Sopwith Camels on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Sopwith Camel is a British
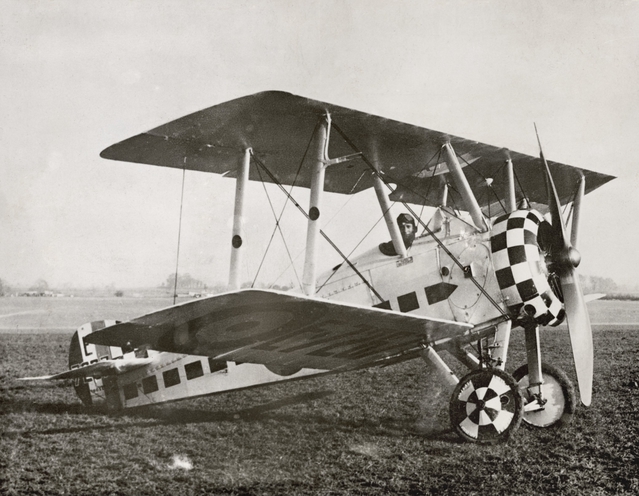 When it became clear the
When it became clear the
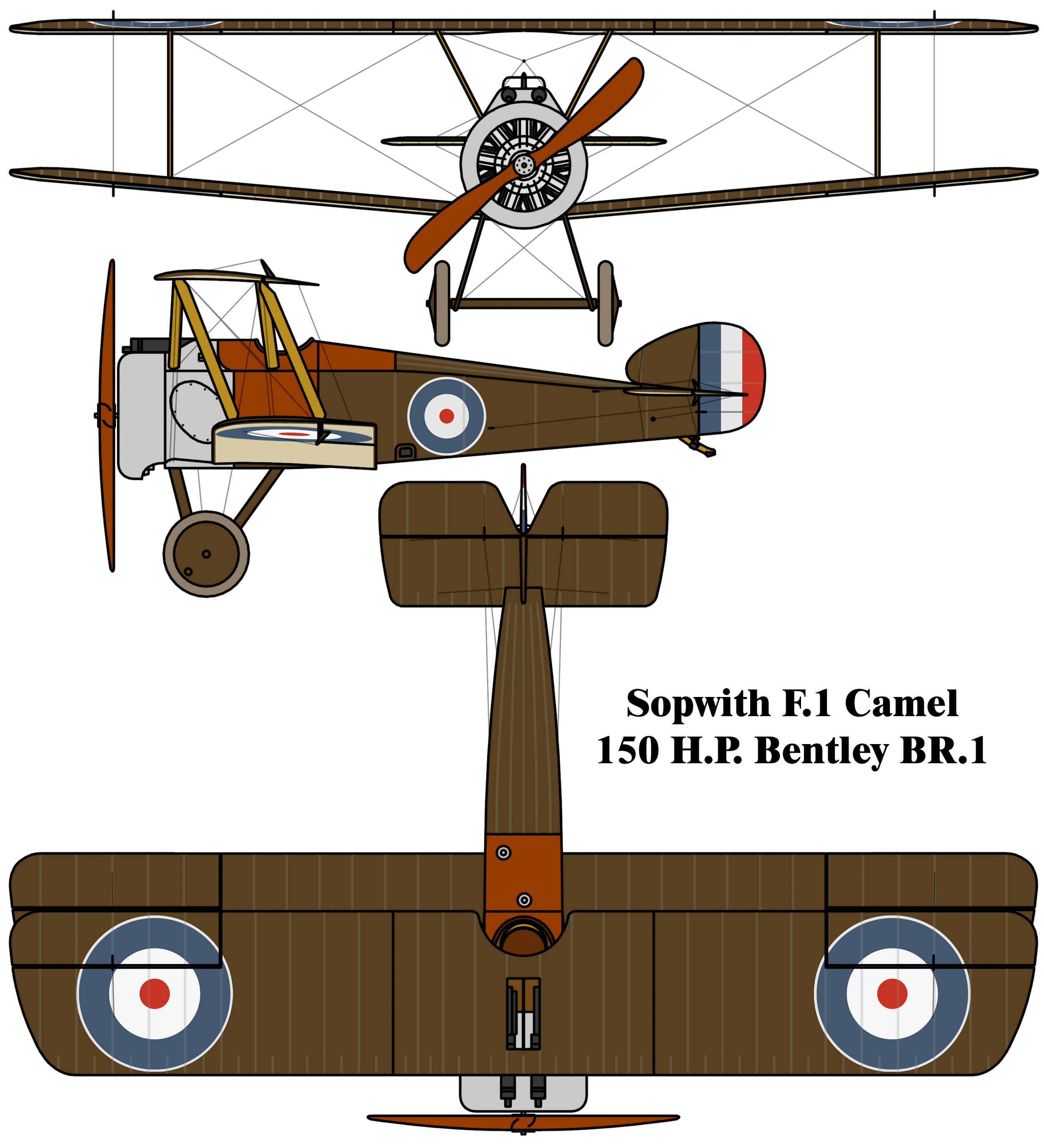
 The Camel had a mostly conventional design for its era, featuring a wooden box-like fuselage structure, an aluminium engine cowling, plywood panels around the cockpit, and a fabric-covered fuselage, wings and tail. While possessing some clear similarities with the Pup, it was furnished with a noticeably bulkier fuselage. For the first time on an operational British-designed fighter, two 0.303 in (7.7 mm)
The Camel had a mostly conventional design for its era, featuring a wooden box-like fuselage structure, an aluminium engine cowling, plywood panels around the cockpit, and a fabric-covered fuselage, wings and tail. While possessing some clear similarities with the Pup, it was furnished with a noticeably bulkier fuselage. For the first time on an operational British-designed fighter, two 0.303 in (7.7 mm)
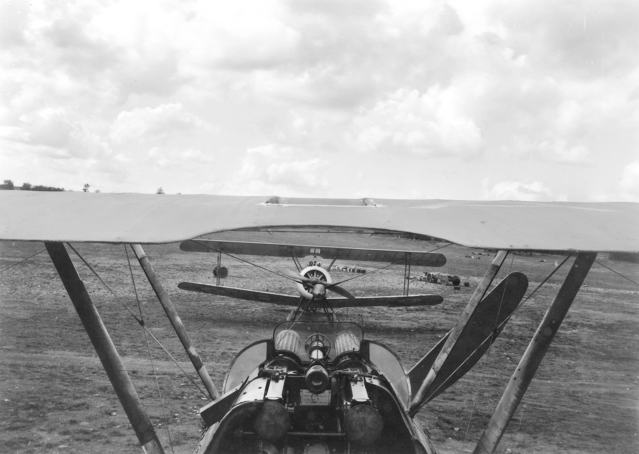
 Unlike the preceding Pup and
Unlike the preceding Pup and
 The Camel night fighter was also operated by 151 Squadron to intercept German night bombers operating over the Western Front. These aircraft were not only deployed defensively, but often carried out night intruder missions against German airstrips. After five months of operations, 151 Squadron had claimed responsibility for shooting down 26 German aircraft.Davis 1999, pp. 98–99.
The Camel night fighter was also operated by 151 Squadron to intercept German night bombers operating over the Western Front. These aircraft were not only deployed defensively, but often carried out night intruder missions against German airstrips. After five months of operations, 151 Squadron had claimed responsibility for shooting down 26 German aircraft.Davis 1999, pp. 98–99.
 The RNAS operated a number of 2F.1 Camels that were suitable for launching from platforms mounted on the turrets of major warships as well as from some of the earliest aircraft carriers to be built. Furthermore, the Camel could be deployed from ''aircraft lighters'', which were specially modified barges; these had to be towed fast enough that a Camel could successfully take off. The aircraft lighters served as means of launching interception sorties against incoming enemy air raids from a more advantageous position than had been possible when using shore bases alone.
During the summer of 1918, a single 2F.1 Camel (''N6814'') participated in a series of trials as a parasite fighter. The aircraft used
The RNAS operated a number of 2F.1 Camels that were suitable for launching from platforms mounted on the turrets of major warships as well as from some of the earliest aircraft carriers to be built. Furthermore, the Camel could be deployed from ''aircraft lighters'', which were specially modified barges; these had to be towed fast enough that a Camel could successfully take off. The aircraft lighters served as means of launching interception sorties against incoming enemy air raids from a more advantageous position than had been possible when using shore bases alone.
During the summer of 1918, a single 2F.1 Camel (''N6814'') participated in a series of trials as a parasite fighter. The aircraft used
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
single-seat biplane fighter aircraft that was introduced on the Western Front in 1917. It was developed by the Sopwith Aviation Company
The Sopwith Aviation Company was a British aircraft company that designed and manufactured aeroplanes mainly for the British Royal Naval Air Service, the Royal Flying Corps and later the Royal Air Force during the First World War, most famously ...
as a successor to the Sopwith Pup
The Sopwith Pup is a British single-seater biplane fighter aircraft built by the Sopwith Aviation Company. It entered service with the Royal Naval Air Service and the Royal Flying Corps in the autumn of 1916. With pleasant flying character ...
and became one of the best known fighter aircraft of the Great War.
The Camel was powered by a single rotary engine
The rotary engine is an early type of internal combustion engine, usually designed with an odd number of cylinders per row in a radial configuration. The engine's crankshaft remained stationary in operation, while the entire crankcase and its ...
and was armed with twin synchronized Vickers machine guns. Though difficult to handle, it was highly manoeuvrable in the hands of an experienced pilot, a vital attribute in the relatively low-speed, low-altitude dogfights of the era. In total, Camel pilots have been credited with downing 1,294 enemy aircraft, more than any other Allied fighter of the conflict. Towards the end of the First World War, the type also saw use as a ground-attack aircraft, partly because the capabilities of fighter aircraft on both sides had advanced rapidly and left the Camel somewhat outclassed.
The main variant of the Camel was designated as the F.1. Other variants included the 2F.1 Ship's Camel, which operated from aircraft carriers; the Comic night fighter variant; and the T.F.1, a "trench fighter" armoured for attacks on heavily defended ground targets. A two-seat variant served as a trainer. The last Camels were withdrawn from RAF service in January 1920.
Development
 When it became clear the
When it became clear the Sopwith Pup
The Sopwith Pup is a British single-seater biplane fighter aircraft built by the Sopwith Aviation Company. It entered service with the Royal Naval Air Service and the Royal Flying Corps in the autumn of 1916. With pleasant flying character ...
was no match for the newer German fighters such as the Albatros D.III
The Albatros D.III was a biplane fighter aircraft used by the Imperial German Army Air Service ('' Luftstreitkräfte'') during World War I. A modified licence model was built by Oeffag for the Austro-Hungarian Air Service ( ''Luftfahrtruppen''). ...
, the Camel was developed to replace it,Bruce ''Flight'' 22 April 1955, p. 527. as well as the Nieuport 17s that had been purchased from the French as an interim measure. It was recognised that the new fighter needed to be faster and have a heavier armament. The design effort to produce this successor, initially designated as the ''Sopwith F.1'', was headed by Sopwith's chief designer, Herbert Smith.Bruce 1965, p. 3.
Early in its development, the Camel was simply referred to as the "Big Pup". A metal fairing over the gun breeches, intended to protect the guns from freezing at altitude, created a "hump" that led pilots to call the aircraft "Camel", although this name was never used officially. On 22 December 1916, the prototype Camel was first flown by Harry Hawker at Brooklands
Brooklands was a motor racing circuit and aerodrome built near Weybridge in Surrey, England, United Kingdom. It opened in 1907 and was the world's first purpose-built 'banked' motor racing circuit as well as one of Britain's first airfie ...
, Weybridge
Weybridge () is a town in the Borough of Elmbridge in Surrey, England, around southwest of central London. The settlement is recorded as ''Waigebrugge'' and ''Weibrugge'' in the 7th century and the name derives from a crossing point of the ...
, Surrey; it was powered by a Clerget 9Z.Jackson 2007, p. 2.
In May 1917, the first production contract for an initial batch of 250 Camels was issued by the British War Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (MoD). This article contains text from ...
.Bruce 1965, p. 5. Throughout 1917, a total of 1,325 Camels were produced, almost entirely the initial F.1 variant. By the time that production of the type came to an end, approximately 5,490 Camels of all types had been built.Bruce ''Flight'' 29 April 1955, p. 563. In early 1918, production of the naval variant of the Sopwith Camel, the "Ship's" Camel 2F.1 began.Bruce 1965, p. 6.
Design
Overview
 The Camel had a mostly conventional design for its era, featuring a wooden box-like fuselage structure, an aluminium engine cowling, plywood panels around the cockpit, and a fabric-covered fuselage, wings and tail. While possessing some clear similarities with the Pup, it was furnished with a noticeably bulkier fuselage. For the first time on an operational British-designed fighter, two 0.303 in (7.7 mm)
The Camel had a mostly conventional design for its era, featuring a wooden box-like fuselage structure, an aluminium engine cowling, plywood panels around the cockpit, and a fabric-covered fuselage, wings and tail. While possessing some clear similarities with the Pup, it was furnished with a noticeably bulkier fuselage. For the first time on an operational British-designed fighter, two 0.303 in (7.7 mm) Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public i ...
machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) ar ...
s were mounted directly in front of the cockpit, synchronised to fire forwards through the propeller disc – initially this consisted of the fitment of the Sopwith firm's own synchronizer design, but after the mechanical-linkage Sopwith-Kauper units began to wear out, the more accurate and easier-to-maintain, hydraulic-link Constantinesco-Colley system replaced it from November 1917 onward. In addition to the machine guns, a total of four Cooper bombs
The Cooper bomb was a British 20 pound bomb used extensively in World War I, it was the first high explosive bomb to be adapted by the Royal Flying Corps.
Design
The bomb was in weight, of which was the bomb casing and was an explosive char ...
could be carried for ground attack purposes.
The bottom wing was rigged with 5° dihedral while the top wing lacked any dihedral; this meant that the gap between the wings was less at the tips than at the roots; this change had been made at the suggestion of Fred Sigrist
Reid and Sigrist was an English engineering company based at New Malden in Surrey. It later acquired sites at Desford and Braunstone in Leicestershire. Initially it developed and manufactured aircraft instrumentation and pilot selection aids but ...
, the Sopwith works manager, as a measure to simplify the aircraft's construction. The upper wing featured a central cutout section for the purpose of providing improved upwards visibility for the pilot.
Production Camels were powered by various rotary engine
The rotary engine is an early type of internal combustion engine, usually designed with an odd number of cylinders per row in a radial configuration. The engine's crankshaft remained stationary in operation, while the entire crankcase and its ...
s, most commonly either the Clerget 9B or the Bentley BR1. In order to evade a potential manufacturing bottleneck
Bottleneck literally refers to the narrowed portion (neck) of a bottle near its opening, which limit the rate of outflow, and may describe any object of a similar shape. The literal neck of a bottle was originally used to play what is now known as ...
being imposed upon the overall aircraft in the event of an engine shortage, several other engines were adopted to power the type as well.
Flight characteristics

 Unlike the preceding Pup and
Unlike the preceding Pup and Triplane
A triplane is a fixed-wing aircraft equipped with three vertically stacked wing planes. Tailplanes and canard foreplanes are not normally included in this count, although they occasionally are.
Design principles
The triplane arrangement m ...
, the Camel was considered to be difficult to fly. With light and sensitive controls the type owed both its extreme manoeuvrability and its difficult handling to the close placement of the engine, pilot, guns and fuel tank (some 90% of the aircraft's weight) within the front of the aircraft, and to the strong gyroscopic
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rot ...
effect of the rotating mass of the cylinders common to rotary engine
The rotary engine is an early type of internal combustion engine, usually designed with an odd number of cylinders per row in a radial configuration. The engine's crankshaft remained stationary in operation, while the entire crankcase and its ...
s.As compared with radial engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized star when viewed from the front, and is ...
s in which a conventional rotating crankshaft is driven by a fixed engine block.
Due to the torque of the rotary engine the Camel turned more slowly to the left, which resulted in a nose-up attitude, but the torque also resulted in being able to turn to the right quicker than other fighters,Clark 1973, p. 134. although that resulted in a tendency towards a nose-down attitude from the turn. Because of the faster turning capability to the right, some pilots preferred to change heading 90° to the left by turning 270° to the right.
Upon entering service, the Camel gained an unfortunate reputation with pilots,Jackson 2005, pp. 15–16. with inexperienced ones crashing on take-off when the full fuel load pushed the aircraft's centre of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ...
beyond the rearmost safe limit.
When in level flight, the Camel was markedly tail-heavy. Unlike the Sopwith Triplane, the Camel lacked a variable incidence tailplane, so that the pilot had to apply constant forward pressure on the control stick to maintain a level attitude at low altitude. The aircraft could be rigged so that at higher altitudes it could be flown "hands off". A stall immediately resulted in a dangerous spin.
RFC pilots used to joke that it offered the choice between "a wooden cross, the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and ...
, or a Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
".
A two-seat trainer version was later built to ease the transition process: in his ''Recollections of an Airman'', Lieutenant Colonel L. A. Strange, who served with the central flying school, wrote: "In spite of the care we took, Camels continually spun down out of control when by pupils on their first solos. At length, with the assistance of Lieut Morgan, who managed our workshops, I took the main tank out of several Camels and replaced hem
A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the g ...
with a smaller one, which enabled us to fit in dual control." Such conversions, and dual instruction, went some way to alleviating the previously unacceptable casualties incurred during the critical type-specific solo training stage.
Despite these issues, its agility in combat made the Camel one of the best-remembered Allied aircraft of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Aviation author Robert Jackson notes that: "in the hands of a novice it displayed vicious characteristics that could make it a killer; but under the firm touch of a skilled pilot, who knew how to turn its vices to his own advantage, it was one of the most superb fighting machines ever built".
Operational history
Western front
In June 1917, the Sopwith Camel entered service with No. 4 Squadron of the Royal Naval Air Service, which was stationed near Dunkirk, France; this was the first squadron to operate the type.Jackson 2007, p. 3. Its first combat flight and reportedly its first victory claim were both made on 4 July 1917. By the end of July, the Camel also equipped No. 3 and No. 9 Naval Squadrons; and it had become operational with No. 70 Squadron of the Royal Flying Corps. By February 1918, 13 squadrons had Camels as their primary equipment. The Camel proved in service to have better manoeuvrability than theAlbatros D.III
The Albatros D.III was a biplane fighter aircraft used by the Imperial German Army Air Service ('' Luftstreitkräfte'') during World War I. A modified licence model was built by Oeffag for the Austro-Hungarian Air Service ( ''Luftfahrtruppen''). ...
and D.V and offered heavier armament and better performance than the Pup and Triplane. Together with the S.E.5a and the SPAD S.XIII
The SPAD S.XIII is a French biplane fighter aircraft of the First World War, developed by '' Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés'' (SPAD) from the earlier and highly successful SPAD S.VII.
During early 1917, the French designer Louis Bé ...
, it helped to re-establish the Allied aerial superiority that lasted well into 1918.
Major Billy Barker used his personal Sopwith Camel ( serial no. ''B6313'', the aircraft in which he scored the majority of his victories) to shoot down 46 aircraft and balloons from September 1917 to September 1918 in 404 operational flying hours, making it the most successful fighter in RAF history.
Home defence and night fighting
An important role for the Camel was home defence. The RNAS flew Camels fromEastchurch
Eastchurch is a village and civil parish on the Isle of Sheppey, in the English county of Kent, two miles east of Minster. The village website claims the area has "a history steeped in stories of piracy and smugglers".
Aviation history
Eastch ...
and Manston airfields against daylight raids by German bombers, including Gothas, from July 1917.Bruce 1965, p. 9.
The public outcry against the night raids and the poor response of London's defences resulted in the RFC deciding to divert Camels that had been heading to the frontlines in France to Britain for the purposes of home defence; in July 1917, 44 Squadron RFC reformed and reequipped with the Camel to conduct the home defence mission.Davis 1999, p. 96. By March 1918, the home defence squadrons had been widely equipped with the Camel and by August 1918, a total of seven home defence squadrons were operating these aircraft.Davis 1999, p. 98.
When the Germans switched to performing nighttime attacks, the Camel proved capable of being flown at night as well. Accordingly, those aircraft assigned to home defence squadrons were quickly modified with navigation lights in order that they could serve as night fighters. A smaller number of Camels were more extensively reconfigured; on these aircraft, the Vickers machine guns were replaced by overwing Lewis guns and the cockpit was moved rearwards so the pilot could reload the guns. This modification, which became known as the "Sopwith Comic" allowed the guns to be fired without affecting the pilot's night vision, and allowed the use of new, more effective incendiary ammunition that was considered unsafe to fire from synchronised Vickers guns.Davis 1999, p. 97.Bruce 1968, p. 151, 153.
The Camel was successfully used to intercept and shoot down German bombers on multiple occasions during 1918, serving in this capacity through to the final German bombing raid upon Britain on the night of the 20/21 May 1918.Jackson 2007, pp. 3-6. During this air raid, a combined force of 74 Camels and Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.5s intercepted 28 Gothas and Zeppelin-Staaken R.VIs; three German bombers were shot down, while two more were downed by anti-aircraft fire from the ground and a further aircraft was lost to engine failure, resulting in the heaviest losses suffered by German bombers during a single night's operation over England.Jackson 2007, p. 6.
 The Camel night fighter was also operated by 151 Squadron to intercept German night bombers operating over the Western Front. These aircraft were not only deployed defensively, but often carried out night intruder missions against German airstrips. After five months of operations, 151 Squadron had claimed responsibility for shooting down 26 German aircraft.Davis 1999, pp. 98–99.
The Camel night fighter was also operated by 151 Squadron to intercept German night bombers operating over the Western Front. These aircraft were not only deployed defensively, but often carried out night intruder missions against German airstrips. After five months of operations, 151 Squadron had claimed responsibility for shooting down 26 German aircraft.Davis 1999, pp. 98–99.
Shipboard and parasite fighter
 The RNAS operated a number of 2F.1 Camels that were suitable for launching from platforms mounted on the turrets of major warships as well as from some of the earliest aircraft carriers to be built. Furthermore, the Camel could be deployed from ''aircraft lighters'', which were specially modified barges; these had to be towed fast enough that a Camel could successfully take off. The aircraft lighters served as means of launching interception sorties against incoming enemy air raids from a more advantageous position than had been possible when using shore bases alone.
During the summer of 1918, a single 2F.1 Camel (''N6814'') participated in a series of trials as a parasite fighter. The aircraft used
The RNAS operated a number of 2F.1 Camels that were suitable for launching from platforms mounted on the turrets of major warships as well as from some of the earliest aircraft carriers to be built. Furthermore, the Camel could be deployed from ''aircraft lighters'', which were specially modified barges; these had to be towed fast enough that a Camel could successfully take off. The aircraft lighters served as means of launching interception sorties against incoming enemy air raids from a more advantageous position than had been possible when using shore bases alone.
During the summer of 1918, a single 2F.1 Camel (''N6814'') participated in a series of trials as a parasite fighter. The aircraft used Airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
'' R23'' as a mothership
A mother ship, mothership or mother-ship is a large vehicle that leads, serves, or carries other smaller vehicles. A mother ship may be a maritime ship, aircraft, or spacecraft.
Examples include bombers converted to carry experimental airc ...
.
Ground attack
By mid-1918, the Camel had become obsolescent as a day fighter as its climb rate, level speed and performance at altitudes over 12,000 ft (3,650 m) were outclassed by the latest German fighters, such as the Fokker D.VII. However, it remained viable as a ground-attack and infantry support aircraft and instead was increasingly used in that capacity. The Camel inflicted high losses on German ground forces, albeit suffering from a high rate of losses itself in turn, through the dropping of 25 lb (11 kg) Cooper bombs and low-level strafing runs. The protracted development of the Camel's replacement, theSopwith Snipe
The Sopwith 7F.1 Snipe was a British single-seat biplane fighter of the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was designed and built by the Sopwith Aviation Company during the First World War, and came into squadron service a few weeks before the end of th ...
, resulted in the Camel remaining in service in this capacity until well after the signing of the Armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the ...
.
During the German spring offensive of March 1918, squadrons of Camels participated in the defence of the Allied lines, harassing the advancing German Army from the skies.Jackson 2007, pp. 7-8. Jackson observed that "some of the most intense air operations took place" during the retreat of the British Fifth Army
The Fifth Army was a field army of the British Army during World War I that formed part of the British Expeditionary Force on the Western Front between 1916 and 1918. The army originated as the Reserve Corps during the preparations for the Brit ...
, in which the Camel provided extensive aerial support. Camels flew at multiple altitudes, some as low as for surprise strafing attacks upon ground forces, while being covered from attack by hostile fighters by the higher altitude aircraft.Jackson 2007, p. 8. Strafing attacks formed a major component of British efforts to contain the offensive, the attacks often having the result of producing confusion and panic amongst the advancing German forces. As the March offensive waned, the Camel was able to operate within and maintain aerial superiority for the remainder of the war.
Postwar service
In the aftermath of the First World War, the Camel saw further combat action. Multiple British squadrons were deployed intoRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
as a part of the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War or Allied Powers intervention in the Russian Civil War consisted of a series of multi-national military expeditions which began in 1918. The Allies first had the goal of helping the Czechoslovak Leg ...
. Between the Camel and the S.E.5, which were the two main types deployed to the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
area to bomb Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
bases and to provide aerial support to the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
warships present, Allied control of the Caspian region had been achieved by May 1919. Starting in March 1919, direct support was also provided for White Russian forces, carrying out reconnaissance, ground attack, and escort operations.Jackson 2007, pp. 8-10. During the summer of 1919, Camels of No. 47 Squadron conducted offensive operations in the vicinity of Tsaritsyn
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stalingrád, label=none; ) ...
, primarily against Urbabk airfield; targets including enemy aircraft, cavalry formations, and river traffic. In September 1919, 47 Squadron was related to Kotluban
Kotluban (russian: Котлубань) is a rural locality (a settlement) and the administrative center of Kotlubanskoye Rural Settlement, Gorodishchensky District, Volgograd Oblast
Volgograd Oblast (russian: Волгогра́дская о́б ...
, where its aircraft operations mainly focused on harassing enemy communication lines. During late 1919 and early 1920, the RAF detachment operated in support of General Vladimir May-Mayevsky
Vladimir Zenonovich May-Mayevsky KCMG (; – 30 November 1920) was a general in the Imperial Russian Army and one of the leaders of the counterrevolutionary White movement during the Russian Civil War.
Biography
According to Peter Kenez, ...
's counter-revolutionary
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revolut ...
volunteer army during intense fighting around Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.Jackson 2007, p. 10.
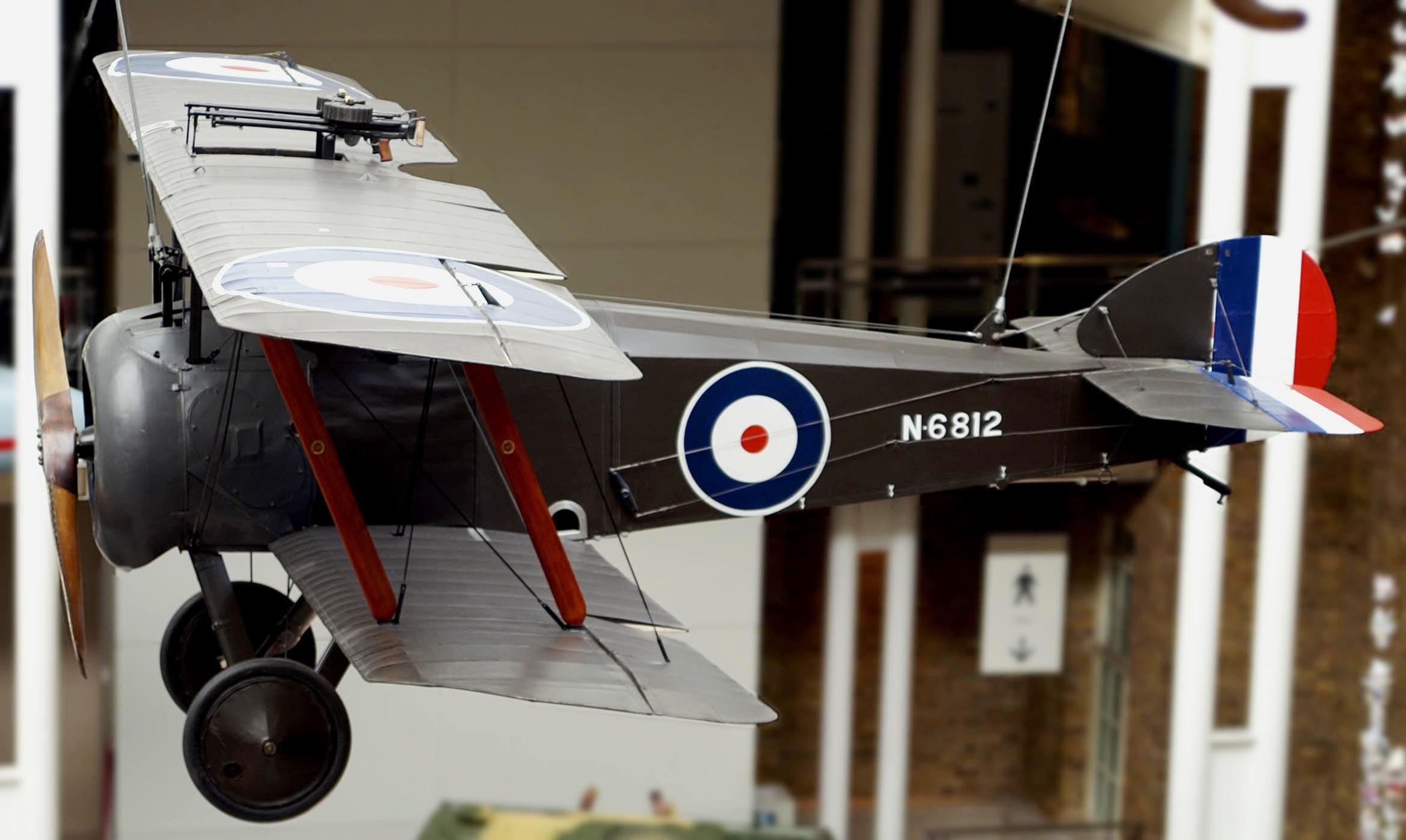 The 2F.1 was a shipboard variant, flown from . It had a slightly shorter wingspan and a Bentley BR1 as its standard engine. Additionally, one Vickers gun was replaced by an overwing Lewis gun to assist in destroying Zeppelins using incendiary ammunition.
The 2F.1 was a shipboard variant, flown from . It had a slightly shorter wingspan and a Bentley BR1 as its standard engine. Additionally, one Vickers gun was replaced by an overwing Lewis gun to assist in destroying Zeppelins using incendiary ammunition.

 ;
*
;
*  ;
* American Expeditionary Force
*
;
* American Expeditionary Force
*
 There are eight known original Sopwith Camels left:
* B5747 – F.1 on static display at the Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History in
There are eight known original Sopwith Camels left:
* B5747 – F.1 on static display at the Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History in
 * Replica - F.1 airworthy in Oliver BC Canada, operated as C-FGHT by the Royal Flying Corps School of Aerial Fighting Ltd. Built from Replicraft plans by Rolland Carlson in Wi.Powered by a Warner Super Scarab 165 hp engine.
* Replica – Type T.57 on static display at the Fleet Air Arm Museum at
* Replica - F.1 airworthy in Oliver BC Canada, operated as C-FGHT by the Royal Flying Corps School of Aerial Fighting Ltd. Built from Replicraft plans by Rolland Carlson in Wi.Powered by a Warner Super Scarab 165 hp engine.
* Replica – Type T.57 on static display at the Fleet Air Arm Museum at
"Sopwith Camel: Historic Military Aircraft No 10: Part I."
''Flight International, Flight'', 22 April 1955, pp. 527–532. * Bruce, J.M
"Sopwith Camel: Historic Military Aircraft No 10: Part II."
''Flight International, Flight'', 29 April 1955. pp. 560–563. * Bruce, J.M. "Aircraft Profile No. 31. The Sopwith Camel F.1" ''Profile Publications'', 1965. * Bruce, J.M. ''War Planes of the First World War: Volume Two Fighters''. London:Macdonald, 1968. . * Clark, Alan. ''Aces High: The War In The Air Over The Western Front 1914 - 1918''. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1973. . * * Davis, Mick. ''Sopwith Aircraft''. Ramsbury, Malborough, UK: The Crowood Press, 1999. . * Ellis, Ken. ''Wrecks & Relics, 21st edition''. Manchester, UK: Crecy Publishing, 2008. . * * Gerdessen, Frederik. "Estonian Air Power 1918 – 1945". ''Air Enthusiast'', No. 18, April – July 1982. pp. 61–76. . * Guttman, Jon: "Sopwith Camel (Air Vanguard; 3)". Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2012. . * Jackson, A.J. ''British Civil Aircraft 1919-1972: Volume III''. London: Putnam, 1988. . * Jackson, Robert. ''Infamous Aircraft - Dangerous Designs and their Vices''. Barnsley, UK:Pen and Sword, 2005. . * Jackson, Robert. ''Britain's Greatest Aircraft''. Pen and Sword, 2007. . * * Leinburger, Ralf. ''Fighter: Technology, Facts, History''. London: Parragon Inc., 2008. . * Mason, Francis K. ''The British Fighter''. London: Putnam, 1992. * Murphy, Justin D. and Matthew A. McNiece. ''Military Aircraft, 1919-1945: An Illustrated History of their Impact''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO, 2009. . * Ralph, Wayne. ''Barker VC: The Classic Story of a Legendary First World War Hero''. London: Grub Street, 1999. . * Robertson, Bruce. ''Sopwith: The Man and His Aircraft''. London: Harleyford, 1970. . * Sturtivant, Ray and Gordon Page. ''The Camel File''. Tunbridge Wells, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 1993. . * Thomas, Andrew. "In the Footsteps of Daedulus: Early Greek Naval Aviation". ''Air Enthusiast'', No. 94, July–August 2001, pp. 8–9. * ''United States Air Force Museum Guidebook''. Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio: Air Force Museum Foundation, 1975. * Williams, Anthony G. and Emmanuel Gustin. ''Flying Guns: World War I and its Aftermath 1914–32''. Ramsbury, Wiltshire: Airlife, 2003. . * Winchester, Jim, ed. "Sopwith Camel." ''Biplanes, Triplanes and Seaplanes'' (Aviation Factfile). London: Grange Books plc, 2004. .
Cole Palen/Nat deFlavia reproduction Camel at Old Rhinebeck Aerodrome
Canadian Aviation Museum Camel
{{Authority control 1910s British fighter aircraft Military aircraft of World War I Sopwith aircraft, Camel Biplanes Single-engined tractor aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1916 Rotary-engined aircraft Parasite aircraft
Variants
Camels were powered by several makes ofrotary engine
The rotary engine is an early type of internal combustion engine, usually designed with an odd number of cylinders per row in a radial configuration. The engine's crankshaft remained stationary in operation, while the entire crankcase and its ...
s:
* Bentley BR1, 150 hp (standard for RNAS aircraft)
* Clerget 9B, 130 hp (standard powerplant)
* Clerget 9Bf, 140 hp
* Le Rhône 9J
The Le Rhône 9J is a nine-cylinder rotary aircraft engine produced in France by Gnome et Rhône. Also known as the Le Rhône 110 hp in a reference to its nominal power rating, the engine was fitted to a number of military aircraf ...
, 110 hp
* Gnome Monosoupape
The ''Monosoupape'' (French for single-valve), was a rotary engine design first introduced in 1913 by Gnome Engine Company (renamed Gnome et Rhône in 1915). It used a clever arrangement of internal transfer ports and a single pushrod-operated e ...
9B-2, 100 hp
* Gnome Monosoupape 9N, 160 hp
Sopwith Camel F.1
The F.1 was the main production version. It was armed with twin synchronised Vickers guns.Sopwith Camel 2F.1
 The 2F.1 was a shipboard variant, flown from . It had a slightly shorter wingspan and a Bentley BR1 as its standard engine. Additionally, one Vickers gun was replaced by an overwing Lewis gun to assist in destroying Zeppelins using incendiary ammunition.
The 2F.1 was a shipboard variant, flown from . It had a slightly shorter wingspan and a Bentley BR1 as its standard engine. Additionally, one Vickers gun was replaced by an overwing Lewis gun to assist in destroying Zeppelins using incendiary ammunition.
Sopwith Camel "Comic" Night fighter
The "Comic" was a Camel variant designed specifically for night-fighting duties. The twin Vickers guns were replaced by two Lewis guns onFoster mounting
The Foster mounting was a device fitted to some fighter aircraft of the Royal Flying Corps during the First World War. It was designed to enable a machine gun (in practice, a Lewis Gun) to fire ''over'', rather than ''through'' the arc of the sp ...
s firing forward over the top wing, as the muzzle flash of the Vickers guns could blind the pilot. The second reason to use Lewis guns was to facilitate the use of incendiary ammunition because of the risk of using it in synchronized guns. To allow reloading of the guns, the pilot was moved about to the rear, and to compensate the fuel tank was moved forward. It served with Home Defence Squadrons against German air raids. The "Comic" nickname was unofficial, and was shared with the night fighter version of the Sopwith 1½ Strutter.
F.1/1
The F1/1 was a version with tapered wings.T.F.1
The T.F.1 was an experimental trench fighter used for development work for theSopwith Salamander
The Sopwith TF.2 Salamander was a British ground-attack aircraft of the First World War designed by the Sopwith Aviation Company which first flew in April 1918. It was a single-engined, single-seat biplane, based on the Sopwith Snipe fighter, wi ...
. Its machine guns were angled downwards for efficient strafing
Strafing is the military practice of attacking ground targets from low-flying aircraft using aircraft-mounted automatic weapons.
Less commonly, the term is used by extension to describe high-speed firing runs by any land or naval craft such ...
, and it featured armour plating for protection.
Trainer
The trainer variant had a second cockpit behind the normal pilot's position. The weapons were removed, although the hump was sometimes kept.Operators

 ;
*
;
* Australian Flying Corps
The Australian Flying Corps (AFC) was the branch of the Australian Army responsible for operating aircraft during World War I, and the forerunner of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). The AFC was established in 1912, though it was not until ...
** No. 4 Squadron AFC in France.
** No. 5
Squadron AFC in the United Kingdom.
** No. 6 (Training) Squadron AFC in the United Kingdom.
** No. 8 (Training) Squadron AFC in the United Kingdom.
;
* Aviation Militaire Belge
** 1ère Escadrille de Chasse
* Groupe de Chasse
** 9ème Escadrille de Chasse
** 11ème Escadrille de Chasse
;
* Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environm ...
;
* Estonian Air Force
The Estonian Air Force ( et, Õhuvägi, ) is the aviation branch of the Estonian Defence Forces. The air force traces its history to 1918, and was re-established in its current form in 1991.
As of 2016, the Estonian Air Force has a strength of ...
;
* French Government
;
* Georgian Air Force
The Aviation and Air Defence Command of the Defence Forces ( ka, თავდაცვის ძალების ავიაციისა და საჰაერო თავდაცვის სარდლობა, tr), (''formerly'' ...
- 3-4 aircraft, 1920
;
* Hellenic NavyDavis 1999, p. 102.
;
* Latvian Air Force
Latvian Air Force ( lv, Latvijas Gaisa spēki) is the aviation branch of the National Armed Forces. The first air force (AF) units were established 1992. It has no air combat capability, thus the defense of Latvian air space is maintained by NATO ...
;
* Royal Netherlands Air Force
;
* Polish Air Force operated 1 Camel post-war (1921)
*Imperial Russian Air Service
The Imperial Russian Air Service (russian: Императорскій военно-воздушный флотъ, , Emperor's Military Air Fleet) was an air force founded in 1912 for Imperial Russia."''12 августа 1912 года прика ...
;
* Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
- Postwar.
;
* Royal Flying Corps / Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
:* 3 Squadron
:* 17 Squadron
:* 28 Squadron
:* 37 Squadron
:* 43 Squadron
:* 44 Squadron
:* 45 Squadron
:* 46 Squadron
:* 47 Squadron
:* 50 Squadron
:* 51 Squadron
:* 54 Squadron
:* 61 Squadron
* 65 Squadron
* 66 Squadron
* 70 Squadron
* 71 Squadron
* 73 Squadron
* 75 Squadron
* 78 Squadron
* 80 Squadron
* 81 Squadron
* 89 Squadron
* 94 Squadron
* 112 Squadron
* 139 Squadron
* 143 Squadron
* 150 Squadron
* 151 Squadron
* 152 Squadron
* 155 Squadron
* 187 Squadron
* 188 Squadron
* 189 Squadron
* 198 Squadron
* 201 Squadron
* 203 Squadron
* 204 Squadron
* 208 Squadron
* 209 Squadron
* 210 Squadron
* 212 Squadron
* 213 Squadron
* 219 Squadron
* 220 Squadron
* 222 Squadron
* 225 Squadron
* 230 Squadron
* 233 Squadron
* 273 Squadron
* Royal Naval Air Service
** No. 1 Squadron RNAS
** No. 3 Squadron RNAS
** No. 4 Squadron RNAS
** No. 6 Squadron RNAS
** No. 8 Squadron RNAS
** No. 9 Squadron RNAS
** No. 10 Squadron RNAS
** No. 12 Squadron RNAS
** No. 13 Squadron RNAS
 ;
* American Expeditionary Force
*
;
* American Expeditionary Force
* United States Army Air Service
The United States Army Air Service (USAAS)Craven and Cate Vol. 1, p. 9 (also known as the ''"Air Service"'', ''"U.S. Air Service"'' and before its legislative establishment in 1920, the ''"Air Service, United States Army"'') was the aerial war ...
** 9th Aero Squadron
The 9th Aero Squadron was an Air Service, United States Army unit that fought on the Western Front during World War I.
The squadron was assigned as an Army Observation Squadron, performing long-range, strategic night reconnaissance over the en ...
** 17th Aero Squadron
** 27th Aero Squadron
The 27th Aero Squadron was a United States Army Air Service unit that fought on the Western Front during World War I.
The squadron was assigned as a Day Pursuit (Fighter) Squadron as part of the 1st Pursuit Group, First United States Army. Its ...
** 37th Aero Squadron
** 148th Aero Squadron
* United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
Surviving aircraft
 There are eight known original Sopwith Camels left:
* B5747 – F.1 on static display at the Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History in
There are eight known original Sopwith Camels left:
* B5747 – F.1 on static display at the Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
.
* B6291 – F.1 on display at the National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center
The Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, also called the Udvar-Hazy Center, is the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum (NASM)'s annex at Washington Dulles International Airport in the Chantilly area of Fairfax County, Virginia. It holds numerous ...
in Chantilly, Virginia
Chantilly is a census-designated place (CDP) in western Fairfax County, Virginia, Fairfax County, Virginia. The population was 24,301 as of the 2020 census. Chantilly is named after an early-19th-century mansion and farm, which in turn took the ...
. After being discovered in the 1960s by Desmond St. Cyrien, the aircraft was restored through the 1980s, with the restoration being completed by Tony Ditheridge at AJD Engineering in the United Kingdom, first flying in 1992. From 2005 the aircraft was part of the Javier Arango Collection in Paso Robles, California
Paso Robles ( ), officially El Paso de Robles (Spanish for "The Pass of Oaks"), is a city in San Luis Obispo County, California, United States. Located on the Salinas River approximately north of San Luis Obispo, the city is known for its hot ...
and was donated to the NASM on Arango's death in April 2017.
* B7280 – F.1 on static display at the Polish Aviation Museum
The Polish Aviation Museum ( pl, Muzeum Lotnictwa Polskiego w Krakowie) is a large museum of historic aircraft and aircraft engines in Kraków, Poland. It is located at the site of the no-longer functional Kraków-Rakowice-Czyżyny Ai ...
in Kraków, Lesser Poland. The aircraft was built in Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincol ...
by Clayton & Shuttleworth
Clayton & Shuttleworth was an engineering company located at Stamp End Works, Lincoln, Lincolnshire, England. The company was established in 1842 when Nathaniel Clayton (1811–1890) formed a partnership with his brother-in-law, Joseph Shuttlewo ...
. On 5 September 1918, when being flown by Captain Herbert A. Patey of No. 210 Squadron RAF over Belgium, it was shot down by Ludwig Beckmann of ''Jasta 56
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 56, commonly abbreviated to Jasta 56, was a "hunting group" (i.e., fighter squadron) of the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. The squadron would score 63 aerial victories d ...
''. Patey survived and was taken prisoner. The Germans repaired the aircraft and flew it until the end of the war. It was then taken to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
and exhibited at the Deutsche Luftfahrt Sammlung (German Aviation Collection). During World War II it was moved to Poland for safekeeping, and put into storage. Restoration began in 2007 and was completed by 2010.
* C8228 – F.1 on static display at the National Naval Aviation Museum
The National Naval Aviation Museum, formerly known as the National Museum of Naval Aviation and the Naval Aviation Museum, is a military and aerospace museum located at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
Founded in 1962 and moved to its cur ...
in Pensacola, Florida.
* F6314 – F.1 on static display at the Royal Air Force Museum London
The Royal Air Force Museum London (also commonly known as the RAF Museum) is located on the former Hendon Aerodrome. It includes five buildings and hangars showing the history of aviation and the Royal Air Force. It is part of the Royal Air Fo ...
in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
. It was built by Boulton & Paul
Boulton & Paul Ltd was a British general manufacturer from Norwich, England that became involved in aircraft manufacture.
Jeld Wen Inc. bought Boulton & Paul (along with another joinery company John Carr) from the Rugby Group plc in 1999 to ...
and is painted to represent an aircraft coded ''B'' of No. 65 Squadron RAF.
* N6812 – 2F.1 on static display at the Imperial War Museum in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
. It was built by William Beardmore and was flown by Flight Sub-Lieutenant Stuart Culley on 11 August 1918 when he shot down Zeppelin LZ 100.Ellis 2008, p. 148.
* N8156 – 2F.1 on static display at the Canada Aviation and Space Museum in Ottawa, Ontario
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
. Manufactured in 1918 by Hooper and Company Limited, it was purchased by the RCAF in 1925 and last flew in 1967.
* ZK-SDL – F.1 airworthy in New Zealand with The Vintage Aviator Ltd (TVAL) and painted as B5663. It was previously displayed in the Aerospace Education Center in Little Rock, Arkansas
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
, until it closed in December 2010, and the aircraft was sold to help pay debts. The Camel was sold to TVAL and restored to flying condition. It was previously registered as N6254.
Reproductions
 * Replica - F.1 airworthy in Oliver BC Canada, operated as C-FGHT by the Royal Flying Corps School of Aerial Fighting Ltd. Built from Replicraft plans by Rolland Carlson in Wi.Powered by a Warner Super Scarab 165 hp engine.
* Replica – Type T.57 on static display at the Fleet Air Arm Museum at
* Replica - F.1 airworthy in Oliver BC Canada, operated as C-FGHT by the Royal Flying Corps School of Aerial Fighting Ltd. Built from Replicraft plans by Rolland Carlson in Wi.Powered by a Warner Super Scarab 165 hp engine.
* Replica – Type T.57 on static display at the Fleet Air Arm Museum at RNAS Yeovilton
Royal Naval Air Station Yeovilton, or RNAS Yeovilton, (HMS ''Heron'') is an airfield of the Royal Navy and British Army, sited a few miles north of Yeovil, Somerset. It is one of two active Fleet Air Arm bases (the other being RNAS Culdrose) ...
near Yeovil, Somerset
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somer ...
. It was built in 1969 Slingsby for use in a Biggles
James Bigglesworth, nicknamed "Biggles", is a fictional pilot and adventurer, the title character and hero of the ''Biggles'' series of adventure books, written for young readers by W. E. Johns (1893–1968). Biggles made his first appearance ...
film. It has a Warner Scarab engine installed and is painted as ''B6401''.
* Replica – F.1 on static display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
in Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. The 2020 U.S. census estimate put the city population at 137,644, while Greater D ...
. This aircraft was built by museum personnel from original First World War factory drawings and was completed in 1974. It is painted and marked as the Camel flown by Lt. George A. Vaughn Jr. while flying with the 17th Aero Squadron.
* Replica – F.1 airworthy at the Cavanaugh Flight Museum
The Cavanaugh Flight Museum is an aviation museum in Addison, Texas, with a non-profit 501(c)(3) status for aviation educational.
Mission
The Museum promotes aviation education, research and American aviation heritage. Further, the Museum pro ...
in Addison, Texas
Addison is an incorporated town in Dallas County, Texas, in the United States. Addison is situated to the immediate north of the city of Dallas, with a 2020 census population of 16,661. Addison and Flower Mound were the only two Texas municipali ...
. It was built by Dick Day from original factory drawings. The aircraft is fitted with original instruments, machine guns and an original Gnome rotary engine. It is painted in the scheme of the World War I flying ace Captain Arthur Roy Brown (RAF officer)
Arthur Roy Brown, (23 December 1893 – 9 March 1944) was a Canadian flying ace of the First World War, credited with ten aerial victories. The Royal Air Force officially credited Brown with shooting down Manfred von Richthofen, the "Red ...
, a Canadian who flew with the Royal Air Force.
* Replica – F.1 on display at the Brooklands Museum in Weybridge, Surrey. It was built in 1977 by Viv Bellamy at Lands End, as a flyable reproduction for Leisure Sport Ltd. Painted to represent ''B7270'' of 209 Squadron, RAF, the machine which Captain Roy Brown flew when officially credited with shooting down Baron Manfred von Richthofen, it has a Clerget rotary engine of 1916 and was registered as G-BFCZ until 2003. First displayed at the museum in January 1988 for Sir Thomas Sopwith
Sir Thomas Octave Murdoch Sopwith, CBE, Hon FRAeS (18 January 1888 – 27 January 1989) was an English aviation pioneer, businessman and yachtsman.
Early life
Sopwith was born in Kensington, London, on 18 January 1888. He was the e ...
’s 100th birthday celebrations, it was purchased by the museum later that year.
* Replica – B6299 at the Old Rhinebeck Aerodrome in Red Hook, New York. It was completed in 1992 with a 160 hp Gnome Monosoupape
The ''Monosoupape'' (French for single-valve), was a rotary engine design first introduced in 1913 by Gnome Engine Company (renamed Gnome et Rhône in 1915). It used a clever arrangement of internal transfer ports and a single pushrod-operated e ...
model 9N rotary, built by Nathaniel deFlavia and Cole Palen. It replaced one of the Dick Day-built and -flown Camel reproductions formerly flown at Old Rhinebeck by Mr. Day in their weekend vintage airshows, which had left the Aerodrome's collection some years earlier.
* Replica – F.1 airworthy with the Javier Arango Collection in Paso Robles, California. It was constructed by Dick Day, is powered by a 160 hp Gnome Monosoupape 9N rotary, and is registered as ''N8343''.
* Replica – Unknown airworthy with the Vintage Aviator Collection in Masterton, New Zealand. It was originally built by Carl Swanson for Gerry Thornhill. It is powered by a 160 hp Gnome Monosoupape
The ''Monosoupape'' (French for single-valve), was a rotary engine design first introduced in 1913 by Gnome Engine Company (renamed Gnome et Rhône in 1915). It used a clever arrangement of internal transfer ports and a single pushrod-operated e ...
rotary engine and is painted as ''B3889''.
* Replica – F.1 on static display at the Canadian Museum of Flight in Langley, British Columbia. Lacking an engine, a full reproduction 130 hp rotary engine has been installed.
* Replica – F.1 on static display at the Aviation Heritage Museum in Bull Creek, Western Australia
Bull Creek is a suburb of Perth, Western Australia, located within the local government area of City of Melville. The suburb lies to the south of a creek of the same name, which flows into the Canning River.
History
Prior to European settlem ...
. The engine is original and the propeller is suspected to also be genuine.
* Replica – F.1 airworthy at the Shuttleworth Collection in Old Warden, Bedfordshire. It was built by the Northern Aeroplane Workshops.
* Replica – F.1 under construction by Koz Aero in Comstock Park, Michigan. It is based on original factory drawings and using many original parts, including an original engine and instruments.
* Replica – F.1 under construction by John S. Shaw. It has an original Clerget 9B 130 CV engine.
* Replica – F.1 under construction by John S. Shaw. It has a new build Gnome Monosoupape 9B-2 100 hp engine.
* Replica – F.1 on static display at Montrose Air Station Heritage Centre in Montrose, Angus
Montrose ( , gd, Monadh Rois) is a town and former royal burgh in Angus, Scotland. Situated north of Dundee and south of Aberdeen, Montrose lies between the mouths of the North and South Esk rivers. It is the northernmost coastal town in Angus ...
. It is painted and marked as B7320 flown by John Todd (RAF officer), Captain John Todd of 70 Squadron Royal Flying Corps.
* Replica – F.1 on static display at Museum of Flight, The Museum of Flight near Seattle Washington.
Specifications (F.1 Camel)

Notable appearances in media
Biggles
James Bigglesworth, nicknamed "Biggles", is a fictional pilot and adventurer, the title character and hero of the ''Biggles'' series of adventure books, written for young readers by W. E. Johns (1893–1968). Biggles made his first appearance ...
flies a Sopwith Camel in the novels by W. E. Johns during Biggles's spell in 266 Squadron during the First World War. The first collection of Biggles stories, titled ''The Camels are Coming'', was published in 1932. The first two collections of stories (broken into three books in Australia) were all true stories or events, lightly fictionalised—some of them are identifiable in official war records, e.g., the accidental discovery of a major camouflaged airfield when rescuing a downed pilot.
The Camel is the "plane" of Snoopy in the ''Peanuts'' comic strip, when he imagines himself as a World War I flying ace and the nemesis of the Manfred von Richthofen, Red Baron.Murphy and McNiece 2003, p. 87.
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* Bowyer, Chaz. ''Sopwith Camel: King of Combat''. Falmouth, Cornwall, UK: Glasney Press, 1978. . * Bruce, J.M"Sopwith Camel: Historic Military Aircraft No 10: Part I."
''Flight International, Flight'', 22 April 1955, pp. 527–532. * Bruce, J.M
"Sopwith Camel: Historic Military Aircraft No 10: Part II."
''Flight International, Flight'', 29 April 1955. pp. 560–563. * Bruce, J.M. "Aircraft Profile No. 31. The Sopwith Camel F.1" ''Profile Publications'', 1965. * Bruce, J.M. ''War Planes of the First World War: Volume Two Fighters''. London:Macdonald, 1968. . * Clark, Alan. ''Aces High: The War In The Air Over The Western Front 1914 - 1918''. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1973. . * * Davis, Mick. ''Sopwith Aircraft''. Ramsbury, Malborough, UK: The Crowood Press, 1999. . * Ellis, Ken. ''Wrecks & Relics, 21st edition''. Manchester, UK: Crecy Publishing, 2008. . * * Gerdessen, Frederik. "Estonian Air Power 1918 – 1945". ''Air Enthusiast'', No. 18, April – July 1982. pp. 61–76. . * Guttman, Jon: "Sopwith Camel (Air Vanguard; 3)". Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2012. . * Jackson, A.J. ''British Civil Aircraft 1919-1972: Volume III''. London: Putnam, 1988. . * Jackson, Robert. ''Infamous Aircraft - Dangerous Designs and their Vices''. Barnsley, UK:Pen and Sword, 2005. . * Jackson, Robert. ''Britain's Greatest Aircraft''. Pen and Sword, 2007. . * * Leinburger, Ralf. ''Fighter: Technology, Facts, History''. London: Parragon Inc., 2008. . * Mason, Francis K. ''The British Fighter''. London: Putnam, 1992. * Murphy, Justin D. and Matthew A. McNiece. ''Military Aircraft, 1919-1945: An Illustrated History of their Impact''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO, 2009. . * Ralph, Wayne. ''Barker VC: The Classic Story of a Legendary First World War Hero''. London: Grub Street, 1999. . * Robertson, Bruce. ''Sopwith: The Man and His Aircraft''. London: Harleyford, 1970. . * Sturtivant, Ray and Gordon Page. ''The Camel File''. Tunbridge Wells, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 1993. . * Thomas, Andrew. "In the Footsteps of Daedulus: Early Greek Naval Aviation". ''Air Enthusiast'', No. 94, July–August 2001, pp. 8–9. * ''United States Air Force Museum Guidebook''. Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio: Air Force Museum Foundation, 1975. * Williams, Anthony G. and Emmanuel Gustin. ''Flying Guns: World War I and its Aftermath 1914–32''. Ramsbury, Wiltshire: Airlife, 2003. . * Winchester, Jim, ed. "Sopwith Camel." ''Biplanes, Triplanes and Seaplanes'' (Aviation Factfile). London: Grange Books plc, 2004. .
External links
Cole Palen/Nat deFlavia reproduction Camel at Old Rhinebeck Aerodrome
Canadian Aviation Museum Camel
{{Authority control 1910s British fighter aircraft Military aircraft of World War I Sopwith aircraft, Camel Biplanes Single-engined tractor aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1916 Rotary-engined aircraft Parasite aircraft