricultural industry. In each year of dry conditions and synchronous heatwaves, a typical cropping farm will experience a substantial loss of approximately $125,000 whilst in a regular year profit exceeds $230,000. Simultaneously, drought years lead to reduction of

 Not only do bushfires destroy Australian
Not only do bushfires destroy Australian
 As a result of Britain's filtering of information to the Australian government, complacent ignorance regarding the tests safety caused environmental and health problems for local Emu Field’s Yanykunytjatjara people. An incident known as “Black Mist” caused significant health problems and several deaths for Indigenous locals. This was denied by the British for 29 years, and only following the Royal Commission, did they admit knowledge of the detriments it caused.
A Maralinga clean-up program, Operation Brumby, would relinquish any British responsibility once the area was deemed safe. The British reported the area safe, until 8 years later, the Liberal-National government questioned the report's authenticity. Britain's declaration that any radioactive contaminants were “irrecoverable” were found to be falsified and Britain were ordered to repatriate half a kilogram of remaining contaminants. Following these fabrications, the Australian government widely rejected Britain's reports, forming their own views and research, leading to a greater recognition of the damage to the Indigenous locals and environment.
As a result of Britain's filtering of information to the Australian government, complacent ignorance regarding the tests safety caused environmental and health problems for local Emu Field’s Yanykunytjatjara people. An incident known as “Black Mist” caused significant health problems and several deaths for Indigenous locals. This was denied by the British for 29 years, and only following the Royal Commission, did they admit knowledge of the detriments it caused.
A Maralinga clean-up program, Operation Brumby, would relinquish any British responsibility once the area was deemed safe. The British reported the area safe, until 8 years later, the Liberal-National government questioned the report's authenticity. Britain's declaration that any radioactive contaminants were “irrecoverable” were found to be falsified and Britain were ordered to repatriate half a kilogram of remaining contaminants. Following these fabrications, the Australian government widely rejected Britain's reports, forming their own views and research, leading to a greater recognition of the damage to the Indigenous locals and environment.
 Whilst Maralinga is declared safe now, it takes to a ghost town, with only 4 people permanently living in the region. One of the radioactive contaminants, Plutonium-239 has a radioactive half-life of 24,000 years, meaning that whilst recovery efforts have proved effective, for a long time coming, the area will still suffer from stigma and caution surrounding the traces of material in soil. However at Emu Field, the test trials only contained materials with short half-lives, leaving the area unexposed to long-term contamination.Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency. ''British nuclear weapons testing in Australia''. Retrieved from
Whilst Maralinga is declared safe now, it takes to a ghost town, with only 4 people permanently living in the region. One of the radioactive contaminants, Plutonium-239 has a radioactive half-life of 24,000 years, meaning that whilst recovery efforts have proved effective, for a long time coming, the area will still suffer from stigma and caution surrounding the traces of material in soil. However at Emu Field, the test trials only contained materials with short half-lives, leaving the area unexposed to long-term contamination.Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency. ''British nuclear weapons testing in Australia''. Retrieved from https://www.arpansa.gov.au/understanding-radiation/sources-radiation/more-radiation-sources/british-nuclear-weapons-testing
states and territories of Australia
The states and territories are federated administrative divisions in Australia, ruled by regional governments that constitute the second level of governance between the federal government and local governments. States are self-governing ...
of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, Victoria, Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding township#Aust ...
and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
. The part of Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
south of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
26° south a definition widely used in law and state government policy is also usually included.
Although it comprises about half of the total area of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, Southern Australia includes about three-quarters of the Australian population, the main agricultural areas and the main industrial centres. The area is also notable for its primarily temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
, mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
, alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
or arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ...
environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scal ...
and climatic conditions which contrasts to the mainly tropical climate of Northern Australia.
Southern Australia has long suffered extreme weather
Extreme weather or extreme climate events includes unexpected, unusual, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Often, extreme events are based on a locat ...
events due to the arid landscape, however in recent times these conditions have been exacerbated due to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
The region has several key industries which contribute to the high gross product and large value of exports. Southern Western Australia largely focuses on mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
as a key export, whilst the states of Victoria and New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
focus on traditional sectors such as manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
, tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
, and finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of f ...
. Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
are regional economies, primarily concentrated on manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
.
* Northern Australia
* Eastern states of Australia
* Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
Economy
Southern Australia is the richest part ofAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, home to a diversified economy
Economic diversity or economic diversification refers to variations in the economic status or the use of a broad range of economic activities in a region or country. Diversification is used as a strategy to encourage positive economic growth and d ...
with an expansive variety of exports including minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed ...
, wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
, dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting or processing (or both) of animal milk – mostly from cows or buffaloes, but also from goats, sheep, horses, or camels – for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on ...
, livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
, education, and tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
. Across the region, there is sustainable employment, with all state's unemployment rates being below 8%.
Economists have suggested that Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
moves at two different speeds, with some states focusing on traditional sectors such as manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
, finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of f ...
and tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
, and others emphasising mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
industries. NSW and Victoria are seen as traditional economies, primarily focusing on said “traditional” industries, whilst South Western Australia emphasises mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
. Regional economies such as Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
prioritise manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
, closing them off to advancing in faster growing industries.
Attributable to the region's rich mineral soils, states such as Southern Western Australia and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
emphasise exports such as petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the ...
and other minerals. Such commodities
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a co ...
account for 36% of Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
’s gross state product, employing approximately 124,000 people state-wide. South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
is also home to rich agricultural soil creating a booming trade of fresh produce
Produce is a generalized term for many farm-produced crops, including fruits and vegetables ( grains, oats, etc. are also sometimes considered ''produce''). More specifically, the term ''produce'' often implies that the products are fres ...
, seafood, and wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
. South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
’s wine industry accounts for 17.2% of overseas exports, also stimulating fortuitous flow on tourism.
Such fertile soils transpire across the region, whereby Victoria exports 80% of Australia's produced dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting or processing (or both) of animal milk – mostly from cows or buffaloes, but also from goats, sheep, horses, or camels – for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on ...
. The state encompasses just 3% of Australian land yet produces 22% of the nation's GDP.
 Whilst
Whilst Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
and Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
have experienced high growth due to the mining resource boom, NSW has recorded dwindling economic growth, measuring lower Gross State Product ( GSP) than national GDP since 2001. Nonetheless, NSW's main economic activities include the exporting of minerals such as coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
and concentrates, livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
, cropping and horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
. NSW's number one export market is Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
grossing $3,068m annually, followed by the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
Contrastingly, the ACT has experienced major growth of approximately 13% over the past 3 years. This is namely due to the prominent tertiary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including univers ...
sector and subsequent increase in popularity among students.
Home to outstanding beauty, Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
’s strongest industry is unsurprisingly tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
. Isolated from mainland Australia, the government invests in numerous infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
projects to strengthen Tasmania's economy.
Climate and geography
Comparative to Northern Australia’s typicaltropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
climate, Southern Australia is home to a variety of climates including alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
, temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
, Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
, and arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ...
. Generally speaking, southern Australia experiences hot, dry summers followed by wet winters. Due to the arid nature of the land and intense heat, the region is prone to regular bushfires throughout the summer months. In addition, these fires have been exacerbated by the south-eastern 13-year drought from 1997 to 2009. However, these natural occurrences have been greatly aggravated due to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
The southern coastline is subject to dramatic temperature changes over the summer months where temperatures regularly reach 45°C. Contrastingly, moving inland, the land converts to desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
landscapes interrupted by fertile soils, home to renowned wine regions such as the Barossa Valley and Margaret River.
The Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs rough ...
runs north to south along Australia's east coast bringing the high elevations of it cold weather, whilst the easterly side receives the most rain and the west plains suffer the heat. Despite the overarching hot environment of southern Australia, regions of NSW, Victoria, and Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
experience winter snowfall, creating several ski resorts.
Majority of southern Australia is uninhabited due to its arid nature, with populations concentrating in the cities of Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mounta ...
, Canberra
Canberra ( )
is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The ci ...
, Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/ Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a metro ...
, Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The dem ...
, and Perth
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth is ...
. Of Australia's 9 main cities in Australia, southern Australia is home to 7 of them, making the region the most populated area of Australia.
Climate change
Southern Australia is experiencing rapid population growth and density, and when paired with increasing weather extremes presents a consequential concern for life and property. Rising temperatures have led to an increased risk of health issues such as heart-related mortality,infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
, and pollen allergies. The effect of large-scale extreme events such as prolonged heat waves not only impacts human activities but mortality rates; this presenting critical reasons to address climate change.
Whilst Australian rainfall has always been variable and influenced by weather patterns such as La Ninã and El Niño, there are underlying trends that implicate global warming as the cause of drier winter seasons across south-eastern and south-western Australia. Since 1970, the region has experienced 20% less rainfall than in the period of 1900–1969, and now since 1999 that has increased to 26% less rainfall. Although southern Australia has experienced declining rainfall in the colder months of April to October, the northern counterpart has seen increasing rainfall since the 1970s. The prevalence of flash flooding is set to continue to intensify, brought by a 7% increase in short-duration extreme rainfall events.
The effect of large-scale extreme events such as prolonged heat waves not only impacts human activities but mortality rates; this presenting critical reasons to address climate change.
Whilst Australian rainfall has always been variable and influenced by weather patterns such as La Ninã and El Niño, there are underlying trends that implicate global warming as the cause of drier winter seasons across south-eastern and south-western Australia. Since 1970, the region has experienced 20% less rainfall than in the period of 1900–1969, and now since 1999 that has increased to 26% less rainfall. Although southern Australia has experienced declining rainfall in the colder months of April to October, the northern counterpart has seen increasing rainfall since the 1970s. The prevalence of flash flooding is set to continue to intensify, brought by a 7% increase in short-duration extreme rainfall events.
 An increase in the simultaneous occurrence of two or more extreme events, known as compound extreme events, has largely impacted Southern Australia's agricultural industry. In each year of dry conditions and synchronous heatwaves, a typical cropping farm will experience a substantial loss of approximately $125,000 whilst in a regular year profit exceeds $230,000. Simultaneously, drought years lead to reduction of
An increase in the simultaneous occurrence of two or more extreme events, known as compound extreme events, has largely impacted Southern Australia's agricultural industry. In each year of dry conditions and synchronous heatwaves, a typical cropping farm will experience a substantial loss of approximately $125,000 whilst in a regular year profit exceeds $230,000. Simultaneously, drought years lead to reduction of livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
herd sizes as we see lower birth rates alongside discretionary forfeiture of dairy cows to the beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quantit ...
trade.Climate change and bushfires
In the past decade, southern Australia has experienced a surge in swelteringsummers
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, with ...
, coupled with low rainfall leading to a longer and more devastating bushfire season. Scientists have stated that the increased regularity and intensity of these conditions is a direct cause of climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, including increasing temperatures. The region is experiencing an increase in yearly fire days, decreased annual rainfall, increases in mean sea level pressure, and tropical cyclones.
2019-2020 summer bushfires
Whilstclimate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
is not the sole contributor to Australia's devastating fire experience, since the 1950s, it has caused an increase in their occurrence and intensity. Such effects have been seen in the 2019-2020 bushfires which ravished mainly NSW and Victoria but additionally South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
and Southern Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
. 2019 was the driest and hottest year on record, with the annual average temperature increase measuring at 1.52°C.

Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
covers 134 million hectares and as at February 18 2020, more than 19 million hectares of land was burned. 33 people died, including the death of 3 US firefighters whose Air Tanker crashed whilst battling a bushfire in NSW. Approximately 48% of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
’s Kangaroo Island land was burned.
WWF commissioned scientists estimate that nearly three billion animals were killed or displaced by the 2019-2020 fires, not including insects. Across NSW, up to 81% of Koala land was burned, and a parliamentary inquiry found that without urgent government intervention and protection, the koala will become extinct in NSW by 2050. Not only do bushfires destroy Australian
Not only do bushfires destroy Australian flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
...
and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is '' flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. ...
, the NSW independent commission into the 2019-2020 “black summer
''Black Summer'' is a comic book limited series written by Warren Ellis, illustrated by Juan Jose Ryp, and published by Avatar Press starting in June 2007. The plot revolves around the consequences of a superhero, John Horus, who kills the Presi ...
” bushfires found that over 400 Australians died prematurely as a result of smoke inhalation. Evidence has shown that sustained poor air quality increases the risk of respiratory illnesses, some cancers, and heart disease. Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
are more susceptible to the health detriments of bushfire smoke due to the demographic prevalence of chronic health conditions. The report implicated the role of climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
and outlined the imperative necessity to address climate change as the proponent for increased bushfire risk.“''Countries that clearly have so much to lose from bushfires and otherTemporary bushfire relief is expected over the 2020-2021 summer season as the region enters into a La Ninã climate pattern.climate change In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...damage and so much to gain from a more rapid transition to arenewable energy Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...economy – must do more. Countries likeAustralia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ..., and within them leading states like NSW''” – Gwen and David Jagger.
Other major bushfires
Other major bushfires within the southern region include 2009’s Victorian Black Saturday where over 2,000 homes were destroyed, and 173 people died. Additionally, 2003’s Victorian and Canberran Alpine bushfires claimed the lives of 10,000 livestock animals and 1.2 million hectares of land.British nuclear testing
In the 1950s and 60s Britain deployed numerous nuclear tests in Australia, namely the South Australian Maralinga and Emu Field tests. The Maralinga sites were chosen due to their “vast, empty useless spaces” despite the area beingIndigenous Australian
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
Anangu Pitjantjatjara land. Meagre Indigenous citizen rights, coupled with rampant racial discrimination
Racial discrimination is any discrimination against any individual on the basis of their skin color, race or ethnic origin.Individuals can discriminate by refusing to do business with, socialize with, or share resources with people of a certain g ...
led to the Indigenous’ prolonged emotional, physical, and mental suffering after having limited access to resources for over 30 years. The British government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
delegated one single officer the task of covering hundreds of thousands of square kilometres, resulting in radiation exposure
Radiation is a moving form of energy, classified into ionizing and non-ionizing type. Ionizing radiation is further categorized into electromagnetic radiation (without matter) and particulate radiation (with matter). Electromagnetic radiation con ...
to oblivious Indigenous inhabitants. Whilst inconclusive, approximately 30% of British and Australian servicemen who worked in the area have died of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
.
 As a result of Britain's filtering of information to the Australian government, complacent ignorance regarding the tests safety caused environmental and health problems for local Emu Field’s Yanykunytjatjara people. An incident known as “Black Mist” caused significant health problems and several deaths for Indigenous locals. This was denied by the British for 29 years, and only following the Royal Commission, did they admit knowledge of the detriments it caused.
A Maralinga clean-up program, Operation Brumby, would relinquish any British responsibility once the area was deemed safe. The British reported the area safe, until 8 years later, the Liberal-National government questioned the report's authenticity. Britain's declaration that any radioactive contaminants were “irrecoverable” were found to be falsified and Britain were ordered to repatriate half a kilogram of remaining contaminants. Following these fabrications, the Australian government widely rejected Britain's reports, forming their own views and research, leading to a greater recognition of the damage to the Indigenous locals and environment.
As a result of Britain's filtering of information to the Australian government, complacent ignorance regarding the tests safety caused environmental and health problems for local Emu Field’s Yanykunytjatjara people. An incident known as “Black Mist” caused significant health problems and several deaths for Indigenous locals. This was denied by the British for 29 years, and only following the Royal Commission, did they admit knowledge of the detriments it caused.
A Maralinga clean-up program, Operation Brumby, would relinquish any British responsibility once the area was deemed safe. The British reported the area safe, until 8 years later, the Liberal-National government questioned the report's authenticity. Britain's declaration that any radioactive contaminants were “irrecoverable” were found to be falsified and Britain were ordered to repatriate half a kilogram of remaining contaminants. Following these fabrications, the Australian government widely rejected Britain's reports, forming their own views and research, leading to a greater recognition of the damage to the Indigenous locals and environment.
Moving forward
Following a 1985 Royal Commission into the events, numerous findings were outlined, implicating Britain as failing to provide sufficient recovery efforts alongside Australia's petty compliance. In December 1993, after multiple attempts by the Australian government to recover payment, Britain paid 20 million euros, despite the clean-up and compensation costing in excess of $110 million AUD. The Maralinga site was only returned to its traditional owners in November 2009. Whilst Maralinga is declared safe now, it takes to a ghost town, with only 4 people permanently living in the region. One of the radioactive contaminants, Plutonium-239 has a radioactive half-life of 24,000 years, meaning that whilst recovery efforts have proved effective, for a long time coming, the area will still suffer from stigma and caution surrounding the traces of material in soil. However at Emu Field, the test trials only contained materials with short half-lives, leaving the area unexposed to long-term contamination.Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency. ''British nuclear weapons testing in Australia''. Retrieved from
Whilst Maralinga is declared safe now, it takes to a ghost town, with only 4 people permanently living in the region. One of the radioactive contaminants, Plutonium-239 has a radioactive half-life of 24,000 years, meaning that whilst recovery efforts have proved effective, for a long time coming, the area will still suffer from stigma and caution surrounding the traces of material in soil. However at Emu Field, the test trials only contained materials with short half-lives, leaving the area unexposed to long-term contamination.Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency. ''British nuclear weapons testing in Australia''. Retrieved from References
{{coord, 31, 24, 23.43, S, 142, 23, 37.73, E, display=title, region:AU_type:city_source:GNS-enwiki Regions of Australia