Second messenger on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or
 There are several different secondary messenger systems (
There are several different secondary messenger systems (
 Binding of a primary messenger to these receptors results in conformational change of the receptor. The α subunit, with the help of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFS), releases GDP, and binds GTP, resulting in the dissociation of the subunit and subsequent activation. The activated α subunit activates phospholipase C, which hydrolyzes membrane bound
Binding of a primary messenger to these receptors results in conformational change of the receptor. The α subunit, with the help of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFS), releases GDP, and binds GTP, resulting in the dissociation of the subunit and subsequent activation. The activated α subunit activates phospholipase C, which hydrolyzes membrane bound
Animation: Second Messenger: cAMP
{{Authority control Signal transduction
cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with p ...
, juxtacrine, paracrine Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over ...
, and endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
and depolarization.
They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades.
Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal tra ...
, cyclic GMP
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in ...
, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s or neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
s, such as epinephrine, growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in ...
, and serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and va ...
. Because peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically are biochemically hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are n ...
molecules, these first messengers may not physically cross the phospholipid bilayer to initiate changes within the cell directly—unlike steroid hormones, which usually do. This functional limitation requires the cell to have signal transduction mechanisms to transduce first messenger into second messengers, so that the extracellular signal may be propagated intracellularly. An important feature of the second messenger signaling system is that second messengers may be coupled downstream to multi-cyclic kinase cascades to greatly amplify the strength of the original first messenger signal. For example, RasGTP signals link with the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade to amplify the allosteric activation of proliferative transcription factors such as Myc and CREB.
Earl Wilbur Sutherland Jr.
Earl Wilbur Sutherland Jr. (November 19, 1915 – March 9, 1974) was an American pharmacologist and biochemist born in Burlingame, Kansas. Sutherland won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanis ...
, discovered second messengers, for which he won the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordi ...
. Sutherland saw that epinephrine would stimulate the liver to convert glycogen to glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
(sugar) in liver cells, but epinephrine alone would not convert glycogen to glucose. He found that epinephrine had to trigger a second messenger, cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal tra ...
, for the liver to convert glycogen to glucose.
The mechanisms were worked out in detail by Martin Rodbell and Alfred G. Gilman
Alfred Goodman Gilman (July 1, 1941 – December 23, 2015) was an American pharmacologist and biochemist. He and Martin Rodbell shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discovery of G-proteins and the role of these prote ...
, who won the 1994 Nobel Prize.
Secondary messenger systems can be synthesized and activated by enzymes, for example, the cyclases that synthesize cyclic nucleotides, or by opening of ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
s to allow influx of metal ions, for example Ca2+ signaling. These small molecules bind and activate protein kinases, ion channels, and other proteins, thus continuing the signaling cascade.
Types of second messenger molecules
There are three basic types of secondary messenger molecules: *Hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, ...
molecules: water-insoluble molecules such as diacylglycerol, and phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol (or Inositol Phospholipid) consists of a family of lipids as illustrated on the right, where red is x, blue is y, and black is z, in the context of independent variation, a class of the phosphatidylglycerides. In such molecul ...
s, which are membrane-associated and diffuse from the plasma membrane into the intermembrane space where they can reach and regulate membrane-associated '' effector proteins.''
* Hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are n ...
molecules: water-soluble molecules, such as cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
, cGMP, IP3, and Ca2+, that are located within the cytosol.
* Gases: nitric oxide (NO), carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) which can diffuse both through cytosol and across cellular membranes.
These intracellular messengers have some properties in common:
* They can be synthesized/released and broken down again in specific reactions by enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s or ion channels.
* Some (such as Ca2+) can be stored in special organelles and quickly released when needed.
* Their production/release and destruction can be ''localized'', enabling the cell to limit space and time of signal activity.
Common mechanisms of second messenger systems
 There are several different secondary messenger systems (
There are several different secondary messenger systems (cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
system, phosphoinositol system, and arachidonic acid
Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid 20:4(ω-6), or 20:4(5,8,11,14). It is structurally related to the saturated arachidic acid found in cupuaçu butter. Its name derives from the New Latin word ''ara ...
system), but they all are quite similar in overall mechanism, although the substances involved and overall effects can vary.
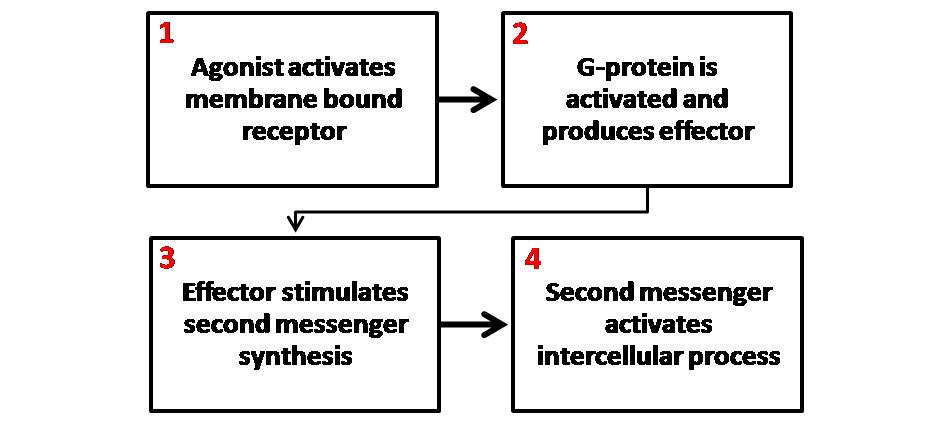
In most cases, a ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
binds to a membrane-spanning receptor protein
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a recept ...
molecule. The binding of a ligand to the receptor causes a conformation change in the receptor. This conformation change can affect the activity of the receptor and result in the production of active second messengers.
In the case of G protein-coupled receptors, the conformation change exposes a binding site for a '' G-protein''. The G-protein (named for the GDP and GTP molecules that bind to it) is bound to the inner membrane of the cell and consists of three subunits: alpha, beta and gamma. The G-protein is known as the " transducer."
When the G-protein binds with the receptor, it becomes able to exchange a GDP (guanosine diphosphate) molecule on its alpha subunit for a GTP (guanosine triphosphate) molecule. Once this exchange takes place, the alpha subunit of the G-protein transducer breaks free from the beta and gamma subunits, all parts remaining membrane-bound. The alpha subunit, now free to move along the inner membrane, eventually contacts another membrane-bound protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
- the "primary effector."
The primary effector then has an action, which creates a signal that can diffuse within the cell. This signal is called the "second (or secondary) messenger." The secondary messenger may then activate a "secondary effector" whose effects depend on the particular secondary messenger system.
Calcium ions
Calcium ions (Ca2+) contribute to the physiology and biochemistry of organisms' cells. They play an important role in signal transduction pathways, where they act as a second messenger, in neurotransmitter release from neurons, in contraction ...
are one type of second messengers and are responsible for many important physiological functions including muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such a ...
, fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
, and neurotransmitter release. The ions are normally bound or stored in intracellular components (such as the endoplasmic reticulum(ER)) and can be released during signal transduction. The enzyme phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role ...
produces diacylglycerol and inositol trisphosphate, which increases calcium ion permeability into the membrane. Active G-protein open up calcium channels to let calcium ions enter the plasma membrane. The other product of phospholipase C, diacylglycerol, activates protein kinase C, which assists in the activation of cAMP (another second messenger).
Examples
Second Messengers in the Phosphoinositol Signaling Pathway
IP3, DAG, and Ca2+ are second messengers in the phosphoinositol pathway. The pathway begins with the binding of extracellular primary messengers such as epinephrine, acetylcholine, and hormones AGT, GnRH, GHRH, oxytocin, and TRH, to their respective receptors. Epinephrine binds to the α1 GTPase Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR) and acetylcholine binds to M1 and M2 GPCR. Binding of a primary messenger to these receptors results in conformational change of the receptor. The α subunit, with the help of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFS), releases GDP, and binds GTP, resulting in the dissociation of the subunit and subsequent activation. The activated α subunit activates phospholipase C, which hydrolyzes membrane bound
Binding of a primary messenger to these receptors results in conformational change of the receptor. The α subunit, with the help of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFS), releases GDP, and binds GTP, resulting in the dissociation of the subunit and subsequent activation. The activated α subunit activates phospholipase C, which hydrolyzes membrane bound phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of ...
(PIP2), resulting in the formation of secondary messengers diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3). IP3 binds to calcium pumps on ER, transporting Ca2+, another second messenger, into the cytoplasm. Ca2+ ultimately binds to many proteins, activating a cascade of enzymatic pathways.
References
External links
*Animation: Second Messenger: cAMP
{{Authority control Signal transduction