Shading on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shading refers to the depiction of
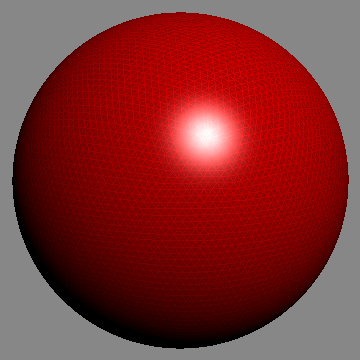 In
In
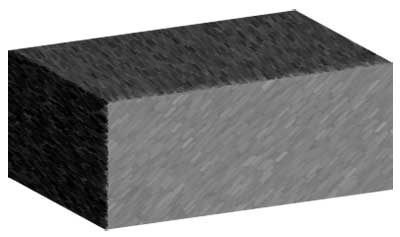
 Here, the lighting is evaluated only once for each polygon (usually for the first vertex in the polygon, but sometimes for the
Here, the lighting is evaluated only once for each polygon (usually for the first vertex in the polygon, but sometimes for the
 In
In
Shape from shading: A method for obtaining the shape of a smooth opaque object from one view
" (1970). (
Introduction to Shading.
{{Authority control Virtual reality
depth perception
Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions.
Depth sensation is the corresponding term for non-hum ...
in 3D model
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based representation of a surface of an object (inanimate or living) in three dimensions via specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, and ...
s (within the field of 3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
) or illustration
An illustration is a decoration, interpretation, or visual explanation of a text, concept, or process, designed for integration in print and digitally published media, such as posters, flyers, magazines, books, teaching materials, animations, vi ...
s (in visual art
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video, image, filmmaking, design, crafts, and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and texti ...
) by varying the level of darkness
Darkness is the condition resulting from a lack of illumination, or an absence of visible light.
Human vision is unable to distinguish colors in conditions of very low luminance because the hue-sensitive photoreceptor cells on the retina a ...
. Shading tries to approximate local behavior of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
on the object's surface and is not to be confused with techniques of adding shadows, such as shadow mapping
Shadow mapping or shadowing projection is a process by which shadows are added to 3D computer graphics. This concept was introduced by Lance Williams in 1978, in a paper entitled "Casting curved shadows on curved surfaces." Since then, it has b ...
or shadow volumes, which fall under global behavior of light.
In drawing
Shading is used traditionally indrawing
Drawing is a Visual arts, visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface, or a digital representation of such. Traditionally, the instruments used to make a drawing include pencils, crayons, and ink pens, some ...
for depicting a range of darkness by applying media more densely or with a darker shade for darker areas, and less densely or with a lighter shade for lighter areas. Light patterns, such as objects having light and shaded areas, help when creating the illusion of depth on paper.
There are various techniques of shading, including cross hatching, where perpendicular lines of varying closeness are drawn in a grid pattern to shade an area. The closer the lines are together, the darker the area appears. Likewise, the farther apart the lines are, the lighter the area appears.
Powder shading is a sketching shading method. In this style, stumping powder and paper stumps
In cricket, the stumps are the three vertical posts that support the bails and form the wicket. '' Stumping'' or ''being stumped'' is a method of dismissing a batsman.
The umpire ''calling stumps'' means the play is over for the day.
Part of ...
are used to draw a picture. (This is also in color.) The stumping powder is smooth and doesn't have any shiny particles. The paper to be used should have small grains on it so that the powder remains on the paper.
In computer graphics
 In
In computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
, shading refers to the process of altering the color of an object/surface/polygon in the 3D scene, based on things like (but not limited to) the surface's angle to lights, its distance from lights, its angle to the camera and material properties (e.g. bidirectional reflectance distribution function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF), symbol f_(\omega_,\, \omega_), is a function of four real variables that defines how light from a source is reflected off an Opacity (optics), opaque surface. It is employed in the optic ...
) to create a photorealistic
Photorealism is a genre of art that encompasses painting, drawing and other graphic media, in which an artist studies a photograph and then attempts to reproduce the image as realistically as possible in another medium. Although the term can b ...
effect.
Shading is performed during the rendering process by a program called a shader
In computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that calculates the appropriate levels of light, darkness, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene—a process known as '' shading''. Shaders have evolved to perform a variety of s ...
.
Surface angle to a light source
Shading alters the colors of faces in a 3D model based on the angle of the surface to a light source or light sources. The first image below has the faces of the box rendered, but all in the same color. Edge lines have been rendered here as well which makes the image easier to see. The second image is the same model rendered without edge lines. It is difficult to tell where one face of the box ends and the next begins. The third image has shading enabled, which makes the image more realistic and makes it easier to see which face is which.Types of lighting
When a shader computes the result color, it uses a lighting model to determine the amount of light reflected at specific points on the surface. Different lighting models can be combined with different shading techniques — while lighting says how much light is reflected, shading determines how this information is used in order to compute the final result. It may for example compute lighting only at specific points and useinterpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one ...
to fill in the rest. The shader may also decide about how many light sources to take into account etc.
Ambient lighting
An ambient light source represents an omnidirectional, fixed-intensity and fixed-color light source that affects all objects in the scene equally (is omnipresent). During rendering, all objects in the scene are brightened with the specified intensity and color. This type of light source is mainly used to provide the scene with a basic view of the different objects in it. This is the simplest type of lighting to implement, and models how light can be scattered orreflected
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The ...
many times, thereby producing a uniform effect.
Ambient lighting can be combined with ambient occlusion to represent how exposed each point of the scene is, affecting the amount of ambient light it can reflect. This produces diffused, non-directional lighting throughout the scene, casting no clear shadows, but with enclosed and sheltered areas darkened. The result is usually visually similar to an overcast day.
Point lighting
Light originates from a single point and spreads outward in all directions.Spotlighting
Models a spotlight: light originates from a single point and spreads outward in acone
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the '' apex'' or '' vertex''.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines ...
.
Area lighting
Light originates from a small area on a single plane. (A more realistic model than a point light source.)Directional lighting
A directional light source illuminates all objects equally from a given direction, like an area light of infinite size and infinite distance from the scene; there is shading, but cannot be any distance falloff. This is like thesun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
.
Distance falloff
Theoretically, two surfaces which are parallel are illuminated virtually the same amount from a ''distant'' unblocked light source such as the sun. The distance falloff effect produces images which have more shading and so would be realistic for proximal light sources. The left image doesn't use distance falloff. Notice that the colors on the front faces of the two boxes are ''exactly'' the same. It may appear that there is a slight difference where the two faces directly overlap, but this is an optical illusion caused by the vertical edge below where the two faces meet. The right image does use distance falloff. Notice that the front face of the closer box is brighter than the front face of the back box. Also, the floor goes from light to dark as it gets farther away.Calculation
Distance falloff can be calculated in a number of ways: * ''Power of the distance'' – For a given point at a distance x from the light source, the light intensity received is proportional to . ** ''None'' () – The light intensity received is the same regardless of the distance between the point and the light source. ** ''Linear'' () – For a given point at a distance x from the light source, the light intensity received is proportional to . ** ''Quadratic'' () – This is how light intensity decreases in reality if the light has a free path (i.e. no fog or any other thing in the air that can absorb or scatter the light). For a given point at a distance x from the light source, the light intensity received is proportional to . * Any number of other mathematical functions may also be used.Shading techniques
During shading asurface normal
In geometry, a normal is an object (e.g. a line, ray, or vector) that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the infinite straight line perpendicular to the tangent line to the ...
is often needed for lighting computation. The normals can be precomputed and stored for each vertex of the model.
Flat shading

centroid
In mathematics and physics, the centroid, also known as geometric center or center of figure, of a plane figure or solid figure is the arithmetic mean position of all the points in the figure. The same definition extends to any object in n-d ...
for triangle meshes), based on the polygon's surface normal and on the assumption that all polygons are flat. The computed color is used for the whole polygon, making the corners look sharp. This is usually used when more advanced shading techniques are too computationally expensive. Specular highlights are rendered poorly with flat shading: If there happens to be a large specular component at the representative vertex, that brightness is drawn uniformly over the entire face. If a specular highlight doesn't fall on the representative point, it is missed entirely. Consequently, the specular reflection component is usually not included in flat shading computation.
Smooth shading
In contrast to flat shading where the colors change discontinuously at polygon borders, with smooth shading the color changes from pixel to pixel, resulting in a smooth color transition between two adjacent polygons. Usually, values are first calculated in the vertices andbilinear interpolation
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is a method for interpolating functions of two variables (e.g., ''x'' and ''y'') using repeated linear interpolation. It is usually applied to functions sampled on a 2D rectilinear grid, though it can be ge ...
is used to calculate the values of pixels between the vertices of the polygons. Types of smooth shading include Gouraud shading and Phong shading.
=Gouraud shading
= # Determine the normal at each polygon vertex. # Apply an illumination model to each vertex to calculate the light intensity from the vertex normal. # Interpolate the vertex intensities usingbilinear interpolation
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is a method for interpolating functions of two variables (e.g., ''x'' and ''y'') using repeated linear interpolation. It is usually applied to functions sampled on a 2D rectilinear grid, though it can be ge ...
over the surface polygon.
Problems:
* Due to lighting being computed only at vertices, the inaccuracies (especially of specular highlights on large triangles) can become too apparent.
* T-junctions with adjoining polygons can sometimes result in visual anomalies. In general, T-junctions should be avoided.
=Phong shading
= Phong shading is similar to Gouraud shading, except that instead of interpolating the light intensities the normals are interpolated between the vertices and the lighting is evaluated per-pixel. Thus, the specular highlights are computed much more precisely than in the Gouraud shading model. # Compute a normal N for each vertex of the polygon. # Usingbilinear interpolation
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is a method for interpolating functions of two variables (e.g., ''x'' and ''y'') using repeated linear interpolation. It is usually applied to functions sampled on a 2D rectilinear grid, though it can be ge ...
compute a normal, Ni for each pixel. (Normal has to be renormalized each time.)
# Apply an illumination model to each pixel to calculate the light intensity from Ni.
Deferred shading
Deferred shading is a shading technique by which computation of shading is deferred to later stage by rendering in two passes, potentially increasing performance by not discarding expensively shaded pixels. The first pass only captures surface parameters (such as depth, normals and material parameters), the second one performs the actual shading and computes the final colors.=Other approaches
= Both Gouraud shading and Phong shading can be implemented usingbilinear interpolation
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is a method for interpolating functions of two variables (e.g., ''x'' and ''y'') using repeated linear interpolation. It is usually applied to functions sampled on a 2D rectilinear grid, though it can be ge ...
. Bishop and Weimer proposed to use a Taylor series
In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor ser ...
expansion of the resulting expression from applying an illumination model and bilinear interpolation of the normals. Hence, second-degree polynomial interpolation
In numerical analysis, polynomial interpolation is the interpolation of a given data set by the polynomial of lowest possible degree that passes through the points in the dataset.
Given a set of data points (x_0,y_0), \ldots, (x_n,y_n), with no ...
was used. This type of biquadratic interpolation was further elaborated by Barrera et al., where one second-order polynomial was used to interpolate the diffuse light of the Phong reflection model and another second-order polynomial was used for the specular light.
Spherical linear interpolation ( Slerp) was used by Kuij and Blake for computing both the normal over the polygon, as well as the vector in the direction to the light source. A similar approach was proposed by Hast, which uses quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. The algebra of quater ...
interpolation of the normals with the advantage that the normal will always have unit length and the computationally heavy normalization is avoided.
Flat vs. smooth shading
Computer vision
 In
In computer vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical ...
, some methods for 3D reconstruction are based on shading, or ''shape-from-shading''. Based on an image's shading, a three-dimensional model can be reconstructed from a single photograph.Horn, Berthold K.P.Shape from shading: A method for obtaining the shape of a smooth opaque object from one view
" (1970). (
PDF
Portable document format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe Inc., Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, computer hardware, ...
)
See also
*Computer graphics lighting
Computer graphics lighting encompasses the range of techniques used to simulate light within computer graphics. These methods vary in computational complexity, offering artists flexibility in both visual detail and performance. Graphics profession ...
* Lambertian reflectance
Lambertian reflectance is the property that defines an ideal "matte" or diffusely reflecting surface. The apparent brightness of a Lambertian surface to an observer is the same regardless of the observer's angle of view. More precisely, the ref ...
* List of art techniques
* List of common shading algorithms
* Shader
In computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that calculates the appropriate levels of light, darkness, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene—a process known as '' shading''. Shaders have evolved to perform a variety of s ...
* Zebra analysis to visualize curvature
References
Further reading
Introduction to Shading.
{{Authority control Virtual reality