Rus'–Byzantine War (970–971) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria refers to a conflict beginning in 967/968 and ending in 971, carried out in the eastern
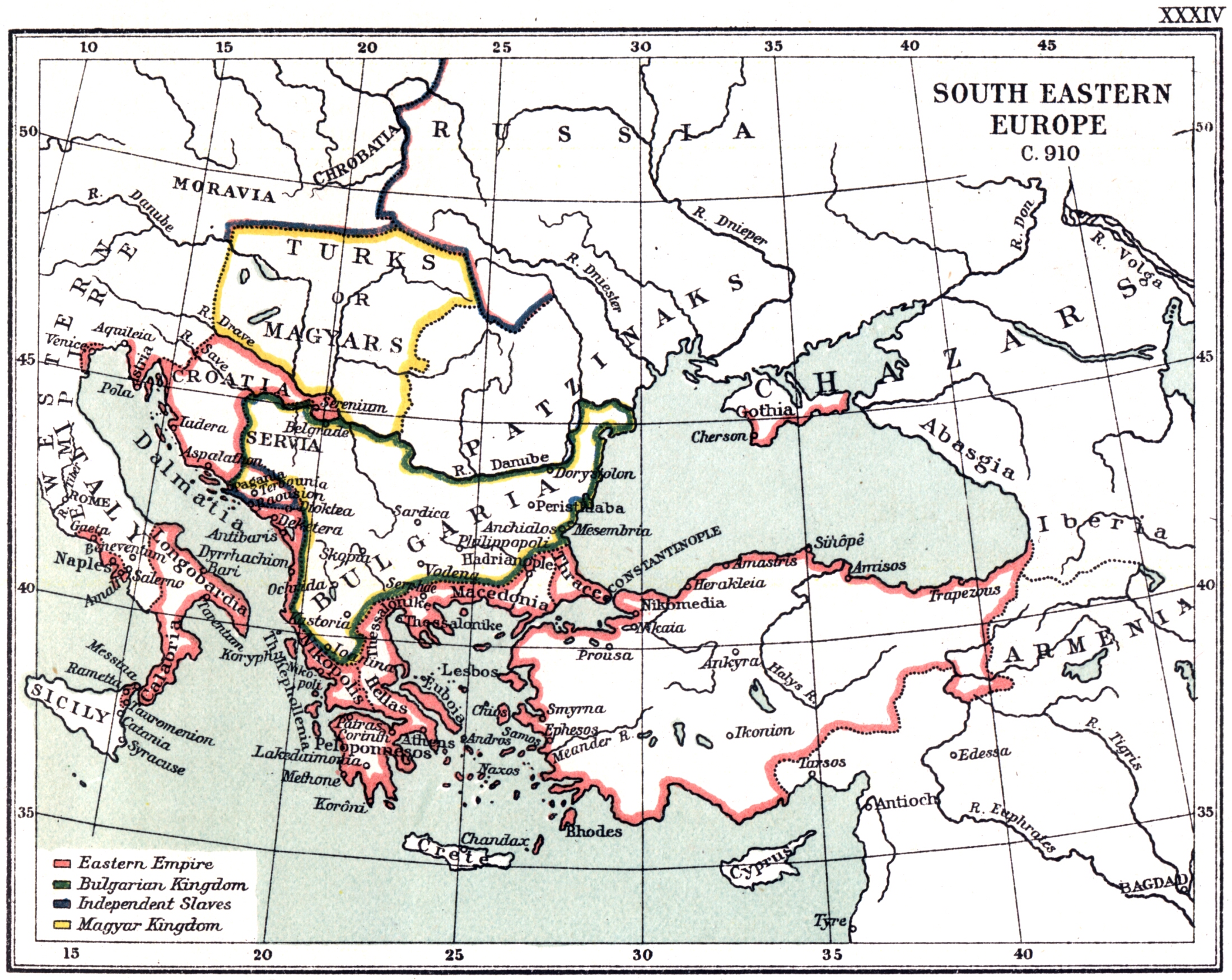 By the beginning of the 10th century, two powers had come to dominate the
By the beginning of the 10th century, two powers had come to dominate the  Sviatoslav enthusiastically agreed to the Byzantine proposal. In August 967 or 968, the Rus' crossed the Danube into Bulgarian territory, defeated a Bulgarian army of 30,000 men in the
Sviatoslav enthusiastically agreed to the Byzantine proposal. In August 967 or 968, the Rus' crossed the Danube into Bulgarian territory, defeated a Bulgarian army of 30,000 men in the  In summer 969, Sviatoslav returned to Bulgaria in force, accompanied by allied Pecheneg and Magyar contingents. In his absence, Pereyaslavets had been recovered by Boris II; the Bulgarian defenders put up a determined fight, but Sviatoslav stormed the city. Thereafter Boris and Roman capitulated, and the Rus' rapidly established control over eastern and northern Bulgaria, placing garrisons in Dorostolon and the Bulgarian capital of
In summer 969, Sviatoslav returned to Bulgaria in force, accompanied by allied Pecheneg and Magyar contingents. In his absence, Pereyaslavets had been recovered by Boris II; the Bulgarian defenders put up a determined fight, but Sviatoslav stormed the city. Thereafter Boris and Roman capitulated, and the Rus' rapidly established control over eastern and northern Bulgaria, placing garrisons in Dorostolon and the Bulgarian capital of
 After being occupied with suppressing the revolt of Bardas Phokas throughout the year 970, Tzimiskes marshalled his forces in early 971 for a campaign against the Rus', moving his troops from Asia to Thrace and gathering supplies and siege equipment. The Byzantine navy accompanied the expedition, tasked with carrying troops to effect a landing in the enemy's rear and to cut off their retreat across the Danube. The emperor chose Easter week of 971 to make his move, catching the Rus' completely by surprise: The passes of the Balkan mountains had been left unguarded, either because the Rus' were busy suppressing Bulgarian revolts or perhaps (as A.D. Stokes suggests) because a peace agreement that had been concluded after the battle of Arcadiopolis made them complacent.
The Byzantine army, led by Tzimiskes in person and numbering 30,000–40,000, advanced quickly and reached Preslav unmolested. The Rus' army was defeated in a battle before the city walls, and the Byzantines proceeded to lay siege. The Rus' and Bulgarian garrison under the Rus' noble Sphangel put up a determined resistance, but the city was stormed on 13 April. Among the captives were Boris II and his family, who were brought to Constantinople along with the Bulgarian imperial regalia. The main Rus' force under Sviatoslav withdrew before the imperial army towards Dorostolon on the Danube. As Sviatoslav feared a Bulgarian uprising, he had 300 Bulgarian nobles executed, and imprisoned many others. The imperial army advanced without hindrance; the Bulgarian garrisons of the various forts and strongholds along the way surrendered peacefully.
As the Byzantines neared Dorostolon, they came upon the Rus' army, which had deployed on a field before the city, ready for battle. After a long and bitter struggle, the Byzantines won the day when Tzimiskes ordered his heavy
After being occupied with suppressing the revolt of Bardas Phokas throughout the year 970, Tzimiskes marshalled his forces in early 971 for a campaign against the Rus', moving his troops from Asia to Thrace and gathering supplies and siege equipment. The Byzantine navy accompanied the expedition, tasked with carrying troops to effect a landing in the enemy's rear and to cut off their retreat across the Danube. The emperor chose Easter week of 971 to make his move, catching the Rus' completely by surprise: The passes of the Balkan mountains had been left unguarded, either because the Rus' were busy suppressing Bulgarian revolts or perhaps (as A.D. Stokes suggests) because a peace agreement that had been concluded after the battle of Arcadiopolis made them complacent.
The Byzantine army, led by Tzimiskes in person and numbering 30,000–40,000, advanced quickly and reached Preslav unmolested. The Rus' army was defeated in a battle before the city walls, and the Byzantines proceeded to lay siege. The Rus' and Bulgarian garrison under the Rus' noble Sphangel put up a determined resistance, but the city was stormed on 13 April. Among the captives were Boris II and his family, who were brought to Constantinople along with the Bulgarian imperial regalia. The main Rus' force under Sviatoslav withdrew before the imperial army towards Dorostolon on the Danube. As Sviatoslav feared a Bulgarian uprising, he had 300 Bulgarian nobles executed, and imprisoned many others. The imperial army advanced without hindrance; the Bulgarian garrisons of the various forts and strongholds along the way surrendered peacefully.
As the Byzantines neared Dorostolon, they came upon the Rus' army, which had deployed on a field before the city, ready for battle. After a long and bitter struggle, the Byzantines won the day when Tzimiskes ordered his heavy
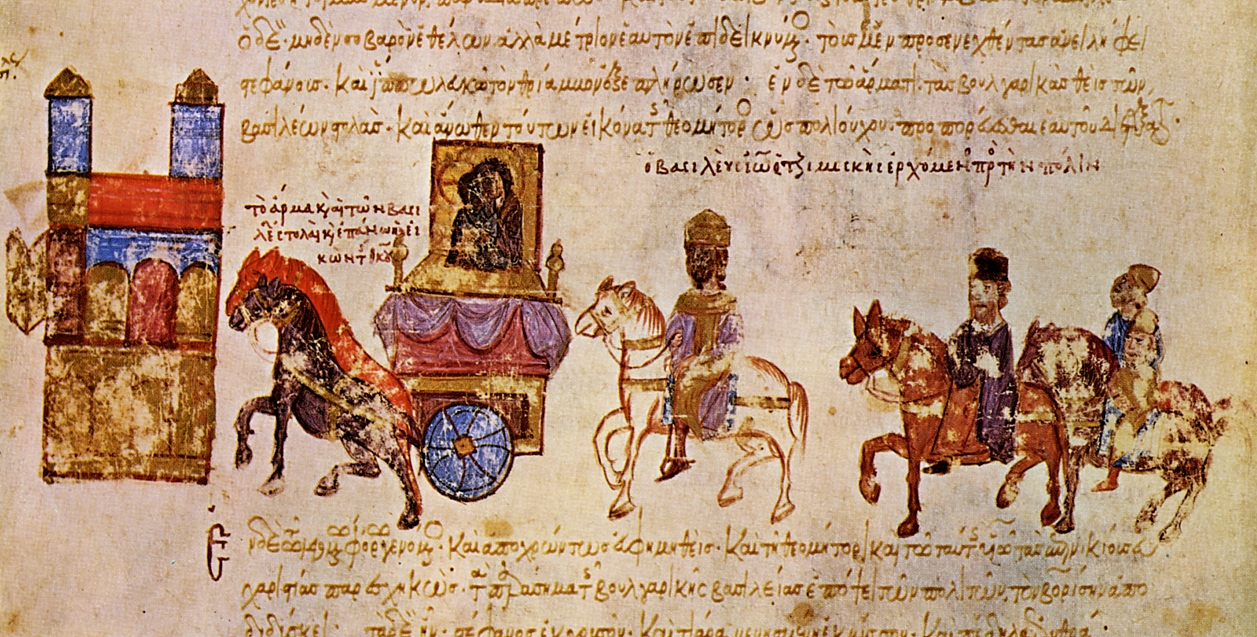 The outcome of the war was a complete Byzantine victory, and Tzimiskes decided to take full advantage. Although he initially recognized Boris II as the legitimate Bulgarian tsar, after the fall of Dorostolon his intentions changed. This became evident during his triumphal return to Constantinople, where the emperor entered the
The outcome of the war was a complete Byzantine victory, and Tzimiskes decided to take full advantage. Although he initially recognized Boris II as the legitimate Bulgarian tsar, after the fall of Dorostolon his intentions changed. This became evident during his triumphal return to Constantinople, where the emperor entered the
The Varangians: In God’s Holy Fire
' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2020), pp. 58-61. * * * * * * * * * {{good article 960s conflicts 970s conflicts 10th century in Bulgaria Rus'–Byzantine wars Wars involving the First Bulgarian Empire 960s in the Byzantine Empire 970s in the Byzantine Empire 967 971 Byzantine Empire–First Bulgarian Empire relations
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, and involving the Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. The Byzantines encouraged the Rus' ruler Sviatoslav to attack Bulgaria, leading to the defeat of the Bulgarian forces and the occupation of the northern and north-eastern part of the country by the Rus' for the following two years. The allies then turned against each other, and the ensuing military confrontation ended with a Byzantine victory. The Rus' withdrew and eastern Bulgaria was incorporated into the Byzantine Empire.
In 927, a peace treaty had been signed between Bulgaria and Byzantium, ending many years of warfare and establishing forty years of peace. Both states prospered during this interlude, but the balance of power gradually shifted in favour of the Byzantines, who made great territorial gains against the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
in the East and formed a web of alliances surrounding Bulgaria. By 965/966, the warlike new Byzantine emperor Nikephoros II Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
refused to renew the annual tribute that was part of the peace agreement and declared war on Bulgaria. Preoccupied with his campaigns in the East, Nikephoros resolved to fight the war by proxy and invited the Rus' ruler Sviatoslav to invade Bulgaria.
Sviatoslav's subsequent campaign greatly exceeded the expectations of the Byzantines, who had regarded him only as a means to exert diplomatic pressure on the Bulgarians. The Rus' prince conquered the core regions of the Bulgarian state in the northeastern Balkans in 967–969, seized the Bulgarian tsar Boris II, and effectively ruled the country through him. Sviatoslav intended to continue his drive south against Byzantium itself, which in turn regarded the establishment of a new and powerful Russo-Bulgarian state in the Balkans with great concern. After stopping a Rus' advance through Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
at the Battle of Arcadiopolis in 970, the Byzantine emperor John I Tzimiskes led an army north into Bulgaria in 971 and captured Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new ...
, the capital. After a three-month siege of the fortress of Dorostolon, Sviatoslav agreed to terms with the Byzantines and withdrew from Bulgaria. Tzimiskes formally annexed Eastern Bulgaria to the Byzantine Empire. However, most of the country in the central and western Balkans remained in effect outside imperial control; this would lead to the revival of the Bulgarian state in these regions under the Cometopuli dynasty
The Kometopuli dynasty ( Bulgarian: ,
Bulgarian; ; Byzantine Greek: , ) was the last royal dynasty in the First Bulgarian Empire, ruling from ca. 976 until the fall of Bulgaria under Byzantine rule in 1018. The most notable member of the dyn ...
.
Background
 By the beginning of the 10th century, two powers had come to dominate the
By the beginning of the 10th century, two powers had come to dominate the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
: the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
controlled the south of the peninsula and the coasts, and the Bulgarian Empire held the central and northern Balkans. The early decades of the century were dominated by Tsar Simeon (r. 893–927), who expanded his empire at Byzantium's expense in a series of wars and secured for himself recognition of his imperial title. Simeon's death in May 927 was soon followed by a rapprochement
In international relations, a rapprochement, which comes from the French word ''rapprocher'' ("to bring together"), is a re-establishment of cordial relations between two countries. This may be done due to a mutual enemy, as was the case with Germ ...
between the two powers, formalized with a treaty and a marriage alliance later that same year. Simeon's second son and successor, Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholico ...
(r. 927–969), married Maria
Maria may refer to:
People
* Mary, mother of Jesus
* Maria (given name), a popular given name in many languages
Place names Extraterrestrial
* 170 Maria, a Main belt S-type asteroid discovered in 1877
* Lunar maria (plural of ''mare''), large, ...
, the granddaughter of the Byzantine emperor Romanos I Lekapenos
Romanos I Lekapenos ( el, Ρωμανός Λεκαπηνός; 870 – 15 June 948), Latinized as Romanus I Lecapenus, was Byzantine emperor from 920 until his deposition in 944, serving as regent for the infant Constantine VII.
Origin
Romanos ...
(r. 920–944), and his imperial title was recognized. An annual tribute (which the Byzantines termed a subsidy for Maria's upkeep, to save face) was agreed to be paid to the Bulgarian ruler in exchange for peace.
The agreement was kept for almost forty years as peaceful relations suited both sides. Bulgaria, despite the barrier formed by the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
, was still menaced in its northern reaches by steppe peoples, the Magyars and the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
. They launched raids throughout Bulgaria, occasionally reaching Byzantine territory as well. The Byzantine–Bulgarian peace nevertheless meant less trouble from the north, as many Pecheneg raids had been sponsored by the Byzantines. Peter's reign, although lacking the military splendour of Simeon's, was still a "golden age" for Bulgaria, with a flourishing economy and a thriving urban society.
Byzantium used the peace to focus its energy on wars against the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
in the East, where a series of campaigns under generals John Kourkouas and Nikephoros Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
greatly expanded imperial territory. At the same time, military reforms created a much more effective and offensively-oriented army. The Byzantines did not neglect the Balkans, working steadily to improve their contacts with the peoples of central and eastern Europe, subtly altering the balance of power in the peninsula. Their Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
n outpost of Cherson maintained trade with the Pechenegs and the emerging power of the Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
; Byzantine missionaries led the Christianization of the Magyars; and the Slavic princes of the western Balkans came to once again acknowledge the suzerainty of the Empire, particularly after Časlav Klonimirović ended Bulgarian control over Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
. These relationships on the periphery of the Bulgarian Empire were an important asset for Byzantine diplomacy: instigating attacks against Bulgaria by the Pechenegs and the Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
was a time-honoured method of applying pressure on the Bulgarians.
Upon the sudden death of Emperor Romanos II
Romanos II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Ρωμανός, 938 – 15 March 963) was Byzantine Emperor from 959 to 963. He succeeded his father Constantine VII at the age of twenty-one and died suddenly and mysteriously four years later. His son Bas ...
in 963, Nikephoros Phokas usurped the throne from Romanos' infant sons and became senior emperor as Nikephoros II
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
(r. 963–969). Nikephoros, a prominent member of the Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
n military aristocracy, also focused mostly on the East, leading his army personally in campaigns that recovered Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
and Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
. Thus things stood when a Bulgarian embassy visited Nikephoros in late 965 or early 966 to collect the tribute owed. Nikephoros, his confidence boosted by his recent successes, and deeming the Bulgarian ruler's demand presumptuous, refused to pay, claiming that with Empress Maria's recent death (ca. 963) any such obligations had ceased. He had the envoys beaten and sent them home with threats and insults. He proceeded with his troops to Thrace, where he staged an elaborate parade as a display of military strength and sacked a few Bulgarian border forts. Nikephoros' decision to effect a breach of relations with Bulgaria was also in response to the recent treaty that Peter I had signed with the Magyars. The treaty stipulated that the Magyars would be allowed to pass through the country and raid Byzantium in exchange for halting their raids in Bulgaria.
Anxious to avoid war, Tsar Peter sent his two sons, Boris and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, as hostages to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. This move failed to appease Nikephoros, but he was not able or willing to campaign against Bulgaria; his forces were engaged in the East, and furthermore, drawing on the Byzantines' past experience, Nikephoros was reluctant to mount an expedition into the mountainous and heavily forested terrain of Bulgaria. Consequently, he resorted to the old Byzantine expedient of calling in a tribe from eastern Europe to attack Bulgaria. In late 966 or early 967, he dispatched the ''patrikios
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Republic, but its relevance waned aft ...
'' Kalokyros, a citizen of Cherson, as his ambassador to Sviatoslav, ruler of the Rus'. The Byzantines had long maintained close relations with the Rus', with whom they were bound by treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pe ...
. With promises of rich rewards and, according to Leo the Deacon Leo the Deacon ( el, Λέων ο Διάκονος) (born c. 950) was a Byzantine Greek historian and chronicler.
He was born around 950 at Kaloe in Asia Minor, and was educated in Constantinople, where he became a deacon in the imperial palace. Whi ...
, a payment of 1,500 pounds of gold, the Rus' ruler was induced to attack Bulgaria from the north. That Nikephoros should call upon Sviatoslav for aid was unusual, since the Pechenegs were traditionally used for such tasks. The historian A.D. Stokes, who examined the questions surrounding the background and chronology of Sviatoslav's Bulgarian campaign, suggested that this move had a second motive of turning the attention of Sviatoslav, who had recently destroyed the Khazar khanate, away from the Byzantine outpost of Cherson.
 Sviatoslav enthusiastically agreed to the Byzantine proposal. In August 967 or 968, the Rus' crossed the Danube into Bulgarian territory, defeated a Bulgarian army of 30,000 men in the
Sviatoslav enthusiastically agreed to the Byzantine proposal. In August 967 or 968, the Rus' crossed the Danube into Bulgarian territory, defeated a Bulgarian army of 30,000 men in the Battle of Silistra
The Battle of Silistra occurred in the spring of 968 near the Bulgarian town of Silistra, but most probably on the modern territory of Romania. It was fought between the armies of Bulgaria and Kievan Rus' and resulted in a Rus' victory. Upon t ...
, and occupied most of the Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
. According to the Bulgarian historian Vasil Zlatarski
Vasil Nikolov Zlatarski ( bg, Васил Николов Златарски; – 15 December 1935) was a Bulgarian historian-medievalist, archaeologist, and epigraphist.
Life
Vasil Zlatarski was born in Veliko Tarnovo in 1866, the youngest c ...
, Sviatoslav seized 80 towns in northeastern Bulgaria. They were looted and destroyed but not permanently occupied. Tsar Peter I suffered an epileptic stroke when he received news of the defeat. The Rus' wintered at Pereyaslavets
Pereyaslavets ( East Slavic: ) or Preslavets ( bg, Преславец) was a trade city located near mouths of the Danube. The city's name is derived from that of the Bulgarian capital of the time, Preslav, and means Little Preslav (). In Greek ...
, while the Bulgarians retreated to the fortress of Dorostolon ( Silistra). The next year, Sviatoslav left with part of his army to counter a Pecheneg attack on his capital at Kiev (incited either by the Byzantines or, according to the East Slavic ''Primary Chronicle'', by the Bulgarians). At the same time, Tsar Peter sent a new embassy to Byzantium, a visit that was recorded by Liutprand of Cremona
Liutprand, also Liudprand, Liuprand, Lioutio, Liucius, Liuzo, and Lioutsios (c. 920 – 972),"LIUTPRAND OF CREMONA" in '' The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'', Oxford University Press, New York & Oxford, 1991, p. 1241. was a historian, diplomat, ...
. In contrast to their previous reception, this time the Bulgarian envoys were treated with great honour. Nevertheless, Nikephoros, confident of his position, demanded harsh terms: Tsar Peter was to resign and be replaced by Boris, and the two young emperors, Basil and Constantine, were to be married to Bulgarian princesses, daughters of Boris.
Peter retired to a monastery, where he died in 969, while Boris was released from Byzantine custody and recognized as Tsar Boris II. For the moment, it appeared that Nikephoros' plan had worked. However, Sviatoslav's brief sojourn into the south awakened in him the desire to conquer these fertile and rich lands. In this intention he was apparently encouraged by the former Byzantine envoy, Kalokyros, who coveted the imperial crown for himself. Thus, after defeating the Pechenegs, he set up viceroys to rule Russia in his absence and turned his sights southward again.
 In summer 969, Sviatoslav returned to Bulgaria in force, accompanied by allied Pecheneg and Magyar contingents. In his absence, Pereyaslavets had been recovered by Boris II; the Bulgarian defenders put up a determined fight, but Sviatoslav stormed the city. Thereafter Boris and Roman capitulated, and the Rus' rapidly established control over eastern and northern Bulgaria, placing garrisons in Dorostolon and the Bulgarian capital of
In summer 969, Sviatoslav returned to Bulgaria in force, accompanied by allied Pecheneg and Magyar contingents. In his absence, Pereyaslavets had been recovered by Boris II; the Bulgarian defenders put up a determined fight, but Sviatoslav stormed the city. Thereafter Boris and Roman capitulated, and the Rus' rapidly established control over eastern and northern Bulgaria, placing garrisons in Dorostolon and the Bulgarian capital of Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new ...
. There Boris continued to reside and exercise nominal authority as Sviatoslav's vassal. In reality he was little more than a figurehead, retained in order to lessen Bulgarian resentment at and reaction to the Rus' presence. Sviatoslav appears to have been successful in enlisting Bulgarian support. Bulgarian soldiers joined his army in considerable numbers, tempted partly by the prospects of booty, but also enticed by Sviatoslav's anti-Byzantine designs and probably mollified by a shared Slavic heritage. The Rus' ruler himself was careful not to alienate his new subjects: he forbade his army from looting the countryside or plundering cities that surrendered peacefully.
Thus Nikephoros' scheme had backfired: Instead of a weak Bulgaria, a new and warlike nation had been established at the Empire's northern border, and Sviatoslav showed every intention of continuing his advance south into Byzantium. The emperor tried to get the Bulgarians to resume the war against the Rus', but his proposals were not heeded. Then, on 11 December 969, Nikephoros was murdered in a palace coup and succeeded by John I Tzimiskes (r. 969–976), to whom fell the task of dealing with the situation in the Balkans. The new emperor sent envoys to Sviatoslav, proposing negotiations. The Rus' ruler demanded a huge sum before he would withdraw, insisting that otherwise the Empire should abandon its European territories to him and withdraw to Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. For the time being, Tzimiskes was preoccupied with consolidating his position and countering the unrest of the powerful Phokas clan and its adherents in Asia Minor. He therefore entrusted the war in the Balkans to his brother-in-law, the Domestic of the Schools
The office of the Domestic of the Schools ( gr, δομέστικος τῶν σχολῶν, domestikos tōn scholōn) was a senior military post of the Byzantine Empire, extant from the 8th century until at least the early 14th century. Originally ...
Bardas Skleros
Bardas Skleros (Greek: Βάρδας Σκληρός) or Sclerus was a Byzantine general who led a wide-scale Asian rebellion against Emperor Basil II during the years 976 to 979.
Background
Bardas belonged to the great family of the Skleroi, ...
, and to the eunuch stratopedarch Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a sur ...
.
In early 970, a Rus' army, with large contingents of Bulgarians, Pechenegs, and Magyars, crossed the Balkan Mountains and headed south. The Rus' stormed the city of Philippopolis (now Plovdiv), and, according to Leo the Deacon, impaled 20,000 of its surviving inhabitants. Skleros, with an army of 10,000–12,000 men, confronted the Rus' advance near Arcadiopolis (now Luleburgaz) in early spring 970. The Byzantine general, whose army was considerably outnumbered, used a feigned retreat
A feigned retreat is a military tactic, a type of feint, whereby a military force pretends to withdraw or to have been routed, in order to lure an enemy into a position of vulnerability.
A feigned retreat is one of the more difficult tactics for ...
to draw the Pecheneg contingent away from the main army into a prepared ambush. The main Rus' army panicked and fled, suffering heavy casualties at the hands of the pursuing Byzantines. The Rus' withdrew north of the Balkan mountain range, which gave Tzimiskes time to deal with internal unrest and to assemble his forces.
Byzantine offensive
 After being occupied with suppressing the revolt of Bardas Phokas throughout the year 970, Tzimiskes marshalled his forces in early 971 for a campaign against the Rus', moving his troops from Asia to Thrace and gathering supplies and siege equipment. The Byzantine navy accompanied the expedition, tasked with carrying troops to effect a landing in the enemy's rear and to cut off their retreat across the Danube. The emperor chose Easter week of 971 to make his move, catching the Rus' completely by surprise: The passes of the Balkan mountains had been left unguarded, either because the Rus' were busy suppressing Bulgarian revolts or perhaps (as A.D. Stokes suggests) because a peace agreement that had been concluded after the battle of Arcadiopolis made them complacent.
The Byzantine army, led by Tzimiskes in person and numbering 30,000–40,000, advanced quickly and reached Preslav unmolested. The Rus' army was defeated in a battle before the city walls, and the Byzantines proceeded to lay siege. The Rus' and Bulgarian garrison under the Rus' noble Sphangel put up a determined resistance, but the city was stormed on 13 April. Among the captives were Boris II and his family, who were brought to Constantinople along with the Bulgarian imperial regalia. The main Rus' force under Sviatoslav withdrew before the imperial army towards Dorostolon on the Danube. As Sviatoslav feared a Bulgarian uprising, he had 300 Bulgarian nobles executed, and imprisoned many others. The imperial army advanced without hindrance; the Bulgarian garrisons of the various forts and strongholds along the way surrendered peacefully.
As the Byzantines neared Dorostolon, they came upon the Rus' army, which had deployed on a field before the city, ready for battle. After a long and bitter struggle, the Byzantines won the day when Tzimiskes ordered his heavy
After being occupied with suppressing the revolt of Bardas Phokas throughout the year 970, Tzimiskes marshalled his forces in early 971 for a campaign against the Rus', moving his troops from Asia to Thrace and gathering supplies and siege equipment. The Byzantine navy accompanied the expedition, tasked with carrying troops to effect a landing in the enemy's rear and to cut off their retreat across the Danube. The emperor chose Easter week of 971 to make his move, catching the Rus' completely by surprise: The passes of the Balkan mountains had been left unguarded, either because the Rus' were busy suppressing Bulgarian revolts or perhaps (as A.D. Stokes suggests) because a peace agreement that had been concluded after the battle of Arcadiopolis made them complacent.
The Byzantine army, led by Tzimiskes in person and numbering 30,000–40,000, advanced quickly and reached Preslav unmolested. The Rus' army was defeated in a battle before the city walls, and the Byzantines proceeded to lay siege. The Rus' and Bulgarian garrison under the Rus' noble Sphangel put up a determined resistance, but the city was stormed on 13 April. Among the captives were Boris II and his family, who were brought to Constantinople along with the Bulgarian imperial regalia. The main Rus' force under Sviatoslav withdrew before the imperial army towards Dorostolon on the Danube. As Sviatoslav feared a Bulgarian uprising, he had 300 Bulgarian nobles executed, and imprisoned many others. The imperial army advanced without hindrance; the Bulgarian garrisons of the various forts and strongholds along the way surrendered peacefully.
As the Byzantines neared Dorostolon, they came upon the Rus' army, which had deployed on a field before the city, ready for battle. After a long and bitter struggle, the Byzantines won the day when Tzimiskes ordered his heavy cataphract
A cataphract was a form of armored heavy cavalryman that originated in Persia and was fielded in ancient warfare throughout Eurasia and Northern Africa.
The English word derives from the Greek ' (plural: '), literally meaning "armored" or ...
cavalry to advance. The Rus' quickly broke ranks and fled inside the fortress. The subsequent siege of Dorostolon
The Battle of Dorostopol was fought in 971 between the Byzantine Empire and forces of Kievan Rus'. The Byzantines, led by John I Tzimiskes, were victorious.
Background
During the course of the Rus'-Bulgarian war, Svyatoslav I of Kiev overran t ...
lasted for three months, during which the Byzantines blockaded the city by land and sea and the Rus' attempted several sallies. Three pitched battles were fought, all of which ended in Byzantine victories. After the final and particularly savage battle in late July, the Rus' were forced to capitulate. According to Byzantine chroniclers, by that time only 22,000 out of an army of originally 60,000 remained. Tzimiskes and Sviatoslav met and agreed to a peace treaty: The Rus' army was allowed to depart, leaving their captives and plunder behind, and their trading rights were re-affirmed in exchange for an oath to never again attack imperial territory. Sviatoslav would not long outlive the peace settlement, as he was slain on his way home in a Pecheneg ambush at the river Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and ...
.
Aftermath
 The outcome of the war was a complete Byzantine victory, and Tzimiskes decided to take full advantage. Although he initially recognized Boris II as the legitimate Bulgarian tsar, after the fall of Dorostolon his intentions changed. This became evident during his triumphal return to Constantinople, where the emperor entered the
The outcome of the war was a complete Byzantine victory, and Tzimiskes decided to take full advantage. Although he initially recognized Boris II as the legitimate Bulgarian tsar, after the fall of Dorostolon his intentions changed. This became evident during his triumphal return to Constantinople, where the emperor entered the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
behind a wagon carrying an icon of the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
as well as the Bulgarian regalia, with Boris and his family following behind Tzimiskes. When the procession reached the Forum of Constantine
The Forum of Constantine ( el, Φόρος Κωνσταντίνου, Fóros Konstantínou; la, Forum Constantini) was built at the foundation of Constantinople immediately outside the old city walls of Byzantium. It marked the centre of the new c ...
, Boris was publicly divested of his imperial insignia, and at the church of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
, the Bulgarian crown was dedicated to God.
This marked the symbolic end of Bulgaria as an independent state, at least in Byzantine eyes. Byzantine generals were installed in the eastern parts of the country along the Danube. Preslav was renamed Ioannopolis in honour of the emperor, and Dorostolon (or perhaps Pereyaslavets) was renamed Theodoropolis after St. Theodore the Stratelate, who was believed to have intervened in the final battle before Dorostolon. Tzimiskes reduced the Bulgarian patriarchate
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
to an archbishopric subject to the Patriarch of Constantinople. He brought the Bulgarian royal family and many nobles to live in Constantinople and Asia Minor, while the region around Philippopolis was settled with Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
. However, outside eastern Bulgaria, and there only in the major urban centres, Byzantine control existed only in theory. Tzimiskes, like Nikephoros Phokas, was more interested in the East. With the Rus' threat banished and Bulgaria seemingly pacified, his attention turned to Syria. No coordinated Byzantine drive to secure the interior of the Balkans was made. As a result, the north-central Balkans and Macedonia, where neither the Rus' nor Tzimiskes' troops had ventured, remained as before in the hands of the local Bulgarian elites.
In these areas, a Bulgarian resistance emerged, taking advantage of the Byzantine civil wars after the death of Tzimiskes in 976, led by the four sons of a count (''comes
''Comes'' ( ), plural ''comites'' ( ), was a Roman title or office, and the origin Latin form of the medieval and modern title "count".
Before becoming a word for various types of title or office, the word originally meant "companion", either i ...
'') Nicholas, who became known as the ''Cometopuli
The Kometopuli dynasty ( Bulgarian: ,
Bulgarian; ; Byzantine Greek: , ) was the last royal dynasty in the First Bulgarian Empire, ruling from ca. 976 until the fall of Bulgaria under Byzantine rule in 1018. The most notable member of the dynas ...
'' ("sons of the count"). The most capable amongst them, Samuel, revived the Bulgarian realm, now centered in Macedonia, and was crowned Tsar in 997. A formidable warrior, he led raiding campaigns into Byzantine territory as far south as the Peloponnese, and he engaged the Byzantine emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
(r. 976–1025) in a series of wars resulting in the final conquest of the Bulgarian state by the Byzantines in 1018. Nevertheless, due to the events of 971, the Byzantines would never regard him as anything other than a rebel against imperial authority, let alone concede the principle of equality enjoyed by the Bulgarian rulers before 971.
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * Jakobsson, Sverrir,The Varangians: In God’s Holy Fire
' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2020), pp. 58-61. * * * * * * * * * {{good article 960s conflicts 970s conflicts 10th century in Bulgaria Rus'–Byzantine wars Wars involving the First Bulgarian Empire 960s in the Byzantine Empire 970s in the Byzantine Empire 967 971 Byzantine Empire–First Bulgarian Empire relations