Sierras Pampeanas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
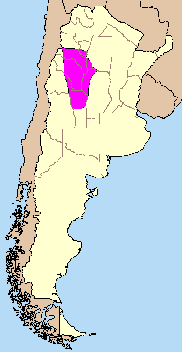


 The Sierras Pampeanas (also called Central Sierras or Pampas Sierras) (English: Pampas Mountains) is a geographical region of
The Sierras Pampeanas (also called Central Sierras or Pampas Sierras) (English: Pampas Mountains) is a geographical region of
 Much of the area is deforested due to desertification, logging ( "clearing"), strip-mining (without resurfacing or replanting), animal overgrazing, and burning to open up areas for grazing.
Much of the area is deforested due to desertification, logging ( "clearing"), strip-mining (without resurfacing or replanting), animal overgrazing, and burning to open up areas for grazing.
Climbing, Mountaineering: www.cumbreaventuras.com.ar
{{coord, 32, S, 65, W, region:AR_type:landmark, display=title Pampeanas Regions of Argentina



Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
.
The Sierras Pampeanas are a chain of mountains that rise sharply from the surrounding pampa region of Northwest Argentina. They run parallel to the Andes Mountains and their crest line is some east of the Andes crest line (running from 29° to 35° S latitude at about 65° W longitude). They cross into seven Argentina provinces: San Luis, San Juan, Córdoba, La Rioja
La Rioja () is an autonomous community and province in Spain, in the north of the Iberian Peninsula. Its capital is Logroño. Other cities and towns in the province include Calahorra, Arnedo, Alfaro, Haro, Santo Domingo de la Calzada, an ...
, Catamarca, Santiago del Estero and Tucumán.
Geography
The highest point of the Sierras Pampeanas is Cerro General Belgrano (6250 m above sea level) in La Rioja, in the Sierra de Famatina. Between the mountain ranges are several salt-filled depressions. The Salinas Grandes depression is located in Cordoba, La Rioja, Catamarca and Santiago del Estero. A characteristic of many of these mountain ranges is their morphological asymmetry: the western slopes are usually steeper than the eastern slopes, thus the former are sometimes called ''coasts'' and the latter are called ''skirts''. The narrow valleys are called "broken" or "open"; the narrow openings between valleys are called "doors". Due to erosion and other geologic forces (volcanoes, glaciers, rivers, tectonic etc.), the surface of this area varies widely. It includes cliffs and narrow channels of some rivers which are named "drawers" (if they are of moderate size) or "guns "(if they are older); there are abundantcave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
s, grottos and overhangs. Some mountains are separated by significant open areas (too large to be considered a "valley"); these are called "barreales" (mud-flats) or "pampas" (grassy plains).
Sub-ranges
The Sierras Pampeanas are composed of several sub-ranges: * Tucumán and Catamarca: Cumbres Calcahaquíes, Sierra del Aconquija; * Catamarca: Sierra de Belén, Sierra de Ambato, Sierra de Ancasti (or Sierra del Alto), Sierra de Fiambalá, Sierra de Hualfín; * La Rioja: Sierra de Famatina, Sierra de Sañogasta, Sierra de Velasco, Sierra de los Llanos, Sierra de los Colorados, Sierra de las Minas, Sierra de Chepes, Sierra de Paganzo; * San Juan: Sierra de Valle Fértil, Sierra de la Huerta, Sierra Guayaguas, Sierra de Pie de Palo; * Santiago del Estero: Sierra de Ambargasta, Sierra de Guasayán, Sierra de Sumampa; * San Luis: Sierra de las Quijadas, Sierra de Varela, Sierra del Portezuelo, Sierra del Alto Pencoso, Sierra del Yulto, Sierras de San Luis, Sierra de Guayaguas, Sierra de Cantantal, Sierra del Tala; * Córdoba: Sierras de Córdoba, including Sierras de Comechingones (which border with San Luis). The name "Pampean Ranges" can be misleading, since the Argentine Pampas cover most of the country's northern and eastern portion. However, other mountains which rise from these expanses are considered distinct geologic formations, not part of the Sierras Pampeanas.Geology
Before the Mesozoic the Sierras Pampeanas was affected by cycles of orogenic events produced by a series continent-continent collisions along the Proto-Pacific margin of Gondwana. The Neoproterozoic–CambrianPampean orogeny
The Pampean orogeny ( es, orogenia pampeana) was an orogeny active in the Cambrian in the western margin of the ancient landmass of Gondwana. The orogen's remains can now be observed in central Argentina, in particular at the Sierras de Córdob ...
was a major event along south-western Gondwana that coincided with the end of the Brasiliano–Pan-African
Pan-Africanism is a worldwide movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all Indigenous and diaspora peoples of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the movement ext ...
orogenies. In the Cambrian, subduction along the Proto-Pacific margin lead to the Famatinian orogeny which accreted the Precordillera Terrane to Gondwana. In the Gondwanide orogeny, Gondwana reached its maximum extent in the Early Carboniferous and began to break-up in the Early Cretaceous. Along the Pacific margin the convergence of tectonic plates lead to renewed subduction which produced the large rhyolitic
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral ...
provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
and plutonic belts of the Permian–Jurassic.
By the end of the Paleozoic erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
had led to the formation of a peneplain
390px, Sketch of a hypothetical peneplain formation after an orogeny.
In geomorphology and geology, a peneplain is a low-relief plain formed by protracted erosion. This is the definition in the broadest of terms, albeit with frequency the usage ...
in the eastern Sierras Pampeanas. Later tectonic movements split this surface into various levels with the highest level being Pampa de Achala.
As the South Atlantic opened following the Paraná-Etendeka flood basalts, the Andean orogeny
The Andean orogeny ( es, Orogenia andina) is an ongoing process of orogeny that began in the Early Jurassic and is responsible for the rise of the Andes mountains. The orogeny is driven by a reactivation of a long-lived subduction system alon ...
began the formation of the Andes, the product of volcanism and compressional forces along the Pacific margin, but also resulted in the development of extensional basins in South America and a passive margin along the Atlantic coast, processes still going on today. The basement of the Sierras Pampeanas was uplifted
''Uplifted'' is the second studio album by Nigerian singer Flavour N'abania. It was released on July 20, 2010, by Obaino Music and 2nite Entertainment. The album features guest appearances from Jay Dey, Oloye, Stormrex, Waga Gee, Asemstone, M-Jay, ...
during the Andean orogeny over a near-horizontal segment of the subducting Nazca Plate. Sierras Pampeanas was also affected by Miocene arc magmatism east of the Chile Trench during this period.
Climate and hydrography
This region has a temperate and semi-arid climate, with warm summers and cool winters. The northern east slope is covered by rainforest, due to high humidity in this subtropical zone. The portions within Córdoba and San Luis enjoy Mediterranean-type climate, with intense summer rainstorms and snowy winters; the vegetation here includes conifer trees. More precipitation falls on the eastern slopes, which meet the moist winds from theAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
.
Groundwater is not abundant in most of this area; the eastern slopes show greater population due to the greater runoff water available there. There are short, torrential rivers and many streams and rivulets that carry low flows, with brief and violent floods caused by summer rains. These rivers are used for the production of hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a w ...
.
Flora and fauna
The flora and fauna of the Sierras Pampeanas varies with elevation and exposure. The Dry Chaco, a region of dry forests, shrublands, and savannas, lies in the lowlands and foothills to the east. The east-facing slopes of the sierras intercept moisture-bearing winds, and are more humid than the adjacent lowlands. These higher-rainfall slopes are home to theSouthern Andean Yungas
The Southern Andean Yungas is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Yungas of southwestern Bolivia and northwestern Argentina.
Geography
The ecoregion occurs along the eastern slope of the Andes from southern Bolivia ...
humid forests. The western slopes are in the more arid rain shadow of the ranges. The High Monte
The High Monte is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion in Argentina.
Geography
The High Monte is located on the eastern slopes of the Andes, extending from the vicinity of Salta (24º S) south to Mendoza (32º S). It is a landscape of m ...
shrublands are found in the western slopes and intermountain valleys and basins west of the Sierras. High-elevation Central Andean Puna grasslands occur along the ridgeline of the Sierra de Aconquija.Godoy-Bürki, Ana C.; Ortega-Baes, Pablo; Sajama, Jesús M; Aagesen, Lone (2014). "Conservation priorities in the Southern Central Andes: mismatch between endemism and diversity hotspots in the regional flora". ''Biodiversity Conservation'' (2014) 23:81–107 DOI 10.1007/s10531-013-0586-1
Flora
Extant species include algarrobo blanco (white carob), algarrobo negro, chañar, jarilla, mistol, piquillin, tala, alpataco, tabaquillo and espinillo. In the more arid regions (the west faces) grow giant or mediumcactus
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Gree ...
and various shrubs (chilca
Chilca was a rocket launch site in Peru at , near Lima. Chilca was in service from 1974 and 1983 and was mainly used for launching Arcas and Nike sounding rockets
A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a subor ...
, tola
Tola may refer to:
Places
* Bella Tola, a mountain in the Pennine Alps in the Swiss canton of Valais
* La Tola, a town and municipality in the Nariño Department, Colombia
*Tola (Shakargarh), a village in Pakistan
* Tola, Rivas, a municipality ...
, etc.)
The Southern Andean Yungas
The Southern Andean Yungas is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Yungas of southwestern Bolivia and northwestern Argentina.
Geography
The ecoregion occurs along the eastern slope of the Andes from southern Bolivia ...
are humid forests found on east-facing slopes with higher rainfall. Trees of the Yungas include Andean alder (''Alnus acuminata''), the conifer ''Podocarpus parlatorei
''Podocarpus parlatorei'' is a species of tree in the family Podocarpaceae and native to Argentina and Bolivia, where it grows on steep hillsides on the eastern flanks of the Andes. It has been harvested commercially in the past but is now protec ...
'', and deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
trees including walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus ''Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''.
Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a true ...
(''Juglans australis''), jacaranda
''Jacaranda'' is a genus of 49 species of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. The generic name is also used as the common name.
The species ''Jacaranda mimosifolia'' has achie ...
, Pisonia
''Pisonia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the four o'clock flower family, Nyctaginaceae. It was named for Dutch physician and naturalist Willem Piso (1611–1678). Certain species in this genus are known as catchbirdtrees, birdcatcher trees o ...
, ''Schinus molle
''Schinus molle'' (Peruvian pepper, also known as American pepper, Peruvian peppertree, escobilla, false pepper, rosé pepper, molle del Peru, pepper tree, (Archived bWebCite peppercorn tree, California pepper tree, pirul (in Mexican Spanish si ...
'', quebracho, acacia, and flowering plants such as orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowerin ...
s, jasmine and bromeliads.
The Sierras de Córdoba in Córdoba and San Luis provinces have abundant vegetation on the eastern slopes, including carob, "coconuts" (local name of palm trees), garabato blanco ( acacia) and willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
.
 Much of the area is deforested due to desertification, logging ( "clearing"), strip-mining (without resurfacing or replanting), animal overgrazing, and burning to open up areas for grazing.
Much of the area is deforested due to desertification, logging ( "clearing"), strip-mining (without resurfacing or replanting), animal overgrazing, and burning to open up areas for grazing.
Fauna
The area boasts a diverse fauna, although several species are moving toward extinction (such as theboa
Kwon Bo-ah (; born November 5, 1986), known professionally as BoA, is a South Korean singer, songwriter, dancer, record producer and actress. One of the most successful and influential Korean entertainers, she has been dubbed the " Queen of K- ...
). Among the native animals: puma, brocket deer (in the north), wildcat
The wildcat is a species complex comprising two small wild cat species: the European wildcat (''Felis silvestris'') and the African wildcat (''F. lybica''). The European wildcat inhabits forests in Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus, while th ...
, fox, armadillo and mule deer
The mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') is a deer indigenous to western North America; it is named for its ears, which are large like those of the mule. Two subspecies of mule deer are grouped into the black-tailed deer.
Unlike the related whi ...
; rodents such as the viscacha
Viscacha or vizcacha (, ) are rodents of two genera ('' Lagidium'' and ''Lagostomus'') in the family Chinchillidae. They are native to South America and convergently resemble rabbits.
The five extant species of viscacha are:
*The plains visc ...
and guinea pig
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy (), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus '' Cavia'' in the family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the word ''cavy'' to describe the ...
.
The observed fauna varies according to the combination of three basic natural factors: the arrangement of mountain ranges, altitude and climate. There are important variances of biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
in the Pampas Sierras: semi-arid areas, rain-forest areas, and moderately fertile areas covered with natural forests (especially in Córdoba and San Luis). In the arid zone of La Rioja and Catamarca are found vicuña
The vicuña (''Lama vicugna'') or vicuna (both , very rarely spelled ''vicugna'', its former genus name) is one of the two wild South American camelids, which live in the high alpine areas of the Andes, the other being the guanaco, which live ...
and some alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. It is similar to, and often confused with, the llama. However, alpacas are often noticeably smaller than llamas. The two animals are closely related and can success ...
. Earlier in the twentieth century jaguar were found in the rainforests. In the eighteenth century there were sightings of spectacled bears.
The avifauna is diverse and relatively abundant in the higher, mostly arid areas. It includes Andean condor
The Andean condor (''Vultur gryphus'') is a giant South American Cathartid vulture and is the only member of the genus ''Vultur''. Found in the Andes mountains and adjacent Pacific coasts of western South America, the Andean condor is the larg ...
s and vulture
A vulture is a bird of prey that scavenges on carrion. There are 23 extant species of vulture (including Condors). Old World vultures include 16 living species native to Europe, Africa, and Asia; New World vultures are restricted to North and ...
s. In the fertile plains of Tucumán Province
Tucumán () is the most densely populated, and the second-smallest by land area, of the provinces of Argentina.
Located in the northwest of the country, the province has the capital of San Miguel de Tucumán, often shortened to Tucumán. Neigh ...
previously were found rhea, turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoide ...
, hummingbird, woodpecker
Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks, and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar, and the extreme polar regions. ...
and pigeons
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily ...
.
Settlers to the region have introduced domestic animals such as horses, donkeys, goats, pigs, cattle and sheep.
Economy
Agriculture is the predominant economic activity in the area. Certain areas are noted forwine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
and olive oil production, as well as cheeses, homemade breads, pies, sweet
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, ketone ...
s (the best known nationally are the sweet potato and quince) and alcohol. Most products are for local consumption. Only where rainfall is more abundant is agricultural output destined for outside sale.
Tree crops are grown in the foothills of the Sierras de Córdoba, including olives, peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-f ...
, pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the po ...
, apricot, fig tree
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending ...
s, quince, lemon trees, and plantations of cypress, cedar
Cedar may refer to:
Trees and plants
*''Cedrus'', common English name cedar, an Old-World genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae
*Cedar (plant), a list of trees and plants known as cedar
Places United States
* Cedar, Arizona
* ...
, ponderosa pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the ...
, eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as e ...
, poplar, oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
, and willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
which are grown for timber and forest products. Shrubs and medicinal herbs grown in the Sierras de Córdoba include peperina
''Minthostachys verticillata'', commonly known as peperina, is the only species of the genus ''Minthostachys'' known from Argentina. It occurs in the northwestern and central regions of the country. It may be the most economically important spe ...
, pennyroyal, dandelion
''Taraxacum'' () is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus is native to Eurasia and Nor ...
, plantain
Plantain may refer to:
Plants and fruits
* Cooking banana, banana cultivars in the genus ''Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking
** True plantains, a group of cultivars of the genus ''Musa''
* ''Plantaginaceae'', a family of flowerin ...
, canchalagua, wild grapes, chamomile
Chamomile (American English) or camomile (British English; see spelling differences) ( or ) is the common name for several plants of the family Asteraceae. Two of the species, ''Matricaria recutita'' and ''Anthemis nobilis'', are commonly us ...
, malva
''Malva'' is a genus of herbaceous annual, biennial, and perennial plants in the family Malvaceae. It is one of several closely related genera in the family to bear the common English name mallow. The genus is widespread throughout the temper ...
, lime
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a color between yellow and green
Lime may also refer to:
Botany ...
and passion fruit
''Passiflora edulis,'' commonly known as passion fruit, is a vine species of passion flower native to southern Brazil through Paraguay and northern Argentina. It is cultivated commercially in tropical and subtropical areas for its sweet, seedy ...
.
In arid areas such as the center and west of La Rioja and Catamarca, irrigated vines thrive, and large plantations of olive trees, (jujube
Jujube (), sometimes jujuba, known by the scientific name ''Ziziphus jujuba'' and also called red date, Chinese date, and Chinese jujube, is a species in the genus '' Ziziphus'' in the buckthorn family Rhamnaceae.
Description
It is a smal ...
was brought by Lebanese immigrants and Syrians in early twentieth century), grains, aloe and jojoba
Jojoba (; botanical name: ''Simmondsia chinensis'')also commonly called goat nut, deer nut, pignut, wild hazel, quinine nut, coffeeberry, and gray box bushis native to the Southwestern United States. ''Simmondsia chinensis'' is the sole specie ...
.
Most of these products are sold within the region, mainly associated with tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
. Due to its climate and spectacular scenery the Sierras Pampeanas are a major tourist destination in Argentina.
Salt mining is an important industry; the salt beds there are the country's largest, covering some 8400 km2.
References
Notes
Sources
*External links
Climbing, Mountaineering: www.cumbreaventuras.com.ar
{{coord, 32, S, 65, W, region:AR_type:landmark, display=title Pampeanas Regions of Argentina