Sourwood on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Oxydendrum arboreum'', the sourwood or sorrel tree, is the sole 
 The bark is gray with a reddish tinge, deeply furrowed and scaly. Branchlets at first are light yellow green, but later turn reddish brown. The wood is reddish brown, with paler sapwood; it is heavy, hard, and close-grained, and will take a high polish. Its specific gravity is 0.7458, with a density of 46.48 lb/cu ft.
The winter buds are axillary, minute, dark red, and partly immersed in the bark. Inner scales enlarge when spring growth begins.
Leaves are
The bark is gray with a reddish tinge, deeply furrowed and scaly. Branchlets at first are light yellow green, but later turn reddish brown. The wood is reddish brown, with paler sapwood; it is heavy, hard, and close-grained, and will take a high polish. Its specific gravity is 0.7458, with a density of 46.48 lb/cu ft.
The winter buds are axillary, minute, dark red, and partly immersed in the bark. Inner scales enlarge when spring growth begins.
Leaves are
Image:Oxydendron arboreum JPG1.jpg, Trunk and leaves
Image:Sourwood in autumn (foliage closeup).JPG, Sourwood in autumn foliage on top of Pilot Mtn., NC. (10-30-2008)
''Oxydendrum arboreum'' images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu
{{Authority control Vaccinioideae Trees of the Southeastern United States Trees of the Northeastern United States Trees of the North-Central United States Trees of the Great Lakes region (North America) Flora of the Appalachian Mountains Natural history of the Great Smoky Mountains Medicinal plants of North America Monotypic Ericaceae genera
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
in the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Oxydendrum'', in the family Ericaceae
The Ericaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the heath or heather family, found most commonly in acidic and infertile growing conditions. The family is large, with c.4250 known species spread across 124 genera, making it th ...
. It is native to eastern North America, from southern Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
south to northwest Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and west to southern Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
; it is most common in the lower chain of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
. The tree is frequently seen as a component of oak-heath forests.

Growth
Sourwood is a smalltree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
or large shrub, growing to tall with a trunk up to diameter. Occasionally on extremely productive sites, this species can reach heights in excess of 30 meters and 60 cm diameter. The leaves are alternately arranged, deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
, long and broad, with a finely serrated
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied p ...
margin; they are dark green in summer, but turn vivid red in fall. The flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechani ...
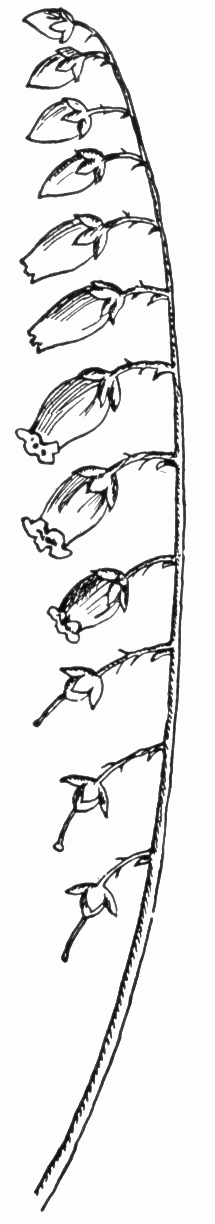
s are white, bell-shaped, 6–9 mm ( 1/4 to 1/3 inch) long, produced on long panicles. The fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
is a small woody capsule. The root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
s are shallow, and the tree grows best when there is little root competition; it also requires acidic soil
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a soil. Soil pH is a key characteristic that can be used to make informative analysis both qualitative and quantitatively regarding soil characteristics. pH is defined as the n ...
s for successful growth. The leaves can be chewed (but should not be swallowed) to help alleviate a dry-feeling mouth.
Description
 The bark is gray with a reddish tinge, deeply furrowed and scaly. Branchlets at first are light yellow green, but later turn reddish brown. The wood is reddish brown, with paler sapwood; it is heavy, hard, and close-grained, and will take a high polish. Its specific gravity is 0.7458, with a density of 46.48 lb/cu ft.
The winter buds are axillary, minute, dark red, and partly immersed in the bark. Inner scales enlarge when spring growth begins.
Leaves are
The bark is gray with a reddish tinge, deeply furrowed and scaly. Branchlets at first are light yellow green, but later turn reddish brown. The wood is reddish brown, with paler sapwood; it is heavy, hard, and close-grained, and will take a high polish. Its specific gravity is 0.7458, with a density of 46.48 lb/cu ft.
The winter buds are axillary, minute, dark red, and partly immersed in the bark. Inner scales enlarge when spring growth begins.
Leaves are alternate
Alternative or alternate may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Alternative (''Kamen Rider''), a character in the Japanese TV series ''Kamen Rider Ryuki''
* ''The Alternative'' (film), a 1978 Australian television film
* ''The Alternative ...
, four to seven inches long, 1.5 to 2.5 inches wide, oblong to oblanceolate
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular ...
, wedge-shaped at the base, serrate, and acute or acuminate
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular ...
. Leaf veins are feather-veined, the midrib
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary o ...
is conspicuous. They emerge from the bud revolute, bronze green and shining, and smooth; when full-grown, they are dark green, shining above, and pale and glaucous below. In autumn, they turn bright scarlet. Petioles are long and slender, with stipule
In botany, a stipule is an outgrowth typically borne on both sides (sometimes on just one side) of the base of a leafstalk (the petiole). Stipules are considered part of the anatomy of the leaf of a typical flowering plant, although in many speci ...
s wanting. They are heavily laden with acid.
In June and July, cream-white flowers are borne in terminal panicles of secund racemes seven to eight inches long; rachis and short pedicels are downy. The calyx is five-parted and persistent; lobes are valvate in bud. The corolla is ovoid-cylindric, narrowed at the throat, cream-white, and five-toothed. The 10 stamens are inserted on the corolla; filaments are wider than the anthers; anthers are two-celled. The pistil is ovary superior, ovoid, and five-celled; the style is columnar; the stigma is simple; the disk is ten-toothed, and ovules are many.
The fruit is a capsule, downy, five-valved, five-angled, and tipped by the persistent style; the pedicels
In botany, a pedicel is a stem that attaches a single flower to the inflorescence. Such inflorescences are described as ''pedicellate''.
Description
Pedicel refers to a structure connecting a single flower to its inflorescence. In the absenc ...
are curving.
Cultivation and uses
The sourwood is perfectly hardy in the north and a worthy ornamental tree in lawns and parks. Its late bloom makes it desirable, and its autumnal coloring is particularly beautiful and brilliant. The leaves are heavily charged with acid, and to some extent have the poise of those of thepeach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-f ...
. The leaves are also a laxative
Laxatives, purgatives, or aperients are substances that loosen stools and increase bowel movements. They are used to treat and prevent constipation.
Laxatives vary as to how they work and the side effects they may have. Certain stimulant, lubri ...
.
It is renowned for nectar, and for the honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
which is produced from it.''National Audubon Society Field Guide to Trees, Eastern Region, North America'', 2003, page 626 Juice from its blooms is used to make sourwood jelly. The shoots were used by the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
and the Catawba Catawba may refer to:
*Catawba people, a Native American tribe in the Carolinas
*Catawba language, a language in the Catawban languages family
*Catawban languages
Botany
*Catalpa, a genus of trees, based on the name used by the Catawba and other N ...
to make arrowshafts.
In Appalachian culture
Sourwood Mountain
"Sourwood Mountain" is a traditional American folk song. Like many folk songs, there are numerous lyrical versions extant; however, there are certain commonalities. The song's theme is a lament over the narrator's true love, from whom he is separ ...
is a popular old-time tune in the Appalachian region of the United States.
Gallery
References
External links
''Oxydendrum arboreum'' images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu
{{Authority control Vaccinioideae Trees of the Southeastern United States Trees of the Northeastern United States Trees of the North-Central United States Trees of the Great Lakes region (North America) Flora of the Appalachian Mountains Natural history of the Great Smoky Mountains Medicinal plants of North America Monotypic Ericaceae genera