San Francisco Bay on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 San Francisco Bay is a large tidal
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal
 In 1921, a tablet was dedicated by a group of men including Lewis Francis Byington, in downtown San Francisco, marking the site of the original shoreline. The tablet reads: "This tablet marks the shore line of San Francisco Bay at the time of the discovery of gold in California, January 24, 1848. Map reproduced above delineates old shore line. Placed by the Historic Landmarks committee,
In 1921, a tablet was dedicated by a group of men including Lewis Francis Byington, in downtown San Francisco, marking the site of the original shoreline. The tablet reads: "This tablet marks the shore line of San Francisco Bay at the time of the discovery of gold in California, January 24, 1848. Map reproduced above delineates old shore line. Placed by the Historic Landmarks committee,  In 1910, the Southern Pacific railroad company built the Dumbarton Rail Bridge, the first bridge crossing San Francisco Bay. The first automobile crossing was the Dumbarton Bridge, completed in January 1927. More crossings were later constructed – the Carquinez Bridge in May 1927, the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge in 1936, the Golden Gate Bridge in 1937, the Richmond–San Rafael Bridge in 1956, and the San Mateo–Hayward Bridge in 1967.
In 1910, the Southern Pacific railroad company built the Dumbarton Rail Bridge, the first bridge crossing San Francisco Bay. The first automobile crossing was the Dumbarton Bridge, completed in January 1927. More crossings were later constructed – the Carquinez Bridge in May 1927, the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge in 1936, the Golden Gate Bridge in 1937, the Richmond–San Rafael Bridge in 1956, and the San Mateo–Hayward Bridge in 1967.

 During the 20th century, the bay was subject to the Reber Plan, which would have filled in parts of the bay in order to increase industrial activity along the waterfront. In 1959, the
During the 20th century, the bay was subject to the Reber Plan, which would have filled in parts of the bay in order to increase industrial activity along the waterfront. In 1959, the
 Despite its urban and industrial character, San Francisco Bay and the
Despite its urban and industrial character, San Francisco Bay and the
 San Francisco Bay's profile changed dramatically in the late 19th century and again with the initiation of dredging by the
San Francisco Bay's profile changed dramatically in the late 19th century and again with the initiation of dredging by the  In the decades surrounding 1900, at the behest of local political officials and following Congressional orders, the U.S. Army Corps began dredging the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers and the deep channels of San Francisco Bay. This work has continued without interruption ever since—an enormous federal subsidy of San Francisco Bay shipping. Some of the dredge spoils were initially dumped in the bay shallows (including helping to create
In the decades surrounding 1900, at the behest of local political officials and following Congressional orders, the U.S. Army Corps began dredging the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers and the deep channels of San Francisco Bay. This work has continued without interruption ever since—an enormous federal subsidy of San Francisco Bay shipping. Some of the dredge spoils were initially dumped in the bay shallows (including helping to create
 San Francisco Bay was traversed by watercraft before the arrival of Europeans. Indigenous peoples used canoes to fish and clam along the shoreline. Sailing ships enabled transportation between the Bay and other parts of the world—and served as ferries and freighters within the Bay and between the Bay and inland ports, such as Sacramento and Stockton. These were gradually replaced by steam-powered vessels starting in the late 19th century. Several shipyards were established around the Bay, augmented during wartime. (e.g., the
San Francisco Bay was traversed by watercraft before the arrival of Europeans. Indigenous peoples used canoes to fish and clam along the shoreline. Sailing ships enabled transportation between the Bay and other parts of the world—and served as ferries and freighters within the Bay and between the Bay and inland ports, such as Sacramento and Stockton. These were gradually replaced by steam-powered vessels starting in the late 19th century. Several shipyards were established around the Bay, augmented during wartime. (e.g., the  The bay also continues to serve as a major
The bay also continues to serve as a major
The Bay of San Francisco: the metropolis of the Pacific Coast and its suburban cities: a history.
Volume I. by Lewis Publishing Company, Chicago, Ill. Published 189
Contains index to biographical sketches
Volume II
– Biographies
''San Francisco Bay: Portrait of an Estuary'', David Sanger and John Hart, University of California Press
''The Islands of San Francisco Bay'', James A. Martin , Michael T. Lee, Down Window PressArmy Corps of Engineers Bay Model: Working scale model of the BaySF Bay Kayak, Canoe, and Boat Launch Ramp guide. A collaboratively edited guide to the SF bay.BoatingSF.com: Photos of SF Bay and its boats, plus online cruising guideSave San Francisco Bay: Protect and Restore San Francisco Baysfbaywildlife.info
Guide to San Francisco Bay wildlife
Early History of the California Coast, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel ItineraryCartography & History ''The representations of San Francisco Bay: a portable harbor in the fragile geography of the North Pacific''
*'' San Francisco Estuary and Watershed Science'': a peer-reviewed online science journal {{Authority control Bays of California Bodies of water of Richmond, California San Francisco Bay watershed Estuaries of California Tourist attractions in the San Francisco Bay Area Ramsar sites in the United States Wetlands of California Bodies of water of San Francisco Bodies of water of Alameda County, California Bodies of water of Santa Clara County, California Bodies of water of Contra Costa County, California Bodies of water of Solano County, California Bodies of water of San Mateo County, California Bays of Marin County, California Estuaries of Marin County, California Bays of Contra Costa County, California
 San Francisco Bay is a large tidal
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
in the U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
state of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from approximately 40 percent of California. Water from the Sacramento
)
, image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250x200px
, map_caption = Location within Sacramento ...
and San Joaquin rivers, and from the Sierra Nevada mountains, flow into Suisun Bay, which then travels through the Carquinez Strait
The Carquinez Strait (; Spanish: ''Estrecho de Carquinez'') is a narrow tidal strait in Northern California. It is part of the tidal estuary of the Sacramento and the San Joaquin rivers as they drain into the San Francisco Bay. The strait is ...
to meet with the Napa River
The Napa River is a river approximately long in the U.S. state of California. It drains a famous wine-growing region called the Napa Valley, in the mountains north of the San Francisco Bay. Milliken Creek and Mt. Veeder watersheds are a few ...
at the entrance to San Pablo Bay, which connects at its south end to San Francisco Bay. It then connects to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
via the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
strait. However, this entire group of interconnected bays is often called the ''San Francisco Bay''. The bay was designated a Ramsar Wetland of International Importance on February 2, 2017.
Size
The bay covers somewhere between , depending on which sub-bays (such as San Pablo Bay), estuaries,wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The p ...
s, and so on are included in the measurement. The main part of the bay measures wide east-to-west and somewhere between 1 and 2 north-to-south. It is the largest Pacific estuary in the Americas.
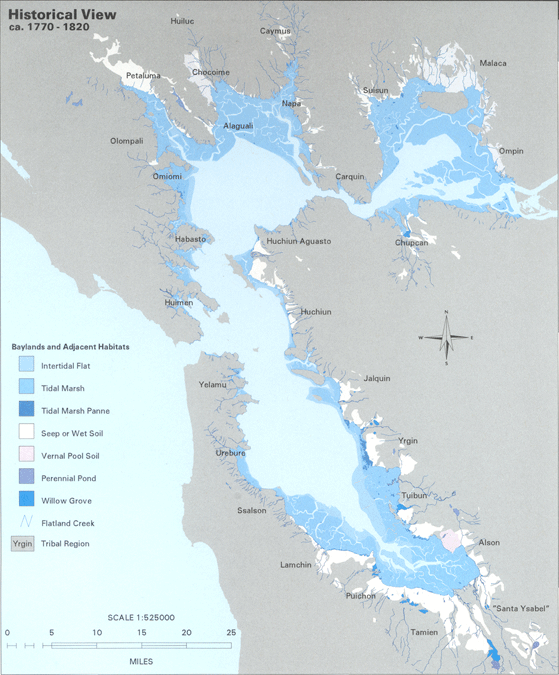
The bay was navigable as far south as San Jose until the 1850s, when hydraulic mining released massive amounts of sediment from the rivers that settled in those parts of the bay that had little or no current. Later, wetlands and inlets were deliberately filled in, reducing the Bay's size since the mid-19th century by as much as one third. Recently, large areas of wetlands have been restored, further confusing the issue of the Bay's size. Despite its value as a waterway and harbor
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
, many thousands of acres of marshy wetlands at the edges of the bay were, for many years, considered wasted space. As a result, soil excavated for building projects or dredged
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
from channels was often dumped onto the wetlands and other parts of the bay as landfill.
From the mid-19th century through the late 20th century, more than a third of the original bay was filled and often built on. The deep, damp soil in these areas is subject to soil liquefaction during earthquakes, and most of the major damage close to the Bay in the Loma Prieta earthquake of 1989 occurred to structures on these areas.
The Marina District of San Francisco, hard hit by the 1989 earthquake, was built on fill that had been placed there for the Panama-Pacific International Exposition, although liquefaction did not occur on a large scale. In the 1990s, San Francisco International Airport proposed filling in hundreds more acres to extend its overcrowded international runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concre ...
s in exchange for purchasing other parts of the bay and converting them back to wetlands. The idea was, and remains, controversial. (''For further details, see the " Bay fill and depth profile" section.'')
There are five large islands in San Francisco Bay. Alameda
An alameda is a Avenue (landscape), street or path lined with trees () and may refer to:
Places Canada
*Alameda, Saskatchewan, town in Saskatchewan
**Grant Devine Dam, formerly ''Alameda Dam'', a dam and reservoir in southern Saskatchewan
Chile
...
, the largest island, was created when a shipping lane was cut to form the Port of Oakland
The Port of Oakland is a major container ship facility located in Oakland, California, in the San Francisco Bay. It was the first major port on the Pacific Coast of the United States to build terminals for container ships. As of 2011 it was the f ...
in 1901. It is now a suburban community. Angel Island was known as "Ellis Island
Ellis Island is a federally owned island in New York Harbor, situated within the U.S. states of New York and New Jersey, that was the busiest immigrant inspection and processing station in the United States. From 1892 to 1954, nearly 12 mil ...
West" because it served as the entry point for immigrants from East Asia. It is now a state park accessible by ferry. Mountainous Yerba Buena Island
Yerba Buena Island ( Spanish: ''Isla Yerba Buena'') sits in San Francisco Bay within the borders of the City and County of San Francisco. The Yerba Buena Tunnel runs through its center and connects the western and eastern spans of the San Franc ...
is pierced by a tunnel linking the east and west spans of the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge. Attached to the north is the artificial and flat Treasure Island
''Treasure Island'' (originally titled ''The Sea Cook: A Story for Boys''Hammond, J. R. 1984. "Treasure Island." In ''A Robert Louis Stevenson Companion'', Palgrave Macmillan Literary Companions. London: Palgrave Macmillan. .) is an adventure no ...
, site of the 1939 Golden Gate International Exposition
The Golden Gate International Exposition (GGIE) (1939 and 1940), held at San Francisco's Treasure Island, was a World's Fair celebrating, among other things, the city's two newly built bridges. The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge opened in 1936 ...
. From the Second World War until the 1990s, both islands served as military bases and are now being redeveloped. Isolated in the center of the Bay is Alcatraz
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pris ...
, the site of the famous federal penitentiary. The federal prison on Alcatraz Island
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pri ...
no longer functions, but the complex is a popular tourist site. Despite its name, Mare Island
Mare Island ( Spanish: ''Isla de la Yegua'') is a peninsula in the United States in the city of Vallejo, California, about northeast of San Francisco. The Napa River forms its eastern side as it enters the Carquinez Strait juncture with the ...
in the northern part of the bay is a peninsula rather than an island.
Geology
San Francisco Bay is thought to represent a down-warping of the Earth's crust between theSan Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is right-lateral strike-slip (horizonta ...
to the west and the Hayward Fault
The Hayward Fault Zone is a right-lateral strike-slip geologic fault zone capable of generating destructive earthquakes. This fault is about long, situated mainly along the western base of the hills on the east side of San Francisco Bay. It run ...
to the east, though the precise nature of this remains under study. About 560,000 years ago, a tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
shift caused the large inland Lake Corcoran to spill out the central valley and through the Carquinez Strait
The Carquinez Strait (; Spanish: ''Estrecho de Carquinez'') is a narrow tidal strait in Northern California. It is part of the tidal estuary of the Sacramento and the San Joaquin rivers as they drain into the San Francisco Bay. The strait is ...
, carving out sediment and forming canyons in what is now the northern part of the San Francisco Bay and Golden Gate strait.
Until the last ice age, the basin which is now filled by the San Francisco Bay was a large linear valley with small hills, similar to most of the valleys of the Coast Ranges. As the great ice sheets began to melt, around 11,000 years ago, the sea level started to rise. By 5000 BC the sea level rose , filling the valley with water from the Pacific. The valley became a bay, and the small hills became islands.
History
The indigenous inhabitants of the San Francisco Bay are Ohlone. The first European to see San Francisco Bay is likelyN. de Morena N. de Morena or N. de Morera, name given to him by his contemporary Fray Juan de Torquemada and by most authors, was a European Maritime pilot, ship pilot in the 1577–1580 expedition of Sir Francis Drake. In ill health, he was reportedly left at N ...
who was left at New Albion
New Albion, also known as ''Nova Albion'' (in reference to an archaic name for Britain), was the name of the continental area north of Mexico claimed by Sir Francis Drake for England when he landed on the North American west coast in 1579. Thi ...
at Drakes Bay
Drakes Bay (Coast Miwok: ''Tamál-Húye'') is a wide bay named so by U.S. surveyor George Davidson in 1875 along the Point Reyes National Seashore on the coast of northern California in the United States, approximately northwest of San Fra ...
in Marin County, California, by Sir Francis Drake in 1579 and then walked to Mexico.
The first recorded European discovery of San Francisco Bay was on November 4, 1769, when Spanish explorer Gaspar de Portolá
Gaspar de Portolá y Rovira (January 1, 1716 – October 10, 1786) was a Spanish military officer, best known for leading the Portolá expedition into California and for serving as the first Governor of the Californias. His expedition laid the ...
, unable to find the Port of Monterey, continued north close to what is now Pacifica and reached the summit of the Sweeney Ridge, now marked as the place where he first sighted San Francisco Bay. Portolá and his party did not realize what they had discovered, thinking they had arrived at a large arm of what is now called Drakes Bay
Drakes Bay (Coast Miwok: ''Tamál-Húye'') is a wide bay named so by U.S. surveyor George Davidson in 1875 along the Point Reyes National Seashore on the coast of northern California in the United States, approximately northwest of San Fra ...
. At the time, Drakes Bay went by the name ''Bahia de San Francisco'' and thus both bodies of water became associated with the name. Eventually, the larger, more important body of water fully appropriated the name ''San Francisco Bay''.
The first European to enter the bay is believed to have been the Spanish explorer Juan de Ayala
Juan Manuel de Ayala y Aranza (28 December 1745 – 30 December 1797) was a Spanish naval officer who played a significant role in the European exploration of California, since he and the crew of his ship the ''San Carlos'' are the first European ...
, who passed through the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
on August 5, 1775, in his ship the ''San Carlos'' and moored in a bay of Angel Island now known as Ayala Cove. Ayala continued to explore the Bay area and the expedition's cartographer, José de Cañizares, gathered the information necessary to produce the first map of the San Francisco Bay Area. A number of place names survive (anglicized) from that first map, including Point Reyes, Angel Island, Farallon Islands and Alcatraz Island
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pri ...
.
The United States seized the region from Mexico during the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
(1846–1848). On February 2, 1848, the Mexican province of Alta California was annexed to the United States with the signing of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
. A year and a half later, California requested to join the United States on December 3, 1849, and was accepted as the 31st State of the Union on September 9, 1850.
 In 1921, a tablet was dedicated by a group of men including Lewis Francis Byington, in downtown San Francisco, marking the site of the original shoreline. The tablet reads: "This tablet marks the shore line of San Francisco Bay at the time of the discovery of gold in California, January 24, 1848. Map reproduced above delineates old shore line. Placed by the Historic Landmarks committee,
In 1921, a tablet was dedicated by a group of men including Lewis Francis Byington, in downtown San Francisco, marking the site of the original shoreline. The tablet reads: "This tablet marks the shore line of San Francisco Bay at the time of the discovery of gold in California, January 24, 1848. Map reproduced above delineates old shore line. Placed by the Historic Landmarks committee, Native Sons of the Golden West
The Native Sons of the Golden West is a fraternal service organization founded in the U.S. state of California in 1875, dedicated to historic preservation, documentation of historic structures and places in the state, the placement of historic ...
, 1921."
The Bay became the center of American settlement and commerce in the Far West through most of the remainder of the 19th century. During the California Gold Rush (1848–1855), San Francisco Bay suddenly became one of the world's great seaports, dominating shipping in the American West until the last years of the 19th century. The bay's regional importance increased further when the First transcontinental railroad was connected to its western terminus at Alameda
An alameda is a Avenue (landscape), street or path lined with trees () and may refer to:
Places Canada
*Alameda, Saskatchewan, town in Saskatchewan
**Grant Devine Dam, formerly ''Alameda Dam'', a dam and reservoir in southern Saskatchewan
Chile
...
on September 6, 1869. The terminus was switched to the Oakland Long Wharf
The Oakland Long Wharf was an 11,000-foot railroad wharf and ferry pier along the east shore of San Francisco Bay located at the foot of Seventh Street in West Oakland. The Oakland Long Wharf was built, beginning 1868, by the Central Pacific Rail ...
two months later on November 8, 1869.

United States Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
released a report stating that if current infill trends continued, the bay would be as big as a shipping channel by 2020. This news created the Save the Bay movement in 1960, which mobilized to stop the infill of wetlands and the bay in general, which had shrunk to two-thirds of its size in the century before 1961.
San Francisco Bay continues to support some of the densest industrial production and urban settlement in the United States. The San Francisco Bay Area is the American West's second-largest urban area, with approximately seven million residents.
Ecology

 Despite its urban and industrial character, San Francisco Bay and the
Despite its urban and industrial character, San Francisco Bay and the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta
The Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta, or California Delta, is an expansive inland river delta and estuary in Northern California. The Delta is formed at the western edge of the Central Valley by the confluence of the Sacramento and San ...
remain perhaps California's most important ecological habitats. California's Dungeness crab, California halibut, and Pacific salmon
''Oncorhynchus'' is a genus of fish in the family Salmonidae; it contains the Pacific salmon and Pacific trout. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek ὄγκος (ónkos, “lump, bend”) + ῥύγχος (rhúnkhos, “snout”), i ...
fisheries rely on the bay as a nursery. The few remaining salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is domin ...
es now represent most of California's remaining salt marsh, supporting a number of endangered species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
and providing key ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. ...
such as filtering pollutants and sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
s from the rivers. San Francisco Bay is recognized for protection by the California Bays and Estuaries Policy, with oversight provided by the San Francisco Estuary Partnership.State Water Resources Control Board ''Water Quality Control Policy for the Enclosed Bays and Estuaries of California'' (1974) State of California
Most famously, the bay is a key link in the Pacific Flyway. Millions of waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
annually use the bay shallows as a refuge. Two endangered species of birds are found here: the California least tern
The California least tern, ''Sternula antillarum browni'', is a subspecies of least tern that breeds primarily in bays of the Pacific Ocean within a very limited range of Southern California, in San Francisco Bay and in northern regions of Mexico ...
and the Ridgway's Rail. Exposed bay muds provide important feeding areas for shorebird
245px, A flock of Dunlins and Red knots">Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots
Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflat ...
s, but underlying layers of bay mud pose geological hazards for structures near many parts of the bay perimeter. San Francisco Bay provided the nation's first wildlife refuge, Oakland's artificial Lake Merritt
Lake Merritt is a large tidal lagoon in the center of Oakland, California, just east of Downtown. It is surrounded by parkland and city neighborhoods. It is historically significant as the United States' first official wildlife refuge, designate ...
, constructed in the 1860s, and America's first urban National Wildlife Refuge, the Don Edwards San Francisco Bay National Wildlife Refuge
Don Edwards San Francisco Bay National Wildlife Refuge (DESFBNWR) is a United States National Wildlife Refuge located in the southern part of San Francisco Bay, California. The Refuge headquarters and visitor center is located in the Baylands dist ...
(SFBNWR) in 1972. The Bay is also plagued by non-native species.
Salt produced from San Francisco Bay is produced in salt evaporation pond
A salt evaporation pond is a shallow artificial salt pan designed to extract salts from sea water or other brines. The Salt pans are shallow and large of size because it will be easier for sunlight to travel and reach the sea water. Natural sal ...
s and is shipped throughout the Western United States to bakeries, canneries, fisheries, cheese makers and other food industries and used to de-ice winter highways, clean kidney dialysis machines, for animal nutrition, and in many industries. Many companies have produced salt in the Bay, with the Leslie Salt Company the largest private land owner in the Bay Area in the 1940s.
Low-salinity salt ponds mirror the ecosystem of the bay, with fish and fish-eating birds in abundance. Mid-salinity ponds support dense populations of brine shrimp
''Artemia'' is a genus of aquatic crustaceans also known as brine shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Artemiidae. The first historical record of the existence of ''Artemia'' dates back to the first half of the 10th century AD from Urmia L ...
, which provide a rich food source for millions of shorebirds. Only salt-tolerant micro-algae survive in the high salinity ponds, and impart a deep red color to these ponds from the pigment within the algae protoplasm. The salt marsh harvest mouse
The salt marsh harvest mouse (''Reithrodontomys raviventris''), also known as the red-bellied harvest mouse, is an endangered rodent endemic to the San Francisco Bay Area salt marshes in California. The two distinct subspecies are both endangere ...
is an endangered species endemic to the wetlands of the San Francisco Bay with a high salt tolerance. It needs native pickleweed, which is often displaced by invasive cordgrass, for its habitat.
The seasonal range of water temperature in the Bay is from January's to September's when measured at Fort Point, which is near the southern end of the Golden Gate Bridge and at the entrance to San Francisco Bay.
For the first time in 65 years, Pacific Harbor Porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena'') returned to the Bay in 2009. Golden Gate Cetacean Research, a non-profit organization focused on research on cetaceans, has developed a photo-identification database enabling the scientists to identify specific porpoise individuals and is trying to ascertain whether a healthier bay has brought their return. Pacific harbor porpoise range from Point Conception
Point Conception (Chumash: ''Humqaq'') is a headland along the Gaviota Coast in southwestern Santa Barbara County, California. It is the point where the Santa Barbara Channel meets the Pacific Ocean, and as the corner between the mostly north ...
, California, to Alaska and across to the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and w ...
and Japan. Recent genetic studies show that there is a local stock from San Francisco to the Russian River and that eastern Pacific coastal populations rarely migrate far, unlike western Atlantic Harbor porpoise.
Pollution
Industrial, mining, and other uses of mercury have resulted in a widespread distribution in the bay, with uptake in the bay's phytoplankton and contamination of its sportfish. In January 1971, two Standard Oil tankers collided in the bay, creating an oil spill disaster, which spurred environmental protection of the bay. In November 2007, a ship named '' COSCO Busan'' collided with the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge and spilled over ofbunker fuel
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), ...
, creating the largest oil spill in the region since 1996.
The Bay was once considered a hotspot for polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers or PBDEs, are a class of organobromine compounds that are used as flame retardants. Like other brominated flame retardants, PBDEs have been used in a wide array of products, including building materials, electronics, ...
) flame retardants used to make upholstered furniture and infant care items less flammable. PBDEs have been largely phased out and replaced with alternative phosphate flame retardants. A 2019 San Francisco Estuary Institute (SFEI) study assayed a wide range of these newer flame retardant chemicals in Bay waters, bivalve California mussels (''Mytilus californianus''), and harbor seal
The harbor (or harbour) seal (''Phoca vitulina''), also known as the common seal, is a true seal found along temperate and Arctic marine coastlines of the Northern Hemisphere. The most widely distributed species of pinniped (walruses, eared se ...
s (''Phoca vitulina'') which haul out in Corkscrew Slough on Bair Island in San Mateo County
San Mateo County ( ), officially the County of San Mateo, is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 764,442. Redwood City is the county seat, and the third most populated city following Daly ...
, with phosphate flame retardant contaminants such as tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl)phosphate (TDCPP) and triphenyl phosphate
Triphenyl phosphate (TPhP) is the chemical compound with the formula OP(OC6H5)3. This colourless solid is the ester (triester) of phosphoric acid and phenol. It is used as a plasticizer and a fire retardant in a wide variety of settings and produc ...
(TPhP) found at levels comparable to thresholds for aquatic toxicity.
Bay fill and depth profile
 San Francisco Bay's profile changed dramatically in the late 19th century and again with the initiation of dredging by the
San Francisco Bay's profile changed dramatically in the late 19th century and again with the initiation of dredging by the US Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
in the 20th century. Before about 1860, most bay shores (with the exception of rocky shores, such as those in Carquinez Strait; along Marin shoreline; Point Richmond; Golden Gate area) contained extensive wetlands that graded nearly invisibly from freshwater wetlands to salt marsh and then tidal mudflat. A deep channel ran through the center of the bay, following the ancient drowned river valley.
In the 1860s and continuing into the early 20th century, miners dumped staggering quantities of mud and gravel from hydraulic mining operations into the upper Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers. GK Gilbert's estimates of debris total more than eight times the amount of rock and dirt moved during construction of the Panama Canal. This material flowed down the rivers, progressively eroding into finer and finer sediment, until it reached the bay system. Here some of it settled, eventually filling in Suisun Bay, San Pablo Bay, and San Francisco Bay, in decreasing order of severity.
By the end of the 19th century, these " slickens" had filled in much of the shallow bay flats, raising the entire bay profile. New marshes were created in some areas.
 In the decades surrounding 1900, at the behest of local political officials and following Congressional orders, the U.S. Army Corps began dredging the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers and the deep channels of San Francisco Bay. This work has continued without interruption ever since—an enormous federal subsidy of San Francisco Bay shipping. Some of the dredge spoils were initially dumped in the bay shallows (including helping to create
In the decades surrounding 1900, at the behest of local political officials and following Congressional orders, the U.S. Army Corps began dredging the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers and the deep channels of San Francisco Bay. This work has continued without interruption ever since—an enormous federal subsidy of San Francisco Bay shipping. Some of the dredge spoils were initially dumped in the bay shallows (including helping to create Treasure Island
''Treasure Island'' (originally titled ''The Sea Cook: A Story for Boys''Hammond, J. R. 1984. "Treasure Island." In ''A Robert Louis Stevenson Companion'', Palgrave Macmillan Literary Companions. London: Palgrave Macmillan. .) is an adventure no ...
on the former shoals to the north of Yerba Buena Island
Yerba Buena Island ( Spanish: ''Isla Yerba Buena'') sits in San Francisco Bay within the borders of the City and County of San Francisco. The Yerba Buena Tunnel runs through its center and connects the western and eastern spans of the San Franc ...
) and used to raise islands in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta. The net effect of dredging has been to maintain a narrow deep channel—deeper perhaps than the original bay channel—through a much shallower bay. At the same time, most of the marsh areas have been filled or blocked off from the bay by dikes.
Large ships transiting the bay must follow deep underwater channels that are maintained by frequent dredging as the average depth of the bay is only as deep as a swimming pool—approximately . Between Hayward and San Mateo to San Jose it is . The deepest part of the bay is under and out of the Golden Gate Bridge, at .
In the late 1990s, a 12-year harbor-deepening project for the Port of Oakland
The Port of Oakland is a major container ship facility located in Oakland, California, in the San Francisco Bay. It was the first major port on the Pacific Coast of the United States to build terminals for container ships. As of 2011 it was the f ...
began; it was largely completed by September 2009. Previously, the bay waters and harbor facilities only allowed for ships with a draft of , but dredging activities undertaken by the United States Army Corps of Engineers in partnership with the Port of Oakland succeeded in providing access for vessels with a draft. Four dredging companies were employed in the US$432 million project, with $244 million paid for with federal funds and $188 million supplied by the Port of Oakland. Some of mud from the dredging was deposited at the western edge of Middle Harbor Shoreline Park
Middle Harbor Shoreline Park (MHSP) is located on San Francisco Bay and the Port of Oakland entrance channel, west of downtown Oakland, California. It is owned and operated by the Port of Oakland. The park entrance is at the intersection of 7th S ...
to become a shallow-water wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The p ...
s habitat for marine and shore life. Further dredging followed in 2011, to maintain the navigation channel. This dredging enabled the arrival of the largest container ship
A container ship (also called boxship or spelled containership) is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermoda ...
ever to enter the San Francisco Bay, the '' MSC Fabiola''. Bay pilots trained for the visit on a simulator at the California Maritime Academy
The California State University Maritime Academy (Cal Maritime or CSU Maritime Academy) is a public university in Vallejo, California. It is one of 23 campuses in the California State University system and the only maritime academy on the Unit ...
for over a year. The ship arrived drawing less than its full draft of because it held only three-quarters of a load after its stop in Long Beach.
Transportation
Kaiser Shipyards
The Kaiser Shipyards were seven major shipbuilding yards located on the United States west coast during World War II. Kaiser ranked 20th among U.S. corporations in the value of wartime production contracts. The shipyards were owned by the Kaise ...
, Richmond Shipyards
The four Richmond Shipyards, in the city of Richmond, California, United States, were run by Permanente Metals and part of the Kaiser Shipyards. In World War II, Richmond built more ships than any other shipyard, turning out as many as three shi ...
) near Richmond in 1940 for World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
for construction of mass-produced, assembly line Liberty
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word freedom.
In modern politics, liberty is understood as the state of being free within society fr ...
and Victory cargo ships.
San Francisco Bay is spanned by nine bridges, eight of which carry cars.
* The Richmond–San Rafael Bridge on Interstate 580 (I-580) connects Marin and Contra Costa counties.
* The Golden Gate Bridge on U.S. Route 101/ State Route 1 (US 101/SR 1) was the largest single span suspension bridge ever built at the time of its 1937 construction. It spans the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
, the strait between San Francisco and Marin County, and is the only bridge in the area not owned by the State of California.
* The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge on I-80
Interstate 80 (I-80) is an east–west transcontinental freeway that crosses the United States from downtown San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey, in the New York metropolitan area. The highway was designated in 1956 as one o ...
connects Alameda and San Francisco counties.
* The San Mateo–Hayward Bridge on SR 92 connects Alameda and San Mateo counties.
* The Dumbarton Bridge on SR 84 connects Alameda and San Mateo counties.
* The Carquinez Bridge (including the Alfred Zampa Memorial Bridge) on I-80 connects Contra Costa and Solano counties.
* The Benicia Bridge on I-680 also connects Contra Costa and Solano counties.
* The Antioch Bridge on SR 160 connects Contra Costa and Sacramento counties.
* The Dumbarton Rail Bridge is an abandoned bridge that used to carry rail traffic.
The Transbay Tube, an underwater rail tunnel, carries BART
Bart is a masculine given name, usually a diminutive of Bartholomew, sometimes of Barton, Bartolomeo, etc.
Bart is a Dutch and Ashkenazi Jewish surname, and derives from the name ''Bartholomäus'', a German form of the biblical name ''Bartho ...
services between Oakland and San Francisco.
Prior to the bridges and, later, the Transbay Tube, transbay transportation was dominated by fleets of ferryboats operated by the Southern Pacific Railroad and the Key System transit company. However, in recent decades, ferries have returned, primarily serving commuters from Marin County, relieving the traffic bottleneck of the Golden Gate Bridge. (See article Ferries of San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay in California has been served by ferries of all types for over 150 years. John Reed established a sailboat ferry service in 1826. Although the construction of the Golden Gate Bridge and the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge l ...
).  The bay also continues to serve as a major
The bay also continues to serve as a major seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
. The Port of Oakland
The Port of Oakland is a major container ship facility located in Oakland, California, in the San Francisco Bay. It was the first major port on the Pacific Coast of the United States to build terminals for container ships. As of 2011 it was the f ...
is one of the largest cargo ports in the United States, while the Port of Richmond
The Port of Richmond, also known as the Richmond Deepwater Terminal, is located on the James River in Richmond, Virginia, United States, inland from Cape Henry and approximately northwest of Newport News, Virginia. It is located at 77° 2 ...
and the Port of San Francisco
The Port of San Francisco is a semi-independent organization that oversees the port facilities at San Francisco, California, United States. It is run by a five-member commission, appointed by the Mayor and approved by the Board of Supervisors. Th ...
provide smaller services.
Recreation
San Francisco Bay is a mecca for sailors (boats, as well aswindsurfing
Windsurfing is a wind propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the aerospace and surf culture of California. Windsurfing ga ...
and kitesurfing
Kiteboarding or kitesurfing is a sport that involves using wind power with a large power kite to pull a rider across a water, land, or snow surface. It combines aspects of paragliding, surfing, windsurfing, skateboarding, snowboarding, and wak ...
), due to consistent strong westerly/northwesterly thermally-generated winds – Beaufort force 6 () is common on summer afternoons – and protection from large open ocean swells. Yachting
Yachting is the use of recreational boats and ships called ''yachts'' for racing or cruising. Yachts are distinguished from working ships mainly by their leisure purpose. "Yacht" derives from the Dutch word '' jacht'' ("hunt"). With sailboats, ...
and yacht racing
Yacht racing is a sailing sport involving sailing yachts and larger sailboats, as distinguished from dinghy racing, which involves open boats. It is composed of multiple yachts, in direct competition, racing around a course marked by buoys or ...
are popular pastimes and the San Francisco Bay Area is home to many of the world's top sailors. A shoreline bicycle and pedestrian trail known as the San Francisco Bay Trail
The San Francisco Bay Trail is a bicycle and pedestrian trail that when finished will allow continuous travel around the shoreline of San Francisco Bay. As of 2020, of the trail have been completed. When finished, the trail will be over of p ...
encircles the edge of the bay. The San Francisco Bay Area Water Trail, a growing network of launching and landing sites around the Bay for non-motorized small boat users (such as kayakers) is being developed. Parks and protected areas around the bay include Eden Landing Ecological Reserve
Eden Landing Ecological Reserve is a nature reserve in Hayward, California, Hayward and Union City, California, on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay. The reserve is managed by the California Department of Fish and Game and comprises 5,040 acr ...
, Hayward Regional Shoreline
Hayward Regional Shoreline is a regional park located on the shores of the San Francisco Bay in Hayward, California. It is part of the East Bay Regional Parks system. The 1,713 acre park extends to the shores of San Lorenzo. Part of the park is fo ...
, Don Edwards San Francisco Bay National Wildlife Refuge
Don Edwards San Francisco Bay National Wildlife Refuge (DESFBNWR) is a United States National Wildlife Refuge located in the southern part of San Francisco Bay, California. The Refuge headquarters and visitor center is located in the Baylands dist ...
, Hayward Shoreline Interpretive Center
The Hayward Shoreline Interpretive Center is a natural history and ecology interpretive nature center located in Hayward, California. It is directly adjacent to the north side of Highway 92 as it approaches the San Mateo–Hayward Bridge, and i ...
, Crown Memorial State Beach
Crown Memorial State Beach is a state park in the city of Alameda, California on the shores of San Francisco Bay. It is operated by East Bay Regional Parks District (EBRPD), under a cooperative agreement with the State of California and the City ...
, Eastshore State Park
McLaughlin Eastshore State Park is a state park and wildlife refuge along the San Francisco Bay shoreline of the East Bay between the cities of Richmond, Albany, Berkeley, Emeryville, and Oakland. It encompasses remnant natural wetlands, rest ...
, Point Isabel Regional Shoreline
Point Isabel Regional Shoreline in Richmond, California, is operated by East Bay Regional Park District, and is a multi-use park for joggers, windsurfers, kayakers, photographers, picnickers, and people walking dogs. It has access for pedestrians ...
, Brooks Island Regional Shoreline, and César Chávez Park.
The California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA) has developed a safe eating advisory for fish caught in the San Francisco Bay based on levels of mercury or PCBs
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act in 1979 and internationally by t ...
found in local species.
The San Francisco Bay Area Water Trail is a planned system of designated trailheads designed to improve non-motorized small boat access to the bay. The California Coastal Conservancy approved funding in March 2011 to begin implementation of the water trail.
Gallery
See also
*Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
* Golden Gate Bridge
* Hydrography of the San Francisco Bay Area
* Islands of San Francisco Bay
* J.C. Barthel, who prepared "plans for the docks and other water-front improvements in the San Francisco Bay district"
* McLaughlin Eastshore State Park
* Mount Diablo
Mount Diablo is a mountain of the Diablo Range, in Contra Costa County of the eastern San Francisco Bay Area in Northern California. It is south of Clayton and northeast of Danville. It is an isolated upthrust peak of , visible from most ...
* Mount Tamalpais State Park
* Napa Sonoma Marsh
The Napa Sonoma Marsh is a wetland at the northern edge of San Pablo Bay, which is a northern arm of the San Francisco Bay in California, United States. This marsh has an area of 48,000 acres (194 km2), of which 13,000 acres (53 km2) are ...
* Point Pinole Regional Shoreline
Point Pinole Regional Shoreline is a regional park on the shores of the San Pablo Bay, California (the northern arm of the San Francisco Bay), in the United States. It is approximately in area, and is operated by the East Bay Regional Park Dis ...
, Richmond
References
Literature
The Bay of San Francisco: the metropolis of the Pacific Coast and its suburban cities: a history.
Volume I. by Lewis Publishing Company, Chicago, Ill. Published 189
Contains index to biographical sketches
Volume II
– Biographies
External links
''San Francisco Bay: Portrait of an Estuary'', David Sanger and John Hart, University of California Press
''The Islands of San Francisco Bay'', James A. Martin , Michael T. Lee, Down Window Press
Guide to San Francisco Bay wildlife
Early History of the California Coast, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
*'' San Francisco Estuary and Watershed Science'': a peer-reviewed online science journal {{Authority control Bays of California Bodies of water of Richmond, California San Francisco Bay watershed Estuaries of California Tourist attractions in the San Francisco Bay Area Ramsar sites in the United States Wetlands of California Bodies of water of San Francisco Bodies of water of Alameda County, California Bodies of water of Santa Clara County, California Bodies of water of Contra Costa County, California Bodies of water of Solano County, California Bodies of water of San Mateo County, California Bays of Marin County, California Estuaries of Marin County, California Bays of Contra Costa County, California