Scania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical
Heathen Gods in Old English Literature
''.
 Between 1719 and 1996, the province was subdivided in two administrative
Between 1719 and 1996, the province was subdivided in two administrative

 During the Danish era, the province had no coat of arms. In Sweden, however, every province had been represented by heraldic arms since 1560. When Charles X Gustav of Sweden suddenly died in 1660 a coat of arms had to be created for the newly acquired province, as each province was to be represented by its arms at his royal funeral. After an initiative from Baron Gustaf Bonde, the Lord High Treasurer of Sweden, the coat of arms of the City of Malmö was used as a base for the new provincial arms. The Malmö coat of arms had been granted in 1437, during the Kalmar Union, by Eric of Pomerania and contains a
During the Danish era, the province had no coat of arms. In Sweden, however, every province had been represented by heraldic arms since 1560. When Charles X Gustav of Sweden suddenly died in 1660 a coat of arms had to be created for the newly acquired province, as each province was to be represented by its arms at his royal funeral. After an initiative from Baron Gustaf Bonde, the Lord High Treasurer of Sweden, the coat of arms of the City of Malmö was used as a base for the new provincial arms. The Malmö coat of arms had been granted in 1437, during the Kalmar Union, by Eric of Pomerania and contains a
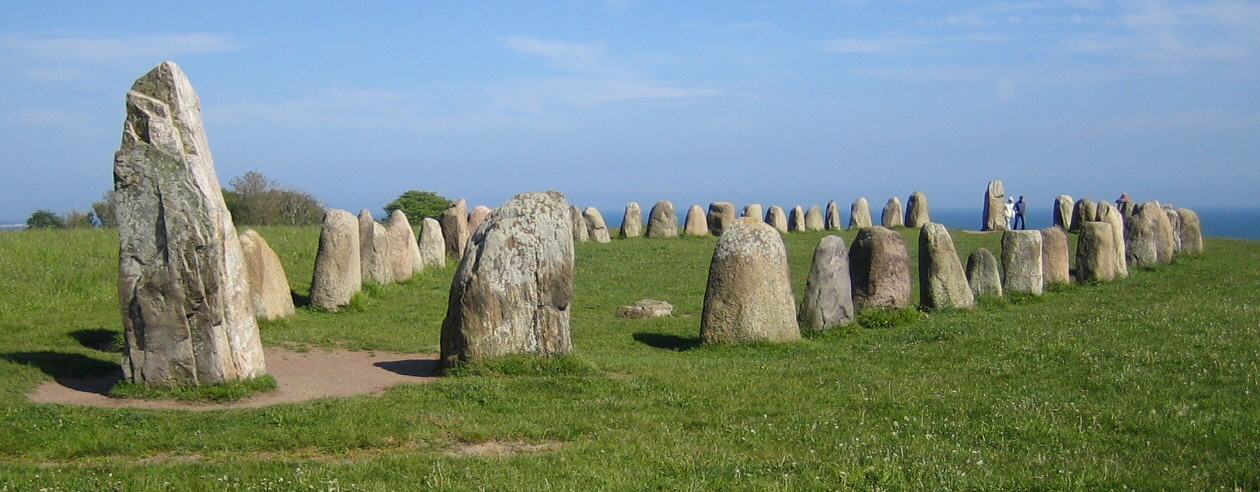


 Scania was first mentioned in written texts in the 9th century. It came under Danish king Harald Bluetooth in the middle of the 10th century. It was then a region that included Blekinge and
Scania was first mentioned in written texts in the 9th century. It came under Danish king Harald Bluetooth in the middle of the 10th century. It was then a region that included Blekinge and
The Europeanisation of Swedish Regional Government
. ''Policy Networks in Sub National Governance: Understanding Power Relations''. Paper 8, Workshop 25, European Consortium of Political Research. 2004 Joint Sessions of Workshops, Uppsala, Sweden. In response to the crisis, the County Governors were given a task by the government in September 1996 to co-ordinate various measures in the counties to increase economic growth and employment by bringing in regional actors. The first proposal for regional autonomy and a regional parliament had been introduced by the Social Democratic Party's local districts in Scania and Västra Götaland already in 1993. When Sweden joined the
"The Regions and Regionalism: Regionalism in Sweden"
. ''CoR Report Sweden''. The Interdisciplinary Centre for Comparative Research in the Social Sciences, EUROPUB Case Study (WP2). The relatively strong regional identity in Scania is often referred to in order to explain the general support in the province for the decentralization efforts introduced by the Swedish government. On the basis of large scale interview investigations about Region Skåne in Scania, scholars have found that the prevailing trend among the inhabitants of Scania is to "

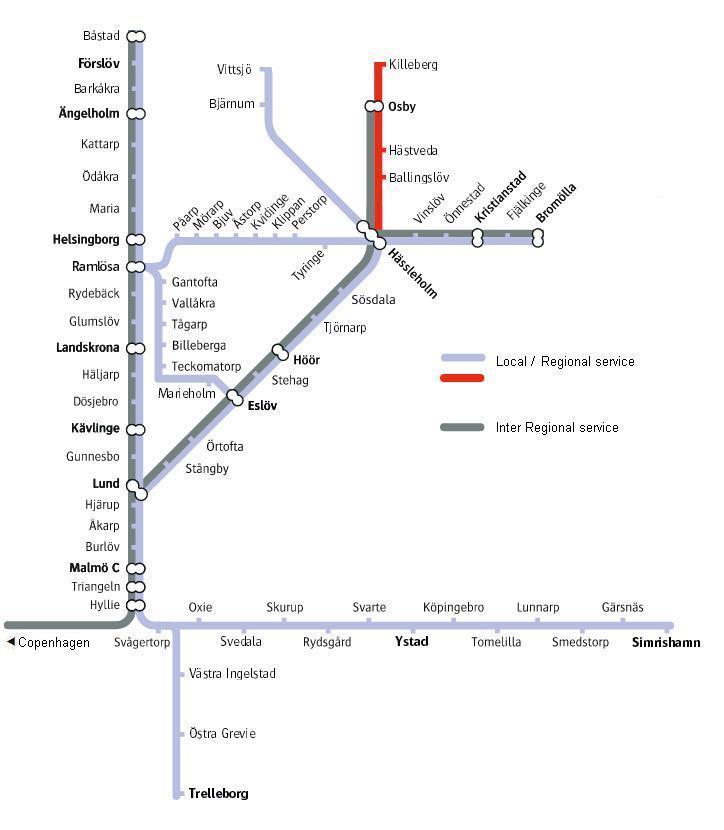 Electrified dual track railroad exists from the border with
Electrified dual track railroad exists from the border with
In Lund, the tracks split into two directions.Sveriges järnvägsnät - Trafikverket
. Trafikverket.se (31 March 2015). Retrieved on 24 June 2015. The dual tracks going towards Gothenburg end at


 Unlike some regions of Sweden, the Scanian landscape is generally not
Unlike some regions of Sweden, the Scanian landscape is generally not  Where the sea meets higher parts of the sloping landscape, cliffs emerge. Such cliffs are white if the soil has a high content of chalk. Good examples of such coastlines exist at the southern side of
Where the sea meets higher parts of the sloping landscape, cliffs emerge. Such cliffs are white if the soil has a high content of chalk. Good examples of such coastlines exist at the southern side of
 Scania is divided into 33 municipalities with population and land surface as the table below shows. There is a large population difference between the western Scania, that is located by, or close to Øresund sea compared to the middle and eastern parts of the province.
* A small part of Båstad municipality is located within the neighbouring province of
Scania is divided into 33 municipalities with population and land surface as the table below shows. There is a large population difference between the western Scania, that is located by, or close to Øresund sea compared to the middle and eastern parts of the province.
* A small part of Båstad municipality is located within the neighbouring province of


 In
In
 It has been estimated that around 1570, Scania had about 110,000 inhabitants. But before the plague in the middle of the 14th century the population of all Danish territory east of Øresund (Scania, Island of Bornholm, Blekinge and Halland) may have exceeded 250,000.
The figures here are from two different sources.
*2015 data.
It has been estimated that around 1570, Scania had about 110,000 inhabitants. But before the plague in the middle of the 14th century the population of all Danish territory east of Øresund (Scania, Island of Bornholm, Blekinge and Halland) may have exceeded 250,000.
The figures here are from two different sources.
*2015 data.
 Scania has the mildest climate in Sweden, but there are some local differences.
The table shows average temperatures in degrees Celsius at ten
Scania has the mildest climate in Sweden, but there are some local differences.
The table shows average temperatures in degrees Celsius at ten
 Scania's long-running and sometimes intense trade relations with other communities along the coast of the European continent through history have made the culture of Scania distinct from other geographical regions of Sweden. Its open landscape, often described as a colourful patchwork quilt of
Scania's long-running and sometimes intense trade relations with other communities along the coast of the European continent through history have made the culture of Scania distinct from other geographical regions of Sweden. Its open landscape, often described as a colourful patchwork quilt of
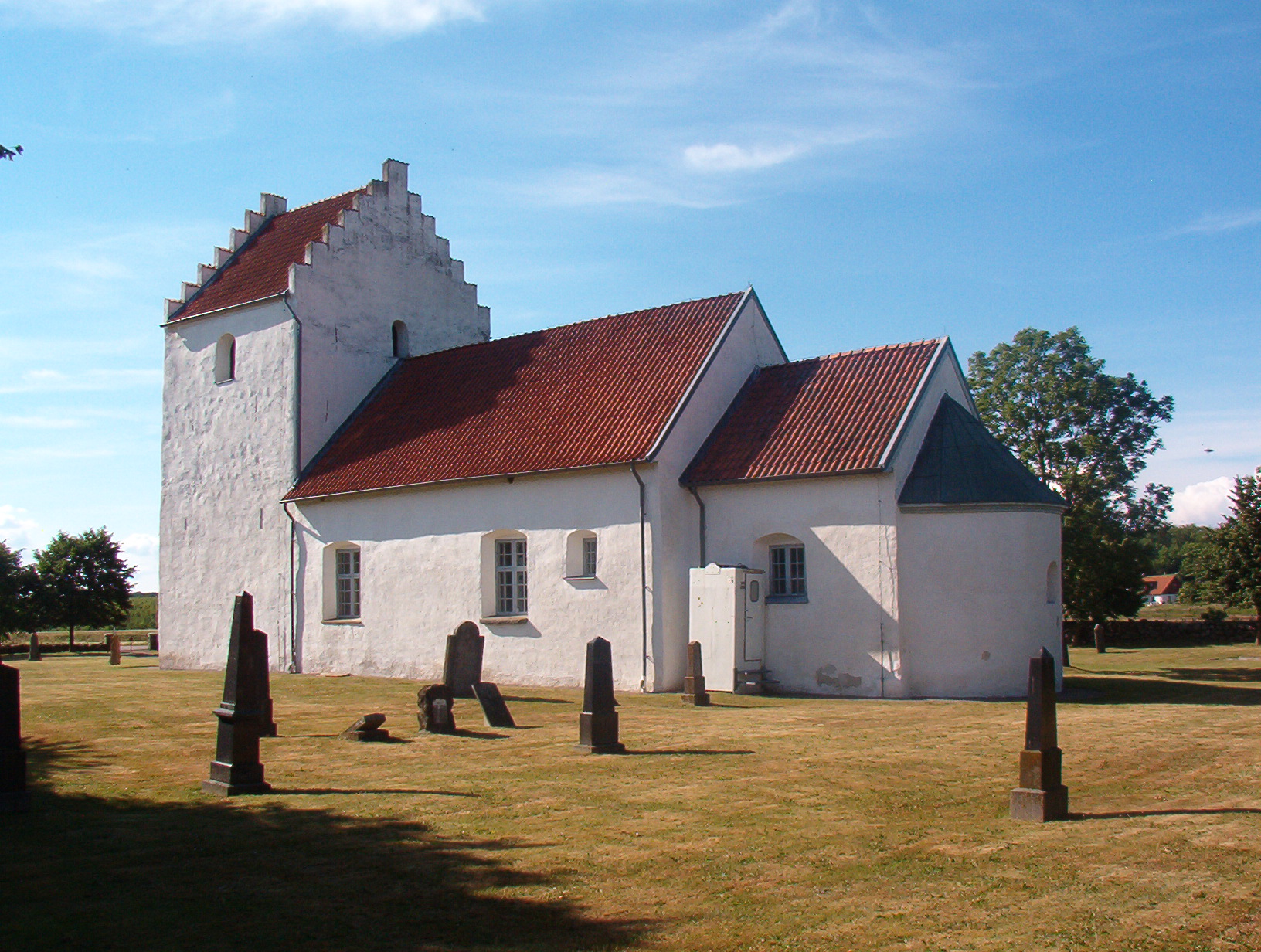
 Traditional Scanian architecture is shaped by the limited availability of wood; it incorporates different applications of the building technique called
Traditional Scanian architecture is shaped by the limited availability of wood; it incorporates different applications of the building technique called
Chapter III: Danmarks Mynthistorie indtil 1146
, an
published online by Gladsaxe Gymnasium. (In Danish). Retrieved 10 January 2007. The archaeological excavations performed in the city indicate that the oldest known
Touchdowns in the History of Lund
. Official site for the City of Lund. Retrieved 10 January 2006. In 1103, Lund was made the archbishopric for all of Scandinavia. Many of the old churches in today's Scanian landscape stem from the medieval age, although many church renovations, extensions and destruction of older buildings took place in the 16th and 19th century. From those that have kept features of the authentic style, it is still possible to see how the medieval, Romanesque or
Lunds Domkyrka
. (In Swedish). Retrieved 11 January 2007. The oldest parts of today's cathedral are from 1085, but the actual cathedral was constructed during the first part of the 12th century with the help of stone cutters and sculptors from the Rhine valley and Scania also has churches built in the gothic style, such as Saint Petri Church in Malmö, dating from the early 14th century. Similar buildings can be found in all Hansa cities around the
Scania also has churches built in the gothic style, such as Saint Petri Church in Malmö, dating from the early 14th century. Similar buildings can be found in all Hansa cities around the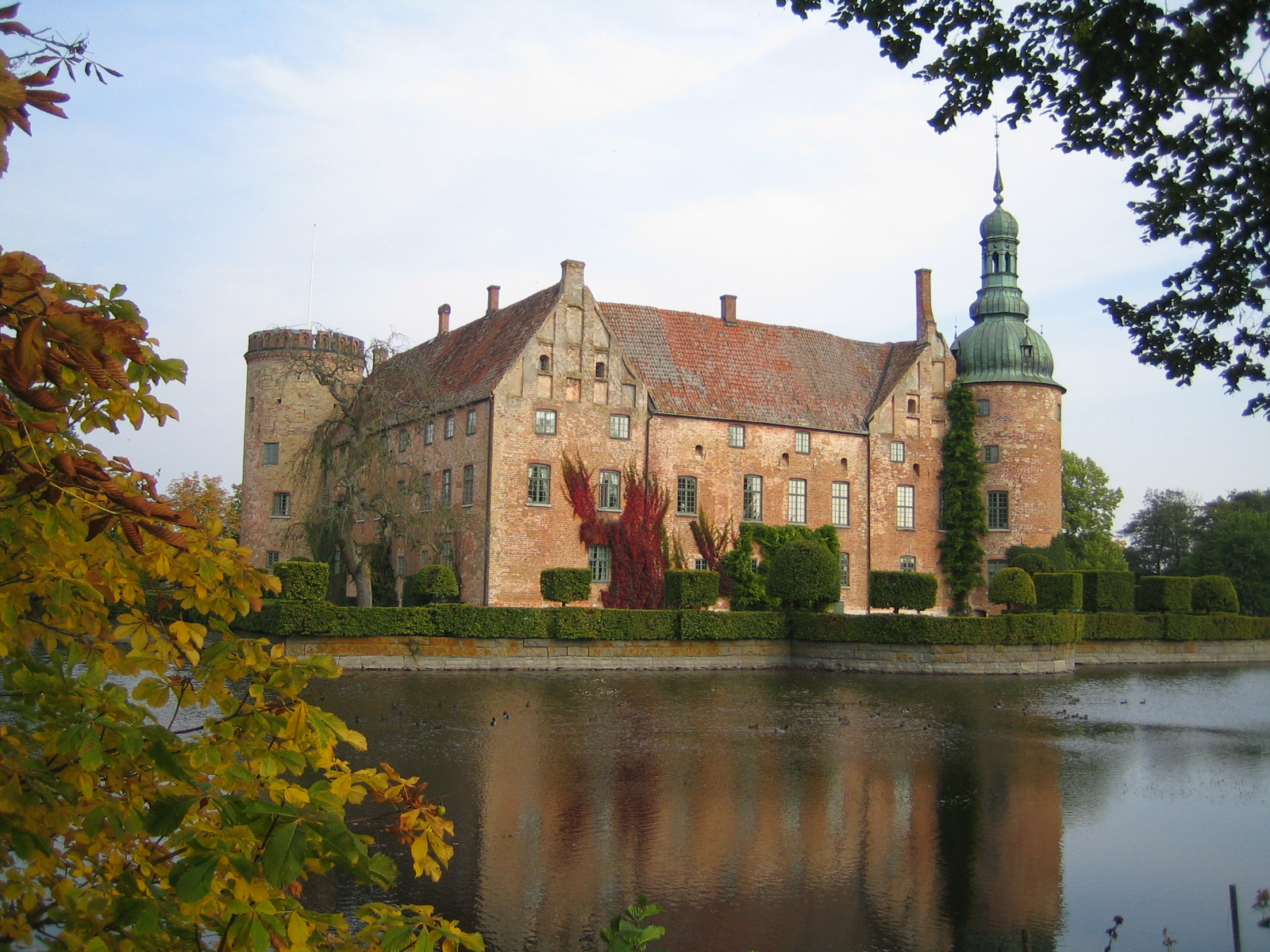  Scania has 240 palaces and country estates—more than any other province in Sweden. Many of them received their current shape during the 16th century, when new or remodelled castles started to appear in greater numbers, often erected by the reuse of stones and material from the original 11th–15th-century castles and abbeys found at the estates. Between 1840 and 1900, the
Scania has 240 palaces and country estates—more than any other province in Sweden. Many of them received their current shape during the 16th century, when new or remodelled castles started to appear in greater numbers, often erected by the reuse of stones and material from the original 11th–15th-century castles and abbeys found at the estates. Between 1840 and 1900, the
 Scanian culture, as expressed through the medium of textile art, has received international attention during the last decade. The art form, often referred to as Scanian Marriage Weavings, flourished from 1750 for a period of 100 years, after which it slowly vanished. Consisting of small textile panels mainly created for wedding ceremonies, the art is strongly symbolic, often expressing ideas about fertility, longevity and a sense of hope and joy. The Scanian artists were female weavers working at home, who had learned to weave at a young age, often in order to have a marriage chest filled with beautiful tapestries as a dowry.
According to international collectors and art scholars, the Scanian patterns are of special interest for the striking similarities with Roman, Byzantine and
Scanian culture, as expressed through the medium of textile art, has received international attention during the last decade. The art form, often referred to as Scanian Marriage Weavings, flourished from 1750 for a period of 100 years, after which it slowly vanished. Consisting of small textile panels mainly created for wedding ceremonies, the art is strongly symbolic, often expressing ideas about fertility, longevity and a sense of hope and joy. The Scanian artists were female weavers working at home, who had learned to weave at a young age, often in order to have a marriage chest filled with beautiful tapestries as a dowry.
According to international collectors and art scholars, the Scanian patterns are of special interest for the striking similarities with Roman, Byzantine and
pdf format
. (In Swedish).
Half-timbered houses
. ''Malmö 1692 - a historical project''. Malmö City Culture Department and Museum of Foteviken. Retrieved 16 January 2007. * Anderson, Carl Edlund (1999). ''Formation and Resolution of Ideological Contrast in the Early History of Scandinavia''. PhD dissertation, Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse & Celtic (Faculty of English), University of Cambridge, 1999. * Björk, Gert and Henrik Persson. "Fram för ett öppet och utåtriktat Skåne". ''Sydsvenskan'', 20 May 2000. Reproduced by FSF. (In Swedish). Retrieved 3 April 2008. * Bjurklint Rosenblad, Kajsa (2005). ''Scenografi för ett ståndsmässigt liv: adelns slottsbyggande i Skåne 1840-1900.'' Malmö: Sekel, 2005. . * Bonney, Richard (1995). ''Economic Systems and State Finance''. Oxford University Press. . * Craig, David J. (2003)
Boston University Bridge, 29 August 2003,• Vol. VII, No. 1. Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Danish National Archives (2006)
(In Danish). Retrieved 20 October 2006. * City of Lund (2006).
Touchdowns in the History of Lund
'. Retrieved 10 January 2006. * Gårding, Eva (1974). "Talar skåningarna svenska". ''Svenskans beskrivning''. Ed. Christer Platzack. Lund: Institutionen för nordiska språk, 1973. (In Swedish) * Germundsson, Tomas (2005). "Regional Cultural Heritage versus National Heritage in Scania’s Disputed National Landscape." ''International Journal of Heritage Studies'', Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2005. . * Hansen, Viveka (1997). ''Swedish Textile Art: Traditional Marriage Weavings from Scania''. Nour Foundation: 1997. . * Hauberg, P. (1900).'' Myntforhold og Udmyntninger i Danmark indtil 1146''. D. Kgl. Danske Vidensk. Selsk. Skr., 6. Række, historisk og filosofisk Afd. V. I.
an
Gladsaxe Gymnasium. (In Danish). Retrieved 10 January 2007. * Haugen, Einar (1976). ''The Scandinavian Languages: An Introduction to Their History''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1976. * Helle, Knut, ed. (2003). ''The Cambridge History of Scandinavia''. Cambridge University Press, 2003. . * Hogan, C.M. (2004). ''Kullaberg environmental analysis''. Lumina Technologies, Aberdeen Library Archives, Aberdeen, Scotland, 17 July 2004. * Jespersen, Knud J. V. (2004) . ''A History of Denmark''. Palgrave Macmillan. . * Keelan, Major Andrew and Wendy Keelan (2006)
The Khalili Family Trust. Retrieved 1 April 2008. * Lidmar-Bergström, Karna and Jens-Ove Näslund (2005). "Uplands and Lowlands in Southern Sweden". ''The Physical Geography of Fennoscandia''. Ed. Matti Seppälä. Oxford University Press, 2005. . * Lindquist, Herman (1995). ''Historien om Sverige – storhet och fall''. Norstedts Förlag, 2006. . (In Swedish). * Linnaeus, Carl (1750). ''Skånska resa''. (In Swedish). * Lund University School of Aviation (2005)
Ljungbyhed airport - ESTL
Retrieved 22 January 2007. * Lundström, Lena (2003). "Vattenväsen i väverskans händer". ''Vårt Trelleborg'', 2:2003. (In Swedish). * Malmö Public Library (2005)
Litteraturhistoria, Malmö
''Infotek Öresund'', 4 November 2005. (In Swedish). * Nevéus, Clara and Bror Jacques de Wærn (1992). ''Ny svensk vapenbok''. Riksarkivet 1992. (In Swedish) * Olin, Martin (2005)
"Royal Galleries in Denmark and Sweden around 1700"
''Kungliga rum – maktmanifestation och distribution''. Historikermöte 2005, Uppsala University. Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Olwig, Kenneth R. (2005). "Introduction: The Nature of Cultural Heritage, and the Culture of Natural Heritage—Northern Perspectives on a Contested Patrimony". ''International Journal of Heritage Studies'', Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2005. * Oresundstid (2008).
The Swedification of Scania
,
Renaissance Houses: Half-timbered houses
. Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Österberg, Klas (2001)
The Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, 25 January 2001. Retrieved 4 November 2006. * Østergård, Uffe (1997). "The Geopolitics of Nordic Identity – From Composite States to Nation States". ''The Cultural Construction of Norden''. Øystein Sørensen and Bo Stråth (eds.), Oslo: Scandinavian University Press 1997. * Peter, Laurence (2006).
Bridge shapes new Nordic hub
. BBC News, 14 September 2006. Retrieved 20 October 2006. * Region Skåne (2007)
Municipalities in SkåneDemocracy-Increased autonomyWhat is typical Skåne?
Retrieved 22 January 2007. * * SCB (2007)
"Skördar"
''Jordbruksstatistisk årsbok 2006''. Statiska Centralbyrån. (In Swedish). Retrieved 10 January 2007. * Skåne Regional Council (1999). ''Newsletter''., No. 2, 1999. * Stadin, Kekke (2005). "The Masculine Image of a Great Power: Representations of Swedish imperial power c. 1630–1690". ''Scandinavian Journal of History'', Vol. 30, No. 1. March 2005, pp. 61–82. . * Stiftelsen för fritidsområden i Skåne (2006
Skåneleden: 6B
''Breanäsleden'' (In Swedish)
Information about the Skaneled Trails
The Foundation for Recreational Areas in Skåne and Region Skåne. Retrieved 11 April 2008. * Strindberg, August (1893). "Skånska landskap med utvikningar". ''Prosabitar från 1890-talet''. Bonniers, Stockholm, 1917. (In Swedish). * SAOB (2008)
In Swedish). Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Sorens, Jason (2005). "The Cross-Sectional Determinants of Secessionism in Advanced Democracies". ''Comparative Political Studies'', Vol. 38, No. 3, 304-326 (2005). 2005 SAGE Publications. * Språk- och Folkminnesinstitutet (2003). ''Svenskt Ortnamnslexikon''. Uppsala, 2003. (In Swedish) * Tägil, Sven (2000). "Regions in Europe – a historical perspective". In ''Border Regions in Comparison''. Ed. Hans-Åke Persson. Studentlitteratur, Lund. . * Terra Scaniae (2008)
''Skånes län efter 1658''''Hårdare försvenskning''"Kuppförsök mot svenskarna 1658"
"Lunds Domkyrka"''1600-talet''''Generalguvernörens uppgifter''
(In Swedish). Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Upton, Anthony F. (1998). ''Charles XI and Swedish Absolutism, 1660–1697''. Cambridge University Press, 1998. . * Vinge, Louise (ed.) ''Skånes litteraturhistoria'', Corona: Malmö, 1996–1997, Part I, , and Part II, . (In Swedish). * Ystad Municipality (2007)
Welcome to Ystad
an
"Pedestrian street"
''A walk through the centuries''. Retrieved 16 January 2007.
Region Skåne
– The County council
Scania's Public Recreational Areas
– Region Skåne's public forests and parks
Skåne
– Business Region Skåne's official website for culture, heritage and tourism
Länsstyrelsen
– County Administration Board
Skåneleden
– Public nature trails through Scania
Oresund Region
– The regional body of the Oresund Region
– Museum in Kristianstad
Kommunförbundet Skåne
– A cooperation between Scania's 33 municipalities
Skånes hembygdsförbund
(in Swedish) – Heritage conservation organization
Terra Scaniae
– History project established for Scanian schools, financed with subsidies from
provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
(''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland
Götaland (; also '' Geatland'', '' Gothia'', ''Gothland'', ''Gothenland'' or ''Gautland'') is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, wit ...
, the province is roughly conterminous with Skåne County, created in 1997. Like the other former provinces of Sweden, Scania still features in colloquial speech and in cultural references, and can therefore not be regarded as an archaic concept. Within Scania there are 33 municipalities that are autonomous within the Skåne Regional Council
Region Scania is the regional council of Scania County in Sweden. Scania County was formed on January 1, 1999, by the amalgamation of the county councils of Malmöhus County and Kristianstad County and some of the tasks handled by Malmö Municip ...
. Scania's largest city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, Malmö, is the third-largest city in Sweden, as well as the fifth-largest in Scandinavia.
To the north, Scania borders the former provinces of Halland
Halland () is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap''), on the western coast of Götaland, southern Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömseb ...
and Småland, to the northeast Blekinge, to the east and south the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, and to the west Öresund. Since 2000, a road and railway bridge, the Öresund Bridge, bridges the Sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' b ...
and connects Scania with Denmark. Scania forms part of the transnational Øresund Region.
From north to south Scania is around 130 km; it covers less than 3% of Sweden's total area. The population of over 1,320,000 represents 13% of the country's population. With 121 inh/km2 Scania is the second-most densely populated
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopul ...
province of Sweden.
Historically, Scania formed part of the kingdom of Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
until the signing of the Treaty of Roskilde
The Treaty of Roskilde (concluded on 26 February ( OS), or 8 March 1658) ( NS) during the Second Northern War between Frederick III of Denmark–Norway and Karl X Gustav of Sweden in the Danish city of Roskilde. After a devastating defeat ...
in 1658. Denmark regained control of the province (1676–1679) during the Scanian War and again briefly in 1711 during the Great Northern War. Scania has been an undisputed part of Sweden since 1720.
Name
Endonym and exonyms
The endonym used in Swedish and otherNorth Germanic languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also ...
is ''Skåne'' (formerly spelled ''Skaane'' in Danish and Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
). The Latinized form ''Scania'' is an exonym in English. Sometimes the endonym Skåne is used in English text, such as in tourist information, even sometimes as ''Skane'' with the diacritic omitted. Scania (as also Dalarna
Dalarna () is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in central Sweden. English exonyms for it are Dalecarlia () and the Dales.
Dalarna adjoins Härjedalen, Hälsingland, Gästrikland, Västmanland and Värmland. It is also bordered by Norwa ...
) is one of the few Swedish provinces for which exonyms are widely used in many languages, such as French ''Scanie'', Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and German ''Schonen'', Polish ''Skania'', Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
''Escania'', Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
''Scania'', etc. For the province's modern administrative counterpart, ''Skåne län'', the endonym ''Skåne'' is used in English.
In the Alfredian translation of Orosius's and Wulfstan's travel accounts, the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
form ''Sconeg'' appears.North, Richard (1997). Heathen Gods in Old English Literature
''.
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pre ...
: 1997, , p. 192. Frankish sources mention a place called ''Sconaowe''; Æthelweard, an Anglo-Saxon historian, wrote about ''Scani''; and in Beowulf's fictional account, the names ''Scedenige'' and ''Scedeland'' appear as names for what is a Danish land.
Etymology
The names ''Scania'' and '' Scandinavia'' are considered to have the same etymology. The southernmost tip of what is today Sweden was called Scania by the Romans and thought to be an island. The actual etymology of the word remains dubious and has long been a matter of debate among scholars. The name is possibly derived from the Germanic root ''*Skaðin-awjã'', which appears inOld Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlemen ...
as . According to some scholars, the Germanic stem can be reconstructed as *''Skaðan-'' meaning "danger" or "damage" (English ''scathing'', German ''Schaden'', Swedish ''skada'').Helle, Knut (2003). "Introduction". ''The Cambridge History of Scandinavia.'' Ed. E. I. Kouri et al. Cambridge University Press, 2003. . Skanör in Scania, with its long Falsterbo reef, has the same stem (''skan'') combined with -''ör'', which means "sandbanks".
Administration
 Between 1719 and 1996, the province was subdivided in two administrative
Between 1719 and 1996, the province was subdivided in two administrative counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
(''län''), Kristianstad County and Malmöhus County, each under a governor (''landshövding'') appointed by the central government of Sweden.
When the first local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-l ...
acts took effect in 1863, each county also got an elected county council (''landsting''). The counties were further divided into municipalities.
The local government reform of 1952 reduced the number of municipalities, and a second subdivision reform, carried out between 1968 and 1974, established today's 33 municipalities ( sv, kommuner) in Scania. The municipalities have municipal governments, similar to city commissions, and are further divided into parishes (''församlingar''). The parishes are primarily entities of the Church of Sweden, but they also serve as a divisioning measure for the Swedish population registration and other statistical uses.
In 1999, the county council areas were amalgamated, forming Skåne Regional Council
Region Scania is the regional council of Scania County in Sweden. Scania County was formed on January 1, 1999, by the amalgamation of the county councils of Malmöhus County and Kristianstad County and some of the tasks handled by Malmö Municip ...
(''Region Skåne''), responsible mainly for public healthcare, public transport
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typi ...
and regional planning
Regional planning deals with the efficient placement of land-use activities, infrastructure, and settlement growth across a larger area of land than an individual city or town. Regional planning is related to urban planning as it relates land ...
and culture.
Heraldry

 During the Danish era, the province had no coat of arms. In Sweden, however, every province had been represented by heraldic arms since 1560. When Charles X Gustav of Sweden suddenly died in 1660 a coat of arms had to be created for the newly acquired province, as each province was to be represented by its arms at his royal funeral. After an initiative from Baron Gustaf Bonde, the Lord High Treasurer of Sweden, the coat of arms of the City of Malmö was used as a base for the new provincial arms. The Malmö coat of arms had been granted in 1437, during the Kalmar Union, by Eric of Pomerania and contains a
During the Danish era, the province had no coat of arms. In Sweden, however, every province had been represented by heraldic arms since 1560. When Charles X Gustav of Sweden suddenly died in 1660 a coat of arms had to be created for the newly acquired province, as each province was to be represented by its arms at his royal funeral. After an initiative from Baron Gustaf Bonde, the Lord High Treasurer of Sweden, the coat of arms of the City of Malmö was used as a base for the new provincial arms. The Malmö coat of arms had been granted in 1437, during the Kalmar Union, by Eric of Pomerania and contains a Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
n griffin's head. To distinguish it from the city's coat of arms the tinctures were changed and the official blazon for the provincial arms is, in English: '' Or, a griffin's head erased gules, crowned azure and armed azure, when it should be armed.''
The province was divided in two administrative counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
1719–1996. Coats of arms were created for these entities, also using the griffin motif. The new Skåne County, operative from 1 January 1997, got a coat of arms that is the same as the province's, but with reversed tinctures. When the county arms is shown with a Swedish royal crown, it represents the County Administrative Board, which is the regional presence of central government authority. In 1999 the two county councils () were amalgamated forming Region Skåne. It is the only one of its kind using a heraldic coat of arms. It is also the same as the province's and the county's, but with a golden griffin's head on a ''blue'' shield. The 33 municipalities within the county also have coats of arms.
The ''Scania Griffin'' has become a well-known symbol for the province and is also used by commercial enterprises. It is, for instance, included in the logotype
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name it represents as in a wordm ...
s of the automotive manufacturer Scania AB
Scania AB is a major Swedish manufacturer headquartered in Södertälje, focusing on commercial vehicles—specifically heavy lorries, trucks and buses. It also manufactures diesel engines for heavy vehicles as well as marine and general ind ...
and the airline
An airline is a company that provides air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines use aircraft to supply these services and may form partnerships or alliances with other airlines for codeshare agreements, in wh ...
Malmö Aviation.
Coat of arms
History


 Scania was first mentioned in written texts in the 9th century. It came under Danish king Harald Bluetooth in the middle of the 10th century. It was then a region that included Blekinge and
Scania was first mentioned in written texts in the 9th century. It came under Danish king Harald Bluetooth in the middle of the 10th century. It was then a region that included Blekinge and Halland
Halland () is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap''), on the western coast of Götaland, southern Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömseb ...
, situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula and formed the eastern part of the kingdom of Denmark. This geographical position made it the focal point of the frequent Dano-Swedish wars
Dano-Swedish War may refer to one of multiple wars which took place between the Kingdom of Sweden and the Kingdom of Denmark (from 1450 in personal union with the Kingdom of Norway) up to 1814:
List of wars Legendary wars between Denmark a ...
for hundreds of years.
By the Treaty of Roskilde
The Treaty of Roskilde (concluded on 26 February ( OS), or 8 March 1658) ( NS) during the Second Northern War between Frederick III of Denmark–Norway and Karl X Gustav of Sweden in the Danish city of Roskilde. After a devastating defeat ...
in 1658, all Danish lands east of Øresund were ceded to the Swedish Crown. First placed under a Governor-General, the province was eventually integrated into the kingdom of Sweden. The last Danish attempt to regain its lost provinces failed after the 1710 Battle of Helsingborg
The Battle of Helsingborg was the last major engagement of the Great Northern War to take place on Swedish soil, and resulted in a decisive victory of a Swedish force of 14,000 men under the command of Magnus Stenbock against a Danish force of ...
.
In 1719, the province was subdivided in two counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
and administered in the same way as the rest of Sweden. Scania has since that year been fully integrated in the Swedish nation. In the following summer, July 1720, the last peace treaty between Sweden and Denmark was signed.
On 28 November 2017 it was ruled that the Scanian flag would become the official flag of Scania.
Politics
During Sweden's financial crisis in the early and mid-1990s, Scania, Västra Götaland and Norrbotten were among the hardest hit in the country, with high unemployment rates as a result.McCallion, Malin Stegmann (2004)The Europeanisation of Swedish Regional Government
. ''Policy Networks in Sub National Governance: Understanding Power Relations''. Paper 8, Workshop 25, European Consortium of Political Research. 2004 Joint Sessions of Workshops, Uppsala, Sweden. In response to the crisis, the County Governors were given a task by the government in September 1996 to co-ordinate various measures in the counties to increase economic growth and employment by bringing in regional actors. The first proposal for regional autonomy and a regional parliament had been introduced by the Social Democratic Party's local districts in Scania and Västra Götaland already in 1993. When Sweden joined the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
two years later, the concept " Regions of Europe" came in focus and a more regionalist-friendly approach was adopted in national politics. These factors contributed to the subsequent transformation of Skåne County into one of the first "trial regions" in Sweden in 1999, established as the country's first "regional experiment".Peterson, Martin (2003)"The Regions and Regionalism: Regionalism in Sweden"
. ''CoR Report Sweden''. The Interdisciplinary Centre for Comparative Research in the Social Sciences, EUROPUB Case Study (WP2). The relatively strong regional identity in Scania is often referred to in order to explain the general support in the province for the decentralization efforts introduced by the Swedish government. On the basis of large scale interview investigations about Region Skåne in Scania, scholars have found that the prevailing trend among the inhabitants of Scania is to "
ook
Ook, OoK or OOK may refer to:
* Ook Chung (born 1963), Korean-Canadian writer from Quebec
* On-off keying, in radio technology
* Toksook Bay Airport (IATA code OOK), in Alaska
* Ook!, an esoteric programming language based on Brainfuck
* Ook, th ...
upon their region with more positive eyes and a firm reliance that it would deliver the goods in terms of increased democracy and constructive results out of economic planning".
Transportation
 Electrified dual track railroad exists from the border with
Electrified dual track railroad exists from the border with Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
at the Øresund Bridge
The Öresund or Øresund Bridge ( da, Øresundsbroen ; sv, Öresundsbron ; hybrid name: ) is a combined railway and motorway bridge across the Øresund strait between Denmark and Sweden. It is the longest in Europe with both roadway and rai ...
to Malmö and onwards to Lund. The latter part is currently being upgraded to four tracks and expected to enter service in 2023.Four tracks Malmö-Lund – TrafikverketIn Lund, the tracks split into two directions.Sveriges järnvägsnät - Trafikverket
. Trafikverket.se (31 March 2015). Retrieved on 24 June 2015. The dual tracks going towards Gothenburg end at
Helsingborg
Helsingborg (, , , ) is a city and the seat of Helsingborg Municipality, Scania (Skåne), Sweden. It is the second-largest city in Scania (after Malmö) and ninth-largest in Sweden, with a population of 113,816 (2020). Helsingborg is the cent ...
, while the other branch continues beyond the provincial border to neighbouring Småland, close to Killeberg
Killeberg () is a locality situated in Osby Municipality, Scania County, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of Swe ...
.; chose "linjekarta för tåg (PDF)" This latter dual track continues to mid-Sweden. There are also a few single track railroads connecting cities like Trelleborg, Ystad
Ystad (; older da, Ysted) is a town and the seat of Ystad Municipality, in Scania County, Sweden. Ystad had 18,350 inhabitants in 2010. The settlement dates from the 11th century and has become a busy ferryport, local administrative centre, a ...
and Kristianstad. Just as five Scanian stations are served partly (Hässleholm
Hässleholm (older da, Hasselholm) is a locality and the seat of Hässleholm Municipality, Scania County, Sweden with 18,500 inhabitants in 2010.
Overview
Hässleholm was gradually developed from 1860 in connection with the construction of the ...
and Osby) or entirely (Ballingslöv
Ballingslöv is a locality situated in Hässleholm Municipality, Skåne County, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom ...
, Hästveda
Hästveda is a locality situated in Hässleholm Municipality, Scania County, Sweden with 1,623 inhabitants in 2010.
The etymology of Hästveda indicates that the name originally signified a wood, or forest where horses were kept.
Hästveda Chur ...
and Killeberg
Killeberg () is a locality situated in Osby Municipality, Scania County, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of Swe ...
) by Småland local trains, the Scanian Pågatåg trains serve Markaryd
Markaryd () is a locality and the seat of Markaryd Municipality, Kronoberg County, Sweden with 3,966 inhabitants in 2010.
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Markaryd is twinned with:
* Bytów, Poland
Poland, officia ...
in Småland.
There are basically three ticket systems: Skånetrafiken tickets can be purchased for all regional traffic including to Denmark, while the Danish Rejsekort system can only be used at stations served by Øresundståg
Øresundståg (, ) is a passenger train network operated by Skånetrafiken and Transdev in the transnational Øresund Region of Denmark and Sweden. The name is a hybrid of the Danish ''Øresundstog'' and the Swedish ''Öresundståg'', both meani ...
and equipped with special card readers. Additionally, Swedish national SJ-tickets are available for longer trips to the north.
The E6 motorway is the main artery through the western part of Scania all the way from Trelleborg to the provincial border towards neighbouring Halland
Halland () is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap''), on the western coast of Götaland, southern Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömseb ...
. It continues along the Swedish west coast to Gothenburg and most of the way to the Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
border. There are also several other motorways, especially around Malmö. Since 2000, the economic focus of the region has changed, with the opening of a road link across the Øresund Bridge to Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
.
The car ferry service between Helsingborg
Helsingborg (, , , ) is a city and the seat of Helsingborg Municipality, Scania (Skåne), Sweden. It is the second-largest city in Scania (after Malmö) and ninth-largest in Sweden, with a population of 113,816 (2020). Helsingborg is the cent ...
and Helsingør
has 70 departures in each direction daily .
There are three minor airports in Sturup, Ängelholm
Ängelholm is a locality and the seat of Ängelholm Municipality in Skåne, Sweden with 39,612 inhabitants in 2010.
History
The old settlement ''Rynestad'' was mentioned around the year 1600.
The city was founded in 1516 as Engelholm by King Chri ...
and Kristianstad. The nearby Copenhagen Airport, which is the largest international airport in the Nordic countries, also serves the province.
Geography and environmental factors


 Unlike some regions of Sweden, the Scanian landscape is generally not
Unlike some regions of Sweden, the Scanian landscape is generally not mountainous
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher th ...
, though a few examples of uncovered cliffs can be found at Hovs Hallar, at Kullaberg
Kullaberg () is a peninsula and nature reserve of land protruding into the Kattegat in Höganäs Municipality near the town of Mölle in southwest Sweden. The site in the province of Skåne is an area of considerable biodiversity supporting a num ...
, and on the island Hallands Väderö. With the exception of the lake-rich and densely forested northern parts ( Göinge), the rolling hills in the north-west (the Bjäre and Kulla peninsulas) and the beech-wood-clad areas extending from the slopes of the horsts, a sizeable portion of Scania's terrain consists of plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s. Its low profile and open landscape distinguish Scania from most other geographical regions of Sweden which consist mainly of waterway-rich, cool, mixed coniferous forest
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All exta ...
s, boreal taiga and alpine tundra. The province has several lakes but there are relatively few compared to Småland, the province directly to the north. Stretching from the north-western to the south-eastern parts of Scania is a belt of deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
forests following the Linderödsåsen ridge and previously marking the border between Malmöhus County and Kristianstad County. The much denser fir forests — typical of the greater part of Sweden — are only found in the north-eastern Göinge parts of Scania along the border with the forest-dominated province of Småland. While the landscape typically has a slightly sloping profile, in some places, such as north of Malmö, the terrain is almost completely flat.
The narrow lakes with a long north to south extent, which are very common further north, are lacking in Scania. The largest lake, Ivösjön in the north-east, has similarities with the lakes further north, but has a different shape. All other lakes tend to be round, oval or of more complex shape and also lack any specific cardinal direction. Ringsjön, in the middle of the province, is the largest of such lakes.
In the winter, some smaller lakes east of Lund often attract young Eurasian sea eagles (''Haliaeetus albicilla'').
Ven
Ven may refer to:
Places
* Ven, Heeze-Leende, a hamlet in the Netherlands
* Ven (Sweden), an island
* Ven, Tajikistan, a town
* VEN or Venezuela
Other uses
* von Economo neurons, also called ''spindle neurons''
* '' Vên'', an EP by Eluveiti ...
, between the towns of Helsingborg and Landskrona, and in parts of the south and south-east coasts. In other Swedish provinces, steep coastlines usually reveal primary rock Primary rock is an early term in geology that refers to crystalline rock formed first in geologic time, containing no organic remains, such as granite, gneiss and schist as well as igneous and magmatic formations from all ages. Webster's Revise ...
instead.
The two major plains, Söderslätt in the south-west and Österlen
Österlen () ( da, Østerlen) is a region in the southeast of the Swedish province of Scania (Skåne). Historically, the region was shared between the counties of Kristianstad and Malmöhus for a small part in the southwest, until Skåne County w ...
in the south-east, consist of highly fertile agricultural land. The yield per unit area is higher than in any other region in Sweden. The Scanian plains are an important resource for Sweden since 25–95% of the total production of various types of cereals come from the region. Almost all Swedish sugar beet comes from Scania; the plant needs a long vegetation period. The same applies also to corn, pea and rape (grown for its oil), although these plants are less imperative in comparison with sugar beets. The soil is among the most fertile in the world.
The Kullaberg
Kullaberg () is a peninsula and nature reserve of land protruding into the Kattegat in Höganäs Municipality near the town of Mölle in southwest Sweden. The site in the province of Skåne is an area of considerable biodiversity supporting a num ...
Nature Preserve in northwest Scania is home to several rare species including spring vetchling, '' Lathyrus sphaericus''.
Geology and geomorphology
The gross relief of Scania reflects more the preglacial development than theerosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
and deposits caused by the Quaternary glaciers. In Swedish the word ''ås'' commonly refers to esker
An esker, eskar, eschar, or os, sometimes called an ''asar'', ''osar'', or ''serpent kame'', is a long, winding ridge of stratified sand and gravel, examples of which occur in glaciated and formerly glaciated regions of Europe and North Ame ...
s, but major landmarks in Scania, such as Söderåsen, are horsts formed by tectonic inversion along the Sorgenfrei-Tornquist Zone
The Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ), also known as the Tornquist Zone, is the crustal boundary between the Precambrian East European Craton and the Phanerozoic orogens of South-Western Europe. The zone runs from the North Sea to the Black Sea. ...
in the late Cretaceous. The Scanian horsts run in a north-west to south-east direction, marking the southwest border of Fennoscandia. Lidmar-Bergström, Karna and Jens-Ove Näslund (2005). "Uplands and Lowlands in Southern Sweden". In ''The Physical Geography of Fennoscandia''. Ed. Matti Seppälä. Oxford University Press, 2005, pp. 255–261. . Tectonic activity of the Sorgenfrei-Tornquist Zone during the break-up of Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
in the Jurassic and Cretaceous epochs led to the formation of hundreds of small volcanoes in central Scania. Remnants of the volcanoes are still visible today. Parallel with volcanism a hilly peneplain formed in northeastern Scania due to weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement) ...
and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
of basement rocks. The kaolinite formed by this weathering can be observed at Ivö Klack. In the Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
age of the Late Cretaceous a sea level rise led to the complete drowning of Scania. Subsequently, marine sediments buried old surfaces preserving the rocky shores and hilly terrain of the day.
In the Paleogene period southern Sweden was at a lower position relative to sea level but was likely still above it as it was covered by sediments. Rivers flowing over the South Småland peneplain flowed also across Scania which was at the time covered by thick sediments. As the relative sea level sank and much of Scania lost its sedimentary cover antecedent rivers begun to incise the Söderåsen horst forming valleys. During deglaciation these valleys likely evacuated large amounts of melt-water. The relief of Scania's south-western landscape was formed by the accumulation of thick Quaternary sediments during the Quaternary glaciations.
Vegetation and vegetation zones
The vast majority of Scania belongs to the European hardwood vegetation zone, a considerable part of which is now agricultural rather than the original forest. This zone covers Europe west ofPoland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and north of the Alps, and includes the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, northern and central France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and the countries and regions to the south and southeast of the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
up to Denmark. A smaller north-eastern part of Scania is part of the pinewood vegetation zone, in which spruce grows naturally. Within the larger part, pine may grow together with birch on sandy soil. The most common tree is beech. Other common trees are willow, oak, ash, alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few sp ...
and elm
Elms are deciduous and semi-deciduous trees comprising the flowering plant genus ''Ulmus'' in the plant family Ulmaceae. They are distributed over most of the Northern Hemisphere, inhabiting the temperate and tropical-montane regions of North ...
(which until the 1970s formed a few forests but now is heavily infected by the elm disease). Also rather southern trees like walnut tree
Walnut trees are any species of tree in the plant genus ''Juglans'', the type genus of the family Juglandaceae, the seeds of which are referred to as walnuts. All species are deciduous trees, tall, with pinnate leaves , with 5–25 leafl ...
, chestnut and hornbeam
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the flowering plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The 30–40 species occur across much of the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Origin of names
The common English name ''hornbeam ...
can be found. In parks horse chestnut, lime
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a color between yellow and green
Lime may also refer to:
Botany ...
and maple are commonly planted as well. Common fruit trees planted in commercial orchards and private gardens include several varieties of apple, pear, cherry and plum; strawberries are commercially cultivated in many locations across the province. Examples of wild berries grown in domesticated form are blackberry, raspberry, cloudberry (in the north-east), blueberry, wild strawberry and loganberry
The loganberry (''Rubus'' × ''loganobaccus'') is a hybrid of the North American blackberry (''Rubus ursinus'') and the European raspberry ('' Rubus idaeus'').
The plant and the fruit resemble the blackberry more than the raspberry, but the fru ...
.
National parks
Three of the 29 National parks of Sweden are situated in Scania. * Dalby Söderskog * Stenshuvud * SöderåsenExtremes
* Southernmost point: Smygehuk, Trelleborg Municipality, (55° 20' N) (also the southernmost point of Sweden) * Northernmost point: Gränsholmen, Osby Municipality * Westernmost point: Kulla udd, Höganäs Municipality * Easternmost point: Nyhult, Bromölla Municipality * Highest point: Highest peak of Söderåsen, 212metres
The metre (British spelling
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable va ...
* Lowest spot: Kristianstad, −2.7 metres
The metre (British spelling
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable va ...
(also the lowest spot in all of Sweden)
* Largest lake: Ivösjön, 55 km2
* Largest island: Ven
Ven may refer to:
Places
* Ven, Heeze-Leende, a hamlet in the Netherlands
* Ven (Sweden), an island
* Ven, Tajikistan, a town
* VEN or Venezuela
Other uses
* von Economo neurons, also called ''spindle neurons''
* '' Vên'', an EP by Eluveiti ...
, 7.5 km2
Population
Halland
Halland () is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap''), on the western coast of Götaland, southern Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömseb ...
, this includes the village Östra Karup and some area around it, around 500 people live in Båstad municipality, but beyond the historical boundaries of the Scanian province.
* The western part of Scania (yellow on the map and close to the Øresund sea) covers 3201.3 km2 of land, and had (in April 2013) 925,982 inhabitants, almost 290 inhabitants/km2
* The other municipalities cover 7281.3 km2of land, and had at the same time only 341,009 inhabitants or 47 inhabitants/km2
* The same figures for the entire province are 10482.6 km2, 1,266,991 inhabitants and 121 inhabitants/km2
These figures can be compared with around to 21 inhabitants per km2 for entire Sweden.
Population around Øresund
Western Scania has a high population density, not only by Scandinavian standards but also by average European standards, at close to 300 inhabitants per square kilometre. But the Danish Copenhagen region at north-eastZealand
Zealand ( da, Sjælland ) at 7,031 km2 is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020.
It is the 1 ...
, on the other side of Øresund Sea, is even more densely populated. The north-east part of Zealand
Zealand ( da, Sjælland ) at 7,031 km2 is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020.
It is the 1 ...
(or the Danish Region Hovedstaden
The Capital Region of Denmark ( da, Region Hovedstaden, ) is the easternmost administrative region of Denmark. The Capital Region has 29 municipalities and a regional council consisting of 41 elected members. As of 1 August 2021 the chairperso ...
without the Baltic island of Bornholm) has a population density of 878 inhabitants/km2, most of Greater Copenhagen
The urban area of Copenhagen (also known as Greater Copenhagen) ( da, Storkøbenhavn or ), lying mostly in the Capital Region of Denmark but also in Region Zealand, consist of Copenhagen and Frederiksberg municipalities and the former Copenhagen ...
included.
By adding the population of western Scania to the same of Metropolitan area of Copenhagen, then close to 3 million people live around the Øresund sea, within a maximum distance from Øresund of 25 to 30 kilometres, at a land surface of approx. 6100 km2 (approx 460 inhabitants/km2). This is in many ways a better measurement of describing the area around Øresund than what the far wider Øresund Region constitutes, as the latter includes also eastern Scania (whose beaches are Baltic Sea ones and is far less populated) as well as all Denmark east of the Great Belt
The Great Belt ( da, Storebælt, ) is a strait between the major islands of Zealand (''Sjælland'') and Funen (''Fyn'') in Denmark. It is one of the three Danish Straits.
Effectively dividing Denmark in two, the Belt was served by the Great B ...
.
Regardless of counting a smaller area with higher population density or a larger one, the Øresund Strait is located in the largest metropolitan area in Scandinavia with Finland.
Cities


 In
In 1658
Events
January–March
* January 13 – Edward Sexby, who had plotted against Oliver Cromwell, dies in the Tower of London.
* January 30 – The " March Across the Belts" (''Tåget över Bält''), Sweden's use of winte ...
, the following ten places in Scania were chartered and held town rights: Lund (since approximately 990), Helsingborg (1085), Falsterbo (approximately 1200), Ystad
Ystad (; older da, Ysted) is a town and the seat of Ystad Municipality, in Scania County, Sweden. Ystad had 18,350 inhabitants in 2010. The settlement dates from the 11th century and has become a busy ferryport, local administrative centre, a ...
(approximately 1200), Skanör (approximately 1200), Malmö (approximately 1250), Simrishamn (approximately 1300), Landskrona (1413), and Kristianstad (1622). Others had existed earlier, but lost their privileges. Ängelholm got new privileges in 1767, and in 1754, Falsterbo and Skanör were merged. The concept of municipalities was introduced in Sweden in 1863, making each of the towns a city municipality of its own. In the 19th and 20th centuries, four more municipalities were granted city status, Trelleborg (1867), Eslöv (1911), Hässleholm
Hässleholm (older da, Hasselholm) is a locality and the seat of Hässleholm Municipality, Scania County, Sweden with 18,500 inhabitants in 2010.
Overview
Hässleholm was gradually developed from 1860 in connection with the construction of the ...
(1914) and Höganäs
Höganäs () (old da, Højenæs) is a locality and the seat of Höganäs Municipality, Scania County, Sweden with 14,107 inhabitants in 2010.
Höganäs is nationally known for its ceramics industry, Höganäs Keramik. Höganäs Keramik is par ...
(1936). The system of city status was abolished in 1971.
Over 90% of Scania's population live in urban areas
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
. In 2000, the Øresund Bridge
The Öresund or Øresund Bridge ( da, Øresundsbroen ; sv, Öresundsbron ; hybrid name: ) is a combined railway and motorway bridge across the Øresund strait between Denmark and Sweden. It is the longest in Europe with both roadway and rai ...
– the longest combined road and rail bridge in Europe – linked Malmö and Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
, making Scania's population part of a 3.6 million total population in the Øresund Region. In 2005, the region had 9,200 commuters crossing the bridge daily, the vast majority of them from Malmö to Copenhagen.
The following localities had more than 10,000 inhabitants (year 2010).
# Malmö, 280,415*
# Helsingborg
Helsingborg (, , , ) is a city and the seat of Helsingborg Municipality, Scania (Skåne), Sweden. It is the second-largest city in Scania (after Malmö) and ninth-largest in Sweden, with a population of 113,816 (2020). Helsingborg is the cent ...
, 97,122
# Lund, 82,800
# Kristianstad, 35,711
# Landskrona, 30,499
# Trelleborg, 28,290
# Ängelholm
Ängelholm is a locality and the seat of Ängelholm Municipality in Skåne, Sweden with 39,612 inhabitants in 2010.
History
The old settlement ''Rynestad'' was mentioned around the year 1600.
The city was founded in 1516 as Engelholm by King Chri ...
, 23,240
# Hässleholm
Hässleholm (older da, Hasselholm) is a locality and the seat of Hässleholm Municipality, Scania County, Sweden with 18,500 inhabitants in 2010.
Overview
Hässleholm was gradually developed from 1860 in connection with the construction of the ...
, 18,500
# Ystad
Ystad (; older da, Ysted) is a town and the seat of Ystad Municipality, in Scania County, Sweden. Ystad had 18,350 inhabitants in 2010. The settlement dates from the 11th century and has become a busy ferryport, local administrative centre, a ...
, 18,350
# Eslöv, 17,748
# Staffanstorp, 14,808
# Höganäs
Höganäs () (old da, Højenæs) is a locality and the seat of Höganäs Municipality, Scania County, Sweden with 14,107 inhabitants in 2010.
Höganäs is nationally known for its ceramics industry, Höganäs Keramik. Höganäs Keramik is par ...
, 14,107
# Kävlinge
Kävlinge () is a locality and the seat of Kävlinge Municipality, Skåne County, Sweden with 32,341 inhabitants in 2021.
In 1996, a train containing large amounts of ammonia derailed and around 9,000 people had to be evacuated from the area. Thi ...
& Furulund
Furulund is a locality situated in Kävlinge Municipality, Skåne County, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of Sw ...
, 13,200
Population development
 It has been estimated that around 1570, Scania had about 110,000 inhabitants. But before the plague in the middle of the 14th century the population of all Danish territory east of Øresund (Scania, Island of Bornholm, Blekinge and Halland) may have exceeded 250,000.
The figures here are from two different sources.
*2015 data.
It has been estimated that around 1570, Scania had about 110,000 inhabitants. But before the plague in the middle of the 14th century the population of all Danish territory east of Øresund (Scania, Island of Bornholm, Blekinge and Halland) may have exceeded 250,000.
The figures here are from two different sources.
*2015 data.
Hundreds
Scania was formerly divided into 23 hundreds.Climate and seasons
Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute
The Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute ( sv, Sveriges meteorologiska och hydrologiska institut, abbreviated SMHI) is a Government agency in Sweden and operates under the Ministry of the Environment. SMHI has expertise within the a ...
(SMHI) weather stations in Scania and three stations further north for comparison issues. Average temperature in this case means the average of the temperature taken throughout both day and night unlike the more usual daily maximum or minimum average. This is done for specific measured periods of thirty years. The last period began at 1 January 1961 and ended at 31 December 1990. The current such period started at 1 January 1991 and will end by 31 December 2020. At that time it will be possible to with a high degree of mathematical certainty to measure possible climate changes, by comparing two separate periods of 30 years with each other.
All three of the northern locations are at low altitude and fairly close to the Baltic Sea.
Compared with locations further north, the Scanian climate differs primary by being far less cold during the winter and in having longer springs and autumns. While the July temperatures doesn't differ much (see table above).
The highest temperature ever recorded in the province is (Ängelholm
Ängelholm is a locality and the seat of Ängelholm Municipality in Skåne, Sweden with 39,612 inhabitants in 2010.
History
The old settlement ''Rynestad'' was mentioned around the year 1600.
The city was founded in 1516 as Engelholm by King Chri ...
, 30 July 1947) and the lowest ever recorded is (Stehag
Stehag () is a locality situated in Eslöv Municipality, Skåne County, Sweden with 1,261 inhabitants as of 2018.
, 26 January 1942) Temperatures below are relatively rare even at night, while summer temperatures above occurs once in a while every summer. Precipitation is spread fairly evenly, both across the province and during the year.
Slightly more precipitation falls during July and August than during the other months.
Winter
A typical winter, with average temperatures around the freezing point during January and February, means that a period of mild weather (often windy or/and rainy) is followed by a colder period (when precipitation falls as snow)—and then the mild weather returns etc., rather than a stable temperature close to zero degrees. During the colder periods, the temperature often is below freezing point also during daytime while during the milder periods temperatures below freezing point are unusual even at night. During the ''mild periods'' temperatures slightly below freezing point only occur if the night is both calm and free of clouds. If the same circumstances occur during a ''cold period,'' the nights can get very cold though. All together this adds up to a 24 hrs/day "winter average" of around 0 degrees In the north-eastern corner (and at the top of the ridges) the winter is in general notably colder though, and a snow cover may last for weeks.Spring
March is locally known as the first month of the spring. The colder periods are fewer and sunny days may even feel pleasant. During April and early May temperature rises rather fast. Though spring (especially in the sense "first heat") arrives later compared to northernmost Germany and Poland. This is particularly notable in the south-eastern corner. This is explained by the open coastline and low temperatures in theBaltic sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
. Øresund is both narrow and shallow, and gets warmer faster. The most common Scanian tree, the beech, usually comes into leaf during the last days of April or the first days of May, but is often delayed by 10–14 days in the south-east, due to the Baltic Sea chill factor.
Summer
Unlike the other seasons, summer is not warmer in Scania compared to many other Swedish provinces. As in winter, the weather usually changes between periods that either are sunny and fairly hot (up to 30 degrees, even higher away from the coastlines), and periods of unstable cloudy and cooler weather. The time between sunset and sunrise during June and earliest July is less than 7 hours, and both the dawn and the dusk are rather long as well. However, there are still a few hours of real night. Further north in Sweden there is no real night, as dusk turns into dawn. (In northernmost Sweden, the sun does not set at all for around two months.)Autumn
The autumn in Scania is a slow process, compared with more northern parts of Sweden (but a faster one, when comparing with any part of the British Isles). During the first half of September, temperatures usually are not so much affected, but the sunset is obviously earlier compared with in June. Temperatures drop in steps. Every new period with sunny weather becomes a bit cooler than the last one. By the end of October the defoliation process becomes evident. But not until late November have all the trees lost their leaves. The period when storms and even hurricanes becomes most likely to occur is between November and February. Most hurricanes come from the Atlantic Ocean and don't involve snow or temperatures below freezing point. Late Scanian autumn is in general benefited from the surrounding waters (the opposite effect early spring).Culture
 Scania's long-running and sometimes intense trade relations with other communities along the coast of the European continent through history have made the culture of Scania distinct from other geographical regions of Sweden. Its open landscape, often described as a colourful patchwork quilt of
Scania's long-running and sometimes intense trade relations with other communities along the coast of the European continent through history have made the culture of Scania distinct from other geographical regions of Sweden. Its open landscape, often described as a colourful patchwork quilt of wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
and rapeseed
Rapeseed (''Brassica napus ''subsp.'' napus''), also known as rape, or oilseed rape, is a bright-yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae (mustard or cabbage family), cultivated mainly for its oil-rich seed, which naturally contains a ...
fields, and the relatively mild climate at the southern tip of the Scandinavian Peninsula, have inspired many Swedish artists and authors to compare it to European regions like Provence in southern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. Among the many authors who have described the "foreign" continental elements of the Scanian landscape, diet and customs are August Strindberg
Johan August Strindberg (, ; 22 January 184914 May 1912) was a Swedish playwright, novelist, poet, essayist and painter.Lane (1998), 1040. A prolific writer who often drew directly on his personal experience, Strindberg wrote more than sixty p ...
and Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalise ...
. In 1893 August Strindberg wrote about Scania: "In beautiful, large wave lines, the fields undulate down toward the lake; a small deciduous forest limits the coastline, which is given the inviting look of the Riviera, where people shall walk in the sun, protected from the north wind. .. The Swede leaves the plains with a certain sense of comfort, because its beauty is foreign to him." In another chapter he states: "The Swedes have a history that is not the history of the South Scandinavians. It must be just as foreign as Vasa’s history is to the Scanian."
In Ystad, singer-songwriter Michael Saxell
Michael Saxell (born 1 October 1956) is a singer-songwriter, composer, lyricist, multi-instrumentalist and producer. He was born in Helsingborg, Sweden but has spent many years on the Canadian west coast. He composed music for the Colin Nutley m ...
's popular Scanian anthem ''Om himlen och Österlen'' (Of Heaven and Österlen), the flat, rolling hill landscape is described as appearing to be a little closer to heaven and the big, unending sky.
Scania's historical connection to Denmark, the vast fertile plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s, the deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
forests and the relatively mild climate make the province culturally and physically distinct from the emblematic Swedish cultural landscape of forests
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
and small hamlets
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. Its size relative to a parish can depend on the administration and region. A hamlet may be considered to be a smaller settlement or subdivision or satellite entity to a lar ...
.
Architecture
 Traditional Scanian architecture is shaped by the limited availability of wood; it incorporates different applications of the building technique called
Traditional Scanian architecture is shaped by the limited availability of wood; it incorporates different applications of the building technique called half-timbering
Timber framing (german: Holzfachwerk) and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and joined timbers with joints secured by large wooden ...
. In the cities, the infill of the façades consisted of bricks, whereas the country-side half-timbered houses had infill made of clay and straw. Unlike many other Scanian towns, the town of Ystad
Ystad (; older da, Ysted) is a town and the seat of Ystad Municipality, in Scania County, Sweden. Ystad had 18,350 inhabitants in 2010. The settlement dates from the 11th century and has become a busy ferryport, local administrative centre, a ...
has managed to preserve a rather large core of its half-timbered architecture in the city center—over 300 half-timbered houses still exist today. Many of the houses in Ystad were built in the renaissance style that was common in the entire Øresund Region, and which has also been preserved in Elsinore (Helsingør). Among Ystad's half-timbered houses is the oldest such building in Scandinavia, ''Pilgrändshuset'' from 1480.
In Göinge, located in the northern part of Scania, the architecture was not shaped by a scarcity of wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
, and the pre-17th-century farms consisted of graying, recumbent timber buildings around a small grass and cobblestone courtyard. Only a small number of the original Göinge farms remain today. During two campaigns, the first in 1612 by Gustav II Adolf
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">N.S_19_December.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/now ...
and the second by Charles XI in the 1680s, entire districts were levelled by fire. In Örkened Parish, in what is now eastern Osby Municipality, the buildings were destroyed to punish the different villages for their protection of members of the Snapphane
A ''snapphane'' was a member of a 17th-century pro- Danish guerrilla organization, auxiliaries or paramilitary troops that fought against the Swedes in the Second Northern and Scanian Wars, primarily in the eastern former Danish provinces that h ...
movement in the late 17th century. An original, 17th century Göinge farm, ''Sporrakulla Farm'', has been preserved in a forest called Kullaskogen, a nature reserve close to Glimåkra in Östra Göinge. According to the local legend, the farmer saved the farm in the first raid of 1612 by setting a forest fire in front of it, making the Swedish troops believe that the farm had already been plundered and set ablaze.
A number of Scanian towns flourished during the Viking Age. The city of Lund is believed to have been founded by the Viking-king Sweyn Forkbeard. Scanian craftsmen and traders were prospering during this era and Denmark's first and largest mint was established in Lund. The first Scanian coins have been dated to 870 AD.Hauberg, P. (1900). ''Myntforhold og Udmyntninger i Danmark indtil 1146''. D. Kgl. Danske Vidensk. Selsk. Skr., 6. Række, historisk og filosofisk Afd. V. I.Chapter III: Danmarks Mynthistorie indtil 1146
, an
published online by Gladsaxe Gymnasium. (In Danish). Retrieved 10 January 2007. The archaeological excavations performed in the city indicate that the oldest known
stave church
A stave church is a medieval wooden Christian church building once common in north-western Europe. The name derives from the building's structure of post and lintel construction, a type of timber framing where the load-bearing ore-pine posts ar ...
in Scania was built by Sweyn Forkbeard in Lund in 990.City of LundTouchdowns in the History of Lund
. Official site for the City of Lund. Retrieved 10 January 2006. In 1103, Lund was made the archbishopric for all of Scandinavia. Many of the old churches in today's Scanian landscape stem from the medieval age, although many church renovations, extensions and destruction of older buildings took place in the 16th and 19th century. From those that have kept features of the authentic style, it is still possible to see how the medieval, Romanesque or
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
churches of Danish Scania looked like. Many Scanian churches have distinctive crow-stepped gable
A stepped gable, crow-stepped gable, or corbie step is a stairstep type of design at the top of the triangular gable-end of a building. The top of the parapet wall projects above the roofline and the top of the brick or stone wall is stacked in ...
s and sturdy church porches, usually made of stone.
The first version of Lund Cathedral was built in 1050, in sandstone from Höör, on the initiative of Canute the Holy
Canute IV ( – 10 July 1086), later known as Canute the Holy ( da, Knud IV den Hellige) or Saint Canute (''Sankt Knud''), was King of Denmark from 1080 until 1086. Canute was an ambitious king who sought to strengthen the Danish monarchy, ...
.Terra ScaniaeLunds Domkyrka
. (In Swedish). Retrieved 11 January 2007. The oldest parts of today's cathedral are from 1085, but the actual cathedral was constructed during the first part of the 12th century with the help of stone cutters and sculptors from the Rhine valley and
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and was ready for use in 1123. It was consecrated in 1145 and for the next 400 years, Lund became the ecclesiastical power center for Scandinavia and one of the most important cities in Denmark. The cathedral was altered in the 16th century by architect Adam van Düren and later by Carl Georg Brunius
Carl Georg Brunius (23 March 1793 – 12 November 1869) was a classical scholar, art historian, archaeologist and architect.
He served as a professor and rector at Lund University. During 1833-59, he led the restoration work of Lund Cathedr ...
and Helgo Zetterwall
Helgo Nikolaus Zettervall, older spelling ''Zetterwall'', (21 November 1831 – 17 March 1907) was a Swedish architect and professor of the Royal Swedish Academy of Arts. He is best known for his drastic restorations of churches and other b ...
.
 Scania also has churches built in the gothic style, such as Saint Petri Church in Malmö, dating from the early 14th century. Similar buildings can be found in all Hansa cities around the
Scania also has churches built in the gothic style, such as Saint Petri Church in Malmö, dating from the early 14th century. Similar buildings can be found in all Hansa cities around the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
(such as Helsingborg and Rostock). The parishes in the countryside did not have the means for such extravagant buildings. Possibly the most notable countryside church is the ancient and untouched stone church in Dalby. It is the oldest stone church in Sweden, built around the same time as Lund cathedral. After the Lund Cathedral was built, many of the involved workers travelled around the province and used their acquired skills to make baptism fonts, paintings and decorations, and naturally architectural constructions.
 Scania has 240 palaces and country estates—more than any other province in Sweden. Many of them received their current shape during the 16th century, when new or remodelled castles started to appear in greater numbers, often erected by the reuse of stones and material from the original 11th–15th-century castles and abbeys found at the estates. Between 1840 and 1900, the
Scania has 240 palaces and country estates—more than any other province in Sweden. Many of them received their current shape during the 16th century, when new or remodelled castles started to appear in greater numbers, often erected by the reuse of stones and material from the original 11th–15th-century castles and abbeys found at the estates. Between 1840 and 1900, the landed nobility Landed nobility or landed aristocracy is a category of nobility in the history of various countries, for which landownership was part of their noble privileges. Their character depends on the country.
*The notion of landed gentry in the United Kin ...
in Scania built and rebuilt many of the castles again, often by modernizing previous buildings at the same location in a style that became typical for Scania. The style is a mixture of different architectural influences of the era, but frequently refers back to the style of the 16th-century castles of the Reformation era, a time when the large estates of the Catholic Church were made Crown property and the abbeys bartered or sold to members of the aristocracy by the Danish king. For many of the 19th century remodels, Danish architects were called in. According to some scholars, the driving force behind the use of historical Scanian architecture, as interpreted by 19th century Danish architects using Dutch Renaissance style, was a wish to refer back to an earlier era when the aristocracy had special privileges and political power in relation to the Danish king.
Language, literature, and art
Scanian dialects
Scanian ( sv, skånska , da, skånsk) is an East Scandinavian dialect spoken in the province of Scania in southern Sweden. Present-day speakers of "Scanian" speak the Scanian dialect of Swedish. Older Scanian formed part of the old Scandina ...
have various local native idioms and speech patterns, and realizes diphthongs and South Scandinavian Uvular trill
The voiced uvular trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a small capital letter ''R''. This consonant is one of several collectively ...
, as opposed to the supradental /r/-sound characteristic of spoken Standard Swedish
Standard Swedish () denotes Swedish as a spoken and written standard language. While Swedish as a written language is uniform and standardized, the spoken standard may vary considerably from region to region. Several prestige dialects have devel ...
. They are very similar to the dialect of Danish spoken in Bornholm, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
. The prosody of the Scanian dialects has more in common with German, Danish and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
(and sometimes also with English, although to a lesser extent) than with the prosody of central Swedish dialects.
Famous Scanian authors include Victoria Benedictsson, (1850–1888) from Domme, Trelleborg, who wrote about the inequality of women in the 19th century society, but who also authored regional stories about Scania, such as ''Från Skåne'' of 1884; Ola Hansson
Ola Hansson (12 November 1860, Hönsinge, Sweden – 26 September 1925, Büyükdere, Turkey) was a Swedish poet, prose writer, and critic.
Biography
Hansson published his first works, ''Dikter'' ("''Poems''") in 1884 and ''Notturno'' in 1 ...
(1860–1925) from Hönsinge, Trelleborg; Vilhelm Ekelund (1880–1949) from Stehag, Eslöv; Fritiof Nilsson Piraten (1895–1972) from Vollsjö, Sjöbo; Hjalmar Gullberg
Hjalmar Gullberg (30 May 1898 – 19 July 1961) was a Swedish poet and translator.
Career
Gullberg was born in Malmö, Scania. As a student at Lund University, he was the editor of the student magazine Lundagård. He was the manager of t ...
(1898–1961) from Malmö; Artur Lundkvist (1906–1991) from Hagstad, Perstorp
Perstorp is a locality and the seat of Perstorp Municipality in Skåne County, Sweden with 6,054 inhabitants (2018). It is twinned with Newton Aycliffe, a town in the North-East of England.
History
19th Century Modernization of Sweden: 18 ...
; Hans Alfredsson
Hans Folke "Hasse" Alfredson (28 June 1931 – 10 September 2017) was a Swedish actor, film director, writer, and comedian. He was born in Malmö, Sweden. He is known for his collaboration with Tage Danielsson as the duo Hasse & Tage and their ...
(1931–2017) and Jacques Werup
Jacques Werup (14 January 1945 – 12 November 2016) was a Swedish musician, author, poet, stage artist and screenwriter, born in Malmö. Werup's poetry is often associated to jazz. He was a childhood friend of Mikael Wiehe and Göran Skytte and ...
(1945–2016), both from Malmö. Birgitta Trotzig
Birgitta Trotzig (11 September 1929 – 14 May 2011) was a Sweden, Swedish writer who was elected to the Swedish Academy in 1993. She was one of Sweden's most celebrated authors, and wrote prose fiction and non-fiction, as well as prose poetry.
B ...
(1929–2011) from Gothenburg has written several historic novels set in Scania, such as ''The Exposed'' of 1957, which describes life in 17th century Scania with a primitive country priest as its main character and the 1961 novel ''A Tale from the Coast'', which recounts a legend about human suffering and is set in Scania in the 15th century. Gabriel Jönsson
Gabriel Jönsson (18 July 1892 – 23 April 1984) was a Swedish author and poet. He is best known for his works inspired by Öresund and farming. He was one of the first members of the Scanian Academy in Sweden.
Early life
Jönsson was born in ...
(1892–1984) from Ålabodarna, Landskrona.
A printing-house was established in the city of Malmö in 1528. It became instrumental in the propagation of new ideas and during the 16th century, Malmö became the center for the Danish reformation.
 Scanian culture, as expressed through the medium of textile art, has received international attention during the last decade. The art form, often referred to as Scanian Marriage Weavings, flourished from 1750 for a period of 100 years, after which it slowly vanished. Consisting of small textile panels mainly created for wedding ceremonies, the art is strongly symbolic, often expressing ideas about fertility, longevity and a sense of hope and joy. The Scanian artists were female weavers working at home, who had learned to weave at a young age, often in order to have a marriage chest filled with beautiful tapestries as a dowry.
According to international collectors and art scholars, the Scanian patterns are of special interest for the striking similarities with Roman, Byzantine and
Scanian culture, as expressed through the medium of textile art, has received international attention during the last decade. The art form, often referred to as Scanian Marriage Weavings, flourished from 1750 for a period of 100 years, after which it slowly vanished. Consisting of small textile panels mainly created for wedding ceremonies, the art is strongly symbolic, often expressing ideas about fertility, longevity and a sense of hope and joy. The Scanian artists were female weavers working at home, who had learned to weave at a young age, often in order to have a marriage chest filled with beautiful tapestries as a dowry.
According to international collectors and art scholars, the Scanian patterns are of special interest for the striking similarities with Roman, Byzantine and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
n art. The designs are studied by art historians tracing how portable decorative goods served as transmitters of art concepts from culture to culture, influencing designs and patterns along the entire length of the ancient trade routes. The Scanian textiles show how goods traded along the Silk Road brought Copt
Copts ( cop, ⲛⲓⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ; ar, الْقِبْط ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group indigenous to North Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt and Sudan since antiquity. Most ethnic Copts are Co ...
ic, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
n, and Chinese designs and symbols into the folk art of far away regions like Scania, where they were reinterpreted and integrated into the local culture. Some of the most ancient designs in Scanian textile art are pairs of birds facing a tree with a "great bird" above, often symbolized simply by its wings.Hansen, Viveka (1997). ''Swedish Textile Art: Traditional Marriage Weavings from Skåne.'' Nour Foundation: 1997. . Regionally derived iconography include mythological Scanian river horses in red ( sv, bäckahästar), with horns on their foreheads and misty clouds from their nostrils. The horse motif has been traced to patterns on 4th- and 5th-century Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
ian fabrics, but in Scanian art it is transformed to illustrate the Norse river horse of Scanian folklore.Lundström, Lena (2003). "Vattenväsen i väverskans händer". Curator's description of the exhibition "Aqvaväsen" at Trelleborgs Museum in ''Vårt Trelleborg'', 2:2003, pp. 20-21. Available online ipdf format
. (In Swedish).
Dukes
The title of duke was reintroduced in Sweden in 1772 and since this time, Swedish princes have been created dukes of various provinces, although the titles are purely nominal. The Dukes of Scania have been: * Crown Prince Carl (from his birth in 1826 until he became king in 1859) *Crown Prince Gustaf Adolf
Gustaf VI Adolf (Oscar Fredrik Wilhelm Olaf Gustaf Adolf; 11 November 1882 – 15 September 1973) was King of Sweden from 29 October 1950 until his death in 1973. He was the eldest son of Gustaf V and his wife, Victoria of Baden. Before Gustaf Ado ...
(from his birth in 1882 until he became king in 1950)
* Prince Oscar 2016-
From his marriage, in 1905, King Gustaf VI Adolf had his summer residence at Sofiero Palace in Helsingborg. He and his family spent their summers there, and the cabinet meetings held there during the summer months forced the ministers to arrive by night train from Stockholm. He died at Helsingborg Hospital in 1973.
Sports
Football has always been the most popular arena and team sport within the province, from attendances not least. Clubs are administered by Skånes Fotbollförbund. Malmö FF has won Allsvenskan 23 times,Helsingborg IF
Helsingborgs IF (full name Helsingborgs Idrottsförening), commonly referred to as HIF (), is a Swedish professional football club located in Helsingborg. They play in the Swedish first tier, Allsvenskan, following promotion in the 2021 Superett ...
7 times and was one of the twelve clubs in the league's very first season, 1924/25. Also Landskrona BoIS
Landskrona Boll och Idrottsällskap ( en, Landskrona Ball and Sports Society, locally referred to as BoIS) is a Sweden, Swedish professional Football club (association football), football club located in Landskrona, Scania, which currently pla ...
was among the twelve original clubs, but has never won. These three clubs are historically the most famous football clubs in Scania. But also IFK Malmö
Idrottsföreningen Kamraterna Malmö, more commonly known as IFK Malmö, is a Swedish sports club with several departments, located in Malmö. The club was founded on 23 April 1899.
The football department of IFK Malmö is one of the oldest footb ...
, Stattena IF
Stattena IF is a Swedish football club located in Helsingborg. The club played two seasons in the Allsvenskan in 1927–28 and 1929–30.
Background
The original club Stattena was one of the two clubs which in 1907 formed Helsingborgs IF. The ...
, Råå IF
Råå IF is a Swedish or Scanian football club located in Råå, a fishing village at Öresund, that grew to be one of Scandinavia's largest in the late 1800's, south of Helsingborg. They became the Swedish Cup champions in 1948, and the vice ...
(the latter two clubs are both from Helsingborg) as well as Trelleborgs FF
Trelleborgs Fotbollsförening, more commonly known as Trelleborgs FF or simply Trelleborg, is a Swedish football club located in Trelleborg. Formed 6 December 1926, the club plays in Superettan, the second tier in the Swedish Football system. ...
have participated.
Handball is also a relatively popular team sport, whilst Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
never really has gained much interest.
Ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
was for a long time thought of as a sport of northern Sweden, but has nevertheless became a popular attendance sport too. Malmö Redhawks
The IF Malmö Redhawks (colloquially referred to simply as Malmö or by past abbreviation MIF) is a Swedish professional ice hockey team based in Malmö which plays in the SHL, with Malmö Arena as the venue for home games.
The history of the ...
has even become Swedish Champions twice, but also Rögle BK
Rögle BK (Rögle Bandyklubb) is a Swedish professional ice hockey club from Ängelholm that has been playing in the SHL since the 2015–16 season. Rögle has previously played in the SHL (previously named Elitserien) in 1992–1996, 2008–20 ...
(from Ängelholm) have participated at the highest level of Swedish ice hockey during quite a lot of seasons.
Rugby is played in Scania by the Skåne Crusaders who play in the Sweden Rugby League
The Sweden Rugby League is the governing body for the sport of rugby league football in Sweden. The Association was formed in 2009. The Swedish rugby league international side debuted in 2010 against their neighbours Norway.
Honours
2013 Nordic ...
.
The overwhelmingly largest sport related events in both Scanian as well as Swedish history, were however the motorcycle Saxtorp TT-races
The Saxtorp TT-races were international motorcycle races, reminiscent of Isle of Man TT and held in ''Saxtorp'', south of Landskrona in Scania, southernmost Sweden. The races were held in August every year during the 1930s. The official name was ...
during the 1930s, which most of the years gathered crowds of 150.000 or more.
Tennis is associated with Båstad during the Swedish Open
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
.
Golf is the most popular sport to exercise after a certain age, at least. Scania has a large amount of golf courses, of which Barsebäck Golf & Country Club is the most well-known. Most Golf courses are open also during the winter, but may sometimes close temporarily in cases of snowy periods.
See also
*2008 Skåne County earthquake
The 2008 Skåne County earthquake occurred at 06.20am CET (05.20 UTC) on 16 December and affected the southern part of Sweden and eastern parts of Denmark. The epicenter was 5 km southwest of Sjöbo and 60 km east of Malmö. The earth ...
* 460 Scania
460 Scania (; ''prov. designation'': ''or'' ) is a background asteroid and a slow rotator from the central regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory on 22 Octo ...
, an asteroid discovered in 1900
* " Sång till Skåne", a song about the province
* East Denmark
East Denmark ( da, Østdanmark) is a geographical term that refers to the part of Denmark east of Great Belt, Storebælt, including Zealand (Denmark), Zealand, Amager, Lolland, Falster, Møn, Bornholm, and Ertholmene. From a linguistic and histor ...
* Skåneland
Skåneland ( Swedish and Danish) or Skånelandene ( Danish) is a region on the southern Scandinavian peninsula. It includes the Swedish provinces of Blekinge, Halland, and Scania. The Danish island of Bornholm is traditionally also include ...
Citations
General references
* Albertsson, Rolf (2007).Half-timbered houses
. ''Malmö 1692 - a historical project''. Malmö City Culture Department and Museum of Foteviken. Retrieved 16 January 2007. * Anderson, Carl Edlund (1999). ''Formation and Resolution of Ideological Contrast in the Early History of Scandinavia''. PhD dissertation, Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse & Celtic (Faculty of English), University of Cambridge, 1999. * Björk, Gert and Henrik Persson. "Fram för ett öppet och utåtriktat Skåne". ''Sydsvenskan'', 20 May 2000. Reproduced by FSF. (In Swedish). Retrieved 3 April 2008. * Bjurklint Rosenblad, Kajsa (2005). ''Scenografi för ett ståndsmässigt liv: adelns slottsbyggande i Skåne 1840-1900.'' Malmö: Sekel, 2005. . * Bonney, Richard (1995). ''Economic Systems and State Finance''. Oxford University Press. . * Craig, David J. (2003)
Boston University Bridge, 29 August 2003,• Vol. VII, No. 1. Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Danish National Archives (2006)
(In Danish). Retrieved 20 October 2006. * City of Lund (2006).
Touchdowns in the History of Lund
'. Retrieved 10 January 2006. * Gårding, Eva (1974). "Talar skåningarna svenska". ''Svenskans beskrivning''. Ed. Christer Platzack. Lund: Institutionen för nordiska språk, 1973. (In Swedish) * Germundsson, Tomas (2005). "Regional Cultural Heritage versus National Heritage in Scania’s Disputed National Landscape." ''International Journal of Heritage Studies'', Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2005. . * Hansen, Viveka (1997). ''Swedish Textile Art: Traditional Marriage Weavings from Scania''. Nour Foundation: 1997. . * Hauberg, P. (1900).'' Myntforhold og Udmyntninger i Danmark indtil 1146''. D. Kgl. Danske Vidensk. Selsk. Skr., 6. Række, historisk og filosofisk Afd. V. I.
an
Gladsaxe Gymnasium. (In Danish). Retrieved 10 January 2007. * Haugen, Einar (1976). ''The Scandinavian Languages: An Introduction to Their History''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1976. * Helle, Knut, ed. (2003). ''The Cambridge History of Scandinavia''. Cambridge University Press, 2003. . * Hogan, C.M. (2004). ''Kullaberg environmental analysis''. Lumina Technologies, Aberdeen Library Archives, Aberdeen, Scotland, 17 July 2004. * Jespersen, Knud J. V. (2004) . ''A History of Denmark''. Palgrave Macmillan. . * Keelan, Major Andrew and Wendy Keelan (2006)
The Khalili Family Trust. Retrieved 1 April 2008. * Lidmar-Bergström, Karna and Jens-Ove Näslund (2005). "Uplands and Lowlands in Southern Sweden". ''The Physical Geography of Fennoscandia''. Ed. Matti Seppälä. Oxford University Press, 2005. . * Lindquist, Herman (1995). ''Historien om Sverige – storhet och fall''. Norstedts Förlag, 2006. . (In Swedish). * Linnaeus, Carl (1750). ''Skånska resa''. (In Swedish). * Lund University School of Aviation (2005)
Ljungbyhed airport - ESTL
Retrieved 22 January 2007. * Lundström, Lena (2003). "Vattenväsen i väverskans händer". ''Vårt Trelleborg'', 2:2003. (In Swedish). * Malmö Public Library (2005)
Litteraturhistoria, Malmö
''Infotek Öresund'', 4 November 2005. (In Swedish). * Nevéus, Clara and Bror Jacques de Wærn (1992). ''Ny svensk vapenbok''. Riksarkivet 1992. (In Swedish) * Olin, Martin (2005)
"Royal Galleries in Denmark and Sweden around 1700"
''Kungliga rum – maktmanifestation och distribution''. Historikermöte 2005, Uppsala University. Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Olwig, Kenneth R. (2005). "Introduction: The Nature of Cultural Heritage, and the Culture of Natural Heritage—Northern Perspectives on a Contested Patrimony". ''International Journal of Heritage Studies'', Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2005. * Oresundstid (2008).
The Swedification of Scania
,
Renaissance Houses: Half-timbered houses
. Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Österberg, Klas (2001)
The Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, 25 January 2001. Retrieved 4 November 2006. * Østergård, Uffe (1997). "The Geopolitics of Nordic Identity – From Composite States to Nation States". ''The Cultural Construction of Norden''. Øystein Sørensen and Bo Stråth (eds.), Oslo: Scandinavian University Press 1997. * Peter, Laurence (2006).
Bridge shapes new Nordic hub
. BBC News, 14 September 2006. Retrieved 20 October 2006. * Region Skåne (2007)
Municipalities in Skåne
Retrieved 22 January 2007. * * SCB (2007)
"Skördar"
''Jordbruksstatistisk årsbok 2006''. Statiska Centralbyrån. (In Swedish). Retrieved 10 January 2007. * Skåne Regional Council (1999). ''Newsletter''., No. 2, 1999. * Stadin, Kekke (2005). "The Masculine Image of a Great Power: Representations of Swedish imperial power c. 1630–1690". ''Scandinavian Journal of History'', Vol. 30, No. 1. March 2005, pp. 61–82. . * Stiftelsen för fritidsområden i Skåne (2006
Skåneleden: 6B
''Breanäsleden'' (In Swedish)
Information about the Skaneled Trails
The Foundation for Recreational Areas in Skåne and Region Skåne. Retrieved 11 April 2008. * Strindberg, August (1893). "Skånska landskap med utvikningar". ''Prosabitar från 1890-talet''. Bonniers, Stockholm, 1917. (In Swedish). * SAOB (2008)
In Swedish). Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Sorens, Jason (2005). "The Cross-Sectional Determinants of Secessionism in Advanced Democracies". ''Comparative Political Studies'', Vol. 38, No. 3, 304-326 (2005). 2005 SAGE Publications. * Språk- och Folkminnesinstitutet (2003). ''Svenskt Ortnamnslexikon''. Uppsala, 2003. (In Swedish) * Tägil, Sven (2000). "Regions in Europe – a historical perspective". In ''Border Regions in Comparison''. Ed. Hans-Åke Persson. Studentlitteratur, Lund. . * Terra Scaniae (2008)
''Skånes län efter 1658''
"Lunds Domkyrka"
(In Swedish). Retrieved 2 April 2008. * Upton, Anthony F. (1998). ''Charles XI and Swedish Absolutism, 1660–1697''. Cambridge University Press, 1998. . * Vinge, Louise (ed.) ''Skånes litteraturhistoria'', Corona: Malmö, 1996–1997, Part I, , and Part II, . (In Swedish). * Ystad Municipality (2007)
Welcome to Ystad
an
"Pedestrian street"
''A walk through the centuries''. Retrieved 16 January 2007.
External links
Official links
Region Skåne
– The County council
Scania's Public Recreational Areas
– Region Skåne's public forests and parks
Skåne
– Business Region Skåne's official website for culture, heritage and tourism
Länsstyrelsen
– County Administration Board
Skåneleden
– Public nature trails through Scania
Organizations
Oresund Region
– The regional body of the Oresund Region
– Museum in Kristianstad
Kommunförbundet Skåne
– A cooperation between Scania's 33 municipalities
Skånes hembygdsförbund
(in Swedish) – Heritage conservation organization
Terra Scaniae
– History project established for Scanian schools, financed with subsidies from
Skåne Regional Council
Region Scania is the regional council of Scania County in Sweden. Scania County was formed on January 1, 1999, by the amalgamation of the county councils of Malmöhus County and Kristianstad County and some of the tasks handled by Malmö Municip ...
.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Skane
Provinces of Sweden