Sealant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of
 Types of sealants fall between the higher-strength, adhesive-derived sealers and
Types of sealants fall between the higher-strength, adhesive-derived sealers and
fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear ...
s through openings in materials, a type of mechanical seal
A mechanical seal is a device that helps join systems and mechanisms together by preventing leakage (e.g. in a pumping system), containing pressure, or excluding contamination. The effectiveness of a seal is dependent on adhesion in the case of ...
. In building construction ''sealant'' is sometimes synonymous with '' caulking'' and also serve the purposes of blocking dust, sound and heat transmission. Sealants may be weak or strong, flexible or rigid, permanent or temporary. Sealants are not adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
s but some have adhesive qualities and are called ''adhesive-sealants'' or ''structural sealants''.
History
Sealants were first used in prehistory in the broadest sense as mud, grass and reeds to seal dwellings from the weather such as the daub inwattle and daub
Wattle and daub is a composite building method used for making walls and buildings, in which a woven lattice of wooden strips called wattle is daubed with a sticky material usually made of some combination of wet soil, clay, sand, animal dung a ...
and thatching
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of ...
. Natural sealants and adhesive-sealants included plant resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on nat ...
s such as pine pitch and birch pitch
Birch tar or birch pitch is a substance (liquid when heated) derived from the dry distillation of the bark of the birch tree.
Compounds
It is composed of phenols such as guaiacol, cresol, xylenol, and creosol.
Ancient and modern uses
Birc ...
, bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
, wax, tar
Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat. "a dark brown or black bi ...
, natural gum
Natural gums are polysaccharides of natural origin, capable of causing a large increase in a solution's viscosity, even at small concentrations. They are mostly botanical gums, found in the woody elements of plants or in seed coatings.
Human ...
, clay (mud) mortar, lime mortar, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
, blood and egg. In the 17th century glazing putty
Putty is a material with high plasticity, similar in texture to clay or dough, typically used in domestic construction and repair as a sealant or filler. Although some types of putty (typically those using linseed oil) slowly polymerise and be ...
was first used to seal window glass made with linseed oil and chalk, later other drying oils were also used to make oil-based putties which were often referred to as ''caulks''. In the 1920s polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s such as acrylic polymer
An acrylate polymer (also known as acrylic or polyacrylate) is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity.
Acrylate polymer is commonly used ...
s, butyl
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four- carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula , derived from either of the two isomers (''n''-butane and isobutane) of butane.
The isomer ''n''-butane can connect in two ways, gi ...
polymers and silicone polymers were first developed and used in sealants. By the 1960s synthetic-polymer-based sealants were widely available.
Function
Sealants, despite not having great strength, convey a number of properties. They seal top structures to the substrate, and are particularly effective inwaterproofing
Waterproofing is the process of making an object or structure waterproof or water-resistant so that it remains relatively unaffected by water or resisting the ingress of water under specified conditions. Such items may be used in wet environme ...
processes by keeping moisture out (or in) the components in which they are used. They can provide thermal and acoustical insulation, and may serve as fire barriers. They may have electrical properties, as well. Sealants can also be used for simple smoothing or filling. They are often called upon to perform several of these functions at once.
A caulking sealant has three basic functions: It fills a gap between two or more substrates; it forms a barrier through the physical properties of the sealant itself and by adhesion to the substrate; and it maintains sealing properties for the expected lifetime, service conditions, and environments. The sealant performs these functions by way of correct formulation to achieve specific application and performance properties. Other than adhesives, however, there are few functional alternatives to the sealing process.
Soldering
Soldering (; ) is a process in which two or more items are joined by melting and putting a filler metal ( solder) into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the adjoining metal. Unlike welding, soldering does not inv ...
or welding
Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing fusion. Welding is distinct from lower temperature techniques such as b ...
can perhaps be used as alternatives in certain instances, depending on the substrates and the relative movement that the substrates will see in service. However, the simplicity and reliability offered by organic elastomers usually make them the clear choice for performing these functions.
Types of sealants
A sealant may be viscous material that has little or no flow characteristics and which stay where they are applied; or they can be thin and runny so as to allow it to penetrate the substrate by means of capillary action. Anaerobic acrylic sealants (generally referred to as impregnants) are the most desirable, as they are required to cure in the absence of air, unlike surface sealants that require air as part of the cure mechanism that changes state to become solid, once applied, and is used to prevent the penetration of air, gas, noise, dust, fire, smoke, or liquid from one location through a barrier into another. Typically, sealants are used to close small openings that are difficult to shut with other materials, such asconcrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
, drywall
Drywall (also called plasterboard, dry lining, wallboard, sheet rock, gypsum board, buster board, custard board, and gypsum panel) is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or without additives, typically extruded between thic ...
, etc. Desirable properties of sealants include insolubility, corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
resistance, and adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another).
The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can ...
. Uses of sealants vary widely and sealants are used in many industries, for example, construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and ...
, automotive and aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and ast ...
industries.
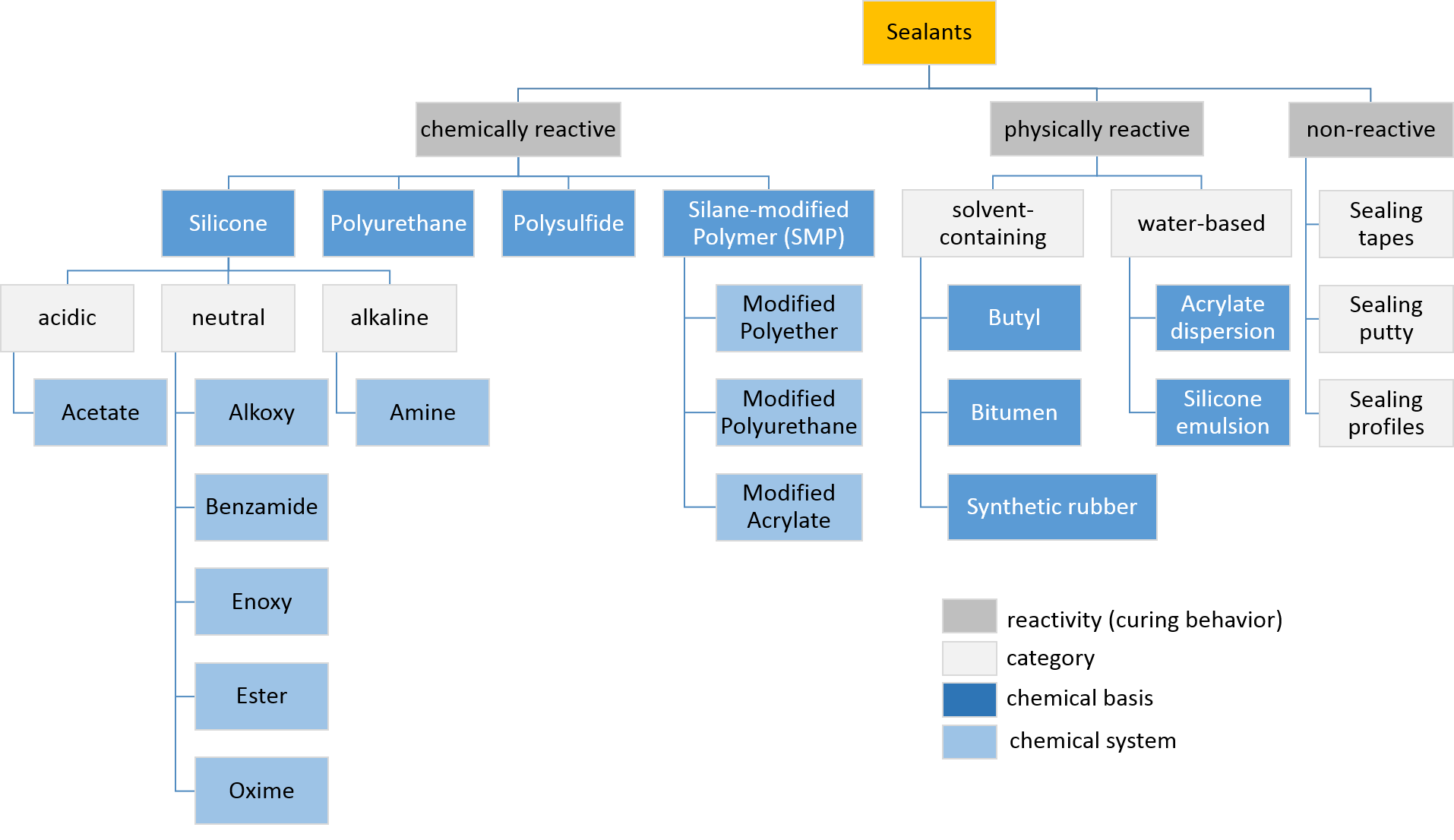
Sealants can be categorized in accordance with varying criteria, e. g. in accordance with the reactivity of the product in the ready-to-use condition or on the basis of its mechanical behavior after installation.
Often the intended use or the chemical basis is used to classify sealants, too. A typical classification system for most commonly used sealants is shown below.
 Types of sealants fall between the higher-strength, adhesive-derived sealers and
Types of sealants fall between the higher-strength, adhesive-derived sealers and coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Pow ...
s at one end, and extremely low-strength putties, waxes, and caulks at the other. Putties and caulks serve only one function – i.e., to take up space and fill voids. Sealants maybe based on Silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cookin ...
- and has a proven long life and is unaffected by UV or extremes of weather or temperature.
See below for other common types of sealants -
Common areas of use
Aerospace sealants
* Firewall Sealants - a two-component, firewall sealant intended for use as a coating, sealant or filleting material in the construction, repair and maintenance of aircraft and is especially useful where fire resistance, exposure to phosphate ester fluids, and/or exposure to extreme temperatures -65°F (-54°C) to 400°F (204°C) are major considerations. * Fuel Tank Sealants - High-temperature fuel resistant sealant intended for use on integral fuel tanks with excellent resistance to other fluids such as water, alcohols, synthetic oils and petroleum-based hydraulic fluids * Access Door Sealants - Access door sealant intended for use on integral fuel tanks and pressurized cabins with low adhesion characteristics and excellent resistance to other fluids such as water, alcohols, synthetic oils and petroleum based hydraulic fluids. * Windshield Sealant - Demonstrated to be a useful sealant in a variety of applications where quick setting is desired, for example, windshield sealants, repair caulks, adhesives, etc.Comparison with adhesives
The main difference betweenadhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
s and sealants is that sealants typically have lower strength and higher elongation than adhesives do. When sealants are used between substrates having different thermal coefficients of expansion or differing elongation under stress, they need to have adequate flexibility and elongation. Sealants generally contain inert filler material and are usually formulated with an elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and Elasticity (physics), elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high Deformation (mechanics), failure strain compared with other mate ...
to give the required flexibility and elongation. They usually have a paste consistency to allow filling of gaps between substrates. Low shrinkage after application is often required. Many adhesive technologies can be formulated into sealants.
References
{{Reflist Seals (mechanical) Materials