Shin Shinano on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
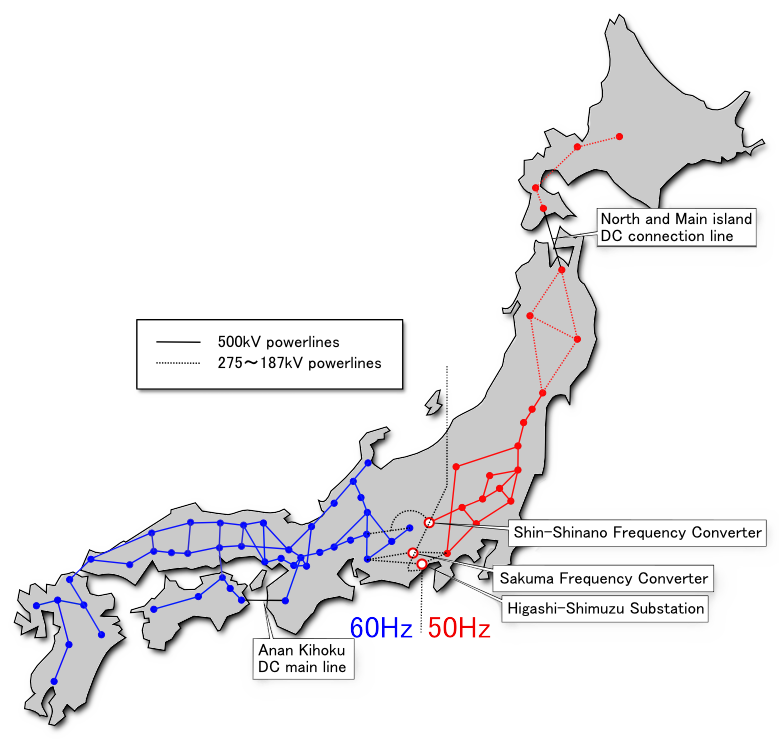 is the designation of a back-to-back connection#Power transmission, back-to-back high-voltage direct current (HVDC) facility in Japan which forms one of four frequency changer, frequency converter stations that link Japan's western and eastern power grids. The other three stations are at Higashi-Shimizu Frequency Converter, Higashi-Shimizu, Minami-Fukumitsu Frequency Converter, Minami-Fukumitsu, and Sakuma Dam#HVDC frequency converter, Sakuma Dam.
is the designation of a back-to-back connection#Power transmission, back-to-back high-voltage direct current (HVDC) facility in Japan which forms one of four frequency changer, frequency converter stations that link Japan's western and eastern power grids. The other three stations are at Higashi-Shimizu Frequency Converter, Higashi-Shimizu, Minami-Fukumitsu Frequency Converter, Minami-Fukumitsu, and Sakuma Dam#HVDC frequency converter, Sakuma Dam.
CIGRÉ B4 Compendium of HVDC Schemes, 2009.
(archived copy)
www.transmission.bpa.gov/cigresc14/Compendium/Shinshin%20Pictures.pdf
(archived copy) Converter stations Electric power infrastructure in Japan Tokyo Electric Power Company Asahi, Nagano Energy infrastructure completed in 1977 Energy infrastructure completed in 1992 {{Japan-struct-stub
 is the designation of a back-to-back connection#Power transmission, back-to-back high-voltage direct current (HVDC) facility in Japan which forms one of four frequency changer, frequency converter stations that link Japan's western and eastern power grids. The other three stations are at Higashi-Shimizu Frequency Converter, Higashi-Shimizu, Minami-Fukumitsu Frequency Converter, Minami-Fukumitsu, and Sakuma Dam#HVDC frequency converter, Sakuma Dam.
is the designation of a back-to-back connection#Power transmission, back-to-back high-voltage direct current (HVDC) facility in Japan which forms one of four frequency changer, frequency converter stations that link Japan's western and eastern power grids. The other three stations are at Higashi-Shimizu Frequency Converter, Higashi-Shimizu, Minami-Fukumitsu Frequency Converter, Minami-Fukumitsu, and Sakuma Dam#HVDC frequency converter, Sakuma Dam.
Converter equipment
The HVDC back-to-back facility Shin Shinano uses line-commutated thyristor converters. The station houses two converters, one of which opened in December 1977,Compendium of HVDC schemes, International Council on Large Electric Systems, CIGRÉ Technical Brochure No. 003, 1987, pp100–103. the other in 1992. The original 1977 converter was one of the first thyristor-based HVDC schemes to be put into operation in the world and used oil-insulated, oil-cooled outdoor thyristor valves supplied by Hitachi (60 Hz end) and Toshiba (50 Hz end). A special workshop was provided on the site, in which valve maintenance (for example replacing failed thyristors) could be carried out under clean conditions in order to avoid contamination of the oil. The 1992 converter uses more conventional air-insulated, water-cooled thyristor valves. In 2008 the original 1977 converter was decommissioned and replaced by a third converter, similar in design to the 1992 converter but using thyristor#Photothyristors, light-triggered thyristors. The Shin-Shinano link operates with a DC link voltage of 125 kV for each converter. The station was initially rated at 300 MW. In 1992, with the addition of the second 300 MW converter, the maximum transferable power was uprated to 600 MW.See also
*Energy in Japan *Kii Channel HVDC system *HVDC Hokkaido–HonshuReferences
External links
CIGRÉ B4 Compendium of HVDC Schemes, 2009.
(archived copy)
www.transmission.bpa.gov/cigresc14/Compendium/Shinshin%20Pictures.pdf
(archived copy) Converter stations Electric power infrastructure in Japan Tokyo Electric Power Company Asahi, Nagano Energy infrastructure completed in 1977 Energy infrastructure completed in 1992 {{Japan-struct-stub