Scapulars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the
 ;Front or subscapular fossa
The front of the scapula (also known as the costal or ventral surface) has a broad concavity called the subscapular fossa, to which the
;Front or subscapular fossa
The front of the scapula (also known as the costal or ventral surface) has a broad concavity called the subscapular fossa, to which the
File:Superior angle of left scapula01.png, Superior angle shown in red
File:Head of scapula02.png, Lateral angle shown in red
File:Scapula ant - anatomical neck and surgical neck.png, Anatomic neck: red, Surgical neck: purple
File:Inferior angle of the left scapula01.png, Inferior angle shown in red
File:Superior border of left scapula01.png, Costal surface of left scapula. Superior border shown in red.
File:Superior border of left scapula - animation01.gif, Left scapula. Superior border shown in red.
File:Superior border of scapula - animation02.gif, Animation. Superior border shown in red.
* The axillary border (or "lateral border") is the thickest of the three. It begins above at the lower margin of the glenoid cavity, and inclines obliquely downward and backward to the inferior angle. It is referred to as the caudal border in animals.
::It begins above at the lower margin of the glenoid cavity, and inclines obliquely downward and backward to the inferior angle.
::Immediately below the glenoid cavity is a rough impression, the infraglenoid tuberosity, about . in length, which gives origin to the long head of the
File:Lateral border of left scapula01.png, Dorsal surface of left scapula. Lateral border shown in red.
File:Lateral border of left scapula - animation.gif, Left scapula. Lateral border shown in red.
File:Lateral border of scapula - animation.gif, Animation. Lateral border shown in red.
* The medial border (also called the vertebral border or medial margin) is the longest of the three borders, and extends from the superior angle to the inferior angle. In animals it is referred to as the dorsal border.
::Four muscles attach to the medial border. Serratus anterior has a long attachment on the anterior lip. Three muscles insert along the posterior lip, the
File:Medial boder of left scapula - animation.gif, Left scapula. Medial border shown in red.
File:Medial boder of scapula - animation.gif, Animation. Medial border shown in red.
File:Medial border of scapula01.png, Still image. Medial border shown in red.
File:Levator scapulae.png,
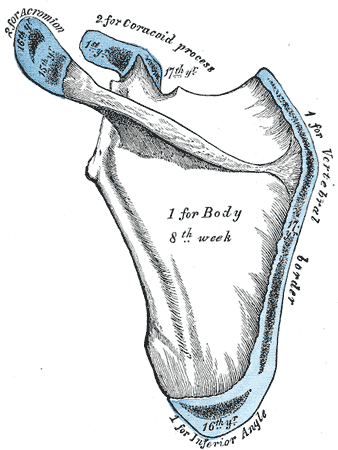 The scapula is ossified from 7 or more centers: one for the body, two for the
The scapula is ossified from 7 or more centers: one for the body, two for the

 Because of its sturdy structure and protected location, fractures of the scapula are uncommon. When they do occur, they are an indication that severe chest trauma has occurred.
Scapular fractures involving the neck of the scapula have two patterns. One (rare) type of fracture is through the anatomical neck of the scapula. The other more common type of fracture is through the surgical neck of the scapula. The surgical neck exits medial to the
Because of its sturdy structure and protected location, fractures of the scapula are uncommon. When they do occur, they are an indication that severe chest trauma has occurred.
Scapular fractures involving the neck of the scapula have two patterns. One (rare) type of fracture is through the anatomical neck of the scapula. The other more common type of fracture is through the surgical neck of the scapula. The surgical neck exits medial to the
 In fish, the scapular blade is a structure attached to the upper surface of the articulation of the
In fish, the scapular blade is a structure attached to the upper surface of the articulation of the
shoulder/bones/bones2
at the Dartmouth Medical School's Department of Anatomy *
shoulder/surface/surface2
at the Dartmouth Medical School's Department of Anatomy * () {{Authority control Bones of the upper limb Flat bones Shoulder
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
that connects the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a r ...
(upper arm bone) with the clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the r ...
(collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later period ...
word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.
In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone.
The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists ...
. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a sem ...
.
Structure
The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrinsic, extrinsic, and stabilizing and rotating muscles. The intrinsic muscles of the scapula include the muscles of therotator cuff
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the supraspi ...
—the subscapularis, teres minor, supraspinatus
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotat ...
, and infraspinatus. These muscles attach to the surface of the scapula and are responsible for the internal and external rotation of the shoulder joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint ...
, along with humeral abduction.
The extrinsic muscles include the biceps
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join t ...
, triceps, and deltoid muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up o ...
s and attach to the coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, and spine of the scapula. These muscles are responsible for several actions of the glenohumeral joint.
The third group, which is mainly responsible for stabilization and rotation of the scapula, consists of the trapezius, serratus anterior, levator scapulae, and rhomboid muscles
The rhomboid muscles (), often simply called the rhomboids, are rhombus-shaped muscles associated with the scapula. There are two rhomboid muscles on each side of the upper back:
* Rhomboid major muscle
* Rhomboid minor muscle
The large rhom ...
. These attach to the medial, superior, and inferior borders of the scapula.
The head, processes, and the thickened parts of the bone contain cancellous
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, a ...
tissue; the rest consists of a thin layer of compact tissue.
The central part of the supraspinatus fossa and the upper part of the infraspinatous fossa
The infraspinous fossa (infraspinatus fossa or infraspinatous fossa) of the scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (coll ...
, but especially the former, are usually so thin in humans as to be semitransparent; occasionally the bone is found wanting in this situation, and the adjacent muscles are separated only by fibrous tissue. The scapula has two surfaces, three borders, three angles, and three processes.
Surfaces
 ;Front or subscapular fossa
The front of the scapula (also known as the costal or ventral surface) has a broad concavity called the subscapular fossa, to which the
;Front or subscapular fossa
The front of the scapula (also known as the costal or ventral surface) has a broad concavity called the subscapular fossa, to which the subscapularis muscle
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the shoulder-joint.
Structure
It arises from its medial two-thirds and
So ...
attaches. The medial two-thirds of the fossa have 3 longitudinal oblique ridges, and another thick ridge adjoins the lateral border; they run outward and upward. The ridges give attachment to the tendinous insertions, and the surfaces between them to the fleshy fibers, of the subscapularis muscle. The lateral third of the fossa is smooth and covered by the fibers of this muscle.
At the upper part of the fossa is a transverse depression, where the bone appears to be bent on itself along a line at right angles to and passing through the center of the glenoid cavity, forming a considerable angle, called the subscapular angle; this gives greater strength to the body of the bone by its arched form, while the summit of the arch serves to support the spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Vertebral column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoolo ...
and acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The ...
.
The costal surface superior of the scapula is the origin of 1st digitation for the serratus anterior origin.
;Back
The back of the scapula (also called the dorsal or posterior surface) is arched from above downward, and is subdivided into two unequal parts by the spine of the scapula. The portion above the spine is called the supraspinous fossa, and that below it the infraspinous fossa. The two fossae are connected by the spinoglenoid notch, situated lateral to the root of the spine.
* The ''supraspinous fossa'', above the spine of scapula, is concave, smooth, and broader at its vertebral than at its humeral end; its medial two-thirds give origin to the Supraspinatus
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotat ...
. At its lateral surface resides the spinoglenoid fossa which is situated by the medial margin of the glenoid. The spinoglenoid fossa houses the suprascpular canal which forms a connecting passage between the suprascapular notch and the spinoglenoid notch conveying the suprascapular nerve and vessels.
* The ''infraspinous fossa'' is much larger than the preceding; toward its vertebral margin a shallow concavity is seen at its upper part; its center presents a prominent convexity, while near the axillary border is a deep groove which runs from the upper toward the lower part. The medial two-thirds of the fossa give origin to the Infraspinatus
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspin ...
; the lateral third is covered by this muscle.
There is a ridge on the outer part of the back of the scapula. This runs from the lower part of the glenoid cavity, downward and backward to the vertebral border, about 2.5 cm above the inferior angle. Attached to the ridge is a fibrous septum, which separates the infraspinatus muscle
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspin ...
from the Teres major
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meaning ...
and Teres minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the ...
muscles. The upper two-thirds of the surface between the ridge and the axillary border is narrow, and is crossed near its center by a groove for the scapular circumflex vessels; the Teres minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the ...
attaches here.
The broad and narrow portions above alluded to are separated by an oblique line, which runs from the axillary border, downward and backward, to meet the elevated ridge: to it is attached a fibrous septum which separates the Teres muscles from each other.
Its lower third presents a broader, somewhat triangular surface, the inferior angle of the scapula, which gives origin to the Teres major
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meaning ...
, and over which the Latissimus dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsorum'') comes from ...
glides; frequently the latter muscle takes origin by a few fibers from this part.
;Side
The acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The ...
forms the summit of the shoulder, and is a large, somewhat triangular or oblong process, flattened from behind forward, projecting at first laterally, and then curving forward and upward, so as to overhang the glenoid cavity.
Angles
There are 3 angles: The superior angle of the scapula or medial angle, is covered by thetrapezius muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the ...
. This angle is formed by the junction of the superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
*Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lake ...
and medial borders of the scapula. The superior angle is located at the approximate level of the second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ea ...
thoracic vertebra. The superior angle of the scapula is thin, smooth, rounded, and inclined somewhat lateralward, and gives attachment to a few fibers of the levator scapulae muscle
The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.
Anatomy
Attachments
The muscle descends diagonally from its origin to its inserti ...
.
The inferior angle of the scapula is the lowest part of the scapula and is covered by the latissimus dorsi muscle
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsorum'') comes from L ...
. It moves forwards round the chest when the arm is abducted. The inferior angle is formed by the union of the medial and lateral borders of the scapula. It is thick and rough and its posterior or back surface affords attachment to the teres major
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meaning ...
and often to a few fibers of the latissimus dorsi. The anatomical plane
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements. In human and animal anatomy, three principal planes are used:
* The sagittal plane or latera ...
that passes vertically through the inferior angle is named the scapular line
The scapular line, also known as the linea scapularis, is a vertical line passing through the inferior angle of the scapula.
It has been used in the evaluation of brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network () of nerves formed by the anter ...
.
The lateral angle of the scapula or glenoid angle also known as the head of the scapula is the thickest part of the scapula. It is broad and bears the glenoid fossa
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from el, gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a sha ...
on its articular surface which is directed forward, laterally and slightly upwards, and articulates with the head of the humerus. The inferior angle is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest. The surface is covered with cartilage in the fresh state; and its margins, slightly raised, give attachment to a fibrocartilaginous structure, the glenoidal labrum, which deepens the cavity. At its apex is a slight elevation, the supraglenoid tuberosity, to which the long head of the biceps brachii
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join ...
is attached.
The anatomic neck of the scapula is the slightly constricted portion which surrounds the head and is more distinct below and behind than above and in front. The surgical neck of the scapula passes directly medial to the base of the coracoid process.
Borders
There are three borders of the scapula: * The superior border is the shortest and thinnest; it is concave, and extends from the superior angle to the base of thecoracoid process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with t ...
. It is referred to as the cranial border in animals.
::At its lateral part is a deep, semicircular notch, the scapular notch, formed partly by the base of the coracoid process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with t ...
. This notch is converted into a foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
by the in
superior transverse scapular ligament
The superior transverse ligament (transverse or suprascapular ligament) converts the suprascapular notch into a foramen or opening.
It is a thin and flat fascicle, narrower at the middle than at the extremities, attached by one end to the base of ...
, and serves for the passage of the suprascapular nerve; sometimes the ligament is ossified.
::The adjacent part of the superior border affords attachment to the omohyoideus.
triceps brachii
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of 3 parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally respon ...
; in front of this is a longitudinal groove, which extends as far as the lower third of this border, and affords origin to part of the subscapularis.
::The inferior third is thin and sharp, and serves for the attachment of a few fibers of the teres major
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meaning ...
behind, and of the subscapularis in front.
levator scapulae
The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.
Anatomy
Attachments
The muscle descends diagonally from its origin to its inserti ...
(uppermost), rhomboid minor (middle), and to the rhomboid major (lower middle).
Levator scapulae muscle
The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.
Anatomy
Attachments
The muscle descends diagonally from its origin to its inserti ...
(red)
File:Rhomboideus minor.png, Rhomboid minor muscle
In human anatomy, the rhomboid minor is a small skeletal muscle on the back that connects the scapula with the vertebrae of the spinal column.
Located inferior to levator scapulae and superior to rhomboid major, it acts together with the latt ...
(red)
File:Rhomboideus major.png, Rhomboid major muscle (red)
Development
 The scapula is ossified from 7 or more centers: one for the body, two for the
The scapula is ossified from 7 or more centers: one for the body, two for the coracoid process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with t ...
, two for the acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The ...
, one for the vertebral border, and one for the inferior angle. Ossification of the body begins about the second month of fetal life, by an irregular quadrilateral plate of bone forming, immediately behind the glenoid cavity. This plate extends to form the chief part of the bone, the scapular spine growing up from its dorsal surface
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position ...
about the third month. Ossification starts as membranous ossification before birth. After birth, the cartilaginous components would undergo endochondral ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in ...
. The larger part of the scapula undergoes membranous ossification. Some of the outer parts of the scapula are cartilaginous at birth, and would therefore undergo endochondral ossification.
At birth, a large part of the scapula is osseous, but the glenoid cavity, the coracoid process, the acromion, the vertebral border and the inferior angle are cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck a ...
. From the 15th to the 18th month after birth, ossification takes place in the middle of the coracoid process, which as a rule becomes joined with the rest of the bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
about the 15th year.
Between the 14th and 20th years, the remaining parts ossify in quick succession, and usually in the following order: first, in the root of the coracoid process, in the form of a broad scale; secondly, near the base of the acromion; thirdly, in the inferior angle and contiguous part of the vertebral border; fourthly, near the outer end of the acromion; fifthly, in the vertebral border.
The base of the acromion is formed by an extension from the spine; the two nuclei of the acromion unite, and then join with the extension from the spine. The upper third of the glenoid cavity is ossified from a separate center (sub coracoid), which appears between the 10th and 11th years and joins between the 16th and the 18th years. Further, an epiphysial plate appears for the lower part of the glenoid cavity, and the tip of the coracoid process frequently has a separate nucleus. These various epiphyses
The epiphysis () is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). At the jo ...
are joined to the bone by the 25th year.
Failure of bony union between the acromion and spine sometimes occurs (see os acromiale
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acr ...
), the junction being effected by fibrous tissue, or by an imperfect articulation; in some cases of supposed fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displ ...
of the acromion with ligamentous union, it is probable that the detached segment was never united to the rest of the bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
.
Function
The following muscles attach to the scapula:Movements
Movements of the scapula are brought about by the scapular muscles. The scapula can perform six actions: * Elevation: uppertrapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports th ...
and levator scapulae
The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.
Anatomy
Attachments
The muscle descends diagonally from its origin to its inserti ...
* Depression: lower trapezius
* Retraction ( adduction): rhomboids and middle trapezius
* Protraction (abduction): serratus anterior
* Upward rotation: upper and lower trapezius, serratus anterior
* Downward rotation: rhomboids, Levator Scapulae, and Pec Minor
Clinical significance
Scapular fractures

 Because of its sturdy structure and protected location, fractures of the scapula are uncommon. When they do occur, they are an indication that severe chest trauma has occurred.
Scapular fractures involving the neck of the scapula have two patterns. One (rare) type of fracture is through the anatomical neck of the scapula. The other more common type of fracture is through the surgical neck of the scapula. The surgical neck exits medial to the
Because of its sturdy structure and protected location, fractures of the scapula are uncommon. When they do occur, they are an indication that severe chest trauma has occurred.
Scapular fractures involving the neck of the scapula have two patterns. One (rare) type of fracture is through the anatomical neck of the scapula. The other more common type of fracture is through the surgical neck of the scapula. The surgical neck exits medial to the coracoid process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with t ...
.
An abnormally protruding inferior angle of the scapula is known as a winged scapula and can be caused by paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 5 ...
of the serratus anterior muscle
The serratus anterior is a muscle that originates on the surface of the 1st to 8th ribs at the side of the chest and inserts along the entire anterior length of the medial border of the scapula. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula fo ...
. In this condition the sides of the scapula nearest the spine are positioned outward and backward. The appearance of the upper back is said to be wing-like. In addition, any condition causing weakness of the serratus anterior muscle may cause scapular "winging".
Scapular dyskenesis
The scapula plays an important role in shoulder impingement syndrome.Kibler, BW. (1998). The role of the scapula in athletic shoulder function. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 26(2), 325-337. Abnormal scapular function is called scapular dyskinesis. One action the scapula performs during a throwing or serving motion is elevation of the acromion process in order to avoid impingement of the rotator cuff tendons. If the scapula fails to properly elevate the acromion, impingement may occur during the cocking and acceleration phase of an overhead activity. The two muscles most commonly inhibited during this first part of an overhead motion are the serratus anterior and the lower trapezius. These two muscles act as a force couple within the glenohumeral joint to properly elevate the acromion process, and if a muscle imbalance exists, shoulder impingement may develop. Other conditions associated with scapular dyskenesis include thoracic outlet syndrome and the relatedpectoralis minor syndrome Pectoralis minor syndrome (PMS) is a condition related to thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) that results from the pectoralis minor muscle being too tight. PMS results from the brachial plexus being compressed under the pectoralis minor while TOS inv ...
.
Etymology
The name ''scapula'' as synonym of ''shoulder blade'' is of Latin origin.Anderson, D.M. (2000). ''Dorland’s illustrated medical dictionary'' (29th edition). Philadelphia/London/Toronto/Montreal/Sydney/Tokyo: W.B. Saunders Company. It is commonly used in medical EnglishDorland, W.A.N. & Miller, E.C.L. (1948). ‘’The American illustrated medical dictionary.’’ (21st edition). Philadelphia/London: W.B. Saunders Company.Dirckx, J.H. (Ed.) (1997).''Stedman’s concise medical dictionary for the health professions.'' (3rd edition). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. and is part of the current official Latin nomenclature, ''Terminologia Anatomica
''Terminologia Anatomica'' is the international standard for human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology, a program of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomi ...
''.Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) (1998). ''Terminologia Anatomica''. Stuttgart: Thieme Shoulder blade is the colloquial name for this bone.
In other animals
 In fish, the scapular blade is a structure attached to the upper surface of the articulation of the
In fish, the scapular blade is a structure attached to the upper surface of the articulation of the pectoral fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
, and is accompanied by a similar coracoid plate on the lower surface. Although sturdy in cartilagenous fish, both plates are generally small in most other fish, and may be partially cartilagenous, or consist of multiple bony elements.
In the early tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s, these two structures respectively became the scapula and a bone referred to as the procoracoid (commonly called simply the " coracoid", but not homologous with the mammalian structure of that name). In amphibians and reptiles (birds included), these two bones are distinct, but together form a single structure bearing many of the muscle attachments for the forelimb. In such animals, the scapula is usually a relatively simple plate, lacking the projections and spine that it possesses in mammals. However, the detailed structure of these bones varies considerably in living groups. For example, in frogs, the procoracoid bones may be braced together at the animal's underside to absorb the shock of landing, while in turtles, the combined structure forms a Y-shape in order to allow the scapula to retain a connection to the clavicle (which is part of the shell). In birds, the procoracoids help to brace the wing against the top of the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sha ...
.
In the fossil therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more ...
s, a third bone, the true coracoid, formed just behind the procoracoid. The resulting three-boned structure is still seen in modern monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals ( Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brai ...
s, but in all other living mammals, the procoracoid has disappeared, and the coracoid bone has fused with the scapula, to become the coracoid process. These changes are associated with the upright gait of mammals, compared with the more sprawling limb arrangement of reptiles and amphibians; the muscles formerly attached to the procoracoid are no longer required. The altered musculature is also responsible for the alteration in the shape of the rest of the scapula; the forward margin of the original bone became the spine and acromion, from which the main shelf of the shoulder blade arises as a new structure.
In dinosaurs
Indinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s the main bones of the pectoral girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of ...
were the scapula (shoulder blade) and the coracoid, both of which directly articulated with the clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the r ...
. The clavicle was present in saurischian dinosaurs but largely absent in ornithischian dinosaurs. The place on the scapula where it articulated with the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a r ...
(upper bone of the forelimb) is called the glenoid. The scapula serves as the attachment site for a dinosaur's back and forelimb muscles.
Gallery
See also
*Scapulimancy
Scapulimancy (also spelled ''scapulomancy'' and ''scapulamancy'', also termed ''omoplatoscopy'' or ''speal bone reading'') is the practice of divination by use of scapulae or speal bones (shoulder blades). It is most widely practiced in China an ...
/Oracle bone
Oracle bones () are pieces of ox scapula and turtle plastron, which were used for pyromancy – a form of divination – in ancient China, mainly during the late Shang dynasty. '' Scapulimancy'' is the correct term if ox scapulae were used for ...
References
* * Nickel, Schummer, & Seiferle; ''Lehrbuch der Anatomie der Haussäugetiere''.External links
* - "Joints of the Upper Extremity: Scapula" *shoulder/bones/bones2
at the Dartmouth Medical School's Department of Anatomy *
shoulder/surface/surface2
at the Dartmouth Medical School's Department of Anatomy * () {{Authority control Bones of the upper limb Flat bones Shoulder