Solifluction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Solifluction is a collective name for gradual processes in which a mass moves down a slope ("
Solifluction is a collective name for gradual processes in which a mass moves down a slope ("

 Solifluction is a collective name for gradual processes in which a mass moves down a slope ("
Solifluction is a collective name for gradual processes in which a mass moves down a slope ("mass wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in ...
") related to freeze-thaw
Frost weathering is a collective term for several mechanical weathering processes induced by stresses created by the freezing of water into ice. The term serves as an umbrella term for a variety of processes such as frost shattering, frost wedg ...
activity. This is the standard modern meaning of solifluction, which differs from the original meaning given to it by Johan Gunnar Andersson
Johan Gunnar Andersson (3 July 1874 – 29 October 1960)"Andersson, Johan Gunnar" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 385. was a Swedish archaeologist, paleontologist and ge ...
in 1906.
Origin and evolution of the concept
In the original sense it meant the movement of waste saturated in water found in periglacial regions. However it was later discovered that various slow waste movements in periglacial regions did not require saturation in water, but were rather associated to freeze-thaw processes. The term solifluction was appropriated to refer to these slow processes, and therefore excludes rapid periglacial movements. In slow periglacial solifluction there are not clear gliding planes, and therefore skinflows andactive layer
In environments containing permafrost, the active layer is the top layer of soil that thaws during the summer and freezes again during the autumn. In all climates, whether they contain permafrost or not, the temperature in the lower levels of the ...
detachments are not included in the concept. On the other hand, movement of waste saturated in water can occur in any humid climate, and therefore this kind of solifluction is not restricted to cold climates.
Slow periglacial solifluction is classified into four types:
* Ice creep
* Frost creep
* Gelifluction
* Plug-like flow
Slow solifluction acts much slower than some geochemical fluxes or than other erosion processes. The relatively low rates at which solifluction operates contrast with its occurrence over wide mountain areas and periglaciated lowlands. Since solifluction is associated with humidity and cold climates it can be used to infer past climates.
Deposits
Deposits of slow periglacial solifluction compromise poorly stratifieddiamicton Diamicton (also diamict) (from Greek ''δια'' (dia-): through and ''µεικτός'' (meiktós): mixed) is a terrigenous sediment (a sediment resulting from dry-land erosion) that is unsorted to poorly sorted and contains particles ranging in siz ...
and diamicton where stratification is wholly lacking. When stratification can be seen it is often distinguished by a buried organic soil. Some other solifluction deposits that have a more defined stratification consist of alternating layers of diamicton and open-work beds, these last representing buried stone-banked lobes and sheets. A common feature in solifluction deposits is the orientation of clasts parallel to the slope.
Landforms
Solifluction lobes and sheets are types of slope failure and landforms. In solifluction lobes sediments form a tongue-shaped feature due to differential downhill flow rates. In contrast, solifluction sheet sediments move more or less uniformly downslope, thus being a less selective form of erosion than solifluction lobes.Extraterrestrial solifluction
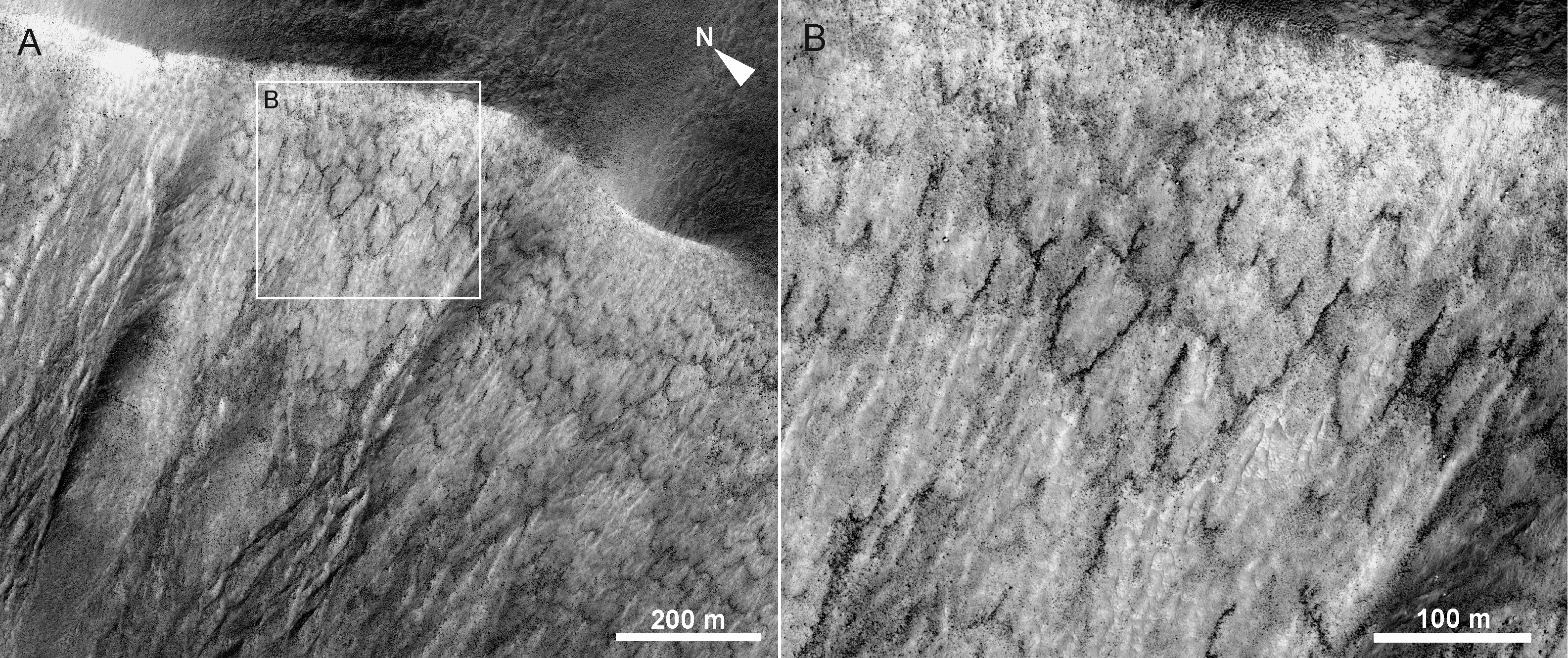
It has been suggested that solifluction might be active onMars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
, even relatively recently (within the last few million years), as observed Martian lobates bear many similarities with solifluction lobes known from Svalbard.
See also
*Mass wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in ...
* Stone run
* Frost weathering
External links
* An example of solifluction can be seen southeast of the Swedish lake LuspasjaureNotes
Notes
References
* Anderson, J.G. 1906. "Solifluction, a Component of Subaërial Denudation", ''The Journal of Geology'', Vol. 14, No. 2 (Feb. – Mar., 1906), pp. 91–112. * French, H. M. 2007. ''The Periglacial Environment'', Third Edition. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 458 pp. * Easterbrook, Don J. Surface ''Processes and Landforms''. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1999 * "Solifluction (geology)" ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Online. n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 2013 {{Periglacial environment Geological hazards Soil erosion