Ryukyuan people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ryukyuan people ( ryu, 琉球民族 (るーちゅーみんずく), Ruuchuu minzuku or ryu, どぅーちゅーみんずく, Duuchuu minzuku, label=none, ja, 琉球民族/りゅうきゅうみんぞく, Ryūkyū minzoku, also Lewchewan or Loochooan) are an
 The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a demic diffusion. The haplogroups D and C are considered of Neolithic and Paleolithic origin, with coalescence time of 19,400 YBP and expansion 12,600 YBP (14,500 YBP and 10,820 YBP respectively), and were isolated for thousands of years once land bridges between Japan and continental Asia disappeared at the end of the last glacial maximum 12,000 YBP. The haplogroup O began its expansion circa 4,000-3,810 years ago, and thus the haplogroups D-M55 and C-M8 belong to the Jomon's male lineage, and haplogroup O belongs to the Yayoi's male lineage. Haplogroup M12 is considered as mitochondrial counterpart of Y chromosome D lineage. This rare haplogroup was detected only in Yamato Japanese, Koreans, and Tibetans, with the highest frequency and diversity in Tibet.
A genetic and morphological analysis in 2021 by Watanabe et al., found that the Ryukyuans are most similar to the southern Jōmon people of
The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a demic diffusion. The haplogroups D and C are considered of Neolithic and Paleolithic origin, with coalescence time of 19,400 YBP and expansion 12,600 YBP (14,500 YBP and 10,820 YBP respectively), and were isolated for thousands of years once land bridges between Japan and continental Asia disappeared at the end of the last glacial maximum 12,000 YBP. The haplogroup O began its expansion circa 4,000-3,810 years ago, and thus the haplogroups D-M55 and C-M8 belong to the Jomon's male lineage, and haplogroup O belongs to the Yayoi's male lineage. Haplogroup M12 is considered as mitochondrial counterpart of Y chromosome D lineage. This rare haplogroup was detected only in Yamato Japanese, Koreans, and Tibetans, with the highest frequency and diversity in Tibet.
A genetic and morphological analysis in 2021 by Watanabe et al., found that the Ryukyuans are most similar to the southern Jōmon people of
 The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from Minamoto clan who wanted to legitimize Japanese domination over Okinawa. The tradition states that the founder of the Tenson dynasty was a descendant of goddess Amamikyu, and the dynasty ruled 17,000 years and had 25 kings i.e. chieftains. However, the 24th throne was usurped from one of Tenson's descendants by a man named Riyu, who was defeated in revolt led by Shunten (1187–1237), lord of Urasoe Castle, Urasoe. Shunten's parental origin is a matter of debate, according to 17th century romantic tales he was a son of a local Okinawan chief's (''Aji (Ryukyu), anji'') daughter and some Japanese adventurer, usually considered Minamoto no Tametomo, while historical and archeological-traditional evidence indicate men from the defeated Taira clan who fled Minamoto's clan vengeance. The Shunten dynasty made two additional chieftains, Shunbajunki (1237-1248) and Gihon (Ryukyu), Gihon (1248–1259). As Gihon abdicated, his sessei Eiso (Ryukyu), Eiso (1260–1299), who claimed Tenson's descent, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#Eiso dynasty, Eiso dynasty.
During the Gusuku period (c. 1187–1314), with recent chronology dated from c. 900-950 CE, Okinawans made significant political, social and economical growth. As the center of power moved away from the seashore to inland, the period is named after many ''gusuku'', castle-like fortifications which were built in higher places. This period is also notable, compared to mainland Japan, for fairly late introduction of agricultural production of rice, wheat, millet and the overseas trading of these goods, as well during Shubanjunki's rule the introduction of Japanese kana writing system in its older and simple phonetic form. After the years of famine and epidemic during the Gihon's rule, Eiso introduced regular taxation system (of weapons, grains and cloth) in 1264 and as the government gained strength, the control extended from Okinawa toward the islands of Kume, Kerama, Iheya, and Amami Ōshima (1266). Between 1272 and 1274, as the Mongol invasions of Japan began, Okinawa on two occasions rejected the Mongols' authority demands. To Eiso's reign period is also ascribed the introduction of Buddhism into Okinawa.
The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from Minamoto clan who wanted to legitimize Japanese domination over Okinawa. The tradition states that the founder of the Tenson dynasty was a descendant of goddess Amamikyu, and the dynasty ruled 17,000 years and had 25 kings i.e. chieftains. However, the 24th throne was usurped from one of Tenson's descendants by a man named Riyu, who was defeated in revolt led by Shunten (1187–1237), lord of Urasoe Castle, Urasoe. Shunten's parental origin is a matter of debate, according to 17th century romantic tales he was a son of a local Okinawan chief's (''Aji (Ryukyu), anji'') daughter and some Japanese adventurer, usually considered Minamoto no Tametomo, while historical and archeological-traditional evidence indicate men from the defeated Taira clan who fled Minamoto's clan vengeance. The Shunten dynasty made two additional chieftains, Shunbajunki (1237-1248) and Gihon (Ryukyu), Gihon (1248–1259). As Gihon abdicated, his sessei Eiso (Ryukyu), Eiso (1260–1299), who claimed Tenson's descent, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#Eiso dynasty, Eiso dynasty.
During the Gusuku period (c. 1187–1314), with recent chronology dated from c. 900-950 CE, Okinawans made significant political, social and economical growth. As the center of power moved away from the seashore to inland, the period is named after many ''gusuku'', castle-like fortifications which were built in higher places. This period is also notable, compared to mainland Japan, for fairly late introduction of agricultural production of rice, wheat, millet and the overseas trading of these goods, as well during Shubanjunki's rule the introduction of Japanese kana writing system in its older and simple phonetic form. After the years of famine and epidemic during the Gihon's rule, Eiso introduced regular taxation system (of weapons, grains and cloth) in 1264 and as the government gained strength, the control extended from Okinawa toward the islands of Kume, Kerama, Iheya, and Amami Ōshima (1266). Between 1272 and 1274, as the Mongol invasions of Japan began, Okinawa on two occasions rejected the Mongols' authority demands. To Eiso's reign period is also ascribed the introduction of Buddhism into Okinawa.
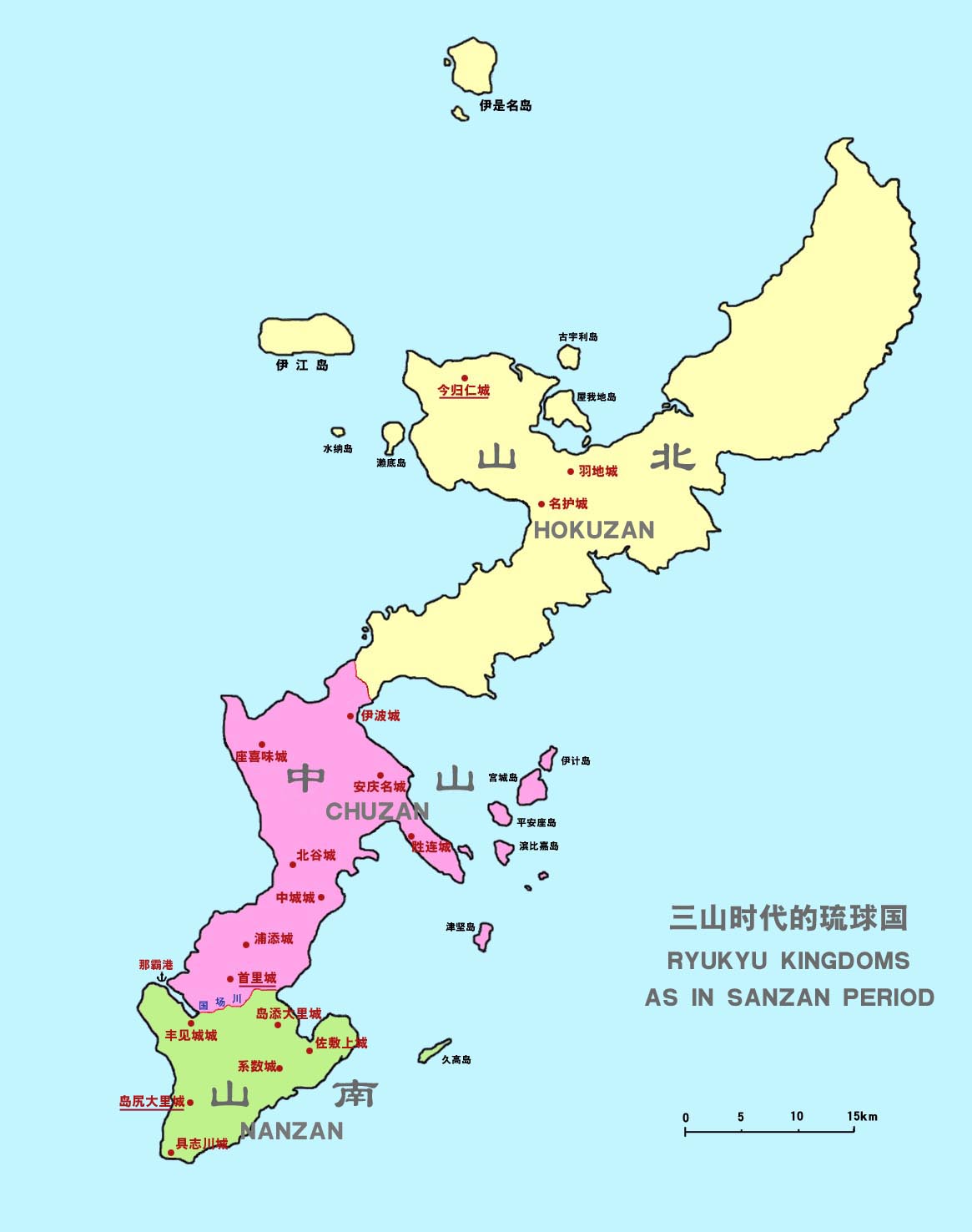 During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson, Tamagusuku (1314–1336), Okinawa became divided into three polities and began the so-called Sanzan period (1314–1429). The north and largest Hokuzan polity was the poorest due to forest and mountainous terrain (in which isolation was an advantage), with primitive farming and fishing. The central Chūzan polity was the most advantaged due to its developed castle towns and harbor facilities. The south Nanzan polity was the smallest, but endured because of good castle positions and sea merchants.
In this period another rapid economical, social and cultural development of Ryukyu began as the polities had developed formal trade relations with Japan, Korea and China. During the Satto's reign, Chūzan made Imperial Chinese tributary system, tributary relations with China's Ming dynasty in 1374 as the Hongwu Emperor sent envoys in 1372 to Okinawa. In the next two decades Chūzan made nine Ryukyuan missions to Imperial China, official missions to the Chinese capital, and the formal relations between them endured until 1872 (see Imperial Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom). Despite significant Chinese economical, cultural and political influence, the polities continued to maintain strong autonomy. In 1392, all three polities began to send extensive Ryukyuan missions to Joseon, missions to the Korean Joseon kingdom. In 1403, Chūzan made formal relations with the Japanese Ashikaga shogunate, and an embassy was sent to Thailand in 1409. The contacts with Siam continued even in 1425, and were newly made with places like Palembang in 1428, Java in 1430, Malacca and Sumatra in 1463.
As in 1371, China initiated its maritime prohibition policy (Haijin) to Japan, Ryukyu gained a lot from its position as intermediary in the trade between Japan and China. They shipped horses, sulphur and seashells to China, from China brought ceramics, copper, and iron, from southeast Asian countries bought tin, ivory, spices (pepper), wood (sappanwood), which they sold to Japan, Korea or China, as well as transporting Chinese goods to Hakata Bay from where swords, silver and gold were brought.
In 1392, 36 Chinese families from Fujian were invited by the chieftain of Okinawa Island's central polity (Chūzan) to settle near the port of Naha and to serve as diplomats, interpreters, and government officials. Some consider that many Ryukyuan officials were descended from these Chinese immigrants, being born in China or having Chinese grandfathers. They assisted the Ryukyuans in advancing their technology and diplomatic relations. From the same year onward Ryukyu was allowed to send official students to China i.e. Guozijian. The tributary relationship with China later became a basis of the 19th century Sino-Japanese disputes about the claims of Okinawa.
During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson, Tamagusuku (1314–1336), Okinawa became divided into three polities and began the so-called Sanzan period (1314–1429). The north and largest Hokuzan polity was the poorest due to forest and mountainous terrain (in which isolation was an advantage), with primitive farming and fishing. The central Chūzan polity was the most advantaged due to its developed castle towns and harbor facilities. The south Nanzan polity was the smallest, but endured because of good castle positions and sea merchants.
In this period another rapid economical, social and cultural development of Ryukyu began as the polities had developed formal trade relations with Japan, Korea and China. During the Satto's reign, Chūzan made Imperial Chinese tributary system, tributary relations with China's Ming dynasty in 1374 as the Hongwu Emperor sent envoys in 1372 to Okinawa. In the next two decades Chūzan made nine Ryukyuan missions to Imperial China, official missions to the Chinese capital, and the formal relations between them endured until 1872 (see Imperial Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom). Despite significant Chinese economical, cultural and political influence, the polities continued to maintain strong autonomy. In 1392, all three polities began to send extensive Ryukyuan missions to Joseon, missions to the Korean Joseon kingdom. In 1403, Chūzan made formal relations with the Japanese Ashikaga shogunate, and an embassy was sent to Thailand in 1409. The contacts with Siam continued even in 1425, and were newly made with places like Palembang in 1428, Java in 1430, Malacca and Sumatra in 1463.
As in 1371, China initiated its maritime prohibition policy (Haijin) to Japan, Ryukyu gained a lot from its position as intermediary in the trade between Japan and China. They shipped horses, sulphur and seashells to China, from China brought ceramics, copper, and iron, from southeast Asian countries bought tin, ivory, spices (pepper), wood (sappanwood), which they sold to Japan, Korea or China, as well as transporting Chinese goods to Hakata Bay from where swords, silver and gold were brought.
In 1392, 36 Chinese families from Fujian were invited by the chieftain of Okinawa Island's central polity (Chūzan) to settle near the port of Naha and to serve as diplomats, interpreters, and government officials. Some consider that many Ryukyuan officials were descended from these Chinese immigrants, being born in China or having Chinese grandfathers. They assisted the Ryukyuans in advancing their technology and diplomatic relations. From the same year onward Ryukyu was allowed to send official students to China i.e. Guozijian. The tributary relationship with China later became a basis of the 19th century Sino-Japanese disputes about the claims of Okinawa.
 Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain Shō Hashi successfully unified the principalities into the Ryukyuan Kingdom (1429–1879) with the castle town Shuri, Okinawa, Shuri as royal capital, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, First Shō dynasty, and the island continued to prosper through maritime trade, especially tributary relations with the Ming dynasty. The period of Shō Shin's (1477–1526) rule, descendant from the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, Second Shō dynasty, is notable for peace and relative prosperity, peak in overseas trade, as well as expansion of the kingdom's firm control to Kikaijima, Miyako-jima and
Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain Shō Hashi successfully unified the principalities into the Ryukyuan Kingdom (1429–1879) with the castle town Shuri, Okinawa, Shuri as royal capital, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, First Shō dynasty, and the island continued to prosper through maritime trade, especially tributary relations with the Ming dynasty. The period of Shō Shin's (1477–1526) rule, descendant from the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, Second Shō dynasty, is notable for peace and relative prosperity, peak in overseas trade, as well as expansion of the kingdom's firm control to Kikaijima, Miyako-jima and
 During the
During the
 Native Ryukyuan religion places strong emphasis upon the role of the women in the community, with women holding positions as shamans and guardians of the home and hearth. The status of women in traditional society is higher than in China and Japan. Although the contemporary kinship system is patrilineal and Patrilocal residence, patrilocal, until the 20th century it was often bilateral and Matrilocal residence, matrilocal, with common village endogamy. Shisa statues can often be seen on or in front of houses—this relates to the ancient Ryukyuan belief that the male spirit is the spirit of the outside and the female spirit is the spirit of the inside. Godhood is mimicked with many attributes, and its in ease without any underlying symbolic order.
The village priestesses, Noro, until the 20th century used the white cloth and magatama beads. The noro's duty was to preserve the generational fire in the hearth, a communal treasure, resulting with tabu system about the fire custodian in which they had to be virgins to maintain close communication with the ancestors. The office became hereditary, usually of the noro's brother's female child. The center of worship was represented by three heartstones within or near the house. The belief in the spiritual predominance of the sister was more prominent in Southern Ryukyus.
The introduction of Buddhism is ascribed to a 13th century priest from Japan (mostly funeral rites), while the 14th century trade relations resulted with Korean Buddhism influences (including some in architecture), as well Shinto practices from Japan. Buddhism and native religion were ideological basis until 18th century, when Confucianism gradually and officially became government ideology during Shō On (1795–1802), much to the dismay of Kumemura. It was mostly important to the upper class families. Among the Catholic converts was not lost the former religious consciousness.
Until the 18th century, the Ryukyuan kings visited the Sefa-utaki (historical sacred place) caves for worship. Another traditional sacred places are springs Ukinju-Hain-ju, where was placed the first rice plantation, and small island Kudaka, where the "five fruits and grains" were introduced by divine people, perhaps strangers with agricultural techniques. The foremost account, which claimed common origin between the Japanese and Ryukyuan people, was made-up by Shō Shōken in the 17th century, to end up the pilgrimage of the Ryukyu king and chief priestess to the Kudaka island.
During the Meiji period the government replaced Buddhism with Shintoism as the islands' state religion, and ordered; rearrangement of statues and redesign of shrines and temples to incorporate native deities into national Shinto pantheon; Shinto worship preceded native, Buddhist, or Christian ritual; transformation of local divinities into guardian gods. In the 1920s was ordered building of Shinto shrines and remodelling of previous with Shinto architectural symbols, paid by local tax money, which was a financial burden due to the collapse of sugar prices in 1921 which devastated Okinawa's economy. In 1932 were ordered to house and support Shinto clergy from the mainland.
Most Ryukyuans of the younger generations are not serious adherents of the native religion anymore. Additionally, since being under Japanese control, Shinto and Buddhism are also practiced and typically mixed with local beliefs and practices.
Native Ryukyuan religion places strong emphasis upon the role of the women in the community, with women holding positions as shamans and guardians of the home and hearth. The status of women in traditional society is higher than in China and Japan. Although the contemporary kinship system is patrilineal and Patrilocal residence, patrilocal, until the 20th century it was often bilateral and Matrilocal residence, matrilocal, with common village endogamy. Shisa statues can often be seen on or in front of houses—this relates to the ancient Ryukyuan belief that the male spirit is the spirit of the outside and the female spirit is the spirit of the inside. Godhood is mimicked with many attributes, and its in ease without any underlying symbolic order.
The village priestesses, Noro, until the 20th century used the white cloth and magatama beads. The noro's duty was to preserve the generational fire in the hearth, a communal treasure, resulting with tabu system about the fire custodian in which they had to be virgins to maintain close communication with the ancestors. The office became hereditary, usually of the noro's brother's female child. The center of worship was represented by three heartstones within or near the house. The belief in the spiritual predominance of the sister was more prominent in Southern Ryukyus.
The introduction of Buddhism is ascribed to a 13th century priest from Japan (mostly funeral rites), while the 14th century trade relations resulted with Korean Buddhism influences (including some in architecture), as well Shinto practices from Japan. Buddhism and native religion were ideological basis until 18th century, when Confucianism gradually and officially became government ideology during Shō On (1795–1802), much to the dismay of Kumemura. It was mostly important to the upper class families. Among the Catholic converts was not lost the former religious consciousness.
Until the 18th century, the Ryukyuan kings visited the Sefa-utaki (historical sacred place) caves for worship. Another traditional sacred places are springs Ukinju-Hain-ju, where was placed the first rice plantation, and small island Kudaka, where the "five fruits and grains" were introduced by divine people, perhaps strangers with agricultural techniques. The foremost account, which claimed common origin between the Japanese and Ryukyuan people, was made-up by Shō Shōken in the 17th century, to end up the pilgrimage of the Ryukyu king and chief priestess to the Kudaka island.
During the Meiji period the government replaced Buddhism with Shintoism as the islands' state religion, and ordered; rearrangement of statues and redesign of shrines and temples to incorporate native deities into national Shinto pantheon; Shinto worship preceded native, Buddhist, or Christian ritual; transformation of local divinities into guardian gods. In the 1920s was ordered building of Shinto shrines and remodelling of previous with Shinto architectural symbols, paid by local tax money, which was a financial burden due to the collapse of sugar prices in 1921 which devastated Okinawa's economy. In 1932 were ordered to house and support Shinto clergy from the mainland.
Most Ryukyuans of the younger generations are not serious adherents of the native religion anymore. Additionally, since being under Japanese control, Shinto and Buddhism are also practiced and typically mixed with local beliefs and practices.
Ryukyuans (Okinawans)
- Minority Rights Group International
Okinawa Peace Network of Los Angeles
- featuring information about Ryukyuan culture worldwide {{DEFAULTSORT:Ryukyuan People Ryukyuan people, Ethnic groups in Japan Ethnic groups in Brazil Ryukyu Islands Indigenous peoples of East Asia History of Northeast Asia
East Asian
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
native to the Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ōsumi, Tokara, Amami, Okinawa, and Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), with Yon ...
, which stretch between the islands of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
. Administratively, they live in either the Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest cit ...
or the Kagoshima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,599,779 (1 January 2020) and has a geographic area of 9,187 km2 (3,547 sq mi). Kagoshima Prefecture borders Kumamoto P ...
within Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
. They speak one of the Ryukyuan languages
The , also Lewchewan or Luchuan (), are the indigenous languages of the Ryukyu Islands, the southernmost part of the Japanese archipelago. Along with the Japanese language and the Hachijō language, they make up the Japonic language family.
...
, considered to be one of the two branches of the Japonic language family, the other being Japanese and its dialects. Hachijō is sometimes considered by linguists to constitute a third branch.
Ryukyuans are not a recognized minority group
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
in Japan, as Japanese authorities consider them just a subgroup of the Japanese people
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Ja ...
, akin to the Yamato people
The (or the )David Blake Willis and Stephen Murphy-Shigematsu''Transcultural Japan: At the Borderlands of Race, Gender and Identity,'' p. 272: "“Wajin,” which is written with Chinese characters that can also be read “Yamato no hito” (Ya ...
. Although officially unrecognized, Ryukyuans constitute the largest ethnolinguistic
Ethnolinguistics (sometimes called cultural linguistics) is an area of anthropological linguistics that studies the relationship between a language and the nonlinguistic cultural behavior of the people who speak that language.
__NOTOC__
Examples ...
minority group in Japan, with 1.4 million living in the Okinawa Prefecture alone. Ryukyuans inhabit the Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest o ...
of Kagoshima Prefecture as well, and have contributed to a considerable Ryukyuan diaspora
The Ryukyuan diaspora are the Ryukyuan emigrants from the Ryukyu Islands, especially Okinawa Island, and their descendants that reside in a foreign country. The first recorded emigration of Ryukyuans was in the 15th century when they established ...
. As many as 800,000 more ethnic Ryukyuans and their descendants are dispersed elsewhere in Japan and worldwide; most commonly in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and, to a lesser extent, in other territories where there is also a sizable Japanese diaspora
The Japanese diaspora and its individual members, known as Nikkei (日系) or as Nikkeijin (日系人), comprise the Japanese emigrants from Japan (and their descendants) residing in a country outside Japan. Emigration from Japan was recorded ...
. In the majority of countries, the Ryukyuan and Japanese diaspora are not differentiated, so there are no reliable statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, indust ...
for the former.
Ryukyuans have a distinct culture with some matriarchal
Matriarchy is a social system in which women hold the primary power positions in roles of authority. In a broader sense it can also extend to moral authority, social privilege and control of property.
While those definitions apply in general En ...
elements, native religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
and cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
which had a fairly late (12th century) introduction of rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
. The population lived on the islands in isolation for many centuries and in the 14th century three separate Okinawan political polities merged into the Ryukyu Kingdom (1429–1879) which continued the maritime trade and tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drai ...
relations started in 1372 with Ming-dynasty China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. In 1609 the Satsuma Domain
The , briefly known as the , was a domain (''han'') of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1602 to 1871.
The Satsuma Domain was based at Kagoshima Castle in Satsuma Province, the core of the modern city of Kagoshima, l ...
(based in Kyushu) invaded the Ryukyu Kingdom. The Kingdom maintained a fictive independence in vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerai ...
status, in a dual subordinate status to both China and Japan, because Tokugawa Japan was prohibited to trade (directly) with China.
During the Japanese Meiji period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912.
The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization ...
the kingdom became the Ryukyu Domain
The was a short-lived domain of the Empire of Japan, lasting from 1872 to 1879, before becoming the current Okinawa Prefecture and other islands at the Pacific edge of the East China Sea.
When the domain was created in 1872, Japan's feudal han ...
(1872–1879), after which it was politically annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
by the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent form ...
. In 1879, after the annexation, the territory was reorganized as Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest cit ...
, with the last king (Shō Tai
was the last king of the Ryukyu Kingdom (8 June 1848 – 10 October 1872) and the head of the Ryukyu Domain (10 October 1872 – 27 March 1879). His reign saw greatly increased interactions with travelers from abroad, particularly from Europe ...
) forcibly exiled to Tokyo. China renounced its claims to the islands in 1895. During this period the Meiji government
The was the government that was formed by politicians of the Satsuma Domain and Chōshū Domain in the 1860s. The Meiji government was the early government of the Empire of Japan.
Politicians of the Meiji government were known as the Meiji ...
, which sought to assimilate the Ryukyuan people as Japanese ( Yamato), suppressed Ryukyuan ethnic identity, tradition, culture and language. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the Ryūkyū Islands were occupied by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
between 1945 and 1950 and then from 1950 to 1972. During this time many violations of human rights occurred. Since the end of World War II Ryukyuans have expressed strong resentment against the Japanese government and against US military facilities stationed in Okinawa.
United Nations special rapporteur on discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of Racial discrimination, r ...
and racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagoni ...
Doudou Diène, in his 2006 report, noted a perceptible level of discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of Racial discrimination, r ...
and xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
against the Ryukyuans, with the most serious discrimination they endure linked to their opposition of American military installations in the archipelago.
Etymology
Their usual ethnic name derives from the Chinese name for the islands, (also spelled as Loo Choo, Lew Chew, Luchu, and more), which in theJapanese language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been ...
is pronounced . In the Okinawan language
The Okinawan language (, , , ) or Central Okinawan, is a Northern Ryukyuan language spoken primarily in the southern half of the island of Okinawa, as well as in the surrounding islands of Kerama, Kumejima, Tonaki, Aguni and a number of sma ...
, it is pronounced . These terms are rarely used, and are politicized markers of a distinct culture.
Origins
Genetic studies
According to the recent genetic studies, the Ryukyuan people share morealleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chrom ...
with the southern Jōmon (16,000–3,000 years ago) hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
s than the Yamato Japanese, have smaller genetic contributions from Asian continental populations, which supports the dual-structure model of K. Hanihara (1991), a widely accepted theory which suggests that the Yamato Japanese are more admixed with Asian agricultural continental people (from the Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
) than the Ainu and the Ryukyuans, with major admixture occurring in and after the Yayoi period
The started at the beginning of the Neolithic in Japan, continued through the Bronze Age, and towards its end crossed into the Iron Age.
Since the 1980s, scholars have argued that a period previously classified as a transition from the Jōm ...
(3,000-1,700 years ago). Within the Japanese population the Ryukyu make a separate and one of the two genome-wide clusters along the main-island Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island s ...
. The Jōmon ancestry is estimated at approximately 28%. The admixture event which formed the admixed Ryukyuans was estimated at least 1100–1075 years ago, which corresponds to the Gusuku period, and is considered to be related to the arrival of migrants from Japan.
According to archaeological evidence, there is a prehistoric cultural differentiation between the Northern Ryukyu Islands (Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest o ...
and Okinawa Islands
The Okinawa Islands ( or ) are an island group in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan and are the principal island group of the prefecture. The Okinawa Islands are part of the larger Ryukyu Islands group and are located between the Amami Islands of Kago ...
) and the Southern Ryukyu Islands (Miyako Islands
The (also Miyako Jima group) are a group of islands in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, belonging to the Ryukyu Islands. They are situated between the Okinawa Island and Yaeyama Islands.
In the early 1870s, the population of the islands was esti ...
and Yaeyama Islands
The Yaeyama Islands (八重山列島 ''Yaeyama-rettō'', also 八重山諸島 ''Yaeyama-shotō'', Yaeyama: ''Yaima'', Yonaguni: ''Daama'', Okinawan: ''Yeema'', Northern Ryukyuan: ''Yapema'') are an archipelago in the southwest of Okinawa P ...
). The genome-wide differentiation was pronounced, especially between Okinawa and Miyako. It is considered to have arisen due to genetic drift rather than admixture with people from neighboring regions, with the divergence dated to the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
, and without major genetic contribution of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
inhabitants to the present-day Southern Islanders. The Amami Islanders are also slightly more similar to the mainland population than the Okinawa Islanders. An autosomal DNA analysis from Okinawan samples concluded that they are most closely related to other Japanese and East Asian contemporary populations, sharing on average 80% admixture with mainland Japanese and 19% admixture with Chinese population, and that have isolate characteristics.
The female mtDNA and male Y chromosome markers are used to study human migrations. The research on the skeletal remains from the Neolithic Shell midden period (also known as Kaizuka period) in Okinawa, as well from the Gusuku Period, showed predominance of female haplogroups D4 and M7a and their genetic continuity in the contemporary female population of Okinawa. It is assumed that M7a represents "Jomon genotype" introduced by a Paleolithic ancestor from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
or the southern region of the Asian continent, around the Last Glacial Maximum with the Ryukyu Islands as one of the probable origin spots; in contrast, the frequency of the D4 haplogroup is relatively high in East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
n populations, including in Japan, indicating immigrant Yayoi people, probably by the end of the late Kaizuka period, while haplogroup B4 presumably ancient aboriginal Taiwanese ancestry. However, as in the contemporary Japanese population M7 showed a decrease, whereas the frequency of the haplogroup N9b showed an increase from the south to north direction, it indicates that the mobility pattern of females and males was different as the distribution of Y haplogroups do not show a geographical gradient in contrast to mtDNA, meaning mainly different maternal origins of the contemporary Ryukyuan and Ainu people.
 The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a demic diffusion. The haplogroups D and C are considered of Neolithic and Paleolithic origin, with coalescence time of 19,400 YBP and expansion 12,600 YBP (14,500 YBP and 10,820 YBP respectively), and were isolated for thousands of years once land bridges between Japan and continental Asia disappeared at the end of the last glacial maximum 12,000 YBP. The haplogroup O began its expansion circa 4,000-3,810 years ago, and thus the haplogroups D-M55 and C-M8 belong to the Jomon's male lineage, and haplogroup O belongs to the Yayoi's male lineage. Haplogroup M12 is considered as mitochondrial counterpart of Y chromosome D lineage. This rare haplogroup was detected only in Yamato Japanese, Koreans, and Tibetans, with the highest frequency and diversity in Tibet.
A genetic and morphological analysis in 2021 by Watanabe et al., found that the Ryukyuans are most similar to the southern Jōmon people of
The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a demic diffusion. The haplogroups D and C are considered of Neolithic and Paleolithic origin, with coalescence time of 19,400 YBP and expansion 12,600 YBP (14,500 YBP and 10,820 YBP respectively), and were isolated for thousands of years once land bridges between Japan and continental Asia disappeared at the end of the last glacial maximum 12,000 YBP. The haplogroup O began its expansion circa 4,000-3,810 years ago, and thus the haplogroups D-M55 and C-M8 belong to the Jomon's male lineage, and haplogroup O belongs to the Yayoi's male lineage. Haplogroup M12 is considered as mitochondrial counterpart of Y chromosome D lineage. This rare haplogroup was detected only in Yamato Japanese, Koreans, and Tibetans, with the highest frequency and diversity in Tibet.
A genetic and morphological analysis in 2021 by Watanabe et al., found that the Ryukyuans are most similar to the southern Jōmon people of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
, Shikoku, and Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island s ...
. Southern Jōmon samples were found to be genetically close to contemporary East Asian people, and quite different from Jōmon samples of Hokkaido and Tohoku. Haplogroup D-M55
Haplogroup D-M55 (M64.1/Page44.1) also known as Haplogroup D1a2a is a Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two branches of Haplogroup D1a. The other is D1a1, which is found with high frequency in Tibetans and other Tibeto-Burmese populations and ...
has the highest diversity within southern Japanese and Ryukyuans, suggesting a dispersal from southwestern Japan towards the North, replacing other Jōmon period lineages through genetic drift. Haplogroup D (D1) can be linked to an East Asian source population from the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Ti ...
("East Asian Highlanders"), which contributed towards the Jōmon period population of Japan, and less to ancient Southeast Asians. Southern Jōmon people were found to share most SNPs alleles with Tujia people
The Tujia ( Northern Tujia: ''Bifjixkhar'' / ''Bifzixkar'', IPA: , Southern Tujia: ''Mongrzzir'', ; ) are an ethnic group and, with a total population of over 8 million, the eighth-largest officially recognized ethnic minority in the People's ...
, Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans liv ...
, Miao people
The Miao are a group of linguistically-related peoples living in Southern China and Southeast Asia, who are recognized by the government of China as one of the 56 official ethnic groups. The Miao live primarily in southern China's mountains, in ...
, and Tripuri people
The Tripuri (also known as Tripura, Tipra, Tiprasa, Twipra) are an ethnic group originating in the Indian state of Tripura. They are the inhabitants of the Twipra/Tripura Kingdom in North-East India and Bangladesh. The Tripuri people through t ...
, rather than Ainu.
Anthropological studies
The comparative studies on the dental diversity also showed long-term gene flow from outside source (main-island Honshu and from the southern part of East Asia), long-term isolation, and genetic drift which produced the morphological diversification of the modern Ryukyuans. However, the analysis contradicts the idea of homogeneity among the Jōmon people and a closer affinity between the Ainu and the Ryukyuans. A recent craniometric study shows that the Ryukyuan people are closely related to the Yamato people and their common main ancestors, theYayoi people
The were an ancient ethnicity that migrated to the Japanese archipelago from Korea and China during the Yayoi period (300 BCE–300 CE). Although highly controversial, a single study that utilized radiometric dating techniques inconclusivel ...
. The Ryukyuans differ strongly from the Ainu people
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Ya ...
, which, according to the authors, is a strong evidence for the heterogeneity of the Jōmon period population.
As previous morphological studies, such as Kondo et al. 2017, the genetic and morphological analysis by Watanabe et al. 2021, confirmed that the Jōmon period people were heterogeneous and differed from each other depending on the region. A North-to-South cline was detected, with the southern Jōmon of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
, Shikoku and southwestern Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island s ...
being closer to contemporary East Asian people, while the northern Jōmon of Hokkaido
is Japan, Japan's Japanese archipelago, second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost Prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own List of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; th ...
and Tohoku being more distant from East Asians. The study results confirmed the "dual-structure theory" regarding the origin of modern Japanese and Ryukyuans, but found that noteworthy amount of East Asian associated alleles were already present within the Jōmon period people prior to the migration of continental East Asians during the Yayoi period. The southern Jōmon, which are ancestral to the Ryukyuans, were anthropologically most similar to modern day East Asians and differed from Jōmon period samples of Hokkaido quite noteworthy.
Challenging the notion of ethnic homogeneity in Japan
The existence of the Ryukyuan challenge the notion of ethnic homogeneity in post-WWII Japan. After the demise of the multi-ethnicEmpire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent form ...
in 1945, successive governments had forged a single Japanese identity by advocating monoculturalism
Monoculturalism is the policy or process of supporting, advocating, or allowing the expression of the culture of a single social or ethnic group. It generally stems from beliefs within the dominant group that their cultural practices are superior t ...
and denying the existence of ethnic minority groups. The notion of ethnic homogeneity was so ingrained in Japan that the former Deputy Prime Minister Taro Aso notably claimed in 2020 that “No other country but this one has lasted for as long as 2,000 years with one language, one ethnic group and one dynasty”. Aso's comment sparked strong criticism from Ryukyuan community.
History
Early history
The Ryukyu Islands were inhabited from at least 32,000–18,000 years ago, but their fate and relation with contemporary Ryukyuan people is uncertain. During theJōmon period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a c ...
(i.e., Kaizuka) or so-called shell midden period (6,700–1,000 YBP) of the Northern Ryukyus, the population lived in a hunter-gatherer society, with similar mainland Jōmon pottery. In the latter part of Jōmon period, archaeological sites moved near the seashore, suggesting the engagement of people in fishery. It is considered that from the latter half of Jōmon period, the Ryukyu Islands developed their own culture. Some scholars consider that the language and cultural influence was more far-reaching than blending of race and physical types. The Yayoi culture which had a major influence on the Japanese islands, is traditionally dated from 3rd century BCE and recently from around 1000 BCE, and is notable for the introduction of Yayoi-type pottery, metal tools and cultivation of rice, however although some Yayoi pottery
Yayoi pottery (弥生土器 Yayoi doki) is earthenware pottery produced during the Yayoi period, an Iron Age era in the history of Japan, by an Island which was formerly native to Japan traditionally dated 300 BC to AD 300. The pottery all ...
and tools were excavated on the Okinawa Islands, the rice was not widely cultivated before the 12th century CE, nor the Yayoi and the following Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
(250–538 CE) culture expanded into the Ryukyus. The Southern Ryukyus culture was isolated from the Northern, and its Shimotabaru period (4,500–3,000 YBP) was characterized by a specific style of pottery, and the Aceramic period (2,500–800 YBP), during which no pottery was produced in this region. Their prehistoric Yaeyama culture showed some intermingled affinities with various Taiwanese cultures, broadly, that the Sakishima Islands
The (or 先島群島, ''Sakishima-guntō'') ( Okinawan: ''Sachishima'', Miyako: ''Saksїzїma'', Yaeyama: ''Sakїzїma'', Yonaguni: ''Satichima'') are an archipelago located at the southernmost end of the Japanese Archipelago. They are part ...
have some traces similar to the Southeast Asian and South Pacific cultures. The Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest o ...
seem to be the islands with the most mainland Japanese influence. However, both north and south Ryukyus were culturally unified in the 10th century.
The finding of ancient Chinese knife money near Naha in Okinawa indicate a probable contact with the ancient Chinese state Yan as early as the 3rd century BCE. According to the , the Yan had relations with the Wa ('dwarf', 'short') people living southeast of Korea, who could be related to both the mainland Japanese or Ryukyuan people. The futile search for the elixir of immortality by Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of " king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Empero ...
, the founder of the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), ...
(221–206 BCE), in which the emperor tried to cooperate with "happy immortals" who dwelt on the islands, could be related to both Japan and Ryukyu Islands. There is a lack of evidence that the missions by the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(206 BCE–220 CE) reached the islands; however, as the Japanese did reach Han's capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
, notes from 57 CE do mention a general practice of tattooing among the people of "hundred kingdoms" in the eastern islands, a practice which was widespread and survived only among the Okinawan's women, Ainu in Hokkaido, and Atayal people in Taiwan. Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE, AusE, and IndE), is a male bovine trained and used as a draft animal. Oxen are commonly castrated adult male cattle; castration inhibits testosterone and aggression, which makes th ...
and swine, and were ruled by women, with a special influence of women sorceresses, related to the Ryukyuan Noro priestesses which were closely associated with local political power until the 20th century, as well as with the Ryukyuan swine economy culture until World War II. It is suggested that the mention of a specific sorceress Pimeku, her death and successive conflict, is related to some socio-political challenges of the ancient matriarchal system.
The first certain mention of the islands and its people by the Chinese and Japanese is dated in the 7th century. Emperor Yang of Sui
Emperor Yang of Sui (隋煬帝, 569 – 11 April 618), personal name Yang Guang (), alternative name Ying (), Xianbei name Amo (), also known as Emperor Ming of Sui () during the brief reign of his grandson Yang Tong, was the second emperor ...
, due to previous tradition, between 607–608 held expeditions in search of the "Land of Happy Immortals". As the Chinese envoy and the islanders linguistically could not understand each other, and the islanders did not want to accept the Sui rule and suzerainty, the Chinese envoy took many captives back to the court. The islands, by the Chinese named Liuqiu (Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the '' Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The ...
: ), would be pronounced by the Japanese as Ryukyu. However, when the Japanese diplomat Ono no Imoko
was a Japanese politician and diplomat in the late 6th and early 7th century, during the Asuka period.
Ono was appointed by Empress Suiko as an official envoy ( Kenzuishi) to the Sui court in 607 (Imperial embassies to China), and he delivere ...
arrived at the Chinese capital he noted that the captives probably arrived from the island of Yaku south of Kyushu. In 616 the Japanese annals for the first time mention the "Southern Islands people", and for the half-century were noted some intruders from Yaku and Tanu Tanu may refer to:
People
* Malietoa Tanumafili I (1879–1939), Samoan prince
* Tanu Nona (1902–1980), Australian pearler and politician
* Tanu Roy (born 1980), Indian actress and model
* Tanu (born 1997), a Finnish/Assyrian rapper
Places
* Ta ...
. According to the , in 698 a small force dispatched by Japanese government successfully claimed the Tane-jima, Yakushima, Amami
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest o ...
, Tokunoshima
, also known in English as is an island in the Amami archipelago of the southern Satsunan Islands of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan.
The island, in area, has a population of approximately 27,000. The island is divided into three administrative ...
and other islands. The recorded that the Hayato people
The , which is Japanese for "falcon-people", were a people of ancient Japan who lived in the Satsuma and Ōsumi regions of southern Kyushu during the Nara period. They frequently resisted Yamato rule. After their subjugation they became subjec ...
in southern Kyushu still had female chieftains in the early 8th century. In 699 are mentioned islands Amami and Tokara, in 714 Shingaki and Kume
is a town located in Shimajiri District, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. The town consists of the islands of Kume, Ōjima, Ōhajima, Torishima, and Iōtorishima. Among the islands, only Kumejima and Ōjima are populated. Kumejima is located appro ...
, in 720 some 232 persons who had submitted to the Japanese capital Nara, and at last Okinawa in 753. Nevertheless the mention or authority, over the centuries the Japanese influence spread slowly among the communities.
Gusuku period
 The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from Minamoto clan who wanted to legitimize Japanese domination over Okinawa. The tradition states that the founder of the Tenson dynasty was a descendant of goddess Amamikyu, and the dynasty ruled 17,000 years and had 25 kings i.e. chieftains. However, the 24th throne was usurped from one of Tenson's descendants by a man named Riyu, who was defeated in revolt led by Shunten (1187–1237), lord of Urasoe Castle, Urasoe. Shunten's parental origin is a matter of debate, according to 17th century romantic tales he was a son of a local Okinawan chief's (''Aji (Ryukyu), anji'') daughter and some Japanese adventurer, usually considered Minamoto no Tametomo, while historical and archeological-traditional evidence indicate men from the defeated Taira clan who fled Minamoto's clan vengeance. The Shunten dynasty made two additional chieftains, Shunbajunki (1237-1248) and Gihon (Ryukyu), Gihon (1248–1259). As Gihon abdicated, his sessei Eiso (Ryukyu), Eiso (1260–1299), who claimed Tenson's descent, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#Eiso dynasty, Eiso dynasty.
During the Gusuku period (c. 1187–1314), with recent chronology dated from c. 900-950 CE, Okinawans made significant political, social and economical growth. As the center of power moved away from the seashore to inland, the period is named after many ''gusuku'', castle-like fortifications which were built in higher places. This period is also notable, compared to mainland Japan, for fairly late introduction of agricultural production of rice, wheat, millet and the overseas trading of these goods, as well during Shubanjunki's rule the introduction of Japanese kana writing system in its older and simple phonetic form. After the years of famine and epidemic during the Gihon's rule, Eiso introduced regular taxation system (of weapons, grains and cloth) in 1264 and as the government gained strength, the control extended from Okinawa toward the islands of Kume, Kerama, Iheya, and Amami Ōshima (1266). Between 1272 and 1274, as the Mongol invasions of Japan began, Okinawa on two occasions rejected the Mongols' authority demands. To Eiso's reign period is also ascribed the introduction of Buddhism into Okinawa.
The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from Minamoto clan who wanted to legitimize Japanese domination over Okinawa. The tradition states that the founder of the Tenson dynasty was a descendant of goddess Amamikyu, and the dynasty ruled 17,000 years and had 25 kings i.e. chieftains. However, the 24th throne was usurped from one of Tenson's descendants by a man named Riyu, who was defeated in revolt led by Shunten (1187–1237), lord of Urasoe Castle, Urasoe. Shunten's parental origin is a matter of debate, according to 17th century romantic tales he was a son of a local Okinawan chief's (''Aji (Ryukyu), anji'') daughter and some Japanese adventurer, usually considered Minamoto no Tametomo, while historical and archeological-traditional evidence indicate men from the defeated Taira clan who fled Minamoto's clan vengeance. The Shunten dynasty made two additional chieftains, Shunbajunki (1237-1248) and Gihon (Ryukyu), Gihon (1248–1259). As Gihon abdicated, his sessei Eiso (Ryukyu), Eiso (1260–1299), who claimed Tenson's descent, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#Eiso dynasty, Eiso dynasty.
During the Gusuku period (c. 1187–1314), with recent chronology dated from c. 900-950 CE, Okinawans made significant political, social and economical growth. As the center of power moved away from the seashore to inland, the period is named after many ''gusuku'', castle-like fortifications which were built in higher places. This period is also notable, compared to mainland Japan, for fairly late introduction of agricultural production of rice, wheat, millet and the overseas trading of these goods, as well during Shubanjunki's rule the introduction of Japanese kana writing system in its older and simple phonetic form. After the years of famine and epidemic during the Gihon's rule, Eiso introduced regular taxation system (of weapons, grains and cloth) in 1264 and as the government gained strength, the control extended from Okinawa toward the islands of Kume, Kerama, Iheya, and Amami Ōshima (1266). Between 1272 and 1274, as the Mongol invasions of Japan began, Okinawa on two occasions rejected the Mongols' authority demands. To Eiso's reign period is also ascribed the introduction of Buddhism into Okinawa.
Sanzan period
 During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson, Tamagusuku (1314–1336), Okinawa became divided into three polities and began the so-called Sanzan period (1314–1429). The north and largest Hokuzan polity was the poorest due to forest and mountainous terrain (in which isolation was an advantage), with primitive farming and fishing. The central Chūzan polity was the most advantaged due to its developed castle towns and harbor facilities. The south Nanzan polity was the smallest, but endured because of good castle positions and sea merchants.
In this period another rapid economical, social and cultural development of Ryukyu began as the polities had developed formal trade relations with Japan, Korea and China. During the Satto's reign, Chūzan made Imperial Chinese tributary system, tributary relations with China's Ming dynasty in 1374 as the Hongwu Emperor sent envoys in 1372 to Okinawa. In the next two decades Chūzan made nine Ryukyuan missions to Imperial China, official missions to the Chinese capital, and the formal relations between them endured until 1872 (see Imperial Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom). Despite significant Chinese economical, cultural and political influence, the polities continued to maintain strong autonomy. In 1392, all three polities began to send extensive Ryukyuan missions to Joseon, missions to the Korean Joseon kingdom. In 1403, Chūzan made formal relations with the Japanese Ashikaga shogunate, and an embassy was sent to Thailand in 1409. The contacts with Siam continued even in 1425, and were newly made with places like Palembang in 1428, Java in 1430, Malacca and Sumatra in 1463.
As in 1371, China initiated its maritime prohibition policy (Haijin) to Japan, Ryukyu gained a lot from its position as intermediary in the trade between Japan and China. They shipped horses, sulphur and seashells to China, from China brought ceramics, copper, and iron, from southeast Asian countries bought tin, ivory, spices (pepper), wood (sappanwood), which they sold to Japan, Korea or China, as well as transporting Chinese goods to Hakata Bay from where swords, silver and gold were brought.
In 1392, 36 Chinese families from Fujian were invited by the chieftain of Okinawa Island's central polity (Chūzan) to settle near the port of Naha and to serve as diplomats, interpreters, and government officials. Some consider that many Ryukyuan officials were descended from these Chinese immigrants, being born in China or having Chinese grandfathers. They assisted the Ryukyuans in advancing their technology and diplomatic relations. From the same year onward Ryukyu was allowed to send official students to China i.e. Guozijian. The tributary relationship with China later became a basis of the 19th century Sino-Japanese disputes about the claims of Okinawa.
During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson, Tamagusuku (1314–1336), Okinawa became divided into three polities and began the so-called Sanzan period (1314–1429). The north and largest Hokuzan polity was the poorest due to forest and mountainous terrain (in which isolation was an advantage), with primitive farming and fishing. The central Chūzan polity was the most advantaged due to its developed castle towns and harbor facilities. The south Nanzan polity was the smallest, but endured because of good castle positions and sea merchants.
In this period another rapid economical, social and cultural development of Ryukyu began as the polities had developed formal trade relations with Japan, Korea and China. During the Satto's reign, Chūzan made Imperial Chinese tributary system, tributary relations with China's Ming dynasty in 1374 as the Hongwu Emperor sent envoys in 1372 to Okinawa. In the next two decades Chūzan made nine Ryukyuan missions to Imperial China, official missions to the Chinese capital, and the formal relations between them endured until 1872 (see Imperial Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom). Despite significant Chinese economical, cultural and political influence, the polities continued to maintain strong autonomy. In 1392, all three polities began to send extensive Ryukyuan missions to Joseon, missions to the Korean Joseon kingdom. In 1403, Chūzan made formal relations with the Japanese Ashikaga shogunate, and an embassy was sent to Thailand in 1409. The contacts with Siam continued even in 1425, and were newly made with places like Palembang in 1428, Java in 1430, Malacca and Sumatra in 1463.
As in 1371, China initiated its maritime prohibition policy (Haijin) to Japan, Ryukyu gained a lot from its position as intermediary in the trade between Japan and China. They shipped horses, sulphur and seashells to China, from China brought ceramics, copper, and iron, from southeast Asian countries bought tin, ivory, spices (pepper), wood (sappanwood), which they sold to Japan, Korea or China, as well as transporting Chinese goods to Hakata Bay from where swords, silver and gold were brought.
In 1392, 36 Chinese families from Fujian were invited by the chieftain of Okinawa Island's central polity (Chūzan) to settle near the port of Naha and to serve as diplomats, interpreters, and government officials. Some consider that many Ryukyuan officials were descended from these Chinese immigrants, being born in China or having Chinese grandfathers. They assisted the Ryukyuans in advancing their technology and diplomatic relations. From the same year onward Ryukyu was allowed to send official students to China i.e. Guozijian. The tributary relationship with China later became a basis of the 19th century Sino-Japanese disputes about the claims of Okinawa.
Ryukyu Kingdom
 Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain Shō Hashi successfully unified the principalities into the Ryukyuan Kingdom (1429–1879) with the castle town Shuri, Okinawa, Shuri as royal capital, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, First Shō dynasty, and the island continued to prosper through maritime trade, especially tributary relations with the Ming dynasty. The period of Shō Shin's (1477–1526) rule, descendant from the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, Second Shō dynasty, is notable for peace and relative prosperity, peak in overseas trade, as well as expansion of the kingdom's firm control to Kikaijima, Miyako-jima and
Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain Shō Hashi successfully unified the principalities into the Ryukyuan Kingdom (1429–1879) with the castle town Shuri, Okinawa, Shuri as royal capital, founded the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, First Shō dynasty, and the island continued to prosper through maritime trade, especially tributary relations with the Ming dynasty. The period of Shō Shin's (1477–1526) rule, descendant from the List of monarchs of the Ryukyu Islands#The First Shō dynasty, Second Shō dynasty, is notable for peace and relative prosperity, peak in overseas trade, as well as expansion of the kingdom's firm control to Kikaijima, Miyako-jima and Yaeyama Islands
The Yaeyama Islands (八重山列島 ''Yaeyama-rettō'', also 八重山諸島 ''Yaeyama-shotō'', Yaeyama: ''Yaima'', Yonaguni: ''Daama'', Okinawan: ''Yeema'', Northern Ryukyuan: ''Yapema'') are an archipelago in the southwest of Okinawa P ...
(1465–1524), while during Shō Sei (1526-1555) to Amami Ōshima (1537).
After the Kyūshū Campaign (1586–1587) by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, his assistant Kamei Korenori, who was interested in southern trade, wanted to be rewarded with the Ryukyu Islands. A paper Hand fan, fan found during the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98) mentioning a title "Kamei, Lord of Ryukyu", reveals that Hideyoshi at least nominally offered the post although he had no legitimate claim upon the islands. In 1591, Kamei ventured with a force to reclaim the islands, but the Shimazu clan stopped him as they guarded their special relationship with the Ryukyu kingdom. Hideyoshi was not very concerned about the quarrel because the invasion of Korea was more important in his mind. As the Ming's influence weakened due to disorder in China, Japanese established posts in Southeast Asia, and the Europeans (Spanish and Portuguese) arrived, the kingdom's overseas trade began to decline.
In the early 17th century during the Tokugawa shogunate (1603–1867), the first ''shōgun'' Tokugawa Ieyasu intended to subject the kingdom to enable intermediary trade with China, and in 1603 ordered the Ryukyuan king to pay his respect to the shogunate. As the king did not react, with the instruction of the ''shōgun'', the Satsuma Domain, Satsuma feudal domain of the Shimazu clan in Kyūshū incorporated some of kingdom's territory during the 1609 Invasion of Ryukyu. They nominally let a certain level of autonomy and independence to the kingdom due to Ming's prohibition of trade with the shogunate, but forbade them trade with other countries except China. The Amami Islands became part of Shimazu's territory, taxes were imposed, making them subordinate in the relations between Japan and China. Until the invasion, the Shimazu clan lords for four centuries had a vague title of the "Lords of the Twelve Southern Islands" or "Southern Islands", although initially meaning the near Kyushu islands, then covering all the Ryukyu Islands. Later in the 1870s this was used as a "justification" of Japan's sovereignty. From 1609 the Ryukyuan missions to Edo started which lasted until 1850.
During the rule of kings Shō Shitsu (1648–1668) and Shō Tei (1669–1709) i.e. sessei Shō Shōken (1666–1673) were recovered the internal social and economical stability with many laws about government organisation, and affairs like sugarcane production, and tax system with emphasis on agricultural production. The production was encouraged because Satsuma's annual tax deprived Ryukyu's internal resources. Although the production of sweet potatoes and sugar industry grew, the peasants were not allowed to enlarge their fields. The agricultural reforms especially continued under king Shō Kei (1713–1752) and his sanshikan advisor Sai On (1728–1752) whose ''Nomucho'' (Directory of Agricultural Affairs) from 1743 became the basis of the agricultural administration until the 19th century. In the Sakishima Islands great part of the tax was paid in textiles made of ramie. The relations with the Qing dynasty improved after their second mission when the first Ryukyuan official students were sent to China in 1688.
In the first half of the 19th century, French politicians like Jean-Baptiste Cécille unsuccessfully tried to conclude a French trade treaty with Ryukyu, with only a promise by Shuri government about the admission of Christian missionaries. However, due to extreme measures in teaching, Bernard Jean Bettelheim's propagation of Protestantism between 1846–1854 was obscured by the government.
Meiji period
Meiji period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912.
The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization ...
(1868–1912) the process began, according to which the Ryukyuan Kingdom came under the jurisdiction of Kagoshima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,599,779 (1 January 2020) and has a geographic area of 9,187 km2 (3,547 sq mi). Kagoshima Prefecture borders Kumamoto P ...
in 1871, encompassing the southern tip of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
and the Ryukyuan islands to its south; this created the Ryukyu Domain
The was a short-lived domain of the Empire of Japan, lasting from 1872 to 1879, before becoming the current Okinawa Prefecture and other islands at the Pacific edge of the East China Sea.
When the domain was created in 1872, Japan's feudal han ...
(1872–1879) of Meiji-era Japan. This method of gradual integration was designed to avoid both Ryukyuan and Chinese protests, with the ruling Shuri Castle, Shuri government unaware of the significance of these developments, including Japan's decision to grant political representation to the Ryukyuan islanders involved in the Japanese invasion of Taiwan (1874).
In 1875, the Ryukyuan people were forced to terminate their tributary relations with China, against their preference for a state of dual allegiance to both China and Japan, something a then-weakened China was unable to stop. A proposal by the 18th U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant for a sovereign Okinawa and the division of the other islands between China and Japan was rejected, with a last-minute decision by the Chinese government not to ratify the agreement rendering it null. On three occasions between 1875 and 1879, the last Ryukyuan King, Shō Tai
was the last king of the Ryukyu Kingdom (8 June 1848 – 10 October 1872) and the head of the Ryukyu Domain (10 October 1872 – 27 March 1879). His reign saw greatly increased interactions with travelers from abroad, particularly from Europe ...
, refused to submit to the demands placed upon his people, and in 1879, his domain was formally abolished and established as Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest cit ...
, forcing his move to Tokyo with the reduced status of Viscount.
Members of the Ryukyuan aristocratic classes such as Kōchi Chōjō and Rin Seikō continued to resist annexation for almost two decades; however, following the First Sino-Japanese War (1894-1895), both Chinese and Ryukyuan interest in sovereignty faded as China renounced its claims to the island. Many historians criticise Meiji-era Japan's characterisation of the process as being considered a relatively simple administrative change, rather than the creation of Japan's first colony and the beginning of its 'inner colonialism'.
During the Meiji period, as with the Ainu people
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Ya ...
of Hokkaido, the Ryukyuan people had their own culture, religion, traditions and language suppressed by the Meiji government in the face of forced assimilation. From the 1880s onwards, schools forbade the display of Ryukyuan styles of dress, hairstyles and other visual aspects, considering them to be backwards and inferior, with students forced to wear Japanese clothing and to assimilate into Japanese culture. Indoctrination into a militaristic and Emperor-centred ideology for children began from the age of beginning elementary school onwards; the ultimate goal of this education was a total unification of the Ryukyuan people into the Yamato people
The (or the )David Blake Willis and Stephen Murphy-Shigematsu''Transcultural Japan: At the Borderlands of Race, Gender and Identity,'' p. 272: "“Wajin,” which is written with Chinese characters that can also be read “Yamato no hito” (Ya ...
, embodying the ideal of ethnic purity, with contemporary literature for the time ignoring Japan's minorities). Ryukyuans often faced prejudice, humiliation in the workplace and ethnic discrimination, with the Ryukyuan elite divided into factions either in support of or in opposition to assimilation.
Around and especially after the Japanese annexation of Taiwan in 1895, Japan's developmental focus shifted away from Okinawa, resulting in a period of famine known as ("Cycad hell"). Between 1920 and 1921, a fall in sugar prices, as well as the transfer of Japan's sugar production to Taiwan, led to Ryukyu being the poorest prefecture, despite having the heaviest taxation burden; the drop in sugar prices would continue into 1931, further worsening the situation. As a result of the ensuing economic crisis, many people were forced to either find work in Japan (often Osaka and Kobe) or abroad in Taiwan. By 1935, roughly 15% of the population had emigrated.
WW2 and modern history
DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and battles like the Battle of Okinawa (1945), approximately 150,000 civilians (1/3 of the population) were killed in Okinawa alone. After the war, the Ryukyu Islands were occupied by the United States Military Government of the Ryukyu Islands (1945–1950), but the U.S. maintained control even after the 1951 Treaty of San Francisco, which went into effect on April 28, 1952, as the USMMGR was replaced by the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands (1950–1972). During this period the U.S. military requisitioned private land for the building of their facilities, with the former owners put into refugee camps, and its personnel committed thousands of crimes against the civilians. Only twenty years later, on 15 May 1972, Okinawa and nearby islands were returned to Japan. Whereas the Japanese had enjoyed political freedom and economic prosperity in the post-war years, the facilities, used for the purposes of Japanese regional security against the Communism, communist Red Scare, threat, had a negative economic impact on the Islands, leading to many Ryukyuans feeling cheated, some considering the facilities a national disgrace. Since 1972 there have been extensive plans to bring Okinawa's economy up to the national level, as well continued support for the local culture and a revival of traditional arts started by the USCAR.
Okinawa comprises just 0.6% of Japan's total land mass, yet about 75 percent of all U.S. military installations stationed in Japan are assigned to bases in Okinawa. The presence of the military remains a sensitive issue in local politics. Negative feelings toward the mainland Government of Japan, Government, Emperor of Japan, Emperor (especially Hirohito due to his involvement in the sacrifice of Okinawa and later military occupation), and United States Armed Forces, U.S. military (United States Forces Japan, USFJ, Special Action Committee on Okinawa, SACO) have often caused open criticism and protests, for example by 85,000 people in 1995 after the U.S. military 1995 Okinawa rape incident, rape incident, and by 110,000 people in 2007 due to the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Ministry of Education's textbook revisions (see Battle of Okinawa#MEXT textbook controversy, MEXT controversy) which critics say downplays the involvement of the Japanese military in the forced mass suicide of the civilians during the Battle of Okinawa. For many years the Emperors avoided visiting Okinawa, with the first ever in history done by Akihito in 1993, since it was assumed that his visits would likely cause uproar, as in July 1975 when Akihito as a crown prince visited Okinawa and a firebomb was thrown at him, although these tensions have eased in recent years. Discrimination against Okinawans both past and present on the part of the mainland Japanese is the cause of their smoldering resentment against the government. There is a small post-war Ryukyu independence movement, but there are also Okinawans who wish to be assimilated with the mainland. A poll in 2017 by the Okinawa Times, Asahi Shimbun and Ryukyusu Asahi Broadcasting Corporation (QAB) jointly conducted prefectural public opinion surveys for voters in the prefecture. 82% of Okinawa citizens chose "I'm glad that Okinawa has returned as a Japanese prefecture". It was 90% for respondents of the ages of 18 to 29, 86% for those in their 30s, 84% for those aged 40–59, 72% for respondents in their 60s, 74% for those over the age of 70.
Demography
Ryukyuans tend to see themselves as bound together by their home island and, especially among older Ryukyuans, usually consider themselves from Okinawa first andJapan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
second. The average annual income per resident of Okinawa in 2006 was ¥2.09 million, placing the prefecture at the bottom of the list of 47.
The Okinawans have a very low age-adjusted mortality rate at older ages and among the lowest prevalence of cardiovascular disease and other age-associated diseases in the world. Furthermore, Okinawa has long had the highest life expectancy at older ages, as well has had among the highest prevalence of centenarians among the 47 Japanese prefectures, also the world, since records began to be kept by the Ministry of Health in the early 1960s despite the high birth rate and expanding population of Okinawa prefecture. This longevity phenotype has been in existence since records have been kept in Japan, and despite the well-known dietary and other nongenetic lifestyle advantages of the Okinawans (Blue Zone), there may be some additional unknown genetic influence favoring this extreme phenotype. The Okinawa Centenarian Study (OCS) research team began to work in 1976, making it the world's longest ongoing population-based study of centenarians.
Culture
Language
Similarities between the Ryukyuan languages, Ryukyuan andJapanese language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been ...
s points to a common origin, possibly of immigrants from continental Asia to the archipelago. Although previously ideologically considered by Japanese scholars as a Japanese dialect and a descendant of Old Japanese, modern linguists such as Thomas Pellard (2015) now classify the Ryukyuan languages as a distinct subfamily of Japonic languages, Japonic that diverged before the Old Japanese period (c. 8th century CE); this places them in contrast to Japonic languages that are direct descendants of Old Japanese, namely Japanese and Hachijō. Early literature which records the language of the Old Japanese language, Old Japanese imperial court shows archaisms which are closer to Okinawan dialects, while later periods of Japanese exhibit more significant Sinicization (such as Sino-Japanese vocabulary) than most Ryukyuan languages. This can be attributed to the fact that the Japanese (or Yamato people
The (or the )David Blake Willis and Stephen Murphy-Shigematsu''Transcultural Japan: At the Borderlands of Race, Gender and Identity,'' p. 272: "“Wajin,” which is written with Chinese characters that can also be read “Yamato no hito” (Ya ...
) received writing from the Sinosphere roughly a millennium before the Ryukyuan languages.
As the Jōmon-Yayoi transition (c. 1000 BCE) represents the formative period of the contemporary Japanese people from a genetic standpoint, it is argued that the Japonic languages are related to the Yayoi migrants as well. The estimated time of separation between Ryukyuan and mainland Japanese is a matter of debate due to methodological problems; older estimates (1959–2009) varied between 300 BCE and 700 CE, while novel (2009–2011) around 2nd century BCE to 100 CE, which has a lack of correlation with archeology and new chronology according to which Yayoi period started around 950 BCE, or the proposed spread of the Proto-Ryukyuan speakers to the islands in the 10–12th century from Kyushu. Based on linguistic differences, they separated at least before the 7th century, before or around Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
(c. 250–538), while mainland Proto-Ryukyuan was in contact with Early Middle Japanese until 13th century.
The Ryukyuan languages can be subdivided into two main groups, Northern Ryukyuan languages and Southern Ryukyuan languages. The Southern Ryukyuan subfamily shows north-to-south expansion, while Northern Ryukyuan does not, and several hypothetical scenarios can be proposed to explain this. It is generally considered that the likely homeland of Japonic—and thus the original expansion of Proto-Ryukyuan—was in Kyushu, though an alternate hypothesis proposes an expansion from the Ryukyu Islands to mainland Japan.
Although authors differ regarding Dialect#Dialect_or_language, which varieties are counted as dialects or languages, one possible classification considers there to be five Ryukyuan languages: Amami language, Amami, Okinawa language, Okinawa, Miyako language, Miyako, Yaeyama language, Yaeyama and Yonaguni language, Yonaguni, while a sixth, Kunigami language, Kunigami, is sometimes differentiated from Okinawan due to its diversity. Within these languages exist dialects of local towns and specific islands, many of which have gone extinct. Although the Shuri, Okinawa, Shuri dialect of Okinawan was historically a prestige language of the Kingdom of Ryukyu, there is no officially standardized Ryukyuan language. Thus, the Ryukyuan languages as a whole constitute a cluster of local dialects that can be considered Abstand and ausbau languages, unroofed abstand languages.
During the Meiji period, Meiji and post-Meiji period, the Ryukyuan languages were considered to be dialects of Japanese and viewed negatively. They were suppressed by the Japanese government in policies of forced assimilation and into using the standard Japanese language. From 1907, children were prohibited to speak Ryukyuan languages in school, and since the mid-1930s there existed dialect cards, a system of punishment for the students who spoke in a non-standard language. Speaking a Ryukyuan language was deemed an unpatriotic act; by 1939, Ryukyuan speakers were denied service and employment in government offices, while by the Battle of Okinawa in 1945, the Japanese military was commanded to consider Ryukyuan speakers as spies to be punished by death, with many reports that such actions were carried out. After World War II, during the United States occupation, the Ryukyuan languages and identity were distinctively promoted, also because of ideo-political reasons to separate the Ryukyus from Japan. However, resentment against the American occupation intensified Ryukyuans' rapport and unification with Japan, and since 1972 there has followed re-incursion of the standard Japanese and further diminution of the Ryukyuan languages.
It is considered that contemporary people older than 85 exclusively use Ryukyuan, between 45 and 85 use Ryukyuan and standard Japanese depending on family or working environment, younger than 45 are able to understand Ryukyuan, while younger than 30 mainly are not able to understand nor speak Ryukyuan languages. Only older people speak Ryukyuan languages, because Japanese replaced it as the daily language in nearly every context. Some younger people speak Okinawan Japanese which is a type of Japanese. It is not a dialect of the Okinawan language
The Okinawan language (, , , ) or Central Okinawan, is a Northern Ryukyuan language spoken primarily in the southern half of the island of Okinawa, as well as in the surrounding islands of Kerama, Kumejima, Tonaki, Aguni and a number of sma ...
. The six Ryukyuan languages are listed on the UNESCO's Red Book of Endangered Languages, Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger since 2009, as they could disappear by the mid-century (2050). It is unclear whether this recognition was too late, despite some positive influence by the Society of Spreading Okinawan.
Religion
 Native Ryukyuan religion places strong emphasis upon the role of the women in the community, with women holding positions as shamans and guardians of the home and hearth. The status of women in traditional society is higher than in China and Japan. Although the contemporary kinship system is patrilineal and Patrilocal residence, patrilocal, until the 20th century it was often bilateral and Matrilocal residence, matrilocal, with common village endogamy. Shisa statues can often be seen on or in front of houses—this relates to the ancient Ryukyuan belief that the male spirit is the spirit of the outside and the female spirit is the spirit of the inside. Godhood is mimicked with many attributes, and its in ease without any underlying symbolic order.
The village priestesses, Noro, until the 20th century used the white cloth and magatama beads. The noro's duty was to preserve the generational fire in the hearth, a communal treasure, resulting with tabu system about the fire custodian in which they had to be virgins to maintain close communication with the ancestors. The office became hereditary, usually of the noro's brother's female child. The center of worship was represented by three heartstones within or near the house. The belief in the spiritual predominance of the sister was more prominent in Southern Ryukyus.
The introduction of Buddhism is ascribed to a 13th century priest from Japan (mostly funeral rites), while the 14th century trade relations resulted with Korean Buddhism influences (including some in architecture), as well Shinto practices from Japan. Buddhism and native religion were ideological basis until 18th century, when Confucianism gradually and officially became government ideology during Shō On (1795–1802), much to the dismay of Kumemura. It was mostly important to the upper class families. Among the Catholic converts was not lost the former religious consciousness.
Until the 18th century, the Ryukyuan kings visited the Sefa-utaki (historical sacred place) caves for worship. Another traditional sacred places are springs Ukinju-Hain-ju, where was placed the first rice plantation, and small island Kudaka, where the "five fruits and grains" were introduced by divine people, perhaps strangers with agricultural techniques. The foremost account, which claimed common origin between the Japanese and Ryukyuan people, was made-up by Shō Shōken in the 17th century, to end up the pilgrimage of the Ryukyu king and chief priestess to the Kudaka island.
During the Meiji period the government replaced Buddhism with Shintoism as the islands' state religion, and ordered; rearrangement of statues and redesign of shrines and temples to incorporate native deities into national Shinto pantheon; Shinto worship preceded native, Buddhist, or Christian ritual; transformation of local divinities into guardian gods. In the 1920s was ordered building of Shinto shrines and remodelling of previous with Shinto architectural symbols, paid by local tax money, which was a financial burden due to the collapse of sugar prices in 1921 which devastated Okinawa's economy. In 1932 were ordered to house and support Shinto clergy from the mainland.
Most Ryukyuans of the younger generations are not serious adherents of the native religion anymore. Additionally, since being under Japanese control, Shinto and Buddhism are also practiced and typically mixed with local beliefs and practices.
Native Ryukyuan religion places strong emphasis upon the role of the women in the community, with women holding positions as shamans and guardians of the home and hearth. The status of women in traditional society is higher than in China and Japan. Although the contemporary kinship system is patrilineal and Patrilocal residence, patrilocal, until the 20th century it was often bilateral and Matrilocal residence, matrilocal, with common village endogamy. Shisa statues can often be seen on or in front of houses—this relates to the ancient Ryukyuan belief that the male spirit is the spirit of the outside and the female spirit is the spirit of the inside. Godhood is mimicked with many attributes, and its in ease without any underlying symbolic order.
The village priestesses, Noro, until the 20th century used the white cloth and magatama beads. The noro's duty was to preserve the generational fire in the hearth, a communal treasure, resulting with tabu system about the fire custodian in which they had to be virgins to maintain close communication with the ancestors. The office became hereditary, usually of the noro's brother's female child. The center of worship was represented by three heartstones within or near the house. The belief in the spiritual predominance of the sister was more prominent in Southern Ryukyus.
The introduction of Buddhism is ascribed to a 13th century priest from Japan (mostly funeral rites), while the 14th century trade relations resulted with Korean Buddhism influences (including some in architecture), as well Shinto practices from Japan. Buddhism and native religion were ideological basis until 18th century, when Confucianism gradually and officially became government ideology during Shō On (1795–1802), much to the dismay of Kumemura. It was mostly important to the upper class families. Among the Catholic converts was not lost the former religious consciousness.
Until the 18th century, the Ryukyuan kings visited the Sefa-utaki (historical sacred place) caves for worship. Another traditional sacred places are springs Ukinju-Hain-ju, where was placed the first rice plantation, and small island Kudaka, where the "five fruits and grains" were introduced by divine people, perhaps strangers with agricultural techniques. The foremost account, which claimed common origin between the Japanese and Ryukyuan people, was made-up by Shō Shōken in the 17th century, to end up the pilgrimage of the Ryukyu king and chief priestess to the Kudaka island.
During the Meiji period the government replaced Buddhism with Shintoism as the islands' state religion, and ordered; rearrangement of statues and redesign of shrines and temples to incorporate native deities into national Shinto pantheon; Shinto worship preceded native, Buddhist, or Christian ritual; transformation of local divinities into guardian gods. In the 1920s was ordered building of Shinto shrines and remodelling of previous with Shinto architectural symbols, paid by local tax money, which was a financial burden due to the collapse of sugar prices in 1921 which devastated Okinawa's economy. In 1932 were ordered to house and support Shinto clergy from the mainland.
Most Ryukyuans of the younger generations are not serious adherents of the native religion anymore. Additionally, since being under Japanese control, Shinto and Buddhism are also practiced and typically mixed with local beliefs and practices.
Cuisine
Okinawan food is rich in vitamins and minerals and has a good balance of protein, fats, and carbohydrates. Althoughrice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
is a staple food (taco rice mixes it with beef), pork (''Pig's ear (food)#Okinawan (Japanese) cuisine, mimigaa and chiragaa'', dishes Rafute and Soki), Edible seaweed, seaweed, rich miso (fermented soybean) pastes and soups (Zosui, Jūshī), sweet potato and brown sugar all feature prominently in native cuisine. Most famous to tourists is the ''Momordica charantia'', ''gōya'' (bitter melon), which is often mixed into a representative Okinawan Stir frying, stir fry dish known as Chanpuru, champurū (Goya champuru). Kōrēgusu is a common hot sauce condiment used in various dishes including noodle soup Okinawa soba. Some specifically consumed algae include Caulerpa lentillifera. Traditional sweets include chinsuko, hirayachi, sata andagi, and muchi. Local beverages include juice from ''Citrus depressa'', turmeric tea (''ukoncha''), and the alcoholic beverage awamori.
The weight-loss Okinawa diet derives from their cuisine and has only 30% of the sugar and 15% of the grains of the average Japanese dietary intake.
Arts
The techniques of self-defense and using farm tools as weapons against armed opponents—called karate by today's martial artists—were created by Ryukyuans who probably incorporated some and native techniques from China into a complete system of attack and defense known simply as (literally meaning "hand"). These martial arts varied slightly from town to town, and were named for their towns of origin, examples being Naha-te (currently known as Goju-Ryū), Tomari-te and Shuri-te. The Kabura-ya (Japanese signal arrow) still has a ceremonial use for house, village or festival celebration in Okinawa. It is considered that the rhythms and patterns of dances, like Eisa (dance), Eisa and Angama (dance), Angama, represent legends and prehistoric heritage. Ryūka genre of songs and poetry originate from the Okinawa Islands. From the Chinese traditional instrument in the 16th century developed the Okinawan instrument from which the and the Japanese derive. Women frequently wore indigo tattoos known as ''hajichi'' on the backs of their hands, a sign of adulthood and talisman to protect them from evil. These tattoos were banned in 1899 by the Meiji government. In remote districts their ''katakashira'' off-center topknot, similar to Yami people, Yami and Filipinos of Malay descent in Mindanao and elsewhere, among men and women also disappeared in the early 20th century. The ''bashôfu'', literally meaning "banana-fibre cloth", is designated as a part of Ryukyu and Japan "important intangible cultural properties". The weaving using indigenous ramie was also widespread in the archipelago, both originated before the 14th century. Originally living in thatching houses, townsmen developed architecture modeled after Japanese, Chinese and Korean structures. Other dwellings suggest a tropical origin, and some villages have high stone walls, with similar structural counterpart in Yami people at Orchid Island. For the listed categories of Cultural Property (Japan), Cultural Properties see; List of Cultural Properties of Japan - archaeological materials (Okinawa), archaeological materials, List of Cultural Properties of Japan - historical materials (Okinawa), historical materials, List of Cultural Properties of Japan - crafts (Okinawa), crafts, List of Cultural Properties of Japan - paintings (Okinawa), paintings, List of Cultural Properties of Japan - sculptures (Okinawa), sculptures, List of Cultural Properties of Japan - writings (Okinawa), writings, List of Intangible Cultural Properties of Japan (Okinawa), intangible, and List of Tangible Folk Cultural Properties of Japan (Okinawa), tangible.Notable Ryukyuans
Martial arts
* Matsumura Sōkon * Ankō Itosu * Ankō Asato * Kenwa Mabuni (Shitō-ryū) * Gichin Funakoshi (Shotokan) * Chōjun Miyagi (Gōjū-ryū) * Motobu Chōki, Chōki Motobu (Motobu-ryu) * Tatsuo Shimabuku (Isshin-ryū) * Kanbun Uechi (Uechi-ryū) * Kentsū Yabu (teacher of Shōrin-ryū)Academics, journalism, and literature
* Sai On * Shō Shōken * Tei Junsoku * Iha Fuyū * Higashionna Kanjun * Ōta Chōfu (journalist) * Tatsuhiro Oshiro (novelist) * Kushi Fusako (novelist)Music
* Namie Amuro * Cocco * Beni (singer), Beni * Chitose Hajime * Gackt (male solo singer-songwriter and actor) * Begin (band), Begin * Orange Range * Mongol800 * Stereopony * High and Mighty Color * Speed (Japanese band), Speed * MAX (band), MAX * Da PumpVisual arts
* Mao Ishikawa (photography) * Yuken Teruya * Chikako Yamashiro (film)Entertainment
* Actress Yui Aragaki, notably for the television drama Nigeru wa Haji da ga Yaku ni Tatsu * Rino Nakasone (choreographer)Sports
* Nagisa Arakaki (baseball) * Hideki Irabu (baseball) * Yukiya Arashiro (bicycle racer) * Kazuki Ganaha (football) * Yoko Gushiken (boxing) * Akinobu Hiranaka (boxing) * Katsuo Tokashiki (boxing) * Daigo Higa (boxing) * Ai Miyazato (golf) * Ken Gushi (drifting)In Hawaii
* Yeiki Kobashigawa (U.S. World War II soldier and Medal of Honor recipient) * Yoshi Oyakawa (Olympic gold medalist) * Ethel Azama (singer) * David Ige (current Governor of Hawaii) * Jake Shimabukuro (ukulele player) * Ryan Higa (Youtuber) * Michael S. Nakamura (Nakandakari) (Former Honolulu Chief of Police)Other parts of the United States
* Kishi Bashi (musician) * Yuki Chikudate (singer) * Tamlyn Tomita (actor) * Brian Tee (actor) * Natasha Allegri (storyboard artist) * Dave Roberts (outfielder), Dave Roberts (baseball player and coach)Throughout the world
* Takeshi Kaneshiro (actor in Taiwan)Notable fictional characters
* Mr. Miyagi (played by Pat Morita) from the ''The Karate Kid (1984 film), Karate Kid'' trilogy * List of Samurai Champloo characters#Mugen, Mugen from the anime series ''Samurai Champloo'' * List of Love Hina characters, Mutsumi Otohime from the manga series ''Love Hina'' * List of characters in the Soul series#Maxi, Maxi from the ''Soulcalibur (series), Soulcalibur'' series of video games * The heroines-leads protagonist Yuri Miyazono from the ''Witchblade, Witchblade: Ao no Shōjo'' novels * Nanjo Takeshi, Arakaki Mari, and Ryuzuka, characters in the 1973 film ''Bodigaado Kiba: Hissatsu sankaku tobi''See also
*History of the Ryukyu Islands *Ryukyu independence movement *Ryukyuan culture *Ethnic issues in Japan *Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest cit ...
*Ryukyuan diaspora
The Ryukyuan diaspora are the Ryukyuan emigrants from the Ryukyu Islands, especially Okinawa Island, and their descendants that reside in a foreign country. The first recorded emigration of Ryukyuans was in the 15th century when they established ...
*Okinawans in Hawaii
*Ryukyuans in Brazil
*Ryukyuan Americans
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*Ouwehand, C. (1985). ''Hateruma: socio-religious aspects of a South-Ryukyuan island culture''. Leiden: E.J. Brill. *Pacific Science Congress, and Allan H. Smith. (1964). ''Ryukyuan culture and society: a survey''. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. *Sakiyama, R. (1995). ''Ryukyuan dance = Ryūkyū buyo''̄. Naha City: Okinawa Dept. of Commerce, Industry & Labor, Tourism & Cultural Affairs Bureau. *Yamazato, Marie. (1995). ''Ryukyuan cuisine''. Naha City, Okinawa Prefecture: Okinawa Tourism & Cultural Affairs Bureau Cultural Promotion Division. *Kreiner, J. (1996). ''Sources of Ryūkyūan history and culture in European collections''. Monographien aus dem Deutschen Institut für Japanstudien der Philipp-Franz-von-Siebold-Stiftung, Bd. 13. München: Iudicium. *Ota, Masahide. (2000). ''Essays on Okinawa Problems''. Yui Shuppan Co.: Gushikawa City, Okinawa, Japan. C0036. *External links
Ryukyuans (Okinawans)
- Minority Rights Group International
Okinawa Peace Network of Los Angeles
- featuring information about Ryukyuan culture worldwide {{DEFAULTSORT:Ryukyuan People Ryukyuan people, Ethnic groups in Japan Ethnic groups in Brazil Ryukyu Islands Indigenous peoples of East Asia History of Northeast Asia