Satellite communication on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A communications satellite is an
A communications satellite is an
 The first artificial Earth satellite was
The first artificial Earth satellite was
 The first satellite purpose-built to actively relay communications was Project SCORE, led by Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) and launched on 18 December 1958, which used a tape recorder to carry a stored voice message, as well as to receive, store, and retransmit messages. It was used to send a Christmas greeting to the world from U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower. The satellite also executed several realtime transmissions before the non-rechargeable batteries failed on 30 December 1958 after eight hours of actual operation.
The direct successor to SCORE was another ARPA-led project called Courier. Courier 1B was launched on 4 October 1960 to explore whether it would be possible to establish a global military communications network by using "delayed repeater" satellites, which receive and store information until commanded to rebroadcast them. After 17 days, a command system failure ended communications from the satellite.
The first satellite purpose-built to actively relay communications was Project SCORE, led by Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) and launched on 18 December 1958, which used a tape recorder to carry a stored voice message, as well as to receive, store, and retransmit messages. It was used to send a Christmas greeting to the world from U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower. The satellite also executed several realtime transmissions before the non-rechargeable batteries failed on 30 December 1958 after eight hours of actual operation.
The direct successor to SCORE was another ARPA-led project called Courier. Courier 1B was launched on 4 October 1960 to explore whether it would be possible to establish a global military communications network by using "delayed repeater" satellites, which receive and store information until commanded to rebroadcast them. After 17 days, a command system failure ended communications from the satellite.
 A
A
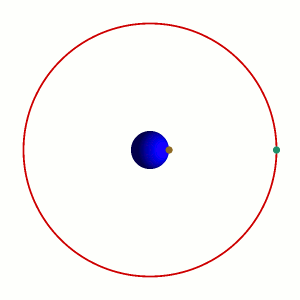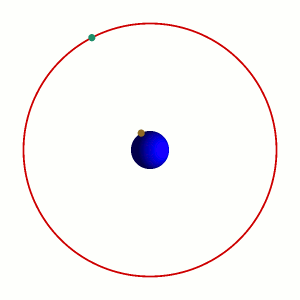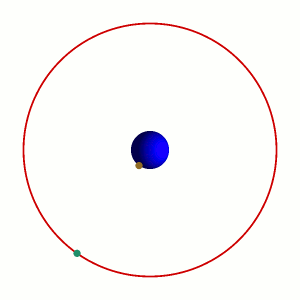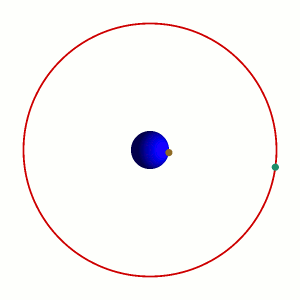 To an observer on Earth, a satellite in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. This is because it revolves around the Earth at Earth's own
To an observer on Earth, a satellite in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. This is because it revolves around the Earth at Earth's own
 The first and historically most important application for communication satellites was in intercontinental
The first and historically most important application for communication satellites was in intercontinental
Satellite Industry Association
by David J. Whalen
{{Authority control Satellite broadcasting Satellites by type Telecommunications-related introductions in 1962 Wireless communication systems
 A communications satellite is an
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisoto ...
that relays and amplifies radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a tr ...
telecommunication signals via a transponder
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight trans ...
; it creates a communication channel
A communication channel refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel in telecommunications and computer networking. A channel is used for informa ...
between a source transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the ...
and a receiver at different locations on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
. Communications satellites are used for television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
, telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
, radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a tr ...
, internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
, and military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitu ...
above the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish
A satellite dish is a dish-shaped type of parabolic antenna designed to receive or transmit information by radio waves to or from a communication satellite. The term most commonly means a dish which receives direct-broadcast satellite televisio ...
antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellation
A satellite constellation is a group of artificial satellites working together as a system. Unlike a single satellite, a constellation can provide permanent global or near-global coverage, such that at any time everywhere on Earth at least one s ...
s in low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently.
The high frequency radio wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (sho ...
s used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications satellites is to relay the signal around the curve of the Earth allowing communication between widely separated geographical points. Communications satellites use a wide range of radio and microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is e ...
. To avoid signal interference, international organizations have regulations for which frequency ranges or "bands" certain organizations are allowed to use. This allocation of bands minimizes the risk of signal interference.
History
Origins
In October 1945,Arthur C. Clarke
Sir Arthur Charles Clarke (16 December 191719 March 2008) was an English science-fiction writer, science writer, futurist, inventor, undersea explorer, and television series host.
He co-wrote the screenplay for the 1968 film '' 2001: A Spac ...
published an article titled "Extraterrestrial Relays" in the British magazine '' Wireless World''. The article described the fundamentals behind the deployment of artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisoto ...
s in geostationary orbits for the purpose of relaying radio signals. Because of this, Arthur C. Clarke is often quoted as being the inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
of the concept of the communications satellite, and the term 'Clarke Belt' is employed as a description of the orbit.
 The first artificial Earth satellite was
The first artificial Earth satellite was Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for ...
which was put into orbit by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
on 4 October 1957. It was developed by Mikhail Tikhonravov
Mikhail Klavdievich Tikhonravov (July 29, 1900 – March 3, 1974) was a Soviet engineer who was a pioneer of spacecraft design and rocketry.
Mikhail Tikhonravov was born in Vladimir, Russia. He attended the Zhukovsky Air Force Academy from 1922 ...
and Sergey Korolev, building on work by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (russian: Константи́н Эдуа́рдович Циолко́вский , , p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj , a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) ...
. Sputnik 1 was equipped with an on-board radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a tr ...
-transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the ...
that worked on two frequencies of 20.005 and 40.002 MHz, or 7 and 15 meters wavelength. The satellite was not placed in orbit for the purpose of sending data from one point on earth to another; the radio transmitter was meant to study the properties of radio wave distribution throughout the ionosphere. The launch of Sputnik 1 was a major step in the exploration of space and rocket development, and marks the beginning of the Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the launch of Sputnik 1 during 1957, and continuing ...
.
Early active and passive satellite experiments
There are two major classes of communications satellites, ''passive
Passive may refer to:
* Passive voice, a grammatical voice common in many languages, see also Pseudopassive
* Passive language, a language from which an interpreter works
* Passivity (behavior), the condition of submitting to the influence of o ...
'' and ''active''. Passive satellites only reflect the signal coming from the source, toward the direction of the receiver. With passive satellites, the reflected signal is not amplified at the satellite, and only a very small amount of the transmitted energy actually reaches the receiver. Since the satellite is so far above Earth, the radio signal is attenuated due to free-space path loss, so the signal received on Earth is very, very weak. Active satellites, on the other hand, amplify the received signal before retransmitting it to the receiver on the ground. Passive satellites were the first communications satellites, but are little used now.
Work that was begun in the field of electrical intelligence gathering at the United States Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. It was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, applied research, technological ...
in 1951 led to a project named Communication Moon Relay
The Communication Moon Relay project (also known as simply Moon Relay, or, alternatively, Operation Moon Bounce) was a telecommunication project carried out by the United States Navy. Its objective was to develop a secure and reliable method of wi ...
. Military planners had long shown considerable interest in secure and reliable communications lines as a tactical necessity, and the ultimate goal of this project was the creation of the longest communications circuit in human history, with the moon, Earth's natural satellite, acting as a passive relay. After achieving the first transoceanic communication between Washington, D.C., and Hawaii on 23 January 1956, this system was publicly inaugurated and put into formal production in January 1960.
 The first satellite purpose-built to actively relay communications was Project SCORE, led by Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) and launched on 18 December 1958, which used a tape recorder to carry a stored voice message, as well as to receive, store, and retransmit messages. It was used to send a Christmas greeting to the world from U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower. The satellite also executed several realtime transmissions before the non-rechargeable batteries failed on 30 December 1958 after eight hours of actual operation.
The direct successor to SCORE was another ARPA-led project called Courier. Courier 1B was launched on 4 October 1960 to explore whether it would be possible to establish a global military communications network by using "delayed repeater" satellites, which receive and store information until commanded to rebroadcast them. After 17 days, a command system failure ended communications from the satellite.
The first satellite purpose-built to actively relay communications was Project SCORE, led by Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) and launched on 18 December 1958, which used a tape recorder to carry a stored voice message, as well as to receive, store, and retransmit messages. It was used to send a Christmas greeting to the world from U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower. The satellite also executed several realtime transmissions before the non-rechargeable batteries failed on 30 December 1958 after eight hours of actual operation.
The direct successor to SCORE was another ARPA-led project called Courier. Courier 1B was launched on 4 October 1960 to explore whether it would be possible to establish a global military communications network by using "delayed repeater" satellites, which receive and store information until commanded to rebroadcast them. After 17 days, a command system failure ended communications from the satellite.
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's satellite applications program launched the first artificial satellite used for passive relay communications in Echo 1 on 12 August 1960. Echo 1 was an aluminized balloon satellite
A balloon satellite is inflated with gas after it has been put into orbit. It is also occasionally referred to as a "satelloon", which is a trademarked name owned by Gilmore Schjeldahl's G.T. Schjeldahl Company.
List of balloon satellites
abbr ...
acting as a passive reflector
Reflector may refer to:
Science
* Reflector, a device that causes reflection (for example, a mirror or a retroreflector)
* Reflector (photography), used to control lighting contrast
* Reflecting telescope
* Reflector (antenna), the part of an ...
of microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
signals. Communication signals were bounced off the satellite from one point on Earth to another. This experiment sought to establish the feasibility of worldwide broadcasts of telephone, radio, and television signals.
More firsts and further experiments
Telstar was the first active, direct relay communications commercial satellite and marked the first transatlantic transmission of television signals. Belonging toAT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the world's largest telecommunications company by revenue and the third largest provider of mobile ...
as part of a multi-national agreement between AT&T, Bell Telephone Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
, NASA, the British General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II in 1660. ...
, and the French National PTT (Post Office) to develop satellite communications, it was launched by NASA from Cape Canaveral
, image = cape canaveral.jpg
, image_size = 300
, caption = View of Cape Canaveral from space in 1991
, map = Florida#USA
, map_width = 300
, type = Cape
, map_caption = Location in Florida
, location ...
on 10 July 1962, in the first privately sponsored space launch.
Another passive relay experiment primarily intended for military communications purposes was Project West Ford, which was led by Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of th ...
's Lincoln Laboratory
The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and d ...
. After an initial failure in 1961, a launch on 9 May 1963 dispersed 350 million copper needle dipoles to create a passive reflecting belt. Even though only about half of the dipoles properly separated from each other, the project was able to successfully experiment and communicate using frequencies in the SHF X band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is rather indefinitely set at approxi ...
spectrum.
An immediate antecedent of the geostationary satellites was the Hughes Aircraft Company
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other ...
's Syncom 2, launched on 26 July 1963. Syncom 2 was the first communications satellite in a geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbita ...
. It revolved around the earth once per day at constant speed, but because it still had north–south motion, special equipment was needed to track it. Its successor, Syncom 3, launched on 19 July 1964, was the first geostationary communications satellite. Syncom 3 obtained a geosynchronous orbit, without a north–south motion, making it appear from the ground as a stationary object in the sky.
A direct extension of the passive experiments of Project West Ford was the Lincoln Experimental Satellite program, also conducted by the Lincoln Laboratory on behalf of the United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national sec ...
. The LES-1
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 1, also known as LES-1, was a communications satellite, the first of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite program. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on February 11, 1965, it pioneered many then ...
active communications satellite was launched on 11 February 1965 to explore the feasibility of active solid-state X band long-range military communications. A total of nine satellites were launched between 1965 and 1976 as part of this series.
International commercial satellite projects
In the United States, 1962 saw the creation of the Communications Satellite Corporation (COMSAT) private corporation, which was subject to instruction by the US Government on matters of national policy. Over the next two years, international negotiations led to the Intelsat Agreements, which in turn led to the launch of Intelsat 1, also known as Early Bird, on 6 April 1965, and which was the first commercial communications satellite to be placed in geosynchronous orbit. Subsequent Intelsat launches in the 1960s provided multi-destination service and video, audio, and data service to ships at sea (Intelsat 2 in 1966–67), and the completion of a fully global network with Intelsat 3 in 1969–70. By the 1980s, with significant expansions in commercial satellite capacity, Intelsat was on its way to become part of the competitive private telecommunications industry, and had started to get competition from the likes ofPanAmSat
The former PanAmSat Corporation founded in 1984 by Reynold (Rene) Anselmo, was a satellite service provider headquartered in Greenwich, Connecticut, United States. It operated a fleet of communications satellites used by the entertainment i ...
in the United States, which, ironically, was then bought by its archrival in 2005.
When Intelsat was launched, the United States was the only launch source outside of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, who did not participate in the Intelsat agreements. The Soviet Union launched its first communications satellite on 23 April 1965 as part of the Molniya program. This program was also unique at the time for its use of what then became known as the Molniya orbit, which describes a highly elliptical orbit, with two high apogees daily over the northern hemisphere. This orbit provides a long dwell time over Russian territory as well as over Canada at higher latitudes than geostationary orbits over the equator.
Satellite orbits
Communications satellites usually have one of three primary types oforbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
, while other orbital classifications are used to further specify orbital details. MEO and LEO are non-geostationary orbit (NGSO).
* Geostationary satellites have a ''geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitu ...
'' (GEO), which is from Earth's surface. This orbit has the special characteristic that the apparent position of the satellite in the sky when viewed by a ground observer does not change, the satellite appears to "stand still" in the sky. This is because the satellite's orbital period is the same as the rotation rate of the Earth. The advantage of this orbit is that ground antennas do not have to track the satellite across the sky, they can be fixed to point at the location in the sky the satellite appears.
* ''Medium Earth orbit
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between above sea level.
'' (MEO) satellites are closer to Earth. Orbital altitudes range from above Earth.
* The region below medium orbits is referred to as ''low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
'' (LEO), and is about above Earth.
As satellites in MEO and LEO orbit the Earth faster, they do not remain visible in the sky to a fixed point on Earth continually like a geostationary satellite, but appear to a ground observer to cross the sky and "set" when they go behind the Earth beyond the visible horizon. Therefore, to provide continuous communications capability with these lower orbits requires a larger number of satellites, so that one of these satellites will always be visible in the sky for transmission of communication signals. However, due to their closer distance to the Earth, LEO or MEO satellites can communicate to ground with reduced latency and at lower power than would be required from a geosynchronous orbit.
Low Earth orbit (LEO)
low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
(LEO) typically is a circular orbit about above the earth's surface and, correspondingly, a period (time to revolve around the earth) of about 90 minutes.
Because of their low altitude, these satellites are only visible from within a radius of roughly from the sub-satellite point. In addition, satellites in low earth orbit change their position relative to the ground position quickly. So even for local applications, many satellites are needed if the mission requires uninterrupted connectivity.
Low-Earth-orbiting satellites are less expensive to launch into orbit than geostationary satellites and, due to proximity to the ground, do not require as high signal strength
In telecommunications, particularly in radio frequency engineering, signal strength refers to the transmitter power output as received by a reference antenna at a distance from the transmitting antenna. High-powered transmissions, such as those u ...
(signal strength falls off as the square of the distance from the source, so the effect is considerable). Thus there is a trade off between the number of satellites and their cost.
In addition, there are important differences in the onboard and ground equipment needed to support the two types of missions.
Satellite constellation
A group of satellites working in concert is known as asatellite constellation
A satellite constellation is a group of artificial satellites working together as a system. Unlike a single satellite, a constellation can provide permanent global or near-global coverage, such that at any time everywhere on Earth at least one s ...
. Two such constellations, intended to provide satellite phone
A satellite telephone, satellite phone or satphone is a type of mobile phone that connects to other phones or the telephone network by radio through orbiting satellites instead of terrestrial cell sites, as cellphones do. The advantage of a sa ...
and low-speed data services, primarily to remote areas, are the Iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density o ...
and Globalstar
Globalstar, Inc. is an American satellite communications company that operates a low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellation for satellite phone and low-speed data communications. The Globalstar second-generation constellation consists of 24 lo ...
systems. The Iridium system has 66 satellites, which orbital inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Ea ...
of 86.4° and inter-satellite links provide service availability over the entire surface of Earth. Starlink
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation operated by SpaceX, providing satellite Internet access coverage to 45 countries. It also aims for global mobile phone service after 2023. SpaceX started launching Starlink satellites in 2019. As ...
is a satellite internet constellation
A satellite internet constellation is a constellation of artificial satellites providing satellite internet service. In particular, the term has come to refer to a new generation of very large constellations (sometimes referred to as a megaco ...
operated by SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal o ...
, that aims for global satellite Internet access
Satellite Internet access is Internet access provided through communication satellites. Modern consumer grade satellite Internet service is typically provided to individual users through geostationary satellites that can offer relatively high d ...
coverage.
It is also possible to offer discontinuous coverage using a low-Earth-orbit satellite capable of storing data received while passing over one part of Earth and transmitting it later while passing over another part. This will be the case with the CASCADE system of Canada's CASSIOPE
Cascade, Smallsat and Ionospheric Polar Explorer (CASSIOPE), is a Canadian Space Agency (CSA) multi-mission satellite operated by the University of Calgary. The mission development and operations from launch to February 2018 was funded through ...
communications satellite. Another system using this store and forward method is Orbcomm
''ORBCOMM'' is an American company that offers industrial Internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine (M2M) communications hardware, software and services designed to track, monitor, and control fixed and mobile assets in markets including ...
.
Medium Earth orbit (MEO)
A medium Earth orbit is a satellite in orbit somewhere between above the earth's surface. MEO satellites are similar to LEO satellites in functionality. MEO satellites are visible for much longer periods of time than LEO satellites, usually between 2 and 8 hours. MEO satellites have a larger coverage area than LEO satellites. A MEO satellite's longer duration of visibility and wider footprint means fewer satellites are needed in a MEO network than a LEO network. One disadvantage is that a MEO satellite's distance gives it a longer time delay and weaker signal than a LEO satellite, although these limitations are not as severe as those of a GEO satellite. Like LEOs, these satellites do not maintain a stationary distance from the earth. This is in contrast to the geostationary orbit, where satellites are always from the earth. Typically the orbit of a medium earth orbit satellite is about above earth. In various patterns, these satellites make the trip around earth in anywhere from 2 to 8 hours.Examples of MEO
* In 1962, the communications satellite, Telstar, was launched. It was a medium earth orbit satellite designed to help facilitate high-speed telephone signals. Although it was the first practical way to transmit signals over the horizon, its major drawback was soon realised. Because its orbital period of about 2.5 hours did not match the Earth's rotational period of 24 hours, continuous coverage was impossible. It was apparent that multiple MEOs needed to be used in order to provide continuous coverage. * In 2013, the first four of a constellation of 20 MEO satellites was launched. TheO3b
O3b is a satellite constellation in Medium Earth orbit (MEO) owned and operated by SES, and designed to provide low-latency broadband connectivity to remote locations for mobile network operators and internet service providers, maritime, aviat ...
satellites provide broadband internet services, in particular to remote locations and maritime and in-flight use, and orbit at an altitude of ).
Geostationary orbit (GEO)
 To an observer on Earth, a satellite in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. This is because it revolves around the Earth at Earth's own
To an observer on Earth, a satellite in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. This is because it revolves around the Earth at Earth's own angular velocity
In physics, angular velocity or rotational velocity ( or ), also known as angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time (i.e. how quickly an object ...
(one revolution per sidereal day, in an equatorial orbit
A near-equatorial orbit is an orbit that lies close to the Equator, equatorial plane of the object orbited. Such an orbit has an inclination near 0°. On Earth, such orbits lie on the celestial equator, the great circle of the imaginary celestial s ...
).
A geostationary orbit is useful for communications because ground antennas can be aimed at the satellite without their having to track the satellite's motion. This is relatively inexpensive.
In applications that require many ground antennas, such as DirecTV
DirecTV (trademarked as DIRECTV) is an American multichannel video programming distributor based in El Segundo, California. Originally launched on June 17, 1994, its primary service is a digital satellite service serving the United States. I ...
distribution, the savings in ground equipment can more than outweigh the cost and complexity of placing a satellite into orbit.
Examples of GEO
* The first geostationary satellite was Syncom 3, launched on 19 August 1964, and used for communication across the Pacific starting with television coverage of the1964 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and commonly known as Tokyo 1964 ( ja, 東京1964), were an international multi-sport event held from 10 to 24 October 1964 in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had been awarded the organization of the 1940 Summer Olympics, but this h ...
. Shortly after Syncom 3, Intelsat I
Intelsat I (nicknamed Early Bird for the proverb "The early bird catches the worm") was the first commercial communications satellite to be placed in geosynchronous orbit, on April 6, 1965. It was built by the Space and Communications Group of ...
, aka ''Early Bird'', was launched on 6 April 1965 and placed in orbit at 28° west longitude. It was the first geostationary satellite for telecommunications over the Atlantic Ocean.
* On 9 November 1972, Canada's first geostationary satellite serving the continent, Anik A1
Anik may refer to:
* Anik (satellite), satellites launched by Canadian telecommunications company Telesat
* Anik, Iran, a village in South Khorasan Province, Iran
* Anik Mountain
* Anik Bissonnette, a Canadian ballet dancer
* Anik Jean (born 1977) ...
, was launched by Telesat Canada
Telesat, formerly Telesat Canada, is a Canadian satellite communications company founded on May 2, 1969. The company is headquartered in Ottawa.
History
Telesat began as Telesat Canada, a Canadian Crown corporation created by an Act of Parl ...
, with the United States following suit with the launch of Westar 1 by Western Union
The Western Union Company is an American multinational financial services company, headquartered in Denver, Colorado.
Founded in 1851 as the New York and Mississippi Valley Printing Telegraph Company in Rochester, New York, the company cha ...
on 13 April 1974.
* On 30 May 1974, the first geostationary communications satellite in the world to be three-axis stabilized
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle/satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, et ...
was launched: the experimental satellite ATS-6 built for NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
.
* After the launches of the Telstar through Westar 1 satellites, RCA Americom (later GE Americom, now SES) launched Satcom 1 in 1975. It was Satcom 1 that was instrumental in helping early cable TV
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with broa ...
channels such as WTBS (now TBS), HBO, CBN (now Freeform) and The Weather Channel
The Weather Channel (TWC) is an American pay television channel owned by Weather Group, LLC, a subsidiary of Allen Media Group. The channel's headquarters are in Atlanta, Georgia. Launched on May 2, 1982, the channel broadcasts weather foreca ...
become successful, because these channels distributed their programming to all of the local cable TV headends using the satellite. Additionally, it was the first satellite used by broadcast television networks in the United States, like ABC, NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American English-language commercial broadcast television and radio network. The flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, its headquarters are l ...
, and CBS, to distribute programming to their local affiliate stations. Satcom 1 was widely used because it had twice the communications capacity of the competing Westar 1 in America (24 transponders
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight tra ...
as opposed to the 12 of Westar 1), resulting in lower transponder-usage costs. Satellites in later decades tended to have even higher transponder numbers.
By 2000, Hughes Space and Communications (now Boeing Satellite Development Center
The Boeing Satellite Development Center is a major business unit of Boeing Defense, Space & Security. It brought together Boeing satellite operations with that of GM Hughes Electronics' Space and Communications division in El Segundo, Califo ...
) had built nearly 40 percent of the more than one hundred satellites in service worldwide. Other major satellite manufacturers include Space Systems/Loral
SSL, formerly Space Systems/Loral, LLC (SS/L), of Palo Alto, California, is a wholly owned manufacturing subsidiary of Maxar Technologies.
SSL designs and builds satellites and space systems for a wide variety of government and commercial cust ...
, Orbital Sciences Corporation
Orbital Sciences Corporation (commonly referred to as Orbital) was an American company specializing in the design, manufacture, and launch of small- and medium- class space and launch vehicle systems for commercial, military and other governmen ...
with the Star Bus
Star Bus is a satellite bus family of Orbital ATK. It was originally developed by Thomas van der Heyden, co-founder of CTAI, and later sold to and manufactured by Orbital Sciences Corporation.
History
The first satellite program based on the Sta ...
series, Indian Space Research Organisation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman o ...
, Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
(owns the former RCA Astro Electronics/GE Astro Space business), Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense technology company. With 90,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $30 billion, it is one of the world's largest weapons manufacturers and military tech ...
, Alcatel Space, now Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space () is a Franco-Italian aerospace manufacturer. A joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (33%), the company is the largest satellite manufactur ...
, with the Spacebus series, and Astrium
Astrium was an aerospace manufacturer subsidiary of the European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS) that provided civil and military space systems and services from 2006 to 2013. In 2012, Astrium had a turnover of €5.8 billion and 1 ...
.
Molniya orbit
Geostationary satellites must operate above the equator and therefore appear lower on the horizon as the receiver gets farther from the equator. This will cause problems for extreme northerly latitudes, affecting connectivity and causing multipath interference (caused by signals reflecting off the ground and into the ground antenna). Thus, for areas close to the North (and South) Pole, a geostationary satellite may appear below the horizon. Therefore, Molniya orbit satellites have been launched, mainly in Russia, to alleviate this problem. Molniya orbits can be an appealing alternative in such cases. The Molniya orbit is highly inclined, guaranteeing good elevation over selected positions during the northern portion of the orbit. (Elevation is the extent of the satellite's position above the horizon. Thus, a satellite at the horizon has zero elevation and a satellite directly overhead has elevation of 90 degrees.) The Molniya orbit is designed so that the satellite spends the great majority of its time over the far northern latitudes, during which its ground footprint moves only slightly. Its period is one half day, so that the satellite is available for operation over the targeted region for six to nine hours every second revolution. In this way a constellation of three Molniya satellites (plus in-orbit spares) can provide uninterrupted coverage. The first satellite of the Molniya series was launched on 23 April 1965 and was used for experimentaltransmission
Transmission may refer to:
Medicine, science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Propulsion transmission, technology allowing controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual transmission
** ...
of TV signals from a Moscow uplink station to downlink stations located in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
and the Russian Far East, in Norilsk
Norilsk ( rus, Нори́льск, p=nɐˈrʲilʲsk, ''Norílʹsk'') is a closed city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located south of the western Taymyr Peninsula, around 90 km east of the Yenisey River and 1,500 km north of Krasnoyarsk. Norilsk ...
, Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( rus, Хабaровск, a=Хабаровск.ogg, r=Habárovsk, p=xɐˈbarəfsk) is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China–Russia border, at the confluence of ...
, Magadan
Magadan ( rus, Магадан, p=məɡɐˈdan) is a port town and the administrative center of Magadan Oblast, Russia, located on the Sea of Okhotsk in Nagayev Bay (within Taui Bay) and serving as a gateway to the Kolyma region.
History
Maga ...
and Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, ...
. In November 1967 Soviet engineers created a unique system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and express ...
of national TV network
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology
* Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
* Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematic ...
of satellite television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna com ...
, called Orbita, that was based on Molniya satellites.
Polar orbit
In the United States, the National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System (NPOESS) was established in 1994 to consolidate the polar satellite operations of NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). NPOESS manages a number of satellites for various purposes; for example, METSAT for meteorological satellite, EUMETSAT for the European branch of the program, and METOP for meteorological operations. These orbits are sun synchronous, meaning that they cross the equator at the same local time each day. For example, the satellites in the NPOESS (civilian) orbit will cross the equator, going from south to north, at times 1:30 P.M., 5:30 P.M., and 9:30 P.M.Structure
Communications Satellites are usually composed of the following subsystems: * Communication Payload, normally composed oftransponders
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight tra ...
, antennas, and switching systems
* Engines used to bring the satellite to its desired orbit
* A station keeping tracking and stabilization subsystem used to keep the satellite in the right orbit, with its antennas pointed in the right direction, and its power system pointed towards the sun
* Power subsystem, used to power the Satellite systems, normally composed of solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
s, and batteries that maintain power during solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six mon ...
* Command and Control subsystem, which maintains communications with ground control stations. The ground control Earth stations monitor the satellite performance and control its functionality during various phases of its life-cycle.
The bandwidth available from a satellite depends upon the number of transponders provided by the satellite. Each service (TV, Voice, Internet, radio) requires a different amount of bandwidth for transmission. This is typically known as link budgeting and a network simulator
In computer network research, network simulation is a technique whereby a software program replicates the behavior of a real network. This is achieved by calculating the interactions between the different network entities such as routers, switche ...
can be used to arrive at the exact value.
Frequency allocation for satellite systems
Allocating frequencies to satellite services is a complicated process which requires international coordination and planning. This is carried out under the auspices of theInternational Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
(ITU).
To facilitate frequency planning, the world is divided into three regions:
* Region 1: Europe, Africa, the Middle East, what was formerly the Soviet Union, and Mongolia
* Region 2: North and South America and Greenland
* Region 3: Asia (excluding region 1 areas), Australia, and the southwest Pacific
Within these regions, frequency bands are allocated to various satellite services, although a given service may be allocated different frequency bands in different regions. Some of the services provided by satellites are:
* Fixed satellite service (FSS)
* Broadcasting satellite service (BSS)
* Mobile-satellite service
Mobile-satellite service (MSS, or mobile-satellite radiocommunication service) is – according to Article 1.25 of the International Telecommunication Union's Radio Regulations
– "A radiocommunication service
* between mobile earth stations an ...
* Radionavigation-satellite service
* Meteorological-satellite service
Applications
Telephony
 The first and historically most important application for communication satellites was in intercontinental
The first and historically most important application for communication satellites was in intercontinental long distance telephony
In telecommunications, a long-distance call (U.S.) or trunk call (also known as a toll call in the U.K. ) is a telephone call made to a location outside a defined local calling area. Long-distance calls are typically charged a higher billing rate ...
. The fixed Public Switched Telephone Network
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) provides infrastructure and services for public telecommunication. The PSTN is the aggregate of the world's circuit-switched telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telep ...
relays telephone call
A telephone call is a connection over a telephone network between the called party and the calling party.
First telephone call
The first telephone call was made on March 10, 1876, by Alexander Graham Bell. Bell demonstrated his ability to "ta ...
s from land line
A landline (land line, land-line, main line, home phone, fixed-line, and wireline) is a telephone connection that uses metal wires or optical fiber telephone line for transmission, as distinguished from a mobile cellular network, which uses ...
telephones to an earth station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves fr ...
, where they are then transmitted to a geostationary satellite. The downlink follows an analogous path. Improvements in submarine communications cable
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the sea bed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. The first submarine communications cables laid beginning in the 1850s carried tel ...
s through the use of fiber-optics caused some decline in the use of satellites for fixed telephony in the late 20th century.
Satellite communications are still used in many applications today. Remote islands such as Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is about from the coast of Africa and from the coast of South America. It is governed as part of the British Overseas Territory of ...
, Saint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constit ...
, Diego Garcia
Diego Garcia is an island of the British Indian Ocean Territory, a disputed overseas territory of the United Kingdom. It is a militarised atoll just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, and the largest of the 60 small islands of ...
, and Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearl ...
, where no submarine cables are in service, need satellite telephones. There are also regions of some continents and countries where landline telecommunications are rare to non existent, for example large regions of South America, Africa, Canada, China, Russia, and Australia. Satellite communications also provide connection to the edges of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
. Other land use for satellite phones are rigs at sea, a backup for hospitals, military, and recreation. Ships at sea, as well as planes, often use satellite phones.
Satellite phone systems can be accomplished by a number of means. On a large scale, often there will be a local telephone system in an isolated area with a link to the telephone system in a main land area. There are also services that will patch a radio signal to a telephone system. In this example, almost any type of satellite can be used. Satellite phones connect directly to a constellation of either geostationary or low-Earth-orbit satellites. Calls are then forwarded to a satellite teleport connected to the Public Switched Telephone Network .
Television
As television became the main market, its demand for simultaneous delivery of relatively few signals of large bandwidth to many receivers being a more precise match for the capabilities ofgeosynchronous
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital ...
comsats. Two satellite types are used for North American television and radio: Direct broadcast satellite
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna comm ...
(DBS), and Fixed Service Satellite
Fixed-satellite service (short: FSS | also: fixed-satellite radiocommunication service) is – according to ''article 1.21'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as ''A radiocommunication s ...
(FSS).
The definitions of FSS and DBS satellites outside of North America, especially in Europe, are a bit more ambiguous. Most satellites used for direct-to-home television in Europe have the same high power output as DBS-class satellites in North America, but use the same linear polarization as FSS-class satellites. Examples of these are the Astra, Eutelsat
Eutelsat S.A. is a French satellite operator. Providing coverage over the entire European continent, the Middle East, Africa, Asia and the Americas, it is the world's third-largest satellite operator in terms of revenues.
Eutelsat's satellite ...
, and Hotbird spacecraft in orbit over the European continent. Because of this, the terms FSS and DBS are more so used throughout the North American continent, and are uncommon in Europe.
Fixed Service Satellite
Fixed-satellite service (short: FSS | also: fixed-satellite radiocommunication service) is – according to ''article 1.21'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as ''A radiocommunication s ...
s use the C band, and the lower portions of the Ku band. They are normally used for broadcast feeds to and from television networks and local affiliate stations (such as program feeds for network and syndicated programming, live shots, and backhauls), as well as being used for distance learning
Distance education, also known as distance learning, is the education of students who may not always be physically present at a school, or where the learner and the teacher are separated in both time and distance. Traditionally, this usually in ...
by schools and universities, business television (BTV), Videoconferencing
Videotelephony, also known as videoconferencing and video teleconferencing, is the two-way or multipoint reception and transmission of audio signal, audio and video signals by people in different locations for Real-time, real time communication. ...
, and general commercial telecommunications. FSS satellites are also used to distribute national cable channels to cable television headends.
Free-to-air
Free-to-air (FTA) services are television (TV) and radio services broadcast in unencrypted form, allowing any person with the appropriate receiving equipment to receive the signal and view or listen to the content without requiring a subscripti ...
satellite TV channels are also usually distributed on FSS satellites in the Ku band. The Intelsat Americas 5, Galaxy 10R
Galaxy 10R was an American communications satellite which was operated by PanAmSat, and later Intelsat. It was constructed by Hughes and is based on the HS-601HP satellite bus. Launch occurred on 25 January 2000, at 01:04. The launch was contract ...
and AMC 3 satellites over North America provide a quite large amount of FTA channels on their Ku band transponder
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight trans ...
s.
The American Dish Network
DISH Network Corporation (DISH, an acronym for DIgital Sky Highway) is an American television provider and the owner of the direct-broadcast satellite provider Dish, commonly known as Dish Network, and the over-the-top IPTV service, Sling ...
DBS service has also recently used FSS technology as well for their programming packages requiring their SuperDish antenna, due to Dish Network needing more capacity to carry local television stations per the FCC's "must-carry" regulations, and for more bandwidth to carry HDTV
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the g ...
channels.
A direct broadcast satellite
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna comm ...
is a communications satellite that transmits to small DBS satellite dish
A satellite dish is a dish-shaped type of parabolic antenna designed to receive or transmit information by radio waves to or from a communication satellite. The term most commonly means a dish which receives direct-broadcast satellite televisio ...
es (usually 18 to 24 inches or 45 to 60 cm in diameter). Direct broadcast satellites generally operate in the upper portion of the microwave Ku band. DBS technology is used for DTH-oriented ( Direct-To-Home) satellite TV services, such as DirecTV
DirecTV (trademarked as DIRECTV) is an American multichannel video programming distributor based in El Segundo, California. Originally launched on June 17, 1994, its primary service is a digital satellite service serving the United States. I ...
, DISH Network and Orby TV in the United States, Bell Satellite TV
Bell Satellite TV (french: Bell Télé; formerly known as Bell ExpressVu, Dish Network Canada and ExpressVu Dish Network and not to be confused with Bell's IPTV Fibe TV service) is the division of BCE Inc. that provides satellite television ser ...
and Shaw Direct
Shaw Direct is a direct broadcast satellite television distributor in Canada and a subsidiary of the telecommunications company Shaw Communications. As of 2010, Shaw Direct had over 900,000 subscribers. It broadcasts on Ku band from two commu ...
in Canada, Freesat
Freesat is a British free-to-air satellite television service, first formed as a joint venture between the BBC and ITV plc and now owned by Digital UK. The service was formed as a memorandum in 2007 and has been marketed since 6 May 2008. Free ...
and Sky in the UK, Ireland, and New Zealand and DSTV
Digital Satellite Television, commonly abbreviated to DStv, is a Sub-Saharan African direct broadcast satellite service owned by MultiChoice and based in Randburg, South Africa. Launched on 6 October 1995, the service provides multiple audio, ...
in South Africa.
Operating at lower frequency and lower power than DBS, FSS satellites require a much larger dish for reception (3 to 8 feet (1 to 2.5 m) in diameter for Ku band, and 12 feet (3.6 m) or larger for C band). They use linear polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarizati ...
for each of the transponders' RF input and output (as opposed to circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to ...
used by DBS satellites), but this is a minor technical difference that users do not notice. FSS satellite technology was also originally used for DTH satellite TV from the late 1970s to the early 1990s in the United States in the form of TVRO (Television Receive Only) receivers and dishes. It was also used in its Ku band form for the now-defunct Primestar satellite TV service.
Some satellites have been launched that have transponders in the Ka band, such as DirecTV's SPACEWAY-1 satellite, and Anik F2. NASA and ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman o ...
have also launched experimental satellites carrying Ka band beacons recently.
Some manufacturers have also introduced special antennas for mobile reception of DBS television. Using Global Positioning System (GPS) technology as a reference, these antennas automatically re-aim to the satellite no matter where or how the vehicle (on which the antenna is mounted) is situated. These mobile satellite antennas are popular with some recreational vehicle
A recreational vehicle, often abbreviated as RV, is a motor vehicle or trailer that includes living quarters designed for accommodation. Types of RVs include motorhomes, campervans, coaches, caravans (also known as travel trailers and campe ...
owners. Such mobile DBS antennas are also used by JetBlue Airways for DirecTV (supplied by LiveTV, a subsidiary of JetBlue), which passengers can view on-board on LCD screens mounted in the seats.
Radio broadcasting
Satellite radio offers audiobroadcast
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio or video content to a dispersed audience via any electronic mass communications medium, but typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a one-to-many model. Broadcasting began wi ...
services in some countries, notably the United States. Mobile services allow listeners to roam a continent, listening to the same audio programming anywhere.
A satellite radio or subscription radio (SR) is a digital radio signal that is broadcast by a communications satellite, which covers a much wider geographical range than terrestrial radio signals.
Amateur radio
Amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency commu ...
operators have access to amateur satellites, which have been designed specifically to carry amateur radio traffic. Most such satellites operate as spaceborne repeaters, and are generally accessed by amateurs equipped with UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
or VHF
Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) from 30 to 300 megahertz (MHz), with corresponding wavelengths of ten meters to one meter.
Frequencies immediately below VHF ...
radio equipment and highly directional antennas such as Yagis or dish antennas. Due to launch costs, most current amateur satellites are launched into fairly low Earth orbits, and are designed to deal with only a limited number of brief contacts at any given time. Some satellites also provide data-forwarding services using the X.25
X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet-switched data communication in wide area networks (WAN). It was originally defined by the International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee (CCITT, now ITU-T) in a series of drafts a ...
or similar protocols.
Internet access
After the 1990s, satellite communication technology has been used as a means to connect to theInternet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
via broadband data connections. This can be very useful for users who are located in remote areas, and cannot access a broadband
In telecommunications, broadband is wide bandwidth data transmission which transports multiple signals at a wide range of frequencies and Internet traffic types, that enables messages to be sent simultaneously, used in fast internet connections. ...
connection, or require high availability of services.
Military
Communications satellites are used formilitary communications
Military communications or military signals involve all aspects of communications, or conveyance of information, by armed forces. Military communications span from pre-history to the present. The earliest military communications were delivered ...
applications, such as Global Command and Control Systems. Examples of military systems that use communication satellites are the MILSTAR
Milstar (Military Strategic and Tactical Relay) is a constellation of military communications satellites in geosynchronous orbit, which are operated by the United States Space Force, and provide secure and jam-resistant worldwide communications ...
, the DSCS
The Defense Satellite Communications System (DSCS) is a United States Space Force satellite constellation that provides the United States with military communications to support globally distributed military users. Beginning in 2007, DSCS is be ...
, and the FLTSATCOM
FLTSATCOM (also FLTSAT) is a satellite communication system of the U.S. Space Force which was used for UHF radio communications between ships, submarines, airplanes and ground stations of the Navy.
Most of the transponders on these satellites ...
of the United States, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
satellites, United Kingdom satellites (for instance Skynet), and satellites of the former Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. India has launched its first Military Communication satellite GSAT-7
GSAT-7 or INSAT-4F is a multi-band military communications satellite developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation. The Indian Navy is the user of the multi-band communication spacecraft, which has been operational since September 2013. Acco ...
, its transponders operate in UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
, F, C and bands. Typically military satellites operate in the UHF, SHF (also known as X-band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is rather indefinitely set at approxi ...
) or EHF (also known as Ka band) frequency bands.
Data collection
Near-groundin situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in ...
environmental monitoring
Environmental monitoring describes the processes and activities that need to take place to characterize and monitor the quality of the environment. Environmental monitoring is used in the preparation of environmental impact assessments, as well a ...
equipment (such as weather station
A weather station is a facility, either on land or sea, with instruments and equipment for measuring atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasts and to study the weather and climate. The measurements taken include tempera ...
s, weather buoy
Weather buoys are instruments which collect weather and ocean data within the world's oceans, as well as aid during emergency response to chemical spills, legal proceedings, and engineering design. Moored buoys have been in use since 1951, wh ...
s, and radiosondes
A radiosonde is a battery-powered telemetry instrument carried into the atmosphere usually by a weather balloon that measures various atmospheric parameters and transmits them by radio to a ground receiver. Modern radiosondes measure or calcul ...
), may use satellites for one-way data transmission
Data transmission and data reception or, more broadly, data communication or digital communications is the transfer and reception of data in the form of a digital bitstream or a digitized analog signal transmitted over a point-to-point or ...
or two-way telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", an ...
and telecontrol
A telecommand or telecontrol is a command sent to control a remote system or systems not directly connected (e.g. via wires) to the place from which the telecommand is sent. The word is derived from ''tele'' = remote (Greek), and ''command'' = to ...
. It may be based on a secondary payload of a weather satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or ...
(as in the case of GOES
Goes () is a city and municipality in the southwestern Netherlands on Zuid-Beveland, in the province of Zeeland. The city of Goes has approximately 27,000 residents.
History
Goes was founded in the 10th century on the edge of a creek: de Korte ...
and METEOSAT
The Meteosat series of satellites are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program.
The MTP program was established to ensure the ope ...
and others in the Argos system) or in dedicated satellites (such as SCD). The data rate is typically much lower than in satellite Internet access.
See also
* Commercialization of space * History of telecommunication *Inter-satellite communications satellite
Inter-satellite service (also: inter-satellite radiocommunication service) is – according to ''Article 1.22'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Sy ...
* List of communication satellite companies
This is a list of all companies currently operating at least one commercial communication satellite or currently has one on order.
Global Top 20
The World Teleport Association publishes lists of companies based on revenues from all customized c ...
* List of communications satellite firsts
Milestones in the history of communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source tra ...
* NewSpace
* Reconnaissance satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications.
Th ...
* Relay (disambiguation)
A relay is an electric switch operated by a signal in one circuit to control another circuit.
Relay may also refer to:
Historical
* Stage station, a place where exhausted horses being used for transport could be exchanged for fresh ones
* Curs ...
* Satcom On The Move
* Satellite data unit
* Satellite delay
* Satellite space segment
The space segment of an artificial satellite system is one of its three operational components (the others being the user and ground segments). It comprises the satellite or satellite constellation and the uplink and downlink satellite links.
Th ...
* Space pollution
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, or space garbage) are defunct human-made objects in space—principally in Earth orbit—which no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacecr ...
References
Notes
Citations
External links
Satellite Industry Association
by David J. Whalen
{{Authority control Satellite broadcasting Satellites by type Telecommunications-related introductions in 1962 Wireless communication systems