Semi Automatic Ground Environment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) was a system of large computers and associated
 The solution was to send all of the radar information to a central control station where operators collated the reports into single ''tracks'', and then reported these tracks to the airbases, or ''sectors''. The sectors used additional systems to track their own aircraft, plotting both on a single large map. Operators viewing the map could then see what direction their fighters would have to fly to approach their targets and relay that simply by telling them to fly along a certain heading or ''vector''. This Dowding system was the first ground-controlled interception (GCI) system of large scale, covering the entirety of the UK. It proved enormously successful during the
The solution was to send all of the radar information to a central control station where operators collated the reports into single ''tracks'', and then reported these tracks to the airbases, or ''sectors''. The sectors used additional systems to track their own aircraft, plotting both on a single large map. Operators viewing the map could then see what direction their fighters would have to fly to approach their targets and relay that simply by telling them to fly along a certain heading or ''vector''. This Dowding system was the first ground-controlled interception (GCI) system of large scale, covering the entirety of the UK. It proved enormously successful during the
 The Committee then had to consider whether or not such a computer was possible. Valley was introduced to
The Committee then had to consider whether or not such a computer was possible. Valley was introduced to
 In a test for the US military at
In a test for the US military at
 The AN/FSQ-7 was developed by the Lincoln Laboratory's Digital Computer Laboratory and Division 6, working closely with IBM as the manufacturer. Each FSQ-7 actually consisted of two nearly identical computers operating in "duplex" for redundancy. The design used an improved version of the Whirlwind I magnetic core memory and was an extension of the Whirlwind II computer program, renamed AN/FSQ-7 in 1953 to comply with Air Force nomenclature. It has been suggested the FSQ-7 was based on the
The AN/FSQ-7 was developed by the Lincoln Laboratory's Digital Computer Laboratory and Division 6, working closely with IBM as the manufacturer. Each FSQ-7 actually consisted of two nearly identical computers operating in "duplex" for redundancy. The design used an improved version of the Whirlwind I magnetic core memory and was an extension of the Whirlwind II computer program, renamed AN/FSQ-7 in 1953 to comply with Air Force nomenclature. It has been suggested the FSQ-7 was based on the
 In 1957, SAGE System groundbreaking at McChord AFB was for DC-12 where the "electronic brain" began arriving in November 1958, and the "first SAGE regional battle post C-01began operating in Syracuse, New York in early 1959". BOMARC "crew training was activated January 1, 1958", and
In 1957, SAGE System groundbreaking at McChord AFB was for DC-12 where the "electronic brain" began arriving in November 1958, and the "first SAGE regional battle post C-01began operating in Syracuse, New York in early 1959". BOMARC "crew training was activated January 1, 1958", and  SAGE Geographic Reorganization: The SAGE Geographic Reorganization Plan of July 25, 1958, by NORAD was "to provide a means for the orderly transition and phasing from
SAGE Geographic Reorganization: The SAGE Geographic Reorganization Plan of July 25, 1958, by NORAD was "to provide a means for the orderly transition and phasing from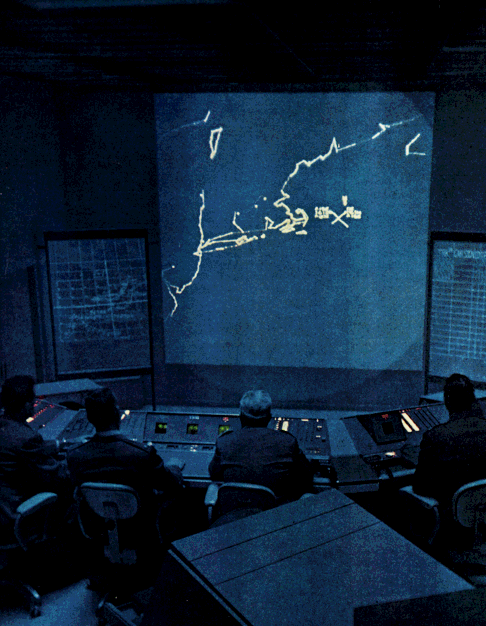  Project Wild Goose teams of
Project Wild Goose teams of
* Some of the originally planned 32 DCs were never completed and DCs were planned at installations for additional sectors: Calypso/
(cited by Volume I p. 257)
Dir.groups.yahoo.com. Retrieved on 2013-09-18.), etc.; and AT&T's "main underground station" was in Kansas (Fairview) with other bunkers in Connecticut (Cheshire), California (Santa Rosa), Iowa (Boone) and Maryland ( Hearthstone Mountain). CDTS
Stories about SAGE
- oral history
"The largest computer ever built"
- "Locklin on science"
On Guard: The Story of SAGE
(1956) IBM Corporation, Military Products Division * Cold War Computing: The SAGE System, Computer Museum {{USAF system codes Computer networks Cold War military equipment of the United States North American Aerospace Defense Command 1950s computers Computer-related introductions in 1958 Lists of Cold War sites 1950s in technology 1950s in the United States
networking
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology
* Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
* Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematic ...
equipment that coordinated data from many radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, Marine radar, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor v ...
sites and processed it to produce a single unified image of the airspace over a wide area. SAGE directed and controlled the NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection ...
response to a possible Soviet air attack, operating in this role from the late 1950s into the 1980s. Its enormous computers and huge displays remain a part of cold war
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
lore, and after decommissioning were common props in movies such as ''Dr. Strangelove
''Dr. Strangelove or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Bomb'', known simply and more commonly as ''Dr. Strangelove'', is a 1964 black comedy film that satirizes the Cold War fears of a nuclear conflict between the Soviet Union and ...
'' and ''Colossus'', and on science fiction TV series such as ''The Time Tunnel
''The Time Tunnel'' is an American color science fiction TV series written around a theme of time travel adventure starring James Darren and Robert Colbert. The show was creator-producer Irwin Allen's third science-fiction television series an ...
''.
The processing power behind SAGE was supplied by the largest discrete component-based computer ever built, the IBM-manufactured AN/FSQ-7. Each SAGE Direction Center (DC) housed an FSQ-7 which occupied an entire floor, approximately not including supporting equipment. The FSQ-7 was actually two computers, "A" side and "B" side. Computer processing was switched from "A" side to "B" side on a regular basis, allowing maintenance on the unused side. Information was fed to the DCs from a network of radar stations as well as readiness information from various defense sites. The computers, based on the raw radar data, developed "tracks" for the reported targets, and automatically calculated which defenses were within range. Operators used light gun
A light gun is a pointing device for computers and a control device for arcade and video games, typically shaped to resemble a pistol.
Early history
The first light guns were produced in the 1930s, following the development of light-sensin ...
s to select targets on-screen for further information, select one of the available defenses, and issue commands to attack. These commands would then be automatically sent to the defense site via teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Init ...
.
Connecting the various sites was an enormous network of telephones, modem
A modulator-demodulator or modem is a computer hardware device that converts data from a digital format into a format suitable for an analog transmission medium such as telephone or radio. A modem transmits data by modulating one or more c ...
s and teleprinters. Later additions to the system allowed SAGE's tracking data to be sent directly to CIM-10 Bomarc
The Boeing CIM-10 BOMARC (Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center) (IM-99 Weapon System prior to September 1962) was a supersonic ramjet powered long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) used during the Cold War for the air defense of Nort ...
missiles and some of the US Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Sig ...
's interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are ...
in-flight, directly updating their autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of an aircraft, marine craft or spacecraft without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator' ...
s to maintain an intercept course without operator intervention. Each DC also forwarded data to a Combat Center (CC) for "supervision of the several sectors within the division" ("each combat center adthe capability to coordinate defense for the whole nation").
SAGE became operational in the late 1950s and early 1960s at a combined cost of billions of dollars. It was noted that the deployment cost more than the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
—which it was, in a way, defending against. Throughout its development, there were continual concerns about its real ability to deal with large attacks, and the Operation Sky Shield tests showed that only about one-fourth of enemy bombers would have been intercepted. Nevertheless, SAGE was the backbone of NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection ...
's air defense system into the 1980s, by which time the tube-based FSQ-7s were increasingly costly to maintain and completely outdated. Today the same command and control task is carried out by microcomputers, based on the same basic underlying data.
Background
Earlier systems
Just prior toWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
(RAF) tests with the new Chain Home
Chain Home, or CH for short, was the codename for the ring of coastal Early Warning radar stations built by the Royal Air Force (RAF) before and during the Second World War to detect and track aircraft. Initially known as RDF, and given the of ...
(CH) radars had demonstrated that relaying information to the fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
directly from the radar sites was not feasible. The radars determined the map coordinates of the enemy, but could generally not see the fighters at the same time. This meant the fighters had to be able to determine where to fly to perform an interception but were often unaware of their own exact location and unable to calculate an interception while also flying their aircraft.
 The solution was to send all of the radar information to a central control station where operators collated the reports into single ''tracks'', and then reported these tracks to the airbases, or ''sectors''. The sectors used additional systems to track their own aircraft, plotting both on a single large map. Operators viewing the map could then see what direction their fighters would have to fly to approach their targets and relay that simply by telling them to fly along a certain heading or ''vector''. This Dowding system was the first ground-controlled interception (GCI) system of large scale, covering the entirety of the UK. It proved enormously successful during the
The solution was to send all of the radar information to a central control station where operators collated the reports into single ''tracks'', and then reported these tracks to the airbases, or ''sectors''. The sectors used additional systems to track their own aircraft, plotting both on a single large map. Operators viewing the map could then see what direction their fighters would have to fly to approach their targets and relay that simply by telling them to fly along a certain heading or ''vector''. This Dowding system was the first ground-controlled interception (GCI) system of large scale, covering the entirety of the UK. It proved enormously successful during the Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defende ...
, and is credited as being a key part of the RAF's success.
The system was slow, often providing information that was up to five minutes out of date. Against propeller driven bombers flying at perhaps this was not a serious concern, but it was clear the system would be of little use against jet-powered bombers flying at perhaps . The system was extremely expensive in manpower terms, requiring hundreds of telephone operators, plotters and trackers in addition to the radar operators. This was a serious drain on manpower, making it difficult to expand the network.
The idea of using a computer to handle the task of taking reports and developing tracks had been explored beginning late in the war. By 1944, analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
s had been installed at the CH stations to automatically convert radar readings into map locations, eliminating two people. Meanwhile, the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
began experimenting with the Comprehensive Display System
The Comprehensive Display System (CDS) was a command, control, and coordination system of the British Royal Navy (RN) that worked with the detection/search Type 984 radar. The system was installed on a total of six ships starting in 1957. The U ...
(CDS), another analog computer that took X and Y locations from a map and automatically generated tracks from repeated inputs. Similar systems began development with the Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack subma ...
, DATAR, and the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, the Naval Tactical Data System
Naval Tactical Data System (NTDS) was a computerized information processing system developed by the United States Navy in the 1950s and first deployed in the early 1960s for use in combat ships. It took reports from multiple sensors on different ...
. A similar system was also specified for the Nike SAM project, specifically referring to a US version of CDS, coordinating the defense over a battle area so that multiple batteries did not fire on a single target. All of these systems were relatively small in geographic scale, generally tracking within a city-sized area.
Valley Committee
When theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
tested its first atomic bomb in August 1949, the topic of air defense
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based ...
of the US became important for the first time. A study group, the "Air Defense Systems Engineering Committee" was set up under the direction of Dr. George Valley to consider the problem, and is known to history as the "Valley Committee".
Their December report noted a key problem in air defense using ground-based radars. A bomber approaching a radar station would detect the signals from the radar long before the reflection off the bomber was strong enough to be detected by the station. The committee suggested that when this occurred, the bomber would descend to low altitude, thereby greatly limiting the radar horizon
The radar horizon is a critical area of performance for aircraft detection systems that is defined by the distance at which the radar beam rises enough above the Earth's surface to make detection of a target at low level impossible. It is asso ...
, allowing the bomber to fly past the station undetected. Although flying at low altitude greatly increased fuel consumption
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
, the team calculated that the bomber would only need to do this for about 10% of its flight, making the fuel penalty acceptable.
The only solution to this problem was to build a huge number of stations with overlapping coverage. At that point the problem became one of managing the information. Manual plotting was ruled out as too slow, and a computerized solution was the only possibility. To handle this task, the computer would need to be fed information directly, eliminating any manual translation by phone operators, and it would have to be able to analyze that information and automatically develop tracks. A system tasked with defending cities against the predicted future Soviet bomber fleet would have to be dramatically more powerful than the models used in the NTDS or DATAR.
(cited by Schaffel p. 197)
Jerome Wiesner
Jerome Bert Wiesner (May 30, 1915 – October 21, 1994) was a professor of electrical engineering, chosen by President John F. Kennedy as chairman of his Science Advisory Committee (PSAC). Educated at the University of Michigan, Wiesner was asso ...
, associate director of the Research Laboratory of Electronics at MIT. Wiesner noted that the Servomechanisms Laboratory
In control engineering a servomechanism, usually shortened to servo, is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. On displacement-controlled applications, it usually includes a built-in e ...
had already begun development of a machine that might be fast enough. This was the Whirlwind I
Whirlwind I was a Cold War-era vacuum tube computer developed by the MIT Servomechanisms Laboratory for the U.S. Navy. Operational in 1951, it was among the first digital electronic computers that operated in real-time for output, and the firs ...
, originally developed for the Office of Naval Research
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) is an organization within the United States Department of the Navy responsible for the science and technology programs of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps. Established by Congress in 1946, its mission is to pl ...
as a general purpose flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they re ...
that could simulate any current or future aircraft by changing its software.
Wiesner introduced Valley to Whirlwind's project lead, Jay Forrester
Jay Wright Forrester (July 14, 1918 – November 16, 2016) was a pioneering American computer engineer and systems scientist. He is credited with being one of the inventors of magnetic core memory, the predominant form of random-access comput ...
, who convinced him that Whirlwind was sufficiently capable. In September 1950, an early microwave early-warning radar system at Hanscom Field was connected to Whirlwind using a custom interface developed by Forrester's team. An aircraft was flown past the site, and the system digitized the radar information and successfully sent it to Whirlwind. With this demonstration, the technical concept was proven. Forrester was invited to join the committee.
Project Charles
With this successful demonstration, Louis Ridenour, chief scientist of the Air Force, wrote a memo stating "It is now apparent that the experimental work necessary to develop, test, and evaluate the systems proposals made by ADSEC will require a substantial amount of laboratory and field effort." Ridenour approached MIT President James Killian with the aim of beginning a development lab similar to the war-era Radiation Laboratory that made enormous progress in radar technology. Killian was initially uninterested, desiring to return the school to its peacetime civilian charter. Ridenour eventually convinced Killian the idea was sound by describing the way the lab would lead to the development of a local electronics industry based on the needs of the lab and the students who would leave the lab to start their own companies. Killian agreed to at least consider the issue, and began Project Charles to consider the size and scope of such a lab. Project Charles was placed under the direction of Francis Wheeler Loomis and included 28 scientists, about half of whom were already associated with MIT. Their study ran from February to August 1951, and in their final report they stated that "We endorse the concept of a centralized system as proposed by the Air Defense Systems Engineering Committee, and we agree that the central coordinating apparatus of this system should be a high-speed electronic digital computer." The report went on to describe a new lab that would be used for generic technology development for the Air Force, Army and Navy, and would be known as Project Lincoln.Project Lincoln
Loomis took over direction of Project Lincoln and began planning by following the lead of the earlier RadLab. By September 1951, only months after the Charles report, Project Lincoln had more than 300 employees. By the end of the summer of 1952 this had risen to 1300, and after another year, 1800. The only building suitable for classified work at that point was Building 22, suitable for a few hundred people at most, although some relief was found by moving the non-classified portions of the project, administration and similar, to Building 20. But this was clearly insufficient space. After considering a variety of suitable locations, a site at Laurence G. Hanscom Field was selected, with the groundbreaking taking place in 1951. The terms of the National Security Act were formulated during 1947, leading to the creation of the US Air Force out of the former US Army Air Force. During April of the same year, US Air Force staff were identifying specifically the requirement for the creation of automatic equipment for radar-detection which would relay information to an air defence control system, a system which would function without the inclusion of persons for its operation. The December 1949 "Air Defense Systems Engineering Committee" led by Dr. George Valley had recommended computerized networking for "radar stations guarding the northern air approaches to the United States" (e.g., in Canada). After a January 1950 meeting, Valley andJay Forrester
Jay Wright Forrester (July 14, 1918 – November 16, 2016) was a pioneering American computer engineer and systems scientist. He is credited with being one of the inventors of magnetic core memory, the predominant form of random-access comput ...
proposed using the Whirlwind I
Whirlwind I was a Cold War-era vacuum tube computer developed by the MIT Servomechanisms Laboratory for the U.S. Navy. Operational in 1951, it was among the first digital electronic computers that operated in real-time for output, and the firs ...
(completed 1951) for air defense. On August 18, 1950, when the " 1954 Interceptor" requirements were issued, the USAF "noted that manual techniques of aircraft warning and control would impose "intolerable" delays" (cited by Volume I p. 187) (Air Materiel Command
Air Materiel Command (AMC) was a United States Army Air Forces and United States Air Force command. Its headquarters was located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio. In 1961, the command was redesignated the Air Force Logistics Command ...
(AMC) published ''Electronic Air Defense Environment for 1954'' in December .) During February–August 1951 at the new Lincoln Laboratory
The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and d ...
, the USAF conducted Project Claude which concluded an improved air defense system was needed.
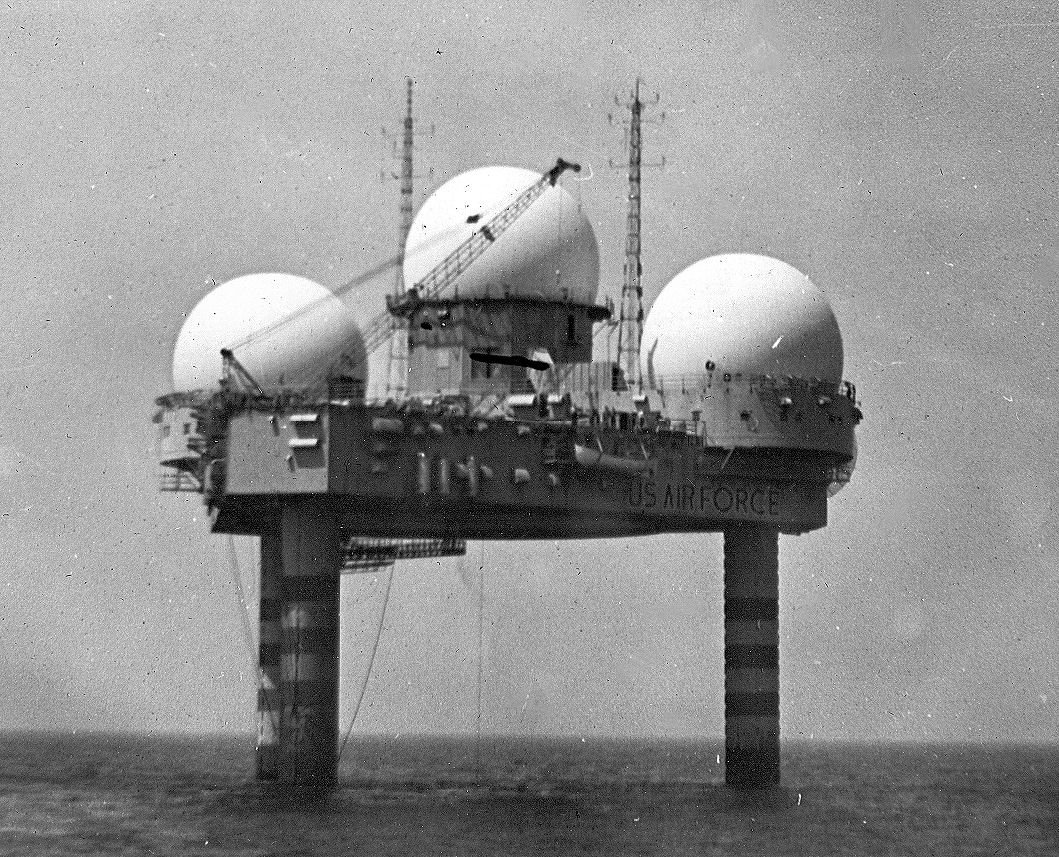
 In a test for the US military at
In a test for the US military at Bedford
Bedford is a market town in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 Census, the population of the Bedford built-up area (including Biddenham and Kempston) was 106,940, making it the second-largest settlement in Bedfordshire, behind Luton, whilst t ...
on 20 April 1951, data produced by a radar was transmitted through telephone lines to a computer for the first time, showing the detection of a mock enemy aircraft. This first test was directed by C. Robert Wieser.(''20th of April 1951'' - p.1, ''National Security Act 1947'' - p.12, ''April 1947'' - p.13)
The "Summer Study Group" of scientists in 1952 recommended "computerized air direction centers…to be ready by 1954."
IBM's "Project High" assisted under their October 1952 Whirlwind subcontract with Lincoln Laboratory
The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and d ...
, and a 1952 USAF Project Lincoln "fullscale study" of "a large scale integrated ground control system" resulted in the SAGE approval "first on a trial basis in 1953". The USAF had decided by April 10, 1953, to cancel the competing ADIS (based on CDS), and the University of Michigan's Aeronautical Research Center withdrew in the spring. Air Research and Development Command
The Air Force Systems Command (AFSC) is an inactive United States Air Force Major Command. It was established in April 1951, being split off from Air Materiel Command. The mission of AFSC was Research and Development for new weapons systems.
Ove ...
(ARDC) planned to "finalize a production contract for the Lincoln Transition System". Similarly, the July 22, 1953, report by the Bull Committee ( NSC 159) identified completing the Mid-Canada Line radars as the top priority and "on a second-priority-basis: the Lincoln automated system" (the decision to control Bomarc with the automated system was also in 1953.)
The Priority Permanent System with the initial (priority) radar stations was completed in 1952 as a "manual air defense system" (e.g., NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection ...
/ ADC used a " Plexiglas plotting board" at the Ent command center.) The Permanent System radar stations included 3 subsequent phases of deployments and by June 30, 1957, had 119 "Fixed CONUS" radars, 29 "Gap-filler low altitude" radars, and 23 control centers". At "the end of 1957, ADC operated 182 radar stations nd 17 control centers … 32 tationshad been added during the last half of the year as low-altitude, unmanned gap-filler radars. The total consisted of 47 gap-filler stations, 75 Permanent System radars, 39 semimobile radars, 19 Pinetree stations,…1 Lashup -era radar and a single Texas Tower". "On 31 December 1958, USAF ADC had 187 operational land-based radar stations" (74 were "P-sites", 29 "M-sites", 13 "SM-sites", & 68 " ZI Gap Fillers").
Development
Jay Forrester
Jay Wright Forrester (July 14, 1918 – November 16, 2016) was a pioneering American computer engineer and systems scientist. He is credited with being one of the inventors of magnetic core memory, the predominant form of random-access comput ...
was instrumental in directing the development of the key concept of an interception system during his work at Servomechanisms Laboratory of MIT. The concept of the system, according to the Lincoln Laboratory
The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and d ...
site was to
"develop a digital computer that could receive vast quantities of data from multiple radars and perform real-time processing to produce targeting information for intercepting aircraft and missiles."
 The AN/FSQ-7 was developed by the Lincoln Laboratory's Digital Computer Laboratory and Division 6, working closely with IBM as the manufacturer. Each FSQ-7 actually consisted of two nearly identical computers operating in "duplex" for redundancy. The design used an improved version of the Whirlwind I magnetic core memory and was an extension of the Whirlwind II computer program, renamed AN/FSQ-7 in 1953 to comply with Air Force nomenclature. It has been suggested the FSQ-7 was based on the
The AN/FSQ-7 was developed by the Lincoln Laboratory's Digital Computer Laboratory and Division 6, working closely with IBM as the manufacturer. Each FSQ-7 actually consisted of two nearly identical computers operating in "duplex" for redundancy. The design used an improved version of the Whirlwind I magnetic core memory and was an extension of the Whirlwind II computer program, renamed AN/FSQ-7 in 1953 to comply with Air Force nomenclature. It has been suggested the FSQ-7 was based on the IBM 701
The IBM 701 Electronic Data Processing Machine, known as the Defense Calculator while in development, was IBM’s first commercial scientific computer and its first series production mainframe computer, which was announced to the public on May ...
but, while the 701 was investigated by MIT engineers, its design was ultimately rejected due to high error rates and generally being "inadequate to the task." IBM's contributions were essential to the success of the FSQ-7 but IBM benefited immensely from its association with the SAGE project, most evidently during development of the IBM 704
The IBM 704 is a large digital mainframe computer introduced by IBM in 1954. It was the first mass-produced computer with hardware for floating-point arithmetic. The IBM 704 ''Manual of operation'' states:
The type 704 Electronic Data-Proce ...
.
On October 28, 1953, the Air Force Council
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
recommended 1955 funding for "ADC to convert to the Lincoln automated system" ("redesignated the SAGE System in 1954"). The "''experimental SAGE subsector, located in Lexington, Mass., was completed in 1955…with a prototype AN/FSQ-7…known as XD-1''" (single computer system in Building F). In 1955, Air Force personnel began IBM training at the Kingston, New York
Kingston is a city in and the county seat of Ulster County, New York, United States. It is north of New York City and south of Albany. The city's metropolitan area is grouped with the New York metropolitan area around Manhattan by the Unite ...
, prototype facility, and the " 4620th Air Defense Wing (experimental SAGE) was established at Lincoln Laboratory"
On May 3, 1956, General Partridge presented ''CINCNORAD The commander of North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) is a Four-star rank, four-star General (United States), general or Admiral (United States), admiral in the United States Armed Forces who serves as the head of all United States and C ...
's Operational Concept for Control of Air Defense Weapons'' to the Armed Forces Policy Council, and a June 1956 symposium presentation identified advanced programming methods of SAGE code. For SAGE consulting Western Electric
The Western Electric Company was an American electrical engineering and manufacturing company officially founded in 1869. A wholly owned subsidiary of American Telephone & Telegraph for most of its lifespan, it served as the primary equipment ma ...
and Bell Telephone Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
formed the Air Defense Engineering Service
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
(ADES), which was contracted in January 1954. IBM delivered the FSQ-7 computer's prototype in June 1956, and Kingston's XD-2 with dual computers guided a Cape Canaveral
, image = cape canaveral.jpg
, image_size = 300
, caption = View of Cape Canaveral from space in 1991
, map = Florida#USA
, map_width = 300
, type = Cape
, map_caption = Location in Florida
, location ...
BOMARC to a successful aircraft intercept on August 7, 1958. Initially contracted to RCA
The RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded as the Radio Corporation of America in 1919. It was initially a patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse, AT&T Corporation and United Fruit Comp ...
, the AN/FSQ-7 production units were started by IBM in 1958 (32 DCs were planned for networking NORAD regions.) IBM's production contract developed 56 SAGE computers for $½ billion (~$18 million per computer pair in each FSQ-7)— cf. the $2 billion WWII Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
.
General Operational Requirements (GOR) 79 and 97 were "the basic USAF documents guiding development and improvement of he semi-automatic
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
ground environment. Prior to fielding the AN/FSQ-7 centrals, the USAF initially deployed "pre-SAGE semiautomatic intercept systems" ( AN/GPA-37) to Air Defense Direction Centers, ADDCs (e.g., at "NORAD Control Center
NORAD Control Centers (NCCs) were Cold War "joint direction centers" for command, control, and coordination of ground-controlled interception by both USAF Air Defense Command (ADC) and Army Air Defense Command (ARADCOM). The Joint Manual Stee ...
s"). On April 22, 1958, NORAD approved Nike AADCPs to be collocated with the USAF manual ADDCs at Duncanville Air Force Station
Duncanville Air Force Station (ADC ID: P-78) is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located on the east side of Duncanville, Texas. It was closed in 1964.
History
Duncanville Air Force Station was one ...
TX, Olathe Air Force Station KS, Belleville Air Force Station IL, and Osceola Air Force Station KS.
Deployment
 In 1957, SAGE System groundbreaking at McChord AFB was for DC-12 where the "electronic brain" began arriving in November 1958, and the "first SAGE regional battle post C-01began operating in Syracuse, New York in early 1959". BOMARC "crew training was activated January 1, 1958", and
In 1957, SAGE System groundbreaking at McChord AFB was for DC-12 where the "electronic brain" began arriving in November 1958, and the "first SAGE regional battle post C-01began operating in Syracuse, New York in early 1959". BOMARC "crew training was activated January 1, 1958", and AT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the world's largest telecommunications company by revenue and the third largest provider of mobile ...
"hardened many of its switching centers, putting them in deep underground bunkers", The North American Defense Objectives Plan (NADOP 59-63) submitted to Canada in December 1958 scheduled 5 Direction Centers and 1 Combat Center to be complete in Fiscal Year 1959, 12 DCs and 3 CCs complete at the end of FY 60, 19 DC/4 CC FY 61, 25/6 FY 62, and 30/10 FY 63. On June 30 NORAD ordered that "Air Defense Sectors (SAGE) were to be designated as NORAD sectors", (the military reorganization had begun when effective April 1, 1958, CONAD
Conad ('), stylized CONAD, is an Italian retail store brand which operates one of the largest supermarket chains in Italy. Created in 1962, Conad is a cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autono ...
"designated four SAGE sectors – New York, Boston, Syracuse, and Washington – as CONAD Sectors".)
 SAGE Geographic Reorganization: The SAGE Geographic Reorganization Plan of July 25, 1958, by NORAD was "to provide a means for the orderly transition and phasing from
SAGE Geographic Reorganization: The SAGE Geographic Reorganization Plan of July 25, 1958, by NORAD was "to provide a means for the orderly transition and phasing from the manual
''The Manual (How to Have a Number One the Easy Way)'' is a 1988 book by "The Timelords" (Jimmy Cauty and Bill Drummond), better known as The KLF. It is a step-by-step guide to achieving a No.1 single with no money or musical skills, and a case ...
to the SAGE system." The plan identified deactivation of the Eastern, Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
, and Western Region/Defense Forces on July 1, 1960, and "current manual boundaries" were to be moved to the new "eight SAGE divisions" (1 in Canada, "the 35th") as soon as possible. Manual divisions "not to get SAGE computers were to be phased out" along with their Manual Air Defense Control Centers at the headquarters base: "9th tGeiger Field
Spokane International Airport is a commercial airport located approximately west-southwest of downtown Spokane, Washington, United States. It is the primary airport serving the Inland Northwest, which consists of 30 counties and includes are ...
… 32d, Syracuse AFS
Hancock Field Air National Guard Base is a United States Air Force base, co-located with Syracuse Hancock International Airport. It is located north-northeast of Syracuse, New York, at 6001 East Molloy Road, Mattydale, NY 13211.
The installatio ...
… 35th, Dobbins AFB… 58th, Wright-Patterson AFB
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene and Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patterson Fields, which were originally Wilbur W ...
… 85th, Andrews AFB". The 26th SAGE Division (New York, Boston, Syracuse & Bangor SAGE sectors)--the 1st of the SAGE divisions—became operational at Hancock Field on 1 January 1959 after the redesignation started for AC&W Squadrons (e.g., the Highlands P-9 unit became the 646th Radar Squadron (SAGE) October 1.) Additional sectors included the Los Angeles Air Defense Sector (SAGE) designated in February 1959. A June 23 JCS memorandum approved the new "March 1959 Reorganization Plan" for HQ NORAD/CONAD/ADC.
 Project Wild Goose teams of
Project Wild Goose teams of Air Materiel Command
Air Materiel Command (AMC) was a United States Army Air Forces and United States Air Force command. Its headquarters was located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio. In 1961, the command was redesignated the Air Force Logistics Command ...
personnel installed the Ground Air Transmit Receive stations for the SAGE TDDL (in April 1961, Sault Ste Marie was the first operational sector with TDDL). By the middle of 1960, AMC had determined that about 800,000 man-hours (involving 130 changes) would be required to bring the F-106 fleet to the point where it would be a valuable adjunct to the air defense system. Part of the work ( Project Broad Jump) was accomplished by Sacramento Air Materiel Area. The remainder ( Project Wild Goose) was done at ADC bases by roving AMC field assistance teams supported by ADC maintenance personnel. (cited by Volume I p. 271 & Schaffel p. 325) After a September 1959 experimental ATABE test between an "abbreviated" AN/FSQ-7 staged at Fort Banks and the Lexington XD-1, the 1961 "SAGE/Missile Master
Missile Master was a type of US Army Missile Command military installation for the Cold War Project Nike, each which were a complex of systems and facilities for surface-to-air missile command and control. Each Missile Master had a nuclear bu ...
test program" conducted large-scale field testing of the ATABE "mathematical model" using radar tracks of actual SAC and ADC aircraft flying mock penetrations into defense sectors. (cites Miller 1961) Similarly conducted was the joint SAC-NORAD Sky Shield II exercise followed by Sky Shield III on 2 September 1962 On July 15, 1963, ESD's CMC Management Office assumed "responsibilities in connection with BMEWS
The RCA 474L Ballistic Missile Early Warning System (BMEWS, "474L System", Project 474L) was a United States Air Force Cold War early warning radar, computer, and communications system, for ballistic missile detection. The network of twelve ra ...
, Space Track, SAGE, and BUIC." The Chidlaw Building
The Chidlaw Building is a former United States Air Force facility located in the Knob Hill neighborhood of Colorado Springs, Colorado. The building was close to, but not within, the Ent Air Force Base complex, and was leased by the military for ...
's computerized NORAD/ADC Combined Operations Center in 1963 became the highest echelon of the SAGE computer network when operations moved from Ent AFB's 1954 manual Command Center to the partially underground "war room". Also in 1963, radar stations were renumbered (e.g., Cambria AFS
Cambria Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located south-southeast of Cambria, California. It was closed in 1980.
History
Cambria Air Force Station was one of twenty-eight stations ...
was redesignated from P-2 to Z-2 on July 31) and the vacuum-tube SAGE System was completed (and obsolete).
On "June 26, 1958,…the New York sector became operational" and on December 1, 1958, the Syracuse sector's DC-03 was operational ("the SAGE system id notbecome operational until January 1959.") Construction of CFB North Bay
Canadian Forces Base North Bay, also CFB North Bay, is an Canadian Forces base, air force base located at the City of North Bay, Ontario, North Bay, Ontario about north of Toronto. The base is subordinate to 1 Canadian Air Division, Winnipeg, ...
in Canada was started in 1959 for a bunker ~ underground (operational October 1, 1963), and by 1963 the system had 3 Combat Centers. The 23 SAGE centers included 1 in Canada, and the "SAGE control centers reached their full 22 site deployments in 1961 (out of 46 originally planned)." (the quotation is annotated with footnote 35) The completed Minot AFB blockhouse received an AN/FSQ-7, but never received the FSQ-8 (the April 1, 1959, Minot Air Defense Sector
The Minot Air Defense Sector (MADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command 29th Air Division, being stationed at Minot Air Force Base, North Dakota. It was inactivated on 1 Dec ...
consolidated with the Grand Forks ADS on March 1, 1963).
SAGE sites
The SAGE system included a direction center (DC) assigned to air defense sectors as they were defined at the time.Raleigh
Raleigh (; ) is the capital city of the state of North Carolina and the seat of Wake County in the United States. It is the second-most populous city in North Carolina, after Charlotte. Raleigh is the tenth-most populous city in the Southeas ...
NC, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
/Shreveport
Shreveport ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is the third most populous city in Louisiana after New Orleans and Baton Rouge, respectively. The Shreveport–Bossier City metropolitan area, with a population of 393,406 in 2020, is ...
LA, Fort Knox
Fort Knox is a United States Army installation in Kentucky, south of Louisville and north of Elizabethtown. It is adjacent to the United States Bullion Depository, which is used to house a large portion of the United States' official gold re ...
KY, Kirtland/Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding i ...
NM, Robins Robins may refer to:
Places United States
* Robins, Iowa, a small city
* Robins, Ohio, an unincorporated community
* Robins Township, Fall River County, South Dakota
*Robins Island, of the coast of New York state
*Robins Air Force Base, Georgia
* ...
/Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
, Scott
Scott may refer to:
Places Canada
* Scott, Quebec, municipality in the Nouvelle-Beauce regional municipality in Quebec
* Scott, Saskatchewan, a town in the Rural Municipality of Tramping Lake No. 380
* Rural Municipality of Scott No. 98, Sask ...
/ St. Louis, Webb
Webb most often refers to James Webb Space Telescope which is named after James E. Webb, second Administrator of NASA.
It may also refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Webb Glacier (South Georgia)
* Webb Glacier (Victoria Land)
* Webb Névé, Victor ...
/San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_ ...
TX.
Description
The environment allowed radar station personnel to monitor the radar data and systems' status (e.g., Arctic Tower radome pressure) and to use the range height equipment to process height requests from Direction Center (DC) personnel. DCs received the Long Range Radar Input from the sector's radar stations, and DC personnel monitored the radar tracks and IFF data provided by the stations, requested height-finder radar data on targets, and monitored the computer's evaluation of which fighter aircraft or Bomarc missile site could reach the threat first. The DC's "NORAD sector commander's operational staff" could designate fighter intercept of a target or, using the Senior Director's keyed console in the Weapons Direction room, launch a Bomarc intercept with automatic Q-7 guidance of the surface-to-air missile to a final homing dive (equipped fighters eventually were automatically guided to intercepts). The "NORAD sector direction center (NSDC) lso had air defense artillery director (ADAD) consoles nd an ArmyADA battle staff officer", and the NSDC automatically communicated crosstelling of "SAGE reference track data" to/from adjacent sectors' DCs and to 10 NikeMissile Master
Missile Master was a type of US Army Missile Command military installation for the Cold War Project Nike, each which were a complex of systems and facilities for surface-to-air missile command and control. Each Missile Master had a nuclear bu ...
AADCPs. Forwardtelling automatically communicated data from multiple DCs to a 3-story Combat Center (CC) usually at one of the sector's DCs ( cf. planned Hamilton AFB CC-05 near the Beale AFB DC-18) for coordinating the air battle in the NORAD region (multiple sectors) and which forwarded data to the NORAD Command Center ( Ent AFB, 1963 Chidlaw Building
The Chidlaw Building is a former United States Air Force facility located in the Knob Hill neighborhood of Colorado Springs, Colorado. The building was close to, but not within, the Ent Air Force Base complex, and was leased by the military for ...
, & 1966 Cheyenne Mountain). NORAD's integration of air warning data (at the ADOC) along with space surveillance, intelligence, and other data allowed attack assessment of an Air Defense Emergency for alerting the SAC command centers (465L SACCS nodes at Offutt AFB
Offutt Air Force Base is a U.S. Air Force base south of Omaha, adjacent to Bellevue in Sarpy County, Nebraska. It is the headquarters of the U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM), the 557th Weather Wing, and the 55th Wing (55 WG) of the ...
& The Notch), The Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense. It was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As a symbol of the U.S. military, the phrase ''The Pentagon'' is often used as a metony ...
/ Raven Rock NMCC/ANMCC, and the public via CONELRAD
CONELRAD (''Control of Electromagnetic Radiation'') was a method of emergency broadcasting to the public of the United States in the event of enemy attack during the Cold War. It was intended to allow continuous broadcast of civil defense inform ...
radio stations.
SAGE Communication Systems
The Burroughs 416L SAGE component ( ESD Project 416L, Semi Automatic Ground Environment System) was theCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
network connecting IBM supplied computer system at the various DC and that created the display and control environment for operation of the separate radars and to provide outbound command guidance
Command guidance is a type of missile guidance in which a ground station or aircraft relay signals to a guided missile via radio control or through a wire connecting the missile to the launcher and tell the missile where to steer to intercept its ...
for ground-controlled interception by air defense aircraft in the "SAGE Defense System" ("Air Defense Weapons System").Alt URL(cited by Volume I p. 257)
Burroughs Corporation
The Burroughs Corporation was a major American manufacturer of business equipment. The company was founded in 1886 as the American Arithmometer Company. In 1986, it merged with Sperry UNIVAC to form Unisys. The company's history paralleled many ...
was a prime contractor for SAGE network interface equipment which included 134 Burroughs AN/FST-2 Coordinate Data Transmitting Sets (CDTS) at radar stations and other sites, the IBM supplied AN/FSQ-7 at 23 Direction Centers, and the AN/FSQ-8 Combat Control Computers at 8 Combat Centers. The 2 computers of each AN/FSQ-7 together weighing used about ⅓ of the DC's 2nd floor space and at ~$50 per instruction had approximately 125,000 "computer instructions support ngactual operational air-defense mission" processing. The AN/FSQ-7 at Luke AFB had additional memory (32K total) and was used as a "computer center for all other" DCs. Project 416L was the USAF predecessor of NORAD, SAC, and other military organizations' "Big L" computer systems (e.g., 438L Air Force Intelligence Data Handling System & 496L Space Detection and Tracking System).
Network communications: The SAGE network of computers connected by a "Digital Radar Relay" (SAGE data system) used AT&T voice lines, microwave towers, switching centers (e.g., SAGE NNX 764 was at Delta, Utah
Delta is the largest city in Millard County, Utah, United States. It is located in the northeastern area of Millard County along the Sevier River and is surrounded by farmland. The population was 3,436 at the 2010 census.
History
Delta was o ...
& 759 at Mounds, Oklahoma
Mounds is a town in Creek County, Oklahoma, United States. It is located just south of Tulsa; the town's population was 1,168 at the 2010 census, an increase of 1.3 percent from the figure of 1,153 recorded in 2000.
History
The post office for thi ...
Yahoo! GroupsDir.groups.yahoo.com. Retrieved on 2013-09-18.), etc.; and AT&T's "main underground station" was in Kansas (Fairview) with other bunkers in Connecticut (Cheshire), California (Santa Rosa), Iowa (Boone) and Maryland ( Hearthstone Mountain). CDTS
modem
A modulator-demodulator or modem is a computer hardware device that converts data from a digital format into a format suitable for an analog transmission medium such as telephone or radio. A modem transmits data by modulating one or more c ...
s at automated radar stations transmitted range and azimuth, and the Air Movements Identification Service (AMIS) provided air traffic data to the SAGE System. Radar tracks by telephone calls (e.g., from Manual Control Centers in the Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding i ...
, Minot
Minot ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Ward County, North Dakota, United States, in the state's north-central region. It is most widely known for the Air Force base approximately north of the city. With a population of 48,377 at the ...
, and Oklahoma City
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat of Oklahoma County, it ranks 20th among United States cities in population, and ...
sectors) could be entered via consoles of the 4th floor "Manual Inputs" room adjacent to the "Communication Recording-Monitoring and VHF" room. In 1966, SAGE communications were integrated into the AUTOVON Network.
SAGE Sector Warning Networks ( cf. NORAD Division Warning Networks) provided the radar netting communications for each DC and eventually also allowed transfer of command guidance
Command guidance is a type of missile guidance in which a ground station or aircraft relay signals to a guided missile via radio control or through a wire connecting the missile to the launcher and tell the missile where to steer to intercept its ...
to autopilots of TDDL-equipped interceptors for vectoring to targetscompiled by via the Ground to Air Data Link Subsystem and the Ground Air Transmit Receive (GATR) network of radio sites for "HF/VHF/UHF voice & TDDL" each generally co-located at a CDTS site. SAGE Direction Centers and Combat Centers were also nodes of NORAD's Alert Network Number 1, and SAC Emergency War Order
The Single Integrated Operational Plan (SIOP) was the United States' general plan for nuclear war from 1961 to 2003. The SIOP gave the President of the United States a range of targeting options, and described launch procedures and target sets ag ...
Traffic included "Positive Control/Noah's Ark instructions" through northern NORAD radio sites to confirm or recall SAC bombers if "SAC decided to launch the alert force before receiving an execution order from the JCS".
A SAGE System ergonomic test at Luke AFB in 1964 "''showed conclusively that the wrong timing of human and technical operations was leading to frequent truncation of the flight path tracking system''" (Harold Sackman). SAGE software development was "grossly underestimated" (60,000 lines in September 1955): "the biggest mistake fthe SAGE computer program was nderestimating thejump from the 35,000 WIinstructions … to the more than 100,000 instructions on the" AN/FSQ-8. NORAD conducted a ''Sage/Missile Master Integration/ECM-ECCM Test'' in 1963, and although SAGE used AMIS input of air traffic information, the 1959 plan developed by the July 1958 USAF Air Defense Systems Integration Division for SAGE Air Traffic Integration (SATIN) was cancelled by the DoD.
Radar stations
SAGE radar stations, including 78DEW Line
The Distant Early Warning Line, also known as the DEW Line or Early Warning Line, was a system of radar stations in the northern Arctic region of Canada, with additional stations along the north coast and Aleutian Islands of Alaska (see Proj ...
sites in December 1961, provided radar tracks to DCs and had frequency diversity (FD) radars United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
picket ships
Picket may refer to:
* Snow picket, a climbing tool
* Picket fence, a type of fence
* Screw picket, a tethering device
* Picket line, to tether horses
*"Picket line" is also used in picketing, a form of protest
**See also: "Strikebreaker, Crossing ...
also provided radar tracks, and seaward radar coverage was provided. By the late 1960s EC-121 Warning Star aircraft based at Otis AFB MA and McClellan AFB
McClellan Air Force Base (1935–2001) is a former United States Air Force base located in the North Highlands area of Sacramento County, northeast of Sacramento, California.
History
For the vast majority of its operational lifetime, McCle ...
CA provided radar tracks via automatic data link to the SAGE System. Civil Aeronautics Administration radars were at some stations (e.g., stations of the Joint Use Site System), and the ARSR-1 Air Route Surveillance Radar rotation rate had to be modified "for SAGE FF/SIFModes III and IV" ("antenna gear box modification" for compatibility with FSQ-7 & FSG-1 centrals.)
Interceptors
ADC aircraft such as the F-94 Starfire, F-89 Scorpion,F-101B Voodoo
The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo is a supersonic jet fighter which served the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF).
Initially designed by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation as a long-range bomber escort (known as a ''p ...
, and F-4 Phantom were controlled by SAGE GCI. The F-104 Starfighter
The Lockheed F-104 Starfighter is an American single-engine, supersonic air superiority fighter which was extensively deployed as a fighter-bomber during the Cold War. Created as a day fighter by Lockheed as one of the " Century Series" of ...
was "too small to be equipped with AGEdata link equipment" and used voice-commanded GCI, but the F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor ...
was equipped for the automated data link (ADL). The ADL was designed to allow Interceptors that reached targets to transmit real-time tactical friendly and enemy movements and to determine whether sector defence reinforcement was necessary.(this source was also referenced at a time earlier than 2015-08-05, for info: ...ADL... - ''Interceptors'')
Familiarization flights allowed SAGE weapons directors to fly on two-seat interceptors to observe GCI operations. Surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft syst ...
installations for CIM-10 Bomarc
The Boeing CIM-10 BOMARC (Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center) (IM-99 Weapon System prior to September 1962) was a supersonic ramjet powered long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) used during the Cold War for the air defense of Nort ...
interceptors were displayed on SAGE consoles.
Improvements
Partially solid-state AN/FST-2B and later AN/FYQ-47 computers replaced the AN/FST-2, and sectors without AN/FSQ-7 centrals requiring a " weapon direction control device" for USAF air defense used the solid-state AN/GSG-5 CCCS instead of the AN/GPA-73 recommended by ADC in June 1958.Back-Up Interceptor Control Backup Interceptor Control (BUIC, ) was the Electronic Systems Division 416M System to backup the SAGE 416L System in the United States and Canada. BUIC deployed Cold War command, control, and coordination systems to SAGE radar stations to create ...
(BUIC) with CCCS dispersed to radar stations for survivability allowed a diminished but functional SAGE capability. In 1962, Burroughs "won the contract to provide a military version of its D825" modular data processing system for BUIC II. BUIC II was first used at North Truro Z-10 in 1966, and the Hamilton AFB BUIC II was installed in the former MCC building when it was converted to a SAGE Combat Center in 1966 (CC-05). On June 3, 1963, the Direction Centers at Marysville CA, Marquette/K I Sawyer AFB (DC-14) MI, Stewart AFB NY (DC-02), and Moses Lake WA (DC-15) were planned for closing and at the end of 1969, only 6 CONUS SAGE DCs remained (DC-03, -04, -10, -12, -20, & -21) all with the vacuum tube AN/FSQ-7 centrals. In 1966, NORAD Combined Operations Center operations at Chidlaw transferred to the Cheyenne Mountain Operations Center
The Cheyenne Mountain Complex is a Space Force installation and defensive bunker located in unincorporated El Paso County, Colorado, next to the city of Colorado Springs, at the Cheyenne Mountain Space Force Station, which hosts the activities of ...
(425L System) and in December 1963, the DoD approved solid state replacement of Martin AN/FSG-1 centrals with the AN/GSG-5 and subsequent Hughes AN/TSQ-51. The "416L/M/N Program Office" at Hanscom Field had deployed the BUIC III by 1971 (e.g., to Fallon NAS), and the initial BUIC systems were phased out 1974–5. ADC had been renamed Aerospace Defense Command on January 15, 1968, and its general surveillance radar stations transferred to ADTAC in 1979 when the ADC major command was broken up (space surveillance stations went to SAC and the Aerospace Defense Center
The Aerospace Defense Center (ADC) was a unit of the United States Air Force. It was under the command of the general that also commanded both North American Aerospace Defense Command and Aerospace Defense Command (ADCOM). The center included the ...
was activated as a DRU.)
Replacement and disposition
For airborne command posts, "as early as 1962 the Air Force began exploring possibilities for anAirborne Warning and Control System
Airborne or Airborn may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Airborne'' (1962 film), a 1962 American film directed by James Landis
* ''Airborne'' (1993 film), a comedy–drama film
* ''Airborne'' (1998 film), an action film sta ...
(AWACS)", and the Strategic Defense Architecture (SDA-2000) planned an integrated air defense and air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airsp ...
network. The USAF declared full operational capability of the first seven Joint Surveillance System
The Joint Surveillance System (JSS) is a joint United States Air Force and Federal Aviation Administration system for the atmospheric air defense of North America. It replaced the Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) system in 1983.
Overvi ...
ROCCs on December 23, 1980, with Hughes AN/FYQ-93 systems, and many of the SAGE radar stations became Joint Surveillance System
The Joint Surveillance System (JSS) is a joint United States Air Force and Federal Aviation Administration system for the atmospheric air defense of North America. It replaced the Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) system in 1983.
Overvi ...
(JSS) sites (e.g., San Pedro Hill Z-39 became FAA Ground Equipment Facility J-31.) The North Bay AN/FSQ-7 was dismantled and sent to Boston's Computer Museum. In 1996, AN/FSQ-7 components were moved to Moffett Federal Airfield
Moffett Federal Airfield , also known as Moffett Field, is a joint civil-military airport located in an unincorporated part of Santa Clara County, California, United States, between northern Mountain View and northern Sunnyvale. On November 10 ...
for storage and later moved to the Computer History Museum
The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a museum of computer history, located in Mountain View, California. The museum presents stories and artifacts of Silicon Valley and the information age, and explores the computing revolution and its impact o ...
in Mountain View, California
Mountain View is a city in Santa Clara County, California, United States. Named for its views of the Santa Cruz Mountains, it has a population of 82,376.
Mountain View was integral to the early history and growth of Silicon Valley, and is t ...
. The last AN/FSQ-7 centrals were demolished at McChord AFB (August 1983) and Luke AFB (February 1984). Decommissioned AN/FSQ-7 equipment was also used as science fiction cinema and TV series props (e.g. Voyage to the Bottom of the Sea, amongst others).
Historiography
SAGE histories include a 1983 special issue of the ''Annals of the History of Computing'', and various personal histories were published, e.g., Valley in 1985 and Jacobs in 1986. In 1998, the SAGE System was identified as 1 of 4 "Monumental Projects", and a SAGE lecture presented the vintage film ''In Your Defense'' followed by anecdotal information from Les Earnest, Jim Wong, and Paul Edwards. In 2013, a copy of a 1950s cover girl image programmed for SAGE display was identified as the "earliest known figurativecomputer art
Computer art is any art in which computers play a role in production or display of the artwork. Such art can be an image, sound, animation, video, CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, video game, website, algorithm, performance or gallery installation. Many tradit ...
". Company histories identifying employees' roles in SAGE include the 1981 ''System Builders: The Story of SDC'' and the 1998 ''Architects of Information Advantage: The MITRE Corporation Since 1958''.
See also
*Photographic Display Unit
The Photographic Display Unit, or PDU, was a large-format display system used by the Royal Air Force to present radar images for interpretation by a number of operators and commanders. Made by Kelvin Hughes, it projected a diameter image that co ...
References
Further reading
*Stories about SAGE
- oral history
"The largest computer ever built"
- "Locklin on science"
External links
On Guard: The Story of SAGE
(1956) IBM Corporation, Military Products Division * Cold War Computing: The SAGE System, Computer Museum {{USAF system codes Computer networks Cold War military equipment of the United States North American Aerospace Defense Command 1950s computers Computer-related introductions in 1958 Lists of Cold War sites 1950s in technology 1950s in the United States