São Miguel Island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
São Miguel Island (; Portuguese for "

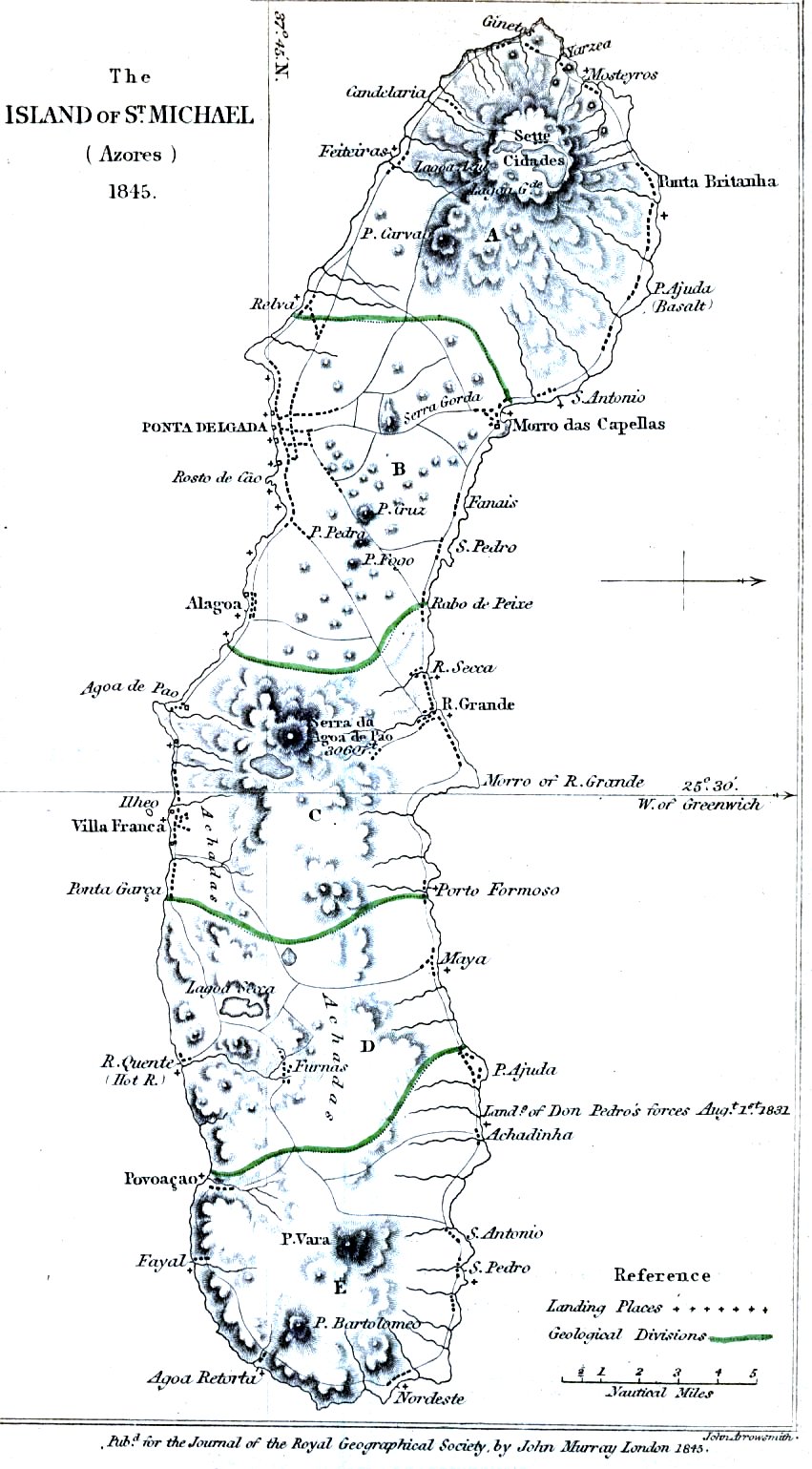 In 1427, São Miguel became the second of the islands discovered by
In 1427, São Miguel became the second of the islands discovered by
Saint Michael
Michael (; he, מִיכָאֵל, lit=Who is like El od, translit=Mīḵāʾēl; el, Μιχαήλ, translit=Mikhaḗl; la, Michahel; ar, ميخائيل ، مِيكَالَ ، ميكائيل, translit=Mīkāʾīl, Mīkāl, Mīkhāʾīl), also ...
"), nicknamed "The Green Island" (''Ilha Verde''), is the largest and most populous island in the Portuguese archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arch ...
of the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
. The island covers and has around 140,000 inhabitants, with 45,000 people residing in Ponta Delgada
Ponta Delgada (; ) is the largest municipality ('' concelho'') and economic capital of the Autonomous Region of the Azores in Portugal. It is located on São Miguel Island, the largest and most populous in the archipelago. As of 2021, it has 67, ...
, the archipelago's largest city.
History

 In 1427, São Miguel became the second of the islands discovered by
In 1427, São Miguel became the second of the islands discovered by Gonçalo Velho Cabral
Gonçalo Velho Cabral ( 1400 – c. 1460) was a Portuguese monk and Commander in the Order of Christ, explorer (credited with the discovery of the Formigas, the re-discovery of the islands of Santa Maria and São Miguel in the Azores) and hered ...
to be settled by colonists from continental Portugal. This date is uncertain, as it is believed that the island was discovered between 1426 and 1437 and inscribed in portolan
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portulano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and wh ...
s from the middle of the 15th century. Its discovery was later recorded by Father
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. An adoptive fathe ...
Gaspar Frutuoso
Gaspar Frutuoso (c.1522 in Ponta Delgada – 1591 in Ribeira Grande) was a Portuguese priest, historian and humanist from the island of São Miguel, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. His major contribution to Portuguese history was hi ...
in the seminal history of the Azores, ''Saudades da Terra'', as he began: "This island of São Miguel where...we are, is mountainous and covered in ravines, and it was, when we discovered it, covered in trees...due to its humidity, with its water showers and ravines warm with sun..."
It was sometime after the initial settlement of Povoação Velha
Povoação Velha is a village in the southwestern part of the island of Boa Vista, Cape Verde.Infante D. Henrique first authorized the settlement of the Azores, and many settlers from the historical provinces of Estremadura, Alto Alentejo,
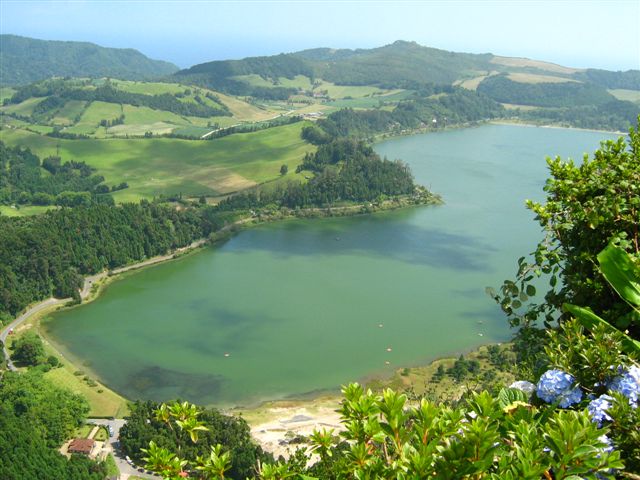


 São Miguel is bisected by many faults from the northwest to southeast in the direction of the Terceira Rift, a triple junction of the African,
São Miguel is bisected by many faults from the northwest to southeast in the direction of the Terceira Rift, a triple junction of the African, 
 These geomorphological structures have resulted from millions of years of compound growth that began in the eastern portion of the island; around 4 million years ago the Nordeste Volcano burst from the ocean floor in effusive and fissural eruptions. These eruptions were composed of basaltic lava flows and spatter cones whose products reached a height of forming the mountainous region of Tronqueiro, Planalto dos Graminhais, Espigão dos Bois and Pico Verde (finding its maximum extent in Pico da Vara). But, about 950,000 years ago a secondary volcano system (Volcanic Complex of Povoação) supplanted the eruptions of the Nordeste Volcano, responsible for new basaltic lavas and pyroclastic deposits. With an age of 200,000 years the third volcano on São Miguel, the Água de Pau Volcano started erupting on the western flank of Povoação volcano in two phases. The first phase, composed of the older materials, erupted from lava flows and Trachyte pyroclasts, the secondary phase corresponded to volcanic products that began erupting 400,000 years ago. These latter deposits included pyroclastic, trachyte flows (lava and surges), mud flows and a mixture of basalts. In what would become the western portion of the island a fourth volcano formed: the Sete Cidades Volcano erupted 200,000 years ago and continued to erupt until about 36,000 years ago.
Between 100,000 and 3,800 years ago fissural eruptions of integrated lava and basaltic pyroclastic deposits occurred in the center of the island between Água de Pau and Povoação, forming the Fissural Volcanic System of Congro. These eruptions were explosive and fed by activities in the neighboring volcanic systems. At about 100,000 years a secondary system developed along the frontier of the Povoação volcano, the "Furnas Volcano" complex (the youngest volcanic system) in three phases mixing
These geomorphological structures have resulted from millions of years of compound growth that began in the eastern portion of the island; around 4 million years ago the Nordeste Volcano burst from the ocean floor in effusive and fissural eruptions. These eruptions were composed of basaltic lava flows and spatter cones whose products reached a height of forming the mountainous region of Tronqueiro, Planalto dos Graminhais, Espigão dos Bois and Pico Verde (finding its maximum extent in Pico da Vara). But, about 950,000 years ago a secondary volcano system (Volcanic Complex of Povoação) supplanted the eruptions of the Nordeste Volcano, responsible for new basaltic lavas and pyroclastic deposits. With an age of 200,000 years the third volcano on São Miguel, the Água de Pau Volcano started erupting on the western flank of Povoação volcano in two phases. The first phase, composed of the older materials, erupted from lava flows and Trachyte pyroclasts, the secondary phase corresponded to volcanic products that began erupting 400,000 years ago. These latter deposits included pyroclastic, trachyte flows (lava and surges), mud flows and a mixture of basalts. In what would become the western portion of the island a fourth volcano formed: the Sete Cidades Volcano erupted 200,000 years ago and continued to erupt until about 36,000 years ago.
Between 100,000 and 3,800 years ago fissural eruptions of integrated lava and basaltic pyroclastic deposits occurred in the center of the island between Água de Pau and Povoação, forming the Fissural Volcanic System of Congro. These eruptions were explosive and fed by activities in the neighboring volcanic systems. At about 100,000 years a secondary system developed along the frontier of the Povoação volcano, the "Furnas Volcano" complex (the youngest volcanic system) in three phases mixing
Algarve
The Algarve (, , ; from ) is the southernmost NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities ( ''concelhos'' or ''municípios'' in Portuguese).
The region has it ...
and Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
travelled to São Miguel, under the ''Carta Régia'' (a decree of the regency). The fertile soils and temperate climate attracted settlers from other countries, notably French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and Flemish people
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all i ...
. Cultural minorities such as Sephardic Jewish New Christians are believed to have comprised as much as 20% of the island's population (i.e., many had surnames such as 'Pereira, Pimentel, Dias, Menezes, Oliveira, Nunes, Mendes, Rodrigues, Pinto etc., and some Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinc ...
were exiled to the island during the inquisition. Its geographic position and fertile soils permitted rapid economic development. The establishment of a military garrison made the island an obligatory port-of-call in the African and Asian commercial trade, while the export of sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
, and later orchil (a dye exported to Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
for the making of cloth) stabilized the island's export trade.
The first capital of the island was Vila Franca do Campo, which was devastated by the 1522 Vila Franca earthquake and landslides. The tragedy helped to elevate Ponta Delgada
Ponta Delgada (; ) is the largest municipality ('' concelho'') and economic capital of the Autonomous Region of the Azores in Portugal. It is located on São Miguel Island, the largest and most populous in the archipelago. As of 2021, it has 67, ...
to the administrative and economic status of capital and business centre from 1546.
During the 1580 Portuguese succession crisis, the people from São Miguel won the naval Battle of Vila Franca against a French squadron that supported the claims of the pretender
A pretender is someone who claims to be the rightful ruler of a country although not recognized as such by the current government. The term is often used to suggest that a claim is not legitimate.Curley Jr., Walter J. P. ''Monarchs-in-Waiting'' ...
António, Prior of Crato
António, Prior of Crato (; 153126 August 1595; sometimes called ''The Determined'', ''The Fighter'', ''The Independentist'' or ''The Resistant''), was a grandson of King Manuel I of Portugal who claimed the Portuguese throne during the 1580 ...
.
With the Portuguese Restoration War
The Portuguese Restoration War ( pt, Guerra da Restauração) was the war between Portugal and Spain that began with the Portuguese revolution of 1640 and ended with the Treaty of Lisbon in 1668, bringing a formal end to the Iberian Union. The ...
(1640), the island regained its position as a commercial centre, establishing new contacts in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, which was heavily colonized during this period. Some of the island's historic buildings, including mansions and churches, date from this period; the island's architectural expansion and developed came from revenues from the export of oranges, mainly to Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
.
In 1831, during the Liberal Wars
The Liberal Wars (), also known as the Portuguese Civil War (), the War of the Two Brothers () or Miguelite War (), was a war between liberal constitutionalists and conservative absolutists in Portugal over royal succession that lasted from 18 ...
, following the landing of troops loyal to Queen Maria II in Nordeste (sent by future Duke of Terceira), a resistance to the Absolutist regime on the Island was organized. In 1832, this militia declared allegiance to the Charter (constitutional monarchy) and Queen Maria, forming a contingent that sailed to the continent where they were involved in the liberation of Porto.
Following the Liberal Wars, the period of Devourism allowed the economy to flourish, and the port of Ponta Delgada expanded, through the export of new crops such as tea, pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centuri ...
, and tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
. The development of the fishing industry, cultivation of food staples and expansion of the dairy industry permitted the growth of many of the population centres on the island.
Following the Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution ( pt, Revolução dos Cravos), also known as the 25 April ( pt, 25 de Abril, links=no), was a military coup by left-leaning military officers that overthrew the authoritarian Estado Novo regime on 25 April 1974 in Lisbo ...
, the island received the seat of the Presidency of the Autonomous Region of the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
, located in Ponta Delgada, while its economic, social and political importance continued to grow within the archipelago.
Geography
Geology

 São Miguel is bisected by many faults from the northwest to southeast in the direction of the Terceira Rift, a triple junction of the African,
São Miguel is bisected by many faults from the northwest to southeast in the direction of the Terceira Rift, a triple junction of the African, Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipela ...
, and North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the ...
tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
. This system is best expressed in the western part of the island with extensive geological formations, such as the Mosteiros Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic conte ...
(along the western flank of the Sete Cidades Massif), the Ribeira Grande Graben (along the northern flank of the Água de Pau Massif
Água de Pau Massif is a stratovolcanic complex, located in central part of the island of São Miguel, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. More recognizable for the Lagoa do Fogo at its centre, the volcanic complex includes centuries ...
), and the many cones and fissural structures along the interior of the island. In the ancient crater of Furnas the faults are aligned west-northwest to east-southeast. Zbysewsky (1959), among others (note references) identifies eight geomorphological
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or ...
structures on São Miguel that correspond to the formative features that built the island, including:
* The Sete Cidades Massif
Sete Cidades Massif is a stratovolcanic complex, referring to a polygenetic volcano and caldera, located in western part of the island of São Miguel, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. More recognizable for the Lagoa das Sete Cidad ...
– an area that occupies the extreme western part of the island, and corresponds to a central volcanic crater
A volcanic crater is an approximately circular depression in the ground caused by volcanic activity. It is typically a bowl-shaped feature containing one or more vents. During volcanic eruptions, molten magma and volcanic gases rise from an und ...
and lake-filled caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
, with various cones, deposits of pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular v ...
, lava domes
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
and maar
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallo ...
s. In the northeastern flank of this volcano the Mosteiros Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic conte ...
, a tectonic structure created from the collapse of lands and located along a northwest to southeast orientation. Along other regional fractures and radial faults there are ancient spatter cones and lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions ...
s;
* The Picos Volcanic System or Picos Region – is situated along a northwest–southeast alignment, and defines a range of spatter cones and relatively level ground between the Sete Cidades and the Água de Pau Massifs;
* The Água de Pau Massif
Água de Pau Massif is a stratovolcanic complex, located in central part of the island of São Miguel, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. More recognizable for the Lagoa do Fogo at its centre, the volcanic complex includes centuries ...
– this central feature corresponds to the central volcano on the island, and includes the ''Lagoa do Fogo'' (Lake of Fire), many lava domes and pumice cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and s ...
s. On the northeastern flank of the Massif the Ribeira Grande Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic conte ...
is visible, representing a tectonic depression oriented northwest to southeast;
* The Achada das Furnas Plateau – a region with a central plain marked by cones and maars, with deposits along a west-northwest to east-southeast and northwest to southeast;
* Furnas Volcano – located in the eastern part of the island, along the southern coast, and comprising two ancient calderas, occupied by a lake (''Lagoa das Furnas''). Within the system one can find many pumice cones, maars and lava domes;
* Povoação Volcano – comprising a central caldera, generally well-eroded and whose southern rim has disappeared to the southern coast. Within its interior, marked by several river-valleys and cliffs, are several spatter cones;
* The Tronqueira Region – it occupies the extreme easterly portion of the island and corresponds to a mountainous region, divided by many river-valleys that are usually delineated by tectonic fractures;
* The Northern Coastal Platform – located along the northeastern portion of the island, and marks a zone of relatively moderate topography, limited by the coast to the north and the northern crater rims of Furnas and Povoação volcanoes to the south.
São Miguel comprises six volcanic zones; all are Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million year ...
in age except the last, which is partly Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Água de Pau Massif
Água de Pau Massif is a stratovolcanic complex, located in central part of the island of São Miguel, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. More recognizable for the Lagoa do Fogo at its centre, the volcanic complex includes centuries ...
; a field of alkali-basalt cinder cones and lava flows with minor trachyte and tristanite; the trachyte stratovolcano of Furnas; and the Nordeste shield, which includes the Povoação caldera and consists of alkali basalt, tristanite and trachyte.Richard B. Moore (1990), p.1 Dormancy ages for these regions include: 400 year for Sete Cidades, 145 for zone 2, 1150 for Água de Pau, and 370 for Furnas, while eruptions in the Nordeste have not occurred in the past 3000 years.

 These geomorphological structures have resulted from millions of years of compound growth that began in the eastern portion of the island; around 4 million years ago the Nordeste Volcano burst from the ocean floor in effusive and fissural eruptions. These eruptions were composed of basaltic lava flows and spatter cones whose products reached a height of forming the mountainous region of Tronqueiro, Planalto dos Graminhais, Espigão dos Bois and Pico Verde (finding its maximum extent in Pico da Vara). But, about 950,000 years ago a secondary volcano system (Volcanic Complex of Povoação) supplanted the eruptions of the Nordeste Volcano, responsible for new basaltic lavas and pyroclastic deposits. With an age of 200,000 years the third volcano on São Miguel, the Água de Pau Volcano started erupting on the western flank of Povoação volcano in two phases. The first phase, composed of the older materials, erupted from lava flows and Trachyte pyroclasts, the secondary phase corresponded to volcanic products that began erupting 400,000 years ago. These latter deposits included pyroclastic, trachyte flows (lava and surges), mud flows and a mixture of basalts. In what would become the western portion of the island a fourth volcano formed: the Sete Cidades Volcano erupted 200,000 years ago and continued to erupt until about 36,000 years ago.
Between 100,000 and 3,800 years ago fissural eruptions of integrated lava and basaltic pyroclastic deposits occurred in the center of the island between Água de Pau and Povoação, forming the Fissural Volcanic System of Congro. These eruptions were explosive and fed by activities in the neighboring volcanic systems. At about 100,000 years a secondary system developed along the frontier of the Povoação volcano, the "Furnas Volcano" complex (the youngest volcanic system) in three phases mixing
These geomorphological structures have resulted from millions of years of compound growth that began in the eastern portion of the island; around 4 million years ago the Nordeste Volcano burst from the ocean floor in effusive and fissural eruptions. These eruptions were composed of basaltic lava flows and spatter cones whose products reached a height of forming the mountainous region of Tronqueiro, Planalto dos Graminhais, Espigão dos Bois and Pico Verde (finding its maximum extent in Pico da Vara). But, about 950,000 years ago a secondary volcano system (Volcanic Complex of Povoação) supplanted the eruptions of the Nordeste Volcano, responsible for new basaltic lavas and pyroclastic deposits. With an age of 200,000 years the third volcano on São Miguel, the Água de Pau Volcano started erupting on the western flank of Povoação volcano in two phases. The first phase, composed of the older materials, erupted from lava flows and Trachyte pyroclasts, the secondary phase corresponded to volcanic products that began erupting 400,000 years ago. These latter deposits included pyroclastic, trachyte flows (lava and surges), mud flows and a mixture of basalts. In what would become the western portion of the island a fourth volcano formed: the Sete Cidades Volcano erupted 200,000 years ago and continued to erupt until about 36,000 years ago.
Between 100,000 and 3,800 years ago fissural eruptions of integrated lava and basaltic pyroclastic deposits occurred in the center of the island between Água de Pau and Povoação, forming the Fissural Volcanic System of Congro. These eruptions were explosive and fed by activities in the neighboring volcanic systems. At about 100,000 years a secondary system developed along the frontier of the Povoação volcano, the "Furnas Volcano" complex (the youngest volcanic system) in three phases mixing pyroclastic surge
A pyroclastic surge is a fluidised mass of turbulent gas and rock fragments that is ejected during some volcanic eruptions. It is similar to a pyroclastic flow but it has a lower density or contains a much higher ratio of gas to rock, which makes ...
s, trachytes
Trachyte () is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava enriched with silica and alk ...
, and lava flows, as well as explosive materials. Finally, two layers of deposits formed the Fissural Volcanic System of Picos between the volcanic Água de Pau and Sete Cidades from 31,000 years ago unifying the island. This formation integrated lavas, basaltic pyroclasts, tuff cones and trachyte domes into two layers (referred to as the Ponta Delgada and Penhal da Paz sub-deposits) and compiled to about 5,000 years ago.
The peak area between Sete Cidades and Fogo is a monogenetic volcanic field
A monogenetic volcanic field is a type of volcanic field consisting of a group of small monogenetic volcanoes, each of which erupts only once, as opposed to polygenetic volcanoes, which erupt repeatedly over a period of time. The small monogeneti ...
composed of 270 volcanoes. They are primarily made up of basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron ( mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than ...
cones which were formed during Strombolian and Hawaiian-style eruptions. This is the part of the island with most recent volcanic activity. The youngest volcanoes are relatively well dated. It is estimated that 19 eruptions have occurred during the last 3,000 years. Several eruptions have been witnessed and recorded by people. The last one took place in the 17th century. The most famous eruption is known as Fogo 2, which occurred in 1652.
Biome
The ancient '' laurisilva'' forest has mostly been replaced by cultivated fields and imported trees and plants, such as the ubiquitouscryptomeria
''Cryptomeria'' (literally "hidden parts") is a monotypic genus of conifer in the cypress family Cupressaceae, formerly belonging to the family Taxodiaceae. It includes only one species, ''Cryptomeria japonica'' ( syn. ''Cupressus japonica'' ...
trees. There are some hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
s (''caldeiras''), generally located in the center of the island, in the area stretching from Povoação to Nordeste.
The highest elevation on São Miguel is the Pico da Vara at . Lying at the eastern end of the island, it is the focus of a Special Protection Area
A Special Protection Area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certa ...
containing the largest remnant of laurisilva forest on the island, which is home to the endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
and critically endangered bird, the Azores bullfinch
The Azores bullfinch (''Pyrrhula murina''), also known as the São Miguel bullfinch, or locally in Portuguese as the ''priolo'', is a threatened passerine bird in the true finch family. It is endemic to São Miguel Island, in the Azores archip ...
.
Whale watching
Whale watching is the practice of observing whales and dolphins (cetaceans) in their natural habitat. Whale watching is mostly a recreational activity (cf. birdwatching), but it can also serve scientific and/or educational purposes.Hoyt, E. 2 ...
tours, starting from Ponta Delgada
Ponta Delgada (; ) is the largest municipality ('' concelho'') and economic capital of the Autonomous Region of the Azores in Portugal. It is located on São Miguel Island, the largest and most populous in the archipelago. As of 2021, it has 67, ...
and Vila Franca do Campo are available. One may see sea turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhe ...
s, dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the b ...
s and humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The hu ...
s.
Climate
São Miguel has a mild maritime climate, which is drier in the summer and wetter in the winter, though according to theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
, four different climatic classifications can be found throughout the island. At lower elevations, the hot-summer Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(''Csa'') dominates over the Humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(''Cfa'') typical of the more westerly islands and truly only found around Capelas. Above altitude, the Mediterranean climate transitions into its warm-summer variant (''Csb''), and past the climate is strictly oceanic (''Cfb'').
The western half of the island is generally drier, due to the lower topography. Precipitation varies from less than in the Northwest coastline between Mosteiros and Ajuda da Bretanha, to over around Pico da Vara in the east.
Similar to other islands in the archipelago, São Miguel is influenced by ocean currents and winds, and, in particular, the cyclonic Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Unit ...
. This stream functions as a moderating force in the islands, keeping temperatures hovering between and throughout the year. The island's location also makes it susceptible to some Atlantic storms, and precipitation tends to be elevated during the winter periods. Winters are very mild by European standards and summers are warm (sometimes very warm due to the high humidity) and relatively dry. Temperatures above or below have never been recorded at the coast.
Human geography
Owing to the predominance of volcanic cones and craters in the interior, human settlement has developed primarily along coastal and interior plains. In addition, there are several communities that have developed within ancient craters (such as Sete Cidades,Furnas
Furnas is a civil parish in the municipality of Povoação on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese Azores. The population in 2011 was 1,439, in an area of 34.43 km2. The parish is one of the largest in the island and in the Azores. ...
or Povoação), river-valleys (such as Ribeira Chã
Ribeira Chã is a civil parish in the municipality of Lagoa in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. It is located along a cliff that overlooks the Atlantic Ocean. The population in 2011 was 396, in an area of 2.50 km2.Pilar da Bretanha) or coastal deltas ( Mosteiros). Regardless, these settlements were largely agrarian and concentrated around the parish churches and the many fertile parcels of land. The communities were largely isolated throughout the year, owing to the great distances and rough landscape of the island, and only became integrated with the development of the many road networks that circle and bisect the island. Two cities have developed, largely because the island was divided by mountainous volcanic cones in the interior: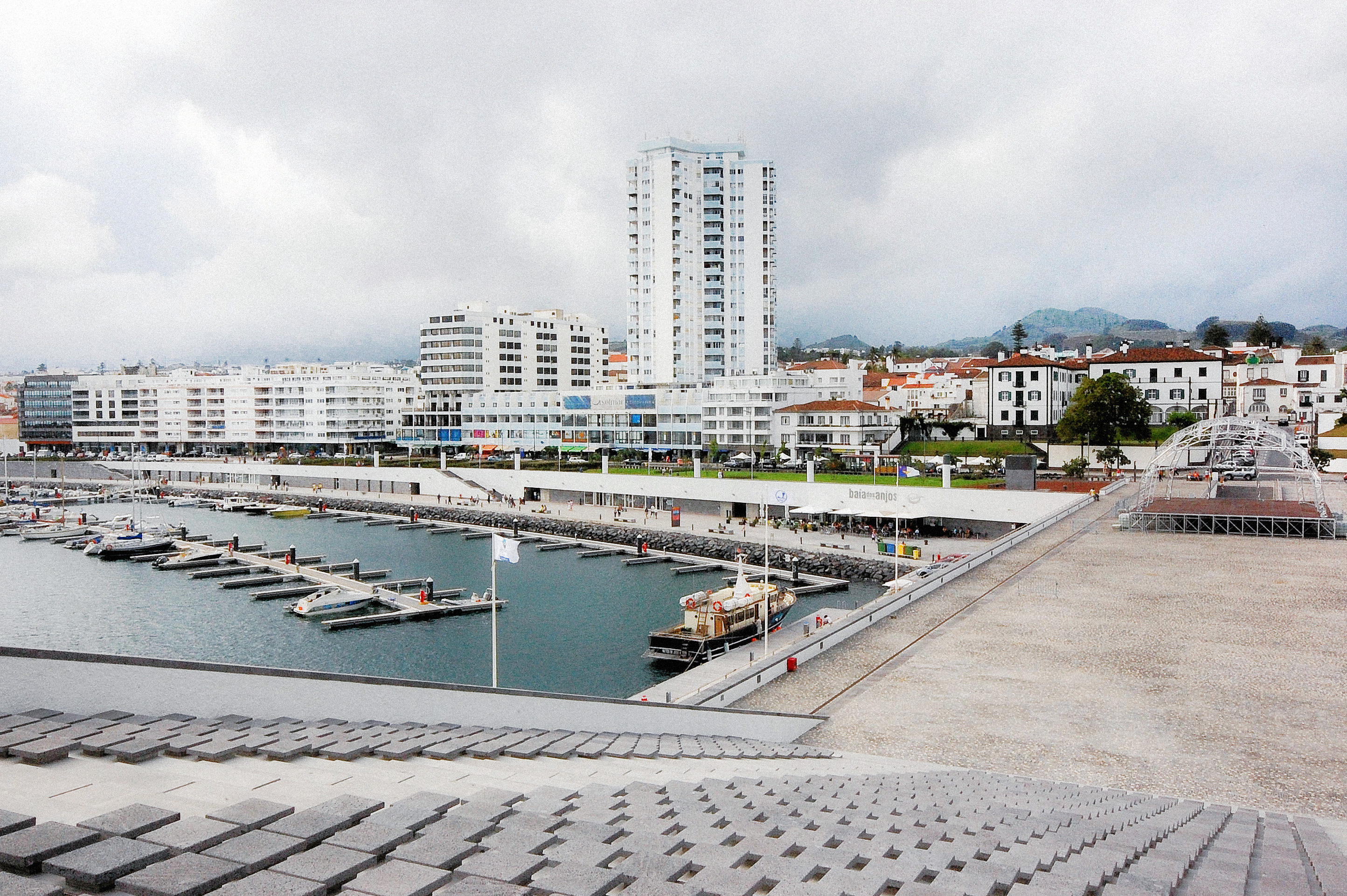  Lagoa, the youngest of the municipalities of São Miguel, has a population of about 14,126 inhabitants (2008 census), incorporating the south-central parishes east of Ponta Delgada;
Lagoa, the youngest of the municipalities of São Miguel, has a population of about 14,126 inhabitants (2008 census), incorporating the south-central parishes east of Ponta Delgada;

 Local government is administered at the local level by the civil parish ( pt, freguesias), which are responsible for the provision of services and implementation of municipal initiatives. Based on the historical ecclesiastical limits established after settlement, the civil parishes are run by a president, treasurer and secretary (at the head of a parish council). These presidents have municipal council standing and represent their constituencies in the assemblies of the ''Câmara Municipal''. On the island of São Miguel there are 64 local area authorities, that include:
* Achada
* Achadinha
*
Local government is administered at the local level by the civil parish ( pt, freguesias), which are responsible for the provision of services and implementation of municipal initiatives. Based on the historical ecclesiastical limits established after settlement, the civil parishes are run by a president, treasurer and secretary (at the head of a parish council). These presidents have municipal council standing and represent their constituencies in the assemblies of the ''Câmara Municipal''. On the island of São Miguel there are 64 local area authorities, that include:
* Achada
* Achadinha
*
Ponta Delgada
Ponta Delgada (; ) is the largest municipality ('' concelho'') and economic capital of the Autonomous Region of the Azores in Portugal. It is located on São Miguel Island, the largest and most populous in the archipelago. As of 2021, it has 67, ...
and Ribeira Grande Ribeira Grande may refer to the following places:
Cape Verde
*Ribeira Grande (stream), a stream on the island of Santo Antão
*Ribeira Grande, Cape Verde, a town on the island of Santo Antão
*Ribeira Grande, Cape Verde (municipality), a municipali ...
. Administratively, the island is governed by five municipalities, with Ponta Delgada and Ribeira Grande having more administrative functions associated with their larger populations:
 Lagoa, the youngest of the municipalities of São Miguel, has a population of about 14,126 inhabitants (2008 census), incorporating the south-central parishes east of Ponta Delgada;
Lagoa, the youngest of the municipalities of São Miguel, has a population of about 14,126 inhabitants (2008 census), incorporating the south-central parishes east of Ponta Delgada;
Nordeste
The Northeast Region of Brazil ( pt, Região Nordeste do Brasil; ) is one of the five official and political regions of the country according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Of Brazil's twenty-six states, it comprises ni ...
, literally the north-eastern municipality, well known for an abundance of natural vegetation and the highest point on the island, Pico da Vara;
Ponta Delgada
Ponta Delgada (; ) is the largest municipality ('' concelho'') and economic capital of the Autonomous Region of the Azores in Portugal. It is located on São Miguel Island, the largest and most populous in the archipelago. As of 2021, it has 67, ...
, includes not only the industrial/commercial city of Ponta Delgada, but also many rural parishes, as well as the large crater of Sete Cidades;
Povoação, home to the first colony on the island, Povoação is located in the south-east corner of the island, and includes active and dormant volcanic features, including Furnas
Furnas is a civil parish in the municipality of Povoação on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese Azores. The population in 2011 was 1,439, in an area of 34.43 km2. The parish is one of the largest in the island and in the Azores. ...
and the crater of Povoação;
Ribeira Grande Ribeira Grande may refer to the following places:
Cape Verde
*Ribeira Grande (stream), a stream on the island of Santo Antão
*Ribeira Grande, Cape Verde, a town on the island of Santo Antão
*Ribeira Grande, Cape Verde (municipality), a municipali ...
, the second largest municipality, with approximately 30,852 inhabitants, received its charter in 1981, and incorporates an extensive area of the northern coast (including the parish of Rabo de Peixe, the largest parish by population); and
Vila Franca do Campo, once the seat of the historical capital of São Miguel (until it was almost destroyed by earthquake and landslides in 1522), it is located along the southern coast between Lagoa and Povoação.
 Local government is administered at the local level by the civil parish ( pt, freguesias), which are responsible for the provision of services and implementation of municipal initiatives. Based on the historical ecclesiastical limits established after settlement, the civil parishes are run by a president, treasurer and secretary (at the head of a parish council). These presidents have municipal council standing and represent their constituencies in the assemblies of the ''Câmara Municipal''. On the island of São Miguel there are 64 local area authorities, that include:
* Achada
* Achadinha
*
Local government is administered at the local level by the civil parish ( pt, freguesias), which are responsible for the provision of services and implementation of municipal initiatives. Based on the historical ecclesiastical limits established after settlement, the civil parishes are run by a president, treasurer and secretary (at the head of a parish council). These presidents have municipal council standing and represent their constituencies in the assemblies of the ''Câmara Municipal''. On the island of São Miguel there are 64 local area authorities, that include:
* Achada
* Achadinha
* Água de Alto
Água de Alto is a civil parish in the municipality of Vila Franca do Campo on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. The population in 2011 was 1,788, in an area of 18.41 km².
History
According to histor ...
* Água de Pau
* Água Retorta
* Algarvia
Algarvia is a civil parish in the municipality of Nordeste, on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese Azores. The population in 2011 was 290, in an area of 5.40 km².Ajuda da Bretanha
*
Arrifes
Arrifes is a civil parish in the municipality of Ponta Delgada on the island of São Miguel in the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in ...
* Cabouco
Cabouco is a civil parish in the municipality of Lagoa on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azo ...
* Calhetas
Calhetas is a ''freguesia'' ("civil parish") in the municipality of Ribeira Grande in the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, ...
* Candelária
* Capelas
* Conceição
* Covoada
* Faial da Terra
* Fajã de Baixo
* Fajã de Cima
Fajã de Cima is a civil parish in the municipality of Ponta Delgada in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. Fajã de Cima is located in the Picos region in the western part of the island of São Miguel, north of central Ponta Delgada. The p ...
* Fenais da Ajuda
Fenais da Ajuda is a civil parish in the municipality of Ribeira Grande in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. The population in 2011 was 1,131, in an area of 13.36 km².Fenais da Luz
Fenais da Luz is a civil parish in the municipality of Ponta Delgada on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. The population in 2011 was 2,009, in an area of .Feteiras
*
Global Volcanism Program: Azores
In depth video from São Miguel Island– Site with abundant information about São Miguel Island
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sao Miguel Island Islands of the Azores
Furnas
Furnas is a civil parish in the municipality of Povoação on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese Azores. The population in 2011 was 1,439, in an area of 34.43 km2. The parish is one of the largest in the island and in the Azores. ...
* Ginetes
Ginetes is a civil parish in the municipality of Ponta Delgada on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese of the Azores. It is situated in the westernmost part of the island, near the coast. The population in 2011 was 1,378, in an area of .
* Livramento
* Lomba da Fazenda
Lomba da Fazenda is a parish in the municipality of Nordeste in the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of t ...
* Lomba da Maia
Lomba da Maia is a civil parish in the municipality of Ribeira Grande in the Portuguese Azores. The population in 2011 was 1,152, in an area of 20.47 km2. It is situated on a plateau that overlooks the northern coast and the neighboring pari ...
* Lomba de São Pedro
Lomba de São Pedro is a civil parish in the municipality of Ribeira Grande in the Portuguese in the archipelago of the Azores. The population in 2011 was 284, in an area of 8.25 km². Lomba de São Pedro is the least-populated parish in R ...
* Maia
* Matriz
* Mosteiros
* Nordeste
The Northeast Region of Brazil ( pt, Região Nordeste do Brasil; ) is one of the five official and political regions of the country according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Of Brazil's twenty-six states, it comprises ni ...
* Nossa Senhora dos Remédios
* Nossa Senhora do Rósario
* Pico da Pedra
Pico da Pedra ( pt, peak of the rock) is a civil parish in the municipality of Ribeira Grande in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. The population in 2011 was 2,909, in an area of 6.58 km².
History
The settlement of the area began ...
* Pilar da Bretanha
* Ponta Garça
Ponta Garça is a civil parish in the municipality of Vila Franca do Campo in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. The population in 2011 was 3,547, in an area of 29.35 km2. It is the largest parish in Vila Franca do Campo.
History
Ga ...
* Porto Formoso
* Povoação
* Rabo de Peixe
* Relva
* Remédios
* Ribeira Chã
Ribeira Chã is a civil parish in the municipality of Lagoa in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. It is located along a cliff that overlooks the Atlantic Ocean. The population in 2011 was 396, in an area of 2.50 km2.Ribeira das Tainhas
Ribeira das Tainhas is a civil parish in the municipality of Vila Franca do Campo in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Lo ...
* Ribeira Quente
* Ribeira Seca (Ribeira Grande)
* Ribeira Seca (Vila Franca do Campo)
Ribeira Seca (Portuguese for "dry stream") is a civil parish in the municipality of Vila Franca do Campo on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, ...
* Ribeirinha
* Salga
Salga is a civil parish in the municipality of Nordeste in Portuguese archipelago of the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, ...
* Santa Bárbara (Ribeira Grande)
* Santa Bárbara (Ponta Delgada)
* Santa Clara
* Santa Cruz
* Santana
* Santo António
Santo António (Portuguese for Saint Anthony), also known as Santo António do Príncipe, is the main settlement of the island of Príncipe in São Tomé and Príncipe. It lies on the north east coast. It is the capital of the Autonomous Regio ...
* Santo António de Nordestinho
Santo António de Nordestinho is a parish in the municipality of Nordeste, Azores in the Portuguese Azores. The population in 2011 was 255, in an area of 7.94 km². The parish was formed on July 16, 2002, when the parish of Nordestinho was sp ...
* São Brás
* São José
* São Miguel
* São Pedro (Ponta Delgada)
* São Pedro (Vila Franca do Campo)
* São Pedro de Nordestinho
São Pedro de Nordestinho is a parish in the municipality of Nordeste in the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Loca ...
* São Roque
* São Sebastião
* São Vicente Ferreira
* Sete Cidades
Transport
Three bus routes operate in Ponta Delgada on weekdays from 07:00 to 19:00. Line A runs in the western part of town, line B in the central/north, and line C in the east. There are bus services between Ponta Delgada and most other towns on the island, but usually only a few times a day. City services and island-wide services are both accessible along "Avenida D. Infante Henriques" and conveniently accessible from major sites in Ponta Delgada. Up to date schedules are available at bus stops and the tourist office. Distances on the island are short with journeys rarely longer than 90 minutes.Notable citizens
References
;Notes ;Sources * * * * * * * * *Global Volcanism Program: Azores
External links
In depth video from São Miguel Island
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sao Miguel Island Islands of the Azores