Sixth-generation jet fighter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A sixth-generation fighter is a conceptualized class of jet
 * Enhanced human-systems integration, with virtual cockpits presented via helmet-mounted displays which allow the pilot 360-degree vision with AI-enhanced battlefield awareness, and replacing conventional instrument panels.
* Advanced stealth airframes and avionics.
* Advanced variable-cycle engines able to cruise economically but still deliver high thrust when required.
* Increased-range stand-off and BVR weapons.
* Potential use of
* Enhanced human-systems integration, with virtual cockpits presented via helmet-mounted displays which allow the pilot 360-degree vision with AI-enhanced battlefield awareness, and replacing conventional instrument panels.
* Advanced stealth airframes and avionics.
* Advanced variable-cycle engines able to cruise economically but still deliver high thrust when required.
* Increased-range stand-off and BVR weapons.
* Potential use of
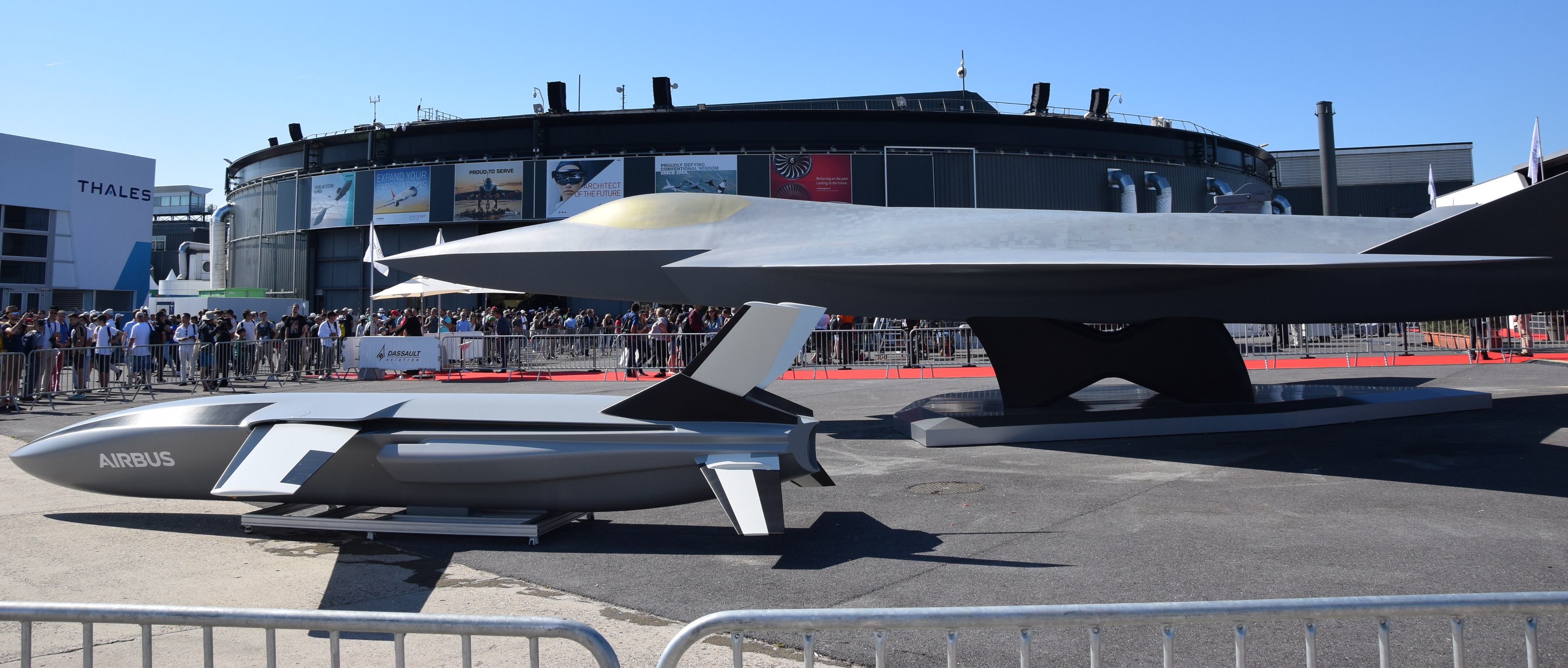
 France, Germany and Spain are also jointly working on a sixth-generation system. A test flight of a demonstrator is expected around 2027 and entry into service around 2040. Also called SCAF to avoid confusion with FCAS Tempest.
France, Germany and Spain are also jointly working on a sixth-generation system. A test flight of a demonstrator is expected around 2027 and entry into service around 2040. Also called SCAF to avoid confusion with FCAS Tempest.
The Race for 6th Generation Fighters - Drones, Lasers & Future Air Dominance
Perun, Youtube {{Jet Fighter Generations 6th generation 21st century in technology
fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
design more advanced than the fifth-generation jet fighter
A fifth-generation fighter is a jet fighter aircraft classification which includes major technologies developed during the first part of the 21st century. , these are the most advanced fighters in operation. The characteristics of a fifth-gene ...
s that are currently in service and development. Several countries have announced the development of a sixth-generation aircraft program, including the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. While Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
have joined together in collaborative multinational programs in an effort to spread development costs. The first sixth-generation fighters are expected to enter service in the 2030s.
Characteristics
While still at an early stage of development, several distinct characteristics common to many sixth-generation fighter concepts have evolved. The fifth-generation abilities for air-to-air capability, battlefield survivability in the anticipated anti-access/area-denial environment and ground support/attack will need to be enhanced and adapted to the future threat environment. An initial focus on air superiority roles has moved away from close-in dogfighting, which is becoming less common, and instead broadened to embrace ground support, cyber warfare and even space warfare capabilities, with beyond-visual-range (BVR) air-to-air missile capability remaining important. The flexibility to undertake manned and unmanned missions is also sought, along with the ability to integrate with more numerous fleets of satellite drones and ground sensors in a high-traffic networked environment to deliver full "data-to-decision" (D2D) capability.Baker 2018. Typical design characteristics anticipated to deliver these roles include: * Advanced digital capabilities including high-capacity networking, AI, data fusion, cyber warfare, D2D and battlefield command, control and communications (C3) capabilities. * Optionally manned, with the same airframe capable of conducting piloted, remote controlled or onboard-AI controlled missions. * Enhanced human-systems integration, with virtual cockpits presented via helmet-mounted displays which allow the pilot 360-degree vision with AI-enhanced battlefield awareness, and replacing conventional instrument panels.
* Advanced stealth airframes and avionics.
* Advanced variable-cycle engines able to cruise economically but still deliver high thrust when required.
* Increased-range stand-off and BVR weapons.
* Potential use of
* Enhanced human-systems integration, with virtual cockpits presented via helmet-mounted displays which allow the pilot 360-degree vision with AI-enhanced battlefield awareness, and replacing conventional instrument panels.
* Advanced stealth airframes and avionics.
* Advanced variable-cycle engines able to cruise economically but still deliver high thrust when required.
* Increased-range stand-off and BVR weapons.
* Potential use of directed-energy weapons
A directed-energy weapon (DEW) is a ranged weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy without a solid projectile, including lasers, microwaves, particle beams, and sound beams. Potential applications of this technology include w ...
such as a laser CIWS
A close-in weapon system (CIWS ) is a point-defense weapon system for detecting and destroying short-range incoming missiles and enemy aircraft which have penetrated the outer defenses, typically mounted on a naval ship. Nearly all classes of l ...
.
The feasibility of some of these characteristics remains uncertain. Development time and cost are likely to prove major factors in laying out practical roadmaps. Specific requirements are anticipated by some observers to crystallize around 2025.
National programs in development
Japan, United Kingdom, Italy, and Sweden
In 2010, the Japanese government revealed a concept sixth-generation jet fighter, the i3 FIGHTER. i3 is short for informed, intelligent and instantaneous. In July 2014,Jane's Information Group
Jane's Information Group, now styled Janes, is a global open-source intelligence company specialising in military, national security, aerospace and transport topics, whose name derives from British author Fred T. Jane.
History
Jane's Informat ...
reported that a House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
Defence Select Committee
The Defence Select Committee is one of the Select Committees of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, having been established in 1979. It examines the expenditure, administration, and policy of the Ministry of Defence and its associated publ ...
had published a report about the UK's "post-2030 combat aviation force structure". The report highlighted a possibility of the UK committing to a next generation fighter program to potentially replace the Eurofighter Typhoon post-2030; the Eurofighter Typhoon has since had its intended service life extended to around 2040. On 22 March 2016, Japan conducted the first flight of the Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin testbed aircraft for this project.
In July 2018, then British Secretary of State for Defense Gavin Williamson unveiled the UK's Combat Air Strategy and announced the development of a sixth-generation fighter concept named the Tempest for the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
at Farnborough Airshow
The Farnborough Airshow, officially the Farnborough International Airshow, is a trade exhibition for the aerospace and defence industries, where civilian and military aircraft are demonstrated to potential customers and investors. Since its fir ...
2018.
In 2019, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
joined the Tempest project. During the same year, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
were also invited to join the project. On 1 April 2020, the Japanese F-X program was announced. In 2022, after preliminary discussions, Japan joined the Sixth generation fighter project with the F-X project merged with the BAE Tempest to form the Global Combat Air Programme.
France, Germany, Spain
Russia
On 26 August 2013, Russia revealed it would proceed with development of a sixth-generation jet fighter. They say the aircraft will most likely be pilotless. However, they would not skip completing development of fifth-generation fighter projects, like theSukhoi Su-57
The Sukhoi Su-57 (russian: Сухой Су-57; NATO reporting name: Felon) is a Twinjet, twin-engine stealth Multirole combat aircraft, multirole fighter aircraft developed by Sukhoi. It is the product of the PAK FA (russian: ПАК ФА, russ ...
.
Mikoyan PAK DP is a Russian program to develop a next generation interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are ...
to replace Mikoyan MiG-31. According to the Russian defense analyst Vasily Kashin, the aircraft would be considered as a 5++ or 6th generation fighter project. In January 2021, Rostec Corporation, the owner of Mikoyan
Russian Aircraft Corporation "MiG" (russian: Российская самолётостроительная корпорация „МиГ“, Rossiyskaya samolyotostroitel'naya korporatsiya "MiG"), commonly known as Mikoyan and MiG, was a Russi ...
, announced that the PAK DP had now entered the development phase, saying "Development of the next generation of interceptor fighters has already begun."
United States
TheUnited States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
(USAF) and United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
(USN) are anticipated to field their first sixth-generation fighters in the 2030 timeframe. The USAF is pursuing development and acquisition of a sixth-generation air superiority fighter
An air superiority fighter (or air-superiority fighter) is a fighter aircraft designed to seize control of enemy airspace by establishing tactical dominance (air superiority) over the opposing air force. Air-superiority fighters are primarily t ...
through the Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program that succeeds the Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor
The Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor is an American single-seat, twin-engine, all-weather stealth tactical fighter aircraft developed for the United States Air Force (USAF). As the result of the USAF's Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) program, th ...
. The USN is pursuing a similar program using the same name with the fighter component called the F/A-XX, likewise intended to complement the smaller Lockheed Martin F-35C Lightning II and replace its existing aircraft such as the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet
The Boeing F/A-18E and F/A-18F Super Hornet are twin-engine, carrier-capable, multirole fighter aircraft variants based on the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet. The F/A-18E single-seat and F/A-18F tandem-seat variants are larger and more ad ...
.
History
The U.S. Navy launched its sixth-generation F/A-XX program in 2008 and the USAF sought initial responses for a Next Generation Tactical Aircraft (Next Gen TACAIR), which would become the F-X program, in 2010. In April 2013,DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.
Originally known as the A ...
initiated a study to try to bring together existing USAF and USN concepts.
Next-generation fighter efforts would initially be led by DARPA under the "Air Dominance Initiative" to develop prototype X-planes. The U.S. Navy and Air Force would each have variants focused on their mission requirements. However, also in 2013, the RAND Corporation
The RAND Corporation (from the phrase "research and development") is an American nonprofit global policy think tank created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is finance ...
recommended that the U.S. military services avoid joint programs for the development of the design of a sixth-generation fighter. They found that in previous joint programs, different service-specific requirements for complex programs had led to design compromises which raised costs far more than normal single-service programs.
In 2014, a broader approach to offensive technologies was proposed, with USAF aircraft anticipated to operate alongside ground-based and non-kinetic anti-aircraft solutions, and with a greater weapon load than current fighters. In 2016, the USAF consolidated this change of course for its Air Superiority 2030 plan, to pursue "a network of integrated systems disaggregated across multiple platforms" rather than focusing on the sixth-generation fighter. The Air Force and Navy requirements had already been merged the year before and were now formally integrated, with the joint focus to be on AI systems and a common airframe.
Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
, Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
and Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense technology company. With 90,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $30 billion, it is one of the world's largest weapons manufacturers and military tech ...
have all announced sixth-generation aircraft development projects. On September 14, 2020, the USAF announced that a prototype aircraft component of the Next-Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program had flown for the first time. The details remained classified.
Concepts and technologies
There are significant differences between Navy and Air Force visions for their respective next-generation jet concepts, but both agree on some fundamental characteristics. These includeartificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech ...
as a decision aid to the pilot, similar in concept to current sensor fusion. They will also have Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT), and communications that allow big data movement between both services' aircraft.
The USAF regard stealth
Stealth may refer to:
Military
* Stealth technology, technology used to conceal ships, aircraft, and missiles
** Stealth aircraft, aircraft which use stealth technology
**Stealth ground vehicle, ground vehicles which use stealth technology
** St ...
as extremely important for the F-X, while the US Navy emphasize the F/A-XX should not be so focused on survivability as to sacrifice speed and payload. Unlike the previous F-22 and F-35
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, all-weather stealth multirole combat aircraft that is intended to perform both air superiority and strike missions. It is also able to provide elect ...
development programs that depended on new technologies that drove up cost and delayed introduction, the Air Force is intending to follow a methodical path of risk reduction to include as much prototyping, technology demonstration, and systems engineering work as possible before creation of an aircraft actually starts. Sixth-generation strike capability is envisioned as a move beyond the limitations inherent to the potential abilities of a single strike aircraft. 6-Gen combat awareness will require a theatre-wide integration of diverse systems beginning with the primary airborne sensory suite and further including real-time data linking of ground-based detection and ranging technology with sensors aboard primary and support aircraft, advanced communication capabilities, unparalleled capacity for continuous onboard info-stream processing utilizing AI for real-time data translation and rendering geared toward optimizing pilot situational awareness while reducing workload, potential near-space capabilities, extension of existing strike/standoff ranges, seamless co-operation with ground-to air defense assets and the ability to deploy aircraft in manned, optionally manned, unmanned and stand-in options.
In March 2015, the Navy revealed they were working with the Air Force to potentially release joint analysis of alternatives (AoA) in 2016 for their next-generation fighters; they are allowed to take a joint AoA, then define a service solution that would be good for each service. The Navy is focusing on replacing the capabilities of the fighter with a wide range of options for the Super Hornet, as well as the EA-18G Growler
The Boeing EA-18G Growler is an American carrier-based electronic warfare aircraft, a specialized version of the two-seat F/A-18F Super Hornet. The EA-18G replaced the Northrop Grumman EA-6B Prowlers in service with the United States Navy. ...
. The AoA will run parallel to several other design and technology efforts including engine technology, airframe molds, broadband and IR stealth, and new ways to dominate the electromagnetic spectrum. Part of the Navy's calculus will be based on how the F-35C performs as a critical forward sensor node for the carrier air wing. How the fifth-generation F-35C integrates with the rest of the air wing to give greater capabilities than what the platform itself can do may lend itself to the sixth-generation F/A-XX. The Navy aircraft is to have greatly increased speed and range compared to the Super Hornet.
In April 2015, the Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments (CSBA) released a report concluding that the next-generation U.S. Air Force fighter should be larger and more resembling a bomber than a small, maneuverable traditional fighter. It analyzed over 1,450 air-to-air engagements since 1965 and found that long-range weapons and sensors have dramatically decreased instances of dogfighting. With the increase of air defense systems using electronic and infrared sensors and high-speed weapons, traditional designs relying on small size, high speed, and maneuverability may be less relevant and easier to intercept. As a result, the CSBA suggests building a fighter significantly larger relying on enhanced sensors, signature control, networked situational awareness, and very-long-range weapons to complete engagements before being detected or tracked. Larger planes would have greater range that would enable them to be stationed further from a combat zone, have greater radar and IR detection capabilities, and carry bigger and longer-range missiles ( Long-Range Engagement Weapon). One airframe could be fitted with various attachments to fill several roles. The concept of a small number of large, intercontinental and heavily armed combat aircraft could link itself to the development of the Long Range Strike Bomber.
In November 2016, the USAF Scientific Advisory Board announced studies for a ''Penetrating Counter Air'' (PCA) platform that would combine long range, supersonic speed, stealth and maneuverability and be fielded by 2030. PCA would have substantially longer range to fly long distances over the Pacific, especially in a situation where airbases in the vicinity of China are not available or if aerial tankers are destroyed. It would also escort bombers deep into Russia or China, where the anticipated threat includes advanced networked air defense radars. It would include stealth against low or very high frequency radars (like those of the S-400 missile system
The S-400 Triumf (russian: link=no, C-400 Триумф – Triumf; translation: Triumph; NATO reporting name: SA-21 Growler), previously known as the S-300 PMU-3, is a mobile, surface-to-air missile (SAM) system developed in the 1990s by Russ ...
), which requires an airframe with no vertical stabilizers. Another requirement is significantly larger payload than current air superiority aircraft like the F-22. Adaptive cycle engine
A variable cycle engine (VCE), also referred to as adaptive cycle engine (ACE), is an aircraft jet engine that is designed to operate efficiently under mixed flight conditions, such as subsonic, transonic and supersonic.
The next generation of ...
technology is an option under consideration for the PCA, given the fact that the alternative would be a very large aircraft.
While current engines operate best at a single point in the flight envelope, sixth-generation engines are expected to have a variable cycle to give optimum efficiency at any speed or altitude, giving greater range, faster acceleration, and greater subsonic cruise efficiency. The engine would configure itself to act like a turbojet at supersonic speeds, while performing like a high-bypass turbofan for efficient cruising at slower speeds; the ability to supercruise
Supercruise is sustained supersonic flight of a supersonic aircraft with a useful cargo, passenger, or weapons load without using afterburner (also known as "reheat"). Many supersonic military aircraft are not capable of supercruise and can only m ...
will likely be available to aircraft with this engine type. The technology is being developed by the Air Force under the Adaptive Engine Transition Program
Adaptation, in biology, is the process or trait by which organisms or population better match their environment
Adaptation may also refer to:
Arts
* Adaptation (arts), a transfer of a work of art from one medium to another
** Film adaptation, a ...
(AETP) and by the Navy under its Variable Cycle Advanced Technology (VCAT) program. The Air Force is aiming for a Milestone A decision by 2018, with a production version to be ready possibly by 2021. Companies involved with next-generation engine development include General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable ene ...
and Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies. Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation (especially airlines) and military av ...
. Risk reduction began in 2012 so that engine development can start around 2020. An engine is to be ready when fighters are introduced by the Navy in 2028 and the Air Force in 2032.
The Air Force is interested in lasers both for low-power illumination and as higher-powered weapons. In November 2013, the Air Force Research Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of aerospace warfighting technologies, pl ...
released a request for information (RFI) for submissions with detailed descriptions in a militarily useful configuration, potential problems and solutions, and cost estimates.
National programs planned
China
After successfully developing its 5th generation fighter J-20, China is now working on the development of a next generation aircraft. Dr. Wang Haifeng, chief designer of theChengdu Aerospace Corporation
The Chengdu Aircraft Industry Group (CAIG) or Chengdu Aerospace Corporation (CAC), a subsidiary of AVIC, is a Chinese aerospace conglomerate that designs and manufactures combat aircraft and is also a manufacturer of aircraft parts. It was fou ...
announced that China had begun pre-research on sixth-generation aircraft in January 2019, predicting that the program would come to fruition by 2035.
India
In an interview on 8 October 2020 to celebrate the 88th anniversary of theIndian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air force, air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct ...
(IAF), Air Chief Marshal Rakesh Bhadauria was asked about plans for sixth generation technologies and he responded that they have a clear roadmap for sixth generation combat systems like directed energy weapons
A directed-energy weapon (DEW) is a ranged weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy without a solid projectile, including lasers, microwaves, particle beams, and sound beams. Potential applications of this technology include we ...
, smart wingman concept, optionally manned combat platforms, swarm drones, hypersonic weapons
Hypersonic weapons are weapons travelling at hypersonic speed – at between 5 and 25 times the speed of sound, about .
Below such speeds, weapons would be characterized as subsonic or supersonic, while above such speeds, the molecules of the ...
, and other equipment.
India has been working to develop its fifth generation AMCA with development completing in 2028 and production commencing in 2029. It is also looking to add some sixth generation technologies in later variants such as an optionally manned, directed energy weapons (possibility as anti-missile system), capable of controlling UCAVs and swarm drones but Indian officials did not claim that this will be a 6th generation fighter.
Air Chief Marshal Vivek Ram Chaudhari
Air Chief Marshal Vivek Ram Chaudhari, is an air officer of the Indian Air Force. He currently serves as the Chief of the Air Staff (CAS). He took over as the 27th CAS succeeding Air Chief Marshal Rakesh Kumar Singh Bhadauria on 30 September 2 ...
on 22 October 2021 confirmed in an interview that IAF is committed towards development of AMCA aiming at sixth generation niche technologies.
However, some analysts have questioned the feasibility of India's ability to develop a sixth generation, let alone a fifth generation fighter aircraft especially as India lacks the industrial base and technical capabilities to do so.
Sixth-generation fighter programs
* // -Global Combat Air Programme
The Global Combat Air Programme (GCAP) is a multinational initiative led by the United Kingdom, Japan, and Italy to develop a sixth-generation stealth fighter. The programme aims to replace the Eurofighter Typhoon in service with the Royal A ...
* // - Dassault/Airbus FCAS
* - Mikoyan PAK DP
* - Next Generation Air Dominance for United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
* - F/A-XX for United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
(under development by Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
)
See also
*Fifth-generation jet fighter
A fifth-generation fighter is a jet fighter aircraft classification which includes major technologies developed during the first part of the 21st century. , these are the most advanced fighters in operation. The characteristics of a fifth-gene ...
* Jet fighter generations
References
Notes
Bibliography
*David Baker; ''Fifth Generation Fighters'', Mortons, 2018. Chapter18, "Enter the Sixth".External links
The Race for 6th Generation Fighters - Drones, Lasers & Future Air Dominance
Perun, Youtube {{Jet Fighter Generations 6th generation 21st century in technology