Serbian culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Serbian culture is a term that encompasses the
Serbian culture is a term that encompasses the

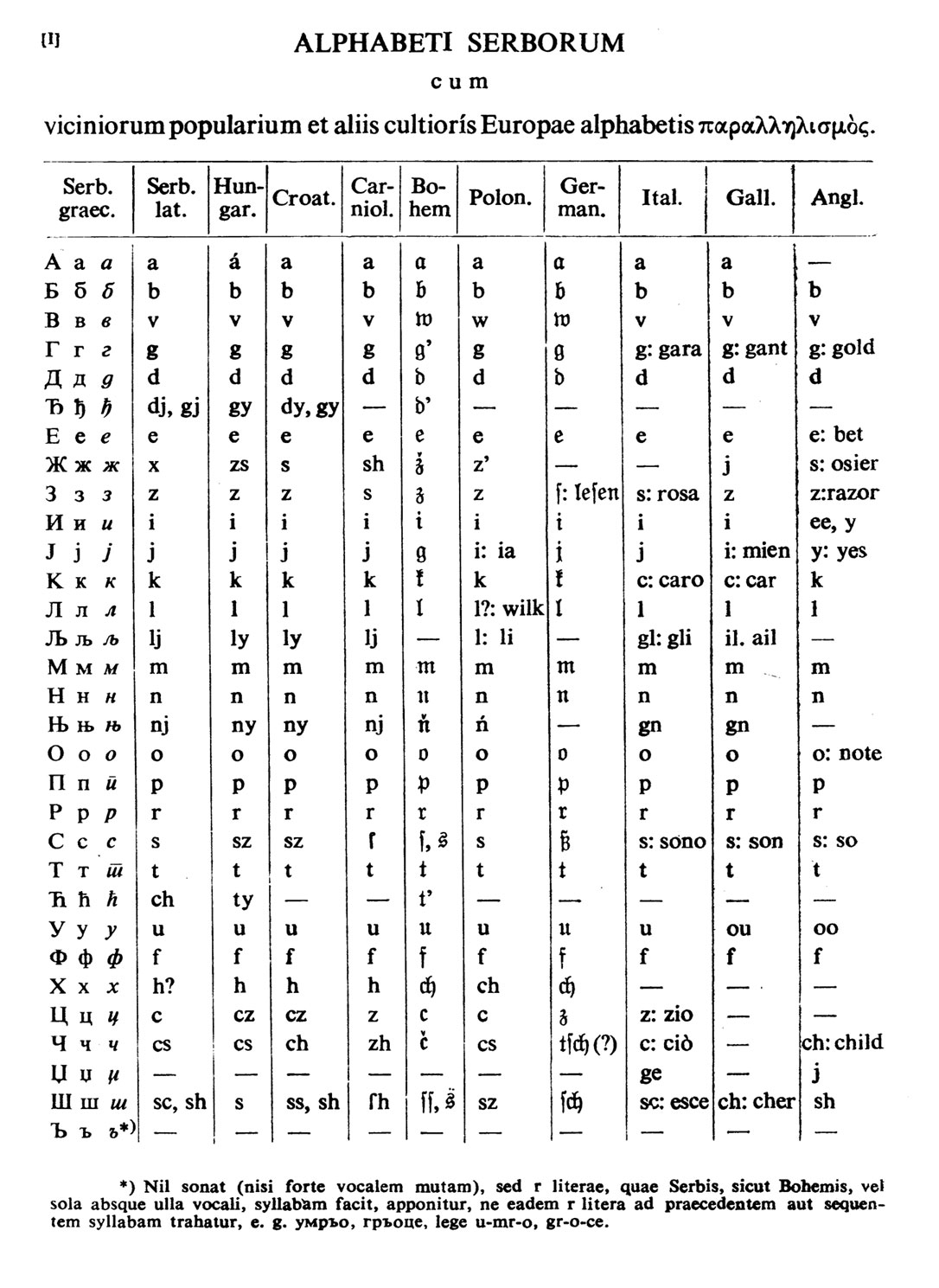 Serbs speak the
Serbs speak the  Serbian is the only European language with active digraphia, using both
Serbian is the only European language with active digraphia, using both
 Milorad Pavić is one of the most widely acclaimed Serbian authors, most notably for his ''
Milorad Pavić is one of the most widely acclaimed Serbian authors, most notably for his ''
 The traditional dance is a
The traditional dance is a
 Serbian culture is a term that encompasses the
Serbian culture is a term that encompasses the artistic
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wh ...
, culinary
Culinary arts are the cuisine arts of food preparation, cooking and presentation of food, usually in the form of meals. People working in this field – especially in establishments such as restaurants – are commonly called chefs ...
, literary
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to includ ...
, musical
Musical is the adjective of music.
Musical may also refer to:
* Musical theatre, a performance art that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance
* Musical film
Musical film is a film genre in which songs by the characters are interwo ...
, political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
and social elements that are representative of Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of ...
and Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
.
History
TheByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
had a great influence on Serbian culture as it initially governed the Byzantine and Frankish frontiers in the name of the emperors. Serbs soon formed an independent country. They were baptised by Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
missionaries and adopted the Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking c ...
, with both Latin and Catholic influences in the southern regions. The Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
influenced the maritime regions of the Serbian state in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. The Serbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches.
The majori ...
gained autocephaly
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Or ...
from Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in 1219. The pope declared Stefan the First Crowned
Stefan Nemanja II ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Немања II, ), or Stephen the First-Crowned ( sr, / , ; – 24 September 1228), was the Grand Prince of Serbia from 1196 and the King of Serbia from 1217 until his death in 1228. He was the first ...
king, starting a prosperous medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
of Serbian culture. The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
conquered the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire ...
in 1459, ending a cultural and political renaissance. Ottomans ruled the territory and influenced Serbian culture, especially in the southern regions. Meanwhile, in the northern regions, the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
expanded into modern-day Serbian territory beginning at the end of the 17th century, culturally binding this part of the nation to Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, rather than the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. After the Serbian Revolution led to autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one' ...
and eventual independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the stat ...
, its people became the primary influence on the culture of Serbia.
Religion
Conversion of theSouth Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austri ...
from Slavic paganism
Slavic mythology or Slavic religion is the religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century. The South Slavs, who likely settled in the Ba ...
to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
began in the early 7th century, long before the Great Schism, the split between the Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
East and the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
West. The Serbs were first Christianised during the reign of Heraclius (610–641). They were fully Christianised by Eastern Orthodox Missionaries (Saints) Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (815–885) were two brothers and Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are credited w ...
in 869 during the reign of Basil I, who sent them following Knez Mutimir's acknowledgement of the suzerainty of the Byzantine Empire.
After the Schism, those who lived under the Byzantine sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
became Orthodox; those who lived under the Roman sphere of influence became Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
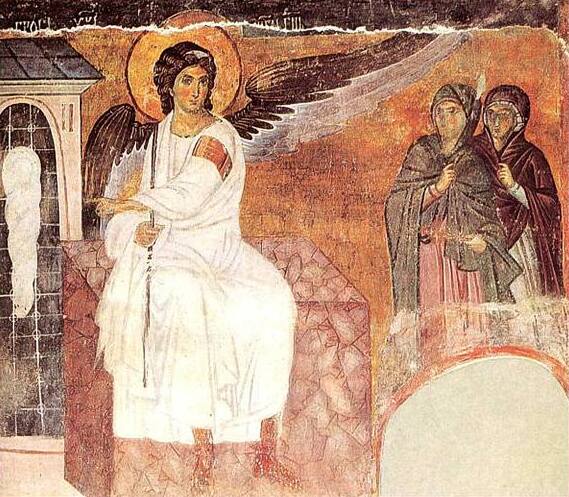
. During Stefan Nemanjić's reign (1169–1196), Serbian principalities were united into a Kingdom and many churches and monasteries were built throughout the territories, including the Studenica Monastery. Nemanjić's youngest son, Saint Sava
Saint Sava ( sr, Свети Сава, Sveti Sava, ; Old Church Slavonic: ; gr, Άγιος Σάββας; 1169 or 1174 – 14 January 1236), known as the Enlightener, was a Serbian prince and Orthodox monk, the first Archbishop of the autocephalou ...
(born as Rastko) was an influential Serbian monk who became the first independent Serbian Archbishop in 1219, granted by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
.
Later, with the arrival of the Ottoman Empire, one group of Serbs converted to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
. Their modern descendants are considered to be members of the Gorani and Bosniak
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry, ...
ethnic groups. The Serbian Orthodox Church was the westernmost bastion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
in Europe, which shaped its historical fate through contacts with Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and Islam.
During World War II the Serbs, who lived in a wide area, were persecuted by various peoples and organisations. Catholic Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic ...
within the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Fascist It ...
recognised the Serbs only as "Croats of the Eastern Greek faith". They held the ideological view that one third of the Serbs were to be murdered, one third were to be converted and the last third expelled. This view led to the deaths of at least 300,000 people, the religious conversion of 250,000 as well as mass expulsion.
According to the 2011 Serbian census, 6,079,396 people (84.6%) identified themselves as Christian Orthodox, five per cent Roman Catholic, three per cent Muslim and one per cent Protestant.
Names
Given names
As with mostWestern cultures
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
, a child is given a first name chosen by their parents but approved by the child's godparents who usually approve their choice). The given name comes first, the surname last, e.g. "Željko Popović", where "Željko" is a first name and "Popović" is a family name. Female names typically end with -a or -ica.
Popular names are mostly of Serbian (Slavic), Christian (Biblical), Greek and Latin origin. Some examples are:
* Serbian: Dragana, Dušan
Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Душан) is a Slavic given name primarily used in countries of Yugoslavia; and among Slovaks and Czechs. The name is derived from the Slavic noun ''duša'' "soul".
Occurrence
In Serbia, it was the 29th most popular nam ...
, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
, Milica
Milica ( sr-Cyrl, Милица; pronounced 'Millitsa') is a feminine name popular in Balkan countries. It is a diminutive form of the given name Mila, meaning 'kind', 'dear' or 'sweet'. The name was used for a number of queens and princesses, incl ...
, Miloš, Nemanja, Uroš, Vuk
* Greek: Aleksandar
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
, Anastasija
Anastasija ( Serbian and Macedonian: Анастасија) is a transliteration of the Greek name Anastasia in Serbian, Macedonian, and Latvian. Its male counterpart is ''Anastasije ( Serbian: Анастасије). It may refer to:
*Saint Anast ...
, Anđela, Đorđe, Jelena, Katarina, Nikola, Stefan
* Biblical: Ana, Lazar, Luka, Jovan or Ivan, Marija
Marija is a feminine given name, a variation of the name Maria, which was in turn a Latin form of the Greek names Μαριαμ, or Mariam, and Μαρια, or Maria, found in the New Testament. Depending on phonological rules concerning consecutiv ...
, Marko, Matija Matija is a South Slavic masculine and feminine given name, a variant of Matthew. Notable people with the name include:
* Matija Ahacel (1779–1845), Carinthian Slovene philologist, publicist, and collector of folk songs
* Matija Antun Relković ...
, Mihajlo, Pavle Pavle ( Macedonian and sr-cyr, Павле; ka, პავლე) is a Serbian, Macedonian, Croatian and Georgian male given name corresponding to English Paul; the name is of biblical origin (cf. Saint Paul).
People known mononymously as Pavle inc ...
, Petar
* Latin: Antonije, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
, Srđan Srđan (Срђан); ; ; ) is a Serbo-Croatian masculine given name, usually written as ''Srdjan'' when the letter đ is unavailable.
It is usually considered to be a form of the name Sergius (name), Sergius, honoring the Christian martyr and sain ...
, Valentina
Surnames
Most Serbian surnames (like Bosnian, Croatian and Montenegrin) have the surname suffix -ić (pronounced , Cyrillic: ''-ић''). This is oftentransliterated
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus ''trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek → , Cyrillic → , Greek → the digraph , Armenian → or L ...
as ''-ic'' or ''-ici''. In history, Serbian names have often been transcribed with a phonetic ending, -ich or -itch. This form is often associated with Serbs from before the early 20th century: hence Milutin Milanković is usually referred to, for historical reasons, as Milutin Milankovitch.
The -ić suffix, with variants "-ović"/"-ević", is originally a Slavic diminutive and its meaning has been extended to create patronymics
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor.
Patronymics are still in use, including mandatory use, in many countries worldwide, alt ...
. Thus the surname Petr(ov)ić signifies "little Petar", as does, for example, "-sen"/"-son" in Scandinavian and to a lesser extent German and English names or a common prefix Mac ("son of") in Scottish and Irish, and O' (grandson of) in Irish names. It is estimated that some two thirds of all Serbian surnames end in -ić but that some 80% of Serbs carry such a surname with many common names being spread out among tens and even hundreds of non-related extended families.
Other common surname suffixes are -ov or -in which is the Slavic possessive case
A possessive or ktetic form ( abbreviated or ; from la, possessivus; grc, κτητικός, translit=ktētikós) is a word or grammatical construction used to indicate a relationship of possession in a broad sense. This can include strict own ...
suffix, thus Nikola's son becomes ''Nikolin,'' Petar's son ''Petrov,'' and Jovan's son ''Jovanov''. Those are more typical for Serbs from Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
. The two suffixes are often combined. The most common surnames are Marković, Nikolić, Petrović, and Jovanović.
Cuisine
Most people in Serbia have three meals daily,breakfast
Breakfast is the first meal of the day usually eaten in the morning. The word in English refers to breaking the fasting period of the previous night.Anderson, Heather Arndt (2013)''Breakfast: A History'' AltaMira Press. Various "typical" or " ...
, lunch
Lunch is a meal eaten around the middle of the day. It is commonly the second meal of the day, after breakfast, and varies in size by culture and region.
Etymology
According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED''), the etymology ...
and dinner
Dinner usually refers to what is in many Western cultures the largest and most formal meal of the day, which is eaten in the evening. Historically, the largest meal used to be eaten around midday, and called dinner. Especially among the elite ...
, with lunch being the largest and most important meal. However, people traditionally ate only lunch and dinner, with breakfast being introduced in the second half of the 19th century.

Background
Traditional Serbian cuisine is varied and can be said to be a mix of European, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern fare. ''Ćevapi
Ćevapi (, ), ćevapčići (formal: diminutive; , ) is a grilled dish of minced meat found traditionally in the countries of southeast Europe (the Balkans). It is considered a national dish of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and is also comm ...
'' consisting of grilled heavily seasoned mixed ground meat
Ground meat, called mince or minced meat outside North America, is meat finely chopped by a meat grinder or a chopping knife. A common type of ground meat is ground beef, but many other types of meats are prepared in a similar fashion, includ ...
patties is considered the national dish. Other notable dishes include '' koljivo'' used in religious rituals, Serbian salad
Serbian salad ( sr, Српска салата / ''Srpska salata'') is a vegetable salad, usually served during summer with roast meat and other dishes. It is made from diced fresh tomatoes, cucumber and onions, usually seasoned with sunflower oil o ...
, '' sarma'' (stuffed wineleaf), pilav (pilaf,a Middle eastern meal similar to rizzoto), moussaka
Moussaka (, , ) is an eggplant- or potato-based dish, often including ground meat, which is common in the Balkans and the Middle East, with many local and regional variations.
The best-known version in Europe and the Americas is the Greek vari ...
and bean soup ('' prebranac''). '' Česnica'' is a traditional bread for Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
Day.
Homemade meals
A number of foods which are easily available in Western supermarkets, are often made at home in Serbia. These include rakija (fruit brandy), ''slatko
Slatko ( sr, / ; mk, слатко, slatko; bg, сладко, sladko; meaning "sweet") is a thin fruit preserve made of fruit or rose petals in Bulgarian, Macedonian, and Serbian cuisine. Almost any kind of fruit can be used, like wild straw ...
'', jam, jelly, and pickled foods (notably sauerkraut
Sauerkraut (; , "sour cabbage") is finely cut raw cabbage that has been fermented by various lactic acid bacteria. It has a long shelf life and a distinctive sour flavor, both of which result from the lactic acid formed when the bacteria ...
, '' ajvar'' and sausage
A sausage is a type of meat product usually made from ground meat—often pork, beef, or poultry—along with salt, spices and other flavourings. Other ingredients, such as grains or breadcrumbs may be included as fillers or extenders. ...
). There can be economic or cultural reasons behind these food choices. Food preparation is a strong part of the Serbian family tradition.
Desserts
Serbian desserts are a mixture of other Balkan desserts and desserts native to central Serbia. The desserts that are usually served include ''uštipci
Uštipci ( sr-cyr, Уштипци, ) are doughnut-like fried dough balls popular in Southeast European countries, namely Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, North Macedonia, Serbia, Slovenia and Albania
Origin
The origin of the uštipci pastry i ...
'', ''tulumbe
Tulumba or Bamiyeh ( Persian: بامیه) is a deep-fried dessert found in Turkey and the regional cuisines of the former Ottoman Empire. It is a fried batter soaked in syrup, similar to jalebis and churros. It is made from unleavened doug ...
'', ''krofne
Krofne ( Albanian and hr, krafne; Bosnian and sr-Latn, krofne, sr-cyr, крофне; sl, krofi; mk, крофни) are airy filled doughnuts. They are round and usually filled with jelly, marmalade, jam or chocolate as well as butter, Nutell ...
'' and ''palačinke
Palatschinke (or palaccinka, plural palatschinken) is a thin crêpe-like variety of pancake of Greco-Roman origin. While the dessert is most common in South and West Slavic countries, it is also generally known in other parts of Central and Easte ...
'' (crepes). ''Slatko'' is a traditional Serbian dessert popular throughout Serbia and it can be found in most Serbian restaurants in the Balkans and in the diaspora.
Drinks
Beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
is widely consumed in Serbia. The most popular brands are Jelen Pivo and Lav Pivo
Lav pivo ( sr-cyr, Лав пиво) is a Serbian beer brand. Produced and bottled by Carlsberg Srbija in the town of Čelarevo (Bačka Palanka municipality), it has the second-biggest market share among the beer brands in Serbia, behind their riva ...
. Rakija, a type of fruit brandy is also widespread, with the plum rakija (''šljivovica'', symbol of Šumadija), and grape rakija (''loza'', southern Serbia). This is Serbia's national drink and is common in other Mediterranean countries. Domestic wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
is also popular. Turkish coffee
Turkish coffee is a style of coffee prepared in a '' cezve'' using very finely ground coffee beans without filtering.
Preparation
Turkish coffee is very finely ground coffee brewed by boiling. Any coffee bean may be used; arabica varieties are ...
(called ''domaća'' or ''srpska'' kafa) is widely consumed as well.
Language
 Serbs speak the
Serbs speak the Serbian language
Serbian (, ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and co-official in Montenegro and ...
, one of the South Slavic group of languages, specifically in the Southwestern Slavic subgroup together with other Serbo-Croatian varieties and Slovenian. It is mutually intelligible
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as a ...
with the Croatian and Bosnian language
Bosnian (; / , ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language mainly used by ethnic Bosniaks. Bosnian is one of three such varieties considered official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina, along with Croatian an ...
s (see Differences in standard Serbian, Croatian and Bosnian
Standard Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, and Serbian are different national variants and official registers of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language.
History
In socialist Yugoslavia, the language was approached as a pluricentric lan ...
) and most linguists consider it one of the standard varieties of the common Serbo-Croatian language
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia a ...
.
The Serbian language comprises several dialects, the standard language is based on the Stokavian dialect.
It is an official language in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
and Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
. In Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
, Croatia, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, it is a regionally recognised minority language.
There are also historical variants of the Serbian language, namely Old Serbian and Slavonic-Serbian, a blend of Church Slavonic
Church Slavonic (, , literally "Church-Slavonic language"), also known as Church Slavic, New Church Slavonic or New Church Slavic, is the conservative Slavic liturgical language used by the Eastern Orthodox Church in Belarus, Bosnia and Her ...
, Russian and Serbian.
 Serbian is the only European language with active digraphia, using both
Serbian is the only European language with active digraphia, using both Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
alphabets. The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, th ...
was devised in 1814 by Vuk Karadžić, who created the alphabet on phonemic
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-west ...
principles. Cyrillic has its origins in the Cyril and Methodius transformation from the Greek script
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as w ...
. The Latin alphabet used for Serbian is Ljudevit Gaj's version shared by all Southwestern Slavic languages.
Loanwords in the Serbian language are mostly from Turkish, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
; words of Hungarian origin are present mostly in the north and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
words mostly in the liturgy.
Two Serbian words that are used in many of the world's languages are vampire
A vampire is a mythical creature that subsists by feeding on the Vitalism, vital essence (generally in the form of blood) of the living. In European folklore, vampires are undead, undead creatures that often visited loved ones and caused mi ...
and paprika
Paprika ( US , ; UK , ) is a spice made from dried and ground red peppers. It is traditionally made from '' Capsicum annuum'' varietals in the Longum group, which also includes chili peppers, but the peppers used for paprika tend to be milder ...
. Slivovitz and ćevapčići are Serbian words which have spread together with the Serbian food/drink they refer to. Vampire entered most West European languages through German-language texts in the early 18th century and has since spread around the world.
Literature
Most Medieval literature was about religious themes. Variousgospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
, psalters
A psalter is a volume containing the Book of Psalms, often with other devotional material bound in as well, such as a liturgical calendar and litany of the Saints. Until the emergence of the book of hours in the Late Middle Ages, psalters were ...
, menologies, hagiographies
A hagiography (; ) is a biography of a saint or an ecclesiastical leader, as well as, by extension, an adulatory and idealized biography of a founder, saint, monk, nun or icon in any of the world's religions. Early Christian hagiographies might ...
, and essays and sermons of the founders of the Serbian Orthodox Church were written. At the end of the 12th century, two of the most important pieces of Serbian medieval literature were created—the Miroslav Gospels
Miroslav Gospel ( sr, Мирослављево jеванђеље / Miroslavljevo jevanđelje, ) is a 362-page Serbian illuminated manuscript Gospel Book on parchment with very rich decorations. It is one of the oldest surviving documents written ...
(UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
's Memory of the World) and the Vukan Gospels, which combined handwritten Biblical texts with painted initials and small pictures. Serbian epic poetry
Serbian epic poetry ( sr, Српске епске народне песме, Srpske epske narodne pesme) is a form of epic poetry created by Serbs originating in today's Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro and North Macedonia. The ...
was a central part of medieval Serbian literature based on historic events such as the Battle of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo ( tr, Kosova Savaşı; sr, Косовска битка) took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan ...
.
Notable Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
authors include Andrija Zmajević
Andrija Zmajević ( cyrl, Андрија Змајевић; 6 June 1628 - 7 September 1694) was a Baroque poet, the Archbishop of Antivari and a theologian.
Biography
Zmajević was born in Perast, in the Bay of Kotor, at the time part of the Republ ...
, Gavril Stefanović Venclović Gavril is a variant of the name Gabriel, may refer to:
* Gavril Atanasov, Macedonian icon painter from Berovo in the 19th century
*Gavril Bănulescu-Bodoni (1746–1821), Romanian clergyman who served as Metropolitan of Moldavia
* Gavril Balint (b ...
, Jovan Rajić and Zaharije Orfelin. Dositej Obradović is the most prominent literary figure of the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, while the most notable Classicist writer is Jovan Sterija Popović
Jovan Sterija Popović (; sr-cyr, Јован Стерија Поповић; 13 January 1806 – 10 March 1856) was a Serbian playwright, poet, lawyer, philosopher and pedagogue who taught at the Belgrade Higher School. Sterija was recognized by ...
, although his works also contain elements of Romanticism. Modern Serbian literature began with Vuk Karadžić's collections of folk song
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has ...
s in the 19th century, and the writings of Njegoš and Branko Radičević
Aleksije "Branko" Radičević ( sr-Cyrl, Алексије Бранко Радичевић, ; 28 March 1824 – 1 July 1853) was a Serbian poet who wrote in the period of Romanticism.
Biography
Branko Radičević was born in Slavonski Brod on ...
. The first prominent representative of Serbian literature in the 20th century is Jovan Skerlić, who wrote in pre–World War I Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 mi ...
and helped to introduce Serbian writers to literary modernism.
In the 20th century, Serbian literature flourished and a myriad of young and talented writers appeared. The most well-known authors are Ivo Andrić
Ivo Andrić ( sr-Cyrl, Иво Андрић, ; born Ivan Andrić; 9 October 1892 – 13 March 1975) was a Yugoslav novelist, poet and short story writer who won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1961. His writings dealt mainly with life in ...
, Miloš Crnjanski
Miloš Crnjanski ( sr-cyr, Милош Црњански, ; 26 October 1893 – 30 November 1977) was a Serbian writer and poet of the expressionist wing of Serbian modernism, author, and a diplomat.
Biography
Crnjanski was born in Csongrád (mod ...
, Meša Selimović
Mehmed "Meša" Selimović (; ; 26 April 1910 – 11 July 1982) was a Yugoslav writer, whose novel '' Death and the Dervish'' is one of the most important literary works in post-World War II Yugoslavia. Some of the main themes in his works are the ...
, Borislav Pekić
Borislav Pekić ( sr-cyr, Борислав Пекић, ; 4 February 1930 – 2 July 1992) was a Serbian and Yugoslav writer and political activist.
He was born in 1930, to a prominent family in Montenegro, at that time part of the Kingdom of Yugo ...
, Danilo Kiš
Danilo Kiš (; born Dániel Kiss; 22 February 1935 – 15 October 1989) was a Yugoslav novelist, short story writer, essayist and translator. His best known works include ''Hourglass'', ''A Tomb for Boris Davidovich'' and '' The Encyclopedia of ...
, Milorad Pavić
Milorad Pavić ( sr-Cyrl, Милорад Павић, ; 15 October 1929 – 30 November 2009) was a Serbian novelist, poet, short story writer, and literary historian. Born in Belgrade in 1929, he published a number of poems, short stories ...
, David Albahari
David Albahari (, ; born 15 March 1948)Biography
at Miodrag Bulatović Miodrag Bulatović ( cnr-Cyrl, Миодраг Булатовић; 20 February 1930 – 15 March 1991), was a writer, novelist, journalist and playwright. He is considered to be one of the best Montenegrin novelists and remains the most translated M ...
, at Miodrag Bulatović Miodrag Bulatović ( cnr-Cyrl, Миодраг Булатовић; 20 February 1930 – 15 March 1991), was a writer, novelist, journalist and playwright. He is considered to be one of the best Montenegrin novelists and remains the most translated M ...
Dobrica Ćosić
Dobrica Ćosić ( sr, Добрица Ћосић, ; 29 December 1921 – 18 May 2014) was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician, writer, and political theorist.
Ćosić was twice awarded the prestigious NIN award for literature and Medal of Pushkin ...
, Zoran Živković among others. Jelena Dimitrijević and Isidora Sekulić
Isidora Sekulić ( sr-cyr, Исидора Секулић, 16 February 1877 – 5 April 1958) was a Serbian writer, novelist, essayist, polyglot and art critic. She was "the first woman academic in the history of Serbia".
Biography
Sekulić was b ...
are two early 20th century women writers; Svetlana Velmar-Janković was the best-known female novelist in mi-20th and early 21st century.
Ivo Andrić won the Nobel Prize in Literature
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, caption =
, awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature
, presenter = Swedish Academy
, holder = Annie Ernaux (2022)
, location = Stockholm, Sweden
, year = 1901
, ...
in 1961.
 Milorad Pavić is one of the most widely acclaimed Serbian authors, most notably for his ''
Milorad Pavić is one of the most widely acclaimed Serbian authors, most notably for his ''Dictionary of the Khazars
''Dictionary of the Khazars: A Lexicon Novel'' ( sr-cyrl, Хазарски речник, rtl=yes, ) is the first novel by Serbian writer Milorad Pavić, published in 1984. Originally written in Serbian, the novel has been translated into many l ...
'', which has been translated into 38 languages.
Traditions and customs
AmongSlavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
and Orthodox Christians, only Serbs have the custom of '' slava''. Each family has one patron saint they venerate on their feast day. Unlike most customs that are common for everyone, each family celebrates its own saint (of course, there is a lot of overlap) who is considered its protector separately. A ''slava'' is passed down mostly, though not exclusively, from father to son. (If a family has no son, and a daughter stays in the parental home and her husband moves in, her ''slava'', not his, is celebrated). Each household celebrates only one saint, so the occasion brings the whole family together. However, since many saints (e.g. St. Nicholas, St. John the Baptist, St. George, St. Archangels of Gabriel and Michael, and the Apostles St. Peter and Paul) have two feast days, both are marked.
* Slava, Serbian Orthodox Patron saint veneration
* Kumstvo, God-parenthood in the Serbian Orthodox Church
* Pobratimstvo, blood-brotherhood
*
* Serbian Christmas traditions
Serbian Christmas traditions are customs and practices of the Serbs associated with Christmas and a period encompassing it, between the third Sunday before Christmas Day and Epiphany. There are many, complex traditions connected with this period. ...
** Badnjak (Serbian)
The ''badnjak'' ( sr-Cyrl, бадњак, ), also called ''veseljak'' (, , literally "the one who brings joy" in Serbian), is a tree branch or entire tree that is central to Serbian Christmas celebrations. It is placed on a fire on Christmas Eve ...
, Christmas tradition
* Serbian epic poetry
Serbian epic poetry ( sr, Српске епске народне песме, Srpske epske narodne pesme) is a form of epic poetry created by Serbs originating in today's Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro and North Macedonia. The ...
, Epic poetry
* Čuvari Hristovog groba is a religious/cultural practice of guarding a representation of Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
's grave on Good Friday
Good Friday is a Christian holiday commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary. It is observed during Holy Week as part of the Paschal Triduum. It is also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday (also Holy ...
in the Church of St. Nicholas by the Serbian Orthodox
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous ( ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian churches.
The majority of the population ...
inhabitants in the town of Vrlika
The Serbs are a highly family-oriented society, which glancing at a Serbian dictionary and the richness of their terminology related to kinship makes clear.
 The traditional dance is a
The traditional dance is a circle dance
Circle dance, or chain dance, is a style of social dance done in a circle, semicircle or a curved line to musical accompaniment, such as rhythm instruments and singing, and is a type of dance where anyone can join in without the need of par ...
called '' kolo'', which is common among Serbs, Montenegrins and Macedonians. It is a collective dance, where a group of people (usually several dozen, at the very least three) hold each other by the hands or around the waist dancing, forming a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is cons ...
(hence the name), semicircle or spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Helices
Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are:
The Serbian Orthodox Church uses the traditional
 A Baroque church 'Our Lady of the Rocks' on an island in the
A Baroque church 'Our Lady of the Rocks' on an island in the
 Serbian music dates from the medieval period with strong church and folk traditions. Church music in Serbia of the time was based on the Osmoglasnik a cycle of religious songs based on the resurrection and lasting for eight weeks. During the
Serbian music dates from the medieval period with strong church and folk traditions. Church music in Serbia of the time was based on the Osmoglasnik a cycle of religious songs based on the resurrection and lasting for eight weeks. During the  During Ottoman rule, Serbs were forbidden to own property, to learn to read and write and denied the use of musical instruments. Church music had to be performed in private. The
During Ottoman rule, Serbs were forbidden to own property, to learn to read and write and denied the use of musical instruments. Church music had to be performed in private. The
 Serbia has a well-established theatrical tradition with many theatres. The Serbian National Theatre was established in 1861. The company started performing opera at the end of the 19th century and the permanent opera was established in 1947. It established a ballet company.
Bitef, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, is one of the oldest theatre festivals in the world. New Theatre Tendencies is the constant subtitle of the Festival. Founded in 1967, Bitef has continually followed and supported the latest theater trends. It has become one of thefive most important and biggest European festivals, and one of the most significant culture institutions of Serbia.
Cinema was established reasonably early in Serbia, with 12 feature films being produced before the start of World War II. The most notable of the prewar films is Mihailo Popovic's ''The Battle of Kosovo'' in 1939.
Serbia has a well-established theatrical tradition with many theatres. The Serbian National Theatre was established in 1861. The company started performing opera at the end of the 19th century and the permanent opera was established in 1947. It established a ballet company.
Bitef, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, is one of the oldest theatre festivals in the world. New Theatre Tendencies is the constant subtitle of the Festival. Founded in 1967, Bitef has continually followed and supported the latest theater trends. It has become one of thefive most important and biggest European festivals, and one of the most significant culture institutions of Serbia.
Cinema was established reasonably early in Serbia, with 12 feature films being produced before the start of World War II. The most notable of the prewar films is Mihailo Popovic's ''The Battle of Kosovo'' in 1939.
 Cinema prospered after World War II. The most notable postwar director is
Cinema prospered after World War II. The most notable postwar director is

 Serbia is very successful in many sports. Among the most popular sports are
Serbia is very successful in many sports. Among the most popular sports are
 At the beginning of the 21st century, there were 32 art galleries and 142 museums in Serbia. Belgrade has many of the most significant with the
At the beginning of the 21st century, there were 32 art galleries and 142 museums in Serbia. Belgrade has many of the most significant with the

 *The
*The
Serbia Ministry of Culture
* ttp://www.rts.rs/ Radio Television Serbia * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060524061201/http://ifj-europe.org/default.asp?index=281&Language=EN European Federation of Journalists Serbia page
Serbian info culture page
Serbian info Art History page
Columbia University Yugoslav Literature article
Treasures National Library Serbia
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandri ...
, so Christmas Day (December 25) falls on January 7 on the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years d ...
and is the day Serbs celebrate Christmas. This is shared with the Orthodox churches of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and the Greek Old Calendarists.Serbs have their own customs regarding Christmas. Early in the morning of Christmas Eve, the head of the family would go to a forest to cut '' badnjak'', a young oak, the oak tree would then be brought into the church to be blessed by the priest. Then it would be stripped of its branches and combined with wheat and other grain products would be burned in the fireplace. The burning of the ''badnjak'' is a ritual which is of pagan origin and is considered a sacrifice to God (or the old pagan gods) so that the coming year may bring plenty of food, happiness, love, luck and riches. Nowadays, with most Serbs living in towns, they go to their church service to be given a small parcel of oak, wheat and other branches tied together to be taken home and set afire. The house floor and church are covered with hay, reminding worshippers of the stable
A stable is a building in which livestock, especially horses, are kept. It most commonly means a building that is divided into separate stalls for individual animals and livestock. There are many different types of stables in use today; the ...
in which Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
was born.
Christmas Day itself is celebrated with a feast, necessarily featuring roasted piglet as the main meal. The most important Christmas meal is ''česnica
A česnica ( Serbian Cyrillic: чесница, ; derived from the noun ''čest'', meaning "share"), also called Božićna pogača (Serbian Cyrillic: Божићна погача, "Christmas pogača") is the ceremonial, round loaf of bread that is a ...
'', a special bread. It contains a coin; during the lunch, the family breaks up the bread and the one who finds the coin is said to be assured of an especially happy year.
Unlike in the West, Christmas is not associated with presents, although it is the day of Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-day Dem ...
, the protector saint of children, to whom presents are given. Most Serbian families give presents on New Year's Day. Santa Claus ('' Deda Mraz'' (literally meaning ''Grandpa Frost'')) and the Christmas tree (generally associated with New Year's Day
New Year's Day is a festival observed in most of the world on 1 January, the first day of the year in the modern Gregorian calendar. 1 January is also New Year's Day on the Julian calendar, but this is not the same day as the Gregorian one. Whi ...
) are also used in Serbia because of globalisation
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
. Serbs celebrate the Old New Year
The Old New Year or the Orthodox New Year is an informal traditional holiday, celebrated as the start of the New Year by the Julian calendar. In the 20th and 21st centuries, the Old New Year falls on January 14 in the Gregorian calendar.
This tra ...
(currently on January 14 of the Gregorian calendar).
On Orthodox Easter, Serbs have the tradition of Slavic Egg decorating.
Another related feature, often lamented by Serbs themselves, is disunity and discord; as Slobodan Naumović puts it, "Disunity and discord have acquired in the Serbian popular imaginary a notorious, quasi-demiurgic status. They are often perceived as being the chief malefactors in Serbian history, causing political or military defeats, and threatening to tear Serbian society completely apart." That disunity is often quoted as the source of Serbian historic tragedies, from the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 to Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
in the 1990s. Even the contemporary notion of "two Serbia's"—one supposedly liberal, pro-European
Pro-Europeanism, sometimes called European Unionism, is a political position that favours European integration and membership of the European Union (EU).Krisztina Arató, Petr Kaniok (editors). ''Euroscepticism and European Integration''. Polit ...
, Eurocentric
Eurocentrism (also Eurocentricity or Western-centrism)
is a worldview that is centered on Western civilization or a biased view that favors it over non-Western civilizations. The exact scope of Eurocentrism varies from the entire Western worl ...
and pro-western—and the other conservative, nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
, Russophilic
Russophilia (literally love of Russia or Russians) is admiration and fondness of Russia (including the era of the Soviet Union and/or the Russian Empire), Russian history and Russian culture. The antonym is Russophobia. In the 19th Cent ...
and Eurosceptic
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies, and seek refor ...
seems to be an extension of the discord. Popular proverbs "two Serbs, three political parties" and "God save us from Serbs that may unite!", and even the unofficial Serbian motto " Only Unity Saves the Serbs" (''Samo sloga Srbina spasava'') illustrates the national frustration with the inability to unite over important issues.
Humour
Serbian has a long tradition of humour and popular jokes. The most common type of humour isblack humour
Black comedy, also known as dark comedy, morbid humor, or gallows humor, is a style of comedy that makes light of subject matter that is generally considered taboo, particularly subjects that are normally considered serious or painful to discu ...
and Serbian jokes are often imitated by other peoples from the Balkans, often with a twist. As with many other peoples, there are popular stereotypes at the local level: in popular jokes and stories, northern Serbs of Vojvodina (''Lale'') are perceived as phlegmatic
The four temperament theory is a proto-psychological theory which suggests that there are four fundamental personality types: sanguine, choleric, melancholic, and phlegmatic. Most formulations include the possibility of mixtures among the types w ...
, undisturbed and slow; Montenegrins are lazy and pushy; people from Pirot
Pirot ( sr-cyr, Пирот) is a city and the administrative center of the Pirot District in southeastern Serbia. According to 2011 census, the urban area of the city has a population of 38,785, while the population of the city administrative are ...
are misers
A miser is a person who is reluctant to spend, sometimes to the point of forgoing even basic comforts and some necessities, in order to hoard money or other possessions. Although the word is sometimes used loosely to characterise anyone who ...
; Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and Pars pro toto#Geography, often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of Southern Europe, south and southeast Euro ...
ns are raw and simple; Serbs from Central Serbia (''Šumadija
Šumadija (, sr-Cyrl, Шумадија) is a geographical region in the central part of Serbia. The area used to be heavily covered with forests, hence the name (from ''šuma'' 'forest'). The city of Kragujevac is the administrative center of ...
'') are often portrayed as capricious and malicious, etc.
Visual arts
There was some resumption of artistic endeavour after the restoration of the Serbian patriarch in 1557. Djordje Mitrofanović was the leading painter of the early 17th century with his work on the church at theMorača Monastery
The Morača ( sr-cyrl, Морача, ) is a major river in Montenegro that originates in the northern region in Kolašin Municipality under Mount Rzača. It meanders southwards for before emptying into Lake Skadar. Its drainage basin cov ...
considered as amongst his best.
 A Baroque church 'Our Lady of the Rocks' on an island in the
A Baroque church 'Our Lady of the Rocks' on an island in the Boka Kotorska
The Bay of Kotor ( Montenegrin and Serbian: , Italian: ), also known as the Boka, is a winding bay of the Adriatic Sea in southwestern Montenegro and the region of Montenegro concentrated around the bay. It is also the southernmost part of the hi ...
, in Montenegro is one of the most notable pieces of architecture in Serbia from the early modern period; many fine specimens of silverware dating from the 17th century are contained within its walls. Traditional Serbian art was beginning to show some Baroque influences at the end of the 18th century as shown in the works of Nikola Nešković
Nikola Nešković (c. 1729 – 1785) was a Serbian religious painter of the 18th century. He is the author of over a thousand works, including many icons, frescos, and portraits. He is the grandfather of Jovan Sterija Popović.
Biography
Neško ...
, Teodor Kračun
Teodor Dimitrijević ( sr-cyr, Теодор Димитријевић; 1730–10 April 1781), known as Teodor Kračun (Теодор Крачун) was a Serbian icon and altar painter.
Biography
He was born at Sremska Kamenica in 1730. His origi ...
and Jakov Orfelin
Jakov Orfelin (Cyrillic Serbian: Јаков Орфелин, born in Vukovar or Sremski Karlovci, Habsburg monarchy, c. mid-eighteenth century – Arad, Habsburg Monarchy, 20 October 1803) was a Serbian Baroque painter.
He made iconostasis fo ...
.
There was somewhat of a resurgence in Serbian art in the 19th century as Serbia gradually regained its autonomy. Prince Aleksandar
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
commissioned the building of a Monument to the Insurgents in Karađorđev Park in 1848 in Vračar. Serbian paintings showed the influence of Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism ...
and Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
during the 19th century. Anastas Jovanović
Anastas Jovanović ( sr-cyrl, Анастас Јовановић, bg, Анастас Йованович 1817 – 1 November 1899) was a Serbian photographer and author.
Biography
Jovanović, was of Bulgarian origin and during his life he al ...
was a pioneering photographer in Serbia, taking the photos of many leading citizens.
Kirilo Kutlik set up the first school of art in Serbia in 1895. Many of his students went to study in Western Europe, especially France and Germany, and brought back avant-garde styles. Fauvism
Fauvism /ˈfoʊvɪzm̩/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), repr ...
influenced Nadežda Petrović, while Sava Šumanović worked in Cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture. In Cubist artwork, objects are analyzed, broken up and reassemble ...
.
After World War I, the Belgrade School of Painting developed in the capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
with some members such as Milan Konjović working in a Fauvist manner, while others such as Marko Čelebonović
Marko Čelebonović ( sr-Cyrl, Марко Челебоновић; 21 November 1902 – 23 June 1986) was one of the most famous Serbian painters of the 20th century.Paja Jovanović
Pavle "Paja" Jovanović ( sr-cyr, Павле "Паја" Јовановић; ; 16 June 1859 – 30 November 1957) was a Serbian painter who painted more than 1,100 works including: '' The Wounded Montenegrin'' (1882), '' Decorating of the Bride'' ...
and Uroš Predić, painting in the Realist style. Their monumental paintings of historical events have inspired generations of Serbian artists.
Performing arts
Music
 Serbian music dates from the medieval period with strong church and folk traditions. Church music in Serbia of the time was based on the Osmoglasnik a cycle of religious songs based on the resurrection and lasting for eight weeks. During the
Serbian music dates from the medieval period with strong church and folk traditions. Church music in Serbia of the time was based on the Osmoglasnik a cycle of religious songs based on the resurrection and lasting for eight weeks. During the Nemanjić dynasty
The House of Nemanjić ( sr-Cyrl, Немањић, Немањићи; Nemanjić, Nemanjići, ) was the most prominent dynasty of Serbia in the Middle Ages. This princely, royal, and later imperial house produced twelve Serbian monarchs, who rule ...
and under other rulers such as Stefan Dušan
Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан, ), known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr, / ; circa 1308 – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Tsar (or Emperor) and autocrat of the Serbs, Gre ...
, musicians enjoyed royal patronage. There was a strong folk tradition in Serbia dating from this time.
 During Ottoman rule, Serbs were forbidden to own property, to learn to read and write and denied the use of musical instruments. Church music had to be performed in private. The
During Ottoman rule, Serbs were forbidden to own property, to learn to read and write and denied the use of musical instruments. Church music had to be performed in private. The gusle
The gusle ( sr-cyrl, гусле) or lahuta ( sq, lahutë) is a single- stringed musical instrument (and musical style) traditionally used in the Dinarides region of Southeastern Europe (in the Balkans). The instrument is always accompanied by ...
, a one-stringed instrument, was used by Serbian peasants during this time in an effort to find a loophole through the stringent Ottoman laws. Filip Višnjić
Filip Višnjić ( sr-cyr, Филип Вишњић, ; 1767–1834) was a Serbian epic poet and '' guslar''. His repertoire included 13 original epic poems chronicling the First Serbian Uprising against the Ottoman Empire and four reinterpreted ...
was a particularly notable guslar (gusle player). In the 18th century, Russian and Greek chant schools were established and the Serbian Orthodox Church accepted Church Slavonic
Church Slavonic (, , literally "Church-Slavonic language"), also known as Church Slavic, New Church Slavonic or New Church Slavic, is the conservative Slavic liturgical language used by the Eastern Orthodox Church in Belarus, Bosnia and Her ...
into their liturgy.
Folk music enjoyed a resurgence in the 19th century. Stevan Mokranjac
Stevan Stojanović ( sr-Cyrl, Стеван Стојановић, ; 9 January 1856 – 28 September 1914), known as Stevan Mokranjac ( sr-Cyrl, Стеван Мокрањац, ) was a Serbian composer and music educator. Born in Negotin in 1 ...
, a composer and musicologist
Musicology (from Greek μουσική ''mousikē'' 'music' and -λογια ''-logia'', 'domain of study') is the scholarly analysis and research-based study of music. Musicology departments traditionally belong to the humanities, although some m ...
, collected folk songs as well as performing his own work. Kornelije Stanković wrote the first Serbian language works for choirs.
Traditional Serbian folk music remains popular today, especially in rural areas. Western rock and pop music has become increasingly popular, mainly in cities with rock acts such as Riblja Čorba
Riblja Čorba ( sr-Cyrl, Рибља Чорба, pronounced ; translation: lit. ''Fish Stew'') is a Serbian and former Yugoslav rock band formed in Belgrade in 1978. The band was one of the most popular and most influential acts of the Yugosla ...
and Đorđe Balašević
Đorđe Balašević ( sr-Cyrl, Ђорђе Балашевић; 11 May 1953 – 19 February 2021) was a Serbian and Yugoslav singer and songwriter, writer, poet and director. He began his career in the late 1970s as a member of the band Rani Mraz, ...
incorporating political statements in their music. Turbo-folk combines Western rock and pop styles with traditional folk music vocals. Serbian immigrants have taken their musical traditions to nations such as the US and Canada.
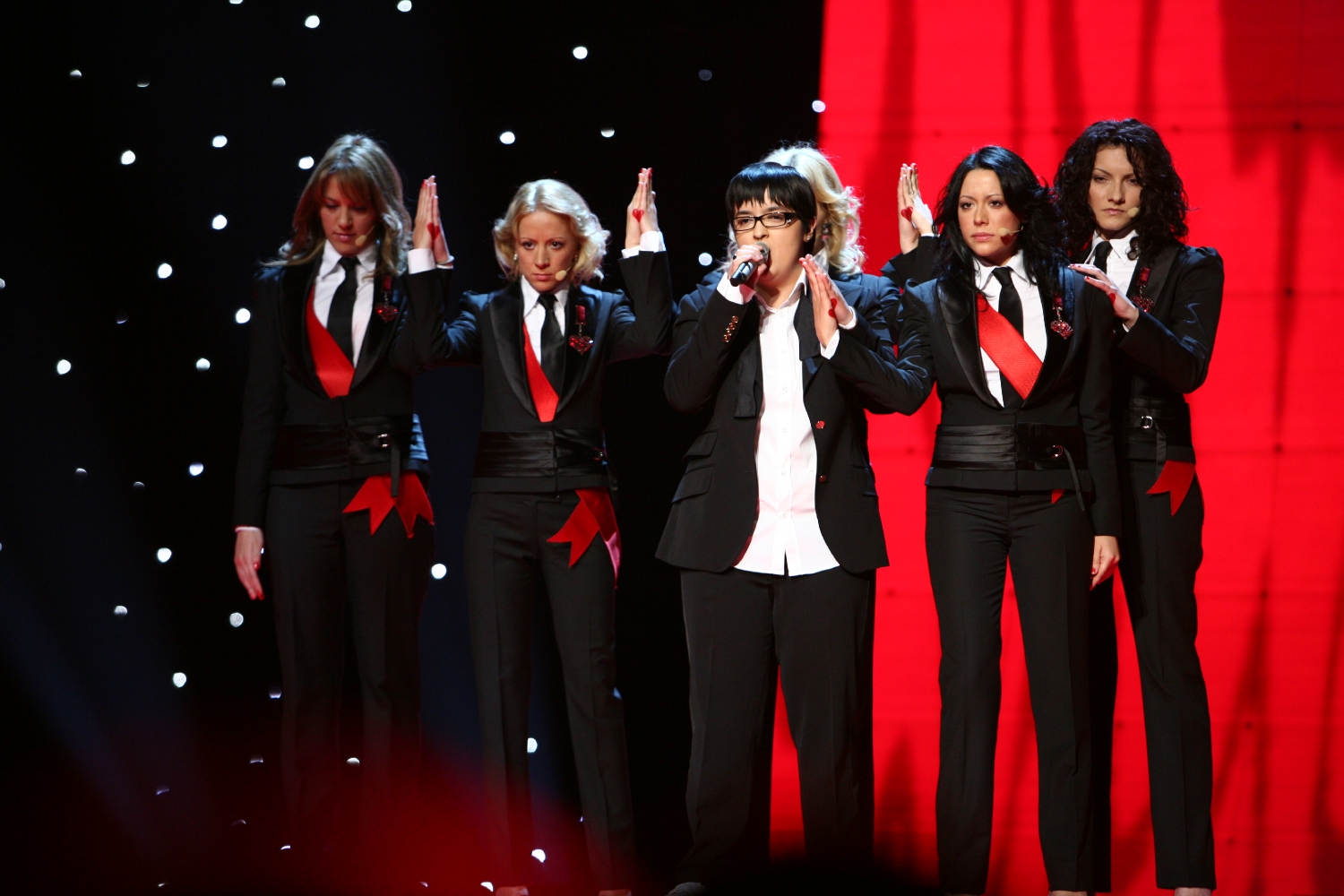
Marija Šerifović
Marija Šerifović ( sr-cyr, Марија Шерифовић, ; born 14 November 1984) is a Serbian singer. Born in Kragujevac as the daughter of Verica Šerifović, she rose to prominence in 2003 with her debut album '' Naj, Najbolja''. Šerif ...
won first place at the 2007 Eurovision Song Contest, and Serbia was the host of the 2008 contest.
Several notable composers used motifs from Serbian folk music and composed works inspired by Serbian history or culture, such as Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid-Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
, Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simpl ...
, Arthur Rubinstein
Arthur Rubinstein ( pl, Artur Rubinstein; 28 January 188720 December 1982) was a Polish-American pianist.
, Antonín Dvořák
Antonín Leopold Dvořák ( ; ; 8 September 1841 – 1 May 1904) was a Czech composer. Dvořák frequently employed rhythms and other aspects of the folk music of Moravia and his native Bohemia, following the Romantic-era nationalist example ...
, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky , group=n ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music would make a lasting impression internationally. He wrote some of the most popu ...
, Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
, Franz Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal wo ...
, Hans Huber and other.
Theatre and cinema
 Serbia has a well-established theatrical tradition with many theatres. The Serbian National Theatre was established in 1861. The company started performing opera at the end of the 19th century and the permanent opera was established in 1947. It established a ballet company.
Bitef, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, is one of the oldest theatre festivals in the world. New Theatre Tendencies is the constant subtitle of the Festival. Founded in 1967, Bitef has continually followed and supported the latest theater trends. It has become one of thefive most important and biggest European festivals, and one of the most significant culture institutions of Serbia.
Cinema was established reasonably early in Serbia, with 12 feature films being produced before the start of World War II. The most notable of the prewar films is Mihailo Popovic's ''The Battle of Kosovo'' in 1939.
Serbia has a well-established theatrical tradition with many theatres. The Serbian National Theatre was established in 1861. The company started performing opera at the end of the 19th century and the permanent opera was established in 1947. It established a ballet company.
Bitef, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, is one of the oldest theatre festivals in the world. New Theatre Tendencies is the constant subtitle of the Festival. Founded in 1967, Bitef has continually followed and supported the latest theater trends. It has become one of thefive most important and biggest European festivals, and one of the most significant culture institutions of Serbia.
Cinema was established reasonably early in Serbia, with 12 feature films being produced before the start of World War II. The most notable of the prewar films is Mihailo Popovic's ''The Battle of Kosovo'' in 1939.
 Cinema prospered after World War II. The most notable postwar director is
Cinema prospered after World War II. The most notable postwar director is Dušan Makavejev
Dušan Makavejev ( sr-Cyrl, Душан Макавејев, ; 13 October 1932 – 25 January 2019) was a Serbian film director and screenwriter, famous for his groundbreaking films of Yugoslav cinema in the late 1960s and early 1970s—many of wh ...
, who is recognised internationally for '' Love Affair: Or the Case of the Missing Switchboard Operator'' in 1969. Makavejev's ''Montenegro'' was made in Sweden in 1981. Zoran Radmilović
Zoran Radmilović ( sr-cyr, Зоран Радмиловић; 11 May 1933 – 21 July 1985) was a Serbian actor who had some of the most memorable roles in the history of former Yugoslav cinema.
He studied law, architecture and philology at the ...
was one of the most notable actors of the postwar period.
Serbian cinema continued to make progress in the 1990s and today, despite the turmoil of the 1990s. Emir Kusturica
Emir Kusturica ( sr-cyrl, Емир Кустурица; born 24 November 1954) is a Serbian film director, screenwriter, actor, producer and musician. He also has French citizenship.http://www.serbia.com/emir-kusturica-artist-builder-and-anti-glo ...
won two Golden Palms for Best Feature Film at the Cannes Film Festival
The Cannes Festival (; french: link=no, Festival de Cannes), until 2003 called the International Film Festival (') and known in English as the Cannes Film Festival, is an annual film festival held in Cannes, France, which previews new films ...
, for ''When Father Was Away on Business
''When Father Was Away on Business'' ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Otac na službenom putu, Отац на службеном путу) is a 1985 Yugoslav film by Serbian director Emir Kusturica. The screenplay was written by the Bosnian dramatist Abdulah Si ...
'' in 1985 and then again for '' Underground'' in 1995. In 1998, Kusturica won a Silver Lion for directing ''Black Cat, White Cat
''Black Cat, White Cat'' ( sr, Црна мачка, бели мачор, Crna mačka, beli mačor) is a 1998 Serbian romantic black comedy film directed by Emir Kusturica. It won the Silver Lion for Best Direction at the Venice Film Festival.
...
''.
Serbian handcrafts
Serbia has a long tradition of handicrafts.Đakovica
Gjakova, ) and Đakovica ( sr-Cyrl, Ђаковица, ) is the seventh largest city of Kosovo and seat of Gjakova Municipality and Gjakova District. The city has 40,827 inhabitants, while the municipality has 94,556 inhabitants.
Geographicall ...
in Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
was known for its black pottery. Pirot in southern Serbia became known for its ceramics under the Ottomans with the potters following Byzantine designs. It also became a centre for the production of kilim
A kilim ( az, Kilim کیلیم; tr, Kilim; tm, Kilim; fa, گلیم ''Gilīm'') is a flat tapestry- woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Ki ...
s or rugs.
The Slavs introduced jewellery making to Serbia in the 6th century AD. Metalworking started to develop on a significant scale following the development of a Serbian state. Workshops were set up in towns, large estates and in monasteries. The Studenica Monastery was known for the quality of its goldsmithing. Coins were minted not only by the kings but some of the wealthier nobility. The nobility was influenced by the wealth of the Byzantine court. Metalworking like many other arts and crafts went into decline following the Ottoman conquest. However, there was a partial revival in later centuries with a strong Baroque influence notably, the 17th century silverware at Our Lady of the Rocks
Our Lady of the Rocks is one of the two islets off the coast of Perast in the Bay of Kotor, Montenegro (the other being Sveti Đorđe island). It is an artificial island created by bulwark of rocks and by sinking old and seized ships loaded with ...
on Boka Kotorska.
Media
As of 2001, there were 27 daily newspapers and 580 other newspapers published in Serbia. Some of them have Internet editions. ''Politika
''Politika'' ( sr-Cyrl, Политика; ''Politics'') is a Serbian daily newspaper, published in Belgrade. Founded in 1904 by Vladislav F. Ribnikar, it is the oldest daily newspaper still in circulation in the Balkans.
Publishing and owners ...
'' founded in 1904 is the oldest daily newspaper in the Balkans. There were also 491 periodical magazines published in Serbia with the '' Nedeljne informativne novine'' (NIN) and '' Vreme'' amongst the notable ones. The state exerts its influence on some daily publications such as '' Večernje novosti'' and ''Politika''.
Television broadcasting started in 1958 with every country in the former Yugoslavia having its own station. In Serbia, the state television station was known as RTB and became known as RTS
RTS may refer to:
Medicine
* Rape trauma syndrome, the psychological trauma experienced by a rape victim
* Revised Trauma Score, a system to evaluate injuries secondary to violent trauma
* Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome, a condition characterized by ...
(Radio Television of Serbia) after the breakup of Yugoslavia. From the time of Yugoslavia until the Bulldozer Revolution
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large, motorized machine equipped with a metal blade to the front for pushing material: soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous tracks, ...
in 2000, the ruling party controlled state broadcasting. NATO bombed the headquarters of the RTS station during its 1999 air-strikes against Yugoslavia, claiming it was being used for propaganda purposes.
There was some private broadcasting with the B92 radio and television station starting in 1989, although it was shut down in 1999 during the hostilities. After the fall of Milošević, RTS became known as the "new" RTS as an assertion of independence while B92 commenced broadcasting. During 2001, there were 70 television centres in Serbia of which 24 were privately owned. In 2003, there was a return to censorship as the government of Zoran Živković temporarily imposed a state of emergency following the assassination of Zoran Djindjic
Zoran ( sr-Cyrl, Зоран) is a common South Slavic name, the masculine form of Zora, which means ''dawn, daybreak''. The name is especially common in Serbia, North Macedonia, Croatia and a little in Slovenia.
Notable people with this given n ...
. The European Federation of Journalists
The European Federation of Journalists is the European regional organisation of the International Federation of Journalists. It is the largest organisation of journalists in Europe, representing about 320,000 journalists in 71 journalists’ organ ...
continues to have concerns over media freedom in the country.
Sport

 Serbia is very successful in many sports. Among the most popular sports are
Serbia is very successful in many sports. Among the most popular sports are football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
, basketball, water polo
Water polo is a competitive team sport played in water between two teams of seven players each. The game consists of four quarters in which the teams attempt to score goals by throwing the ball into the opposing team's goal. The team with th ...
, sport shooting
Sport pertains to any form of Competition, competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and Skill, skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to specta ...
, handball
Handball (also known as team handball, European handball or Olympic handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of throwing it into the ...
, volleyball and tennis.
The two most popular football clubs in Serbia are Red Star Belgrade
Fudbalski klub Crvena zvezda ( sr-Cyrl, Фудбалски клуб Црвена звезда, lit=Red Star Football Club, ), commonly known as Red Star Belgrade in English-language media, is a Serbian professional football club based in Be ...
and FK Partizan
Fudbalski klub Partizan ( sr-Cyrl, Фудбалски клуб Партизан, ; en, Partizan Football Club), sometimes known as Partizan Belgrade in English, is a Serbia, Serbian professional football club (association football), football ...
. Their supporters are the Delije and the Grobari
Grobari (Serbian Cyrillic: Гробари, English: ''Gravediggers'' or ''Undertakers'') are the organized supporters group of the Serbian football club Partizan Belgrade. They are one of two major football fan groups in Serbia. They generally ...
, respectively. The Serbian national football team participated in the 2010 FIFA World Cup
, image = 2010 FIFA World Cup.svg
, size = 200px
, caption = ''Ke Nako. (Tswana and Sotho for "It's time") Celebrate Africa's Humanity'It's time. Celebrate Africa's Humanity'' (English)''Dis tyd. Vier Afrika se mensd ...
.
In basketball, Serbian clubs are successful and participate regularly in European competitions, where they often make quarter-final and semi-final appearances. The Serbian national basketball team
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguation ...
is successful in international competitions, having won several FIBA World Championship
The FIBA Basketball World Cup, also known as the FIBA World Cup of Basketball or simply the FIBA World Cup, between 1950 and 2010 known as the FIBA World Championship, is an international basketball competition contested by the senior men's nat ...
, EuroBasket
EuroBasket, also commonly referred to as the European Basketball Championship, is the main international basketball competition that is contested quadrennially, by the senior men's national teams that are governed by FIBA Europe, which is the ...
and Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece bet ...
gold medals.
Serbian men's and women's teams are also World Champions in sports, such as water polo and volleyball.
Serbian tennis players have been successful. Novak Djokovic
Novak Djokovic ( sr-Cyrl, Новак Ђоковић, translit=Novak Đoković, ; born 22 May 1987) is a Serbian professional tennis player. He has been ranked world No. 1 for a record total 373 weeks, and has finished as the year-end No. ...
is the current World No. 1, and he has won nineteen Grand Slam Singles titles so far. Janko Tipsarević
Janko Tipsarević ( sr-cyr, Јанко Типсаревић, ; born 22 June 1984) is a Serbian former tennis player. His career-high singles ranking is world No. 8, achieved on 2 April 2012. In his career, he won 4 ATP World Tour titles, one ...
, Viktor Troicki
Viktor Troicki ( sr-Cyrl, Виктор Троицки, ; born 10 February 1986) is a Serbian former professional tennis player. He won his first ATP singles title at the 2010 Kremlin Cup, and his second and third ATP singles titles at the 2015 ...
, Jelena Janković
Jelena Janković ( sr-Cyrl, Јелена Јанковић, ; born 28 February 1985) is a Serbian former tennis player. A former world No. 1, Janković reached the top ranking before her career-best major performance, a runner-up finish at the ...
and Ana Ivanovic
Ana Schweinsteiger ( sr, Ана Швајнштајгер / ''Ana Švajnštajger''; born 6 November 1987), professionally known by her birth name Ana Ivanovic (Ана Ивановић / ''Ana Ivanović'', ), is a Serbian former world No. 1 tenn ...
are also successful. The Serbia Davis Cup team won the 2010 Davis Cup
The 2010 Davis Cup (also known as the 2010 Davis Cup by BNP Paribas for sponsorship purposes) was the 99th edition of the most important annual tournament among national teams in men's tennis worldwide. In the dramatic final, Serbia defeated Fra ...
Final held in the Belgrade Arena
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 million ...
.
Cultural institutions
 At the beginning of the 21st century, there were 32 art galleries and 142 museums in Serbia. Belgrade has many of the most significant with the
At the beginning of the 21st century, there were 32 art galleries and 142 museums in Serbia. Belgrade has many of the most significant with the National Museum of Serbia
The National Museum of Serbia ( sr, / ) is the largest and oldest museum in Belgrade, Serbia. It is located in the central zone of Belgrade on a square plot between the Republic Square, formerly Theatre Square, and three streets: Čika Ljubina ...
in Belgrade, the Gallery of Frescoes featuring Orthodox Church art, the Ethnographic Museum Ethnographic museums conserve, display and contextualize items relevant to the field of ethnography, the systematic study of people and cultures. Such museums include:
List by country/region Albania
* Ethnographic Museum of Kavajë,
* Gjirokastë ...
and the Princess Ljubica's Residence
Princess Ljubica's Residence ( sr, Конак књегиње Љубице, ) is a palace located in Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. Because of its cultural and architectural importance the residence has been designated a Monument of Culture of Ex ...
. Novi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; hu, Újvidék, ; german: Neusatz; see below for other names) is the second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the P ...
contains the Museum of Vojvodina
The Museum of Vojvodina ( sr-cyr, Музеј Војводине) is an art and natural history museum in Novi Sad, Serbia. The museum houses a collection of over 400,000 specimens and a library of over 50,000 volumes.
Notable paintings
Among other ...
, Gallery of Matica Srpska as well as the Petrovaradin
Petrovaradin ( sr-cyr, Петроварадин, ) is a historic town in the Serbian province of Vojvodina, now a part of the city of Novi Sad. As of 2011, the urban area has 14,810 inhabitants. Lying on the right bank of the Danube, across from t ...
fortress.
Matica Srpska
The Matica srpska ( sr-Cyrl, Матица српска, Matica srpska, la, Matrix Serbica, grc, Μάτιτσα Σρπσκα) is the oldest Serbian language independent, non-profit, non-governmental and cultural-scientific Serbian national in ...
is the oldest and most notable cultural and scientific organisation in today's Serbia. Its name is translated in Serbian as the Serbian matrix or parent body of the Serbs. It was founded in 1826 in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
and moved to Novi Sad in 1864. Amongst other achievements, it compiled a six-volume study of the Serbian language between 1967 and 1976. Its journal ''Letopis Matice Srpske'' is one of the oldest periodicals examining scientific and cultural issues anywhere in the world. Vojvodina province of Austro-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern ...
became attractive for Serbs ever since the fall of Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
in the 15th century, and was the site of the Great Serbian Migrations
The Great Migrations of the Serbs ( sr, Велике сеобе Срба), also known as the Great Exoduses of the Serbs, refers mainly to two large migrations of Serbs from various territories under the rule of the Ottoman Empire to regions u ...
, when Serbs colonised the area escaping Turkish vengeance. Sremski Karlovci
Sremski Karlovci ( sr-cyrl, Сремски Карловци, ; hu, Karlóca; tr, Karlofça) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the banks of the Danu ...
became the spiritual, political and cultural centre of the Serbs in the Habsburg Empire, with the Metropolitan of the Serbian Orthodox Church residing in the town. To this day, Serbian Patriarch
This article lists the heads of the Serbian Orthodox Church, since the establishment of the church as an autocephalous archbishopric in 1219 to today's patriarchate. The list includes all the archbishops and patriarchs that led the Serbian Ortho ...
retains the title of ''Metropolitan of (Sremski) Karlovci''. The town featured the earliest Serb and Slavic grammar school (Serbian: gimnazija/гимназија, French: Lycée
In France, secondary education is in two stages:
* ''Collèges'' () cater for the first four years of secondary education from the ages of 11 to 15.
* ''Lycées'' () provide a three-year course of further secondary education for children between ...
) founded on August 3, 1791. In 1794, an Orthodox seminary was also founded in the town, ranking second oldest in the world (after the Spiritual Academy in Kiev). Novi Sad is home to Serbia's oldest professional theatre, founded in 1861 as Serbian National Theatre (''serbian'': Srpsko Narodno Pozorište), followed by Belgrade in 1868; however two other cities claim this title: City of Kragujevac
Kragujevac ( sr-Cyrl, Крагујевац, ) is the fourth largest city in Serbia and the administrative centre of the Šumadija District. It is the historical centre of the geographical region of Šumadija in central Serbia, and is situated on ...
Knjazesko Srbski Teatar since 1835 and Subotica
Subotica ( sr-cyrl, Суботица, ; hu, Szabadka) is a city and the administrative center of the North Bačka District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. Formerly the largest city of Vojvodina region, contemporary Subotica i ...
since 1851 (*there were theatres throughout Serbia long before that time but cannot be classified as "professional").
There is a network of libraries with three national libraries, 689 public libraries, 143 higher education libraries and 11 non-specialised libraries as of 1998. The National Library of Serbia
The National Library of Serbia ( sr, Народна библиотека Србије, Narodna biblioteka Srbije) is the national library of Serbia, located in the capital city of Belgrade. It is the biggest library, and oldest institution in Ser ...
is the most significant of these. Project Rastko
Project Rastko — Internet Library of Serb Culture ( sr, Пројекат Растко — Електронска библиотека српске културе, Projekat Rastko — Elektronska biblioteka srpske kulture) is a non-profit and no ...
, founded in 1997, is an Internet library of Serb culture.
The roots of the Serbian education system date back to the 11th and 12th centuries when the first Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
colleges were founded in Vojvodina (Titel, Bac). Medieval Serbian education, however, was mostly conducted in Serbian Orthodox monasteries (UNESCO protected Sopoćani
)
, other_names =
, image = Manastir Sopocani 2.jpg
, caption = Overview of the Sopoćani
, order = Serbian Orthodox
, established = 1259 - 1270
, disestablished = 1689
, reestablished = 1926
, ...
, Studenica, Patriarchate of Peć) starting from the rise of Raška in the 12th century, when Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of ...
overwhelmingly embraced Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonic ...
rather than Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. The first European-style higher education facilities, however, were founded in Catholic Vojvodina, Teacher's College in Subotica in 1689, although several facilities have functioned even before (e.g. Jesuit School in Belgrade, since 1609). Following the short-lived Serbian independence between 1804 and 1813, Belgrade officially became the educational centre of the country (excluding Vojvodina). The University of Belgrade
The University of Belgrade ( sr, / ) is a public university in Serbia. It is the oldest and largest modern university in Serbia.
Founded in 1808 as the Belgrade Higher School in revolutionary Serbia, by 1838 it merged with the Kragujevac-ba ...
is the largest and most prestigious institution of higher education in Serbia, founded as the Belgrade Higher School
The University of Belgrade ( sr, / ) is a public university in Serbia. It is the oldest and largest modern university in Serbia.
Founded in 1808 as the Belgrade Higher School in revolutionary Serbia, by 1838 it merged with the Kragujevac- ...
in 1808. The Gymnasium Jovan Jovanović Zmaj
Jovan Jovanović Zmaj Gymnasium ( sr, Гимназија "Јован Јовановић Змај", Gimnazija "Jovan Jovanović Zmaj") is a Gymnasium (school), secondary school in Novi Sad, Serbia. It is named after Jovan Jovanović Zmaj, a Serb p ...
was founded in 1810 and many important Serb cultural figures studied there.
Within the Government of Serbia
The Government of Serbia ( sr, Влада Србије, Vlada Srbije), formally the Government of the Republic of Serbia ( sr, Влада Републике Србије, Vlada Republike Srbije), commonly abbreviated to Serbian Government ( sr, � ...
, the Serbian Ministry for Culture is responsible for administering its cultural facilities.
National symbols
Serbian flag
The flag of Serbia ( sr, Застава Србије, Zastava Srbije), also known as the Tricolour ( sr, тробојка, ''trobojka''), is a tricolour consisting of three equal horizontal bands, red on the top, blue in the middle, and white o ...
is a red-blue-white horizontal tricolour
A tricolour () or tricolor () is a type of flag or banner design with a triband design which originated in the 16th century as a symbol of republicanism, liberty, or revolution. The flags of France, Italy, Romania, Mexico, and Ireland were ...
.
*The Serbian eagle, a white two-headed eagle, which represents dual power and sovereignty (monarch and church), was the coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
of the Nemanjić dynasty
The House of Nemanjić ( sr-Cyrl, Немањић, Немањићи; Nemanjić, Nemanjići, ) was the most prominent dynasty of Serbia in the Middle Ages. This princely, royal, and later imperial house produced twelve Serbian monarchs, who rule ...
.
*The Serbian cross
The Serbian Cross ( sr, Cрпски крст / Srpski krst) is a national symbols of Serbia, national symbol of Serbia, part of the coat of arms of Serbia, coat of arms and flag of Serbia, and of the Serbian Orthodox Church. It is based on the tetr ...
is based on the Byzantine cross, but where the Byzantine Cross held four Greek letter 'V' (or 'B') meaning King of Kings, ruling over Kings, the Serbian cross turned the Byzantine "B" into four Cyrillic letters of 'S' (C) with little stylistic modification, for a whole new message (traditionally rendered as '' Samo sloga Srbina spasava''—Only Unity Saves the Serbs). If displayed on a field, traditionally it is on a red field, but could be used with no field at all.
Both the eagle and the cross, besides being the basis for various Serbian coats of arms through history, are the basis for the symbols of various Serbian organisations, political parties, institutions and companies.
Serbian folk attire varies, mostly because of the very diverse geography and climate of the territory inhabited by the Serbs. Some parts of it are, however, common:
*A traditional shoe that is called the '' opanak''. It is recognisable by its distinctive tips that spiral backward. Each region of Serbia has a different kind of tips.
*A traditional hat that is called the '' šajkača''. It is easily recognisable by its top part that looks like the letter V or like the bottom of a boat (viewed from above), after which it got its name. It gained wide popularity in the early 20th century as it was the hat of the Serbian army in the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. It is still worn every day by some villagers today, and it was a common item of headgear among Bosnian Serb
The Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sr-Cyrl, Срби у Босни и Херцеговини, Srbi u Bosni i Hercegovini) are one of the three constitutive nations (state-forming nations) of the country, predominantly residing in the politi ...
military commanders during the Bosnian War
The Bosnian War ( sh, Rat u Bosni i Hercegovini / Рат у Босни и Херцеговини) was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started ...
in the 1990s. However, the ''šajkača'' is common mostly for the Serbian population living in the region of Central Serbia
Central Serbia ( sr, централна Србија / centralna Srbija), also referred to as Serbia proper ( sr, link=no, ужа Србија / uža Srbija), is the region of Serbia lying outside the autonomous province of Vojvodina to the nor ...
(Šumadija
Šumadija (, sr-Cyrl, Шумадија) is a geographical region in the central part of Serbia. The area used to be heavily covered with forests, hence the name (from ''šuma'' 'forest'). The city of Kragujevac is the administrative center of ...
), while Serbs living in Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
, Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
, and Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = " Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capi ...
had different types of traditional hats, which are not similar to ''šajkača''. Different types of traditional hats could also be found in eastern and southern parts of Central Serbia.
See also
*Architecture of Serbia
The architecture of Serbia has a long, rich and diverse history. Some of the major European style from Ancient Roman architecture, Roman to Postmodern architecture, Postmodern are demonstrated, including renowned examples of Raška architectural ...
* Cultural Heritage of Serbia
* Serbian literature
Serbian literature ( sr-Cyrl, Српска књижевност), refers to literature written in Serbian and/or in Serbia and all other lands where Serbs reside.
The history of Serbian literature begins with the independent works from the Ne ...
* Serbian printing
Serbian printing refers to the history of printing among Serbs, and focusing on development of book printing in Serbian, with the use of the Serbian Cyrillic alphabet, from the end of the 15th century up to the end of the 18th century. The first ...
* Tourism in Serbia
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Online references
Serbia Ministry of Culture
* ttp://www.rts.rs/ Radio Television Serbia * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060524061201/http://ifj-europe.org/default.asp?index=281&Language=EN European Federation of Journalists Serbia page
Serbian info culture page
Serbian info Art History page
Columbia University Yugoslav Literature article
Treasures National Library Serbia
Other references
* "Serbia and Montenegro", ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2005 * "Serbia", ''Grove Art Online'', 2005 * "Serbia", ''Grove Music Online'', 2005 * ''The Statesman's Yearbook 2005: The Politics, Cultures and Economies of the World'', London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2004, {{DEFAULTSORT:Serbian Culture