Society of the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The society of the United States is based on
The society of the United States is based on
 Working-class Americans as well as many of those in the middle class may also face occupation alienation. In contrast to upper-middle-class professionals who are mostly hired to conceptualize, supervise and share their thoughts, many Americans enjoy only little autonomy or creative latitude in the workplace. As a result, white collar professionals tend to be significantly more satisfied with their work. More recently those in the center of the income strata, who may still identify as middle class, have faced increasing economic insecurity, supporting the idea of a working-class majority.
Political behavior is affected by class; more affluent individuals are more likely to vote, and education and income affect whether individuals tend to vote for the Democratic or Republican party.
Working-class Americans as well as many of those in the middle class may also face occupation alienation. In contrast to upper-middle-class professionals who are mostly hired to conceptualize, supervise and share their thoughts, many Americans enjoy only little autonomy or creative latitude in the workplace. As a result, white collar professionals tend to be significantly more satisfied with their work. More recently those in the center of the income strata, who may still identify as middle class, have faced increasing economic insecurity, supporting the idea of a working-class majority.
Political behavior is affected by class; more affluent individuals are more likely to vote, and education and income affect whether individuals tend to vote for the Democratic or Republican party.
 The society in United States
Race in the United States is based on physical characteristics and skin color and has played an essential part in shaping American society even before the nation's conception. Until the civil rights movement of the 1960s, racial minorities in the United States faced discrimination and social as well as economic
The society in United States
Race in the United States is based on physical characteristics and skin color and has played an essential part in shaping American society even before the nation's conception. Until the civil rights movement of the 1960s, racial minorities in the United States faced discrimination and social as well as economic
 As the United States is a diverse nation, it is home to numerous organization and social groups and individuals may derive their group affiliated identity from a variety of sources. Many Americans, especially white collar professionals belong to professional organizations such as the APA, ASA or ATFLC , although books like '' Bowling Alone'' indicate that Americans affiliate with these sorts of groups less often than they did in the 1950s and 1960s.
Today, Americans derive a great deal of their identity through their work and professional affiliation, especially among individuals higher on the economic ladder. Recently professional identification has led to many clerical and low-level employees giving their occupations new, more respectable titles, such as "Sanitation service engineer" instead of "Janitor."
Additionally many Americans belong to non-profit organizations and religious establishments and may volunteer their services to such organizations. The
As the United States is a diverse nation, it is home to numerous organization and social groups and individuals may derive their group affiliated identity from a variety of sources. Many Americans, especially white collar professionals belong to professional organizations such as the APA, ASA or ATFLC , although books like '' Bowling Alone'' indicate that Americans affiliate with these sorts of groups less often than they did in the 1950s and 1960s.
Today, Americans derive a great deal of their identity through their work and professional affiliation, especially among individuals higher on the economic ladder. Recently professional identification has led to many clerical and low-level employees giving their occupations new, more respectable titles, such as "Sanitation service engineer" instead of "Janitor."
Additionally many Americans belong to non-profit organizations and religious establishments and may volunteer their services to such organizations. The
, Bureau of Transportation Statistics, U.S. Department of Transportation, accessed May 21, 2006 Lower energy and land costs favor the production of relatively large, powerful cars. The culture in the 1950s and 1960s often catered to the automobile with
 Since the late nineteenth century,
Since the late nineteenth century,
 The cuisine of the United States is extremely diverse, owing to the vastness of the continent, the relatively large population (1/3 of a billion people) and the number of native and immigrant influences. The types of
The cuisine of the United States is extremely diverse, owing to the vastness of the continent, the relatively large population (1/3 of a billion people) and the number of native and immigrant influences. The types of
 Historically, the United States' religious tradition has been dominated by
Historically, the United States' religious tradition has been dominated by
 About half of Americans now live in what is known as the
About half of Americans now live in what is known as the
 Today, family arrangements in the United States reflect the diverse and dynamic nature of contemporary American society. Although for a relatively brief period of time in the 20th century most families adhered to the
Today, family arrangements in the United States reflect the diverse and dynamic nature of contemporary American society. Although for a relatively brief period of time in the 20th century most families adhered to the
and
where monthly rents commonly exceed $1000 a month. Single-parent households are households consisting of a single adult (most often a woman) and one or more children. In the single-parent household, one parent typically raises the children with little to no help from the other. This parent is the sole "breadwinner" of the family and thus these households are particularly vulnerable economically. They have higher rates of Poverty in the United States, poverty, and children of these households are more likely to have educational problems.
A Quick Guide for Living in the US
Life in the USA: The Complete Guide for Immigrants and Americans
* ttp://eneida.over-blog.net Culture, Hedonism & Lifestyle
CommonCensus Map Project
- Identifying geographic spheres of influence {{DEFAULTSORT:Society Of The United States American studies
Western culture
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
, and has been developing since long before the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
became a country with its own unique social and cultural characteristics such as dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is ...
, music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
, arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
, social habits, cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
, and folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, rangin ...
. Today, the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
is an ethnically and racially diverse country as a result of large-scale immigration from many different countries throughout its history.
Its chief early influences came from English and Irish settlers of colonial America. British culture
British culture is influenced by the combined nations' history; its historically Christian religious life, its interaction with the cultures of Europe, the traditions of England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland and the impact of the British Empire ...
, due to colonial ties with Britain that spread the English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the ...
, legal system
The contemporary national legal systems are generally based on one of four basic systems: civil law, common law, statutory law, religious law or combinations of these. However, the legal system of each country is shaped by its unique history an ...
and other cultural inheritances, had a formative influence. Other important influences came from other parts of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
The United States has often been thought of as a melting pot, but recent developments tend towards cultural diversity
Diversity, diversify, or diverse may refer to:
Business
*Diversity (business), the inclusion of people of different identities (ethnicity, gender, age) in the workforce
*Diversity marketing, marketing communication targeting diverse customers
* ...
, pluralism and the image of a salad bowl rather than a melting pot. Due to the extent of American culture there are many integrated but unique social subculture
A subculture is a group of people within a culture that differentiates itself from the parent culture to which it belongs, often maintaining some of its founding principles. Subcultures develop their own norms and values regarding cultural, poli ...
s within the United States. The cultural affiliations an individual in the United States may have commonly depend on social class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of hierarchical social categories, the most common being the upper, middle and lower classes. Membership in a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, inc ...
, political orientation and a multitude of demographic characteristics such as religious background, occupation and ethnic group membership. The strongest influences on American culture came from northern European cultures, most prominently from Britain, Ireland, and Germany.
Social class and work
Though most Americans today identify themselves asmiddle class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. C ...
, American society and its culture are considerably more fragmented. Social class, generally described as a combination of educational attainment, income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. Fo ...
and occupational prestige, is one of the greatest cultural influences in America. Nearly all cultural aspects of mundane interactions and consumer behavior in the US are guided by a person's location within the country's social structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally rel ...
.
Distinct lifestyles, consumption patterns and values are associated with different classes. Early sociologist-economist Thorstein Veblen
Thorstein Bunde Veblen (July 30, 1857 – August 3, 1929) was a Norwegian-American economist and sociologist who, during his lifetime, emerged as a well-known critic of capitalism.
In his best-known book, ''The Theory of the Leisure Class'' ...
, for example, noted that those at the very top of the social ladder engage in conspicuous leisure as well as conspicuous consumption
In sociology and in economics, the term conspicuous consumption describes and explains the consumer practice of buying and using goods of a higher quality, price, or in greater quantity than practical. In 1899, the sociologist Thorstein Veblen c ...
. Upper-middle-class
In sociology, the upper middle class is the social group constituted by higher status members of the middle class. This is in contrast to the term ''lower middle class'', which is used for the group at the opposite end of the middle-class strat ...
persons commonly identify education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
and being cultured as prime values. Persons in this particular social class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of hierarchical social categories, the most common being the upper, middle and lower classes. Membership in a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, inc ...
tend to speak in a more direct manner that projects authority, knowledge and thus credibility. They often tend to engage in the consumption of so-called mass luxuries, such as designer label clothing. A strong preference for natural materials and organic foods as well as a strong health consciousness tend to be prominent features of the upper middle class
In sociology, the upper middle class is the social group constituted by higher status members of the middle class. This is in contrast to the term ''lower middle class'', which is used for the group at the opposite end of the middle-class strat ...
. Middle-class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Com ...
individuals in general value expanding one's horizon, partially because they are more educated and can afford greater leisure and travels. Working-class individuals take great pride in doing what they consider to be "real work," and keep very close-knit kin networks that serve as a safeguard against frequent economic instability.
 Working-class Americans as well as many of those in the middle class may also face occupation alienation. In contrast to upper-middle-class professionals who are mostly hired to conceptualize, supervise and share their thoughts, many Americans enjoy only little autonomy or creative latitude in the workplace. As a result, white collar professionals tend to be significantly more satisfied with their work. More recently those in the center of the income strata, who may still identify as middle class, have faced increasing economic insecurity, supporting the idea of a working-class majority.
Political behavior is affected by class; more affluent individuals are more likely to vote, and education and income affect whether individuals tend to vote for the Democratic or Republican party.
Working-class Americans as well as many of those in the middle class may also face occupation alienation. In contrast to upper-middle-class professionals who are mostly hired to conceptualize, supervise and share their thoughts, many Americans enjoy only little autonomy or creative latitude in the workplace. As a result, white collar professionals tend to be significantly more satisfied with their work. More recently those in the center of the income strata, who may still identify as middle class, have faced increasing economic insecurity, supporting the idea of a working-class majority.
Political behavior is affected by class; more affluent individuals are more likely to vote, and education and income affect whether individuals tend to vote for the Democratic or Republican party. Income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. Fo ...
also had a significant impact on health as those with higher incomes had better access to health care facilities, higher life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
, lower infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
and increased health consciousness.
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
occupation is one of the prime factors of social class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of hierarchical social categories, the most common being the upper, middle and lower classes. Membership in a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, inc ...
and is closely linked to an individual's identity. The average work week in the US for those employed full-time was 42.9 hours long with 30% of the population working more than 40 hours a week. Many of those in the top two earning quintiles often worked more than 50 hours a week. The Average American worker earned $16.64 an hour in the first two quarters of 2006.
Overall Americans worked more than their counterparts in other developed post-industrial nations. While the average worker in Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
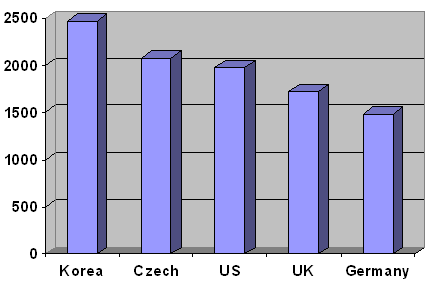
enjoyed 30 days of vacation annually, the average American only had 16 annual vacation days. In 2000 the average American worked 1,978 hours per year, 500 hours more than the average German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, yet 100 hours less than the average Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
. Overall the US labor force was the most productive in the world (overall, not by hour worked), largely due to its workers working more than those in any other post-industrial country (excluding South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
). Americans generally hold working and being productive in high regard; being busy and working extensively may also serve as the means to obtain esteem.
Race and ancestry
marginalization
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. It is used across discipline ...
.
Today, the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of the Census recognizes four races, Native American or American Indian, African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, Asian and White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
(European American
European Americans (also referred to as Euro-Americans) are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes people who are descended from the first European settlers in the United States as well as people who are descended from more recent Eu ...
). According to the U.S. government, Hispanic Americans do not constitute a race, but rather an ethnic group. During the 2000 U.S. census, Whites made up 75.1% of the population with those being Hispanic or Latino constituting the nation's prevalent minority with 12.5% of the population. African Americans made up 12.3% of the total population, 3.6% were Asian American and 0.7% were Native American.
Approximately 62% of White Americans today are either wholly or partly of English, Welsh, Irish, or Scottish ancestry. Approximately 86% of White Americans are of northwestern European descent, and 14% are of southern and eastern European ancestry.
Until the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Thirteenth Amendment (Amendment XIII) to the United States Constitution abolished slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. The amendment was passed by the Senate on April 8, 1864, by the House of Representative ...
was ratified on December 6, 1865, the United States was a slave society. While the northern states had outlawed slavery in their territory in the late 18th and early 19th century their industrial economies relied on the raw materials produced by slave labor. Following the Reconstruction period in the 1870s, Southern states initialized an apartheid regulated by Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the S ...
that provided for legal segregation. Lynching occurred throughout the US until the 1930s, continuing well into the civil rights movement in the South.
Asian Americans were also marginalized during much of US history. Between 1882 and 1943 the United States government instituted the Chinese Exclusion Act
The Chinese Exclusion Act was a United States federal law signed by President Chester A. Arthur on May 6, 1882, prohibiting all immigration of Chinese laborers for 10 years. The law excluded merchants, teachers, students, travelers, and diplo ...
which prohibited Chinese immigrants from entering the nation. During the second world war roughly 120,000 Japanese Americans
are Americans of Japanese people, Japanese ancestry. Japanese Americans were among the three largest Asian Americans, Asian American ethnic communities during the 20th century; but, according to the 2000 United States census, 2000 census, they ...
, 62% of whom were U.S. citizens, were imprisoned in Japanese internment camps. Hispanic Americans also faced segregation and other types of discrimination; they were regularly subject to second class citizen status, in practice if not by law.
Largely as a result of being de jure or de facto excluded and marginalized from so-called mainstream society, racial minorities in the United States developed their own unique sub-cultures. During the 1920s for example, Harlem, New York
Harlem is a neighborhood in Upper Manhattan, New York City. It is bounded roughly by the Hudson River on the west; the Harlem River and 155th Street on the north; Fifth Avenue on the east; and Central Park North on the south. The greater H ...
became home to the Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
. Music styles such as Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a m ...
, Blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the ...
and Rap, Rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock 'n' roll, or rock 'n roll) is a genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It originated from African-American music such as jazz, rhythm ...
as well as numerous folk-songs such as Blue Tail Fly (Jimmy Crack Corn) originated within the realms of African American culture. Chinatowns can be found in many cities across the nation and Asian cuisine has become a common staple in America.
The Mexican community has also had a dramatic impact on American culture. Today, Catholics are the largest religious denomination in the United States and out-number Protestants in the South-west and California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
. Mariachi music and Mexican cuisine are commonly found throughout the Southwest, with some Latin dishes of Mexican origin, such burritos and tacos found anywhere in the nation. Economic discrepancies and de facto segregation, however, continue and is a prominent feature of mundane life in the United States.
While Asian Americans
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian ancestry (including naturalized Americans who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). Although this term had historically been used for all the indigenous peopl ...
have prospered and have a median household income
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways ...
and educational attainment exceeding that of Whites, the same cannot be said for the other races. African Americans, Hispanics and Native Americans have considerably lower income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. Fo ...
and education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
than do White American
White Americans are Americans who identify as and are perceived to be white people. This group constitutes the majority of the people in the United States. As of the 2020 Census, 61.6%, or 204,277,273 people, were white alone. This represented ...
s. In 2005 the median household income
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways ...
of Whites was 62.5% higher than that of African American, nearly one-quarter of whom live below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for ...
. Furthermore, 46.9% of homicide victims in the United States are African American indicating the many severe socio-economic problems African Americans and minorities in general continue to face in the twenty-first century.
Some aspects of American culture codify racism. For example, the prevailing idea in American culture
The culture of the United States of America is primarily of Western, and European origin, yet its influences includes the cultures of Asian American, African American, Latin American, and Native American peoples and their cultures. The U ...
, perpetuated by the media, has been that black features are less attractive or desirable than white features. The idea that blackness was ugly was highly damaging to the psyche of African Americans, manifesting itself as internalized racism. The Black is beautiful
Black is beautiful is a cultural movement that was started in the United States in the 1960s by African Americans. It later spread beyond the United States, most prominently in the writings of the Black Consciousness Movement of Steve Biko in ...
cultural movement sought to dispel this notion.
In the years after the September 11th terrorist attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commerci ...
, discrimination against Arabs and Muslims in the U.S. has increased significantly. The American-Arab Anti-Discrimination Committee
The American-Arab Anti-Discrimination Committee (ADC) states that it is "the largest Arab American grassroots civil rights organization in the United States." According to its webpage it is open to people of all backgrounds, faiths and ethnicities ...
(ADC) reported an increase in hate speech, cases of airline discrimination, hate crimes, police misconduct and racial profiling. The USA Patriot Act
The USA PATRIOT Act (commonly known as the Patriot Act) was a landmark Act of the United States Congress, signed into law by President George W. Bush. The formal name of the statute is the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appro ...
, signed into effect by President Bush on October 26, 2001, has also raised concerns for violating civil liberties. Section 412 of the act provides the government with "sweeping new powers to detain immigrants and other foreign nationals indefinitely with little or no due process at the discretion of the Attorney General." Other sections also allow the government to conduct secret searches, seizures and surveillance, and to freely interpret the definition of 'terrorist activities'.
Group affiliations
 As the United States is a diverse nation, it is home to numerous organization and social groups and individuals may derive their group affiliated identity from a variety of sources. Many Americans, especially white collar professionals belong to professional organizations such as the APA, ASA or ATFLC , although books like '' Bowling Alone'' indicate that Americans affiliate with these sorts of groups less often than they did in the 1950s and 1960s.
Today, Americans derive a great deal of their identity through their work and professional affiliation, especially among individuals higher on the economic ladder. Recently professional identification has led to many clerical and low-level employees giving their occupations new, more respectable titles, such as "Sanitation service engineer" instead of "Janitor."
Additionally many Americans belong to non-profit organizations and religious establishments and may volunteer their services to such organizations. The
As the United States is a diverse nation, it is home to numerous organization and social groups and individuals may derive their group affiliated identity from a variety of sources. Many Americans, especially white collar professionals belong to professional organizations such as the APA, ASA or ATFLC , although books like '' Bowling Alone'' indicate that Americans affiliate with these sorts of groups less often than they did in the 1950s and 1960s.
Today, Americans derive a great deal of their identity through their work and professional affiliation, especially among individuals higher on the economic ladder. Recently professional identification has led to many clerical and low-level employees giving their occupations new, more respectable titles, such as "Sanitation service engineer" instead of "Janitor."
Additionally many Americans belong to non-profit organizations and religious establishments and may volunteer their services to such organizations. The Rotary Club
Rotary International is one of the largest service organizations in the world. Its stated mission is to "provide service to others, promote integrity, and advance world understanding, goodwill, and peace through hefellowship of business, prof ...
, the Knights of Columbus
The Knights of Columbus (K of C) is a global Catholic fraternal service order founded by Michael J. McGivney on March 29, 1882. Membership is limited to practicing Catholic men. It is led by Patrick E. Kelly, the order's 14th Supreme Knight. ...
or even the Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals are examples of such non-profit and mostly volunteer-run organizations. Ethnicity plays another important role in providing some Americans with group identity,
especially among those who recently immigrated.
Many American cities are home to ethnic enclaves such as a Chinatown
A Chinatown () is an ethnic enclave of Chinese people located outside Greater China, most often in an urban setting. Areas known as "Chinatown" exist throughout the world, including Europe, North America, South America, Asia, Africa and Aust ...
and Little Italies which still remain in some cities. Local patriotism may be also provide group identity. For example, a person may be particularly proud to be from California or New York City, and may display clothing from a local sports team
A sports team is a group of individuals who play sports ( sports player), usually team sports, on the same team. The number of players in the group depends on type of the sports requirements.
Historically, sports teams and the people who pl ...
.
Political lobbies such as the AARP
AARP (formerly called the American Association of Retired Persons) is an interest group in the United States focusing on issues affecting those over the age of fifty. The organization said it had more than 38 million members in 2018. The magazi ...
, ADL
Adl ( ar, عدل, ) is an Arabic word meaning 'justice', and is also one of the names of God in Islam. It is equal to the concept of ''Insaf'' انصاف (lit. sense of justice) in the Baháʼí Faith.
Adil ( ar, عادل, ), and Adeel ( ar, ع ...
, NAACP
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is a civil rights organization in the United States, formed in 1909 as an interracial endeavor to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E.&n ...
, NOW and GLAAD
GLAAD (), an acronym of Gay & Lesbian Alliance Against Defamation, is an American non-governmental media monitoring organization originally founded as a protest against defamatory coverage of gay and lesbian demographics and their portrayal ...
(examples being civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life ...
activist organizations) not only provide individuals with a sentiment of intra-group allegiance but also increase their political representation in the nation's political system. Combined, profession, ethnicity, religious, and other group affiliations have provided Americans with a multitude of options to derive group based identity from.
Technology, gadgets, and automobiles
Americans, by and large, are often fascinated by new technology and new gadgets. There are many within the United States that share the attitude that through technology, many of the evils in the society can be solved. Many of the new technological innovations in the modern world were either first invented in the United States and/or first widely adopted by Americans. Examples include: thelightbulb
An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the ...
, the airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad ...
, the transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
, the personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or te ...
, video games
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedbac ...
and online shopping
Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce which allows consumers to directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser or a mobile app. Consumers find a product of interest by visiting the website of t ...
, as well as the development of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
. By comparison with Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, however, only a small fraction of electronic devices make it to sale in the US, and household items such as toilets are rarely festooned with remotes and electronic buttons as they are in some parts of Asia.
Automobiles play a great role in American culture, whether it is in the mundane lives of private individuals or in the areas of arts and entertainment. The rise of suburbs and the desire for workers to commute to cities brought about the popularization of automobiles. In 2001, 90% of Americans drove to work in cars.Highlights of the 2001 National Household Travel Survey, Bureau of Transportation Statistics, U.S. Department of Transportation, accessed May 21, 2006 Lower energy and land costs favor the production of relatively large, powerful cars. The culture in the 1950s and 1960s often catered to the automobile with
motel
A motel, also known as a motor hotel, motor inn or motor lodge, is a hotel designed for motorists, usually having each room entered directly from the parking area for motor vehicles rather than through a central lobby. Entering dictionarie ...
s and drive-in restaurants. Americans tend to view obtaining a driver's license as a rite of passage. Outside of a relative few urban areas, it is considered a necessity for most Americans to own and drive cars. More than one hundred people are killed every day from motor vehicle crashes in the United States. Motor vehicle crashes are the leading cause of death in the workplace in the United States accounting for 35 percent of all workplace fatalities. There are about three million nonfatal vehicle injuries annually (about one injury per hundred people). Road transport is the most dangerous situation people deal with on a daily basis; but these casualty figures attract less media attention than other, less frequent events. New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
is the only locality in the United States where more than half of all households do not own a car.
Drugs, alcohol, and smoking
American attitudes towardsdrug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhala ...
s and alcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol that acts Alcohol (drug), as a drug and is produced by Ethanol fermentation, fermentat ...
s have evolved considerably throughout the country's history.
During the nineteenth century, alcohol was readily available and consumed, and no laws restricted the use of other drugs. A movement to ban alcoholic beverages, called the temperance movement
The temperance movement is a social movement promoting temperance or complete abstinence from consumption of alcoholic beverages. Participants in the movement typically criticize alcohol intoxication or promote teetotalism, and its leaders emph ...
, emerged in the late-nineteenth century. Several American Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
religious groups, as well as women's groups such as the Women's Christian Temperance Union
The Woman's Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) is an international temperance organization, originating among women in the United States Prohibition movement. It was among the first organizations of women devoted to social reform with a program th ...
, supported the movement.
In 1919, prohibitionists succeeded in amending the Constitution to prohibit the sale of alcohol. Although the Prohibition period did result in lowering alcohol consumption overall, banning alcohol outright proved to be unworkable, as the previously legitimate distillery industry was replaced by criminal gangs which trafficked in alcohol. Prohibition was repealed in 1931. States and localities retained the right to remain "dry", and to this day, a handful still do.
During the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
era, attitudes swung well away from prohibition. Commentators noted that an eighteen-year-old could be drafted into the military to fight in a war overseas, but could not buy a beer. Most states lowered the legal drinking age to eighteen.
Since 1980, the trend has been toward greater restrictions on alcohol and drug use. The focus this time, however, has been to criminalize behaviors associated with alcohol, rather than attempt to prohibit consumption outright. New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
was the first state to enact tough drunk driving
Drunk driving (or drink-driving in British English) is the act of driving under the influence of alcohol. A small increase in the blood alcohol content increases the relative risk of a motor vehicle crash.
In the United States, alcohol is i ...
laws in 1980; since then all other states have followed suit. A " Just Say No to Drugs" movement replaced the more libertine ethos of the 1960s.
Sports
 Since the late nineteenth century,
Since the late nineteenth century, baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding t ...
is regarded as the national sport
A national sport is considered to be an intrinsic part of the culture of a nation. Some sports are ''de facto'' (not established by law) national sports, as sumo is in Japan and Gaelic games are in Ireland and field hockey in Pakistan, while othe ...
; American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
, basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
, and ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
are the country's three other leading professional team sports. College football
College football (french: Football universitaire) refers to gridiron football played by teams of student athletes. It was through college football play that American football in the United States, American football rules first gained populari ...
and basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
also attract large audiences. Football is now by several measures the most popular spectator sport
A spectator sport is a sport that is characterized by the presence of spectators, or watchers, at its competitions. Spectator sports may be professional sports or amateur sports. They often are distinguished from participant sports, which are ...
in the United States. Soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
, though not a leading professional sport in the country, is played widely at the youth and amateur levels.
Boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
and horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic pr ...
were once the most watched individual sports, but they have been eclipsed by golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping wi ...
and auto racing
Auto racing (also known as car racing, motor racing, or automobile racing) is a motorsport involving the racing of automobiles for competition.
Auto racing has existed since the invention of the automobile. Races of various sorts were organise ...
, particularly NASCAR
The National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing, LLC (NASCAR) is an American auto racing sanctioning and operating company that is best known for stock car racing. The privately owned company was founded by Bill France Sr. in 1948, and ...
. Tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball cov ...
and many outdoor sports are also popular.
Food
 The cuisine of the United States is extremely diverse, owing to the vastness of the continent, the relatively large population (1/3 of a billion people) and the number of native and immigrant influences. The types of
The cuisine of the United States is extremely diverse, owing to the vastness of the continent, the relatively large population (1/3 of a billion people) and the number of native and immigrant influences. The types of food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is in ...
served at home vary greatly and depend upon the region of the country and the family's own cultural heritage. Recent immigrants tend to eat food similar to that of their country of origin, and Americanized
Americanization or Americanisation (see spelling differences) is the influence of American culture and business on other countries outside the United States of America, including their media, cuisine, business practices, popular culture, tec ...
versions of these cultural foods, such as American Chinese cuisine
American Chinese cuisine is a cuisine derived from Chinese cuisine that was developed by Chinese Americans. The dishes served in many North American Chinese restaurants are adapted to American tastes and often differ significantly from tho ...
or Italian-American cuisine
Italian-American cuisine is a style of Italian cuisine adapted throughout the United States. Italian-American food has been shaped throughout history by various waves of immigrants and their descendants, called Italian Americans.
As immigrants ...
often eventually appear; an example is Vietnamese cuisine
Vietnamese cuisine encompasses the foods and beverages of Vietnam. Meals feature a combination of five fundamental tastes ( vi, ngũ vị, links=no, label=none): sweet, salty, bitter, sour, and spicy. The distinctive nature of each dish refle ...
, Korean cuisine
Korean cuisine has evolved through centuries of social and political change. Originating from ancient agricultural and nomadic traditions in Korea and southern Manchuria, Korean cuisine reflects a complex interaction of the natural envi ...
and Thai cuisine
Thai cuisine ( th, อาหารไทย, , ) is the national cuisine of Thailand.
Thai cooking places emphasis on lightly prepared dishes with strong aromatic components and a spicy edge. Australian chef David Thompson, an expert on Thai ...
.
German cuisine
The cuisine of Germany () is made up of many different local or regional cuisines, reflecting the country's federal history. Germany itself is part of the larger cultural region of Central Europe, sharing many culinary traditions with neighbo ...
has a profound impact on American cuisine, especially mid-western cuisine, with potatoes, noodles, roasts, stews and cakes/pastries being the most iconic ingredients in both cuisines. Dishes such as the hamburger, pot roast, baked ham and hot dogs are examples of American dishes derived from German cuisine.
Different regions of the United States have their own cuisine and styles of cooking. The state of Louisiana, for example, is known for its Cajun and Creole cooking. Cajun and Creole cooking are influenced by French, Acadian, and Haitian cooking, although the dishes themselves are original and unique. Examples include Crawfish Etouffee, Red Beans and Rice, Seafood or Chicken Gumbo, Jambalaya, and Boudin. Italian, German, Hungarian and Chinese influences, traditional Native American, Caribbean, Mexican and Greek dishes have also diffused into the general American repertoire. It is not uncommon for a 'middle-class' family from 'middle-America' to eat, for example, restaurant pizza, home-made pizza, enchiladas con carne, chicken paprikas, beef stroganoff and bratwurst with sauerkraut for dinner throughout a single week.
Clothing
Apart from professional business attire, clothing in the United States is eclectic and predominantly informal. While Americans' diverse cultural roots are reflected in their clothing, particularly those of recent immigrants,cowboy hat
The cowboy hat is a high-crowned, wide-brimmed hat best known as the defining piece of attire for the North American cowboy. Today it is worn by many people, and is particularly associated with ranch workers in the western and southern Unit ...
s and boots
A boot is a type of footwear.
Boot or Boots may also refer to:
Businesses
* Boot Inn, Chester, Cheshire, England
* Boots (company), a high-street pharmacy chain and manufacturer of pharmaceuticals in the United Kingdom
* The Boot, Cromer St ...
and leather motorcycle jackets are emblematic of specifically American styles.
Blue jeans were popularized as work clothes in the 1850s by merchant Levi Strauss
Levi Strauss (; born Löb Strauß ; February 26, 1829 – September 26, 1902) was a German-born American businessman who founded the first company to manufacture blue jeans. His firm of Levi Strauss & Co. (Levi's) began in 1853 in San Francisc ...
, a Jewish-German immigrant in San Francisco, and adopted by many American teenagers a century later. They are now widely worn on every continent by people of all ages and social classes. Along with mass-marketed informal wear in general, blue jeans are arguably U.S. culture's primary contribution to global fashion. The country is also home to the headquarters of many leading designer labels such as Ralph Lauren
Ralph Lauren, ( ; ; born October 14, 1939) is an American fashion designer, philanthropist, and billionaire businessman, best known for the Ralph Lauren Corporation, a global multibillion-dollar enterprise. He has become well known for his c ...
and Calvin Klein
Calvin Richard Klein (born November 19, 1942) is an American fashion designer who launched the company that would later become Calvin Klein Inc., in 1968. In addition to clothing, he also has given his name to a range of perfumes, watches, an ...
. Labels such as Abercrombie & Fitch
Abercrombie & Fitch (A&F) is an American lifestyle retailer that focuses on casual wear. Its headquarters are in New Albany, Ohio. The company operates three other offshoot brands: Abercrombie Kids, Hollister Co., and Gilly Hicks. As of Februa ...
and Eckō Unltd.
Yakira, L.L.C. (trade name: Ecko Unltd.) is an American urban fashion company founded by Marc Ecko in 1993. The company makes apparel and accessories under brands including the men's Ecko Unltd. line and the Ecko Red line for girls and women. ...
cater to various niche market
A niche market is the subset of the market on which a specific product is focused. The market niche defines the product features aimed at satisfying specific market needs, as well as the price range, production quality and the demographics that i ...
s.
Education
Education in the United States is provided mainly by government, with control and funding coming from three levels: federal,state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
, and local. School attendance is mandatory and nearly universal at the elementary
Elementary may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Elementary'' (Cindy Morgan album), 2001
* ''Elementary'' (The End album), 2007
* ''Elementary'', a Melvin "Wah-Wah Watson" Ragin album, 1977
Other uses in arts, entertainment, a ...
and high school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper seconda ...
levels (often known outside the United States as the primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
...
and secondary
Secondary may refer to: Science and nature
* Secondary emission, of particles
** Secondary electrons, electrons generated as ionization products
* The secondary winding, or the electrical or electronic circuit connected to the secondary winding i ...
levels).
Students have the options of having their education held in public schools, private school
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
s, or home school. In most public and private schools, education is divided into three levels: elementary school
A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ed ...
, junior high school
A middle school (also known as intermediate school, junior high school, junior secondary school, or lower secondary school) is an educational stage which exists in some countries, providing education between primary school and secondary school. ...
(also often called middle school), and high school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper seconda ...
. In almost all schools at these levels, children are divided by age groups into grades. Post-secondary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including univers ...
, better known as "college" or "university" in the United States, is generally governed separately from the elementary and high school system.
In the year 2000, there were 76.6 million students enrolled in schools from kindergarten
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th cen ...
through graduate school
Postgraduate or graduate education refers to academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate ( bachelor's) degree.
The organization and ...
s. Of these, 72 percent aged 12 to 17 were judged academically "on track" for their age (enrolled in school at or above grade level). Of those enrolled in compulsory education, 5.2 million (10.4 percent) were attending private schools. Among the country's adult population, over 85 percent have completed high school and 27 percent have received a bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to si ...
or higher.
Language
The primary, although not official, language of the United States isEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
. According to the 2000 U.S. Census
The United States census of 2000, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 cen ...
, more than 93% of Americans can speak English well, and for 81% it is the only language spoken at home. Nearly 30 million native speakers of Spanish also reside in the US. There are more than 300 languages besides English which can claim native speakers in the United States—some of which are spoken by the indigenous peoples (about 150 living languages) and others which were imported by immigrants.
American Sign Language
American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States of America and most of Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual language that is expre ...
, used mainly by the deaf, is also native to the country. Hawaiian is also a language native to the United States, as it is indigenous nowhere else except in the state of Hawaii. Spanish is the second most common language in the United States, and is one of the official languages, and the most widely spoken, in the U.S. Commonwealth of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
.
There are four major regional dialects
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ...
in the United States: northeastern, south, inland north, and midwestern. The Midwestern accent (considered the "standard accent" in the United States, and analogous in some respects to the received pronunciation
Received Pronunciation (RP) is the accent traditionally regarded as the standard and most prestigious form of spoken British English. For over a century, there has been argument over such questions as the definition of RP, whether it is geo ...
elsewhere in the English-speaking world) extends from what were once the "Middle Colonies
The Middle Colonies were a subset of the Thirteen Colonies in British America, located between the New England Colonies and the Southern Colonies. Along with the Chesapeake Colonies, this area now roughly makes up the Mid-Atlantic states.
Mu ...
" across the Midwest to the Pacific states.
Religion
 Historically, the United States' religious tradition has been dominated by
Historically, the United States' religious tradition has been dominated by Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
. As of 2016, 74% of Americans identify as Christian with 49% identifying as Protestant. Catholicism (23%) is the largest Christian denomination, as Protestants belong to a variety of denominations. Also practiced in the United States are many other religions, such as Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
, Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
, and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
. Approximately 18% of Americans are unaffiliated; a majority of these are those not affiliated with any one religion, it also includes agnostics
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
and atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
.
The government is a secular institution, with what is often called the "separation of church and state
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular s ...
" prevailing.
Housing
Immediately afterWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Americans began living in increasing
numbers in the suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separ ...
s, belts around major cities with higher density than rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are de ...
areas, but much lower than urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities ...
s. This move has been attributed to many factors such as the automobile, the availability of large tracts of land, the convenience of more and longer paved roads, the increasing violence in urban centers (see white flight
White flight or white exodus is the sudden or gradual large-scale migration of white people from areas becoming more racially or ethnoculturally diverse. Starting in the 1950s and 1960s, the terms became popular in the United States. They refer ...
), and cheaper housing. These new single-family houses were usually one or two stories tall, and often were part of large contracts of homes built by a single developer.
The resulting low-density development has been given the pejorative label urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
. This is changing, however. White flight
White flight or white exodus is the sudden or gradual large-scale migration of white people from areas becoming more racially or ethnoculturally diverse. Starting in the 1950s and 1960s, the terms became popular in the United States. They refer ...
is reversing, with many Yuppies
Yuppie, short for "young urban professional" or "young upwardly-mobile professional", is a term coined in the early 1980s for a young professional person working in a city. The term is first attested in 1980, when it was used as a fairly neu ...
and upper-middle-class, empty nest
''Empty Nest'' is an American television sitcom that aired for seven seasons on NBC from October 8, 1988, to April 29, 1995. The series, which was created as a spin-off of ''The Golden Girls'' by creator and producer Susan Harris, starred Ri ...
Baby Boomers
Baby boomers, often shortened to boomers, are the Western demographic cohort following the Silent Generation and preceding Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964, during the mid-20th century baby boom. ...
returning to urban living, usually in condominia, such as in New York City's Lower East Side, and Chicago's South Loop. The result has been the displacement of many poorer, inner-city residents. (see gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ...
).
American cities with housing prices near the national median have also been losing the middle income
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Comm ...
neighborhoods, those with median income between 80% and 120% of the metropolitan area's median household income. Here, the more affluent members of the middle-class, who are also often referred to as being professional or upper middle-class, have left in search of larger homes in more exclusive suburbs. This trend is largely attributed to the so-called " Middle class squeeze", which has caused a starker distinction between the statistical middle class and the more privileged members of the middle class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. C ...
. In more expensive areas such as California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, however, another trend has been taking place where an influx of more affluent middle-class households has displaced those in the actual middle of society and converted former middle-middle-class neighborhoods into upper-middle-class
In sociology, the upper middle class is the social group constituted by higher status members of the middle class. This is in contrast to the term ''lower middle class'', which is used for the group at the opposite end of the middle-class strat ...
neighborhoods.
The population of rural areas has been declining over time as more and more people migrate to cities for work and entertainment. The great exodus from the farms came in the 1940s; in recent years fewer than 2% of the population lives on farms (though many others live in the countryside and commute to work). Electricity and telephone, and sometimes cable and Internet services are available to all but the most remote regions. As in the cities, children attend school up to and including high school and only help with farming
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
during the summer months or after school.
 About half of Americans now live in what is known as the
About half of Americans now live in what is known as the suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separ ...
s. The suburban nuclear family has been identified as part of the " American dream": a married couple with children owning a house in the suburbs. This archetype is reinforced by mass media, religious practices, and government policies and is based on traditions from Anglo-Saxon cultures. One of the biggest differences in suburban living as compared to urban living is the housing occupied by the families. The suburbs are filled with single-family homes separated from retail districts, industrial areas, and sometimes even public schools. However, many American suburbs are incorporating these districts on smaller scales, attracting more people to these communities.
Housing in urban areas may include more apartment
An apartment (American English), or flat (British English, Indian English, South African English), is a self-contained housing unit (a type of residential real estate) that occupies part of a building, generally on a single story. There are ma ...
s and semi-attached homes than in the suburbs or small towns. Aside from housing, the major difference from suburban living is the density and diversity of many different subcultures, as well as retail and manufacturing buildings mixed with housing in urban areas. Urban residents are also more likely to travel by mass transit, and children are more likely to walk or cycle rather than being driven by their parents.
Gender relations
Courtship, cohabitation, and sexuality
Couples often meet through religious institutions, work, school, or friends. "Dating services," services that are geared to assist people in finding partners, are popular both on and offline. The trend over the past few decades has been for more and more couples deciding to cohabit before, or instead of, getting married. The 2000 Census reported 9,700,000 opposite-sex partners living together and about 1,300,000 same-sex partners living together. These cohabitation arrangements have not been the subject of many laws regulating them, though some states now havedomestic partner
A domestic partnership is a legal relationship, usually between couples, who live together and share a common domestic life, but are not married (to each other or to anyone else). People in domestic partnerships receive benefits that guarantee ...
statutes and judge-made palimony doctrines that confer some legal support for unmarried couples.
Adolescent sex
''Adolescent Sex'' is the debut album by the English band Japan, released in April 1978 by record label Hansa. To avoid controversy over the title, the album was renamed simply as ''Japan'' in some countries.
Content
According to AllMusic, ' ...
is common; most Americans first have sexual intercourse in their teenage years. The current data suggests that by the time a person turns eighteen years old, slightly more than half of females and nearly two-thirds of males will have had sexual relations. More than half of sexually active teens have had sexual partners they are dating. Risky sexual behaviors that involve "anything intercourse related" are "rampant" among teenagers. Teenage pregnancies in the United States decreased 28% between 1990 and 2000 from 117 pregnancies per every 1,000 teens to 84 per 1,000. The United States is rated, based on 2002 estimates, 84 out of 170 countries based on teenage fertility rate, according to the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
.
Marriage and divorce
Marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
laws are established by individual states. Same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same sex or gender. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 33 countries, with the most recent being Mexico, constituting ...
has been legal nationwide since 2015.
In many states, it is illegal to cross state lines to obtain a marriage that would be illegal in the home state. The typical wedding
A wedding is a ceremony where two people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnic groups, religions, countries, and social classes. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of marriage vo ...
involves a couple proclaiming their commitment to one another in front of their close relatives and friends, often presided over by a religious figure such as a minister, priest, or rabbi, depending upon the faith of the couple. In traditional Christian ceremonies, the bride's father will "give away" (hand off) the bride to the groom. Secular weddings are also common, often presided over by a judge, Justice of the Peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or '' puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the s ...
, or other municipal official.
Divorce
Divorce (also known as dissolution of marriage) is the process of terminating a marriage or marital union. Divorce usually entails the canceling or reorganizing of the legal duties and responsibilities of marriage, thus dissolving th ...
is the province of state governments, so divorce law varies from state to state. Prior to the 1970s, divorcing spouses had to prove that the other spouse was at fault, for instance for being guilty of adultery
Adultery (from Latin ''adulterium'') is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and legal ...
, abandonment, or cruelty; when spouses simply could not get along, lawyers were forced to manufacture "uncontested" divorces. The no-fault divorce revolution began in 1969 in California and ended with New York. No-fault divorce (on the grounds of "irreconcilable differences", "irretrievable breakdown of marriage", "incompatibility", or after a separation period etc.) is now available in all states.
As with other Western countries, the United States has now a substantial proportion of children born outside of marriage: in 2010, 40.7% of all births were to unmarried women.
State law provides for child support
Child support (or child maintenance) is an ongoing, periodic payment made by a parent for the financial benefit of a child (or parent, caregiver, guardian) following the end of a marriage or other similar relationship. Child maintenance is paid d ...
where children are involved, and sometimes for alimony
Alimony, also called aliment (Scotland), maintenance (England, Ireland, Northern Ireland, Wales, Canada, New Zealand), spousal support (U.S., Canada) and spouse maintenance (Australia), is a legal obligation on a person to provide financial sup ...
. "Married adults now divorce two-and-a-half times as often as adults did 20 years ago and four times as often as they did 50 years ago... between 40% and 60% of ''new'' marriages will eventually end in divorce. The probability within... the first five years is 20%, and the probability of its ending within the first 10 years is 33%... Perhaps 25% of children ages sixteen and under live with a step-parent." The median length for a marriage in the US today is eleven years with 90% of all divorces being settled out of court.
Gender roles
Since the 1970s, traditionalgender role
A gender role, also known as a sex role, is a social role encompassing a range of behaviors and attitudes that are generally considered acceptable, appropriate, or desirable for a person based on that person's sex. Gender roles are usually cen ...
s of male and female have been increasingly challenged by both legal and social means. Today, there are far fewer roles that are legally restricted by one's sex.
Most social roles are not gender-restricted by law, though there are still cultural inhibitions surrounding certain roles. More and more women have entered the workplace, and in the year 2000, made up 46.6% of the labor force; up from 18.3% in 1900. Most men, however, have not taken up the traditional full-time homemaker
Homemaking is mainly an American and Canadian term for the management of a home, otherwise known as housework, housekeeping, housewifery or household management. It is the act of overseeing the organizational, day-to-day operations of a hous ...
role; likewise, few men have taken traditionally feminine jobs such as receptionist
A receptionist is an employee taking an office or administrative support position. The work is usually performed in a waiting area such as a lobby or front office desk of an organization or business. The title ''receptionist'' is attributed t ...
or nurse
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
(although nursing was traditionally a male role prior to the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
).
Death rituals
It is customary for Americans to hold a wake in afuneral home
A funeral home, funeral parlor or mortuary, is a business that provides burial and funeral services for the dead and their families. These services may include a prepared wake and funeral, and the provision of a chapel for the funeral.
Services ...
within a couple days of the death of a loved one. The body of the deceased may be embalmed and dressed in fine clothing if there will be an open-casket viewing. Traditional Jewish and Muslim practice include a ritual bath and no embalming. Friends, relatives and acquaintances gather, often from distant parts of the country, to "pay their last respects" to the deceased. Flowers are brought to the coffin
A coffin is a funerary box used for viewing or keeping a corpse, either for burial or cremation.
Sometimes referred to as a casket, any box in which the dead are buried is a coffin, and while a casket was originally regarded as a box for j ...
and sometimes eulogies
A eulogy (from , ''eulogia'', Classical Greek, ''eu'' for "well" or "true", ''logia'' for "words" or "text", together for "praise") is a speech or writing in praise of a person or persons, especially one who recently died or retired, or a ...
, elegies
An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, and in English literature usually a lament for the dead. However, according to ''The Oxford Handbook of the Elegy'', "for all of its pervasiveness ... the 'elegy' remains remarkably ill defined: sometime ...
, personal anecdotes or group prayers are recited. Otherwise, the attendees sit, stand or kneel in quiet contemplation or prayer. Kissing the corpse on the forehead is typical among Italian Americans and others. Condolences
Condolences (from Latin ''con'' (with) + ''dolore'' (sorrow)) are an expression of sympathy to someone who is experiencing pain arising from death, deep mental anguish, or misfortune.
When individuals condole, or offer their condolences to a par ...
are also offered to the widow or widower and other close relatives.
A funeral
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect ...
may be held immediately afterwards or the next day. The funeral ceremony varies according to religion and culture. American Catholics typically hold a funeral mass
A Requiem or Requiem Mass, also known as Mass for the dead ( la, Missa pro defunctis) or Mass of the dead ( la, Missa defunctorum), is a Mass of the Catholic Church offered for the repose of the soul or souls of one or more deceased persons, ...
in a church, which sometimes takes the form of a Requiem
A Requiem or Requiem Mass, also known as Mass for the dead ( la, Missa pro defunctis) or Mass of the dead ( la, Missa defunctorum), is a Mass of the Catholic Church offered for the repose of the soul or souls of one or more deceased persons, ...
mass. Jewish Americans may hold a service in a synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of wor ...
or temple. Pallbearer
A pallbearer is one of several participants who help carry the casket at a funeral. They may wear white gloves in order to prevent damaging the casket and to show respect to the deceased person.
Some traditions distinguish between the roles o ...
s carry the coffin of the deceased to the hearse
A hearse is a large vehicle, originally a horse carriage but later with the introduction of motor vehicles, a car, used to carry the body of a deceased person in a coffin at a funeral, wake, or memorial service. They range from deliberately a ...
, which then proceeds in a procession
A procession is an organized body of people walking in a formal or ceremonial manner.
History
Processions have in all peoples and at all times been a natural form of public celebration, as forming an orderly and impressive ceremony. Religious ...
to the place of final repose, usually a cemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite or graveyard is a place where the remains of dead people are buried or otherwise interred. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek , "sleeping place") implies that the land is specifically designated as a bu ...
. The unique Jazz funeral of New Orleans features joyous and raucous music and dancing during the procession.
Mount Auburn Cemetery
Mount Auburn Cemetery is the first rural, or garden, cemetery in the United States, located on the line between Cambridge and Watertown in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, west of Boston. It is the burial site of many prominent Boston Brah ...
(founded in 1831) is known as "America's first garden cemetery." American cemeteries
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite or graveyard is a place where the remains of dead people are buried or otherwise interred. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek , "sleeping place") implies that the land is specifically designated as a bu ...
created since are distinctive for their park-like setting. Rows of grave
A grave is a location where a dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as grav ...
s are covered by lawn
A lawn is an area of soil-covered land planted with grasses and other durable plants such as clover which are maintained at a short height with a lawnmower (or sometimes grazing animals) and used for aesthetic and recreational purposes. ...
s and are interspersed with trees and flowers. Headstone
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, ...
s, mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be cons ...
s, statuary or simple plaques typically mark off the individual graves. Cremation
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a Cadaver, dead body through Combustion, burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India ...
is another common practice in the United States, though it is frowned upon by various religions. The ashes of the deceased are usually placed in an urn, which may be kept in a private house, or they are interred. Sometimes the ashes are released into the atmosphere. The "sprinkling" or "scattering" of the ashes may be part of an informal ceremony, often taking place at a scenic natural feature (a cliff
In geography and geology, a cliff is an area of rock which has a general angle defined by the vertical, or nearly vertical. Cliffs are formed by the processes of weathering and erosion, with the effect of gravity. Cliffs are common on co ...
, lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
or mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher ...
) that was favored by the deceased.
A so-called death industry has developed in the United States that has replaced earlier, more informal traditions. Before the popularity of funeral homes, a wake would be held in an ordinary, private house. Often the most elegant room was reserved for this purpose.
Household arrangements
nuclear family
A nuclear family, elementary family, cereal-packet family or conjugal family is a family group consisting of parents and their children (one or more), typically living in one home residence. It is in contrast to a single-parent family, the larg ...
concept (two-married adults with a biological child), single-parent families, childless/childfree
Voluntary childlessness, also called being childfree, describes the voluntary choice to not have children.
In most societies and for most of human history, choosing not to have children was both difficult and undesirable. The availability of rel ...
couples, and fused families now constitute the majority of families.
Most Americans will marry and get divorced at least once during their life; thus, most individuals will live in a variety of family arrangements. A person may grow up in a single-parent family, go on to marry and live in childless couple arrangement, then get divorced, live as a single for a couple of years, remarry, have children and live in a nuclear family arrangement.
"The nuclear family... is the idealized version of what most people think when they think of "family..." The old definition of what a family is... the nuclear family- no longer seems adequate to cover the wide diversity of household arrangements we see today, according to many social scientists (Edwards 1991; Stacey 1996). Thus has arisen the term ''postmodern family'', which is meant to describe the great variability in family forms, including single-parent families and child-free couples."- Brian K. Williams, Stacey C. Sawyer, Carl M. Wahlstrom, ''Marriages, Families & Intinamte Relationships'', 2005.Other changes to the landscape of American family arrangements include dual-income earner households and delayed independence among American youths. Whereas most families in the 1950s and 1960s relied on one income earner, more commonly the husband, the vast majority of family households now have two-income earners. Another change is the increasing age at which young Americans leave their parental home. Traditionally, a person past "college age" who lived with their parent(s) was viewed negatively, but today it is not uncommon for children to live with their parents until their mid-twenties. This trend can be mostly attributed to rising
living costs
Cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living. Changes in the cost of living over time can be operationalized in a cost-of-living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare the cost of maintaining a cer ...
that far exceed those in decades past. Thus, many young adults now remain with their parents well past their mid-20s. This topic was a cover article of TIME magazine in 2005.
Exceptions to the custom of leaving home in one's mid-20s can occur especially among Italian and Hispanic Americans, and in expensive urban real estate markets such as New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
br>California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
br>and
Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the isla ...
br>where monthly rents commonly exceed $1000 a month. Single-parent households are households consisting of a single adult (most often a woman) and one or more children. In the single-parent household, one parent typically raises the children with little to no help from the other. This parent is the sole "breadwinner" of the family and thus these households are particularly vulnerable economically. They have higher rates of Poverty in the United States, poverty, and children of these households are more likely to have educational problems.
Regional variations
Cultural differences in the variousregions of the United States
This is a list of some of the ways ''regions'' is defined in the United States. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the federal government; others by shared culture and history, and others by economic factors.
Interstate regions C ...
are explored in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
, Mid-Atlantic States, Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
, Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
, Southwest United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado ...
, Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the We ...
and Pacific Northwestern United States pages. The western coast of the continental United States consisting of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, and the state of Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
is also sometimes referred to as the Left Coast, indicating its left-leaning political orientation and tendency towards liberal norms, folkways and values.
Strong cultural differences have a long history in the US with the southern slave society in the antebellum period serving as a prime example. Not only social, but also economic tensions between the Northern and Southern states were so severe that they eventually caused the South to declare itself an independent nation, the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
; thus provoking the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
. One example of regional variations is the attitude towards the discussion of sex, often sexual discussions would have less restrictions in the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
, but yet is seen as taboo in the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
.
In his 1989 book, ''Albion's Seed
''Albion's Seed: Four British Folkways in America'' is a 1989 book by David Hackett Fischer that details the folkways of four groups of people who moved from distinct regions of Great Britain (Albion) to the United States. The argument is that ...
'' (), David Hackett Fischer
David Hackett Fischer (born December 2, 1935) is University Professor of History Emeritus at Brandeis University. Fischer's major works have covered topics ranging from large macroeconomic and cultural trends ('' Albion's Seed,'' '' The Great Wave ...
suggests that the United States is made up today of four distinct regional cultures. The book's focus is on the folkways of four groups of settlers from the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
that emigrated from distinct regions of Britain and Ireland to the British American colonies during the 17th and 18th centuries. Fischer's thesis is that the culture and folkways of each of these groups persisted, with some modification over time, providing the basis for the four modern regional cultures of the United States.
According to Fischer, the foundation of American culture was formed from four mass migrations from four different regions of the British Isles by four distinct socio-religious groups. New England's earliest settlement period occurred between 1629 and 1640 when Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
s, mostly from East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
in England, settled there, forming the New England regional culture. The next mass migration was of southern English cavalier
The term Cavalier () was first used by Roundheads as a term of abuse for the wealthier royalist supporters of King Charles I and his son Charles II of England during the English Civil War, the Interregnum, and the Restoration (1642 – ). ...
s and their Irish and Scottish domestic servants to the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
region between 1640 and 1675, producing the Southern American culture. Then, between 1675 and 1725, thousands of Irish, English and German Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
s, led by William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
, settled in the Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
.
This settlement resulted in the formation of what is today considered the "General American" culture, although, according to Fischer, it is really just a regional American culture, even if it does today encompass most of the U.S. from the mid-Atlantic states to the Pacific Coast. Finally, Irish, Scottish and English settlers from the borderlands of Britain and Ireland migrated to Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, C ...
between 1717 and 1775. They formed the regional culture of the Upland South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern and lower Midwestern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, econom ...
, which has since spread west to such areas as West Texas
West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the arid and semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Abilene, and Del Rio.
No consensus exists on the boundary betw ...
and parts of the U.S. Southwest
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, N ...
. Fischer says that the modern U.S. is composed only of regional cultures, with characteristics determined by the place of departure and time of arrival of these four distinct founding populations.
Criticisms
Gun violence
The US is considered to have some of the most permissive gun laws among developed countries. Americans make up 4 percent of the world's population but own 46 percent of the global stock of privately held firearms. This is about 294 million guns with a population of 301 million (2007 figures), almost one gun for every American on average. In 2001–2, the United States had above-average levels of violent crime and particularly high levels ofgun violence
Gun-related violence is violence committed with the use of a firearm. Gun-related violence may or may not be considered criminal. Criminal violence includes homicide (except when and where ruled justifiable), assault with a deadly weapon, and ...
compared to other developed nations. A cross-sectional analysis of the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
Mortality Database from 2010 showed that United States "homicide rates were 7.0 times higher than in other high-income countries, driven by a gun homicide rate that was 25.2 times higher." Gun ownership rights continue to be the subject of contentious political debate.
Money in politics
In his dissent in ''Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission
''Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission'', 558 U.S. 310 (2010), was a landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States regarding campaign finance laws and free speech under the First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. It wa ...
'', Supreme Court Justice John Paul Stevens wrote:In the context of election to public office, the distinction between corporate and human speakers is significant. Although they make enormous contributions to our society, corporations are not actually members of it. They cannot vote or run for office. Because they may be managed and controlled by nonresidents, their interests may conflict in fundamental respects with the interests of eligible voters. The financial resources, legal structure, and instrumental orientation of corporations raise legitimate concerns about their role in the electoral process. Our lawmakers have a compelling constitutional basis, if not also a democratic duty, to take measures designed to guard against the potentially deleterious effects of corporate spending in local and national races.
Wealth gap
In the 2013 documentary ''Inequality for All
''Inequality for All'' is a 2013 documentary film directed by Jacob Kornbluth and narrated by American economist, author and professor Robert Reich. Based on Reich's 2010 book ''Aftershock: The Next Economy and America's Future'', the film exam ...
'', Robert Reich
Robert Bernard Reich (; born June 24, 1946) is an American professor, author, lawyer, and political commentator. He worked in the administrations of Presidents Gerald Ford and Jimmy Carter, and served as Secretary of Labor from 1993 to 1997 in ...
argued that income inequality is a defining issue for the United States. He stated that 95% of post-recession economic gains went to the top 1% net worth (HNWI
High-net-worth individual (HNWI) is a term used by some segments of the financial services industry to designate persons whose investible wealth (assets such as stocks and bonds) exceeds a given amount. Typically, these individuals are defined ...
) since 2009, when the recovery is agreed to have started.
See also
*American middle class
Though the American middle class does not have a definitive definition, contemporary social scientists have put forward several ostensibly congruent theories on it. Depending on the class model used, the middle class constitutes anywhere from 25% ...
* American dream
* Protestant work ethic
The Protestant work ethic, also known as the Calvinist work ethic or the Puritan work ethic, is a work ethic concept in theology, sociology, economics and history which emphasizes that diligence, discipline, and frugality are a result of a per ...
* Social structure of the United States
Social class in the United States refers to the idea of grouping Americans by some measure of social status, typically economic. However, it could also refer to social status or location. The idea that American society can be divided into socia ...
* Body contact and personal space in the United States
References
Further reading
* Coffin, Tristam P.; Cohen, Hennig, (editors), ''Folklore in America; tales, songs, superstitions, proverbs, riddles, games, folk drama and folk festivals'', Garden City, N.Y. : Doubleday, 1966. Selections from the ''Journal of American folklore''. * * Shell, Ellen Ruppel, ''Cheap: The High Cost of Discount Culture'', New York : Penguin Press, 2009. * Swirski, Peter. ''American Utopia and Social Engineering in Literature, Social Thought, and Political History.'' New York, Routledge (2011)External links
A Quick Guide for Living in the US
* ttp://eneida.over-blog.net Culture, Hedonism & Lifestyle
CommonCensus Map Project
- Identifying geographic spheres of influence {{DEFAULTSORT:Society Of The United States American studies