Salt spray test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The salt spray test (or salt fog test) is a standardized and popular
 Many of these modified tests originally arose within particular
Many of these modified tests originally arose within particular  ASTM G85 Annex A1 – Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (non-cyclic)
This test can be used to determine the relative resistance to corrosion of decorative chromium plating on steel and
ASTM G85 Annex A1 – Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (non-cyclic)
This test can be used to determine the relative resistance to corrosion of decorative chromium plating on steel and  ASTM G85 Annex A2 – Acidified Salt Fog Test (cyclic).
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of
ASTM G85 Annex A2 – Acidified Salt Fog Test (cyclic).
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of  ASTM G85 Annex A3 – Seawater Acidified Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of coated or uncoated aluminium alloys and other metals, when exposed to a changing climate of acidified synthetic seawater spray, followed by a high humidity, both at an elevated temperature. This test is also referred to as a SWAAT test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate that comprises the following 2 part repeating cycle. First, a 30 minute exposure to a continuous indirect spray of synthetic seawater solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 2.8–3.0) by the addition of acetic acid. This spray is set to fall-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by a 90 minute exposure to a high humidity climate (above 98% RH). The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 49 °C (may be reduced to 24–35 °C for organically coated specimens). The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
ASTM G85 Annex A3 – Seawater Acidified Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of coated or uncoated aluminium alloys and other metals, when exposed to a changing climate of acidified synthetic seawater spray, followed by a high humidity, both at an elevated temperature. This test is also referred to as a SWAAT test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate that comprises the following 2 part repeating cycle. First, a 30 minute exposure to a continuous indirect spray of synthetic seawater solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 2.8–3.0) by the addition of acetic acid. This spray is set to fall-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by a 90 minute exposure to a high humidity climate (above 98% RH). The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 49 °C (may be reduced to 24–35 °C for organically coated specimens). The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.

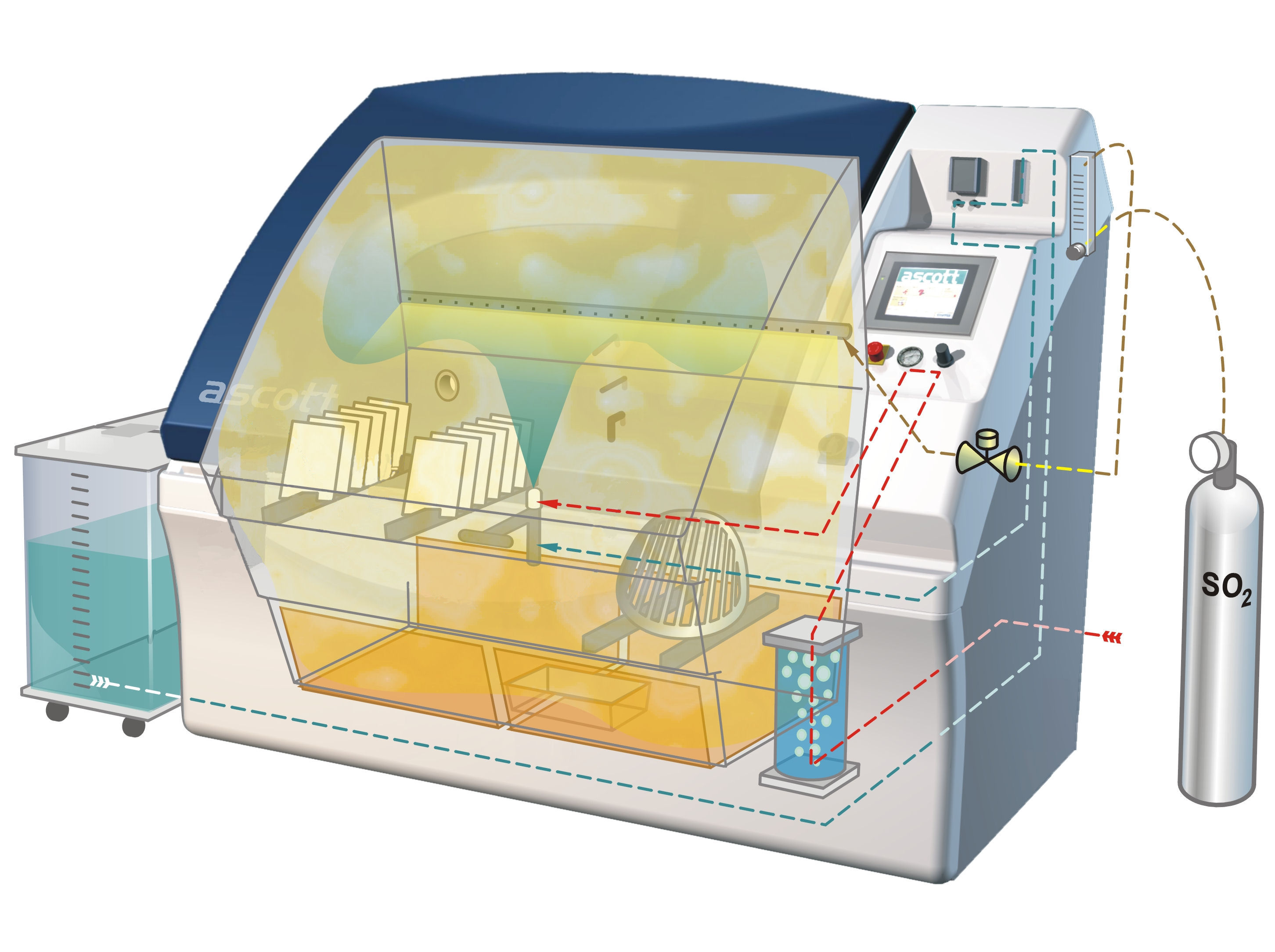 ASTM G85 Annex A4 – Salt Spray Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of product samples that are likely to encounter a combined /salt spray/acid rain environment during their usual service life.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to 1 of 2 possible changing climate cycles. In either case, the exposure to salt spray may be salt water spray or synthetic sea water prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard. The most appropriate test cycle and spray solutions are to be agreed between parties.
The first climate cycle comprises a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. During this spraying, the chamber is dosed with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume, for 1 hour in every 6 hours of spraying. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
The second climate cycle comprises 0.5 hours of continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by 0.5 hours of dosing with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume. This is followed by 2 hours of high humidity soak. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
ASTM G85 Annex A4 – Salt Spray Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of product samples that are likely to encounter a combined /salt spray/acid rain environment during their usual service life.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to 1 of 2 possible changing climate cycles. In either case, the exposure to salt spray may be salt water spray or synthetic sea water prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard. The most appropriate test cycle and spray solutions are to be agreed between parties.
The first climate cycle comprises a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. During this spraying, the chamber is dosed with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume, for 1 hour in every 6 hours of spraying. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
The second climate cycle comprises 0.5 hours of continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by 0.5 hours of dosing with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume. This is followed by 2 hours of high humidity soak. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
 ASTM G85 Annex A5 – Dilute Electrolyte Salt Fog/Dry Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of paints on steel when exposed to a changing climate of dilute salt spray at ambient temperature, followed by air drying at elevated temperature.
It is a popular test in the surface coatings industry, where it is also referred to as the PROHESION test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate with the following 2-part cycle.
First, a 1-hour exposure to a continuous indirect spray of salt water solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 3.1–3.3) by the addition of acetic acid.
This spray is set to fall on the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour, in an ambient chamber temperature (21–27 °C). This is followed by a 1-hour exposure to an air drying (purge) climate at 35 °C.
The cycle repeats until the desired duration has been achieved.
ASTM G85 Annex A5 – Dilute Electrolyte Salt Fog/Dry Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of paints on steel when exposed to a changing climate of dilute salt spray at ambient temperature, followed by air drying at elevated temperature.
It is a popular test in the surface coatings industry, where it is also referred to as the PROHESION test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate with the following 2-part cycle.
First, a 1-hour exposure to a continuous indirect spray of salt water solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 3.1–3.3) by the addition of acetic acid.
This spray is set to fall on the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour, in an ambient chamber temperature (21–27 °C). This is followed by a 1-hour exposure to an air drying (purge) climate at 35 °C.
The cycle repeats until the desired duration has been achieved.
Salt Spray Chamber
''{{ISO standards Corrosion Metallurgical processes Measuring instruments Coatings Environmental testing ISO standards
corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
test method, used to check corrosion resistance of materials and surface coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Pow ...
s. Usually, the materials to be tested are metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
lic (although stone, ceramics, and polymers may also be tested) and finished with a surface coating which is intended to provide a degree of corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
protection to the underlying metal.
Salt spray testing is an accelerated corrosion test that produces a corrosive attack to coated samples in order to evaluate (mostly comparatively) the suitability of the coating for use as a protective finish. The appearance of corrosion products (rust
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO( ...
or other oxides) is evaluated after a pre-determined period of time. Test duration depends on the corrosion resistance of the coating; generally, the more corrosion resistant the coating is, the longer the period of testing before the appearance of corrosion or rust.
The salt spray test is one of the most widespread and long-established corrosion tests. ASTMB117 was the first internationally recognized salt spray standard, originally published in 1939. Other important relevant standards are ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
9227, JISZ2371 and ASTMG85.
Application
Salt spray testing is popular because it is relatively inexpensive, quick, well standardized, and reasonably repeatable. Although there may be a weak correlation between the duration in salt spray test and the expected life of acoating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Pow ...
in certain coatings such as hot-dip galvanized steel
Galvanization or galvanizing ( also spelled galvanisation or galvanising) is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. The most common method is hot-dip galvanizing, in which the parts are submerg ...
, this test has gained worldwide popularity due to low cost and quick results. Most Salt Spray Chambers today are being used NOT to predict the corrosion resistance of a coating, but to maintain coating processes such as pre-treatment and painting, electroplating, galvanizing, and the like, on a comparative basis. For example, pre-treated + painted components must pass 96 hours Neutral Salt Spray, to be accepted for production. Failure to meet this requirement implies instability in the chemical process of the pre-treatment, or the paint quality, which must be addressed immediately so that the upcoming batches are of the desired quality. The longer the accelerated corrosion test, the longer the process remains out of control, and larger is the loss in the form of non-conforming batches.
The principal application of the salt spray test is, therefore, enabling quick comparisons to be made between actual and expected corrosion resistance
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engin ...
. Most commonly, the time taken for oxides to appear on the samples under test is compared to expectations, to determine whether the test is passed or failed. For this reason, the salt spray test is most often deployed in a quality audit role, where, for example, it can be used to check the effectiveness of a production process, such as the surface coating of a metallic part.
The salt spray test has little application in predicting how materials or surface coatings will resist corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
in the real world, because it does not create, replicate or accelerate real-world corrosive conditions. Cyclic corrosion testing is better suited to this.
Testing equipment
The apparatus for testing consists of a closed testing cabinet/chamber, where a salt water (5% NaCl) solution is atomized by means of spray nozzle(s) using pressurized air. This produces acorrosive
A corrosive substance is one that will damage or destroy other substances with which it comes into contact by means of a chemical reaction.
Etymology
The word ''corrosive'' is derived from the Latin verb ''corrodere'', which means ''to gnaw'', ...
environment of dense salt water fog (also referred to as a mist or spray) in the chamber, so that test samples exposed to this environment are subjected to severely corrosive conditions. Chamber volumes vary from supplier to supplier. If there is a minimum volume required by a particular salt spray test standard, this will be clearly stated and should be complied with. There is a general historical consensus that larger chambers can provide a more homogeneous testing environment.
Variations to the salt spray test solutions depend upon the materials to be tested. The most common test for steel based materials is the Neutral Salt Spray test (often abbreviated to NSS) which reflects the fact that this type of test solution is prepared to a neutral pH of 6.5 to 7.2. Results are represented generally as testing hours in NSS without appearance of corrosion products (e.g. 720 h in NSS according to ISO 9227). Synthetic seawater solutions are also commonly specified by some companies and standards. Other test solutions have other chemicals
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
added including acetic acid (often abbreviated to ASS) and acetic acid with copper chloride (often abbreviated to CASS) each one chosen for the evaluation of decorative coatings, such as electroplated copper-nickel-chromium, electroplated copper-nickel or anodized aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
. These acidified test solutions generally have a pH of 3.1 to 3.3
Some sources do not recommend using ASS or CASS test cabinets interchangeably for NSS tests, due to the risk of cross-contamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
...
. It is claimed that a thorough cleaning of the cabinet after CASS test is very difficult. ASTM does not address this issue, but ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
9227 does not recommend it and if it is to be done, advocates a thorough cleaning.
Although the majority of salt spray tests are continuous, i.e.; the samples under test are exposed to the continuous generation of salt fog for the entire duration of the test, a few do not require such exposure. Such tests are commonly referred to as modified salt spray tests. ASTM G85 is an example of a test standard which contains several modified salt spray tests which are variations to the basic salt spray test.
Modified salt spray tests
ASTM G85 is the most popular global test standard covering modified salt spray tests. There are five such tests altogether, referred to in ASTM G85 as annexes A1 through to A5. Many of these modified tests originally arose within particular
Many of these modified tests originally arose within particular industry sector
Industry classification or industry taxonomy is a type of economic taxonomy that classifies companies, organizations and traders into industrial groupings based on similar production processes, similar products, or similar behavior in financial ...
, in order to address the need for a corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
test capable of replicating the effects of naturally occurring corrosion and accelerate these effects.
This acceleration arises through the use of chemically altered salt spray solutions, often combined with other test climates and in most cases, the relatively rapid cycling of these test climates over time. Although popular in certain industries, modified salt spray testing has in many cases been superseded by cyclic corrosion testing (CCT)
The type of environmental test chambers
An environmental chamber, also called a climatic chamber or climate chamber, is an enclosure used to test the effects of specified environmental conditions on biological items, industrial products, materials, and electronic devices and components ...
used for modified salt spray testing to ASTM G85 are generally similar to the chambers used for testing to ASTM B117, but will often have some additional features, such as an automatic climate cycling control system.
 ASTM G85 Annex A1 – Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (non-cyclic)
This test can be used to determine the relative resistance to corrosion of decorative chromium plating on steel and
ASTM G85 Annex A1 – Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (non-cyclic)
This test can be used to determine the relative resistance to corrosion of decorative chromium plating on steel and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
based die casting
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly ...
when exposed to an acetic acid salt spray climate at an elevated temperature. This test is also referred to as an ASS test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of salt water solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 3.1–3.3) by the addition of acetic acid. This spray is set to fall-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour, in a chamber temperature of 35 °C. This climate is maintained under constant steady state conditions. The test duration is variable.
 ASTM G85 Annex A2 – Acidified Salt Fog Test (cyclic).
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of
ASTM G85 Annex A2 – Acidified Salt Fog Test (cyclic).
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
alloys when exposed to a changing climate of acetic acid salt spray, followed by air drying, followed by high humidity, all at an elevated temperature. This test is also referred to as a MASTMAASIS test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate that comprises the following 3 part repeating cycle. 0.75 hours exposure to a continuous indirect spray of salt water solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 2.8–3.0) by the addition of acetic acid. This spray is set to fall-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by a 2 hour exposure to an air drying (purge) climate. This is followed by 3.25 hours exposure to a high humidity climate which gradually rises to between 65% RH and 95% RH. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 49 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
 ASTM G85 Annex A3 – Seawater Acidified Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of coated or uncoated aluminium alloys and other metals, when exposed to a changing climate of acidified synthetic seawater spray, followed by a high humidity, both at an elevated temperature. This test is also referred to as a SWAAT test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate that comprises the following 2 part repeating cycle. First, a 30 minute exposure to a continuous indirect spray of synthetic seawater solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 2.8–3.0) by the addition of acetic acid. This spray is set to fall-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by a 90 minute exposure to a high humidity climate (above 98% RH). The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 49 °C (may be reduced to 24–35 °C for organically coated specimens). The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
ASTM G85 Annex A3 – Seawater Acidified Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of coated or uncoated aluminium alloys and other metals, when exposed to a changing climate of acidified synthetic seawater spray, followed by a high humidity, both at an elevated temperature. This test is also referred to as a SWAAT test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate that comprises the following 2 part repeating cycle. First, a 30 minute exposure to a continuous indirect spray of synthetic seawater solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 2.8–3.0) by the addition of acetic acid. This spray is set to fall-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by a 90 minute exposure to a high humidity climate (above 98% RH). The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 49 °C (may be reduced to 24–35 °C for organically coated specimens). The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.

 ASTM G85 Annex A4 – Salt Spray Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of product samples that are likely to encounter a combined /salt spray/acid rain environment during their usual service life.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to 1 of 2 possible changing climate cycles. In either case, the exposure to salt spray may be salt water spray or synthetic sea water prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard. The most appropriate test cycle and spray solutions are to be agreed between parties.
The first climate cycle comprises a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. During this spraying, the chamber is dosed with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume, for 1 hour in every 6 hours of spraying. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
The second climate cycle comprises 0.5 hours of continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by 0.5 hours of dosing with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume. This is followed by 2 hours of high humidity soak. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
ASTM G85 Annex A4 – Salt Spray Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of product samples that are likely to encounter a combined /salt spray/acid rain environment during their usual service life.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to 1 of 2 possible changing climate cycles. In either case, the exposure to salt spray may be salt water spray or synthetic sea water prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard. The most appropriate test cycle and spray solutions are to be agreed between parties.
The first climate cycle comprises a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. During this spraying, the chamber is dosed with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume, for 1 hour in every 6 hours of spraying. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
The second climate cycle comprises 0.5 hours of continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5–7.2) salt water/synthetic seawater solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour. This is followed by 0.5 hours of dosing with gas at a rate of 35 cm3/minute/m3 of chamber volume. This is followed by 2 hours of high humidity soak. The entire test cycle is at a constant chamber temperature of 35 °C. The number of cycle repeats and therefore the test duration is variable.
 ASTM G85 Annex A5 – Dilute Electrolyte Salt Fog/Dry Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of paints on steel when exposed to a changing climate of dilute salt spray at ambient temperature, followed by air drying at elevated temperature.
It is a popular test in the surface coatings industry, where it is also referred to as the PROHESION test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate with the following 2-part cycle.
First, a 1-hour exposure to a continuous indirect spray of salt water solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 3.1–3.3) by the addition of acetic acid.
This spray is set to fall on the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour, in an ambient chamber temperature (21–27 °C). This is followed by a 1-hour exposure to an air drying (purge) climate at 35 °C.
The cycle repeats until the desired duration has been achieved.
ASTM G85 Annex A5 – Dilute Electrolyte Salt Fog/Dry Test (cyclic)
This test can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of paints on steel when exposed to a changing climate of dilute salt spray at ambient temperature, followed by air drying at elevated temperature.
It is a popular test in the surface coatings industry, where it is also referred to as the PROHESION test.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber, and exposed to a changing climate with the following 2-part cycle.
First, a 1-hour exposure to a continuous indirect spray of salt water solution, prepared in accordance with the requirements of the test standard and acidified (pH 3.1–3.3) by the addition of acetic acid.
This spray is set to fall on the specimens at a rate of 1–2 ml/80 cm2/hour, in an ambient chamber temperature (21–27 °C). This is followed by a 1-hour exposure to an air drying (purge) climate at 35 °C.
The cycle repeats until the desired duration has been achieved.
Standardization
Chamber construction, testing procedure and testing parameters are standardized under national and international standards, such as ASTM B 117 and ISO 9227. These standards describe the necessary information to carry out this test; testing parameters such as temperature, air pressure of the sprayed solution, preparation of the spraying solution, concentration, pH, etc. Daily checking of testing parameters is necessary to show compliance with the standards, so records shall be maintained accordingly. ASTM B117 and ISO 9227 are widely used as reference standards. Testing cabinets are manufactured according to the specified requirements here. However, these testing standards neither provide information of testing periods for the coatings to be evaluated, nor the appearance of corrosion products in form of salts. Requirements are agreed between customer and manufacturer. In the automotive industry requirements are specified under material specifications. Different coatings have different behavior in salt spray test and consequently, test duration will differ from one type of coating to another. For example, a typical electroplated zinc and yellow passivated steel part lasts 96 hours in salt spray test without white rust. Electroplated zinc-nickel steel parts can last more than 720 hours in NSS test without red rust (or 48 hours in CASS test without red rust) Requirements are established in test duration (hours) and coatings shall comply with minimum testing periods.Artificial seawater
Artificial seawater (abbreviated ASW) is a mixture of dissolved mineral salts (and sometimes vitamins) that simulates seawater. Artificial seawater is primarily used in marine biology and in marine and reef aquaria, and allows the easy preparation ...
which is sometimes used for Salt Spray Testing can be found at ASTM International
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, ...
. The standard for Artificial Seawater is ASTM D1141-98 which is the standard practice for the preparation of substitute ocean water.
Uses
Typical coatings that can be evaluated with this method are: *Phosphated (pre-treated) surfaces (with subsequent paint/primer/lacquer/rust preventive) *Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
and zinc-alloy plating (see also electroplating). See ISO 4042 for guidance
*Electroplated chromium, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
*Coatings not applied electrolytically, such as zinc flake coatings according to ISO 10683
*Organic coatings, such as rust preventives
*Paint Coating
Hot-dip galvanized surfaces are not generally tested in a salt spray test (see ISO 1461 or ISO 10684). Hot-dip galvanizing produces zinc carbonates
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
when exposed to a natural environment, thus protecting the coating metal and reducing the corrosion rate. The zinc carbonates are not produced when a hot-dip galvanized specimen is exposed to a salt spray fog, therefore this testing method does not give an accurate measurement of corrosion protection. ISO 9223 gives the guidelines for proper measurement of corrosion resistance for hot-dip galvanized specimens.
Painted surfaces with an underlying hot-dip galvanized coating can be tested according to this method. See ISO 12944-6.
Testing periods range from a few hours (e.g. 8 or 24 hours of phosphated steel) to more than a month (e.g. 720 hours of zinc-nickel coatings, 1000 hours of certain zinc flake coatings).
Bibliography
*Metal Finishing. Guidebook and directory issue. Published by ''Metal Finishing'' Magazine, 1996See also
*Corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
*Corrosion engineering
Corrosion engineering is an engineering specialty that applies scientific, technical, engineering skills, and knowledge of natural laws and physical resources to design and implement materials, structures, devices, systems, and procedures to mana ...
* Cyclic corrosion testing
*Environmental chamber
An environmental chamber, also called a climatic chamber or climate chamber, is an enclosure used to test the effects of specified environmental conditions on biological items, industrial products, materials, and electronic devices and components ...
*Japanese Industrial Standards
are the standards used for industrial activities in Japan, coordinated by the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC) and published by the Japanese Standards Association (JSA). The JISC is composed of many nationwide committees and pla ...
*ASTM International
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, ...
*International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
Further reading
* ASTM G85 Modified Salt Spray Test standard * Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. DIN 50021 Sprühnebelprüfungen mit verschiedenen Natriumchloridlösungen. Beuth Verlag GmbH, 1988. This standard has been superseded by ISO 9227 and it is only mentioned for bibliographic purposes * ISO International Organization for Standardization. ISO 9227 Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres—Salt spray tests, 2006 * ISO International Organization for Standardization. ISO 4628-3 Paints and varnishes. Evaluation of degradation of coatings. Designation of quantity and size of defects, and of intensity of uniform changes in appearance. Part 3 Assessment of degree of rusting *MIL-STD-810
MIL-STD-810, U S Department of Defense Test Method Standard, Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests, is a United States Military Standard that emphasizes tailoring an equipment's environmental design and test limits to the ...
Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests
* ASTM B117 Test Conditions, Method & Application
References
'Salt Spray Chamber
''{{ISO standards Corrosion Metallurgical processes Measuring instruments Coatings Environmental testing ISO standards