Silicate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

 With two shared oxides bound to each silicon, cyclic or polymeric structures can result. The cyclic
With two shared oxides bound to each silicon, cyclic or polymeric structures can result. The cyclic 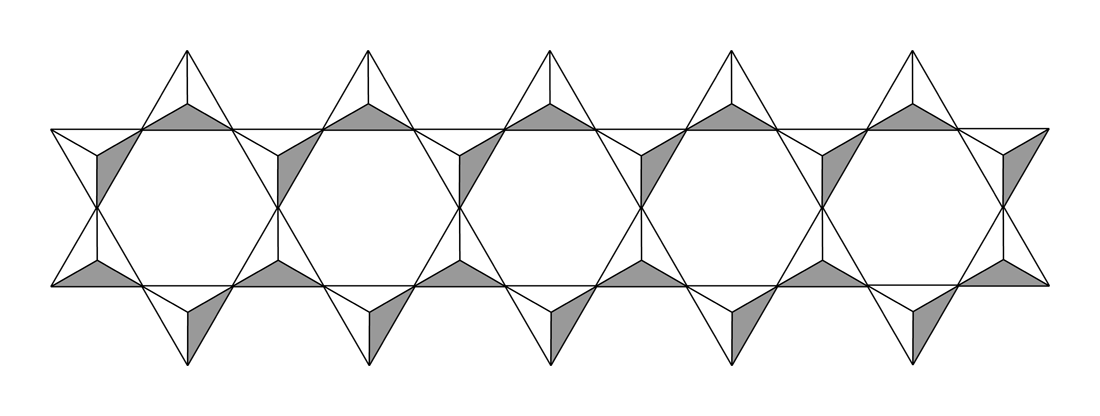 Double-chain silicates, the other category of inosilicates, occur when tetrahedra form a double chain (not always but mostly) by sharing two or three oxygen atoms each. Common minerals for this group are amphiboles.
Double-chain silicates, the other category of inosilicates, occur when tetrahedra form a double chain (not always but mostly) by sharing two or three oxygen atoms each. Common minerals for this group are amphiboles.
 In this group, known as phyllosilicates, tetrahedra all share three oxygen atoms each and in turn link to form two-dimensional sheets. This structure does lead to minerals in this group having one strong cleavage plane. Micas fall into this group. Both muscovite and
In this group, known as phyllosilicates, tetrahedra all share three oxygen atoms each and in turn link to form two-dimensional sheets. This structure does lead to minerals in this group having one strong cleavage plane. Micas fall into this group. Both muscovite and
 In
In chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate
In chemistry, orthosilicate is the anion , or any of its salts and esters. It is one of the silicate anions. It is occasionally called the silicon tetroxide anion or group.C. A. Kumins, and A. E. Gessler (1953), "Short-Cycle Syntheses of Ultra ...
(), metasilicate 320 px, Idealized structure of sodium metasilicate.
Metasilicates are silicates containing ions of empirical formula . Common stoichiometries include MSiO3 and MIISiO3. Metasilicates can be cyclic, usually the hexamer or chains .
Common comp ...
(), and pyrosilicate
A pyrosilicate is a type of chemical compound; either an ionic compound that contains the pyrosilicate anion , or an organic compound with the hexavalent ≡-O-≡ group. The anion is also called disilicateViktor Renman (2017): "Structural and ...
(, ). The name is also used for any salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually con ...
.
For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
, gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gravel is classifi ...
, and garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different ...
) and artificial (such as Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19t ...
, ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
s, glass
Glass is a non- crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenchin ...
, and waterglass).
Structural principles
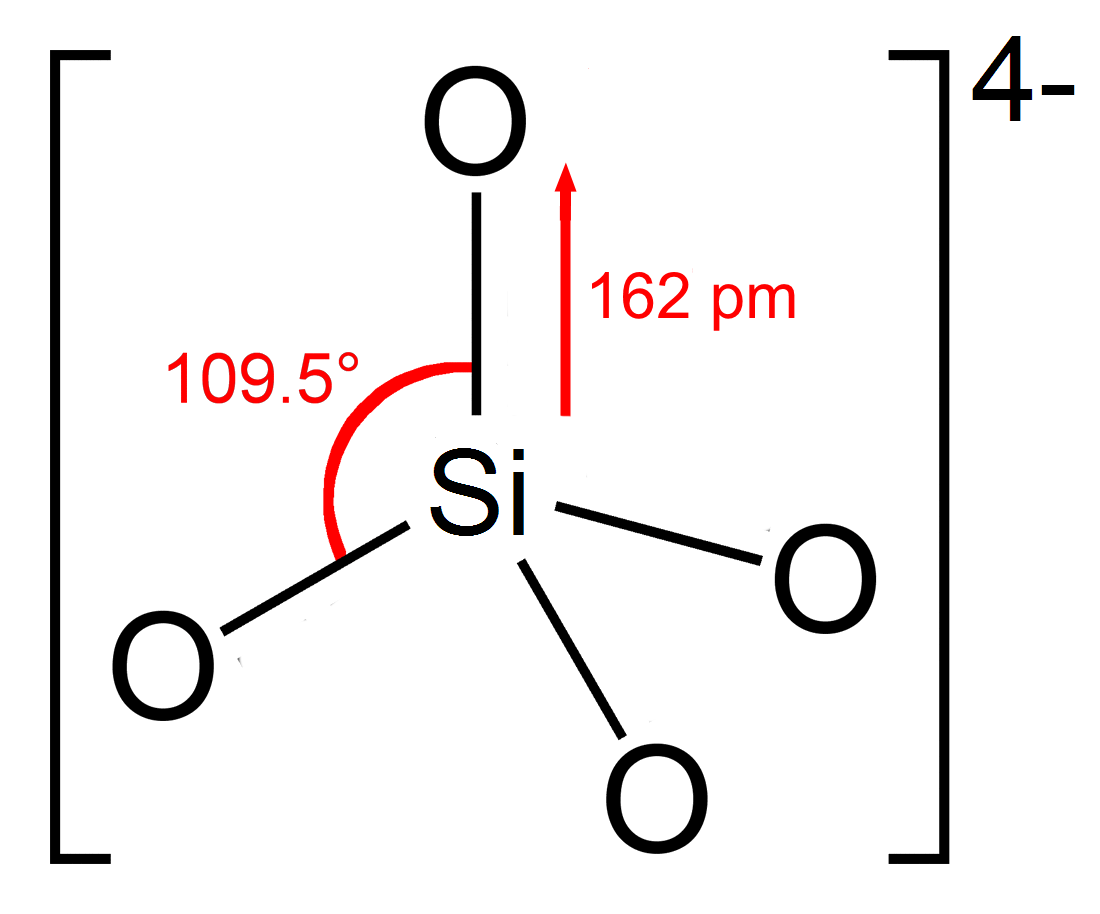
In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealizedtetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all ...
whose corners are four oxygen atoms, connected to it by single covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between ato ...
s according to the octet rule. The oxygen atoms, which bears some negative charge, link to other cations (Mn+). This Si-O-M-O-Si linkage is strong and rigid, which properties are manifested in the rock-like silicates. The silicates can be classified according to the length and crosslinking of the silicate anions.Isolated silicates
Isolatedorthosilicate
In chemistry, orthosilicate is the anion , or any of its salts and esters. It is one of the silicate anions. It is occasionally called the silicon tetroxide anion or group.C. A. Kumins, and A. E. Gessler (1953), "Short-Cycle Syntheses of Ultra ...
anions have the formula . A common mineral in this group is olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers qui ...
().
Ttwo or more silicon atoms can share oxygen atoms in various ways, to form more complex anions, such as pyrosilicate
A pyrosilicate is a type of chemical compound; either an ionic compound that contains the pyrosilicate anion , or an organic compound with the hexavalent ≡-O-≡ group. The anion is also called disilicateViktor Renman (2017): "Structural and ...
.
Chains

 With two shared oxides bound to each silicon, cyclic or polymeric structures can result. The cyclic
With two shared oxides bound to each silicon, cyclic or polymeric structures can result. The cyclic metasilicate 320 px, Idealized structure of sodium metasilicate.
Metasilicates are silicates containing ions of empirical formula . Common stoichiometries include MSiO3 and MIISiO3. Metasilicates can be cyclic, usually the hexamer or chains .
Common comp ...
ring is a hexamer of SiO32-. Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
ic silicate anions of can exist also as long chains.
In single-chain silicates, which are a type of inosilicate, tetrahedra link to form a chain by sharing two oxygen atoms each. A common mineral in this group is pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe I ...
.
 Double-chain silicates, the other category of inosilicates, occur when tetrahedra form a double chain (not always but mostly) by sharing two or three oxygen atoms each. Common minerals for this group are amphiboles.
Double-chain silicates, the other category of inosilicates, occur when tetrahedra form a double chain (not always but mostly) by sharing two or three oxygen atoms each. Common minerals for this group are amphiboles.
Sheets
 In this group, known as phyllosilicates, tetrahedra all share three oxygen atoms each and in turn link to form two-dimensional sheets. This structure does lead to minerals in this group having one strong cleavage plane. Micas fall into this group. Both muscovite and
In this group, known as phyllosilicates, tetrahedra all share three oxygen atoms each and in turn link to form two-dimensional sheets. This structure does lead to minerals in this group having one strong cleavage plane. Micas fall into this group. Both muscovite and biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron- endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more ...
have very weak layers that can be peeled off in sheets.
Framework
In a framework silicate, known as a tectosilicate, each tetrahedron shares all 4 oxygen atoms with its neighbours, forming a 3D structure.Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
and feldspars
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspa ...
are in this group.
Silicates with non-tetrahedral silicon
Although the tetrahedron is a common coordination geometry for silicon(IV) compounds, silicon may also occur with higher coordination numbers. For example, in the anion hexafluorosilicate , the silicon atom is surrounded by sixfluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reactiv ...
atoms in an octahedral arrangement. This structure is also seen in the hexahydroxysilicate anion that occurs in thaumasite
Thaumasite is a calcium silicate mineral, containing Si atoms in unusual octahedral configuration, with chemical formula Ca3 Si(O H)6( C O3)( SO4)·12 H2O, also sometimes more simply written as CaSiO3·CaCO3·CaSO4·15H2O.
It occurs as colorless ...
, a mineral found rarely in nature but sometimes observed among other calcium silicate hydrates artificially formed in cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel (aggregate) together. Cement mixe ...
and concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
submitted to a severe sulfate attack
Cement hydration and strength development mainly depend on two silicate phases: tricalcium silicate (C3S) (alite), and dicalcium silicate (C2S) (belite). Upon hydration, the main reaction products are calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) and calcium ...
.
At very high pressure, such as exists in the majority of the earth's crust, even SiO2 adopts the six-coordinated octahedral geometry in the mineral stishovite
Stishovite is an extremely hard, dense tetragonal form ( polymorph) of silicon dioxide. It is very rare on the Earth's surface; however, it may be a predominant form of silicon dioxide in the Earth, especially in the lower mantle.
Stishovite ...
, a dense polymorph of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
found in the lower mantle of the Earth and also formed by shock during meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object ...
impacts.
Chemical properties
Silicates with alkali cations and small or chain-like anions, such as sodium ortho- andmetasilicate 320 px, Idealized structure of sodium metasilicate.
Metasilicates are silicates containing ions of empirical formula . Common stoichiometries include MSiO3 and MIISiO3. Metasilicates can be cyclic, usually the hexamer or chains .
Common comp ...
, are fairly soluble in water. They form several solid hydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understo ...
s when crystallized from solution. Soluble sodium silicate
Sodium silicate is a generic name for chemical compounds with the formula or ·, such as sodium metasilicate , sodium orthosilicate , and sodium pyrosilicate . The anions are often polymeric. These compounds are generally colorless transparent ...
s and mixtures thereof, known as waterglass are in fact important industrial and household chemicals. Silicates of non-alkali cations, or with sheet and tridimensional polymeric anions, generally have negligible solubility in water at normal conditions.
Reactions
Silicates are generally inert chemically. Hence they are common minerals. Their resiliency also recommends their use as building materials. When treated with calcium oxides and water, silicate minerals formPortland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19t ...
.
Equilibria involving hydrolysis of silicate minerals are difficult to study. The chief challenge is the very low solubility of SiO44- and its various protonated forms. Such equilibria are relevant to the processes occurring on geological time scales.G. B. Alexander (1953): "The Reaction of Low Molecular Weight Silicic Acids with Molybdic Acid". ''Journal of the American Chemical Society, volume 75, issue 22, pages 5655–5657. Some plants excrete ligands that dissolve silicates, a step in biomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often to harden or stiffen existing tissues. Such tissues are called mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon; ...
.
Detection
Silicate anions in solution react withmolybdate
In chemistry a molybdate is a compound containing an oxoanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxoanions which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, altho ...
anions yielding yellow silicomolybdate complexes. In a typical preparation, monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; '' mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
...
ic orthosilicate was found to react completely in 75 seconds; dimer
Dimer may refer to:
* Dimer (chemistry), a chemical structure formed from two similar sub-units
** Protein dimer, a protein quaternary structure
** d-dimer
* Dimer model, an item in statistical mechanics, based on ''domino tiling''
* Julius Dimer ( ...
ic pyrosilicate in 10 minutes; and higher oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relati ...
s in considerably longer time. In particular, the reaction is not observed with suspensions of colloidal silica.
Zeolite formation
The nature of soluble silicates is relevant to understandingbiomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often to harden or stiffen existing tissues. Such tissues are called mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon; ...
and the synthesis of aluminosilicates, such as the industrially important catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s called zeolite
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a metal ion or H+. These p ...
s.
See also
* * Alkali-silica reaction *Carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major compon ...
* Carbonate-silicate cycle
* Ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxid ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Silicon-oxygen tetrahedron Silicates