Sonographer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
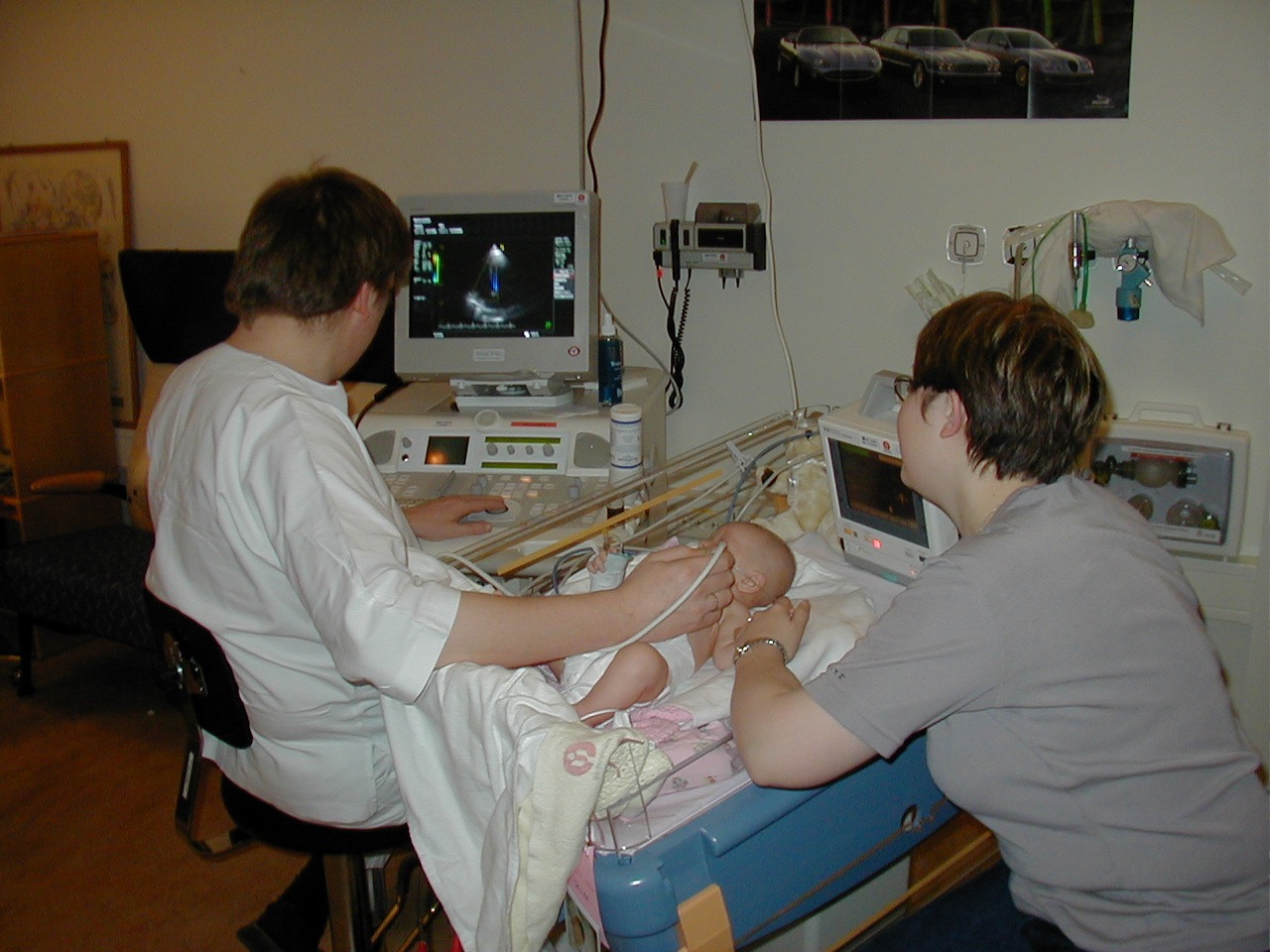 A sonographer is an allied healthcare professional who specializes in the use of ultrasonic imaging devices to produce diagnostic images, scans, videos or three-dimensional volumes of anatomy and diagnostic data. The requirements for clinical practice vary greatly by country. Sonography requires specialized education and skills to acquire, analyze and optimize information in the image. Due to the high levels of decisional latitude and diagnostic input, sonographers have a high degree of responsibility in the diagnostic process. Many countries require medical sonographers to have professional certification. Sonographers have core knowledge in ultrasound physics, cross-sectional anatomy, physiology, and pathology.
A sonologist is a
A sonographer is an allied healthcare professional who specializes in the use of ultrasonic imaging devices to produce diagnostic images, scans, videos or three-dimensional volumes of anatomy and diagnostic data. The requirements for clinical practice vary greatly by country. Sonography requires specialized education and skills to acquire, analyze and optimize information in the image. Due to the high levels of decisional latitude and diagnostic input, sonographers have a high degree of responsibility in the diagnostic process. Many countries require medical sonographers to have professional certification. Sonographers have core knowledge in ultrasound physics, cross-sectional anatomy, physiology, and pathology.
A sonologist is a
/ref>
medical doctor
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, mai ...
who has undergone formal medical ultrasound
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, mu ...
training to diagnose and treat diseases. Sonologist is licensed to perform and write ultrasound imaging reports independently or verifies a sonographer's report, prescribe medications and medical certificates, and give clinical consultations.
A sonologist may practice in multiple modalities or specialize in only one field, such as obstetric
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a ...
, gynecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see American and British English spelling differences, spelling differences) is the area of medicine that involves the treatment of women's diseases, especially those of the reproductive organs. It is often paired with ...
, heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
, emergency and vascular
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
ultrasound.
Terminology
Sonographer is the preferred term for the allied healthcare professionals who perform diagnostic medical sonography, or diagnosticultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
. The alternative term "ultrasonographer" is much less commonly used.Sonography, What is it?/ref>
Training and licensing
Australia
The Australasian Sonographers Association (ASA) was formed in 1992 in response to the desire of sonographers across Australia for an organisation that represents and considers issues important to sonographers in the Australian healthcare environment. The ASA now has more than 5000 individual member sonographers from Australia and New Zealand, and about 30 corporate partners. The ASA has pledged to pursue high standards within the practice of medical sonography, and has a structure of a board of directors and multiple representative branches in all Australian states and New Zealand. Australian sonographers must be accredited by the Australian Sonographers Accreditation Registry (ASAR), whose brief is to accredit and reaccredit on a regular basis, postgraduate ultrasound programs offered by Australian universities, and to establish the criteria against which those programs and any other future Australian and New Zealand programs are to be judged. In addition, a register of accredited medical sonographers and accredited student sonographers is maintained and their continuing professional development activities monitored and recorded. The Health Insurance Commissison in association with the ASAR introduced in 2002 a program of accreditation and continuing professional education for sonographers. The ASAR recognises registration with the Australian Orthoptic Board as appropriate accreditation for orthoptists to undertake sonography in relation to ocular structures.Canada
The vast majority of Canadian sonographers have received their education through an accredited sonography program. Many programs are available across the country and may include direct-entry programs for degrees, advanced diplomas, and second-discipline graduate certificate programs. Sonography Canada registers sonographers in three credentials: generalist, cardiac, and vascular. To become registered, eligible candidates must successfully meet Sonography Canada's clinical (Canadian Clinical Skills Assessment) and academic requirements. Sonography Canada-credentialed sonographers must also document their continuing education by maintaining a minimum 40 continuing professional development credits every three years. The Nova Scotia Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonographers is currently working with the Nova Scotia Association of Medical Radiation Technologists to add diagnostic ultrasound as a new discipline in the proposed college. This means that diagnostic sonography would become a self-regulated profession in Nova Scotia, along with radiography, nuclear medicine, magnetic resonance imaging, and radiation therapy. The Department of Health is now considering their application; the appropriate act and associated regulations have been drafted, and the associations are aiming for approval at the spring 2012 session of the legislature.United Kingdom
In the UK, sonographers are also responsible for the interpretation of the images and issue diagnostic reports. They are educated to a high level, and their training is delivered as a MSc/PGDip/PGCert by the universities and overseen by the Consortium for Accreditation of Sonographic Education; as training is delivered at postgraduate level, all sonographers must have a bachelor's degree or equivalent prior to undertaking this specialty, and this means training can take a minimum of 4 years. Currently, no requirement exists for a sonographer to be state registered in the UK, although the majority are registered with theHealth and Care Professions Council
The Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC, formerly the Health Professions Council, HPC) is a statutory regulator of over 280,000 professionals from 15 health and care professions in the United Kingdom. The Council reports its main purpose ...
(HCPC) as a radiographer. State registration of sonographers in their own right is being eagerly sought by the profession. However, the HCPC has previously sought to require statutory registration of sonographers, a motion supported by a number of professional bodies, and the HCPC was rejected by the Department of Health. The rationale for this rejection remains controversial, but a voluntary registry is currently maintained by the College of Radiographers.
Within the United Kingdom, sonographers are employed by hospitals within the National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
and by private companies offering healthcare services.
United States
The profession is subdivided in specialties such ascardiac
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
, obstetrical, vascular, and general sonographers. General sonographers are registered in abdominal and/or obstetric and gynecologic sonography.
Around 1 1/2 years may be needed to get a degree in diagnostic medical sonography. In the United States, the most widely accepted sonographic education is provided by CAAHEP/JRC-DMS accredited programs. The two credentialing bodies in the United States for sonographers are the Cardiovascular Credentialing International established in 1968 and the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) established in 1975. Accreditation is granted through the American National Standards Institute. Recognition of ARDMS programs in providing credentials has also earned the ARDMS accreditation with the National Commission for Certifying Agencies, which is the accrediting arm of the National Organization for Competency Assurance (NOCA). Established in 1977 as a nonprofit organization, NOCA sets quality standards for certifying organizations.
In 2009, New Mexico and Oregon became the first two states to require licensure of sonographers.
Work-related injury
During their careers, 84% of sonographers report experiencing some form of work-related musculoskeletal pain due to scanning in compromised positions, incorrect gripping of the transducer, spending too much time manipulating the transducer on technically difficult exams such as obese or large pregnant patients, and a lack of upper body fitness. Stretching protocols have been suggested to be a useful tool in reducing risk of musculoskeletal injury, pain, and repetitive strain injury in sonographers.See also
*Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
* Radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiati ...
* Sonograph
A spectrogram is a visual representation of the spectrum of frequencies of a signal as it varies with time.
When applied to an audio signal, spectrograms are sometimes called sonographs, voiceprints, or voicegrams. When the data are represen ...
References
{{Reflist Cardiology Medical ultrasonography Ultrasonographers