Siraces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
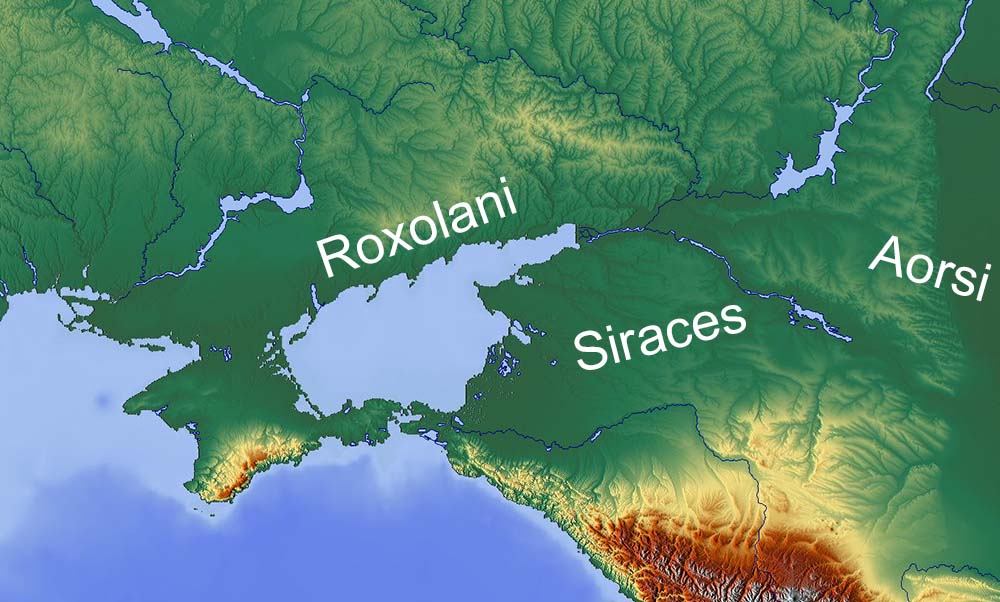 The Siraces ( gr, Sirakoi, lat, Siraci, also ''Siraceni'' and ''Seraci'' ) were a
The Siraces ( gr, Sirakoi, lat, Siraci, also ''Siraceni'' and ''Seraci'' ) were a 
 The Siraces ( gr, Sirakoi, lat, Siraci, also ''Siraceni'' and ''Seraci'' ) were a
The Siraces ( gr, Sirakoi, lat, Siraci, also ''Siraceni'' and ''Seraci'' ) were a hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
tribe that inhabited Sarmatia Asiatica
Sarmatia Asiatica ("Asiatic Sarmatia") was the name used in Ptolemy's ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'' (ca. 150) for a part of "Sarmatia", a large region which included parts of Europe and Asia. Another part was Sarmatia Europea ("European Sarmat ...
; the coast of Achardeus at the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
north of the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
, Siracena Siracena ( grc-gre, Σιρακηνή) is the alleged capital settlement or village of the tribe of Siraces, a powerful, hellenized Sarmatian tribe on the steppe. It was ruled by the kings of the Siraces, most notably Aripharnes, who engaged in the B ...
is mentioned by Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
as one of their settlements. They were said to be relatively small nation but with great morale. (bad link as of 20feb16, probably Brzezinski's book.) They were neighbours to the later enemy tribe of Aorsi
The Aorsi, known in Greek sources as the Aorsoi (Ἄορσοι), were an ancient Iranian people of the Sarmatian group, who played a major role in the events of the Pontic Steppe from the 1st century BC to the 1st century AD.
They are often rega ...
.
They migrated from the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
region. By the late 4th century, they had occupied lands between the Caucasus mountains and the Don, becoming masters of the Kuban region. They were the first Sarmatian tribe to have contact with the Hellenic groups on the coast of the Black Sea.
In 310–309 BC, their king Aripharnes
Aripharnes (fl. 310–309 BC) or Arypharnasha the Thataean was ruler of the Sarmatian tribe of Siraces and took part in the First Bosporan Civil War of 310-309 between king Satyros II and his brother Eumelos, a pretender to the throne.
At first, ...
took part in the Bosporan Civil War
The Bosporan Civil War was a war of succession that happened in the Bosporan Kingdom somewhere between 311 and 308 BCE and lasted for about a year. The casus belli was the death of archon Paerisades I, whose sons disputed the succession. These ...
and lost at the battle of the River Thatis
The Battle of the River Thatis was part of a succession dispute in the Bosporan Kingdom that was fought out during 310/309 BC. After the death of Paerisades I, his eldest son Satyros II became king. His brother Eumelus of Bosporus, Eumelus dispu ...
(a tributary of the Kuban river).
In the 1st century BC during the rule of Pharnaces II of Pontus
Pharnaces II of Pontus ( grc-gre, Φαρνάκης; about 97–47 BC) was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithrida ...
, King of Siraces Abeacus organized 20,000 horses after the Roman occupation of the Kingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( grc-gre, Πόντος ) was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus (region), Pontus and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty (of Persian people, Persian origin), which possibly may have been di ...
(63–62 BC).
They and the Aorsi were merchants who traded with goods of Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
through the Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
and Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, with camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. ...
s. They profited greatly from this, seen in their clothing attributed with much gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
.
King Zorsines
Zorsines was a 1st-century King (''rex Siracorum'') of the Siraces mentioned in Tacitus' ''Annals'' of the Roman Empire (XII.15-19) around 50 AD, a people he reports as residing somewhere between the Caucasus mountains and the Don river.
He had a ...
fought in the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
under Mithridates, the king of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
, against the Dandaridae. Their ally Mithridates later turned against the Romans who had put Mithridates on the throne in 41. Mithridates eluded the Romans and recovered his kingdom. In the Bosporan War, The Aorsi
The Aorsi, known in Greek sources as the Aorsoi (Ἄορσοι), were an ancient Iranian people of the Sarmatian group, who played a major role in the events of the Pontic Steppe from the 1st century BC to the 1st century AD.
They are often rega ...
under Prince Eunones, sent by Aquila and Cotys is sent after Mithridates and his lands, fights with Zorsines and sieges Uspe in 49 AD (The town offers 10,000 slaves for their capitulation but the assault continues as the Romans decline), Zorsines finally decides to leave Mithridates to rule his paternal lands, after giving hostages to the Romans and thus making peace. He acknowledged Roman superiority before the image of Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor ...
and the power of the Siraces is greatly weakened.
They were the most hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
of the Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
, and maintained good relations with the Bosporans.
Ptolemy mentions their colony in Sinai in the second century.Retsö, Jan. 2003. The Arabs in Antiquity: Their History from the Assyrians to the Umayyads. Routledge. pp.505-506 In 193 AD, after another conflict in the Bosporus, the Siraces disappears from the history.
There is one town in Hungary called Szirák, in Nógrád county, that still bears their name.
The name Siraces is thought to have been given to the Circassians by the Greeks, and the names Siraces and Circassian are of the same origin.

Kings
*Aripharnes
Aripharnes (fl. 310–309 BC) or Arypharnasha the Thataean was ruler of the Sarmatian tribe of Siraces and took part in the First Bosporan Civil War of 310-309 between king Satyros II and his brother Eumelos, a pretender to the throne.
At first, ...
, fl. 310–309 BC
* Abeacus, fl. 63–47 BC
*Zorsines
Zorsines was a 1st-century King (''rex Siracorum'') of the Siraces mentioned in Tacitus' ''Annals'' of the Roman Empire (XII.15-19) around 50 AD, a people he reports as residing somewhere between the Caucasus mountains and the Don river.
He had a ...
, fl. 41–49 AD
See also
*Cherkessk
Cherkessk (russian: Черке́сск) is the capital city of Karachay-Cherkessia, Russia, as well as its political, economic, and cultural center. Population:
It was previously known as ''Batalpashinskaya'' (until 1931), ''Batalpashinsk'' (un ...
(Siracena)
*Circassia
Circassia (; also known as Cherkessia in some sources; ady, Адыгэ Хэку, Адыгей, lit=, translit=Adıgə Xəku, Adıgey; ; ota, چرکسستان, Çerkezistan; ) was a country and a historical region in the along the northeast ...
*Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
References
See Marek Jan Olbrycht, Die Aorser, die Oberen Aorser und die Siraker bei Strabon. Zur Geschichte und Eigenart der Völker im nordostpontischen und nordkaukasischen Raum im 2.-1. Jh. v. Chr. he Aorsians, the Upper Aorsians, and the Sirakians in Strabo. On the History and Characteristics of the Peoples in the Northeastern Pontic and North Caucasian regions in the 2nd -1st century BC. Klio 83(2001):425-450; DOI:10.1524/klio.2001.83.2.425 {{Scythia Sarmatian tribes Nomadic groups in Eurasia Iranian nomads History of the North Caucasus