Six-bar linkage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
a six-bar linkage with the Watt topology.
/ref> A six-bar linkage can also be constructed by first assembling five binary links into a pentagon, which uses five of the seven joints, and then completing the linkage by adding a binary link that connects two sides of the pentagon. This again creates two ternary links that are now separated by one or more binary links. This type of six-bar linkage is said to have the Stephenson topology. The Klann linkage has the Stephenson topology.
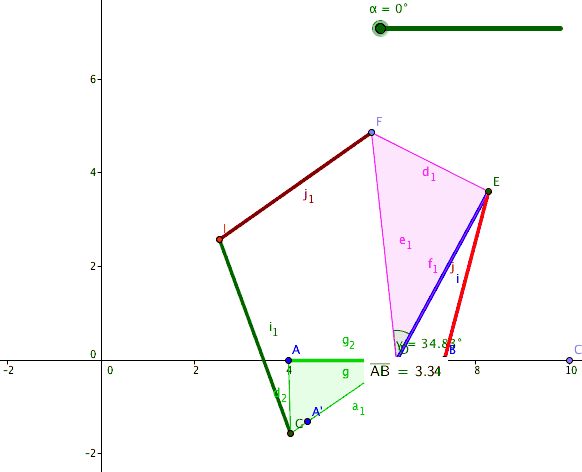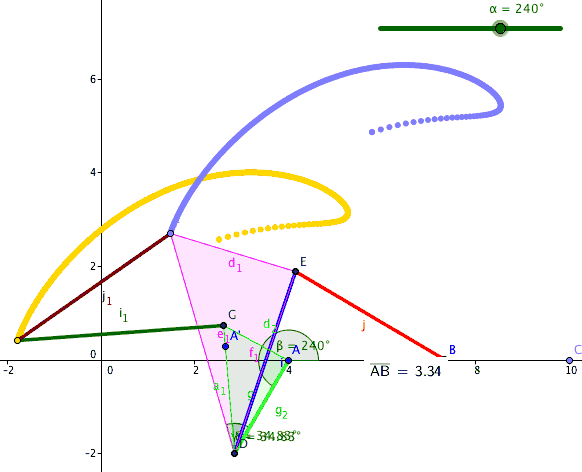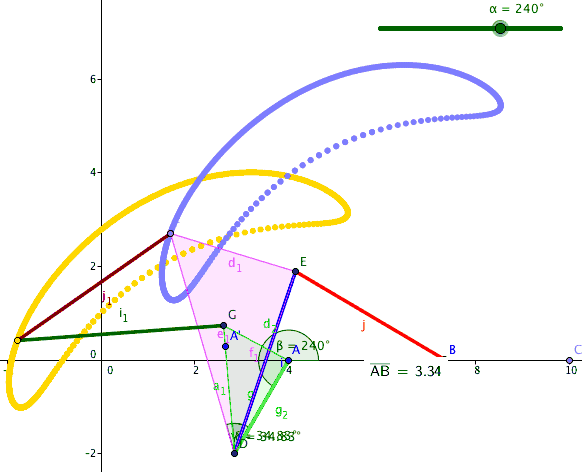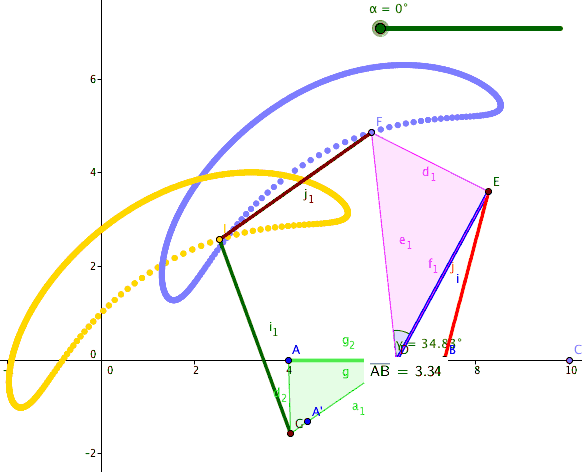
A six-bar straight-line linkage in the collection of Reuleaux models at Cornell University
Mechanism animations including the Klann linkage
Example of a six-bar function generator that compute the angle for a given range.
Animations of six-bar linkage for a bicycle suspension.
A variety of six-bar linkage designs.
Lecture on the design of six-bar and eight-bar linkages
Article about patents and six-bar linkages
{{Linkages Linkages (mechanical)
 In
In mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to object ...
, a six-bar linkage is a mechanism
Mechanism may refer to:
* Mechanism (engineering), rigid bodies connected by joints in order to accomplish a desired force and/or motion transmission
*Mechanism (biology), explaining how a feature is created
*Mechanism (philosophy), a theory that ...
with one degree of freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or ...
that is constructed from six links and seven joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s. An example is the Klann linkage used to drive the legs of a walking machine.
In general, each joint of a linkage connects two links, and a binary link supports two joints. If we consider a hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A '' regular hexagon'' has ...
constructed from six binary links with six of the seven joints forming its vertices, then the seventh joint can be added to connect two sides of the hexagon to form a six-bar linkage with two ternary links connected by one joint. This type of six-bar linkage is said to have the Watt topology.An animation oa six-bar linkage with the Watt topology.
/ref> A six-bar linkage can also be constructed by first assembling five binary links into a pentagon, which uses five of the seven joints, and then completing the linkage by adding a binary link that connects two sides of the pentagon. This again creates two ternary links that are now separated by one or more binary links. This type of six-bar linkage is said to have the Stephenson topology. The Klann linkage has the Stephenson topology.
Watt six-bar linkage
Watt's parallel motion generator consists of the four-bar linkage that has a coupler curve that traces an approximately straight line trajectory, combined with a parallelogram linkage that copies this straight line movement to a desired location. This configuration of six bars and seven joints has two four-bar loops.
Stephenson six-bar linkage
The six-bars and seven joints of the Stephenson linkage comprise one four-bar loop and one five-bar loop. It has two ternary links that are separated by a binary link. This means the two ternary links are not connected to each other by a joint as in the case of the Watt topology. The Stephenson has three forms depending on the link that is selected as the frame, which are denoted Stephenson I, II and III.See also
* Mechanism (engineering) *Linkage (mechanical)
A mechanical linkage is an assembly of systems connected to manage forces and movement. The movement of a body, or link, is studied using geometry so the link is considered to be rigid. The connections between links are modeled as providing i ...
* Five-bar linkage
References
External links
A six-bar straight-line linkage in the collection of Reuleaux models at Cornell University
Mechanism animations including the Klann linkage
Example of a six-bar function generator that compute the angle for a given range.
Animations of six-bar linkage for a bicycle suspension.
A variety of six-bar linkage designs.
Lecture on the design of six-bar and eight-bar linkages
Article about patents and six-bar linkages
{{Linkages Linkages (mechanical)