Saskatchewan Legislative Building on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Saskatchewan Legislative Building is located in Regina,
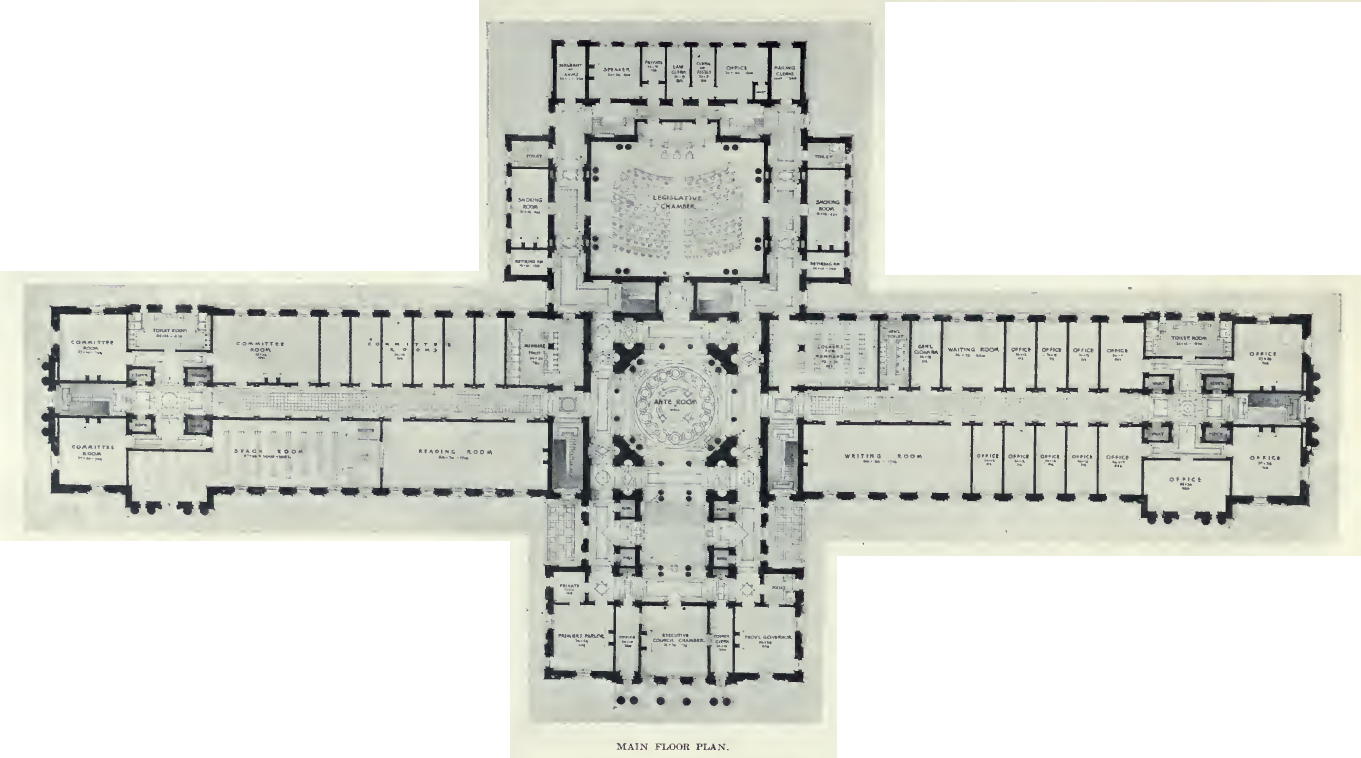
 The Saskatchewan Legislative Building was built between 1908 and 1912 in the Beaux Arts style to a design by
The Saskatchewan Legislative Building was built between 1908 and 1912 in the Beaux Arts style to a design by
 Diverging from parliamentary tradition, the carpet in the legislative chamber was red until 2012. Traditionally, red carpet is used for houses of unelected members, such as the
Diverging from parliamentary tradition, the carpet in the legislative chamber was red until 2012. Traditionally, red carpet is used for houses of unelected members, such as the

Drawings of unsuccessful designs in the 1907 competition for the commission to plan the Legislative Building Canadian Registry of Historic Places
{{Authority control Government buildings completed in 1912 Legislative buildings in Canada Buildings and structures in Regina, Saskatchewan Beaux-Arts architecture in Canada Government buildings with domes National Historic Sites in Saskatchewan Canadian Register of Historic Places in Saskatchewan Saskatchewan Legislature Tourist attractions in Regina, Saskatchewan 1912 establishments in Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
, Canada, and houses the Legislative Assembly of Saskatchewan.
History
 The Saskatchewan Legislative Building was built between 1908 and 1912 in the Beaux Arts style to a design by
The Saskatchewan Legislative Building was built between 1908 and 1912 in the Beaux Arts style to a design by Edward
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sax ...
and William Sutherland Maxwell of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
. The Maxwells also supervised construction of the building by the Montreal company P. Lyall & Sons, who later built the Centre Block of the federal Parliament Building in Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
after the 1866 Parliament Building was destroyed by fire in 1916. Piles began to be drilled for the foundations during the autumn of 1908 and in 1909 the Governor General of Canada
The governor general of Canada (french: gouverneure générale du Canada) is the federal viceregal representative of the . The is head of state of Canada and the 14 other Commonwealth realms, but resides in oldest and most populous realm ...
, the Earl Grey, laid the cornerstone. In 1912, Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught, by then the serving governor general, inaugurated the building.
The design contemplates expansion of the building by the addition of wings extending south from the east and west ends and coming together to form a courtyard. The plans originally called for the exterior of the building to be red brick but after construction had begun and red bricks were already on the site, Premier Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels '' Ivanhoe'', '' Rob Roy ...
decided that Manitoba Tyndall stone would give the building greater grandeur and the plans were adjusted with the substitution increasing the building cost by $50,000. The total cost of construction came to $1.75 million by the time of its opening in October 1912, ten months after the assembly had begun meeting in the yet-uncompleted building.
In 1965, Clifford Wiens started a major project of renovation and restoration which took some fourteen years to complete. Leslie Jen, associate editor at ''Canadian Architect'', called it a "masterful" renovation.
Characteristics
 Diverging from parliamentary tradition, the carpet in the legislative chamber was red until 2012. Traditionally, red carpet is used for houses of unelected members, such as the
Diverging from parliamentary tradition, the carpet in the legislative chamber was red until 2012. Traditionally, red carpet is used for houses of unelected members, such as the Senate of Canada
The Senate of Canada (french: region=CA, Sénat du Canada) is the upper house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the House of Commons, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada.
The Senate is modelled after the ...
, and houses of elected members are given blue or green carpet. Walter Scott preferred red carpet, and for a century the Saskatchewan Legislative Building stood as one of only two in Canada to feature red carpet in its legislative chamber (British Columbia's being the other). The red carpet was replaced by green carpet in the summer of 2012.
Walter Scott anticipated that the building might "for a century yet be credible enough to form the main building on the Capital grounds", the general assumption of the time being that Saskatchewan's population would grow to several million. That century has long since elapsed; the provincial legislative building remains the main building on the "Capital grounds", but indeed, continues to be the most imposing structure in a city smaller than its founders envisioned.
Such planning is evident in the legislative chamber itself, designed to accommodate 125 members. The assembly has never expanded beyond 66 MLAs (and currently has 61). As a result, even after those elections which yielded massive majorities (such as those held in 1982
Events January
* January 1 – In Malaysia and Singapore, clocks are adjusted to the same time zone, UTC+8 (GMT+8.00).
* January 13 – Air Florida Flight 90 crashes shortly after takeoff into the 14th Street Bridge in Washington, D.C ...
, 1991, and 2011
File:2011 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: a protester partaking in Occupy Wall Street heralds the beginning of the Occupy movement; protests against Libyan dictator Muammar Gaddafi, who was killed that October; a young man celebrates ...
) there has been plenty of space to seat all government members to the speaker's right. However, this peculiar practice has been abandoned (at least temporarily) as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
- currently, to satisfy physical distancing requirements, desks are spaced in such a manner that a relatively equal number need to be placed on each side of the Speaker, meaning some government backbenchers will sit on the Speaker's left.
The Institute for stained glass in Canada has documented the stained glass at Saskatchewan Legislature.
The Saskatchewan Legislative Building is located at 2405 Legislative Drive, Regina, overlooking Wascana Lake. Free tours of the facility are offered throughout the week.
Significance
The legislative building and its grounds were designated aNational Historic Site of Canada
National Historic Sites of Canada (french: Lieux historiques nationaux du Canada) are places that have been designated by the federal Minister of the Environment on the advice of the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada (HSMBC), as being ...
in 2005. It is also a Provincial Heritage Property under the Heritage Property Act.
Of historical significance, the table that was used during the meeting of the Fathers of Confederation in Quebec City in 1864 resides in the building's library, albeit with six feet of it removed. Lieutenant-Governor Edgar Dewdney of the North-West Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
brought the table to Regina, which was the capital of the territory at the time. It was used in the offices of the Indian commissioner for Manitoba and the North-West Territories until 1896. Six feet of the table length was removed from the middle so that it could fit within the limited confines of the Prince Edward Building
The Prince Edward Building is the current official (albeit seldom noted) name of the historic post office building in Regina, Saskatchewan, located at the corner of Scarth Street and 11th Avenue. The site had been occupied by the original Knox Pr ...
, the temporary home of the Legislative Assembly of Saskatchewan while the Saskatchewan Legislative Building was under construction.
Statues at Legislature

Current statues
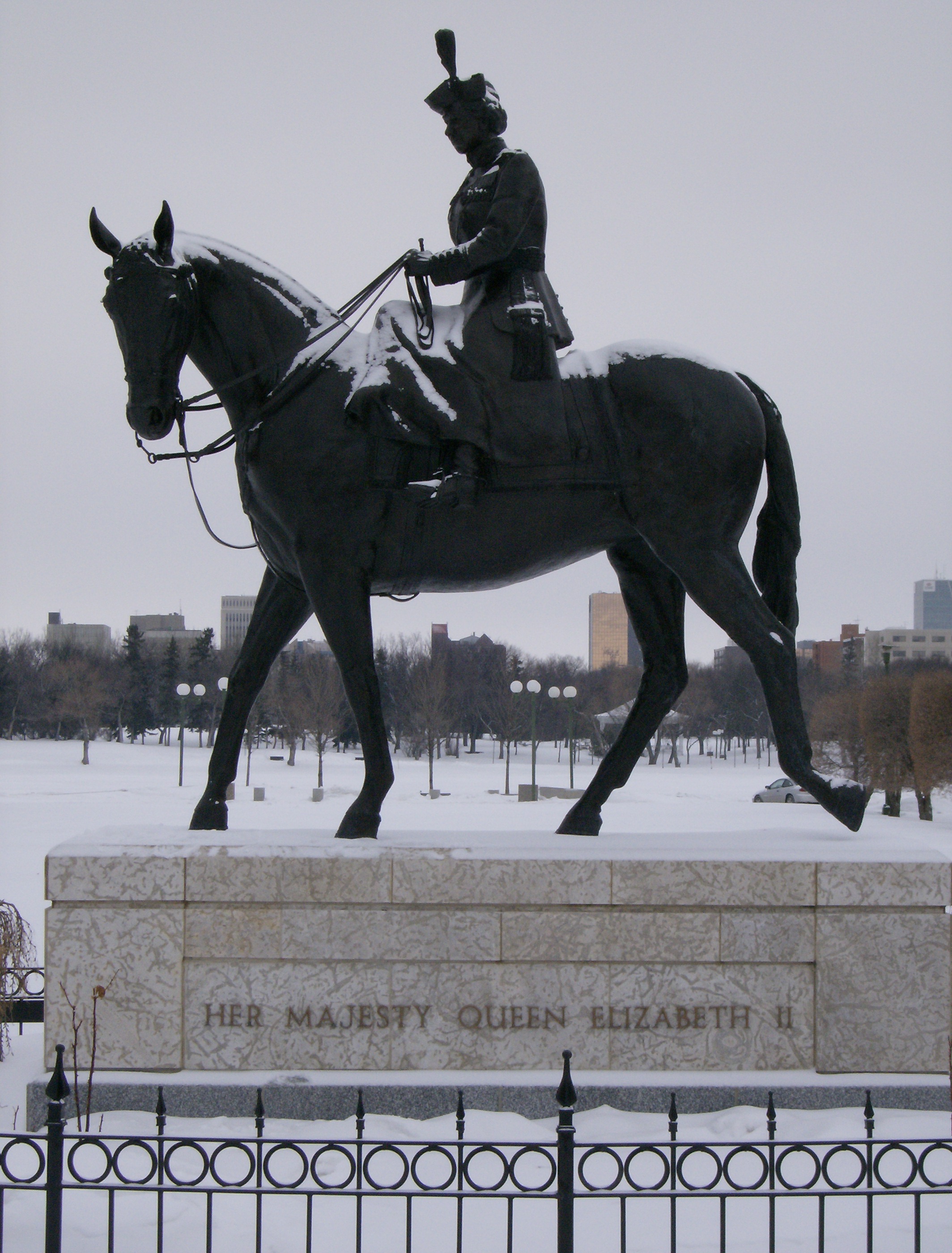
An equestrian statue of QueenElizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states durin ...
unveiled in 2005 at the renamed Queen Elizabeth II Gardens stands in front of the legislative building. It was designed by Susan Velder. The statue depicts the Queen atop Burmese, her favourite horse, a gift from the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal and national police service of Canada. As poli ...
in 1969. The horse was originally bred in Saskatchewan.
On the eastern side of the building there is a fountain, one of two brought from London's Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson comm ...
, the other having been taken to Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
(and now located at Confederation Park
Confederation Park ''(French: Parc de la Confédération)'' is a public park and National Historic Site of Canada, located in the downtown core of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It is bordered on the south by Laurier Avenue and Ottawa City Hall; on the ...
). The Peterhead granite fountain was designed by McDonald and Leslie and were relocated before the mid-1930s when Trafalgar Square obtained new fountains designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens
Sir Edwin Landseer Lutyens ( ; 29 March 1869 – 1 January 1944) was an English architect known for imaginatively adapting traditional architectural styles to the requirements of his era. He designed many English country houses, war memor ...
.
Removed statue
The commissioned statue of Louis Riel by John Cullen Nugent unveiled in 1968 stood on the grounds of the legislature until 1991, when it was removed at the insistence of the Saskatchewan Métis Society and others. Some found the work demoralizing for depicting Louis Riel in a "disrespectful" manner: "gaunt" and semi-nude, in the moment of ultimate Métis humiliation. Others argued that the sculpture was Euro-Canadian appropriation.
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Drawings of unsuccessful designs in the 1907 competition for the commission to plan the Legislative Building
{{Authority control Government buildings completed in 1912 Legislative buildings in Canada Buildings and structures in Regina, Saskatchewan Beaux-Arts architecture in Canada Government buildings with domes National Historic Sites in Saskatchewan Canadian Register of Historic Places in Saskatchewan Saskatchewan Legislature Tourist attractions in Regina, Saskatchewan 1912 establishments in Saskatchewan