Russian Poland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a
 Alexander I's successor, Nicholas I was crowned King of Poland on 24 May 1829 in Warsaw, but he declined to swear to abide by the Constitution and continued to limit the independence of the Polish kingdom. Nicholas' rule promoted the idea of Official Nationality, consisting of Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality. In relation to Poles, those ideas meant assimilation: turning them into loyal subjects through gradual religious and cultural conversion. The principle of Orthodoxy was the result of the special role it played in the Russian Empire, as the Church was in fact becoming a department of state, and other religions discriminated against; for instance, Papal bulls could not be read in the largely Catholic Kingdom of Poland without agreement from the Russian government.
The rule of Nicholas also meant the end of political traditions in Poland; democratic institutions were removed, an appointed—rather than elected—centralized administration was put in place, and efforts were made to change the relations between the state and the individual. All of this led to discontent and resistance among the Polish population. In January 1831, the Sejm deposed Nicholas I as
Alexander I's successor, Nicholas I was crowned King of Poland on 24 May 1829 in Warsaw, but he declined to swear to abide by the Constitution and continued to limit the independence of the Polish kingdom. Nicholas' rule promoted the idea of Official Nationality, consisting of Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality. In relation to Poles, those ideas meant assimilation: turning them into loyal subjects through gradual religious and cultural conversion. The principle of Orthodoxy was the result of the special role it played in the Russian Empire, as the Church was in fact becoming a department of state, and other religions discriminated against; for instance, Papal bulls could not be read in the largely Catholic Kingdom of Poland without agreement from the Russian government.
The rule of Nicholas also meant the end of political traditions in Poland; democratic institutions were removed, an appointed—rather than elected—centralized administration was put in place, and efforts were made to change the relations between the state and the individual. All of this led to discontent and resistance among the Polish population. In January 1831, the Sejm deposed Nicholas I as
 The government of Congress Poland was outlined in the
The government of Congress Poland was outlined in the
/ref> however, the role of "namestnik"—
/ref>—or, to be more specific, of the Warsaw Military District (Russian Empire), Warsaw Military District ( pl, Warszawski Okręg Wojskowy, russian: Варшавский Военный Округ). The governor-general answered directly to the Emperor and exercised much broader powers than had the "namiestnik". In particular, he controlled all the military forces in the region and oversaw the judicial systems (he could impose
 The administrative divisions of the Kingdom changed several times over its history, and various smaller reforms were also carried out which either changed the smaller administrative units or merged/split various subdivisions.
Immediately after its creation in 1815, the Kingdom of Poland was divided into
The administrative divisions of the Kingdom changed several times over its history, and various smaller reforms were also carried out which either changed the smaller administrative units or merged/split various subdivisions.
Immediately after its creation in 1815, the Kingdom of Poland was divided into
 Despite the fact that the economic situation varied at times, Congress Poland was one of the largest economies in the world. In the mid 1800s the region became heavily
Despite the fact that the economic situation varied at times, Congress Poland was one of the largest economies in the world. In the mid 1800s the region became heavily
** ''Mimo wprowadzenia oficjalnej nazwy Kraj Przywiślański terminy Królestwo Polskie, Królestwo Kongresowe lub w skrócie Kongresówka były nadal używane, zarówno w języku potocznym jak i w niektórych publikacjach.'' ** ''Despite the official name Kraj Przywiślański terms such as, Kingdom of Poland, Congress Poland, or in short Kongresówka were still in use, both in everyday language and in some publications.''
POWSTANIE STYCZNIOWE
Encyklopedia Interia: ** ''po upadku powstania zlikwidowano ostatnie elementy autonomii Królestwa Pol. (łącznie z nazwą), przekształcając je w "Kraj Przywiślański";'' ** ''after the fall of the uprising last elements of autonomy of the Kingdom of Poland (including the name) were abolished, transforming it into the "Vistula land;"''
Królestwo Polskie
WIEM Encyklopedia: ** ''Królestwo Polskie po powstaniu styczniowym: Nazwę Królestwa Polskiego zastąpiła, w urzędowej terminologii, nazwa Kraj Przywiślański.'' Jednakże w artykule jest także: ''Po rewolucji 1905-1907 w Królestwie Polskim...'' i ''W latach 1914-1916 Królestwo Polskie stało się...''. ** ''Kingdom of Poland after the January Uprising: the name Kingdom of Poland was replaced, in official documents, by the name of Vistula land.'' However the same article also states: ''After the revolution 1905-1907 in the Kingdom of Poland'' and ''In the years 1914-1916 the Kingdom of Poland became...''.
Królestwo Polskie, Królestwo Kongresowe
Internetowa encyklopedia PWN, Encyklopedia PWN: ** ''1915–18 pod okupacją niem. i austro-węgierską; K.P. przestało istnieć po powstaniu II RP (XI 1918).'' ** ''[Congress Poland was] under German and Austro-Hungarian occupation from 1915 to 1918; it was finally abolished after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in November 1918''
polity
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of ...
created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
as a semi-autonomous Polish state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
, a successor to Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
. It was established when the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
ceded a part of Polish territory to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
following France's defeat in the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
. In 1915, during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, it was replaced by the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
-controlled nominal Regency Kingdom
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state ''pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy, ...
until Poland regained independence in 1918.
Following the partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
at the end of the 18th century, Poland ceased to exist as an independent nation for 123 years. The territory, with its native population, was split between the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
, and the Russian Empire. After 1804, an equivalent to Congress Poland within the Austrian Empire was the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria
The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria,, ; pl, Królestwo Galicji i Lodomerii, ; uk, Королівство Галичини та Володимирії, Korolivstvo Halychyny ta Volodymyrii; la, Rēgnum Galiciae et Lodomeriae also known as ...
, also commonly referred to as "Austrian Poland
The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria,, ; pl, Królestwo Galicji i Lodomerii, ; uk, Королівство Галичини та Володимирії, Korolivstvo Halychyny ta Volodymyrii; la, Rēgnum Galiciae et Lodomeriae also known as ...
". The area incorporated into Prussia and subsequently the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
had little autonomy and was merely a province – the Province of Posen
The Province of Posen (german: Provinz Posen, pl, Prowincja Poznańska) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1848 to 1920. Posen was established in 1848 following the Greater Poland Uprising as a successor to the Grand Duchy of Posen, ...
.
The Congress Kingdom of Poland was theoretically granted considerable political autonomy by the liberal constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these pr ...
. However, its rulers, the Russian Emperors, generally disregarded any restrictions on their power. It was, therefore, little more than a puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sove ...
in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
with the Russian Empire. The autonomy was severely curtailed following uprisings in 1830–31 and 1863
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Abraham Lincoln signs the Emancipation Proclamation during the third year of the American Civil War, making the abolition of slavery in the Confederate states an official war goal. It proclaim ...
, as the country became governed by viceroys, and later divided into governorates (provinces). Thus, from the start, Polish autonomy remained little more than fiction.Agnieszka Barbara Nance, ''Nation without a State: Imagining Poland in the Nineteenth Century'', dissertation for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, The University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
, pp. 169-88
The capital was located in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
, which towards the beginning of the 20th century became the Russian Empire's third-largest city after St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
. The moderately multicultural population of Congress Poland was estimated at 9,402,253 inhabitants in 1897. It was mostly composed of Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
, Polish Jews
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the l ...
, ethnic Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and a small Russian minority. The predominant religion was Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and the official language used within the state was Polish until the failed January Uprising (1863) when Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
became co-official as a consequence. Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
and German were widely spoken by their native speakers.
The territory of Congress Poland roughly corresponds to modern-day Kalisz Region Kalisz Region ( pl, Kaliskie) is a historical and ethnographical area of Poland, located in central Poland mainly in the Greater Poland Lakes Area and South Greater Poland Plain. It forms the eastern part of Greater Poland proper.
Kalisz Region e ...
and the Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
, Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of ca ...
, Masovian, Podlaskie
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest ci ...
and Holy Cross Voivodeships of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as ...
as well as southwestern Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
and a small part of the Grodno District of Belarus.
The Kingdom of Poland effectively came to an end with the Great Retreat
The Great Retreat (), also known as the retreat from Mons, was the long withdrawal to the River Marne in August and September 1914 by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army. The Franco-British forces on the Western Fro ...
of Russian forces in 1915 and was succeeded by the Government General of Warsaw
The General Government of Warsaw (german: Generalgouvernement Warschau) was an administrative civil district created by the German Empire in World War I.Liulevicius, Vejas G. (2000). ''War Land on the Eastern Front: Culture, Identity, and German ...
, established by the Germans. In 1917, part of this was renamed as the short-lived Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
, a client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite sta ...
of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
, which had a Regency Council
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state ''pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy, ...
instead of a king.
Naming
Although the official name of the state was the ''Kingdom of Poland'' ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; rus, Царство Польское), in order to distinguish it from other Kingdoms of Poland, it is often referred to as "Congress Poland".History
The Congress Kingdom of Poland was created out of theDuchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
, a French client state, at the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
in 1815 when the great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power i ...
s reorganized Europe following the Napoleonic war
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
s. The Kingdom was created from parts of the Polish territory that had been partitioned between Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
which had been transformed into the Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
by Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in 1807. After Napoleon's 1812 defeat, the fate of the Duchy of Warsaw was dependent on Russia. Prussia insisted on the Duchy being completely eliminated; after Russian troops reached Paris in 1812, Tsar Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Pope Alexander I (died 115), early bishop of Rome
* Pope Alexander I of Alexandria (died 320s), patriarch of A ...
intended to annex the Duchy and parts of Lithuanian lands which were historically in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
. However, both Austria and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
strongly disapproved of the idea, Austria issuing a memorandum on returning to the 1795 resolutions with support from the United Kingdom under George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten y ...
, Prime Minister Robert Jenkinson and the British delegate to the Congress, Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh
Robert Stewart, 2nd Marquess of Londonderry, (18 June 1769 – 12 August 1822), usually known as Lord Castlereagh, derived from the courtesy title Viscount Castlereagh ( ) by which he was styled from 1796 to 1821, was an Anglo-Irish politician ...
.
Following the Congress, Russia gained a larger share of Poland (with Warsaw) and, after crushing an insurrection in 1831, the Congress Kingdom's autonomy was abolished. Poles faced confiscation of property, deportation, forced military service, and the closure of their own universities. The Congress was important enough in the creation of the state to cause the new country to be informally named for it. The Kingdom lost its status as a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
state in 1831 and the administrative divisions were reorganized. It was sufficiently distinct that its name remained in official Russian use, although in the later years of Russian rule it was replaced with the "Vistula Land
Vistula Land, Vistula Country (russian: Привислинский край, ''Privislinsky krai''; pl, Kraj Nadwiślański) was the name applied to the lands of Congress Poland from 1867, following the defeats of the November Uprising (1830–3 ...
" (Russian: Привислинский Край). Following the defeat of the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in W ...
its separate institutions and administrative arrangements were abolished as part of increased Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cult ...
to be more closely integrated with the Russian Empire. However, even after this formalized annexation, the territory retained some degree of distinctiveness and continued to be referred to informally as Congress Poland until the Russian rule there ended as a result of the advance by the armies of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
in 1915 during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
The Kingdom was 128,500 km2 in area and originally had a population of approximately 3.3 million. The new state would be one of the smallest Polish states ever, smaller than the preceding Duchy of Warsaw and much smaller than the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
which had a population of over 10 million and an area of 1 million km2. Its population reached 6.1 million by 1870 and 10 million by 1900. The majority of ethnic Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
within the Russian Empire lived in the Congress Kingdom, although some areas outside its borders were also inhabited by strong Polish and Roman Catholic minorities.
The Kingdom of Poland largely re-emerged as a result of the efforts of Adam Jerzy Czartoryski
Adam Jerzy Czartoryski (; lt, Аdomas Jurgis Čartoriskis; 14 January 177015 July 1861), in English known as Adam George Czartoryski, was a Polish nobleman, statesman, diplomat and author.
The son of a wealthy prince, he began his political c ...
, a Pole who aimed to resurrect the Polish state in alliance with Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
. The Kingdom of Poland was one of the few contemporary constitutional monarchies
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
in Europe, with the Emperor of Russia serving as the self-proclaimed King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th ...
.
Initial independence
Theoretically, the Polish Kingdom in its 1815 form was a semi-autonomous state inpersonal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
with Russia through the rule of the Russian Emperor. The state possessed the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Konstytucja Królestwa Polskiego) was granted to the 'Congress' Kingdom of Poland by King of Poland Alexander I of Russia in 1815, who was obliged to issue a constitution to the newly recreated Pol ...
, one of the most liberal in 19th century Europe, a Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
(parliament) responsible to the King capable of voting laws, an independent army, currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general ...
, budget
A budget is a calculation play, usually but not always financial, for a defined period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including time, costs and expenses, environme ...
, penal code
A criminal code (or penal code) is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might ...
and a customs
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs ...
boundary separating it from the rest of Russian lands. Poland also had democratic traditions (Golden Liberty
Golden Liberty ( la, Aurea Libertas; pl, Złota Wolność, lt, Auksinė laisvė), sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth ( pl, Rzeczpospolita Szlachecka or ''Złota wolność szlachecka'') was a pol ...
) and the Polish nobility
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
deeply valued personal freedom. In reality, the Kings had absolute power and the formal title of ''Autocrat'', and wanted no restrictions on their rule. All opposition to the Emperor of Russia was suppressed and the law was disregarded at will by Russian officials. Though the absolute rule demanded by Russia was difficult to establish due to Poland's liberal traditions and institutions, the independence of the Kingdom lasted only 15 years; initially Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Pope Alexander I (died 115), early bishop of Rome
* Pope Alexander I of Alexandria (died 320s), patriarch of A ...
used the title of the King of Poland and was obligated to observe the provisions of the constitution. However, in time the situation changed and he granted the viceroy, Grand Duke Konstantin Pavlovich, almost dictatorial powers. Very soon after Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
resolutions were signed, Russia ceased to respect them. In 1819, Alexander I abolished freedom of the press and introduced preventive censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
. Resistance to Russian control began in the 1820s. Russian secret police commanded by Nikolay Nikolayevich Novosiltsev
Count Nikolay Nikolayevich Novosiltsev (Novoselcev) (russian: Граф Никола́й Никола́евич Новосельцев (Новоси́льцев), pl, Nikołaj Nowosilcow) (1761–1838) was a Russian statesman and a close aide t ...
started the persecution of Polish secret organizations and in 1821 the King ordered the abolition of Freemasonry
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
, which represented Poland's patriotic traditions. Beginning in 1825, the sessions of the Sejm were held in secret.
Uprisings and loss of autonomy
King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th ...
in response to his repeated curtailing of its constitutional rights. Nicholas reacted by sending Russian troops into Poland, resulting in the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in W ...
.
Following an 11-month military campaign, the Kingdom of Poland lost its semi-independent status and was integrated much more closely with the Russian Empire. This was formalized through the issuing of the Organic Statute of the Kingdom of Poland
The Organic Statute of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Statut Organiczny dla Królestwa Polskiego) was a statute which replaced the Constitution of 1815 in the aftermath of the failed November Uprising in the Russian Partition of Poland. The Statute ...
by the Emperor in 1832, which abolished the constitution, army and legislative assembly. Over the next 30 years, a series of measures bound Congress Poland ever more closely to Russia. In 1863 the January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at ...
broke out but lasted only two years before being crushed. As a direct result, any remaining separate status of the kingdom was removed and the political entity was directly incorporated into the Russian Empire. The unofficial name ''Privislinsky Krai
Vistula Land, Vistula Country (russian: Привислинский край, ''Privislinsky krai''; pl, Kraj Nadwiślański) was the name applied to the lands of Congress Poland from 1867, following the defeats of the November Uprising (1830– ...
'' (russian: Привислинский Край), i.e., 'Vistula Land', replaced 'Kingdom of Poland' as the area's official name and the area became a ''namestnichestvo'' under the control of a namiestnik
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "k ...
until 1875, when it became a Guberniya.
Government
 The government of Congress Poland was outlined in the
The government of Congress Poland was outlined in the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Konstytucja Królestwa Polskiego) was granted to the 'Congress' Kingdom of Poland by King of Poland Alexander I of Russia in 1815, who was obliged to issue a constitution to the newly recreated Pol ...
in 1815. The Emperor of Russia was the official head of state, considered the King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th ...
, with the local government headed by the Viceroy of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Namiestnik), Council of State
A Council of State is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head o ...
and Administrative Council
Administrative Council () was a part of Council of State of the Congress Poland. Introduced by the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland in 1815, it was composed of 5 ministers, special nominees of the King and the Namestnik of the Kingdom of Polan ...
, in addition to the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
.
In theory, Congress Poland possessed one of the most liberal governments of the time in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, but in practice, the area was a puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sove ...
of the Russian Empire. The liberal provisions of the constitution, and the scope of the autonomy, were often disregarded by the Russian officials.
Polish remained an official language until the mid-1860s when it was replaced by Russian. This resulted in bilingual street signs and documents, however, the full implementation of Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking c ...
into the Polish language failed.
Executive leadership
The office of "''Namiestnik
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "k ...
''" was introduced in Poland by the 1815 constitution of Congress Poland. The Viceroy was chosen by the King from among the noble citizens of the Russian Empire or the Kingdom of Poland. The Viceroy supervised the entire public administration
Public Administration (a form of governance) or Public Policy and Administration (an academic discipline) is the implementation of public policy, administration of government establishment ( public governance), management of non-profit es ...
and, in the monarch's absence, chaired the Council of State
A Council of State is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head o ...
, as well as the Administrative Council
Administrative Council () was a part of Council of State of the Congress Poland. Introduced by the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland in 1815, it was composed of 5 ministers, special nominees of the King and the Namestnik of the Kingdom of Polan ...
. He could veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto ...
the councils' decisions; other than that, his decisions had to be countersigned by the appropriate government minister. The Viceroy exercised broad powers and could nominate candidates for most senior government posts (ministers, senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
s, judges of the High Tribunal, councilors of state, referendaries, bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
s, and archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdio ...
s). He had no competence in the realms of finances and foreign policy; his military competence varied.
The office of "namiestnik" or Viceroy was never abolished; however, the last "namiestnik" was Friedrich Wilhelm Rembert von Berg
Friedrich Wilhelm Rembert Graf von Berg (german: Friedrich Wilhelm Rembert von Berg, russian: Фёдор Фёдорович Берг, tr. ; ) was a Baltic German nobleman, statesman, diplomat and general who served in the Imperial Russian Army. ...
, who served from 1863 to his death in 1874. No "namiestnik" was named to replace him;Hugo Stumm, ''Russia's Advance Eastward'', 1874, p. 140, note 1. Google Prin/ref> however, the role of "namestnik"—
viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
of the former kingdom passed to the Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
of Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
Thomas Mitchell, ''Handbook for Travellers in Russia, Poland, and Finland'', 1888, p. 460. Google Prin/ref>—or, to be more specific, of the Warsaw Military District (Russian Empire), Warsaw Military District ( pl, Warszawski Okręg Wojskowy, russian: Варшавский Военный Округ). The governor-general answered directly to the Emperor and exercised much broader powers than had the "namiestnik". In particular, he controlled all the military forces in the region and oversaw the judicial systems (he could impose
death sentence
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that ...
s without trial). He could also issue " declarations with the force of law," which could alter existing laws.
Administrative Council
The ''Administrative Council'' () was a part ofCouncil of State
A Council of State is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head o ...
of the Kingdom. Introduced by the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Konstytucja Królestwa Polskiego) was granted to the 'Congress' Kingdom of Poland by King of Poland Alexander I of Russia in 1815, who was obliged to issue a constitution to the newly recreated Pol ...
in 1815, it was composed of 5 ministers, special nominees of the King and the Viceroy of the Kingdom of Poland. The Council executed the King's will and ruled in the cases outside the minister's competence and prepared projects for the Council of State.
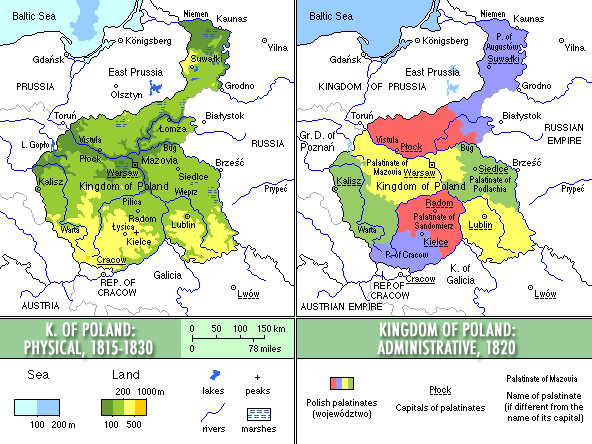
Administrative divisions
 The administrative divisions of the Kingdom changed several times over its history, and various smaller reforms were also carried out which either changed the smaller administrative units or merged/split various subdivisions.
Immediately after its creation in 1815, the Kingdom of Poland was divided into
The administrative divisions of the Kingdom changed several times over its history, and various smaller reforms were also carried out which either changed the smaller administrative units or merged/split various subdivisions.
Immediately after its creation in 1815, the Kingdom of Poland was divided into departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
, a relic from the times of the French-dominated Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
.
On 16 January 1816 the administrative division was reformed, with the departments being replaced with more traditionally Polish voivodeship
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
s (of which there were eight), obwód Obwód (plural ''obwody'') is a term used in Polish to denote administrative districts in various countries, particularly as a translation of the Russian '' oblast''. As administrative subdivisions of Poland itself, obwody existed as subdivisions o ...
s and powiat
A ''powiat'' (pronounced ; Polish plural: ''powiaty'') is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture ( LAU-1, formerly NUTS-4) in other countries. The term "''powiat ...
s. On 7 March 1837, in the aftermath of the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in W ...
earlier that decade, the administrative division was reformed again, bringing Congress Poland closer to the structure of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, with the introduction of guberniyas (governorate
A governorate is an administrative division of a state. It is headed by a governor. As English-speaking nations tend to call regions administered by governors either states or provinces, the term ''governorate'' is often used in translation from ...
, Polish spelling '). In 1842 the powiat
A ''powiat'' (pronounced ; Polish plural: ''powiaty'') is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture ( LAU-1, formerly NUTS-4) in other countries. The term "''powiat ...
s were renamed okręg
District is a term used in Poland, to denote regions and jurisdictions of various types, including electoral constituencies. As historical administrative subdivisions of Poland, districts existed in the later part of the Congress Poland
Con ...
s, and the obwód Obwód (plural ''obwody'') is a term used in Polish to denote administrative districts in various countries, particularly as a translation of the Russian '' oblast''. As administrative subdivisions of Poland itself, obwody existed as subdivisions o ...
s were renamed powiats. In 1844 several governorates were merged with others, and some others were renamed; five governorates remained.
In 1867, following the failure of the January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at ...
, further reforms were instituted which were designed to bring the administrative structure of Poland (now ''de facto'' the Vistulan Country
Vistula Land, Vistula Country (russian: Привислинский край, ''Privislinsky krai''; pl, Kraj Nadwiślański) was the name applied to the lands of Congress Poland from 1867, following the defeats of the November Uprising (1830–3 ...
) closer to that of the Russian Empire. It divided larger governorates into smaller ones, introduced the gmina
The gmina (Polish: , plural ''gminy'' , from German ''Gemeinde'' meaning ''commune'') is the principal unit of the administrative division of Poland, similar to a municipality. , there were 2,477 gminas throughout the country, encompassing over 4 ...
(a new lower-level entity), and restructured the existing five governorates into 10. The 1912 reform created a new governorate – Kholm Governorate Kholm Governorate may refer to:
* Kholm Governorate (Russian Empire), a region of the Russian Empire in 1912–1915, centered in Kholm (today Chełm in Poland)
* Kholm Governorate (Ukraine) :''You may also be looking for Kholm Governorate of the ...
– from parts of the Sedlets and Lublin Governorate
Lublin Governorate (russian: Люблинская губерния, pl, Gubernia lubelska) was an administrative unit (governorate) of Congress Poland.
History
The Lublin Governorate was created in 1837 from the Lublin Voivodeship, and had th ...
s. It was split off from the Vistulan Country and made part of the Southwestern Krai
Southwestern Krai (russian: Юго-западный край, Yugo-zapadny kray), also known as Kiev General Governorate or Kiev, Podolia, and Volhynia General Governorate ( rus, Киевское, Подольское и Волынское г ...
of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
.
Economy
 Despite the fact that the economic situation varied at times, Congress Poland was one of the largest economies in the world. In the mid 1800s the region became heavily
Despite the fact that the economic situation varied at times, Congress Poland was one of the largest economies in the world. In the mid 1800s the region became heavily industrialized
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econ ...
, however, agriculture still maintained a major role in the economy. In addition, the export of wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, rye and other crops was significant in stabilizing the financial output. An important trade partner of Congress Poland was Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
, which imported goods in large amounts.
Since agriculture was equivalent to 70% of the national income, the most important economic transformations included the establishment of mines and the textile industry; the development of these sectors brought more profit and higher tax revenues. The beginnings were difficult due to floods and an intense diplomatic relationship with Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
. It was not until 1822 when Prince Francis Xavier Drucki-Lubecki negotiated to open the Polish market to the world. He also tried to introduce appropriate protective duties. A large and profitable investment was the construction of the Augustów Canal
be, Аўгустоўскі канал
, image = Bulwar w Augustowie.JPG
, image_caption = Augustów Canal in Augustów
, original_owner =
, engineer = Ignacy Prądzyński
, other_engineer = Jan Chrzciciel de Grandvill ...
connecting Narew
The Narew (; be, Нараў, translit=Naraŭ; or ; Sudovian: ''Naura''; Old German: ''Nare''; uk, Нарва, translit=Narva) is a 499-kilometre (310 mi) river primarily in north-eastern Poland, which is also a tributary of the river Vi ...
and Neman
The Neman, Nioman, Nemunas or MemelTo bankside nations of the present: Lithuanian: be, Нёман, , ; russian: Неман, ''Neman''; past: ger, Memel (where touching Prussia only, otherwise Nieman); lv, Nemuna; et, Neemen; pl, Niemen; ; ...
Rivers, which allowed to bypass Danzig (Gdańsk) and high Prussian tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and p ...
s. Drucki-Lubecki also founded the Bank of Poland
The Bank of Poland (Bank Polski) is the name of two former banks in Poland, each of which acted as a central bank. The first institution was founded by Prince Francis Xavier Drucki-Lubecki in 1828 in the Kingdom of Congress Poland. The second was ...
, for which he is mostly remembered.
The first Polish steam mill
A steam mill is a type of grinding mill using a stationary steam engine to power its mechanism.
* And did those feet in ancient time
"And did those feet in ancient time" is a poem by William Blake from the preface to his epic '' Milton: A ...
was built in 1828 in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
- Solec; the first textile machine was installed in 1829. Greater use of machines led to production in the form of workshops. The government was also encouraging foreign specialists, mostly Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, to upkeep larger establishments, or to undertake production. The Germans were also relieved of the tax burden. This allowed to create one of the largest European textile centres in Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of ca ...
and in surrounding towns like Ozorków
Ozorków ( yi, אוזורקוב, translit=Ozorkov) is a town on the Bzura River in central Poland, with 19,128 inhabitants (2020). It has been situated in the Łódź Voivodeship (Lodz Province) since 1919.
History
The city's history dates ba ...
and Zduńska Wola
Zduńska Wola is a city in central Poland with 40,730 inhabitants (2021). It is the seat of Zduńska Wola County in the Łódź Voivodeship. The city was once one of the largest cloth, linen and cotton weaving centres in Poland and is the birt ...
. These small and initially insignificant settlements later developed into large and multicultural cities, where Germans and Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
were the majority in the population. With the abolition of border customs in 1851 and further economic growth, Polish cities were gaining wealth and importance. Most notably, Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
, being associated with the construction of railway lines and bridges, gained priority in the entire Russian market.
Although the economic and industrial progress occurred rapidly, most of the farms, called ''folwark
''Folwark''; german: Vorwerk; uk, Фільварок; ''Filwarok''; be, Фальварак; ''Falwarak''; lt, Palivarkas is a Polish word for a primarily serfdom-based farm and agricultural enterprise (a type of ''latifundium''), often very ...
s'', chose to rely on serfs
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
and paid workforce. Only a few have experimented by obtaining proper machinery and plowing equipment from England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. New crops were being cultivated like sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet ('' Beta vulgaris''). Together ...
, which marked the beginning of Polish sugar refineries. The use of iron cutters and plows was also favoured among the farmers. During the January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at ...
the occupying authorities sought to deprive peasant insurgents of their popularity among landed gentry
The landed gentry, or the ''gentry'', is a largely historical British social class of landowners who could live entirely from rental income, or at least had a country estate. While distinct from, and socially below, the British peerage, t ...
. Taxes were raised and the overall economic situation of commoners worsened. The noblemen and landowners were, on the other hand, provided with more privileges, rights and even financial support in the form of bribery
Bribery is the offering, giving, receiving, or soliciting of any item of value to influence the actions of an official, or other person, in charge of a public or legal duty. With regard to governmental operations, essentially, bribery is "Cor ...
. The aim of this was to weaken their support for the rebellion against the Russian Empire.
Congress Poland was the largest supplier of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
in Europe. The development of the zinc industry took place at the beginning of the 19th century. It was mostly caused by the significant increase of demand for zinc mainly in industrialized countries of Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
.
In 1899, Aleksander Ginsberg founded the company ''FOS'' (''Fabryka Przyrządów Optycznych''-"Factory of Optical Equipment") in Warsaw. It was the only firm in the Russian Empire which crafted and produced cameras, telescopes, Objective (optics), objectives and Stereoscopy, stereoscopes. Following the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
the factory was moved to St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
.
Demographics
According to the Russian Empire Census, Russian Empire Census of 1897, Congress Poland had a population of 9,402,253: 4,712,090 men and 4,690,163 women.See also
* Geographical Dictionary of the Kingdom of Poland * Grand Duchy of Finland (1809–1917) * Grand Duchy of Posen *Great Retreat
The Great Retreat (), also known as the retreat from Mons, was the long withdrawal to the River Marne in August and September 1914 by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army. The Franco-British forces on the Western Fro ...
– the withdrawal of Russian forces from Poland in 1915
* History of Poland (1795–1918)
* Pale of Settlement
References
Note
a Sources agree that after the fall of theJanuary Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at ...
in 1864, the autonomy of Congress Poland was drastically reduced. They disagree however on whether the Kingdom of Poland, colloquially known as Congress Poland, as a state, was officially replaced by Vistula Land
Vistula Land, Vistula Country (russian: Привислинский край, ''Privislinsky krai''; pl, Kraj Nadwiślański) was the name applied to the lands of Congress Poland from 1867, following the defeats of the November Uprising (1830–3 ...
(''Privislinsky Krai''), a province of the Russian Empire, as many sources still use the term Congress Poland for the post-1864 period. The sources are also unclear as to when Congress Poland (or Vistula land) officially ended; some argue that it ended when the German and Austro-Hungarian occupying authorities assumed control of the area during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
; others, that it ended with the creation of the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
in 1917; finally, some argue that it ended only with the creation of the independent Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland in 1918. Examples:
* Ludność Polski w XX Wieku = The Population of Poland in the 20th Century / Andrzej Gawryszewski. Warszawa: Polska Akademia Nauk, Instytut Geografii i Przestrzennego Zagospodorowania im. Stanisława Leszczyckiego, 2005 (Monografie; 5), p 539** ''Mimo wprowadzenia oficjalnej nazwy Kraj Przywiślański terminy Królestwo Polskie, Królestwo Kongresowe lub w skrócie Kongresówka były nadal używane, zarówno w języku potocznym jak i w niektórych publikacjach.'' ** ''Despite the official name Kraj Przywiślański terms such as, Kingdom of Poland, Congress Poland, or in short Kongresówka were still in use, both in everyday language and in some publications.''
POWSTANIE STYCZNIOWE
Encyklopedia Interia: ** ''po upadku powstania zlikwidowano ostatnie elementy autonomii Królestwa Pol. (łącznie z nazwą), przekształcając je w "Kraj Przywiślański";'' ** ''after the fall of the uprising last elements of autonomy of the Kingdom of Poland (including the name) were abolished, transforming it into the "Vistula land;"''
Królestwo Polskie
WIEM Encyklopedia: ** ''Królestwo Polskie po powstaniu styczniowym: Nazwę Królestwa Polskiego zastąpiła, w urzędowej terminologii, nazwa Kraj Przywiślański.'' Jednakże w artykule jest także: ''Po rewolucji 1905-1907 w Królestwie Polskim...'' i ''W latach 1914-1916 Królestwo Polskie stało się...''. ** ''Kingdom of Poland after the January Uprising: the name Kingdom of Poland was replaced, in official documents, by the name of Vistula land.'' However the same article also states: ''After the revolution 1905-1907 in the Kingdom of Poland'' and ''In the years 1914-1916 the Kingdom of Poland became...''.
Królestwo Polskie, Królestwo Kongresowe
Internetowa encyklopedia PWN, Encyklopedia PWN: ** ''1915–18 pod okupacją niem. i austro-węgierską; K.P. przestało istnieć po powstaniu II RP (XI 1918).'' ** ''[Congress Poland was] under German and Austro-Hungarian occupation from 1915 to 1918; it was finally abolished after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in November 1918''
Citations
Further reading
* Davies, Norman. ''God's Playground: A History of Poland''. Vol. 2: ''1795 to the Present'' (Oxford University Press, 1982) pp. 306–33 * Getka-Kenig, Mikolaj. "The Genesis of the Aristocracy in Congress Poland," ''Acta Poloniae Historica'' (2009), Issue 100, pp. 79–112; . Covers the transition from feudalism to capitalism; the adjustment of the aristocracy's power and privilege from a legal basis to one of only social significance; the political changes instigated by the jurisdictional partitions and reorganizations of the state. * * * Leslie, R. F. "Politics and economics in Congress Poland," ''Past and Present'' (1955), 8#1, pp. 43–63 * * Zamoyski, Adam. Poland: a history. New York: Hippocrene Books, 2012External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Poland, Congress Congress Poland, 1815 establishments in Poland 1867 disestablishments in Poland 19th century in Poland, Congress Poland Former kingdoms Personal unions States and territories disestablished in 1867 States and territories disestablished in 1915 States and territories established in 1815