Sassari on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sassari (, ; sdc, Sàssari ; sc, Tàtari, ) is an Italian city and the second-largest of

Many archaeological sites and ancient ruins are located inside or around the town: the prehistoric step pyramid of Monte d'Accoddi, a large number of Nuraghes and Domus de Janas (Fairy Houses), the ruins of a Roman aqueduct, the ruins of a Roman villa discovered under San Nicholas Cathedral, and a portion of the ancient road that connected the Latin city of Turris Libisonis with
 The origin of the city remains uncertain. Among the theses, according to folk tradition the first village was founded around the 9th–10th century AD by the inhabitants of the ancient Roman port of ''Turris Libisonis'' (current Porto Torres), who sought refuge in the mainland to escape the
The origin of the city remains uncertain. Among the theses, according to folk tradition the first village was founded around the 9th–10th century AD by the inhabitants of the ancient Roman port of ''Turris Libisonis'' (current Porto Torres), who sought refuge in the mainland to escape the  In 1284 the Pisans were defeated by the Genoese fleet at the
In 1284 the Pisans were defeated by the Genoese fleet at the  From 1323 the Republic of Sassari decided to side with the King of Aragon, in whose hands it remained for much of the following centuries, though the population revolted at least three times. The revolts ceased when King
From 1323 the Republic of Sassari decided to side with the King of Aragon, in whose hands it remained for much of the following centuries, though the population revolted at least three times. The revolts ceased when King
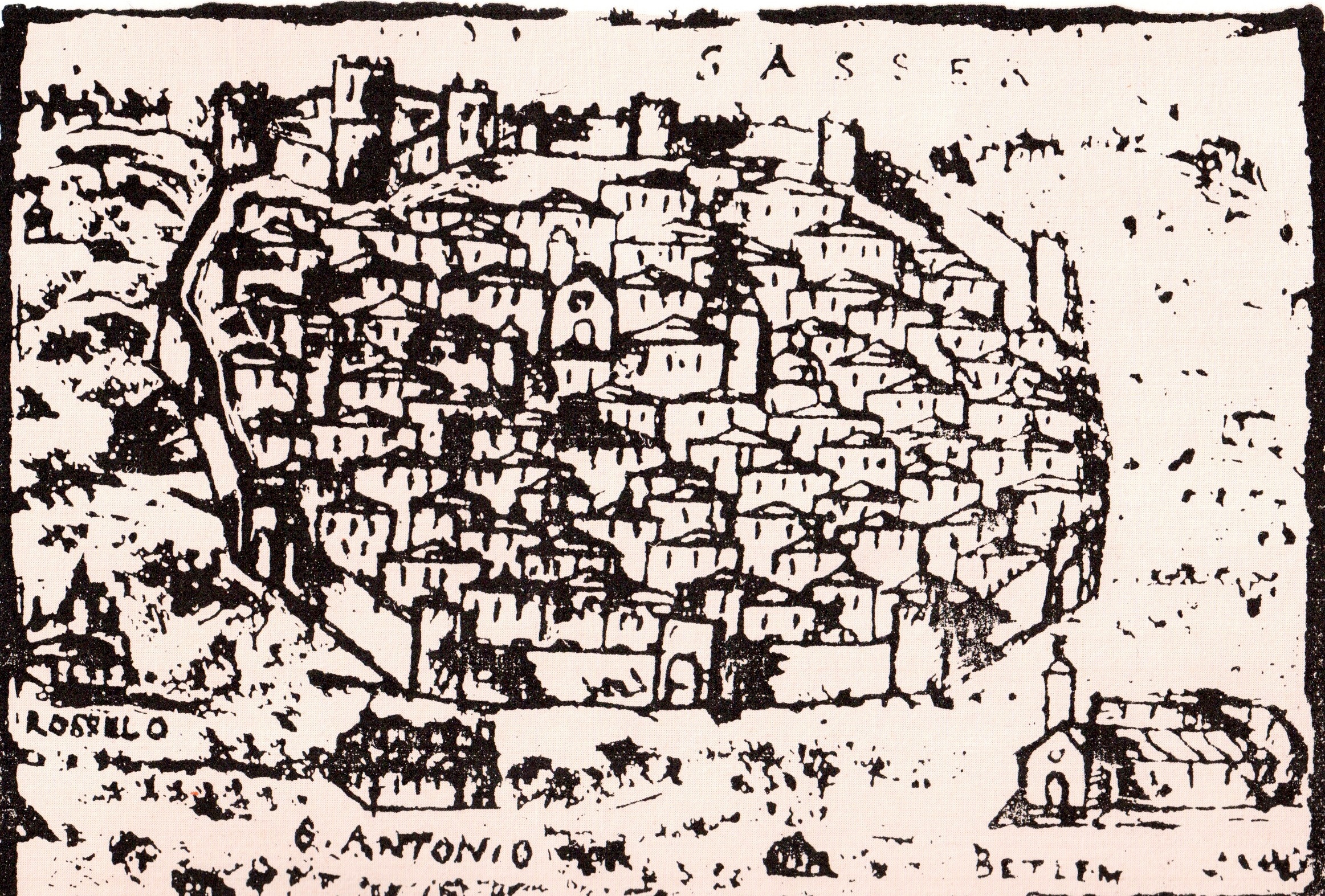
 After the end of the Spanish period following the European wars of the early 18th century, the brief period of
After the end of the Spanish period following the European wars of the early 18th century, the brief period of


 * Archeological site of Monte d'Accoddi: a unique prehistoric monument with a step pyramid construction
*The
* Archeological site of Monte d'Accoddi: a unique prehistoric monument with a step pyramid construction
*The
 * National Archaeological and Ethnographic "G.A. Sanna" Museum
* National Pinacotheca "Mus'A"
* Historical Museum of " Brigata Sassari"
* Museum of Science and Technology (it is constituted by many collections located in several university faculties: mineralogical, botanic, Entomological, zoological,
* National Archaeological and Ethnographic "G.A. Sanna" Museum
* National Pinacotheca "Mus'A"
* Historical Museum of " Brigata Sassari"
* Museum of Science and Technology (it is constituted by many collections located in several university faculties: mineralogical, botanic, Entomological, zoological,
 * The '' Faradda di li candareri'' (''The Descent of the Candelieri''): it's a devotional procession, in which enormous wooden candles are carried by members of the city guilds from the town centre to the church of Santa Maria of Betlem, in commemoration of the end of the plague in 1582, but it probably has older origins, from a cultural tradition from Pisa that as early as in the second half of the 13th century was practiced in some parts of Sardinia.
* The '' Cavalcata Sarda'' (the Sardinian Cavalcade), a main event in Sardinia. On the last Sunday of May thousands of people come from all over Sardinia to Sassari to parade through the city in their local folk costumes on foot and ride on hundreds of the best Sardinian horses.
* '' Sardinia Film Festival'' was founded in 2006. With 500 films, short subjects, animated cartoons and
* The '' Faradda di li candareri'' (''The Descent of the Candelieri''): it's a devotional procession, in which enormous wooden candles are carried by members of the city guilds from the town centre to the church of Santa Maria of Betlem, in commemoration of the end of the plague in 1582, but it probably has older origins, from a cultural tradition from Pisa that as early as in the second half of the 13th century was practiced in some parts of Sardinia.
* The '' Cavalcata Sarda'' (the Sardinian Cavalcade), a main event in Sardinia. On the last Sunday of May thousands of people come from all over Sardinia to Sassari to parade through the city in their local folk costumes on foot and ride on hundreds of the best Sardinian horses.
* '' Sardinia Film Festival'' was founded in 2006. With 500 films, short subjects, animated cartoons and
 The Municipal Council of Sassari is led by a left-wing majority, first elected in May 2005 and confirmed in 2010 and 2014. The mayor is Nicola Sanna, member of the Democratic Party.
The Municipal Council of Sassari is led by a left-wing majority, first elected in May 2005 and confirmed in 2010 and 2014. The mayor is Nicola Sanna, member of the Democratic Party.
 The economy of town is mainly focused on services and the advanced tertiary sector. It is the principal administrative centre of central and northern Sardinia. The main Sardinian banks ( Banco di Sardegna and Banca di Sassari) have head office and presidency in the city.
Several research centers are located in town: the University ones, the Center of Regional Weather Service (''Meteo Sar.''), the Regional Agency for Environmental Protection (''ARPA''), the Zooprophylaxis Institute of Sardinia, and many labs of the National Research Center ( CNR): the Institute of Biometeorology (''IBIMET''), the Institute of Biomolecular Chemistry (''ICB''), the Institute of Ecosystem Studies (''ISE''), the Institute of Sciences of Food Production (''ISPA''), and the Institute for Animal Production System in Mediterranean Environment (''ISPAAM'').
Manufacturing includes construction, pharmaceutical, food, typographic industry, and also, indirectly, petrochemical and the new greenchemicals located in Porto Torres.
Tourism is concentrated mainly along the coasts.
The economy of town is mainly focused on services and the advanced tertiary sector. It is the principal administrative centre of central and northern Sardinia. The main Sardinian banks ( Banco di Sardegna and Banca di Sassari) have head office and presidency in the city.
Several research centers are located in town: the University ones, the Center of Regional Weather Service (''Meteo Sar.''), the Regional Agency for Environmental Protection (''ARPA''), the Zooprophylaxis Institute of Sardinia, and many labs of the National Research Center ( CNR): the Institute of Biometeorology (''IBIMET''), the Institute of Biomolecular Chemistry (''ICB''), the Institute of Ecosystem Studies (''ISE''), the Institute of Sciences of Food Production (''ISPA''), and the Institute for Animal Production System in Mediterranean Environment (''ISPAAM'').
Manufacturing includes construction, pharmaceutical, food, typographic industry, and also, indirectly, petrochemical and the new greenchemicals located in Porto Torres.
Tourism is concentrated mainly along the coasts.
 The nearest airport, Fertilia International Airport, is from the city center, and the closest seaport is located at Porto Torres, away.
Urban and suburban
The nearest airport, Fertilia International Airport, is from the city center, and the closest seaport is located at Porto Torres, away.
Urban and suburban
 * A.S.D. Torres Calcio football club, founded in 1903, playing in
* A.S.D. Torres Calcio football club, founded in 1903, playing in
Official website
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
in terms of population with 127,525 inhabitants, and a Functional Urban Area of about 260,000 inhabitants. One of the oldest cities on the island, it contains a considerable collection of art.
Since its origins at the turn of the 12th century, Sassari has been ruled by the Giudicato of Torres
The Judicate of Logudoro or Torres ( sc, Judicadu de Logudoro or ''Torres'', ''Rennu de Logudoro'' or ''Logu de Torres'') was a state in northwest Sardinia from the tenth through the thirteenth century. Its original capital was Porto Torres. The ...
, the Pisans, as an independent republic in alliance with Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
, by the Aragonese and the Spanish, all of whom have contributed to Sassari's historical and artistic heritage. Sassari is a city rich in art, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
and history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
, and is well known for its palazzi, the Fountain of the Rosello, and its elegant neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing sty ...
, such as Piazza d'Italia (Italy Square) and the Teatro Civico (Civic Theatre).
As Sardinia's second most populated city, it has a considerable amount of cultural, touristic
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
, commercial and political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
importance in the island. The city's economy mainly relies on tourism and services, however also partially on research
Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
, construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and ...
, pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
s and the petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
industry.
Geography
Sassari is located in north-western Sardinia, atabove sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance ( height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''.
Th ...
. The area rises up on a wide karstic plateau that slopes gently down towards the Gulf of Asinara and the Nurra plain. The city is surrounded by a green belt
A green belt is a policy and land-use zone designation used in land-use planning to retain areas of largely undeveloped, wild, or agricultural land surrounding or neighboring urban areas. Similar concepts are greenways or green wedges, which h ...
of thousands of hectares of olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ' ...
plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
s, which from the 19th century have partly replaced the mixed woodlands of oak and other Mediterranean trees as well as the maquis shrubland
220px, Low maquis in Corsica
220px, High ''macchia'' in Sardinia
( , , ) or ( , ; often in Italian; hr, makija; ; ) is a shrubland biome in the Mediterranean region, typically consisting of densely growing evergreen shrubs.
Maquis is c ...
. The thinly populated Nurra Plain, located to the west, occupies the main part of the region of Sassari, while the urban agglomeration, with a population of about 275,000 inhabitants, is located to the south east. The abundance of water, with about 400 springs and artesian wells, has made for much development of horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
over the centuries.
Climate
History
Prehistory and ancient history
Although Sassari was founded in theearly Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, the surrounding area has been inhabited since the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
age, and throughout ancient history
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cove ...
, by the Nuragics and the Romans. Many archaeological sites and ancient ruins are located inside or around the town: the prehistoric step pyramid of Monte d'Accoddi, a large number of Nuraghes and Domus de Janas (Fairy Houses), the ruins of a Roman aqueduct, the ruins of a Roman villa discovered under San Nicholas Cathedral, and a portion of the ancient road that connected the Latin city of Turris Libisonis with
Caralis
Cagliari (, also , , ; sc, Casteddu ; lat, Caralis) is an Italian municipality and the capital of the island of Sardinia, an autonomous region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name ''Casteddu'' means ''castle''. It has about 155,000 inhabita ...
. In the locality of ''Fiume Santo'' is also found a fossil site where an ''Oreopithecus bambolii
''Oreopithecus'' (from the Greek , and , , meaning "hill-ape") is an extinct genus of hominoid primate from the Miocene epoch whose fossils have been found in today's Tuscany and Sardinia in Italy. It existed nine to seven million years ...
'', a prehistoric anthropomorphic primate, was discovered, dated at 8.5 million years.
Middle Ages
 The origin of the city remains uncertain. Among the theses, according to folk tradition the first village was founded around the 9th–10th century AD by the inhabitants of the ancient Roman port of ''Turris Libisonis'' (current Porto Torres), who sought refuge in the mainland to escape the
The origin of the city remains uncertain. Among the theses, according to folk tradition the first village was founded around the 9th–10th century AD by the inhabitants of the ancient Roman port of ''Turris Libisonis'' (current Porto Torres), who sought refuge in the mainland to escape the Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia ...
attacks from the sea.
It developed from the merger of a number of separate villages, such as San Pietro di Silki, San Giacomo di Taniga, and San Giovanni di Bosove. The oldest mention of the village is in an 1131 document in the archive of the Monastery of St. Peter in Silki where is cited a guy named ''Jordi de Sassaro'' (George of Sassari), a serf from the nearby village of Bosove. Sassari was sacked by the Genoese in 1166. Immigration continued until, in the early 13th century, it was the most populous city in the Giudicato of Torres
The Judicate of Logudoro or Torres ( sc, Judicadu de Logudoro or ''Torres'', ''Rennu de Logudoro'' or ''Logu de Torres'') was a state in northwest Sardinia from the tenth through the thirteenth century. Its original capital was Porto Torres. The ...
, and its last capital. After the assassination of Michele Zanche, the latter's last ruler in 1275, Sassari became subject to the Republic of Pisa with a semi-independent status.
 In 1284 the Pisans were defeated by the Genoese fleet at the
In 1284 the Pisans were defeated by the Genoese fleet at the Battle of Meloria
The Battle of Meloria was fought near the islet of Meloria in the Ligurian Sea on 5 and 6 August 1284 between the fleets of the Republics of Genoa and Pisa as part of the Genoese-Pisan War. The victory of Genoa and the destruction of the Pisa ...
, and the city was able to free itself: it became the Republic of Sassari, the first and only early independent renaissance city-state of Sardinia, with statutes of its own, allied to Genoa; the Genoese were pleased to see it thus withdrawn from Pisan control. Its statutes of 1316 are remarkable for the leniency of the penalties imposed when compared with the penal laws of the Middle Ages.
Alfonso V of Aragon
Alfonso the Magnanimous (139627 June 1458) was King of Aragon and King of Sicily (as Alfonso V) and the ruler of the Crown of Aragon from 1416 and King of Naples (as Alfonso I) from 1442 until his death. He was involved with struggles to the ...
nominated the town as a Royal Burg, directly ruled by the King and free from feudal taxation, during a period in which it may have been the most populous city in Sardinia. Further attempts made by Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
to conquer the city failed. In 1391 it was conquered by Brancaleone Doria
Brancaleone Doria was the husband of Eleanor of Arborea. He was a scion of an influential family (the Doria) of the Republic of Genoa, the son of the elder Brancaleone and a woman named Giacomina. On 16 March 1357, he became a vassal of Peter IV ...
and Marianus V of Arborea
Marianus V (1378 or 1379 – 1407) was the Judge of Arborea from 1387 until his death. His surname was Doria, but since he belonged to the ruling house of Arborea he is often dynastically called Bas-Serra, or Doria-Bas. Younger brother and suc ...
, of the independent Sardinian Giudicato of Arborea
The Judicate of Arborea ( sc, Judicadu de Arbaree, it, Giudicato di Arborea, ) or the Kingdom of Arborea (, , ) was one of the four independent judicates into which the island of Sardinia was divided in the Middle Ages. It occupied the central ...
, of which it became the last capital. However, in 1420 the city was sold along with the remaining territory for 100,000 florins to the Crown of Aragon, replaced by Spain after 1479 on the joining of the Aragonese and Castilian thrones. During the period of Aragonese and then Spanish domination the city was known as ''Sàsser'' in Catalan language
Catalan (; autonym: , ), known in the Valencian Community and Carche as '' Valencian'' (autonym: ), is a Western Romance language. It is the official language of Andorra, and an official language of three autonomous communities in eastern ...
and ''Saçer'' in old Spanish.
Renaissance
The city alternated years of crisis, featuring economic exploitation, the decrease of the maritime trade, made unsafe by the daily raids ofSaracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia ...
pirates, political corruption of its rulers, the sacking of Sassari in 1527 by the French, and two plagues in 1528 and 1652, with periods of cultural and economic prosperity. The Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
founded the first Sardinian university
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
in Sassari in 1562. In the same year the first printing press was introduced and the ideals of Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
became more widely known. Several artists of the Mannerist and Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
schools practiced their art in the city.
Modern history

 After the end of the Spanish period following the European wars of the early 18th century, the brief period of
After the end of the Spanish period following the European wars of the early 18th century, the brief period of Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
rule (1708–1717) was succeeded by domination by the Piedmontese, who then took over the Title of Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861). In 1795 an anti-feudal uprising broke out in the town, led by the Emissary of the Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
Giovanni Maria Angioy
Giovanni Maria Angioy (; sc, Juanne Maria Angioy, italics=no ; 21 October 1751, Bono – 22 February 1808, Paris) was a Sardinian politician and patriot and is considered to be a national hero by Sardinian nationalists. Although best known f ...
, a Sardinian civil servant, who later fought unsuccessfully against the house of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of ...
. The city was occupied by troops at the time. The dynasty of the Piedmontese King of Sardinia went on to the monarchs of Italy. Sassari, along with the rest of Italy, became part of the newly created Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
.
At the end of the 18th century the university
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
was restored. In 1836, after six hundred years, the medieval walls were partially demolished, allowing the town to expand. New urban plans were developed, on the model of the capital of the new regime's, (Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
), with geometric streets and squares.
Sassari became an important industrial center. In the 19th century it was the second most important town in what was to become the future Italy for the production of leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hog ...
, and in 1848 the Sassarese entrepreneur Giovanni Antonio Sanna gained control of the mine at Montevecchio, becoming the third richest man in the new Kingdom of Italy. The first railway was opened in 1872.
In 1877 the old Aragonese castle was demolished, and on the site the "Caserma La Marmora" was built, where the headquarters of " Brigata Sassari" is still located. Founded in 1915, it still consists mainly of Sardinian soldiers.
At the end of the 19th century new urban developments grew on Cappuccini Hill and to the south of the city, architecturally dominated by Eclecticism
Eclecticism is a conceptual approach that does not hold rigidly to a single paradigm or set of assumptions, but instead draws upon multiple theories, styles, or ideas to gain complementary insights into a subject, or applies different theories i ...
, Art Nouveau and Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unit ...
styles, which created a movement towards the hybrid experimentation of new local architectural styles, known as the ''Sassarese Liberty''.
During the Fascist dictatorship the town had over fifty thousand inhabitants and new neighbourhoods were built, the most important of these being Monte Rosello and Porcellana, typical examples of Rationalist Architecture
In architecture, Rationalism is an architectural current which mostly developed from Italy in the 1920s and 1930s. Vitruvius had claimed in his work '' De architectura'' that architecture is a science that can be comprehended rationally. The for ...
. On the other hand, the newspaper ''La Nuova Sardegna
''La Nuova Sardegna'' is an Italian regional daily newspaper for the island of Sardinia.
History and profile
''La Nuova Sardegna'' was founded in 1891 by Enrico Berlinguer, grandfather and namesake of Enrico Berlinguer, national secretary of ...
'', considered subversive, was closed down.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
three Allied attempts to bomb the town failed: only the railway station was damaged, and there was only one casualty.
Today Sassari is the main cultural, administrative and historical centre of Northern Sardinia.
Culture
University
The University of Sassari is the oldest in Sardinia (founded by theJesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
in 1562), and has a high reputation, especially in Jurisprudence, Veterinary Medicine, Medicine, and Agriculture. Its libraries contain a number of ancient documents, among them the condaghes, Sardinia's first legal codes and the first documents written in the Sardinian language (11th century) and the famous Carta de Logu
The Carta de Logu was a legal code of the Judicate of Arborea, written in the Sardinian language and promulgated by the ("Lady Judge") Eleanor of Arborea in 1392. It was in force in Sardinia until it was superseded by the Savoyard code of Ch ...
(the constitution issued by Marianus IV of Arborea
Marianus IV (in Sardinian: Marianu IV de Arbarèe, in Catalan: Marià IV d'Arborea, 1319–1376), called the Great, was the Judge (king) of Arborea, kingdom in the island of Sardinia, from 1347 to his death. He was, as his nickname indicate ...
and updated later by his daughter the ''Giudichessa'' Eleanor of Arborea
Eleanor of Arborea or Eleanor De Serra Bas ( Sardinian: Elianora de Arbarée / Elianora De Serra Bas, Italian: Eleonora d'Arborea / Eleonora De Serra Bas; 1347— June 1404) was one of the most powerful and important, and one of the last, judges ...
) in the 14th century.
The University of Sassari gained first place in 2009 in the ranking for the best “medium-sized” Italian university, awarded by the Censis Research Institute.
Language
Sassarese
Sassarese (natively ''sassaresu'' or ''turritanu''; sc, tataresu ) is an Italo-Dalmatian language and transitional variety between Sardinian and Corsican. It is regarded as a Corso– Sardinian language because of Sassari's historic ties ...
(''Sassaresu'' or ''Turritanu'') is much closer to Corsican and Tuscan language than it is to Sardinian, although this fact has caused some political controversy. It originated as a lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
between the first Sardinians, Corsicans, Tuscans and Liguria
Liguria (; lij, Ligûria ; french: Ligurie) is a Regions of Italy, region of north-western Italy; its Capital city, capital is Genoa. Its territory is crossed by the Alps and the Apennine Mountains, Apennines Mountain chain, mountain range and is ...
n people, during the period of the maritime republics. The original Tuscan structure was influenced by the Sardinian Logudorese spoken in the area, with a strong influence that can be felt in its phonetics and vocabulary, and by Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
and Spanish in vocabulary.
Sassarese is spoken in Sassari and its immediate area by approximately 120,000 people out a total population of 175,000 inhabitants; it is also the language of the north-west of Sardinia, including Stintino, Sorso
Sorso ( sdc, Sòssu) is a '' comune'' (municipality) of c. 14,700 inhabitants in the province of Sassari in the Italian region Sardinia, located about north of Sassari.
Overview
Sorso is a tourist resort facing the Gulf of Asinara. Apart touri ...
and Porto Torres; in the mid-northern areas of Sardinia, its ''Castellanesi'' dialects of Castelsardo
Castelsardo ( sdc, Castheddu; sc, Casteddu Sardu) is a town and '' comune'' in Sardinia, Italy, located in the northwest of the island within the Province of Sassari, at the east end of the Gulf of Asinara.
History
Archaeological excavations ...
, Tergu and Sedini are more similar to the Gallurese.
Main sights
 * Archeological site of Monte d'Accoddi: a unique prehistoric monument with a step pyramid construction
*The
* Archeological site of Monte d'Accoddi: a unique prehistoric monument with a step pyramid construction
*The Pisan
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and '' comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the cit ...
City Walls that in the 13th century surrounded the city with 36 towers (at the moment only 6 remain), and the Catalan-Aragonese Castle named Castello di Sassari, demolished in 1877, whose ruins, including some rooms, the basement, and part of a tower were rediscovered in 2008.
* The church of St. Peter in Silki, built in the 12th century but renovated in the 17th century. Here were found the medieval codes known as Condaghe di san Pietro in Silki.
* ''Corso Vittorio Emanuele'' is the main street of the medieval town, surrounded by interesting buildings of different ages, such as several examples of Catalan-gothic (as the so-called ''House of Re Enzo''), the baroque church of ''Sant' Andrea'', built by Corsican community, the neoclassic ''Civic Theatre'' and ''Quesada's palace''.
* The Cathedral of St. Nicholas of Bari, built in the 13th century and enlarged in Catalan Gothic style from 1480; there is a monument to the Duca di Moriana inside. The façade, belonging to the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
Spanish colonial restorations of 1650–1723, has a rectangular portico surmounted by three niches housing statues of saints. The bell tower is in Romanesque style.
* The church and monastery of ''Santa Maria di Bètlem'' (13th–19th century). The original façade and parts of monastery are in Lombard Romanesque
The term Lombard refers to people or things related to Lombardy, a region in northern Italy.
History and culture
* Lombards, a Germanic tribe
* Lombards of Sicily, a linguistic minority living in Sicily, southern Italy
* Lombard League, a me ...
style, some chapels in International Gothic, while the rest of the building, include the big dome, was rebuilt in Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
and Neoclassic style, by the Sardinian architect Antonio Cano in 1829–34.
* The Church of the Most Blessed Trinity contains a beautiful picture by an unknown artist of the Quattrocento.
* The Cimitero comunale di Sassari (Sassari Cemetery) opened in 1837 adjacent to the Chiesa San Paolo al Cimitero just west of the main railway station
Central stations or central railway stations emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century as railway stations that had initially been built on the edge of city centres were enveloped by urban expansion and became an integral part of the ...
* ''Palazzo D'Usini'', most important example of civilian architecture of the Renaissance period in Sardinia (now housing the main Public Library, therefore open to visits from the public).
* The Fountain of the Rosello, built in 1606 by Genoese craftsmen. It is made by two squared parts surmounted by two crossing arches supporting the statue of St. Gavino.
* University Palace (17th–20th century), originally a Jesuit school.
* The Ducal Palace (current Town Hall, 1775–1806), built for the Duke of the Asinara in the 18th century.
* ''Piazza d'Italia'' (19th century) is the main square in Sassari. It is surrounded by interesting buildings such as the Neo-Gothic "Palazzo Giordano" and the neoclassical "Palace of Sassari's Province", where the ancient royal apartments of the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of ...
were once located.
* Teatro Verdi Teatro Verdi may refer to:
* Teatro Verdi (Brindisi), Brindisi
* Teatro Giuseppe Verdi, Busseto
* Teatro Verdi (Florence), Florence
* Teatro Verdi (Padova), Padova, by architect Achille Sfondrini
* Teatro Verdi (Pisa), Pisa
* Teatro Verdi (Sal ...
, opera house and theater for concerts and plays
Museums
anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
collection " Luigi Rolando", physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ...
and agronomic collection)
* Ethnographic Museum "Francesco Bande"
* Contemporary Art Museum "Masedu"
* Museum and Treasury of the Cathedral
* Museum of History of Sassari
* Museum of Sassari's Diocese
* Museum of Candelieri
* Mario Sironi art collection
* Art gallery " Giuseppe Biasi"
* Pavilion of Sardinian handicraft EXPO "I.S.O.L.A."
Festivals and traditions
 * The '' Faradda di li candareri'' (''The Descent of the Candelieri''): it's a devotional procession, in which enormous wooden candles are carried by members of the city guilds from the town centre to the church of Santa Maria of Betlem, in commemoration of the end of the plague in 1582, but it probably has older origins, from a cultural tradition from Pisa that as early as in the second half of the 13th century was practiced in some parts of Sardinia.
* The '' Cavalcata Sarda'' (the Sardinian Cavalcade), a main event in Sardinia. On the last Sunday of May thousands of people come from all over Sardinia to Sassari to parade through the city in their local folk costumes on foot and ride on hundreds of the best Sardinian horses.
* '' Sardinia Film Festival'' was founded in 2006. With 500 films, short subjects, animated cartoons and
* The '' Faradda di li candareri'' (''The Descent of the Candelieri''): it's a devotional procession, in which enormous wooden candles are carried by members of the city guilds from the town centre to the church of Santa Maria of Betlem, in commemoration of the end of the plague in 1582, but it probably has older origins, from a cultural tradition from Pisa that as early as in the second half of the 13th century was practiced in some parts of Sardinia.
* The '' Cavalcata Sarda'' (the Sardinian Cavalcade), a main event in Sardinia. On the last Sunday of May thousands of people come from all over Sardinia to Sassari to parade through the city in their local folk costumes on foot and ride on hundreds of the best Sardinian horses.
* '' Sardinia Film Festival'' was founded in 2006. With 500 films, short subjects, animated cartoons and documentaries
A documentary film or documentary is a non-fictional motion-picture intended to "document reality, primarily for the purposes of instruction, education or maintaining a historical record". Bill Nichols has characterized the documentary in term ...
in 2009, it has become the most prominent film festival in Sardinia.
Sport & Infrastructures
Soccer
The city of Sassari hasU.S.D. Latte Dolce
Sassari Calcio Latte Dolce is an Italian football club based in Sassari / Usini , Sardinia. They currently play in Eccellenza.
History
The club was founded in 1973 as ''Unione Sportiva Latte Dolce'', as the club of the omonymous neighborhood in ...
, the Torres Calcio Femminile
Associazione Sportiva Dilettantistica FC Sassari Torres Femminile (usually referred to simply as Torres or sometimes named Eurospin Torres due to sponsorship) is an Italian women's association football club based in Sassari, Sardinia. The clu ...
that won seven Serie A
The Serie A (), also called Serie A TIM for national sponsorship with TIM, is a professional league competition for football clubs located at the top of the Italian football league system and the winner is awarded the Scudetto and the Cop ...
titles, eight Coppa Italia
The ("Italy Cup") is an annual knockout cup competition in Italian football organized by the FIGC until the 2009–10 season and the Lega Serie A ever since.
History
The beginning of the tournament was turbulent, due to the complexity of ...
, seven Supercoppa Italiana and two Italy Women's Cup The Italy Women's Cup was an Italian invitational women's football competition organized by the Lega Nazionale Dilettanti confronting the 2nd, 3rd and 4th ranking teams in the Serie A Femminile, the Italian Women's Cup champion or runner-up and se ...
. The main soccer team is S.E.F. Torres 1903
Torres is an Italian football club based in the city of Sassari. It plays in Serie C, the third division of the Italian football league system.
Re-founded in 2017, the club is the continuation of the Società per l'Educazione Fisica Torres, bor ...
who won the two Serie C2 in 1986-87 and 1999-00. The club is also famous for lanching players like Gianfranco Zola, Pietro Paolo Virdis, Antonello Cuccureddu
Antonello Cuccureddu (, ; 4 October 1949) is an Italian association football coach and former player who played as a defender. He last managed Lega Pro Prima Divisione club Grosseto in 2014.
Club career
A central defender, Cuccureddu spent hi ...
, Comunardo Niccolai
Comunardo Niccolai (; born 15 December 1946) is an Italian former footballer, who played as a defender.
Club career
A tough, physically strong centre-back, Niccolai initially began his career with Torres in 1963, before joining Cagliari Calcio ...
, Theofilos Karasavvidis, Walter Mazzarri.
Basketball
Sassari has the main basketball team that Dinamo Sassari in the 2014–15 wonItalian League
The Italic League or Most Holy League was an international agreement concluded in Venice on 30 August 1454, between the Papal States, the Republic of Venice, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, and the Kingdom of Naples, following the T ...
, the club won also the Italian Cup
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional It ...
in 2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wa ...
and 2015 and the Italian Supercup in 2014 and 2019. in 2018–19 the club won the FIBA Europe Cup
The FIBA Europe Cup (FEC) is an annual professional club basketball competition organised by FIBA for eligible European clubs. It is FIBA's European-wide second level. Clubs mainly qualify for the competition based on their performance in natio ...
.
Infrastructures
The city has the main Stadio Vanni Sanna where it is held some concerts and where plays theTorres Calcio Femminile
Associazione Sportiva Dilettantistica FC Sassari Torres Femminile (usually referred to simply as Torres or sometimes named Eurospin Torres due to sponsorship) is an Italian women's association football club based in Sassari, Sardinia. The clu ...
, S.E.F. Torres 1903
Torres is an Italian football club based in the city of Sassari. It plays in Serie C, the third division of the Italian football league system.
Re-founded in 2017, the club is the continuation of the Società per l'Educazione Fisica Torres, bor ...
and U.S.D. Latte Dolce
Sassari Calcio Latte Dolce is an Italian football club based in Sassari / Usini , Sardinia. They currently play in Eccellenza.
History
The club was founded in 1973 as ''Unione Sportiva Latte Dolce'', as the club of the omonymous neighborhood in ...
. The Palasport Roberta Serradimigni is the indor basketball arena where the basketball team of Dinamo Sassari plays and where it is held some concerts.
Notable people
Notable people born here include the former presidents of the ItalianRepublic
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
, Antonio Segni and Francesco Cossiga, and Enrico Berlinguer, secretary of the Italian Communist Party.
Sassari is also the birthplace of Domenico Alberto Azuni, a jurist expert in commercial law.
Personalities
Notable historical personages *Salvatore Alepus
Salvatore Alepus (or Salvator Salapusj) (1503 in Morella, Castellón – 1568 in Sardinia) was a Spanish Roman Catholic archbishop, who ruled the archdiocese of Sassari in the sixteenth century.
Biography
He was the son of the nobles Gabriel an ...
, theologist and poet (Morilla – Valencia)
* Edina Altara, artist
* Giovanni Maria Angioy
Giovanni Maria Angioy (; sc, Juanne Maria Angioy, italics=no ; 21 October 1751, Bono – 22 February 1808, Paris) was a Sardinian politician and patriot and is considered to be a national hero by Sardinian nationalists. Although best known f ...
, politician
* Domenico Alberto Azuni, jurist
* Enrico Berlinguer, leader of Italian Communist Party
* Mario Berlinguer, politician
* Giuseppe Biasi, painter
* Daniel Bovet, biochemist (Nobel Prize)
* Italo Calvino, writer
* Francesco Cetti
Francesco Cetti (9 August 1726 – 20 November 1778) was an Italian Jesuit priest, zoologist and mathematician.
Cetti was born in Mannheim in Germany, but his parents were natives of Como. He was educated in Lombardy and at the Jesuit colleg ...
* Eva Mameli
* Fernando Clemente, architect
* Francesco Cossiga, President of the Italian Republic
* Enrico Costa, astrophysicist, known for studies of gamma-ray bursts
* Giovanni del Giglio, painter better known as ''Maestro di Ozieri''
* Vico Mossa, architect
* Costantino Nivola
Costantino (also known as Antine, in Sardinia, or Tino, in the US) Nivola (July 5, 1911 – May 6, 1988) was an Italian sculptor, architectural sculptor, muralist, designer, and teacher.
Born in Sardinia, Nivola had already started his care ...
, artist
* Antonio Pigliaru,
* Luigi Rolando, anatomist
* Aligi Sassu
Aligi Sassu (17 July 1912 – 17 July 2000) was an Italian painter and sculptor.
Biography
Aligi Sassu was born in Milan, Lombardy. He was the son of Lina Pedretti (from Parma, Emilia) and Antonio Sassu (from Sassari, Sardinia). His father A ...
, painter
* Antonio Segni, President of the Italian Republic
* Mario Sironi, painter of creator of the '' Novecento''
* Giovanni Spano
Giovanni Spano (born Ploaghe, Sardinia, 3 March 1803; died Cagliari, Sardinia, 3 April 1878), also a priest and a linguist, is considered one of the first archaeologists to study the Mediterranean island of Sardinia.
After elementary school in ...
, writer
* Eugenio Tavolara
Eugenio Tavolara (1901–1963) was an artist born in Sassari, Sardinia, Italy, with interests in many disciplines. He is well known for his hand-crafted "toys", most prominently small statues in terracotta representing Sardinians in traditio ...
, artist
* Palmiro Togliatti, leader of the Italian Communist Party
* Pasquale Tola, politician and magistrate
* Michel Zanche, politician named by Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ' ...
in the '' Divina Commedia''
Contemporary personalities
* Valeria Alzari, Chemist, Unesco
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
and AIM prize
* Gavino Angius, member of the Democrats of the Left
* Paola Antonelli, senior Curator in the Department of Architecture and Design at the Museum of Modern Art
The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) is an art museum located in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, on 53rd Street between Fifth and Sixth Avenues.
It plays a major role in developing and collecting modern art, and is often identified as one of t ...
in New York
* Giovanni Berlinguer
Giovanni Berlinguer (; 9 July 1924 – 6 April 2015) was an Italian politician, humanist and professor of social medicine.
Life and career
He was born in Sassari, Sardinia, the son of Mario Berlinguer. A physician and professor of public heal ...
, one of the main members of the Democrats of the Left
* Enzo Calzaghe
Pietro Vincenzo "Enzo" Calzaghe (1 January 1949 – 17 September 2018) was an Italian-born Welsh boxing trainer. He was the father of Joe Calzaghe and the head trainer for Team Calzaghe at the Newbridge boxing club. He, along with son Joe, wa ...
, boxing trainer, father of Joe Calzaghe
* Elisabetta Canalis
Elisabetta Canalis (; born 12 September 1978) is an Italian actress and showgirl.
Early life
Canalis was born in Sassari, Sardinia in Italy. Her father, Cesare, is a radiologist in University of Sassari's clinic, and her mother, Bruna, was a te ...
, actress and television host
* Bruno Dettori, politician
* Antonello Grimaldi, film director
* Filomena Moretti
Filomena Moretti (born 11 June 1973)Maurice J. Summerfield: ''The Classical Guitar. Its Evolution, Players and Personalities Since 1800'', 5th edition (Blaydon-on-Tyne: Ashley Mark Publishing Co., 2002), p. 202. is an Italian classical guitarist. ...
, guitarist
* Arturo Parisi, former minister of Defence and member of The Daisy
* Giuseppe Pisanu, Former Italian Minister of the Interior
The Minister of the Interior (Italian: ''Ministro dell'Interno'') in Italy is one of the most important positions in the Council of Ministers (Italy), Italian Council of Ministers and leads the Ministry of the Interior (Italy), Ministry of the ...
and now president of the Antimafia Commission
* Giovanni Puggioni
Giovanni "Gianni" Puggioni (born 19 March 1966) is a former Italian sprinter who specialized in the 200 metres.
Biography
Puggioni was born in Sassari, Sardinia, he won eleven medals at the International athletics competitions, five of these w ...
, runner
* Roberto Tola, musician, composer, Recording Academy Member (Grammy Awards)
* Mario Segni
Mariotto Segni (born 16 May 1939) is an Italian politician and professor of civil law. He founded several parties, which focused on fighting for electoral reform through referendums. He is the son of the politician Antonio Segni, one time Presid ...
, member of European parliament
* Tazenda
Tazenda is a Sardinian ethnic pop-rock band. The group was formed in Sardinia in 1988 by Andrea Parodi, Gigi Camedda and Gino Marielli. The group's music is characterized by the influence from traditional Sardinian music; the lyrics of most ...
, ethno-pop-rock band
Government
Administrative subdivision
The Municipality of Sassari was subdivided into ten ''circoscrizioni'' (administrative districts), reduced to six since the elections of May 3, 2000, and four since the elections of May 31, 2010.Economy

 The economy of town is mainly focused on services and the advanced tertiary sector. It is the principal administrative centre of central and northern Sardinia. The main Sardinian banks ( Banco di Sardegna and Banca di Sassari) have head office and presidency in the city.
Several research centers are located in town: the University ones, the Center of Regional Weather Service (''Meteo Sar.''), the Regional Agency for Environmental Protection (''ARPA''), the Zooprophylaxis Institute of Sardinia, and many labs of the National Research Center ( CNR): the Institute of Biometeorology (''IBIMET''), the Institute of Biomolecular Chemistry (''ICB''), the Institute of Ecosystem Studies (''ISE''), the Institute of Sciences of Food Production (''ISPA''), and the Institute for Animal Production System in Mediterranean Environment (''ISPAAM'').
Manufacturing includes construction, pharmaceutical, food, typographic industry, and also, indirectly, petrochemical and the new greenchemicals located in Porto Torres.
Tourism is concentrated mainly along the coasts.
The economy of town is mainly focused on services and the advanced tertiary sector. It is the principal administrative centre of central and northern Sardinia. The main Sardinian banks ( Banco di Sardegna and Banca di Sassari) have head office and presidency in the city.
Several research centers are located in town: the University ones, the Center of Regional Weather Service (''Meteo Sar.''), the Regional Agency for Environmental Protection (''ARPA''), the Zooprophylaxis Institute of Sardinia, and many labs of the National Research Center ( CNR): the Institute of Biometeorology (''IBIMET''), the Institute of Biomolecular Chemistry (''ICB''), the Institute of Ecosystem Studies (''ISE''), the Institute of Sciences of Food Production (''ISPA''), and the Institute for Animal Production System in Mediterranean Environment (''ISPAAM'').
Manufacturing includes construction, pharmaceutical, food, typographic industry, and also, indirectly, petrochemical and the new greenchemicals located in Porto Torres.
Tourism is concentrated mainly along the coasts. Platamona
Platamona (Sassarese: "Pratamona or Prattamona") is a coastal area in northern Sardinia, Italy, located along the Gulf of Asinara, in the municipality of Sassari, between the commune of Sorso and Porto Torres.
The name ''Platamona'' comes fro ...
, Porto Ferro, Porto Palmas and Argentiera are the principal seaside tourist spots of the municipality.
Average income in Sassari is 24,006 euros per person.
Transportation
 The nearest airport, Fertilia International Airport, is from the city center, and the closest seaport is located at Porto Torres, away.
Urban and suburban
The nearest airport, Fertilia International Airport, is from the city center, and the closest seaport is located at Porto Torres, away.
Urban and suburban public transport
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typi ...
is operated by about 25 bus lines of ''Azienda Trasporti Pubblici'' (ATP) and by a light rail transit of ''Azienda Regionale Sarda Trasporti'' (ARST). Two different railway companies connect the town to the rest of the island: Trenitalia
Trenitalia is the primary train operator in Italy. A subsidiary of Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane, itself owned by the Italian government, the company was established in 2000 following a European Union directive on the deregulation of rail transp ...
links Sassari to Porto Torres, Oristano
Oristano (; sc, Aristanis ) is an Italian city and '' comune'', and capital of the Province of Oristano in the central-western part of the island of Sardinia. It is located on the northern part of the Campidano plain. It was established as the ...
, Cagliari
Cagliari (, also , , ; sc, Casteddu ; lat, Caralis) is an Italian municipality and the capital of the island of Sardinia, an autonomous region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name ''Casteddu'' means ''castle''. It has about 155,000 inhabitant ...
, Olbia
Olbia (, ; sc, Terranoa; sdn, Tarranoa) is a city and commune of 60,346 inhabitants (May 2018) in the Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called ''Olbia'' in the Roman age ...
, Golfo Aranci
Golfo Aranci (Gallurese: ''Figari'', sc, Figari) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Sassari in the Italian region Sardinia, located about north of Cagliari and about northeast of Olbia.
History
The town's name ("Gulf of the O ...
, and the ARST reaches Alghero, Sorso
Sorso ( sdc, Sòssu) is a '' comune'' (municipality) of c. 14,700 inhabitants in the province of Sassari in the Italian region Sardinia, located about north of Sassari.
Overview
Sorso is a tourist resort facing the Gulf of Asinara. Apart touri ...
, Nulvi and Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
.
Dual carriage motorways link Sassari to Porto Torres, Platamona
Platamona (Sassarese: "Pratamona or Prattamona") is a coastal area in northern Sardinia, Italy, located along the Gulf of Asinara, in the municipality of Sassari, between the commune of Sorso and Porto Torres.
The name ''Platamona'' comes fro ...
, Cagliari
Cagliari (, also , , ; sc, Casteddu ; lat, Caralis) is an Italian municipality and the capital of the island of Sardinia, an autonomous region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name ''Casteddu'' means ''castle''. It has about 155,000 inhabitant ...
('' SS131''), Olbia
Olbia (, ; sc, Terranoa; sdn, Tarranoa) is a city and commune of 60,346 inhabitants (May 2018) in the Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called ''Olbia'' in the Roman age ...
('' SS199'') and to Alghero ('' SS291''). High-capacity traffic roads connect Sassari to Tempio Pausania ('' SS672'') and Ittiri.
Sport
 * A.S.D. Torres Calcio football club, founded in 1903, playing in
* A.S.D. Torres Calcio football club, founded in 1903, playing in Serie C
The Serie C () is the third-highest division in the Italian football league system after the Serie B and Serie A. The Lega Italiana Calcio Professionistico (Lega Pro) is the governing body that runs the Serie C.
The unification of the Lega P ...
* Torres Calcio Femminile
Associazione Sportiva Dilettantistica FC Sassari Torres Femminile (usually referred to simply as Torres or sometimes named Eurospin Torres due to sponsorship) is an Italian women's association football club based in Sassari, Sardinia. The clu ...
women's football club, playing in Serie B
The Serie B (), currently named Serie BKT for sponsorship reasons, is the second-highest division in the Italian football league system after the Serie A. It has been operating for over ninety years since the 1929–30 season. It had been ...
, winners of seven national championships and eight national cups.
* Dinamo Basket Sassari, playing in Lega Basket Serie A
* HC Tangram 1 Sassari women's team handball club, playing in Serie A1
* ''Yellow Team Sassari Baseball'', playing in Serie C1
* ''Sassari Baseball Softball Club'', playing in serie C2
* ''A.S.D. Rugby Sassari'', playing in Serie C
Consulates
* *Twin towns – sister cities
Sassari is twinned with: *Gorizia
Gorizia (; sl, Gorica , colloquially 'old Gorizia' to distinguish it from Nova Gorica; fur, label= Standard Friulian, Gurize, fur, label= Southeastern Friulian, Guriza; vec, label= Bisiacco, Gorisia; german: Görz ; obsolete English ''Gori ...
, Italy, since 1983
* Timișoara, Romania, since 1990
* Gubbio
Gubbio () is an Italian town and '' comune'' in the far northeastern part of the Italian province of Perugia (Umbria). It is located on the lowest slope of Mt. Ingino, a small mountain of the Apennines.
History
The city's origins are very ancient. ...
, Italy, since 2002, between the Faradda and the Saint Ubaldo Day
Saint Ubaldo Day or ''Festa dei Ceri'' is an event celebrated on 15 May in the Italian town of Gubbio. It honors the life of Bishop Ubaldo Baldassini who was canonized as protector of Gubbio. It is also celebrated in the American town of Jessup, ...
* Viterbo
Viterbo (; Viterbese: ; lat-med, Viterbium) is a city and ''comune'' in the Lazio region of central Italy, the capital of the province of Viterbo.
It conquered and absorbed the neighboring town of Ferento (see Ferentium) in its early history ...
, Italy, since 2006, between the ''Faradda'' and the Macchina di Santa Rosa
* Nola
Nola is a town and a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, southern Italy. It lies on the plain between Mount Vesuvius and the Apennines. It is traditionally credited as the diocese that introduced bells to Christian wo ...
, Italy, since 2006, between the ''Faradda'' and the Festa dei Gigli
* Palmi, Italy since 2006, between the ''Faradda'' and the Varia di Palmi
* Napoli, Italy since 2009, between the ''Faradda'' and the Dedication of Saint Mary Major
* Campobasso
Campobasso (, ; nap, label= Campobassan, Cambuàsce ) is a city and '' comune'' in southern Italy, the capital of the region of Molise and of the province of Campobasso. It is located in the high basin of the Biferno river, surrounded by ...
, Italy since 2009, between the ''Faradda'' and the Festival dei Misteri
* Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, Spain, since 2010 ("''artistic twinning''")
See also
*Sassarese language
Sassarese (natively ''sassaresu'' or ''turritanu''; sc, tataresu ) is an Italo-Dalmatian language and transitional variety between Sardinian and Corsican. It is regarded as a Corso– Sardinian language because of Sassari's historic ties ...
* Province of Sassari
The province of Sassari ( it, provincia di Sassari, sc, provìntzia de Tàtari, sdc, prubìnzia di Sàssari, ca, província de Sàsser, french: province de Sassari, co, pruvincia di Sassari) is a province in the autonomous island region of Sa ...
* University of Sassari
The University of Sassari ( it, Università degli Studi di Sassari, UniSS) is a university located in Sassari, Italy. It was founded in 1562 and is organized in 13 departments.
The University of Sassari earned first place in the rankings for ...
* Sassari Mechanized Brigade
References
External links
Official website
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Sardinia