Saint-Sulpice church on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, image = Paris Saint-Sulpice Fassade 4-5 A.jpg
, image_size =
, pushpin map = Paris
, pushpin label position =
, coordinates =
, location =
6th arrondissement,
South tower: , materials = , bells = , bells hung = , bell weight = , parish = , archdiocese =
(''Organiste titulaire du grand-orgue'') , embedded = The Church of Saint-Sulpice () is a
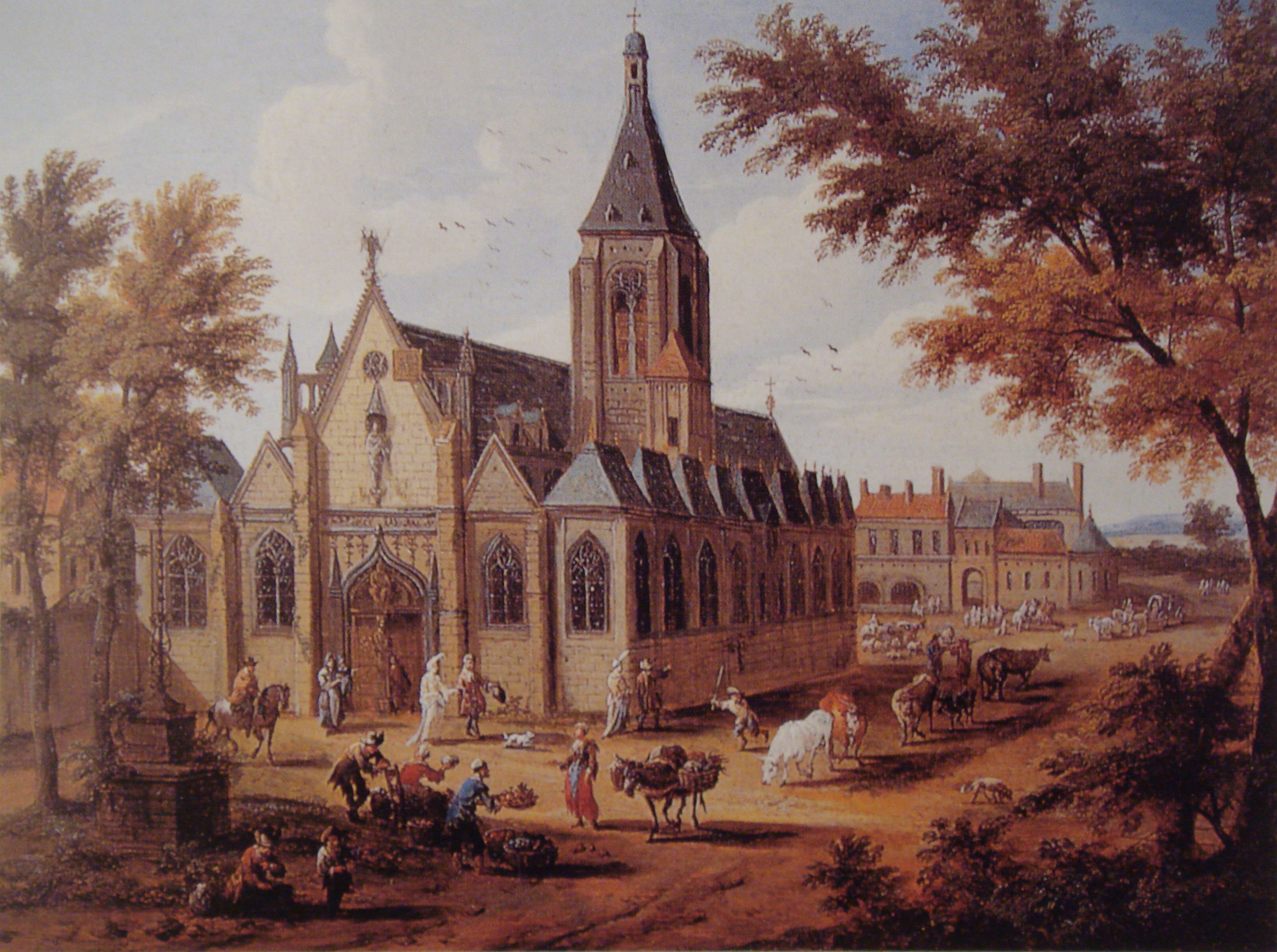 The present church is the second building on the site, erected over a Romanesque church originally constructed during the 13th century. Additions were made over the centuries, up to 1631. The new building was founded in 1646 by parish priest Jean-Jacques Olier (1608–1657) who had established the
The present church is the second building on the site, erected over a Romanesque church originally constructed during the 13th century. Additions were made over the centuries, up to 1631. The new building was founded in 1646 by parish priest Jean-Jacques Olier (1608–1657) who had established the
Plan Église Saint-Sulpice - Paris.svg, Plan of the church
Paris Saint-Sulpice Innen Chor 2.jpg, Inner choir with pilasters
Saint-Sulpice south transept interior - Mbzt.jpg, South transept
He also built a bell-tower on top of the transept crossing (c. 1725), which threatened to collapse the structure because of its weight and had to be removed. This miscalculation may account for the fact that Oppenord was then relieved of his duties as an architect and restricted to designing decoration.
Cathédrale St-Paul - entrée principale.jpg, Saint Paul's, London
Servandoni - Façade de Saint-Sulpice.jpg, Servandoni's design
Saint-Sulpice on 1739 Turgot map of Paris - KU.jpg, On the 1739 Turgot map
Unfinished at the time of his death in 1766, the work was continued by others, primarily the obscure Oudot de Maclaurin, who erected twin towers to Servandoni's design. Servandoni's pupil
Saint-Sulpice west facade design by Servandoni with third order - Middleton 1980 p106.jpg, Design with a third order by Servandoni (1752)
Saint-Sulpice - Grand Portail - Architecture françoise Tome2 Livre3 Ch5 Pl2.jpg, Design from Blondel (1752)
P1000718 Paris VI Eglise Saint-Sulpice reductwk1.JPG, The current façade with mis-matched towers (2010)
The principal facade now exists in somewhat altered form. Servandoni's

 Inside the church to either side of the entrance are the two halves of an enormous shell (''
Inside the church to either side of the entrance are the two halves of an enormous shell (''
File:P1000823 Paris VI Eglise Sainte-Sulpice Chapelle de la Vierge reductwk.JPG, Lady Chapel
File:Paris 06 - St Sulpice chap V 03.jpg, Statue of Mary
File:P1000726 Paris VI Eglise Saint-Sulpice Chapelle de la Vierge coupole reductwk.JPG, Dome of the Lady Chapel
File:Paris 06 - St Sulpice pulpit 01.jpg, Pulpit
During the
File:Jacob Angel Delacroix.jpg, ''Jacob Wrestling with the Angel''
File:Eugène Delacroix - Heliodoros Driven from the Temple - WGA06222 (cropped).jpg, ''Heliodorus Driven from the Temple''
 The church has a long-standing tradition of talented organists that dates back to the eighteenth century (see below). In 1862, Aristide Cavaillé-Coll rebuilt the existing organ built by François-Henri Clicquot. The case was designed by
The church has a long-standing tradition of talented organists that dates back to the eighteenth century (see below). In 1862, Aristide Cavaillé-Coll rebuilt the existing organ built by François-Henri Clicquot. The case was designed by
 In 1727, Jean-Baptiste Languet de Gergy, then priest of Saint-Sulpice, requested the construction of a gnomon in the church as part of its new construction, to help him determine the time of the equinoxes and hence of
In 1727, Jean-Baptiste Languet de Gergy, then priest of Saint-Sulpice, requested the construction of a gnomon in the church as part of its new construction, to help him determine the time of the equinoxes and hence of
File:Saint-Sulpice from Rue Servandroni.JPG, South side of Saint-Sulpice
File:StSulpice Chor von NO.JPG, Choir from the northeast
File:Francois-Etienne Villeret St Sulpice Paris.jpg, Saint-Sulpice, watercolor by
Oxford Art Online
(subscription required). * Kauffmann, Jean-Paul (2002). ''Wrestling with the Angel: The Mystery of Delacroix's Mural''. London: Harvill. . Also titled ''The Angel of the Left Bank: The Secrets of Delacroix's Parisian Masterpiece'' and ''The Struggle with the Angel: Delacroix, Jacob, and the God of Good and Evil.'' * Terrien, Laurence, translator (2004). ''Saint-Sulpice''. Paris: Paroisse Saint-Sulpice. .
Daniel Roth, titular organist at St. Sulpice since 1985
Photographs of the Saint-Sulpice church
Official Website on the organs and organists at St. Sulpice
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saint-Sulpice, Paris, Church of Roman Catholic churches in the 6th arrondissement of Paris Roman Catholic churches completed in 1870 Burials at Saint-Sulpice, Paris 1646 establishments in France Burial sites of the House of la Tour d'Auvergne 19th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in France
Place Saint-Sulpice
Place Saint Sulpice is a large public square, dominated on its eastern side by the Church of Saint-Sulpice. It was built in 1754 as a tranquil garden in the Latin Quarter of the 6th arrondissement of Paris.
Features
In addition to the church, ...
6th arrondissement,
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
, country = France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, denomination = Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
, religious institute = Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice
The Society of Priests of Saint-Sulpice (french: Compagnie des Prêtres de Saint-Sulpice), abbreviated PSS also known as the Sulpicians is a society of apostolic life of Pontifical Right for men, named after the Church of Saint-Sulpice, Paris ...
, website =
, bull date =
, founded date =
, founder =
, dedication = Sulpitius the Pious
, dedicated date =
, consecrated date =
, relics =
, status = Parish church
, functional status = Active
, heritage designation =
, architect =
, style = Baroque
, years built =
, groundbreaking = 1646
, completed date = 1870
, capacity =
, length =
, width =
, tower quantity = 2
, tower height = North tower: South tower: , materials = , bells = , bells hung = , bell weight = , parish = , archdiocese =
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
, province = Paris
, priestincharge = Jean-Loup Lacroix
, organist = Daniel Roth(''Organiste titulaire du grand-orgue'') , embedded = The Church of Saint-Sulpice () is a
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* C ...
in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, on the east side of Place Saint-Sulpice
Place Saint Sulpice is a large public square, dominated on its eastern side by the Church of Saint-Sulpice. It was built in 1754 as a tranquil garden in the Latin Quarter of the 6th arrondissement of Paris.
Features
In addition to the church, ...
, in the Latin Quarter
The Latin Quarter of Paris (french: Quartier latin, ) is an area in the 5th and the 6th arrondissements of Paris. It is situated on the left bank of the Seine, around the Sorbonne.
Known for its student life, lively atmosphere, and bistro ...
of the 6th arrondissement. It is only slightly smaller than Notre-Dame and thus the second-largest church in the city. It is dedicated to Sulpitius the Pious. Construction of the present building, the second church on the site, began in 1646. During the 18th century, an elaborate gnomon, the Gnomon of Saint-Sulpice, was constructed in the church.
History
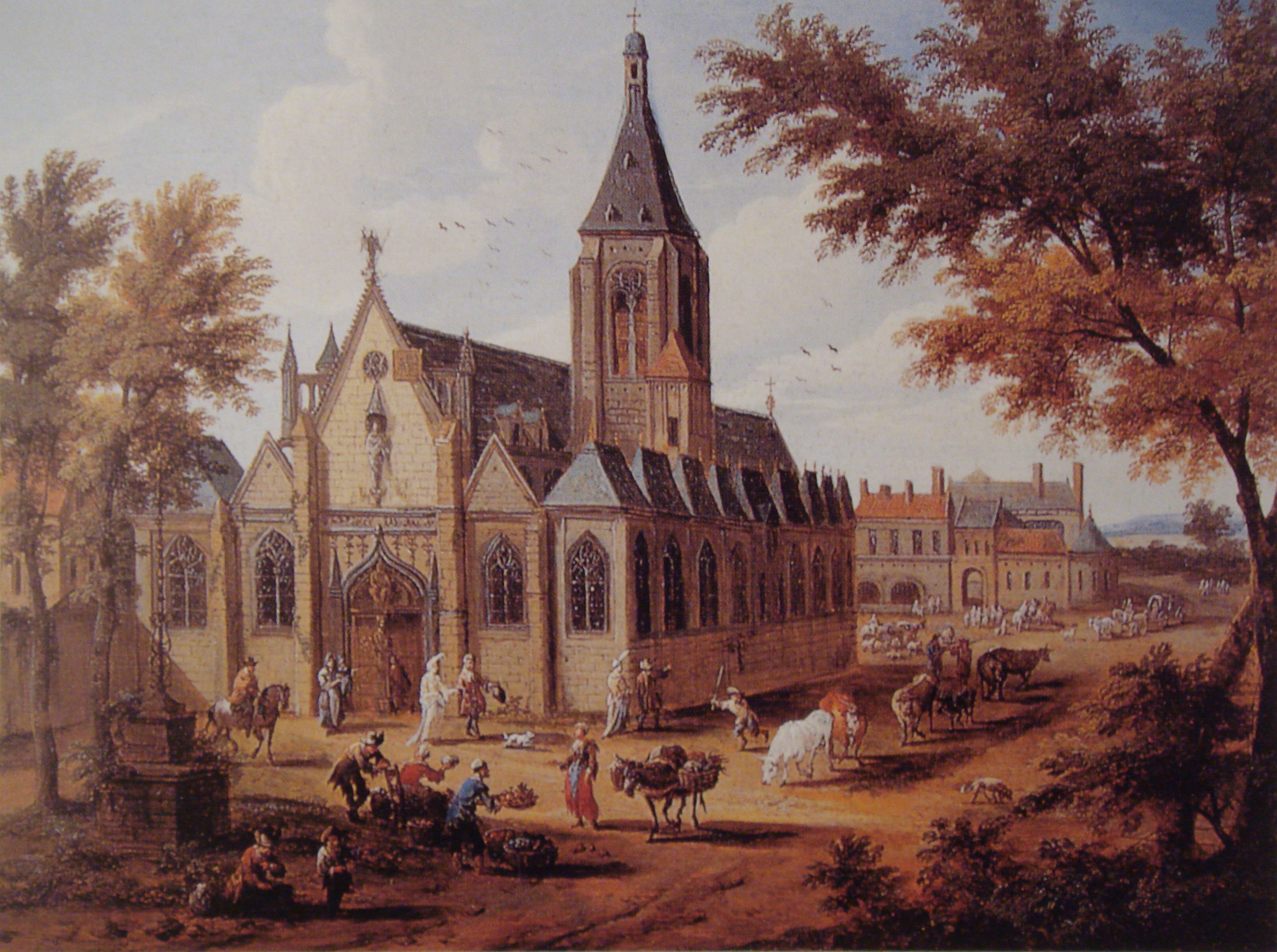 The present church is the second building on the site, erected over a Romanesque church originally constructed during the 13th century. Additions were made over the centuries, up to 1631. The new building was founded in 1646 by parish priest Jean-Jacques Olier (1608–1657) who had established the
The present church is the second building on the site, erected over a Romanesque church originally constructed during the 13th century. Additions were made over the centuries, up to 1631. The new building was founded in 1646 by parish priest Jean-Jacques Olier (1608–1657) who had established the Society of Saint-Sulpice
The Society of Priests of Saint-Sulpice (french: Compagnie des Prêtres de Saint-Sulpice), abbreviated PSS also known as the Sulpicians is a society of apostolic life of Pontifical Right for men, named after the Church of Saint-Sulpice, Paris ...
, a clerical congregation, and a seminary attached to the church. Anne of Austria
Anne of Austria (french: Anne d'Autriche, italic=no, es, Ana María Mauricia, italic=no; 22 September 1601 – 20 January 1666) was an infanta of Spain who became Queen of France as the wife of King Louis XIII from their marriage in 1615 un ...
laid the first stone.
Construction began in 1646 to designs which had been created in 1636 by Christophe Gamard
Christophe Gamard, Gamar or Gamart, was a 17th-century French architect, who worked in Paris and died there in 1649.
Biography
He was a master mason in 1613, an architect of the old Saint-Sulpice in 1623 (and began its reconstruction after 164 ...
, but the Fronde
The Fronde () was a series of civil wars in France between 1648 and 1653, occurring in the midst of the Franco-Spanish War, which had begun in 1635. King Louis XIV confronted the combined opposition of the princes, the nobility, the law cour ...
interfered, and only the Lady Chapel had been built by 1660, when Daniel Gittard
Daniel Gittard (March 14, 1625 – December 15, 1686) was a French architect.
Biography
Daniel Gittard was born in Blandy-les-Tours. He died in Paris.
In 1671, he became one of the first eight members of the Académie royale d'architecture ...
provided a new general design for most of the church. Gittard completed the sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a sa ...
, ambulatory
The ambulatory ( la, ambulatorium, ‘walking place’) is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th ...
, apsidal chapels, transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building wi ...
, and north portal (1670–1678), after which construction was halted for lack of funds.Himmelfarb 1998; Ayers 2004, pp. 126–127.
Gilles-Marie Oppenord and Giovanni Servandoni Giovanni may refer to:
* Giovanni (name), an Italian male given name and surname
* Giovanni (meteorology), a Web interface for users to analyze NASA's gridded data
* ''Don Giovanni'', a 1787 opera by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, based on the legend of ...
, adhering closely to Gittard's designs, supervised further construction (mainly the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
and side-chapels, 1719–1745). The decoration was executed by the brothers Sébastien-Antoine Slodtz (1695–1742) and Paul-Ambroise Slodtz (1702–1758).Terrien 2004, p. 17.
In 1723–1724 Oppenord created the north and south portals of the transept with an unusual interior design for the ends: concave walls with nearly engaged Corinthian Corinthian or Corinthians may refer to:
*Several Pauline epistles, books of the New Testament of the Bible:
**First Epistle to the Corinthians
**Second Epistle to the Corinthians
**Third Epistle to the Corinthians (Orthodox)
*A demonym relating to ...
columns instead of the pilaster
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wal ...
s found in other parts of the church.
West facade
In 1732 a competition was held for the design of the west facade, won by Servandoni, who was inspired by the entrance elevation of Christopher Wren'sSaint Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in London and is the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London. It is on Ludgate Hill at the highest point of the City of London and is a Gr ...
in London.Ayers 2004, pp. 126–127. The 1739 Turgot map of Paris
The Turgot map of Paris (french: link=no, Plan de Turgot) is a highly accurate and detailed map of the city of Paris, France, as it existed in the 1730s. The map was commissioned by Parisian municipality chief Michel-Étienne Turgot, drawn up b ...
shows the church without Oppenord's crossing bell-tower, but with Servandoni's pedimented façades mostly complete, still lacking, however, its two towers.
Jean Chalgrin
Jean-François-Thérèse Chalgrin (1739 – 21 January 1811) was a French architect, best known for his design for the Arc de Triomphe, Paris.
Biography
His neoclassic orientation was established from his early studies with the prophet of neocla ...
rebuilt the north tower (1777–1780), making it taller and modifying Servandoni's baroque design to one that was more neoclassical, but the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
intervened, and the south tower was never replaced. Chalgrin also designed the decoration of the chapels under the towers.
pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape.
Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds.
A pedim ...
, criticized as classically incorrect because its width was based on the entire front rather than the size of the order on which it rested, was removed after it was struck by lightning in 1770 and replaced with a balustrade. This change and the absence of the belvederes on the towers bring the design closer in spirit to that of the severely classical east front of the Louvre
The Louvre Colonnade is the easternmost façade of the Palais du Louvre in Paris.
It has been celebrated as the foremost masterpiece of French Architectural Classicism since its construction, mostly between 1667 and 1674. The design, dominated b ...
.
The facade is an unorthodox essay in which a double colonnade, Ionic order over Roman Doric with loggia
In architecture, a loggia ( , usually , ) is a covered exterior gallery or corridor, usually on an upper level, but sometimes on the ground level of a building. The outer wall is open to the elements, usually supported by a series of columns ...
s behind them, unifies the bases of the corner towers with the façade; this fully classicising statement was made at the height of the rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
.
Its revolutionary character was recognised by the architect and teacher Jacques-François Blondel
Jacques-François Blondel (8 January 1705 – 9 January 1774) was an 18th-century French architect and teacher. After running his own highly successful school of architecture for many years, he was appointed Professor of Architecture at the Acad ...
, who illustrated the elevation of the façade in his ''Architecture françoise'' of 1752, remarking: "The entire merit of this building lies in the architecture itself... and its greatness of scale, which opens a practically new road for our French architects." Large arched windows fill the vast interior with natural light. The result is a simple two-storey west front with three tiers of elegant columns. The overall harmony of the building is, some say, only marred by the two mismatched towers.
Another point of interest dating from the time of the Revolution, when Christianity was suppressed and Saint-Sulpice became a place for worship of the "Supreme Being", is a printed sign over the center door of the main entrance. One can still barely make out the printed words ''Le Peuple Français Reconnoit L'Etre Suprême Et L'Immortalité de L'Âme'' ("The French people recognize the Supreme Being and the immortality of the soul").Terrien 2004, p. 33.
Interior

 Inside the church to either side of the entrance are the two halves of an enormous shell (''
Inside the church to either side of the entrance are the two halves of an enormous shell (''Tridacna gigas
The giant clams are the members of the clam genus ''Tridacna'' that are the largest living bivalve mollusks. There are actually several species of "giant clams" in the genus ''Tridacna'', which are often misidentified for ''Tridacna gigas'', ...
'') given to King Francis I by the Venetian Republic
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
. They function as holy water font
A holy water font or stoup is a vessel containing holy water which is generally placed near the entrance of a church. It is often placed at the base of a crucifix or religious representation. It is used in the Catholic Church, Anglican Churche ...
s and rest on rock-like bases sculpted by Jean-Baptiste Pigalle.
Pigalle also designed the large white marble statue of Mary in the Lady Chapel at the far end of the church. The stucco decoration surrounding it is by Louis-Philippe Mouchy
Louis-Philippe Mouchy (31 March 1734 – 10 December 1801) was a French sculptor.
Early years
Louis-Philippe Mouchy was born in 1734.
He was a student of Jean-Baptiste Pigalle, and married Pigalle's niece.
Mouchy followed Pigalle's style closely ...
. Pigalle's work replaced a solid-silver statue by Edmé Bouchardon
Edmé Bouchardon (; 29 May 169827 July 1762) was a French sculptor best known for his neoclassical statues in the gardens of the Palace of Versailles, his medals, his equestrian statue of Louis XV of France for the Place de la Concorde (destroy ...
, which vanished at the time of the Revolution. It was cast from silverware donated by parishioners and was known as "Our Lady of the Old Tableware".
The baroque interior of the Lady Chapel (rebuilt by Servandoni in 1729) was designed by Charles de Wailly
Charles de Wailly () (9 November 1730 – 2 November 1798) was a French architect and urbanist, and furniture designer, one of the principals in the Neoclassical revival of the Antique. His major work was the Théâtre de l'Odéon for the Comédi ...
in 1774, after the chapel was badly damaged by a fire which destroyed the nearby Foire Saint-Germain in 1762. The dome, lit by natural light from hidden windows devised by de Wailly, contains a fresco by François Lemoyne
François Lemoyne or François Le Moine (; 1688 – 4 June 1737) was a French rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which co ...
depicting the Assumption of Mary
The Assumption of Mary is one of the four Marian dogmas of the Catholic Church. Pope Pius XII defined it in 1950 in his apostolic constitution '' Munificentissimus Deus'' as follows:
We proclaim and define it to be a dogma revealed by ...
, which dates from 1734, although it has been restored several times since then. De Wailly also designed the pulpit (in the nave), completed in 1788. The oak canopy broadcasts sound very well and it was from here that the parish priest of Saint-Sulpice declared his refusal to accept the Civil Constitution of the Clergy. Revolutionary orators used it later also.Kauffmann 2003, p. 37.
Directory
Directory may refer to:
* Directory (computing), or folder, a file system structure in which to store computer files
* Directory (OpenVMS command)
* Directory service, a software application for organizing information about a computer network's u ...
, Saint-Sulpice was used as a Temple of Victory. Redecorations to the interior, to repair extensive damage still remaining from the Revolution, were begun after the Concordat of 1801
The Concordat of 1801 was an agreement between Napoleon Bonaparte and Pope Pius VII, signed on 15 July 1801 in Paris. It remained in effect until 1905, except in Alsace-Lorraine, where it remains in force. It sought national reconciliation ...
. Eugène Delacroix
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix ( , ; 26 April 1798 – 13 August 1863) was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school.Noon, Patrick, et al., ''Crossing the Channel: Britis ...
added murals (1855–1861) that adorn the walls of the Chapel of the Holy Angels (first side-chapel on the right). The most famous of these are '' Jacob Wrestling with the Angel'' and ''Heliodorus Driven from the Temple''. A third, on the ceiling, is ''Saint Michael Vanquishing the Demon''.
Notable events
The Marquis de Sade andCharles Baudelaire
Charles Pierre Baudelaire (, ; ; 9 April 1821 – 31 August 1867) was a French poet who also produced notable work as an essayist and art critic. His poems exhibit mastery in the handling of rhyme and rhythm, contain an exoticism inherited ...
were baptized in Saint-Sulpice (1740 and 1821, respectively), and the church also saw the marriage of Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
to Adèle Foucher (1822).
During the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defended ...
(1871) one faction, called the Club de la Victoire, chose Saint-Sulpice as its headquarters and Louise Michel
Louise Michel (; 29 May 1830 – 9 January 1905) was a teacher and important figure in the Paris Commune. Following her penal transportation to New Caledonia she embraced anarchism. When returning to France she emerged as an important French a ...
spoke from the pulpit.
Louise Élisabeth de Bourbon and Louise Élisabeth d'Orléans
Louise Élisabeth d'Orléans ( es, Luisa Isabel; 9 December 1709 – 16 June 1742) was Queen of Spain as the wife of King Louis I. Their reign is regarded as one of the shortest in history, lasting for seven months. Louise Élisabeth was the fo ...
, granddaughters of Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Ver ...
and Madame de Montespan Madame may refer to:
* Madam, civility title or form of address for women, derived from the French
* Madam (prostitution), a term for a woman who is engaged in the business of procuring prostitutes, usually the manager of a brothel
* ''Madame'' ( ...
are buried in the church. Louise de Lorraine
Louise of Lorraine (Louise Henriette Gabrielle; 30 December 1718 – 5 September 1788) was a French noblewoman and member of the House of Lorraine. She married into the House of La Tour d'Auvergne and was Duchess of Bouillon.
Biography
Born ...
, duchesse de Bouillon and wife of Charles Godefroy de La Tour d'Auvergne
Charles Godefroy de La Tour d'Auvergne (16 July 1706 – 24 October 1771) was a French nobleman and member of the powerful House of La Tour d'Auvergne.
Biography
His parents, Emmanuel Théodose de La Tour d'Auvergne (1668–1730) and Marie Arma ...
, was buried here in 1788.
On Sunday 17 March 2019, the church caught on fire. Spectators at an organ concert alerted firefighters. The fire badly damaged the doors, a stained-glass window, and a bas-relief; and a staircase near the doorway went up in flames. Police later confirmed the fire was an arson attack. The City of Paris is required to pay for the building's repair and restoration.
A funeral mass was held in the church for Jacques Chirac, former President of France
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (french: Président de la République française), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency i ...
, on 30 September 2019.
Organs
 The church has a long-standing tradition of talented organists that dates back to the eighteenth century (see below). In 1862, Aristide Cavaillé-Coll rebuilt the existing organ built by François-Henri Clicquot. The case was designed by
The church has a long-standing tradition of talented organists that dates back to the eighteenth century (see below). In 1862, Aristide Cavaillé-Coll rebuilt the existing organ built by François-Henri Clicquot. The case was designed by Jean-François-Thérèse Chalgrin
Jean-François-Thérèse Chalgrin (1739 – 21 January 1811) was a French architect, best known for his design for the Arc de Triomphe, Paris.
Biography
His neoclassic orientation was established from his early studies with the prophet of neoc ...
and built by Monsieur Joudot.
Though using many materials from Clicquot's French Classical organ, it is considered to be Cavaillé-Coll's magnum opus, featuring 102 speaking stops on five manuals and pedal
A pedal (from the Latin '' pes'' ''pedis'', "foot") is a lever designed to be operated by foot and may refer to:
Computers and other equipment
* Footmouse, a foot-operated computer mouse
* In medical transcription, a pedal is used to control p ...
, and is perhaps the most impressive instrument of the romantic French symphonic-organ era.
Its titular organists have been renowned, starting with Nicolas Séjan in the 18th century, and continuing with Charles-Marie Widor
Charles-Marie-Jean-Albert Widor (21 February 1844 – 12 March 1937) was a French organist, composer and teacher of the mid-Romantic era, most notable for his ten organ symphonies. His Toccata from the fifth organ symphony has become one of th ...
(organist 1870–1933), Marcel Dupré
Marcel Jean-Jules Dupré () (3 May 1886 – 30 May 1971) was a French organist, composer, and pedagogue.
Biography
Born in Rouen into a wealthy musical family, Marcel Dupré was a child prodigy. His father Aimable Albert Dupré was titular o ...
(organist 1934–1971), and Jean-Jacques Grunenwald (organist 1973–1982), organists and composers of high international reputation. For over a century (1870–1971), Saint-Sulpice employed only two organists, and much credit is due to these musicians for preserving the instrument in its original state. The current organists are Daniel Roth (titular organist, since 1985) and Sophie-Véronique Cauchefer-Choplin (organiste titulaire-adjointe, since 1985).
Aside from a re-arrangement of the manuals and replacement of a few stops in 1903 by Charles Mutin (Cavaillé-Coll's direct successor), the installation of an electric blower in the 1920s, and the addition of two Pedal stops upon Widor's retirement in 1933 (Principal 16' and Principal 8', donated by the Société Cavaille-Coll), the organ is maintained today almost exactly as Cavaillé-Coll originally completed it in 1862.
In Saint-Sulpice, Sunday organ concerts are held on a regular basis ("Auditions des Grandes Orgues à Saint Sulpice", following the 11:00 am Mass, starting around 12:00 noon). The Sunday Mass is preceded by a 15-minute Prelude of the Great Organ, starting at 10:45 am.
The church is also home to a two-manual-and-pedal choir organ by Aristide Cavaillé-Coll from 1858.
Accessories:
* Machine à grêle
* Rossignol
Couplers:
* Grand-Chœur/Ped, Grand-Orgue/Ped, Récit/Ped
* Keyboards: I/II, II/I, III/I, IV/I, V/I, IV/III
* I/I, II/I, III/III, IV/IV, V/V
Wind pressures (mm)
* Grand-orgue : 95, 100
* Grand-chœur : 95, 115
* Solo : 100, 115, 127
* Positif : 100, 115, 120
* Récit : 100, 115
* Pedal : 90 – 100
* Trompette coudée : 140 – 150
Couplers: II/I, I/P, II/P. Trémolo (Récit), reeds G.O., reeds Récit
List of organists
The dates indicate when the organist was ''titulaire''. *Nicolas Pescheur (died 1601 or 1614) *Vincent Coppeau ( – ) *Guillaume-Gabriel Nivers
Guillaume-Gabriel Nivers (c. 1632, Paris – 13 November 1714) was a French organist, composer and theorist. His first ''livre d'orgue'' is the earliest surviving published collection with traditional French organ school forms (a collection by Lou ...
( – 1702)
*Louis-Nicolas Clérambault
Louis-Nicolas Clérambault (19 December 1676 – 26 October 1749) was a French musician, best known as an organist and composer. He was born, and died, in Paris.
Biography
Clérambault came from a musical family (his father and two of his sons ...
(1715 – 1749)
*César-François Clérambault (1749 – 1760)
*Evrard-Dominique Clérambault (1761 – 1773)
*Claude-Étienne Luce (1773 – 1783)
* Nicolas Séjan (1783 – 1819)
* Louis-Nicolas Séjan (1819 – 1849)
*Georg Schmitt
Johann Georg Gerhard Schmitt (11 March 1821 - 7 December 1900), in French Jean-Georges Gérard Schmitt, was a Paris-based composer and organist, originally from the Prussian Lower Rhine province. He was only 14 when he took over as organist at ...
(1850 – 1863)
* Alfred Lefébure-Wély (1863 – 1869)
*Charles-Marie Widor
Charles-Marie-Jean-Albert Widor (21 February 1844 – 12 March 1937) was a French organist, composer and teacher of the mid-Romantic era, most notable for his ten organ symphonies. His Toccata from the fifth organ symphony has become one of th ...
(1870 – 1934)
*Marcel Dupré
Marcel Jean-Jules Dupré () (3 May 1886 – 30 May 1971) was a French organist, composer, and pedagogue.
Biography
Born in Rouen into a wealthy musical family, Marcel Dupré was a child prodigy. His father Aimable Albert Dupré was titular o ...
(1934 – 1971)
* Jean-Jacques Grunenwald (1973 – 1982)
* Daniel Roth (since 1985)
* Sophie-Véronique Cauchefer-Choplin (cotitular since 1985)
The gnomon
 In 1727, Jean-Baptiste Languet de Gergy, then priest of Saint-Sulpice, requested the construction of a gnomon in the church as part of its new construction, to help him determine the time of the equinoxes and hence of
In 1727, Jean-Baptiste Languet de Gergy, then priest of Saint-Sulpice, requested the construction of a gnomon in the church as part of its new construction, to help him determine the time of the equinoxes and hence of Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel ...
.Easter Sunday is to be celebrated on the first Sunday following the full moon after the spring equinox. A meridian line of brass was inlaid across the floor and ascending a white marble obelisk, nearly eleven metres high, at the top of which is a sphere surmounted by a cross. The obelisk is dated 1743.
In the south transept window a small opening with a lens was set up, so that a ray of sunlight shines onto the brass line. At noon on the winter solstice (21 December), the ray of light touches the brass line on the obelisk. At noon on the equinoxes (21 March and 21 September), the ray touches an oval plate of copper in the floor near the altar.
Constructed by the English clock-maker and astronomer Henry Sully, the gnomon was also used for various scientific measurements. This rational use may have protected Saint-Sulpice from being destroyed during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
.
References in popular culture
Act III, scene ii ofMassenet
Jules Émile Frédéric Massenet (; 12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic music, Romantic era best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty. The two most frequently staged are ''Manon'' (1884) ...
's opera '' Manon'' takes place in Saint-Sulpice, where Manon convinces des Grieux to run away with her once more.
Abbé Herrera from ''Splendeurs et misères des courtisanes
''Splendeurs et misères des courtisanes'', translated variously as ''The Splendors and Miseries of Courtesans'', ''A Harlot High and Low'', or as ''Lost Souls'', is an 1838-1847 novel by French novelist Honoré de Balzac, published in four initia ...
'' by Honoré de Balzac
Honoré de Balzac ( , more commonly , ; born Honoré Balzac;Jean-Louis Dega, La vie prodigieuse de Bernard-François Balssa, père d'Honoré de Balzac : Aux sources historiques de La Comédie humaine, Rodez, Subervie, 1998, 665 p. 20 May 179 ...
celebrated Mass in the church and lived nearby in the rue Cassette.
The fashionable public side of Saint-Sulpice inspired Joris-Karl Huysmans
Charles-Marie-Georges Huysmans (, ; 5 February 1848 – 12 May 1907) was a French novelist and art critic who published his works as Joris-Karl Huysmans (, variably abbreviated as J. K. or J.-K.). He is most famous for the novel '' À rebour ...
perversely to set action there in his 1891 novel '' Là-Bas'', dealing with Satanism in which the ritual magician "Eliphas Levi Eliphaz is one of Esau's sons in the Bible.
Eliphaz or Eliphas is also the given name of:
* Eliphaz (Job), another person in the Bible
* Eliphaz Dow (1705-1755), the first male executed in New Hampshire, for murder
* Eliphaz Fay (1797–1854), fo ...
" attended the seminary attached to the church.
A major part of Djuna Barnes
Djuna Barnes (, June 12, 1892 – June 18, 1982) was an American artist, illustrator, journalist, and writer who is perhaps best known for her novel ''Nightwood'' (1936), a cult classic of lesbian fiction and an important work of modernist liter ...
's 1936 novel ''Nightwood
''Nightwood'' is a 1936 novel by American author Djuna Barnes that was first published by publishing house Faber and Faber. It is one of the early prominent novels to portray explicit homosexuality between women, and as such can be considered ...
'' takes place around Saint-Sulpice, especially in the renowned Café de la Mairie du VIe.
References to the church of Saint-Sulpice are found in the so-called ''Dossiers Secrets The ''Dossiers Secrets d'Henri Lobineau'' ("Secret Files of Henri Lobineau"), supposedly compiled by Philippe Toscan du Plantier, is a 27-page document which was deposited in the Bibliothèque nationale de France on 27 April 1967. The document purpo ...
'' that were planted in the Bibliothèque Nationale
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a vi ...
in the 1960s.
In Lynn Picknett and Clive Prince's '' The Templar Revelation'' (1997), Saint-Sulpice is noted.
Dan Brown
Daniel Gerhard Brown (born June 22, 1964) is an American author best known for his thriller novels, including the Robert Langdon novels ''Angels & Demons'' (2000), '' The Da Vinci Code'' (2003), ''The Lost Symbol'' (2009), '' Inferno'' (2013), ...
's 2003 novel ''The Da Vinci Code
''The Da Vinci Code'' is a 2003 mystery thriller novel by Dan Brown. It is Brown's second novel to include the character Robert Langdon: the first was his 2000 novel ''Angels & Demons''. ''The Da Vinci Code'' follows symbologist Robert Lang ...
'' was an international bestseller that brought crowds of tourists to Saint-Sulpice. This note has been on display in the church:
In 2005, the Archdiocese of Paris
The Archdiocese of Paris (Latin: ''Archidioecesis Parisiensis''; French: ''Archidiocèse de Paris'') is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in France. It is one of twenty-three archdioceses in France. ...
refused Ron Howard
Ronald William Howard (born March 1, 1954) is an American director, producer, screenwriter, and actor. He first came to prominence as a child actor, guest-starring in several television series, including an episode of ''The Twilight Zone''. He ...
permission to film inside Saint-Sulpice when he was making ''The Da Vinci Code
''The Da Vinci Code'' is a 2003 mystery thriller novel by Dan Brown. It is Brown's second novel to include the character Robert Langdon: the first was his 2000 novel ''Angels & Demons''. ''The Da Vinci Code'' follows symbologist Robert Lang ...
''.
In David Alexanian's novel, ''Laplace's Demon'', the church is the setting of Laplace's confession and the death of a priest by a demon. The novel is the first in a series known as the Sword Demon Series, published by Mystic Publishers Inc.
In 2018, the South Korean group Monsta X referenced the painting of the Dome of the Lady Chapel in the music video for their single "Jealousy".
Image gallery
See also
* :Burials at Saint-Sulpice, Paris * Saint-Sulpice Seminary (Issy-les-Moulineaux)Notes
Bibliography
* Ayers, Andrew (2004). ''The Architecture of Paris''. Stuttgart: Axel Menges. . * Himmelfarb, Hélène (1996). "Gittard, Daniel", vol. 12, p. 747, in ''The Dictionary of Art
''Grove Art Online'' is the online edition of ''The Dictionary of Art'', often referred to as the ''Grove Dictionary of Art'', and part of Oxford Art Online, an internet gateway to online art reference publications of Oxford University Press, ...
'' (34 volumes), edited by Jane Turner. New York: Grove. . See also aOxford Art Online
(subscription required). * Kauffmann, Jean-Paul (2002). ''Wrestling with the Angel: The Mystery of Delacroix's Mural''. London: Harvill. . Also titled ''The Angel of the Left Bank: The Secrets of Delacroix's Parisian Masterpiece'' and ''The Struggle with the Angel: Delacroix, Jacob, and the God of Good and Evil.'' * Terrien, Laurence, translator (2004). ''Saint-Sulpice''. Paris: Paroisse Saint-Sulpice. .
External links
Daniel Roth, titular organist at St. Sulpice since 1985
Photographs of the Saint-Sulpice church
Official Website on the organs and organists at St. Sulpice
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saint-Sulpice, Paris, Church of Roman Catholic churches in the 6th arrondissement of Paris Roman Catholic churches completed in 1870 Burials at Saint-Sulpice, Paris 1646 establishments in France Burial sites of the House of la Tour d'Auvergne 19th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in France